Event-Driven Data Orchestration: A Modular Approach for High-Volume Real-Time Processing †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work and Background
- The data production module;
- The data transfer module;
- The data processing and storage module.
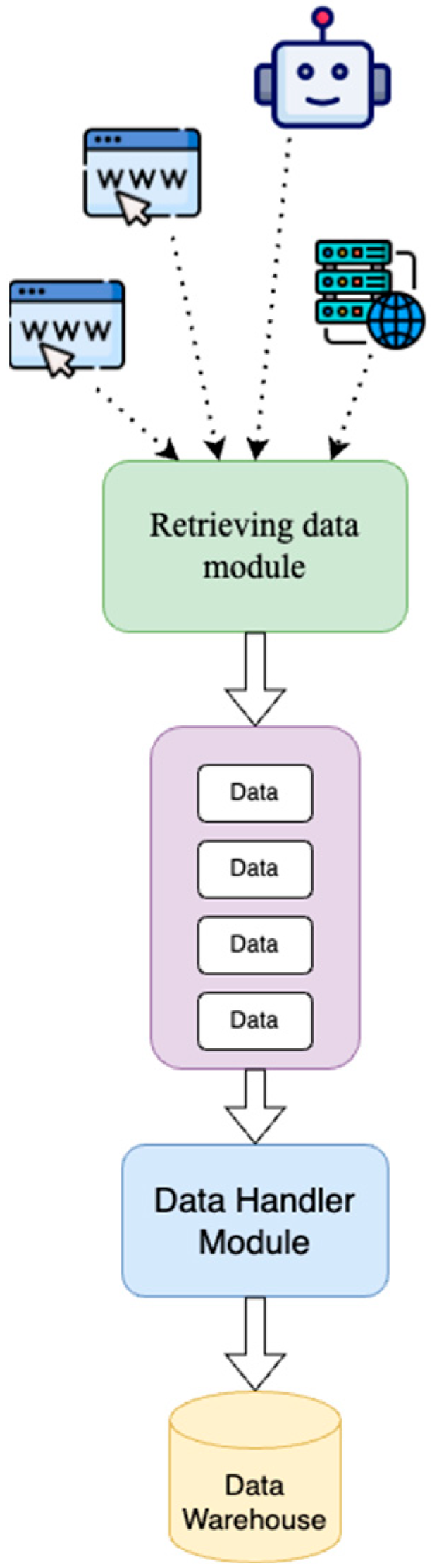
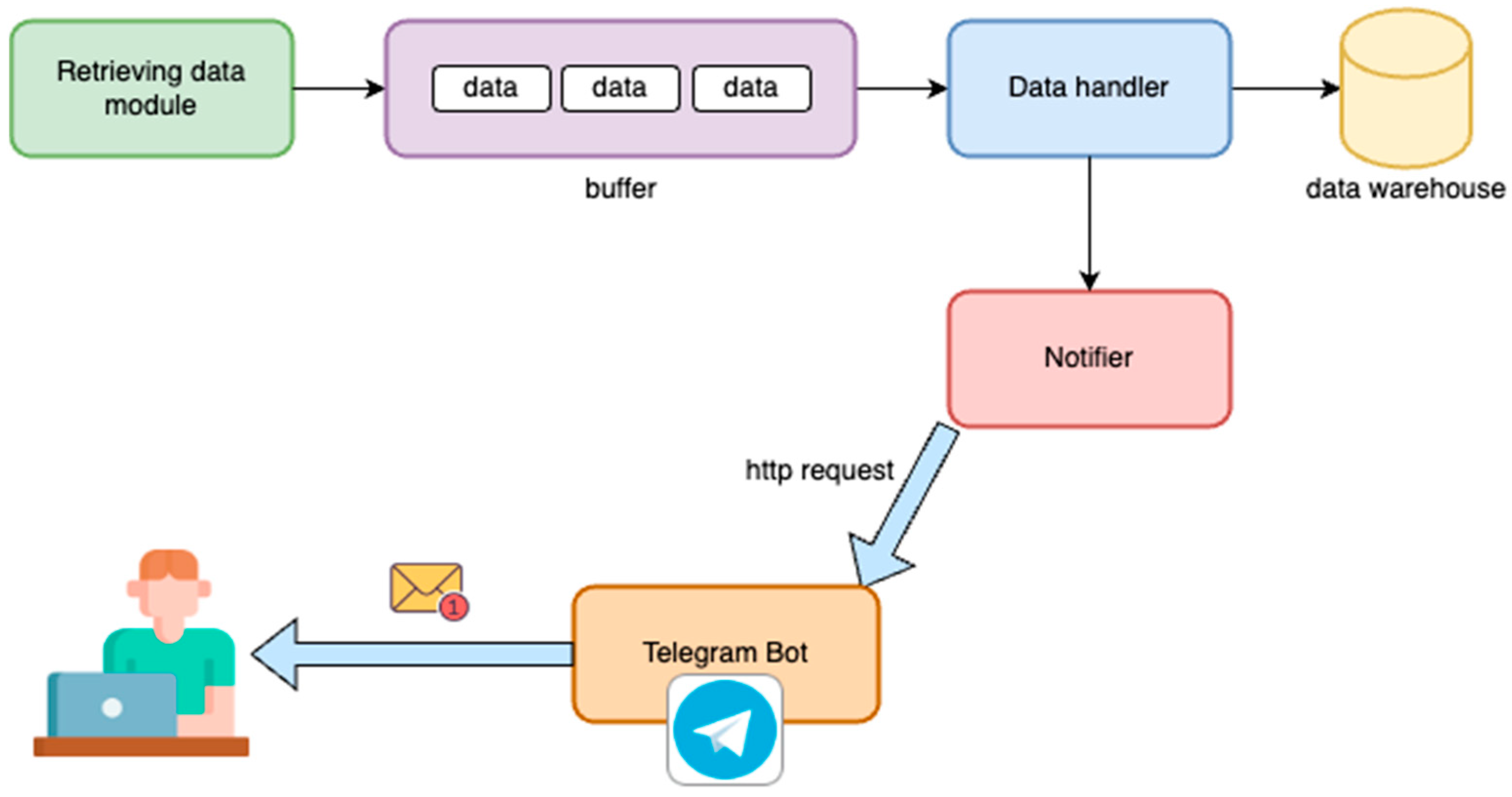
2.1. Data Producer Module
- -
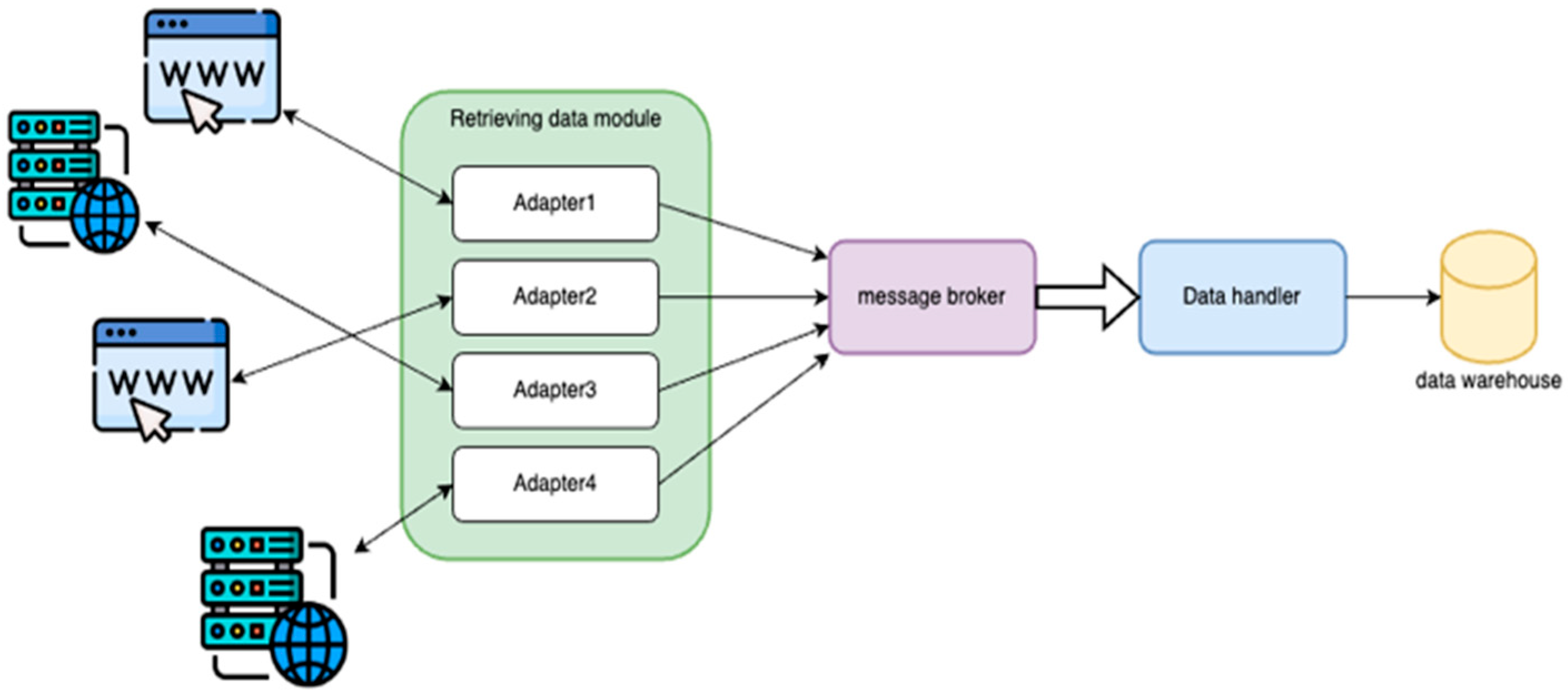
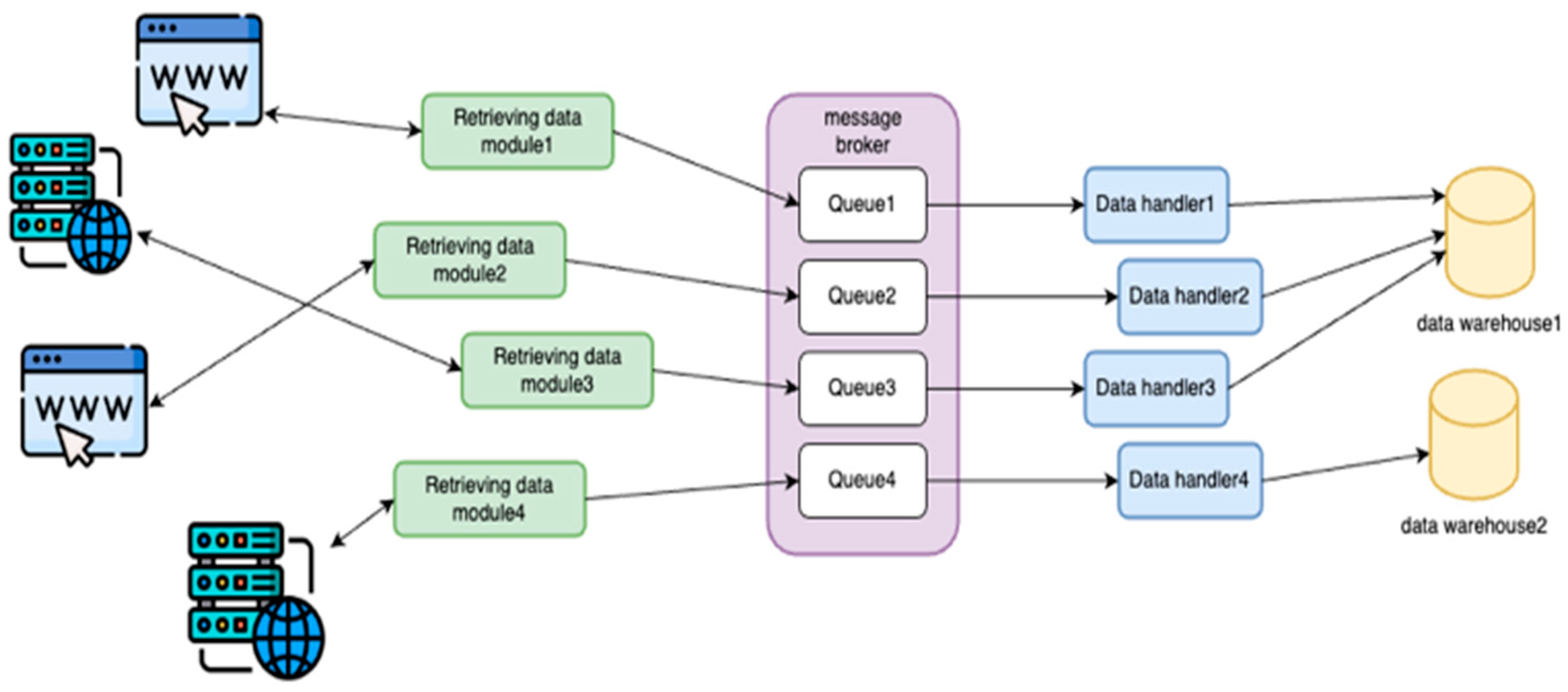
- Modular Data Producer
- -
- Each data producer in a separate process
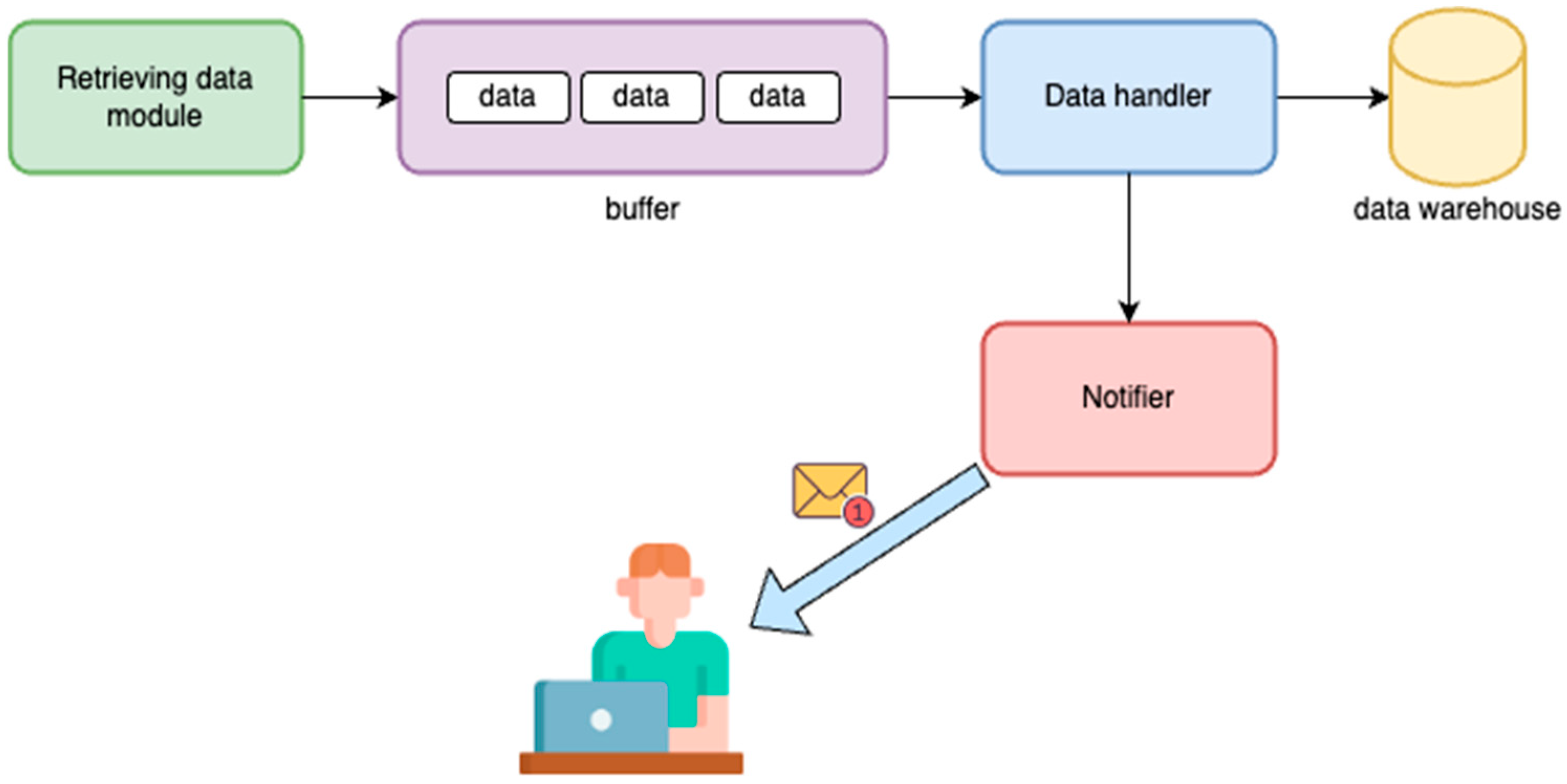
2.2. Data Buffering Module
2.3. Data Consumption and Processing Module
- -
- The component as a set of processes
2.4. Event Detection and Notification System
3. Resource Optimization and Performance Insights
3.1. Experimental Data and Scenario
- Emulate real-world data heterogeneity, as objects featured variations in attributes;
- Test the adaptability of the ingestion layer to dynamic data formats through modular adapters;
- Validate processing and storage efficiency under realistic streaming workloads.
3.2. Performance Benchmarking and Results
3.3. Results of System Objectives
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Murad, S. Big data marketing. In The Essentials of Today’s Marketing; Tarakçı, i.E., Aslan, R., Eds.; Efe Academy Publishing: Muğla, Turkey, 2023; pp. 265–284. [Google Scholar]
- Divyeshkumar, V. Big Data in Marketing Strategy. Available online: https://www.igi-global.com/gateway/chapter/359370 (accessed on 1 July 2025).
- K, S.K. Exploring Real-Time Data Processing Using Big Data Frameworks. Commun. Appl. Nonlinear Anal. 2024, 31, 620–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inmon, W.H. Building the Data Warehouse; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Kimball, R. The Data Warehouse Toolkit: Practical Techniques for Building Dimensional Data Warehouses; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Bystrov, S.; Kushnerov, A. Asynchronous Data Processing. Behavior Analysis. 2022. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Alexander-Kushnerov/publication/362910934_Asynchronous_Data_Processing_Behavior_Analysis/links/6307535a61e4553b9538f614/Asynchronous-Data-Processing-Behavior-Analysis.pdf (accessed on 15 July 2025).
- Alfaia, E.C.; Dusi, M.; Fiori, L.; Gringoli, F.; Niccolini, S. Fault-Tolerant Streaming Computation with BlockMon. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM), San Diego, CA, USA, 6–10 December 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Pogiatzis, A.; Samakovitis, G. An Event-Driven Serverless ETL Pipeline on AWS. Appl. Sci. 2020, 11, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khriji, S.; Benbelgacem, Y.; Chéour, R.; Houssaini, D.E.; Kanoun, O. Design and implementation of a cloud-based event-driven architecture for real-time data processing in wireless sensor networks. J. Supercomput. 2022, 78, 3374–3401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatipamula, S. Real-Time vs. Batch Data Processing: When speed matters. World J. Adv. Res. Rev. 2025, 26, 1612–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speckhard, D.; Bechtel, T.; Ghiringhelli, L.M.; Kuban, M.; Rigamonti, S.; Draxl, C. How big is Big Data? Faraday Discuss. 2024, 256, 483–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmstedt, J. Development of a modular open systems approach to achieve power distribution component commonality. In Proceedings of the Ground Vehicle Systems Engineering and Technology Symposium (GVSETS), 2024, Novi, MI, USA, 15–17 August 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M. Design and implementation of asynchronous FIFO. Appl. Comput. Eng. 2024, 70, 220–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meixia, M.; Siqi, Z.; Jiawei, L.; Jianghong, W. Aggregatably Verifiable Data Streaming. IEEE Internet Things J. 2024, 11, 24109–24122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, D.; Sonwane, A.; Wadhwa, N.; Mehrotra, A.; Utpala, S.; Bairi, R.; Kanade, A.; Natarajan, N. MASAI: Modular Architecture for Software-engineering AI Agents. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2406.11638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mainali, D.; Nagarkoti, M.; Dangol, J.; Pandit, D.; Adhikari, O.; Sharma, O.P. Cloud Computing Fault Tolerance. Int. J. Innov. Sci. Res. Technol. (IJISRT) 2024, 9, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouvier, T.; Nicolae, B.; Chaugier, H.; Costan, A.; Foster, I.; Antoniu, G. Efficient Data-Parallel Continual Learning with Asynchronous Distributed Rehearsal Buffers. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE 24th International Symposium on Cluster, Cloud and Internet Computing (CCGrid), Philadelphia, PA, USA, 6–9 May 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, M.; Jang, J.; Choi, Y.; Yang, H.J. Distributed Task Offloading and Resource Allocation for Latency Minimization in Mobile Edge Computing Networks. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2024, 23, 15149–15166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyjach, S.; Plechawska-Wójcik, M. Efficiency comparison of message brokers. J. Comput. Sci. Inst. 2024, 31, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mager, T. Big Data Forensics on Apache Kafka. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Information Systems Security, Raipur, India, 16–20 December 2023; pp. 42–56. [Google Scholar]
- Ayanoglu, E.; Aytas, Y.; Nahum, D. Mastering RabbitMQ; Packt Publishing Ltd.: Birmingham, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Banowosari, L.Y.; Purnamasari, D. Approach for Unwrapping the Unstructured to Structured Data the Case of Classified Ads in HTML Format. Adv. Sci. Lett. 2016, 22, 1909–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cheruku, S.R.; Jain, S.; Aggarwal, A. Building Scalable Data Warehouses: Best Practices and Case Studies. Mod. Dyn. Math. Prog. 2016, 1, 116–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Z.; Wang, H.; Dong, Z. Feature Selection on Inconsistent Data. In Dirty Data Processing for Machine Learning; Springer: Singapore, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, A.; Prasad, R. Java Classes. 2024. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/380464284_Java_Classes?channel=doi&linkId=663da12008aa54017af11b2b&showFulltext=true (accessed on 15 July 2025).
- Setiawan, I.P.E.; Desnanjaya, I.G.M.N.; Supartha, K.D.G.; Ariana, A.G.B.; Putra, I.D.P.G.W. Implementation of Telegram Notification System for Motorbike Accidents Based on Internet of Things. J. Galaksi 2024, 1, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Architecture | CPU Usage (%) | Memory Usage (MB) | Throughput (Messages/s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Parallel Consumers | 75 | 1200 | 5000 |
| Unified Consumer | 40 | 300 | 4500 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dakov, S.; Dakova, M. Event-Driven Data Orchestration: A Modular Approach for High-Volume Real-Time Processing. Eng. Proc. 2025, 100, 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025100048
Dakov S, Dakova M. Event-Driven Data Orchestration: A Modular Approach for High-Volume Real-Time Processing. Engineering Proceedings. 2025; 100(1):48. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025100048
Chicago/Turabian StyleDakov, Stanislav, and Megi Dakova. 2025. "Event-Driven Data Orchestration: A Modular Approach for High-Volume Real-Time Processing" Engineering Proceedings 100, no. 1: 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025100048
APA StyleDakov, S., & Dakova, M. (2025). Event-Driven Data Orchestration: A Modular Approach for High-Volume Real-Time Processing. Engineering Proceedings, 100(1), 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025100048






