Integrated Evaluation of CPAP Therapy in Type 2 Diabetic Patients with Sleep Apnea: Quality of Life and Effects on Metabolic Function and Inflammation in Outpatient Care
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics of the Study Groups
3.2. Follow-Up at the 6th Month
3.3. Dynamics Between the Baseline and the 6th Month in the Study Groups
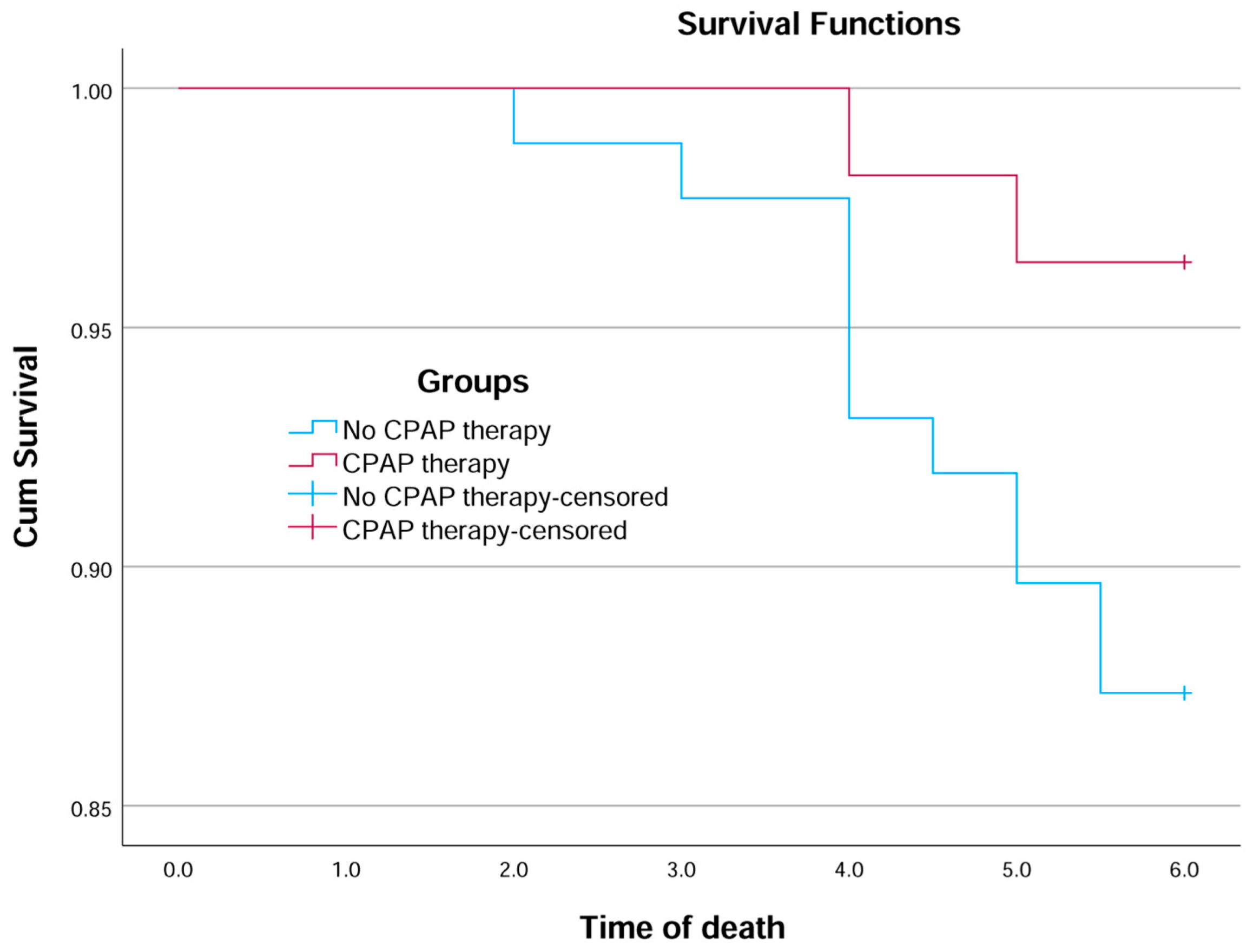
3.4. Survival Analysis
4. Discussion
Strengths and Limitations of the Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACE | Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme |
| AHI | Apnea-Hypopnea Index |
| ARB | Angiotensin II Receptor Blocker |
| BMI | Body Mass Index |
| CPAP | Continuous Positive Airway Pressure |
| CRP | C-Reactive Protein |
| DPP4 | Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitor |
| eGFR | Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate |
| ESS | Epworth Sleepiness Scale |
| GLP-1 RA | Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonist |
| HbA1c | Hemoglobin A1c |
| HDL | High-Density Lipoprotein |
| HR | Hazard Ratio |
| HSAT | Home Sleep Apnea Testing |
| hsCRP | High-Sensitivity C-Reactive Protein |
| IL-6 | Interleukin 6 |
| IQR | Interquartile Range |
| LDL | Low-Density Lipoprotein |
| MACE | Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events |
| MCS | Mental Component Summary (from SF-36) |
| NYHA | New York Heart Association |
| ODI | Oxygen Desaturation Index |
| OSA | Obstructive Sleep Apnea |
| PCS | Physical Component Summary (from SF-36) |
| QoL | Quality of Life |
| RCT | Randomized Controlled Trial |
| SDB | Sleep-Disordered Breathing |
| SF-36 | 36-Item Short Form Health Survey |
| SGLT2i | Sodium–Glucose Co-Transporter 2 Inhibitor |
| SpO2 | Peripheral Capillary Oxygen Saturation |
| T2D | Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus |
References
- Zhao, X.; Zhang, W.; Xin, S.; Yu, X.; Zhang, X. Effect of CPAP on blood glucose fluctuation in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep Breath. 2022, 26, 1875–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, G.; Han, D. Benefits of continuous positive airway pressure on glycaemic control and insulin resistance in patients with type 2 diabetes and obstructive sleep apnoea: A meta-analysis. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2021, 23, 540–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banghøj, A.M.; Krogager, C.; Kristensen, P.L.; Hansen, K.W.; Laugesen, E.; Fleischer, J.; Cichosz, S.L.; Poulsen, P.L.; Kirkegaard, M.G.; Thorsteinsson, B.; et al. Effect of 12-week continuous positive airway pressure therapy on glucose levels assessed by continuous glucose monitoring in people with type 2 diabetes and obstructive sleep apnoea; a randomized controlled trial. Endocrinol. Diabetes Metab. 2020, 4, e00148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aurora, R.N.; Rooney, M.R.; Wang, D.; Selvin, E.; Punjabi, N.M. Effects of Positive Airway Pressure Therapy on Glycemic Variability in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes and OSA: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Chest 2023, 164, 1057–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makhdom, E.A.; Maher, A.; Ottridge, R.; Nicholls, M.; Ali, A.; Cooper, B.G.; Ajjan, R.A.; Bellary, S.; Hanif, W.; Hanna, F.; et al. The impact of obstructive sleep apnea treatment on microvascular complications in patients with type 2 diabetes: A feasibility randomized controlled trial. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2024, 20, 947–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, Y.; Sakai, R.; Ikeda, K.; Fukui, M. Association between sleep disorder and quality of life in patients with type 2 diabetes: A cross-sectional study. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2020, 20, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, M.A.; Simpson, F.C. Obstructive sleep apnea and psychiatric disorders: A systematic review. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2015, 11, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.C.; Wu, H.T.; Huang, P.C.; Ma, H.P.; Lo, Y.L.; Huang, Y.H. Portable Sleep Apnea Syndrome Screening and Event Detection Using Long Short-Term Memory Recurrent Neural Network. Sensors 2020, 20, 6067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, I.; Marques, F.; André, S.; Araújo, M.; Marques, S.; Ferreira, R.; Moniz, P.; Proença, M.; Borrego, P.; Fonseca, C. Diagnosis of sleep apnea in patients with stable chronic heart failure using a portable sleep test diagnostic device. Sleep Breath. 2018, 22, 749–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McHorney, C.A.; Ware, J.E., Jr.; Raczek, A.E. The MOS 36-Item Short-Form Health Survey (SF-36): II. Psychometric and clinical tests of validity in measuring physical and mental health constructs. Med. Care 1993, 31, 247–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johns, M.W. A new method for measuring daytime sleepiness: The Epworth sleepiness scale. Sleep 1991, 14, 540–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimaldi, D.; Beccuti, G.; Touma, C.; Van Cauter, E.; Mokhlesi, B. Association of obstructive sleep apnea in rapid eye movement sleep with reduced glycemic control in type 2 diabetes: Therapeutic implications. Diabetes Care 2014, 37, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Cerón, E.; Barquiel, B.; Bezos, A.M.; Casitas, R.; Galera, R.; Garcia-Benito, C.; Hernanz, A.; Alonso-Fernandez, A.; Garcia-Rio, F. Effect of Continuous Positive Airway Pressure on Glycemic Control in Patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnea and Type 2 Diabetes. A Randomized Clinical Trial. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 194, 476–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heffernan, A.; Duplancic, D.; Kumric, M.; Ticinovic Kurir, T.; Bozic, J. Metabolic Crossroads: Unveiling the Complex Interactions between Obstructive Sleep Apnoea and Metabolic Syndrome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 3243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.M.; Ryu, S.Y.; Han, M.A.; Choi, S.W. Loss of significant association between high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP) and metabolic syndrome after adjustment for waist circumference found in 2022 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey data. J. Physiol. Anthropol. 2025, 44, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Luo, Q.; Wang, Z.; Chen, S.; Chen, G.; Huang, S. Effects of continuous positive airway pressure therapy on inflammatory markers in patients with obstructive sleep apnea: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Sleep Breath. 2025, 29, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malhotra, A.; Heilmann, C.R.; Banerjee, K.K.; Dunn, J.P.; Bunck, M.C.; Bednarik, J. Weight reduction and the impact on apnea-hypopnea index: A systematic meta-analysis. Sleep Med. 2024, 121, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miralles-Llumà, L.; Vilarrasa, N.; Monasterio, C.; López-Padrós, C.; Alves, C.; Planas, R.; Arribas, L.; Montserrat, M.; Pérez-Ramos, S.; Pallarès, N. Effects of a One-Year Intensified Weight Loss Program on Body Composition Parameters in Patients with Severe Obesity and Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA): A Randomized Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2024, 16, 4255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pidd, K.; Breeze, P.; Ahern, A.; Griffin, S.J.; Brennan, A. Effects of weight loss and weight gain on HbA1c, systolic blood pressure and total cholesterol in three subgroups defined by blood glucose: A pooled analysis of two behavioural weight management trials in England. BMJ Open 2025, 15, e095046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battisha, A.; Kahlon, A.; Kalra, D.K. Sleep-Disordered Breathing and Hypertension-A Systematic Review. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 3115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onyegbule, C.J.; Muoghalu, C.G.; Ofoegbu, C.C.; Ezeorah, F. The Impact of Poor Sleep Quality on Cardiovascular Risk Factors and Quality of Life. Cureus 2025, 17, e77397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi-Ghahramanloo, A.; Soltani-Kermanshahi, M.; Mansori, K.; Khazaei-Pool, M.; Sohrabi, M.; Baradaran, H.R.; Talebloo, Z.; Gholami, A. Comparison of SF-36 and WHOQoL-BREF in Measuring Quality of Life in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2020, 13, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiviott, S.D.; Berg, D.D. SGLT2 Inhibitors Reduce Heart Failure Hospitalization and Cardiovascular Death: Clarity and Consistency. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2023, 81, 2388–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanou, M.I.; Theodorou, A.; Malhotra, K.; Aguiar de Sousa, D.; Katan, M.; Palaiodimou, L.; Katsanos, A.H.; Koutroulou, I.; Lambadiari, V.; Lemmens, R.; et al. Risk of major adverse cardiovascular events and stroke associated with treatment with GLP-1 or the dual GIP/GLP-1 receptor agonist tirzepatide for type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. Stroke J. 2024, 9, 530–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Cheng, J.X.; Zhang, D.; Yi, F.; Ji, Q. Association between Obstructive Sleep Apnea and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Dose-Response Meta-Analysis. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2021, 2021, 1337118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, P.H.; Hui, C.K.M.; Lui, M.M.S.; Lam, D.C.L.; Fong, D.Y.T.; Ip, M.S.M. Incident Type 2 Diabetes in OSA and Effect of CPAP Treatment: A Retrospective Clinic Cohort Study. Chest 2019, 156, 743–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Billings, M.E.; Kapur, V.K. Medicare long-term CPAP coverage policy: A cost-utility analysis. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2013, 9, 1023–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murase, K.; Tanizawa, K.; Minami, T.; Matsumoto, T.; Tachikawa, R.; Takahashi, N.; Tsuda, T.; Toyama, Y.; Ohi, M.; Akahoshi, T.; et al. A Randomized Controlled Trial of Telemedicine for Long-Term Sleep Apnea Continuous Positive Airway Pressure Management. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2020, 17, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McEvoy, R.D.; Antic, N.A.; Heeley, E.; Luo, Y.; Ou, Q.; Zhang, X.; Mediano, O.; Chen, R.; Drager, L.F.; Liu, Z.; et al. CPAP for Prevention of Cardiovascular Events in Obstructive Sleep Apnea. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 919–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peker, Y.; Glantz, H.; Eulenburg, C.; Wegscheider, K.; Herlitz, J.; Thunström, E. Effect of Positive Airway Pressure on Cardiovascular Outcomes in Coronary Artery Disease Patients with Nonsleepy Obstructive Sleep Apnea. The RICCADSA Randomized Controlled Trial. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 194, 613–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-de-la-Torre, M.; Sánchez-de-la-Torre, A.; Bertran, S.; Abad, J.; Duran-Cantolla, J.; Cabriada, V.; Mediano, O.; Masdeu, M.J.; Alonso, M.L.; Masa, J.F.; et al. Effect of obstructive sleep apnoea and its treatment with continuous positive airway pressure on the prevalence of cardiovascular events in patients with acute coronary syndrome (ISAACC study): A randomised controlled trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patil, S.P.; Ayappa, I.A.; Caples, S.M.; Kimoff, R.J.; Patel, S.R.; Harrod, C.G. Treatment of Adult Obstructive Sleep Apnea with Positive Airway Pressure: An American Academy of Sleep Medicine Clinical Practice Guideline. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2019, 15, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Parameter | No CPAP Therapy | CPAP Therapy | p | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | % | n | % | |||
| Sex | f | 29 | 33.3 | 18 | 32.7 | 0.940 |
| m | 58 | 66.7 | 37 | 67.3 | ||
| Atrial Fibrillation | No | 71 | 81.6 | 42 | 76.4 | 0.450 |
| Yes | 16 | 18.4 | 13 | 23.6 | ||
| Dyslipidemia | No | 40 | 46.0 | 32 | 58.2 | 0.156 |
| Yes | 47 | 54.0 | 23 | 41.8 | ||
| Coronary artery disease | No | 62 | 71.3 | 35 | 63.6 | 0.341 |
| Yes | 25 | 28.7 | 20 | 36.4 | ||
| Beta blockers | No | 23 | 26.4 | 21 | 38.2 | 0.140 |
| Yes | 64 | 73.6 | 34 | 61.8 | ||
| ACE | No | 55 | 63.2 | 33 | 60.0 | 0.700 |
| Yes | 32 | 36.8 | 22 | 40.0 | ||
| ARB | No | 50 | 57.5 | 31 | 56.4 | 0.897 |
| Yes | 37 | 42.5 | 24 | 43.6 | ||
| HCTZ | No | 47 | 54.0 | 26 | 47.3 | 0.433 |
| Yes | 40 | 46.0 | 29 | 52.7 | ||
| Mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist | No | 75 | 86.2 | 48 | 87.3 | 0.856 |
| Yes | 12 | 13.8 | 7 | 12.7 | ||
| Loop diuretics | No | 76 | 87.4 | 47 | 85.5 | 0.746 |
| Yes | 11 | 12.6 | 8 | 14.5 | ||
| Statins | No | 58 | 66.7 | 40 | 72.7 | 0.447 |
| Yes | 29 | 33.3 | 15 | 27.3 | ||
| Semaglutide or Liraglutide | No | 65 | 74.7 | 43 | 78.2 | 0.690 |
| Yes | 22 | 25.3 | 12 | 21.8 | ||
| SGLT2i | No | 58 | 66.7 | 38 | 69.1 | 0.764 |
| Yes | 29 | 33.3 | 17 | 30.9 | ||
| Metformin | No | 15 | 17.2 | 14 | 25.5 | 0.237 |
| Yes | 72 | 82.8 | 41 | 74.5 | ||
| Insulins | No | 75 | 86.2 | 45 | 81.8 | 0.481 |
| Yes | 12 | 13.8 | 10 | 18.2 | ||
| DPP4 | No | 68 | 78.2 | 48 | 87.3 | 0.171 |
| Yes | 19 | 21.8 | 7 | 12.7 | ||
| Sulfonylureas | No | 72 | 82.8 | 45 | 81.8 | 0.886 |
| Yes | 15 | 17.2 | 10 | 18.2 | ||
| Chronic kidney disease | No | 71 | 81.6 | 43 | 78.2 | 0.617 |
| Yes | 16 | 18.4 | 12 | 21.8 | ||
| Parameter | Measure | No CPAP Therapy | CPAP Therapy | p | No CPAP Therapy | CPAP Therapy | p (6th Month) | p Baseline-6th Month No CPAP | p Baseline-6th Month CPAP | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median/Mean | IQR/sd | Median/Mean | IQR/sd | Median/Mean | IQR/sd | Median/Mean | IQR/sd | ||||||
| Age | Median; IQR | 60 | 54–63 | 57 | 51–64 | 0.508 | |||||||
| Body mass index (BMI, kg/m2) | Median; IQR | 28.9 | 27.2–30.3 | 28.6 | 26.6–30.6 | 0.87 | 28.9 | 27.0–30.7 | 28 | 25.6–29.2 | 0.072 | 0.599 | <0.001 |
| Epworth Sleepiness Scale | Median; IQR | 11 | 14-Jul | 11 | 13-Aug | 0.826 | 11 | 8–15 | 7 | 5–10 | <0.001 | 0.702 | <0.001 |
| SF-36 Physical Component | Mean; sd | 45 | 9 | 46 | 10 | 0.562 | 46 | 9 | 48 | 10 | 0.098 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| SF-36 Mental Component | Median; IQR | 43 | 38–53 | 44 | 40–52 | 0.537 | 44 | 39–53 | 46 | 40–54 | 0.291 | 0.299 | <0.001 |
| AHI | Mean; sd | 44.4 | 14.5 | 44.6 | 14.8 | 0.939 | 44.4 | 14.7 | 3.6 | 2.1 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.033 |
| Oxygen Desaturation Index | Mean; sd | 40.3 | 13.8 | 40.7 | 15.1 | 0.86 | 39.4 | 15.7 | 4.6 | 5.3 | <0.001 | 0.594 | <0.001 |
| Average SpO2 | Median; IQR | 91 | 89–92 | 90 | 90–92 | 0.992 | 91 | 89–92 | 97 | 97–97 | <0.001 | 0.884 | <0.001 |
| Lowest desaturation | Median; IQR | 85 | 83–87 | 87 | 85–88 | 0.023 | 85 | 83–87 | 94 | 92–95 | <0.001 | 0.179 | <0.001 |
| Time spent with oxygen saturation below 90% | Mean; sd | 11.4 | 6 | 12.2 | 6.9 | 0.439 | 11.1 | 6.3 | 5 | 3.2 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Cheyne–Stokes respirations | Median; IQR | 5.1 | 3.4–6.8 | 14.4 | 12.1–16.9 | <0.001 | 5.1 | 3.5–6.4 | 6.7 | 4.0–8.8 | 0.005 | 0.183 | <0.001 |
| eGFR Cockroft (mL/min/1.73 m2) | Mean; sd | 79.3 | 17.2 | 77.3 | 16.8 | 0.493 | 79.4 | 17.2 | 80.3 | 16.2 | 0.761 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| HbA1c (%) | Median; IQR | 8.6 | 7.9–9.4 | 8.2 | 7.5–9.5 | 0.289 | 8.3 | 7.6–9.1 | 7.7 | 6.7–8.7 | 0.005 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| hsCRP (mg/L) | Median; IQR | 2.68 | 2.08–3.39 | 2.34 | 1.81–3.41 | 0.309 | 2.76 | 2.09–3.27 | 1.45 | 1.25–2.20 | <0.001 | 0.847 | <0.001 |
| Total cholesterol (mmol/L) | Median; IQR | 5.52 | 4.92–6.10 | 5.33 | 4.87–6.02 | 0.487 | 5.37 | 4.88–5.84 | 4.95 | 4.58–5.41 | 0.004 | 0.673 | 0.852 |
| LDL (mmol/L) | Median; IQR | 3.61 | 3.02–4.10 | 3.6 | 3.03–3.89 | 0.857 | 3.68 | 3.04–4.08 | 3.22 | 2.68–3.48 | <0.001 | 0.843 | <0.001 |
| HDL (mmol/L) | Median; IQR | 1.36 | 1.16–1.54 | 1.46 | 1.22–1.62 | 0.205 | 1.37 | 1.17–1.54 | 1.59 | 1.38–1.73 | <0.001 | 0.396 | <0.001 |
| Triglycerides (mmol/L) | Median; IQR | 2.04 | 1.38–2.62 | 2.19 | 1.75–2.74 | 0.089 | 1.99 | 1.45–2.57 | 1.56 | 1.18–2.19 | 0.002 | 0.046 | <0.001 |
| Systolic blood pressure (mmHg) | Mean; sd | 122 | 11 | 124 | 10 | 0.523 | 119 | 6 | 115 | 7 | 0.003 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Diastolic blood pressure (mmHg) | Mean; sd | 77 | 5 | 78 | 6 | 0.378 | 77 | 6 | 75 | 6 | 0.18 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kalaydzhiev, P.; Velikova, T.; Davidkova, Y.; Ilieva, R.; Kinova, E.; Naseva, E. Integrated Evaluation of CPAP Therapy in Type 2 Diabetic Patients with Sleep Apnea: Quality of Life and Effects on Metabolic Function and Inflammation in Outpatient Care. Diabetology 2025, 6, 87. https://doi.org/10.3390/diabetology6090087
Kalaydzhiev P, Velikova T, Davidkova Y, Ilieva R, Kinova E, Naseva E. Integrated Evaluation of CPAP Therapy in Type 2 Diabetic Patients with Sleep Apnea: Quality of Life and Effects on Metabolic Function and Inflammation in Outpatient Care. Diabetology. 2025; 6(9):87. https://doi.org/10.3390/diabetology6090087
Chicago/Turabian StyleKalaydzhiev, Petar, Tsvetelina Velikova, Yanitsa Davidkova, Radostina Ilieva, Elena Kinova, and Emilia Naseva. 2025. "Integrated Evaluation of CPAP Therapy in Type 2 Diabetic Patients with Sleep Apnea: Quality of Life and Effects on Metabolic Function and Inflammation in Outpatient Care" Diabetology 6, no. 9: 87. https://doi.org/10.3390/diabetology6090087
APA StyleKalaydzhiev, P., Velikova, T., Davidkova, Y., Ilieva, R., Kinova, E., & Naseva, E. (2025). Integrated Evaluation of CPAP Therapy in Type 2 Diabetic Patients with Sleep Apnea: Quality of Life and Effects on Metabolic Function and Inflammation in Outpatient Care. Diabetology, 6(9), 87. https://doi.org/10.3390/diabetology6090087









