The Diabetes-Pancreatic Cancer Risk Relationship over Time: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
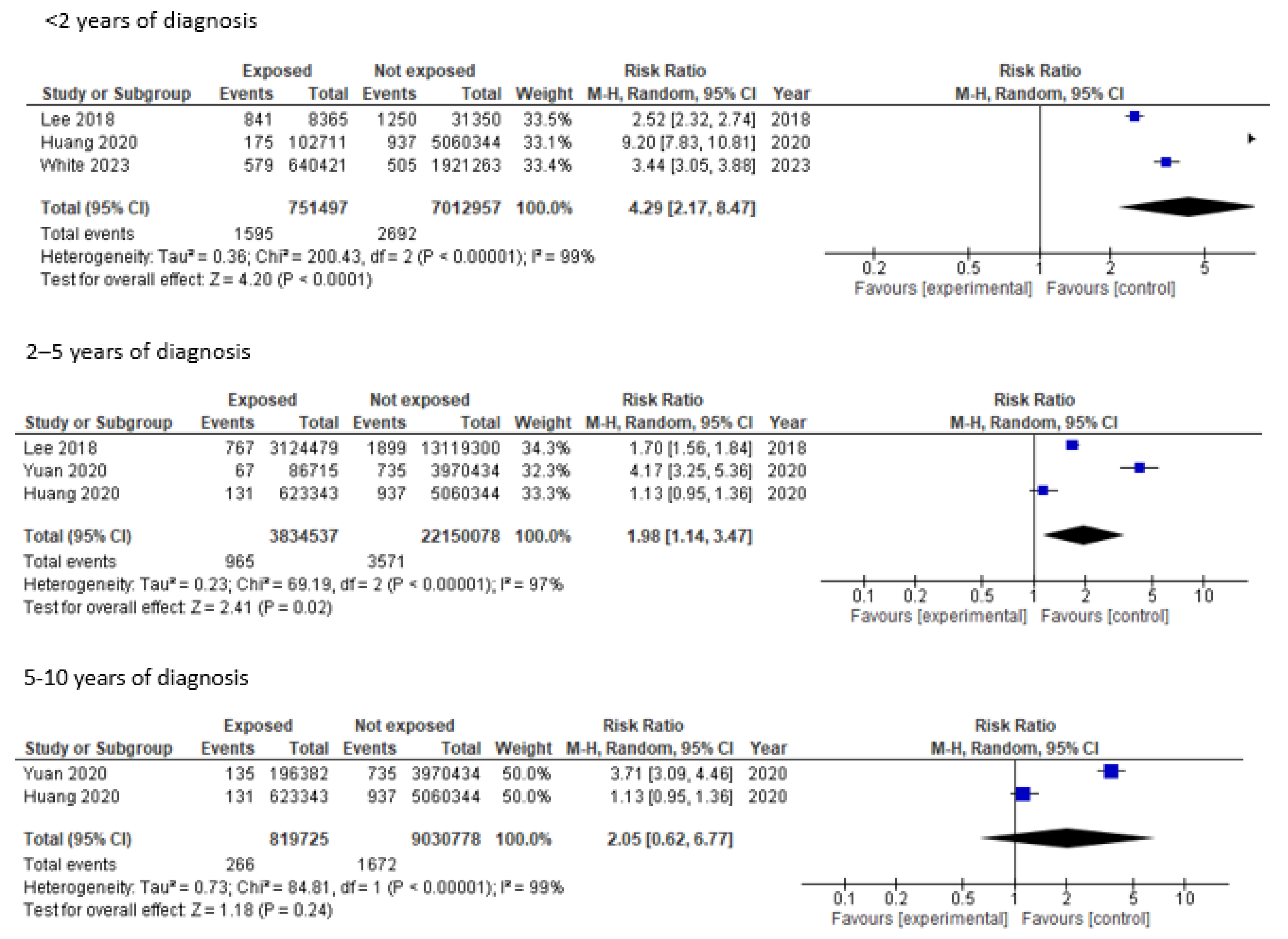
3. Results
| Author and Year | Title | Country | Age | Sample | Men | Women | PCa Cases in Patients with Diabetes | Patients with Diabetes | Controls with Diabetes | Total Controls | OR | Confidence Interval | Others |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Van Tran T, 2021 [23] | Risk factors of Pancreatic Cancer in Vietnam: A Matched Case-Control Hospital-Based Study | Vietnam | 59 | 392 | 232 | 160 | 35 | 196 | 20 | 188 | 3.09 | 1.54–6.68 | Cancer family history, tobacco use, alcohol, inflammatory diseases, hepatitis B virus infection |
| Li X, 2018 [26] | ABO Blood Group and Diabetes Mellitus Influence the Risk for Pancreatic Cancer in a Population from China | China | 63.5 | 672 | 357 | 315 | 61 | 264 | 66 | 423 | 1.62 | 1.10–2.39 | Family history of pancreatic cancer, tobacco, alcohol, chronic hepatitis B infection, chronic pancreatitis, ABO blood type |
| Olson SH, 2016 [17] | Weight Loss, Diabetes, Fatigue, and Depression Preceding Pancreatic Cancer | USA | 61.9 | 973 | 514 | 459 | 63 | 463 | 23 | 463 | 3.55 (<3 years DM) | 1.35–3.66 | Body mass index, tobacco, family history of pancreatic cancer, history of prior cancer, weight loss, fatigue, depression, concentration |
| Valente R, 2017 [19] | Risk and protective factors for the occurrence of sporadic pancreatic endocrine neoplasms | Europa | 59 | 840 | 237 | 603 | 35 | 281 | 58 | 603 | 2.09 | 1.27–3.45 | Tobacco, alcohol, insulin, past medical history, family history of pancreatic cancer |
| Tan PS, 2023 [24] | Temporality of body mass index, blood tests, comorbidities and medication use as early markers for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC): a nested case-control study | England | >18 | 288,356 | 143,912 | 145,444 | 6925 | 28,137 | 32,962 | 261,219 | 4.93 | 1.36–3.88 | Body mass index, alcohol, tobacco, comorbidities, medications (metformin, insulin) |
| Ben Q, 2016 [16] | Risk factors for sporadic pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors: A case-control study | China | 49.7 | 999 | 448 | 552 | 24 | 142 | 50 | 614 | 2.29 | 1.36–3.88 | Tobacco, alcohol, family history of pancreatic cancer |
| Zheng Z, 2016 [18] | Risk Factors for Pancreatic Cancer in China: A Multicenter Case-Control Study | China | 58.85 | 646 | 362 | 284 | 49 | 223 | 26 | 281 | 2.96 | 1.48–5.92 | Obesity tobacco, family history of pancreatic cancer, tea and coffee consumption |
| Antwi SO, 2016 [15] | Pancreatic cancer: associations of inflammatory potential of diet, cigarette smoking and long-standing diabetes | USA | 66.5 | 2573 | 1416 | 1157 | 211 | 817 | 151 | 756 | 3.27 | 2.58–4.17 | Inflammatory diet, tobacco, duration of type II diabetes |
| Lu Y, 2015 [25] | New-onset type 2 diabetes, elevated HbA1c, anti-diabetic medications, and risk of pancreatic cancer | Sweden-England | 20–75 | 5529 | 3166 | 2363 | 175 | 529 | 856 | 5000 | 2.36 | 1.94–2.89 | Body mass index, alcohol, tobacco, fasting glucose, fasting insulin, allergies |
| Walker EJ, 2015 [27] | Metformin use among type 2 diabetics and risk of pancreatic cancer in a clinic-based case-control study | USA | 61.5 | 1405 | 704 | 701 | 81 | 536 | 89 | 869 | 1.41 | 1.02–1.96 | Body mass index, tobacco, alcohol, pancreatitis, family history of pancreatic cancer, diabetes duration, medication use (metformin, insulin…) |
| Petrusel L, 2020 [20] | Risk Factors in Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma: The Interrelation with Familial History and Predictive Role on Survival | Romania | 63.4 | 624 | 376 | 248 | 115 | 279 | 36 | 312 | 4.1/new-onset: 11.78 | 2.58–31.42 | Body mass index, alcohol, tobacco, coffee, chronic pancreatitis, family history of pancreatic cancer |
| Dayem Ullah AZM, 2021 [22] | Temporality of clinical factors associated with pancreatic cancer: a case-control study using linked electronic health records | England | 55.1 | 8962 | 4569 | 4373 | 360 | 965 | 1045 | 4355 | 1.74/new-onset: 1.95 | 1.25–3.03 | Comorbidities (gastrointestinal, cardiometabolic and respiratory), obesity, tobacco, alcohol |
| Farias AJ, 2020 [21] | Diabetes-related complications and pancreatic cancer incidence in the multiethnic cohort | USA | Tramo edad | 2161 | 1025 | 1136 | 197 | 433 | 524 | 1728 | 1.22 | 1.09–1.36 | Tobacco, alcohol, body mass index, comorbidities |
| Wang Y, 2016 [28] | Complex interplay between type 2 diabetes and pancreatic cancer: insights from observational and mendelian randomization analyses | China | 67.34 | 1163 | 766 | 497 | 194 | 581 | 107 | 582 | 2.06 | 1.56–2.71 | Duration of type II diabetes, obesity, tobacco, alcohol, medication (oral medication or insulin) |
| Author and Year | Title | Country | Middle Ages | Sample | Men | Women | PCa Number | PCa Cases in Patients with Diabetes | Patients with Diabetes | PCa in Patients Without Diabetes | Patients’ Cohort Without Diabetes | HR | Confidence Interval | Other Parameters |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yuan C, 2020 [35] | Diabetes, weight change, and pancreatic cancer risk | USA | 62.0 | 159,025 | 46,207 | 112,818 | 1116 | 135 | 196,382 | 735 | 3,970,434 | 2.97 | 2.31–3.82 | Weight loss, body mass index, tobacco, alcohol, diabetes duration, race/ethnicity |
| Park BK, 2022 [30] | Lifestyle, body mass index, diabetes, and the risk of pancreatic cancer | South Korea | 53.9 | 7,445,944 | 3,768,191 | 3,677,753 | 22,543 | 4434 | 802 | 18,109 | 6,644,308 | 1.48 | 1.43–1.53 | Obesity, tobacco, alcohol, hyperlipidemia use, and physical activity |
| Lee DY, 2018 [34] | The influence of diabetes and antidiabetic medications on the risk of pancreatic cancer | Corea del Sur | >30 | 4,945,886 | 2,748,061 | 2,197,825 | 8589 | 2916 | 966,492 | 5673 | 3,979,394 | 2.2 | 2.12–2.32 | Alcohol and comorbidities (chronic pancreatitis, acute pancreatitis, hepatitis B, hepatitis C), medication (oral or insulin) |
| Huang BZ, 2020 [38] | New-onset diabetes, longitudinal trends in metabolic markers, and risk of pancreatic cancer | USA | 57.9 | 1,499,627 | 672,167 | 827,460 | 2002 | 759 | 1,675,673 | 937 | 506,034 | 3.17 (HR DM prevalent 1.85) | 2.75–3.65 (1.67–2.05) | Body mass index, alcohol, family history of pancreatic cancer, pancreatitis |
| Er KC, 2016 [29] | Effect of glycemic control on the risk of pancreatic cancer | Taiwan | 49.15 | 699,115 | 341,940 | 357,175 | 497 | 82 | 46,973 | 415 | 652,142 | 2.53 | 1.34–9.78 | Alcohol, tobacco, obesity, chronic pancreatitis and other comorbidities |
| White MJ, 2023 [32] | The association of new-onset diabetes with subsequent pancreatic cancer | USA | 51 | 2,561,684 | 1,275,720 | 1,285,964 | 1084 | 579 | 640,421 | 505 | 1,921,263 | 3.47 | 3.08–3.92 | Tobacco, comorbidities |
| Setiawan VW, 2018 [36] | Pancreatic cancer following incident Diabetes in African Americans and Latinos | USA | 48,995 | 21,483 | 27,512 | 408 | 128 | 15,833 | 280 | 33,162 | 2.39/new-onset Latino: 4.08/African American: 3.38 | 1.91–2.98/Latino: 2.76–6.03/African-American: 2.30–4.98) | Body mass index, tobacco, alcohol | |
| Safadi H, 2024 [33] | Associations between diabetes and cancer: 10-year study | Hungary | 61.4 | 3,681,774 | 1,678,889 | 1,719,388 | 17,328 | 892 | 93,852 | 16,436 | 3,796,764 | 2.294 | 2.099–2.507 | Other cancers (breast, liver, colorectal, kidney…) |
| de Jong RGPJ, 2017 [37] | Impact of detection bias on the risk of gastrointestinal cancer in T2DM | Netherlands | 63.9 | 34,038 | 17,343 | 16,695 | 34,038 | 53,804 | 34,038 | 34,038 | 34,038 | 4.1 | 1.09–1.36 | Other cancers (breast, liver, colorectal, gastric) |
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sacerdote, C.; Ricceri, F. Epidemiological dimensions of the association between type 2 diabetes and cancer: A review of observational studies. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2018, 143, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, E.; Lim, S.; Lamptey, R.; Webb, D.R.; Davies, M.J. Type 2 diabetes. Lancet 2022, 400, 1803–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferlay, J.; Colombet, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Parkin, D.M.; Piñeros, M.; Znaor, A. Cancer statistics for the year 2020: An overview. Int. J. Cancer 2021, 149, 778–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, A.P. Pancreatic cancer epidemiology: Understanding the role of lifestyle and inherited risk factors. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 18, 493–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; You, Y.; Guo, F.; Xu, J.; Dai, H.; Bie, P. Association of elevated risk of pancreatic cancer in diabetic patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 13, 1247–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, T.M.; Lophatananon, A.; Muir, K.R. Risk Factors Associated with Pancreatic Cancer in the UK Biobank Cohort. Cancers 2022, 14, 4991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyashita, M.Y.; Hitsumoto, H.T.; Fukuda, F.H.; Kim, K.J.; Ito, I.S.; Kimoto, K.N. Metabolic syndrome is linked to the incidence of pancreatic cancer. Lancet 2023, 67, 102353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A.; Sahoo, J.; Kamalanathan, S.; Naik, D.; Mohan, P.; Kalayarasan, R. Diabetes and pancreatic cancer: Exploring the two-way traffic. World J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 27, 4939–4962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, S.; Wang, B.; Zhang, X.; Hao, L.; Hu, X.; Li, Z. Long-term diabetes mellitus is associated with an increased risk of pancreatic cancer: A meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0134321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batabyal, P.; Vander Hoorn, S.; Christophi, C.; Nikfarjam, M. Association of diabetes mellitus and pancreatic adenocarcinoma: A meta-analysis of 88 studies. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2014, 21, 2453–2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huxley, R.; Ansary-Moghaddam, A.; Berrington De González, A.; Barzi, F.; Woodward, M. Type-II diabetes and pancreatic cancer: A meta-analysis of 36 studies. Br. J. Cancer 2005, 92, 2076–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Y.; Kartsonaki, C.; Guo, Y.; Bragg, F.; Yang, L.; Bian, Z. Diabetes, plasma glucose and incidence of pancreatic cancer: A prospective study of 0.5 million Chinese adults and a meta-analysis of 22 cohort studies. Int. J. Cancer 2017, 140, 1781–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begg, C.B.; Mazumdar, M. Operating characteristics of a rank correlation test for publication bias. Biometrics 1994, 50, 1088–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antwi, S.O.; Oberg, A.L.; Shivappa, N.; Bamlet, W.R.; Chaffee, K.G.; Steck, S.E. Pancreatic cancer: Associations of inflammatory potential of diet, cigarette smoking and long-standing diabetes. Carcinogenesis 2016, 37, 481–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben, Q.; Zhong, J.; Fei, J.; Chen, H.; Yv, L.; Tan, J. Risk Factors for Sporadic Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors: A Case-Control Study. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, S.H.; Xu, Y.; Herzog, K.; Saldia, A.; DeFilippis, E.M.; Li, P. Weight Loss, Diabetes, Fatigue, and Depression Preceding Pancreatic Cancer. Pancreas 2016, 45, 986–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Z.; Zheng, R.; He, Y.; Sun, X.; Wang, N.; Chen, T. Risk Factors for Pancreatic Cancer in China: A Multicenter Case-Control Study. J. Epidemiol. 2016, 26, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valente, R.; Hayes, A.J.; Haugvik, S.P.; Hedenström, P.; Siuka, D.; Korsæt, E. Risk and protective factors for the occurrence of sporadic pancreatic endocrine neoplasms. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2017, 24, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrusel, L.; Bilibou, M.; Drug, V.; Leucuta, D.C.; Seicean, R.; Cainap, C. Risk Factors in Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma: The Interrelation with Familial History and Predictive Role on Survival. J. Gastrointestin Liver Dis. 2020, 29, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farias, A.J.; Wu, A.H.; Porcel, J.; Le Marchand, L.; Wilkens, L.R.; Monroe, K.R. Diabetes-related complications and pancreatic cancer incidence in the multiethnic cohort. JNCI Cancer Spectr. 2020, 4, pkaa035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayem Ullah, A.Z.M.; Stasinos, K.; Chelala, C.; Kocher, H.M. Temporality of clinical factors associated with pancreatic cancer: A case-control study using linked electronic health records. BMC Cancer 2021, 21, 1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Tran, T.; Van Dao, T.; Nguyen, K.D.; van Ta, T.; Vu, K.T.; Trinh, S.H. Risk factors of Pancreatic Cancer in Vietnam: A Matched Case–Control Hospital-Based Study. Cancer Control 2021, 28, 1073274821989320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, P.S.; Garriga, C.; Clift, A.; Liao, W.; Patone, M.; Coupland, C. Temporality of body mass index, blood tests, comorbidities and medication use as early markers for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC): A nested case-control study. Gut 2023, 72, 512–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Rodríguez, L.A.G.; Malgerud, L.; González-Pérez, A.; Martín-Pérez, M.; Lagergren, J.; Bexelius, T.S. New-onset type 2 diabetes, elevated HbA1c, anti-diabetic medications, and risk of pancreatic cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2015, 113, 1607–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Xu, H.; Gao, P. ABO Blood Group and Diabetes Mellitus Influence the Risk for Pancreatic Cancer in a Population from China. Med. Sci. Monit. 2018, 24, 9392–9398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, E.J.; Ko, A.H.; Holly, E.A.; Bracci, P.M. Metformin use among type 2 diabetics and risk of pancreatic cancer in a clinic-based case-control study. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 136, E646–E653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xie, L.; Gu, Y.; Jin, H.; Yang, J.; Liu, Q.; Zang, X. Complex interplay between type 2 diabetes mellitus and pancreatic cancer: Insights from observational and mendelian randomization analyses. BMC Cancer 2025, 25, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Er, K.C.; Hsu, C.Y.; Lee, Y.K.; Huang, M.Y.; Su, Y.C. Effect of glycemic control on the risk of pancreatic cancer: A nationwide cohort study. Medicine 2016, 21, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, B.K.; Seo, J.H.; Chung, J.B.; Choi, J.K. Lifestyle, body mass index, diabetes, and the risk of pancreatic cancer in a nationwide population-based cohort study with 7.4 million Korean subjects. Br. J. Cancer 2022, 127, 549–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Liu, F.; Chen, A.M.; Yang, P.F.; Peng, Y.; Gong, J.P. Type 2 diabetes prevention diet and the risk of pancreatic cancer: A large prospective multicenter study. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 5595–5604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, M.J.; Sheka, A.C.; LaRocca, C.J.; Irey, R.L.; Ma, S.; Wirth, K.M. The association of new-onset diabetes with subsequent diagnosis of pancreatic cancer—Novel use of a large administrative database. J. Public Health 2023, 45, e266–e274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safadi, H.; Balogh, A.; Lám, J.; Nag, A.; Belicz, E. Associations between diabetes and cancer: A 10-year national population-based retrospective cohort study. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2024, 211, 111665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.Y.; Yu, J.H.; Park, S.; Han, K.; Kim, N.H.; Yoo, H.J. The influence of diabetes and antidiabetic medications on the risk of pancreatic cancer: A nationwide population-based study in Korea. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 9719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.; Babic, A.; Khalaf, N.; Nowak, J.A.; Brais, L.K.; Rubinson, D.A. Diabetes, Weight Change, and Pancreatic Cancer Risk. JAMA Oncol. 2020, 6, e202948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Setiawan, V.W.; Stram, D.O.; Porcel, J.; Chari, S.T.; Maskarinec, G.; Le Marchand, L. Pancreatic cancer following incident diabetes in African Americans and Latinos: The multiethnic cohort. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2019, 111, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Jong, R.G.P.J.; Burden, A.M.; de Kort, S.; van Herk-Sukel, O.O.; Vissers, P.A.J.; Janssen, P.K.C. Impact of detection bias on the risk of gastrointestinal cancer and its subsites in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Eur. J. Cancer 2017, 79, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, B.Z.; Pandol, S.J.; Jeon, C.Y.; Chari, S.T.; Sugar, C.A.; Chao, R. New-Onset Diabetes, Longitudinal Trends in Metabolic Markers, and Risk of Pancreatic Cancer in a Heterogeneous Population. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 18, 1812–1821.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.J.; Jia, J.P.; Shao, Q.; Wang, Y.K. Diabetes mellitus and risk of pancreatic cancer in China: A meta-analysis based on 26 case-control studies. Prim. Care Diabetes 2019, 13, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellenthin, C.; Balaban, V.D.; Dugic, A.; Cullati, S. Risk Factors for Pancreatic Cancer in Patients with New-Onset Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancers 2022, 14, 4684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Shi, J.; Huang, J.; Cheng, M.; Geng, S.; Yu, W. Case-Control Trials on Risk Factors for Pancreatic Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Iran. J. Public Health 2023, 52, 1578–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, B.; Li, Y.; Sheng, C.S.; Liu, L.; Hou, T.; Xia, N. Association between age at diabetes onset or diabetes duration and subsequent risk of pancreatic cancer: Results from a longitudinal cohort and mendelian randomization study. Lancet Reg. Health West. Pac. 2023, 30, 100596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parajuli, P.; Nguyen, T.L.; Prunier, C.; Razzaque, M.S.; Xu, K.; Atfi, A. Pancreatic cancer triggers diabetes through TGF-β-mediated selective depletion of islet β-cells. Life Sci. Alliance 2020, 3, e201900573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueberberg, S.; Nauck, M.A.; Uhl, W.; Montemurro, C.; Tannapfel, A.; Clark, A. Islet Amyloid in Patients with Diabetes Due to Exocrine Pancreatic Disorders, Type 2 Diabetes, and Nondiabetic Patients. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 105, 2595–2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, S.Y.; Lee, E.K.; Han, S.S.; Lee, Y.J.; Hwangbo, Y.; Kang, Y.H. Favorable glycemic response after pancreatoduodenectomy in both patients with pancreatic cancer and patients with non-pancreatic cancer. Medicine 2018, 97, e0590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, S.W.; Seo, D.W.; So, H.; Hwang, J.S.; Joo, H.D.; Oh, D. Effects of pancreatic resection for benign pancreatic neoplasms on pancreatic volume and endocrine function: A long-term computed tomographybased study. Pancreatology 2020, 20, 1732–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toledo, F.G.S.; Chari, S.; Yadav, D. Understanding the Contribution of Insulin Resistance to the Risk of Pancreatic Cancer. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 116, 669–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiefari, E.; Mirabelli, M.; La Vignera, S.; Tanyolaç, S.; Foti, D.P.; Aversa, A. Insulin resistance and cancer: In search for a causal link. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Xue, J. Inflammation and development of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Chin. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 8, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kandikattu, H.K.; Venkateshaiah, S.U.; Mishra, A. Chronic Pancreatitis and the Development of Pancreatic Cancer. Endocr. Metab. Immune Disord.-Drug Targets 2020, 20, 1182–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wlodarczyk, B.; Gasiorowska, A.; Malecka-Panas, E. The Role of Insulin-like Growth Factor (IGF) Axis in Early Diagnosis of Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma (PDAC). J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2018, 52, 569–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ollberding, N.J.; Chen, I.; Wilkens, L.R.; Henderson, B.E.; Pollak, M.N.; Kolonel, L.N. Genetic variants, prediagnostic circulating levels of insulin-like growth factors, insulin, and glucose and the risk of colorectal cancer: The Multiethnic Cohort study. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2012, 21, 810–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Echouffo-Tcheugui, J.B.; Perreault, L.; Ji, L.; Dagogo-Jack, J.S. Diagnosis and Management of Prediabetes: A Review. JAMA 2023, 329, 1206–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizuno, S.; Nakai, Y.; Isayama, H.; Yanai, A.; Takahara, N.; Miyabayashi, K. Risk factors and early signs of pancreatic cancer in diabetes: Screening strategy based on diabetes onset age. J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 48, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carreras-Torres, R.; Johansson, M.; Gaborieau, V.; Haycock, P.C.; Wade, K.H.; Relton, C.L. The Role of Obesity, Type 2 Diabetes, and Metabolic Factors in Pancreatic Cancer: A Mendelian Randomization Study. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2017, 109, djx012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, S.F.; Price, S.; Kony, J.; Blummers, S.; Walter, F.M.; Neal, R.D. Risk factors for pancreatic cancer in electronic health records: An umbrella review of systematic reviews and meta-analyses. EClinicalMedicine 2025, 85, 103297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
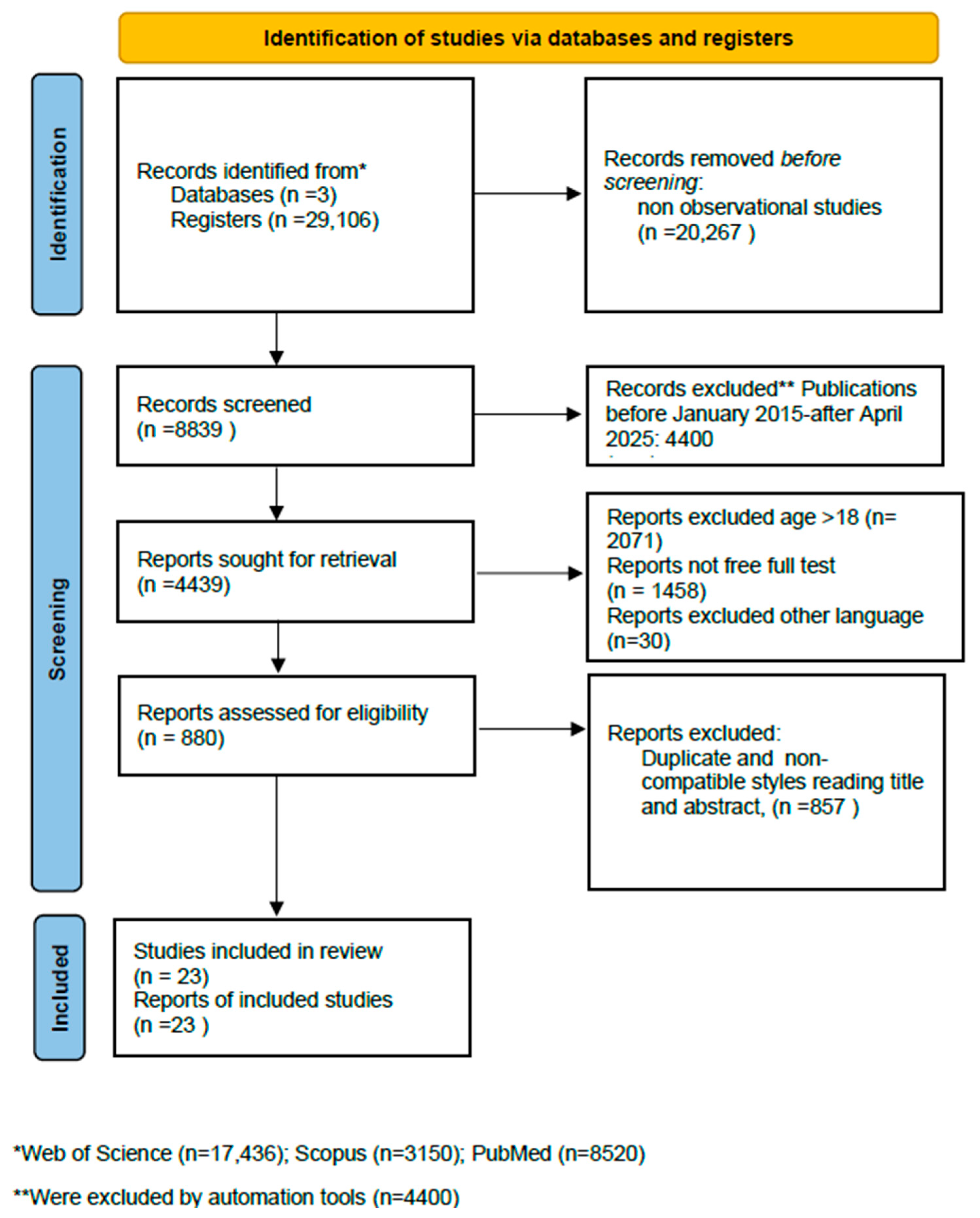
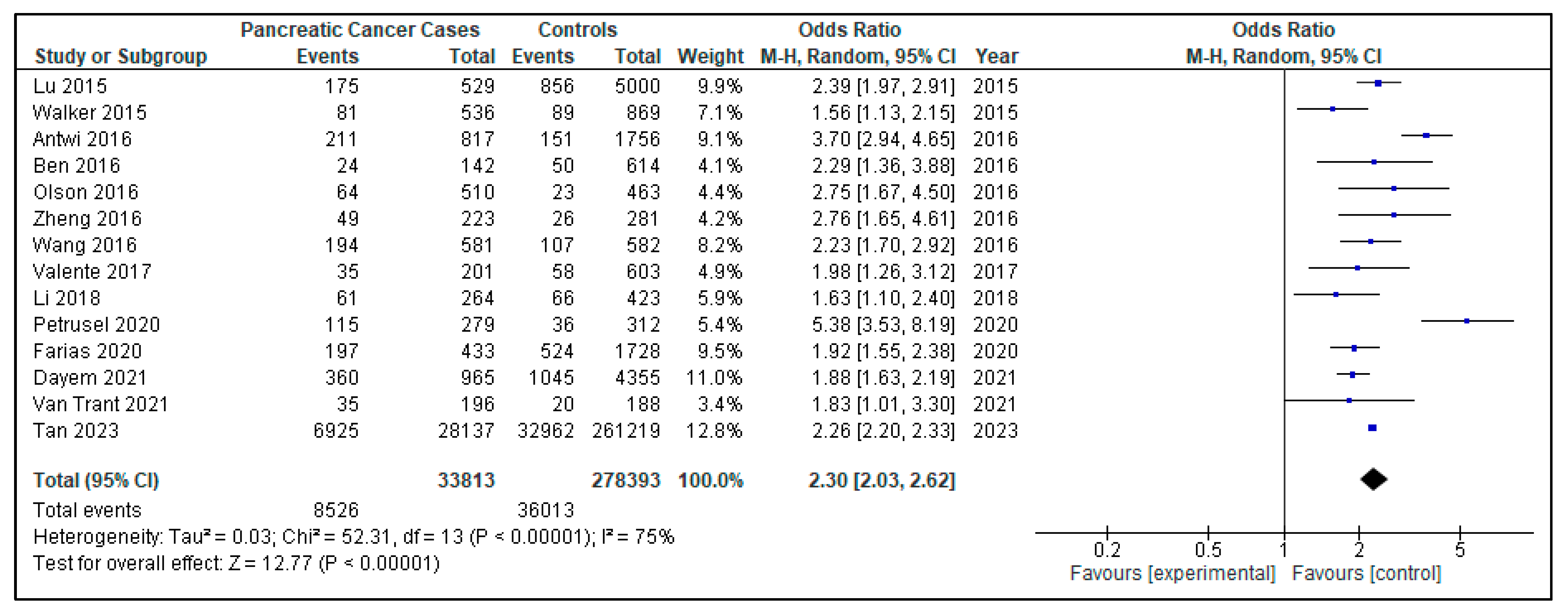
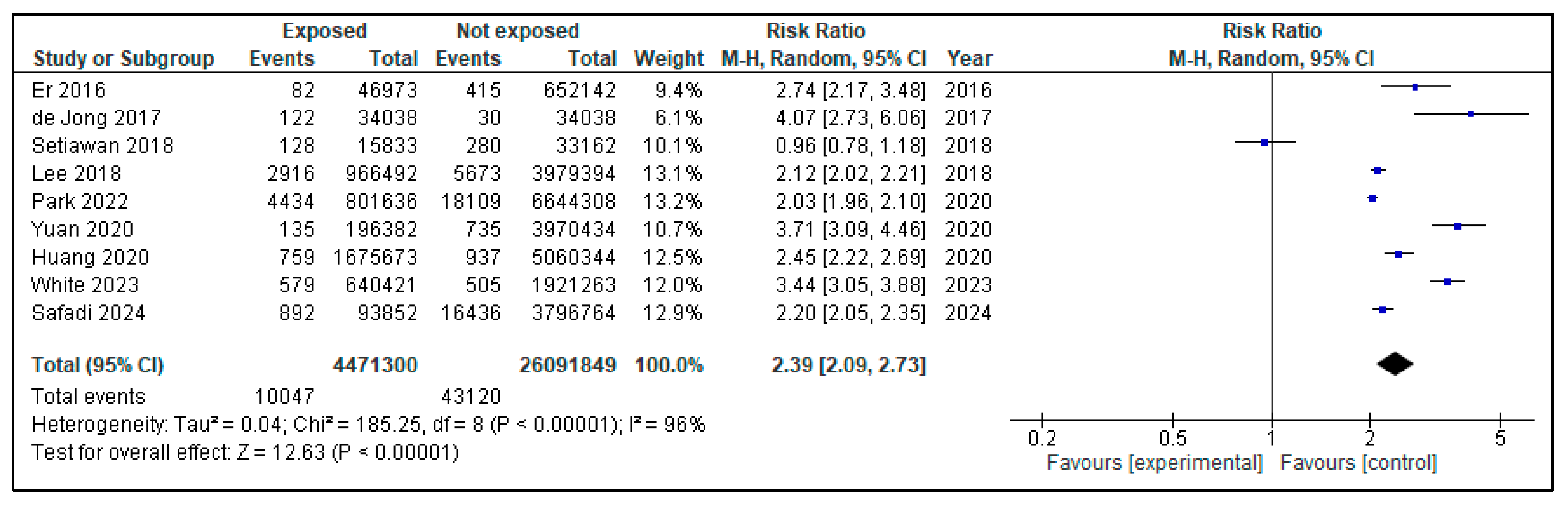
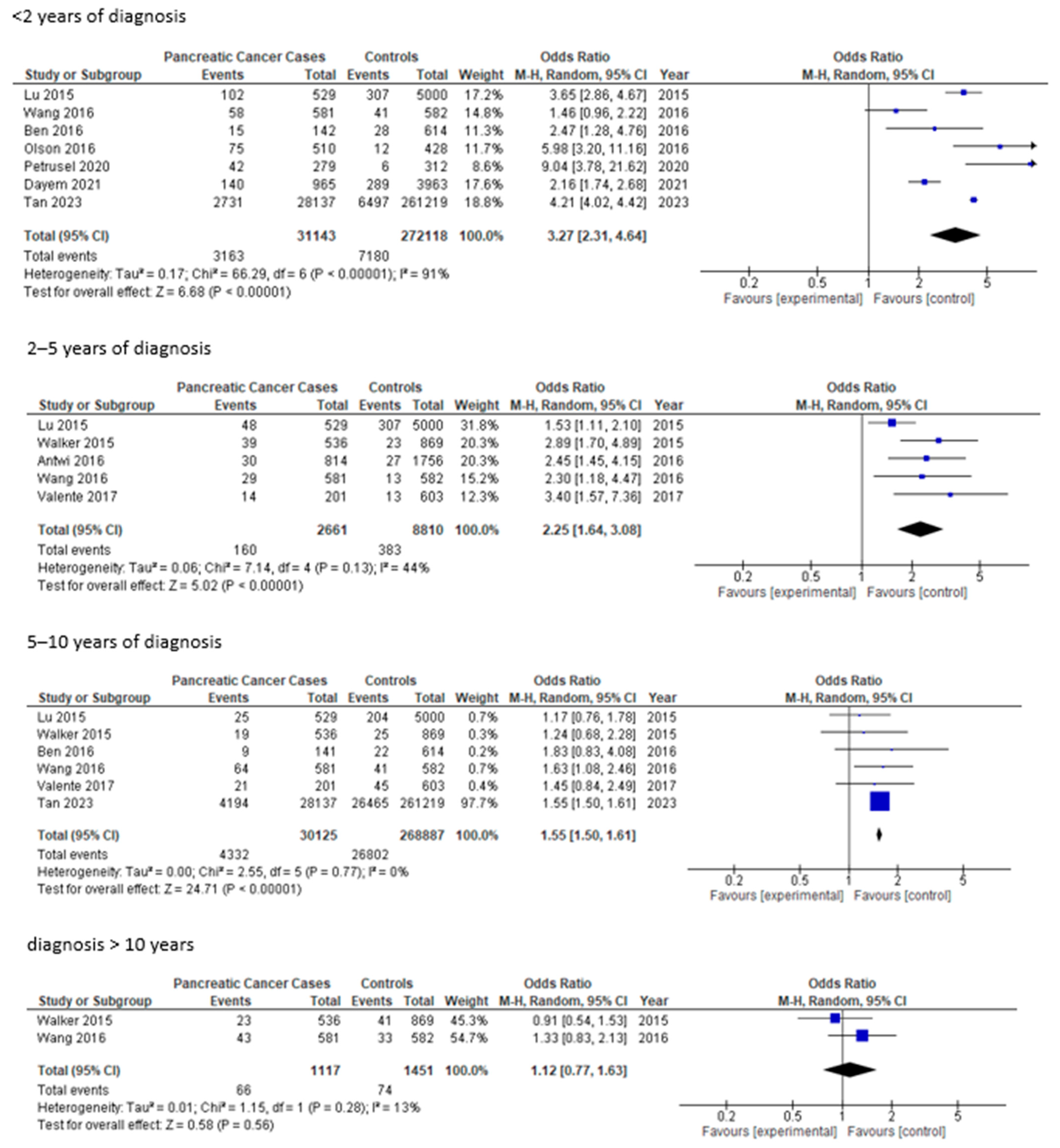

| Author | Title | Year | Quality | Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Van Tran T [23] | Risk factors of Pancreatic Cancer in Vietnam: A Matched Case-Control Hospital-Based Study | 2021 | Selection: 4 Comparability: 2 Exposure: 3 | 9 Good |
| Dayem Ullah AZM [22] | Temporality of clinical factors associated with pancreatic cancer: a case-control study using linked electronic health records | 2021 | Selection: 3 Comparability: 1 Exposure: 2 | 7 Good |
| Li X [26] | ABO Blood Group and Diabetes Mellitus Influence the Risk for Pancreatic Cancer in a Population from China | 2018 | Selection: 3 Comparability: 2 Exposure: 3 | 8 Good |
| Olson SH [17] | Weight Loss, Diabetes, Fatigue, and Depression Preceding Pancreatic Cancer | 2016 | Selection: 4 Comparability: 2 Exposure: 3 | 9 Good |
| Valente R [19] | Risk and protective factors for the occurrence of sporadic pancreatic endocrine neoplasms | 2017 | Selection: 3 Comparability: 1 Exposure: 3 | 7 Good |
| Tan PS [24] | Temporality of body mass index, blood tests, comorbidities and medication use as early markers for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC): a nested case-control study | 2023 | Selection: 3 Comparability: 2 Exposure: 3 | 8 Good |
| Ben Q [16] | Risk Factors for Sporadic Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors: A Case-Control Study | 2016 | Selection: 3 Comparability: 2 Exposure: 3 | 8 Good |
| Zheng Z [18] | Risk Factors for Pancreatic Cancer in China: A Multicenter Case-Control Study | 2016 | Selection: 4 Comparability: 2 Exposure: 3 | 9 Good |
| Antwi SO [15] | Pancreatic cancer: associations of inflammatory potential of diet, cigarette smoking and long-standing diabetes | 2016 | Selection: 3 Comparability: 1 Exposure: 2 | 6 Fair |
| Lu Y [25] | New-onset type 2 diabetes, elevated HbA1c, anti-diabetic medications, and risk of pancreatic cancer | 2015 | Selection: 4 Comparability: 2 Exposure: 3 | 9 Good |
| Walker EJ [19] | Metformin use among type 2 diabetics and risk of pancreatic cancer in a clinic-based case-control study | 2015 | Selection: 4 Comparability: 2 Exposure: 3 | 9 Good |
| Petrusel L [20] | Risk Factors in Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma: the Interrelation with Familial History and Predictive Role on Survival | 2020 | Selection: 3 Comparability: 1 Exposure: 2 | 6 Fair |
| Farias AJ [21] | Diabetes-related complications and pancreatic cancer incidence in the multiethenic cohort | 2020 | Selection: 4 Comparability: 2 Exposure: 3 | 9 Good |
| Wang Y [28] | Complex interplay between type 2 diabetes mellitus and pancreatic cancer: insights from observational and mendelian randomization analyses | 2025 | Selection: 3 Comparability: 2 Exposure: 3 | 8 Good |
| Author | Title | Year | Quality | Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yuan C [35] | Diabetes, Weight Change, and Pancreatic Cancer Risk | 2020 | Selection: 2 Comparability: 2 Outcomes: 3 | 7 Good |
| Park BK [30] | Lifestyle, body mass index, diabetes, and the risk of pancreatic cancer in a nationwide population-based cohort study with 7.4 million Korean subjects | 2022 | Selection: 4 Comparability: 2 Outcomes: 3 | 9 Good |
| Huang BZ [38] | New-Onset Diabetes, Longitudinal Trends in Metabolic Markers, and Risk of Pancreatic Cancer in a Heterogeneous Population | 2020 | Selection: 3 Comparability: 1 Outcomes: 3 | 7 Good |
| Er KC [29] | Effect of glycemic control on the risk of pancreatic cancer: A nationwide cohort study | 2016 | Selection: 3 Comparability: 1 Outcomes: 3 | 7 Good |
| White MJ [32] | The association of new-onset diabetes with subsequent diagnosis of pancreatic cancer-novel use of a large administrative database | 2023 | Selection: 4 Comparability: 2 Outcomes: 3 | 9 Good |
| Lee DY [34] | The influence of diabetes and antidiabetic medications on the risk of pancreatic cancer: a nationwide population-based study in Korea | 2018 | Selection: 3 Comparability: 1 Outcomes: 3 | 7 Good |
| Setiawan VW [36] | Pancreatic cancer following Incident Diabetes in African Americans and Latinos: The multiethnic cohort | 2018 | Selection: 4 Comparability: 1 Outcomes: 3 | 8 Good |
| Safadi H [33] | Associations between diabetes and cancer: A 10-year national population-based retrospective cohort study | 2024 | Selection: 4 Comparability: 1 Outcomes: 2 | 7 Good |
| de Jong RGPJ [37] | Impact of detection bias on the risk of gastrointestinal cancer and its subsites in type 2 diabetes mellitus | 2017 | Selection: 4 Comparability: 1 Outcomes: 3 | 8 Good |
| Author [Reference] | Year | Cohort Studies | Case-Control Studies | Total Studies | RR/OR * Summary | 95% CI * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Huxley [11] | 2005 | 19 | 17 | 36 | 1.82 | 1.66–1.89 |
| Batabyal [10] | 2013 | 50 | 39 | 89 | 1.97 | 1.78–2.18 |
| Song [9] | 2015 | 21 | 23 | 44 | 1.64 | 1.52–1.78 |
| Pang [12] | 2017 | 22 | 0 | 22 | 1.87 | 1.48–2.37 |
| Zhang [39] | 2018 | 0 | 26 | 26 | 3.69 | 3.12–4.37 |
| Mellenting [40] | 2022 | 13 | 8 | 21 | 3.35 | 2.75–4.09 |
| Yang [41] | 2023 | 0 | 8 | 8 | 2.69 | 2.52–2.88 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fuentes, A.; Montserrat-Capdevila, J.; Florensa, D.; Godoy, S.; Serrano, J.; Godoy, P. The Diabetes-Pancreatic Cancer Risk Relationship over Time: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Diabetology 2025, 6, 131. https://doi.org/10.3390/diabetology6110131
Fuentes A, Montserrat-Capdevila J, Florensa D, Godoy S, Serrano J, Godoy P. The Diabetes-Pancreatic Cancer Risk Relationship over Time: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Diabetology. 2025; 6(11):131. https://doi.org/10.3390/diabetology6110131
Chicago/Turabian StyleFuentes, Araceli, Josep Montserrat-Capdevila, Didac Florensa, Sofia Godoy, Judith Serrano, and Pere Godoy. 2025. "The Diabetes-Pancreatic Cancer Risk Relationship over Time: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Diabetology 6, no. 11: 131. https://doi.org/10.3390/diabetology6110131
APA StyleFuentes, A., Montserrat-Capdevila, J., Florensa, D., Godoy, S., Serrano, J., & Godoy, P. (2025). The Diabetes-Pancreatic Cancer Risk Relationship over Time: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Diabetology, 6(11), 131. https://doi.org/10.3390/diabetology6110131





