The Preparation and Characterization of Different Types of Eggshells Acidified with Acetic Acid †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Eggshells Treatment with Acetic Acid
2.3. Characterization Techniques
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. TEM
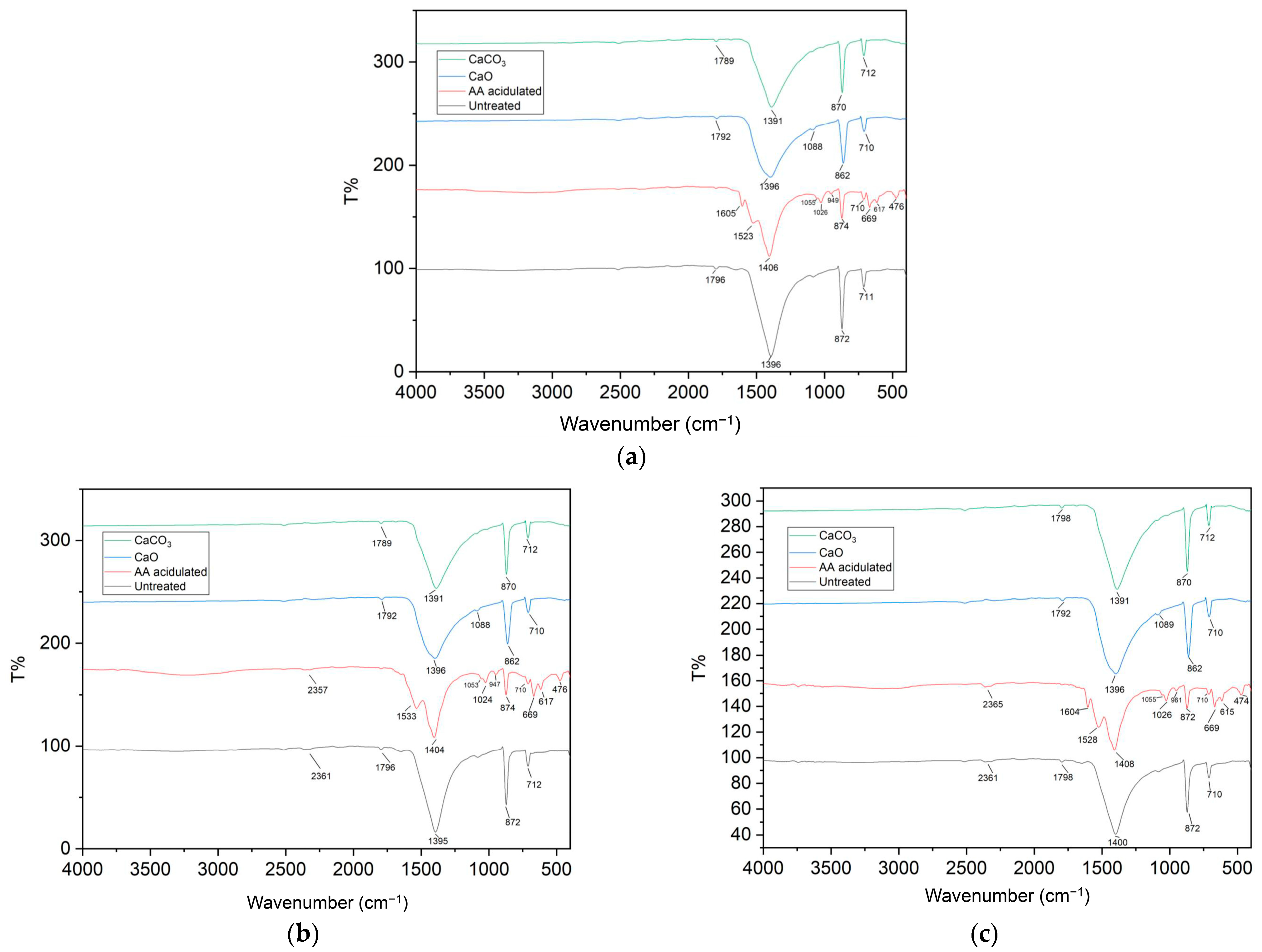
3.2. FT-IR
3.3. Eggshells’ Thermal Decomposition
- Weight loss, 40–205 °C: Organic eggshells exhibited the highest residue weight (5.89%), while commercial eggshells had the lowest (4.16%). Hatched eggshells had a residue weight of 4.23%.
- Weight loss, 205–550 °C: ecological eggshells also had the highest weight loss (24.59%) at a maximum temperature of 421 °C, with commercial (22.68%) and hatched (22.83%) eggshells following closely, but at higher temperatures, 426–427 °C.
- Weight loss, 550–850 °C: commercial eggshells had the highest weight loss (32.78%) in this range, at 738 °C, whereas hatched (32.48%) and ecological (30.95%) eggshells had slightly lower values, but also at a lower temperature, namely 735 °C.
- Weight loss, 850–1000 °C: ecological eggshells exhibited the highest residue weight loss (0.49%), followed by commercial (0.46%) and hatched (0.21%) eggshells.
- Commercial eggshells had the highest weight loss (40.38%) at 1000 °C, followed by hatched (40.44%) and ecological (38.55%) eggshells.
- Residue weight loss: ecological eggshells had the lowest residue weight loss (38.07%) over 1000 °C, while hatched (40.23%) and commercial (39.91%) eggshells had slightly higher values.
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ahmed, T.A.E.; Wu, L.; Younes, M.; Hincke, M. Biotechnological Applications of Eggshell: Recent Advances. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 675364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanani, F.; Heidari, M.D.; Gilroyed, B.H.; Pelletier, N. Waste valorization technology options for the egg and broiler industries: A review and recommendations. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 262, 121129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aditya, S.; Stephen, J.; Radhakrishnan, M. Utilization of eggshell waste in calcium-fortified foods and other industrial applications: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 115, 422–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, Y. Preparation of Calcium Magnesium Acetate Snow Melting Agent Using Raw Calcium Acetate-Rich Made from Eggshells. Waste Biomass Valorization 2020, 11, 6757–6767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; Tsai, W.-S.; Chen, S.-T. Reusing shell waste as a soil conditioner alternative? A comparative study of eggshell and oyster shell using a life cycle assessment approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 265, 121845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ok, Y.S.; Lee, S.S.; Jeon, W.-T.; Oh, S.-E.; Usman, A.R.A.; Moon, D.H. Application of eggshell waste for the immobilization of cadmium and lead in a contaminated soil. Environ. Geochem. Health 2011, 33, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Angelis, G.; Medeghini, L.; Conte, A.M.; Mignardi, S. Recycling of eggshell waste into low-cost adsorbent for Ni removal from wastewater. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 164, 1497–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Xu, C.; Li, B. Application of waste eggshell as low-cost solid catalyst for biodiesel production. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 2883–2885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, S.-L.; Li, F.-Y.; Lin, P.-Y.; Beck, D.E.; Kirankumar, R.; Wang, G.-J.; Hsieh, S. CaO recovered from eggshell waste as a potential adsorbent for greenhouse gas CO2. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 297, 113430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waheed, M.; Yousaf, M.; Shehzad, A.; Inam-Ur-Raheem, M.; Khan, M.K.I.; Khan, M.R.; Ahmad, N.; Abdullah; Aadil, R.M. Channelling eggshell waste to valuable and utilizable products: A comprehensive review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 106, 78–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quina, M.J.; Soares, M.A.R.; Quinta-Ferreira, R. Applications of industrial eggshell as a valuable anthropogenic resource. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2017, 123, 176–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aina, S.T.; Du Plessis, B.J.; Mjimba, V.; Brink, H.G. From Waste to Best: Valorization and Upcycling of Chicken Eggshells. In Waste Management; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2022; pp. 140–155. [Google Scholar]
- Witoon, T. Characterization of calcium oxide derived from waste eggshell and its application as CO2 sorbent. Ceram. Int. 2011, 37, 3291–3298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEA. CO2 Emissions—Global Energy Review 2021—Analysis—IEA. Available online: https://www.iea.org/reports/global-energy-review-2021/co2-emissions (accessed on 12 October 2023).
- Sayari, A.; Belmabkhout, Y.; Serna-Guerrero, R. Flue gas treatment via CO2 adsorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 171, 760–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Otto, A.; Robinius, M.; Stolten, D. A Review of Post-combustion CO2 Capture Technologies from Coal-fired Power Plants. Energy Procedia 2017, 114, 650–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cormos, C.-C. Techno-economic assessment of calcium and magnesium-based sorbents for post-combustion CO2 capture applied in fossil-fueled power plants. Fuel 2021, 298, 120794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvez-Martos, J.-L.; Elhoweris, A.; Morrison, J.; Al-horr, Y. Conceptual design of a CO2 capture and utilisation process based on calcium and magnesium rich brines. J. CO2 Util. 2018, 27, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Duan, L.; Sun, Z. Review on the Development of Sorbents for Calcium Looping. Energy Fuels 2020, 34, 7806–7836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erans, M.; Manovic, V.; Anthony, E.J. Calcium looping sorbents for CO2 capture. Appl. Energy 2016, 180, 722–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, N.; Alonso, M.; Abanades, J.C. Average activity of CaO particles in a calcium looping system. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 156, 388–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perejón, A.; Romeo, L.M.; Lara, Y.; Lisbona, P.; Martínez, A.; Valverde, J.M. The Calcium-Looping technology for CO2 capture: On the important roles of energy integration and sorbent behavior. Appl. Energy 2016, 162, 787–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieter, H.; Bidwe, A.R.; Varela-Duelli, G.; Charitos, A.; Hawthorne, C.; Scheffknecht, G. Development of the calcium looping CO2 capture technology from lab to pilot scale at IFK, University of Stuttgart. Fuel 2014, 127, 23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacia, E.R.; Ramkumar, S.; Phalak, N.; Fan, L.-S. Synthesis and Regeneration of Sustainable CaO Sorbents from Chicken Eggshells for Enhanced Carbon Dioxide Capture. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2013, 1, 903–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawar, A.; Ali, M.; Khoja, A.H.; Waqas, A.; Anwar, M.; Mahmood, M. Enhanced CO2 capture using organic acid structure modified waste eggshell derived CaO sorbent. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 104871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imani, M.; Tahmasebpoor, M.; Sánchez-Jiménez, P.E.; Valverde, J.M.; Moreno, V. Improvement in cyclic CO2 capture performance and fluidization behavior of eggshell-derived CaCO3 particles modified with acetic acid used in calcium looping process. J. CO2 Util. 2022, 65, 102207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, R.; Shi, Y.; An, P.; Hu, X.; Wan, Y. Optimization of preparation of calcium acetate from eggshell by Response Surface Methodology (RSM). Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 42, e114421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strelec, I.; Tomičić, K.; Zajec, M.; Ostojčić, M.; Budžaki, S. Eggshell-Waste-Derived Calcium Acetate, Calcium Hydrogen Phosphate and Corresponding Eggshell Membranes. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 7372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawar, A.; Ghaedi, H.; Ali, M.; Zhao, M.; Iqbal, N.; Khan, R. Recycling waste-derived marble powder for CO2 capture. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2019, 132, 214–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minakshi, M.; Higley, S.; Baur, C.; Mitchell, D.R.G.; Jones, R.T.; Fichtner, M. Calcined chicken eggshell electrode for battery and supercapacitor applications. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 26981–26995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tangboriboon, N.; Kunanuruksapong, R.; Sirivat, A. Preparation and properties of calcium oxide from eggshells via calcination. Mater. Sci.-Pol. 2012, 30, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohadi, R.; Anggraini, K.; Riyanti, F.; Lesbani, A. Preparation Calcium Oxide from Chicken Eggshells. Sriwij. J. Environ. 2016, 1, 32–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, L.-F.; Lien, C.-F.; Lin, J.-L. FTIR study of adsorption and photoreactions of acetic acid on TiO2. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2001, 3, 3831–3837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Eggshell Sample | 40–205 °C | 205–550 °C | 550–850 °C | 850–1000 °C | Residue | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wt. loss | Wt. loss | Tmax | Wt. loss | Tmax | Wt. loss | 850 °C | 1000 °C | |
| % | % | °C | % | °C | % | % | % | |
| Hatched | 4.23 | 22.83 | 426.2 | 32.48 | 735.0 | 0.21 | 40.44 | 40.23 |
| Conventional | 4.16 | 22.68 | 427.3 | 32.78 | 737.8 | 0.46 | 40.38 | 39.91 |
| Organic | 5.89 | 24.59 | 421.2 | 30.95 | 735.3 | 0.49 | 38.55 | 38.07 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Brettfeld, E.-G.; Popa, D.-G.; Somoghi, R.; Nicolae, C.A.; Birtas, A.; Constantinescu-Aruxandei, D.; Oancea, F. The Preparation and Characterization of Different Types of Eggshells Acidified with Acetic Acid. Chem. Proc. 2023, 13, 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemproc2023013032
Brettfeld E-G, Popa D-G, Somoghi R, Nicolae CA, Birtas A, Constantinescu-Aruxandei D, Oancea F. The Preparation and Characterization of Different Types of Eggshells Acidified with Acetic Acid. Chemistry Proceedings. 2023; 13(1):32. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemproc2023013032
Chicago/Turabian StyleBrettfeld, Eliza-Gabriela, Daria-Gabriela Popa, Raluca Somoghi, Cristian Andi Nicolae, Adrian Birtas, Diana Constantinescu-Aruxandei, and Florin Oancea. 2023. "The Preparation and Characterization of Different Types of Eggshells Acidified with Acetic Acid" Chemistry Proceedings 13, no. 1: 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemproc2023013032
APA StyleBrettfeld, E.-G., Popa, D.-G., Somoghi, R., Nicolae, C. A., Birtas, A., Constantinescu-Aruxandei, D., & Oancea, F. (2023). The Preparation and Characterization of Different Types of Eggshells Acidified with Acetic Acid. Chemistry Proceedings, 13(1), 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemproc2023013032








