1. Introduction and Background Results
In the 21st century, electronic games are a common pastime for children, who spend excessive amounts of time on electronic devices, making these games an indispensable part of their daily routine. Introducing electronic games into education has generated some opposition due to concerns about addiction, but the positive aspects should not be overlooked. Comprehensive research, exploring relevant facts and data, can provide the answers being sought. This paper presents a comprehensive study on the development and analysis of the available literature sources focusing on educational processes conducted using electronic educational games in primary education schools. The articles selected for analysis include theoretical and historical approaches, providing essential information for understanding the topic under investigation. Additionally, the empirical research questions aimed to provide conclusions regarding this topic.
The main purpose of this literature review and research method was to investigate the impact of digital games on student learning and their effects on the teaching process. Focusing on primary school students and teachers, publications irrelevant to this grade were excluded to provide a realistic picture of the outcomes. By examining published articles on educated and teaching methods, the most essential and relevant content was retained for the research. Essentially, educational games are used by many teachers across all school levels, as they are a well-known teaching method. While some teachers have not yet tried this new learning approach, they represent a small percentage that are not the focus of this study.
This research is based on investigating and analyzing published papers available on Google Scholar and Scopus, as well as currently available educational computer games. After a systematic search and screening, specific relevant articles and common elements were selected for testing on samples of interest. Given the vast amount of information on the web about computer games, our review focused on those related to education and teaching. Although most articles were recent, some older publications containing relevant and positive elements were included in our review. Furthermore, empirical research was also conducted to summarize the basic questions related to our topic and draw additional conclusions. The survey we distributed among teachers was a key tool for obtaining our conclusions. The contributions of this paper result from a comprehensive and analytical methodology aimed at discovering and synthesizing data, leading to a clear understanding of the use of electronic games in the educational process. Our research, studying existing sources, adds to existing studies on the same or related topics. In other words, this research can be considered an additional piece of research that contributes to providing further clarification on the subject, addressing concerns, and suggesting potential improvements for the future.
1.1. Principles of Learning and Gamification
The utilization of computer games in teaching could be considered the result of humanity’s great dependence on technological devices, which are the most modern and up-to-date tool a teacher could apply in the delivery of lessons. An educational computer game must be applied rationally, and first checked to ensure it meets the right learning conditions by the teacher or any responsible person, who should assess each game on a case-by-case basis before it is shown to children. The characteristics that separate one game from others in its class are mostly based on fundamental pedagogical theories of learning in which the learner is guided through experience to understanding and knowledge [
1].
There are three main learning theories that a game must be based on to be considered properly educational. The first is Behaviouralism, which is based on behavioral approaches [
2]; the second is Constructivism, which emphasizes the construction of knowledge by each child; and the third is the Sociocultural Theory of Learning, which supports cognition and teaching in the context of society [
3]. These learning theories characterize the learner-centered approach to education and are directly related to the educational value of online gaming. At present, the concept of play has taken on a new dimension, and at the sound of this concept, everyone’s mind runs to something different from the usual. The playful design projected from the computer screen during a game immediately captures attention. The introduction of computer games in the educational sector aimed to enhance student interaction and create new motivation in the learning process, with a high success rate being noted [
4]. The use of Gamification aims to render lessons more enjoyable and accessible for students, thus moving into a modernized era where everything becomes simpler, more immediate, and more interesting. Gamification has essentially been used to break down such stereotypes and create situations involving collaboration and teamwork, providing young children with motivation and the school with a new environment where the spirit of teamwork and friendliness prevails [
5,
6,
7,
8,
9,
10].
1.2. Historical Evolution of Computer Games
Games are not something new and groundbreaking, but they are a concept interwoven with human nature and date back thousands of years, with many sources referring to games from antiquity, such as those of the Ancient Greeks [
11]. The rapid development of technology in recent years is transforming perceptions associated with the word “game” and, by extension, relegating the traditional concept of games to the background [
12]. Games in digital form are shattering every kind of game that existed until now, establishing themselves in everyone’s daily life. Students’ engagement with mobile phones and tablets is commonplace today and accepted by society, although there have often been objections from parents and teachers [
13]. Their immense attraction to games has been a significant motivation for creating an educational model of games that will be displayed on a computer or tablet screen and can contribute to the formation of an individual’s personality, even when combined with ecological elements [
14].
Globally today, many societies fully recognize the pedagogical value of electronic games to the increased revenues for each company that manufactures them [
15]. Educational institutions are quickly changing because of the introduction of modern technologies and creative teaching methods. This development highlights the significance of grasping teachers’ views on the efficiency of technology in course delivery and knowledge acquisition.
1.3. Types of Computer Games in Primary Education
In recent years, there has been a particular emphasis on educational online games, both by teachers and students. An electronic game is designed to evoke a sense of curiosity and creativity in the player through graphics and animations while providing an engaging gameplay experience [
16]. This kind of game requires strategy and, in many cases, more thinking than other games of the same category, to find the solution and complete the game. Moreover, the design of this game is based on interactive methods that aim to project a mediated learning, to convey information without tiring, and to make the child see from a different perspective some lessons that may hide a higher degree of difficulty than others.
In Primary Education, the games displayed are divided into categories according to their type and style. The first is Digital Educational Games (DEGs) that allow students to identify which questions they answered incorrectly and the ones they answered correctly, rewarding them for their progress and successful completion [
17,
18,
19,
20]. These games are compatible with the abilities and level of the students they are aimed at, and offer an alternative way of teaching. It is a category of digital games found in education that has many features and is gradually being enhanced and improved.
The second category includes Serious Games (SGs), which provide numerous alternative learning opportunities and are based on computational thinking and motivating the players, i.e., the students [
21,
22,
23,
24]. These games actively contribute to the psychology of the player by using entertainment and fun to convey knowledge. To achieve this, they set a very high level of goals, tying the fun and entertainment of the individual to the resolution of the activity. Furthermore, Serious Games offer strong learning achievements to students and motivate them to broaden their cognitive subjects, even offering them intellectual growth through it. Addiction to them is common due to the intense nature they project and, in some cases, can lead to apathy and indifference in the player [
25]. Moreover, Serious Games, by displaying each child’s final score, allow everyone to know their performance and enable the teacher to assess the level of each student in the class [
26].
Furthermore, Games-Based Learning (GBL) is another category that is often used as a complementary tool in learning and teaching rather than as a primary one. Although it is well-known among educators and makes significant contributions to the educational process, there is still a perceived lack of basic evidence regarding its effectiveness. Finally, it is important to note the educational game—based platforms, which are a highly popular method of motivating students to enhance their performance in lessons. The use of Gamification in these platforms allows students to monitor their progress, while teachers can track student progress as well, rewarding students with bonuses, scores, or even prizes [
27,
28,
29]. They also contribute to relaxation for children, helping them eliminate any stress and concerns they may have [
30].
1.4. Learning Principles of Computer Games
For an electronic game to be classified as educational and effectively used in education and teaching, it must meet certain standards and requirements [
31]. The right teaching game creates intrinsic motivation in children and adults, creating a comfortable and relaxed atmosphere, without the fear of mistakes or unfair results. This view is supported by many researchers who believe it is essential to identify basic criteria that an electronic game must satisfy to be considered educational and to create intrinsic motivation in both children and adults [
32]. The criteria, therefore, that should be considered by the creators of such games are specific and could be said to constitute their basic learning principles. Principles of Learning, as defined by James Paul Gee [
33], illustrate how an online game can be an essential tool for achieving learning goals [
34]. The Learning Principles that Gee pointed out are based on elements activated when a child engages with a well-structured computer game. These principles present the conditions that make a game appealing to young people without hesitation and present a set of rules that, when applied to the game in question, immediately take on an educational form and become an essential tool for achieving many educational goals.
1.5. The Pros and Cons of Using Digital Educational Serious Games
Learning and teaching through digital games is considered the learning stream of the future [
35] with strong motivation about their usefulness. Children are more engaged and motivated to participate in lessons, thereby expanding their critical thinking by taking part in enjoyable games. Furthermore, Gamification in the school environment enhances young people’s creativity and allows them to develop other skills by engaging their imagination in a virtual environment with attractive content. Primary school children quickly become familiar with the appealing learning environment presented by online games, making the teaching and learning process easier for them. The school routine changes, and students are no longer bored with the traditional lesson format, as they now study digital material structured in a way that provides additional motivation to learn [
36]. Immediate feedback helps identify areas where they are lagging, and the sense of teamwork increases as students work collaboratively, eliminating discrimination.
However, the institutionalization of these games in schools brings some objections related to their influence and potential disruption of the course. Their impact extends beyond learning to influence the student’s personality. It is important to choose game content that promotes positive values and avoids inappropriate models. Concerns about addiction leading to isolation and misperception of reality are valid, given the prevalence of such issues among young people today [
37,
38]. While children are drawn to this new way of learning, they are not equipped to filter out non-educational games that promote negative standards, which can change their daily habits. The presentation of violence and crime, particularly in non-educational games, should be managed by teachers, who are responsible for selecting appropriate content for students [
39].
2. Research Methodology
This research and systematic review aim to clarify whether it is beneficial to use educational computer games during the learning process and what effects they have on the student profile. The purpose of this review is to inform the reader about educational computer games and provide a clearer picture of their use by children. It is an innovation in the field of education, and this method of teaching could be considered the future of educational profiling. Through an electronic game, the player can experience a beautiful virtual world that often goes beyond the limits of imagination, offering a unique experience. This applies to every type of electronic game, regardless of the categories that distinguish them; the basis of their creation and the foundations of their construction are common. Regarding educational games, there is an additional focus where the manufacturer must pay special attention: the educational nature that such a game must support.
However, for commercial reasons, some educational games may project in correct standards and convey misinformation to students. This is why every educator should review each game carefully. To record and collect all available information, a systematic survey was performed, including screening and evaluation stages. This process involved searching for relevant publications, leading to information that allowed us to draw clear conclusions. The empirical research that followed was implemented using questionnaires and provided a clearer picture οf the topic, despite limitations and difficulties encountered. More specifically, our survey was designed to answer the following research questions (RQ):
RQ1: What is the teachers’ opinion on the use of computer games in the classroom?
RQ2: Can children adapt to this new way of teaching?
RQ3: Which type of game is more usable and familiar to teachers and children?
RQ4: What effects do games played on the computer screen have on children?
Through the bibliographic research, our questions were answered to a significant extent. Frequently repeating the term “educational computer games” helped maintain focus on the topic and avoid diverging into the broader and more diverse general category. Even alternative terminology, such as digital educational games or electronic content games, was used and provided valuable information.
2.1. Empirical Research
Keeping in mind that computer games have made their presence felt in educational structures, the questions that are considered very important and will lead us to our conclusions focus particularly on those cases that use them. The case study was based on quantitative data collected through a questionnaire. The survey involved primary school teachers working in public schools across the country, with the anonymity of each respondent fully respected. More specifically, the questionnaire consisted of 33 questions, most of them closed-ended, some multiple-choice, a few Likert scale questions, and an optional open-ended question. Considering that there are also cases of teachers who have never used any digital games in teaching, we gave the option to go to the last section of the questionnaire, where there are judgment questions independent of whether they have chosen this method of teaching or not.
In particular, the questions are divided into the following categories:
- i.
General questions about their effect on children.
- ii.
Questions that analyze each game individually.
- iii.
Questions about their application in schools in general.
2.2. Demographic Data
A total of 90 responses were collected and analyzed. Of these, 49 were from women (54.44% of the sample) and 41 were from men (45.56%). Analyzing the age group of the sample, it is found that most of the teachers who participated in the survey are between 31 and 45 years old, with a percentage of 73.33%. Regarding the educational background of most of the respondents, 63.33% have a master’s degree.
Furthermore, in terms of the teachers’ specialties, it should be noted that the largest percentage of responses is from classroom teachers, marking 44.44%, followed by IT teachers, who make up 25.56% of the total. Regarding the educational experience of the respondents, the majority stated that they have 6 to 15 years of educational experience, with a percentage of 38.89%.
3. Results
3.1. RQ1: What Is the Teachers’ Opinion on the Use of Computer Games in the Classroom?
Teachers’ opinions on the use of computer games in the classroom are presented here. Based on data collection, literature review, and empirical research, the choice of digital games emerges as a modern and legitimate method embraced by educators for teaching children. Most teachers already incorporate this genre, either entirely or partially, into their lessons. They find it a very tempting proposition to use digital games to engage children. In primary school, teachers often struggle with keeping young students focused, as they may not fully understand their surroundings or the lessons being taught, but this method of teaching counters that issue.
3.2. RQ2: Can Children Cope with This New Way of Teaching?
This question aimed to assess how well-prepared young learners are to navigate the new reality of digital learning. Most positive responses indicate that children are quite ready for this change. As mentioned before, digital learning is not unfamiliar to them. The use of gamification from a young age is now very common, and as children grow older, they acquire skills that help them transition more easily into this realm. Of course, within the school context, an online game must have a teaching profile and corresponding learning objectives, but it is structured with the same logic as other educational games available online.
3.3. RQ3: Which Type of Game Is Most Usable and Familiar to Teachers?
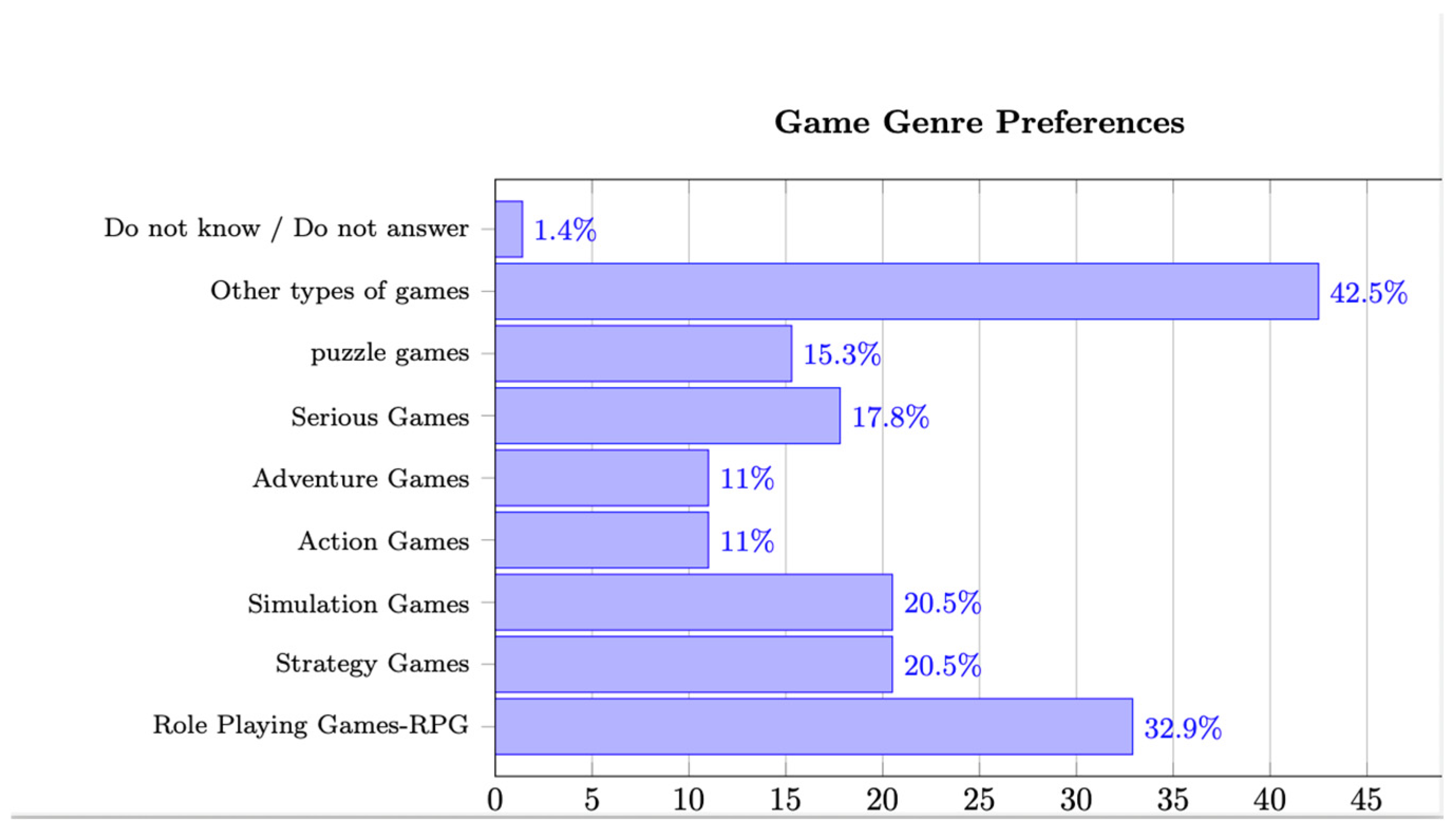
This question was posed to clarify which games teachers prefer for children and which genres they tend to avoid. Puzzle games lead over other genres. Electronic puzzle games share many features with tactile puzzles, making them familiar to both students and teachers. Puzzles are games that exercise the mind and imagination, make you think from different perspectives, and require the use of memory at regular intervals. All these elements are enticing and strong suggestions for teachers who want to incorporate games into their teaching. It should also be noted that children often show interest in action and adventure games, where their imagination can run wild and lead them into fantastical worlds.
3.4. RQ4: What Are the Effects of Computer Games on Children?
A technological device inevitably influences the young student, making this a fundamental question. The effects of computer games on children can be both positive and negative. According to the responses received, teachers strongly believe that using online games in the classroom enhances children’s participation in the lesson and motivates them to attend. Learning outcomes are improved, and the evaluation process becomes more immediate, with feedback displayed instantly on the screen. Additionally, children’s familiarity with computer games contributes significantly to the positive handling of the process, making the course they are following more understandable and reducing questions and concerns in most cases.
3.5. Figures
The results of the empirical research are presented in the following
Figure 1.
4. Discussion
Serious games have a positive impact on primary school students’ cognition and learning achievements, though competition and inadequate methodology can increase anxiety. These games are as effective as traditional methods, such a sprinted text, in health care education and STEM subjects, promoting good performance and satisfaction. Game-based learning enhances motivation and results, particularly in logical-mathematical, naturalistic, and linguistic abilities.
Serious games and gamification are valuable tools in education, combining serious intent with playful elements to create a safe and engaging learning environment. They significantly improve knowledge, skills, and satisfaction, though the approach’s methodology must be carefully considered to avoid negative impacts. Overall, serious games enhance curriculum aspects, promoting student engagement, motivation, independence, autonomy, and self-esteem across all educational levels. Integrating serious games into primary education can significantly enhance students’ learning experiences and engagement. These games transform learning into a fun, interactive experience, making the educational process more enjoyable and effective for primary school students. They serve as versatile teaching tools, particularly effective in subjects like road safety, sustainability, and mathematics. Additionally, serious games offer tailored learning experiences for neurotypical children, including those with dyslexia, addressing diverse learning needs [
40,
41,
42,
43]. To design effective serious games for primary education, it is essential to focus on simplicity and intuitive gameplay, especially for older primary school students. Incorporating engaging elements like card collecting mechanics, geo-referencing, and augmented reality can significantly enhance the learning experience. Involving primary school students and education professionals in the design process ensures that the games meet the specific needs and preferences of the target audience.
Implementing serious games in primary school curricula requires alignment with learning objectives and the syllabus. Providing open access to Serious Games is key to widespread adoption. Continuous evaluation of the effectiveness and usability of serious games helps ensure the quality of educational resources and identify areas for improvement.
4.1. Case: Serious Games and Children with Disabilities
The learning outcomes of children with disabilities in basic education are significantly improved by playing serious games. These games enhance motivation and interest, leading to increased participation and sustained attention, as children find the material more engaging and entertaining. The interactive and immersive aspects of serious games help children who struggle with attention, memory, and executive control to stay focused. Serious games also improve reading proficiency, particularly in metaphonological and literacy skills. Most existing games focus on literacy skills like reading, but often neglect basic abilities like spelling and text comprehension [
44,
45,
46,
47].
Furthermore, serious games enhance motor and cognitive abilities, improving motor skills, hand-eye coordination, and cognitive reinforcement. Including serious games in rehabilitation therapies for kids with impairments adds variety to traditional therapy methods, making the learning process more interactive and enjoyable.
Professionals who assist students with disabilities and the students themselves view serious games and technology positively. These games are seen as helpful tools for parents, teachers, and children to enhance the educational experience for kids with disabilities, improving overall engagement and learning outcomes [
48,
49].
4.2. Serious Games Limitations
Incorporating educational games into elementary schooling shows promise yet encounters various obstacles. Not every student has the technological resources required, such as computers, tablets, or dependable internet access. Some schools do not have the modern technology or enough internet capacity to accommodate serious games. Furthermore, challenges like compatibility issues with varying devices and operating systems, as well as the necessity for continuous technical assistance and upkeep, present major obstacles. It can be challenging from a teaching perspective to make sure that educational video games are in sync with the curriculum and learning objectives. Conventional evaluation techniques may not accurately gauge student development using these modern resources. Teachers might encounter gaps in training as well, missing the necessary skills to effectively implement serious games in their classrooms. Resistance to change could also act as an obstacle, with certain educators favoring conventional teaching approaches or feeling hesitant towards adopting new technologies.
When it comes to educational value, games may be very captivating, but there is a concern that the fun elements could outshine the educational material. It is difficult to ensure that serious games offer profound and significant learning experiences, rather than mere superficial engagement. Moreover, excessive use of games could lessen students’ inner drive to learn, and they may also divert attention from other crucial learning aspects.
In terms of finances, developing and incorporating high-quality educational games in schools can come with a hefty price tag. Frequent updates, payment for licenses, and upkeep contribute to the financial load. Ultimately, serious games have the potential to enhance learning by increasing engagement and interaction, although their implementation is crucial.
5. Conclusions
This paper investigated the use of educational computer games during the school process in the context of primary education. It also aimed to study the effect that they have when used on students’ learning. Gamification, on its face, is now a promising solution to traditional learning systems, incorporating elements of play mechanisms that help to enhance the child’s motivation. Although at the sound of this word, one’s mind may be transported to fun and entertainment, their introduction to schools and their integration into the teaching of children in the classroom through them is something innovative and completely legitimate to teachers and children. Nowadays, there is a plethora of digital games with an educational profile, the purpose of their use being to develop the child’s strategies and skills through a virtual world. In the research that was carried out, an attempt was made to detect the general opinion of primary school teachers towards the use of computer games in teaching. So, during our research methodology, some conclusions were also found, which are derived from all the data collected and extensively researched.
Through the survey, questions were asked that could be answered by both teachers who use them and by teachers who have never used them. Based on the answers we received, it appears that teachers are generally aware of the use of computer games in the educational process and consider that this method has a very positive impact on the whole process. It seems, therefore, that they are a very powerful tool for every teacher today, given that children are already very familiar with most technological tools. The digital game broadens their interest in the classroom, enhances teamwork and participation in the lesson, and promotes their critical thinking in an orderly way without them realizing it. If used in the right way by students, there is much to be gained by both the teacher and the child. A basic prerequisite for all this, of course, is the proper information of the teacher on their correct use and the correct way of teaching them. To achieve this, a basic requirement is the proper preparation by the teacher to make the right choice of game in each case according to the profile of the children to whom it is addressed. Some games are not appropriate for children, but for commercial reasons declare themselves educational and that they be aimed at children of a young age group.
In conclusion, given the importance of the very fast development of technology, the education sector should be modernized with the new data and not lag to any extent. The technological sector has invaded the daily life of all of us, and many times we cannot imagine our life without its elements. Even someone who is not particularly involved in technology has some knowledge of it, as many things cannot be implemented without it, which makes it a necessity, we could say. Thus, we should not overlook our constant information about every single development that exists, but instead we should be informed, if not about everything, about the absolute necessities. Regarding the educational process and school units, this is even more essential as we are addressing children whose minds are in constant progress. Thus, the education system should not remain stagnant, but, on the contrary, we should further develop everything connected with the future of children.
Therefore, our study displays some results that can be considered in the future, reinforcing the positive aspects of their use and anticipating situations that may have negative consequences. The student’s interest remains at the center of the lesson, and the teacher’s teaching becomes an easier process, promoting through this the evolution of technological media within educational contexts. However, it should be noted that their use poses risks in some cases of misuse by children. In conclusion, it is noted that it is essential to train teachers to extract the information correctly and make proper use of the game in question.
6. Future Trends
During the research period, some limitations were noted regarding the questionnaire, the available computer games, as well as the time frame of the study, and their search that was performed. Therefore, in future research, it is suggested to conduct qualitative research by interviewing both teachers and students since it is something that concerns them directly. Furthermore, comparing the collected data with future data could provide insights into potential improvements or negative consequences associated with the current findings. From an educational standpoint, serious games will be incorporated into the curriculum more smoothly, connecting with learning goals and encouraging interdisciplinary learning and critical thinking abilities. Teachers can use real-time analytics to receive feedback, monitor student progress, and pinpoint areas in need of extra assistance. Competency-based evaluations will enable students to advance depending on their mastery level instead of their age or grade, encouraging a more individualized learning experience.
Socially, increased games will enhance collaboration, teamwork, and communication abilities by engaging in group challenges and projects. Online platforms provide the opportunity for students from various locations to engage with each other and gain knowledge collectively, encouraging global understanding and cultural sharing. Serious games will incorporate more elements that foster social-emotional learning (SEL), aiding in the growth of empathy, self-regulation, and interpersonal skills in students.
When creating future serious games, designers will prioritize universal access to accommodate a wide range of learning needs and disabilities. Games will provide language choices to help students of different linguistic backgrounds. With technology becoming cheaper, more schools can incorporate serious games without facing major financial obstacles.
Educational policies will start to acknowledge the importance of serious games, offering financial support and resources for their implementation. Governments and schools will provide additional training opportunities for educators to effectively integrate serious games into their teaching. Collaborations among educational institutions, game developers, and tech companies will foster innovation and guarantee that games adhere to educational standards.