Peripheral Blood Gene Expression Profiling in Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy Using NanoString Technology
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Patients
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. RNA Extraction
2.4. NanoString Technique
2.5. Molecular Analysis Procedure
2.6. Bioinformatics Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Gene Expression Analysis
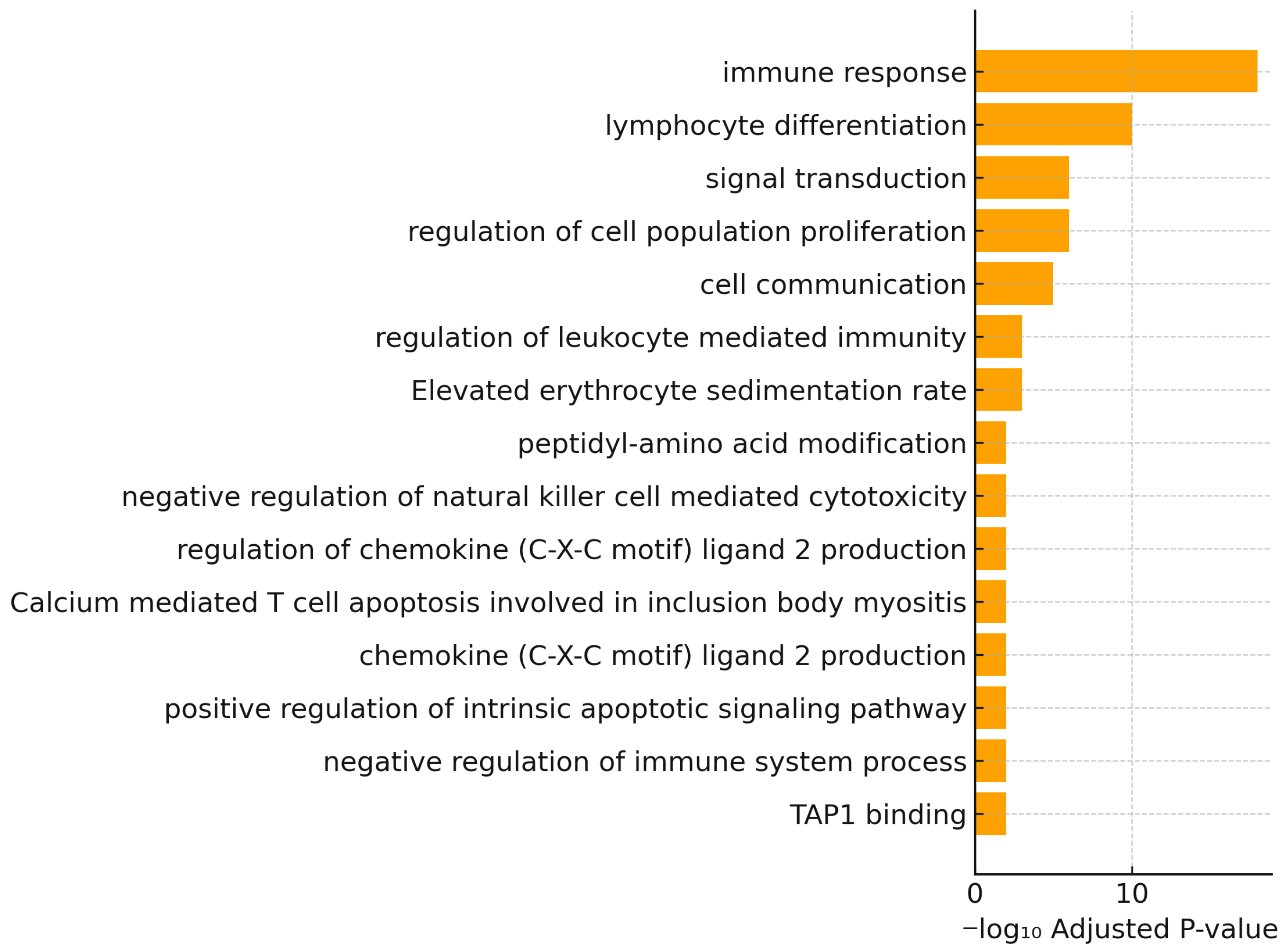
3.2. Gene Ontology Enrichment Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PDR | Proliferative diabetic retinopathy |
| NPDR | Non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy |
| DR | Diabetic retinopathy |
| VEGF | Vascular endothelial growth factor |
| MDA | Malondialdehyde |
| 4HNE | 4-hydroxynonenal |
| SOD | Superoxide dismutase |
| CAT | Catalase |
| TLR4 | Toll-like receptor 4 |
References
- Choi, T.B.; Boado, R.J.; Pardridge, W.M. Blood-brain barrier glucose transporter mRNA is increased in experimental diabetes mellitus. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1989, 164, 375–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veenstra, A.; Liu, H.; Lee, C.A.; Du, Y.; Tang, J.; Kern, T.S. Diabetic retinopathy: Retina-specific methods for maintenance of diabetic rodents and evaluation of vascular histopathology and molecular abnormalities. Curr. Protoc. Mouse Biol. 2015, 5, 247–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pusparajah, P.; Lee, L.H.; Abdul Kadir, K. Molecular markers of diabetic retinopathy: Potential screening tool of the future? Front. Physiol. 2016, 7, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.; Sobrin, L. Genetics of diabetic retinopathy. Curr. Diab. Rep. 2014, 14, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morya, A.K.; Ramesh, P.V.; Nishant, P.; Kaur, K.; Gurnani, B.; Heda, A.; Salodia, S. Diabetic retinopathy: A review on its pathophysiology and novel treatment modalities. World J. Methodol. 2024, 14, 95881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, I.P.; Ribeiro, M.L.; Santos, T.; Reste-Ferreira, D.; Mendes, L.; Martinho, A.C.; Santos, A.R.; Figueira, J.; Lobo, C.; Cunha-Vaz, J. Patterns of progression of nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy using non-invasive imaging. Transl. Vis. Sci. Technol. 2024, 13, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrlich, R.; Zahavi, A.; Axer-Siegel, R.; Budnik, I.; Dreznik, A.; Dahbash, M.; Nisgav, Y.; Megiddo, E.; Kenet, G.; Weinberger, D.; et al. Correlation between Interleukin-6 and thrombin-antithrombin iii complex levels in retinal diseases. Curr. Eye Res. 2017, 42, 1269–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuboi, K.; Mazloumi, M.; Guo, Y.; Wang, J.; Flaxel, C.J.; Bailey, S.T.; Wilson, D.J.; Huang, D.; Jia, Y.; Hwang, T.S. Early sign of retinal neovascularization evolution in diabetic retinopathy: A longitudinal OCT angiography study. Ophthalmol. Sci. 2023, 4, 100382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorchy, H.; Claes, C.; Verougstraete, C. Risk factors of developing proliferative retinopathy in type 1 diabetic patients: Role of BMI. Diabetes Care 2002, 25, 798–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Sharma, A.; Valle, M.L.; Beveridge, C.; Liu, Y.; Sharma, S. Unraveling the role of genetics in the pathogenesis of diabetic retinopathy. Eye 2019, 33, 534–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrovič, D. Candidate genes for proliferative diabetic retinopathy. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 540416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warpeha, K.M.; Chakravarthy, U. Molecular genetics of microvascular disease in diabetic retinopathy. Eye 2003, 17, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, D.P. Human genetics of diabetic retinopathy: Current perspectives. J. Ophthalmol. 2010, 2010, 172593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.; Chen, H.; Tinkham, N.H.; Zhang, K. Genetic susceptibility of diabetic retinopathy. Curr. Diab. Rep. 2008, 8, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrovic, M.G.; Korosec, P.; Kosnik, M.; Osredkar, J.; Hawlina, M.; Peterlin, B.; Petrovic, D. Local and genetic determinants of vascular endothelial growth factor expression in advanced proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Mol. Vis. 2008, 14, 1382–1387. [Google Scholar]
- Estopinal, C.B.; Chocron, I.M.; Parks, M.B.; Wade, E.A.; Roberson, R.M.; Burgess, L.G.; Brantley, M.A., Jr.; Samuels, D.C. Mitochondrial haplogroups are associated with severity of diabetic retinopathy. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2014, 55, 5589–5595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.W.; West, X.Z.; Byzova, T.V. Inflammation and oxidative stress in angiogenesis and vascular disease. J. Mol. Med. 2013, 91, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrés-Blasco, I.; Gallego-Martínez, A.; Machado, X.; Cruz-Espinosa, J.; Di Lauro, S.; Casaroli-Marano, R.; Alegre-Ituarte, V.; Arévalo, J.F.; Pinazo-Durán, M.D. Oxidative stress, inflammatory, angiogenic, and apoptotic molecules in proliferative diabetic retinopathy and diabetic macular edema patients. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Chen, E.; Liu, M.; Wang, J.; Yin, J.; Zhao, P.; Xu, Y. Identification of immune-related endoplasmic reticulum stress genes in proliferative diabetic retinopathy using bioinformatics analysis. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1341206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, A.; Lu, J.; Wang, Y.; Mao, S.; Cui, Y.; Pan, J.; Li, L.; Luo, Y. Identification of the aberrantly methylated differentially expressed genes in proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Exp. Eye Res. 2020, 199, 108141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, G.; Que, L.; Liu, Y.; Lu, Q. Interplay of endothelial-mesenchymal transition, inflammation, and autophagy in proliferative diabetic retinopathy pathogenesis. Heliyon 2024, 10, e25166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, X.; Liao, N.; Ji, Y.; Mi, L.; Gan, Y.; Su, Y.; Wen, F. Identification of NLRP3 inflammation-related gene promoter hypomethylation in diabetic retinopathy. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2020, 61, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manoel-Caetano, F.S.; Xavier, D.J.; Evangelista, A.F.; Takahashi, P.; Collares, C.V.; Puthier, D.; Foss-Freitas, M.C.; Foss, M.C.; Donadi, E.A.; Passos, G.A.; et al. Gene expression profiles displayed by peripheral blood mononuclear cells from patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus focusing on biological processes implicated on the pathogenesis of the disease. Gene 2012, 511, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jena, L.; Kaur, P.; Singh, T.; Sharma, K.; Kotru, S.; Munshi, A. Gene expression analysis in T2DM and its associated microvascular diabetic complications: Focus on risk factor and RAAS pathway. Mol. Neurobiol. 2024, 61, 8656–8667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, M.W. Anti-VEGF therapy for diabetic macular edema. Curr. Diab. Rep. 2014, 14, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semeraro, F.; Cancarini, A.; dell’Omo, R.; Rezzola, S.; Romano, M.R.; Costagliola, C. Diabetic retinopathy: Vascular and inflammatory disease. J. Diabetes Res. 2015, 2015, 582060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rübsam, A.; Parikh, S.; Fort, P.E. Role of inflammation in diabetic retinopathy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.; Kern, T.S. Inflammation in diabetic retinopathy. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2011, 30, 343–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coucha, M.; Elshaer, S.L.; Eldahshan, W.S.; Mysona, B.A.; El-Remessy, A.B. Molecular mechanisms of diabetic retinopathy: Potential therapeutic targets. Middle East Afr. J. Ophthalmol. 2015, 22, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, S.; Kharouba, R.; Abu-Dbai, J.; Gagarin, O.; Kratz, A.; Obied, B.; Zahavi, A.; Goldenberg-Cohen, N. Screening blood and vitreous for biomarkers associated with proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honoré, B.; Cehofski, L.J.; Heegaard, S.; Brandslund, I.; Vorum, H.; Slidsborg, C. Proteomic blood-biomarkers for personalized risk stratification of diabetic retinopathy patients. Expert Rev. Proteom. 2025, 22, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, X.; Han, F.; Zhang, H.; Luo, T.; Jiang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, T.; Li, Y.; Yang, L.; Yan, W.; et al. Integrative single-cell and bulk transcriptomics with Mendelian randomization reveals NAD-related biomarkers in diabetic retinopathy: Insights and experimental validation. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2025, 159, 114949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
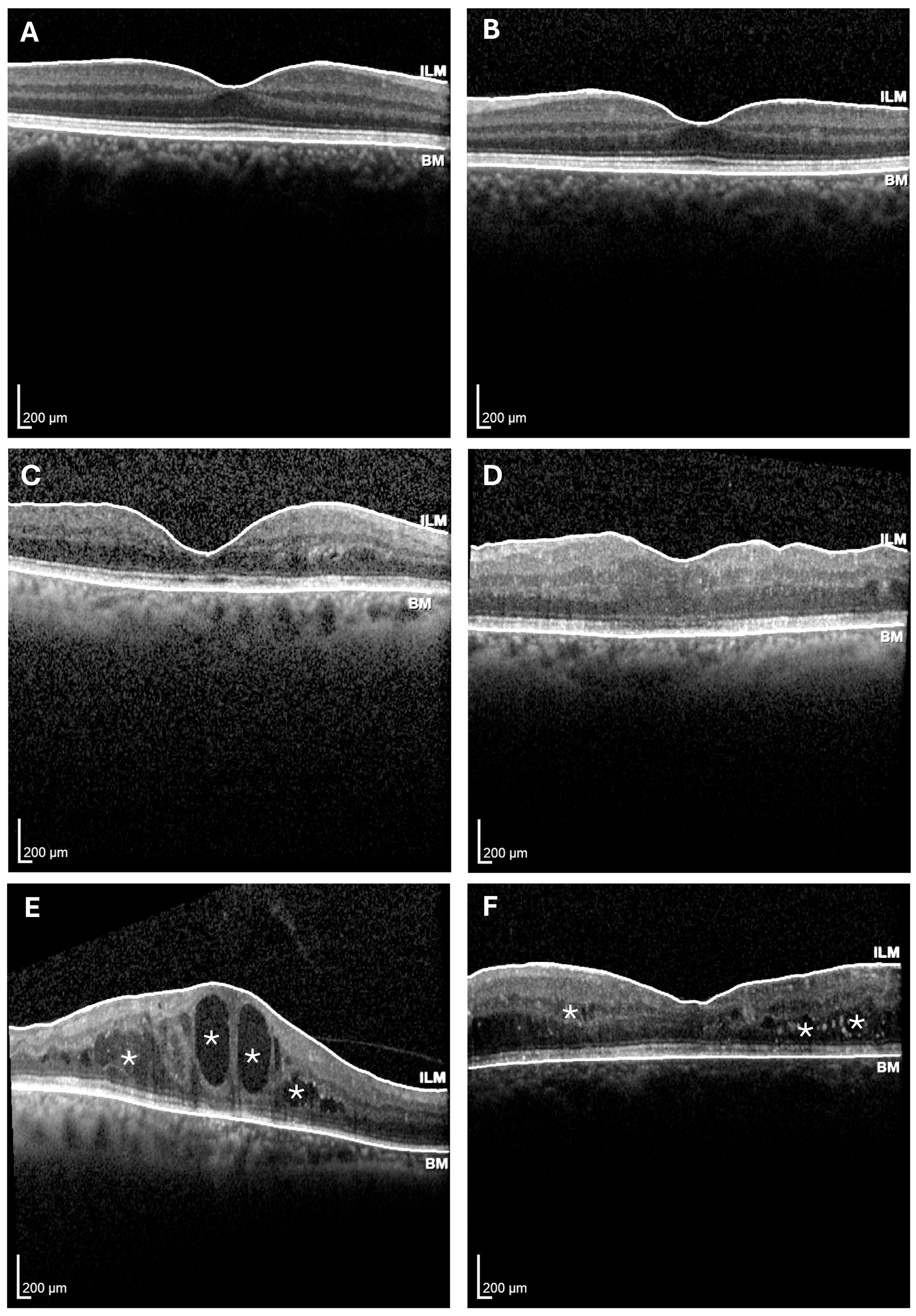
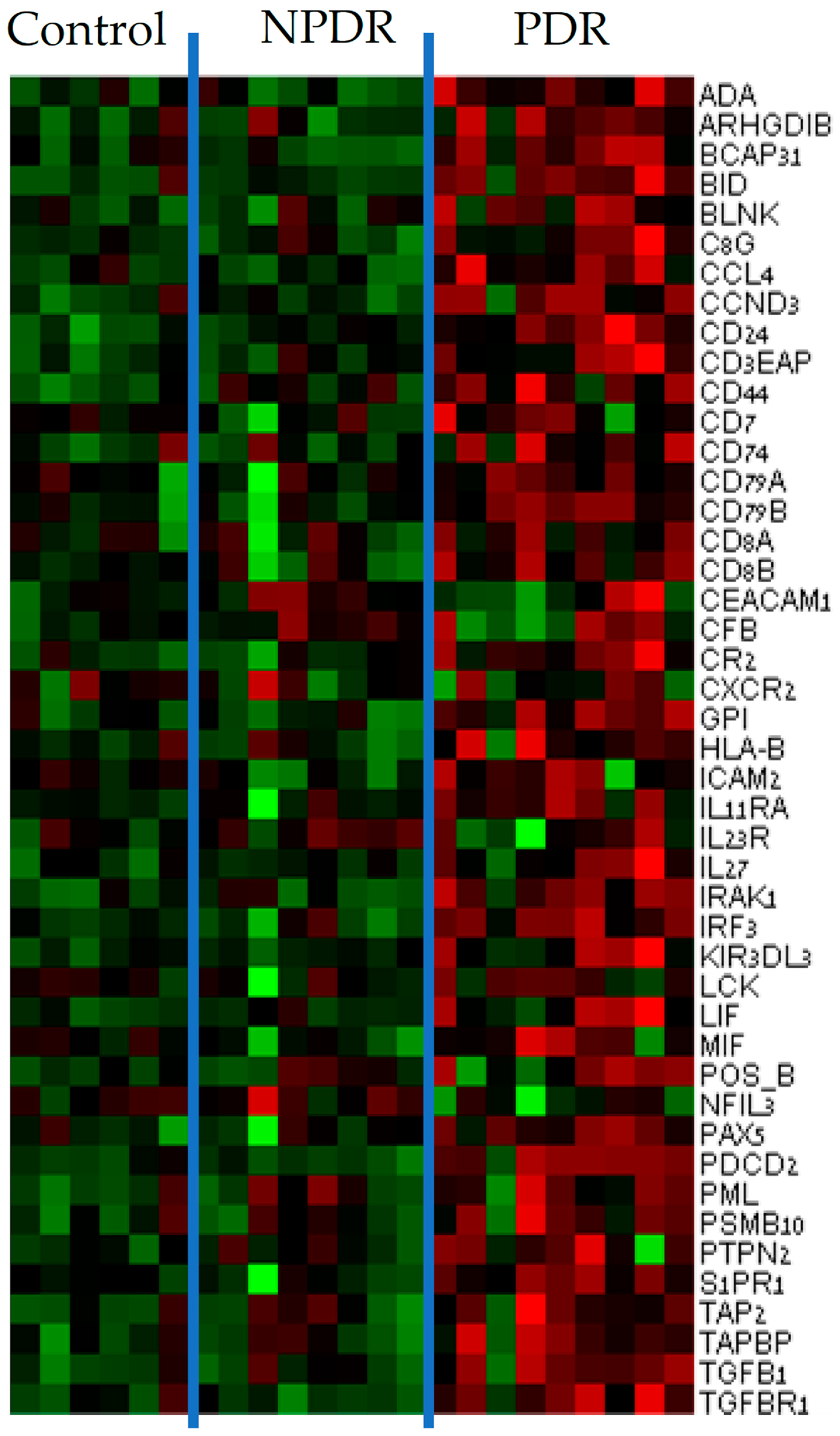
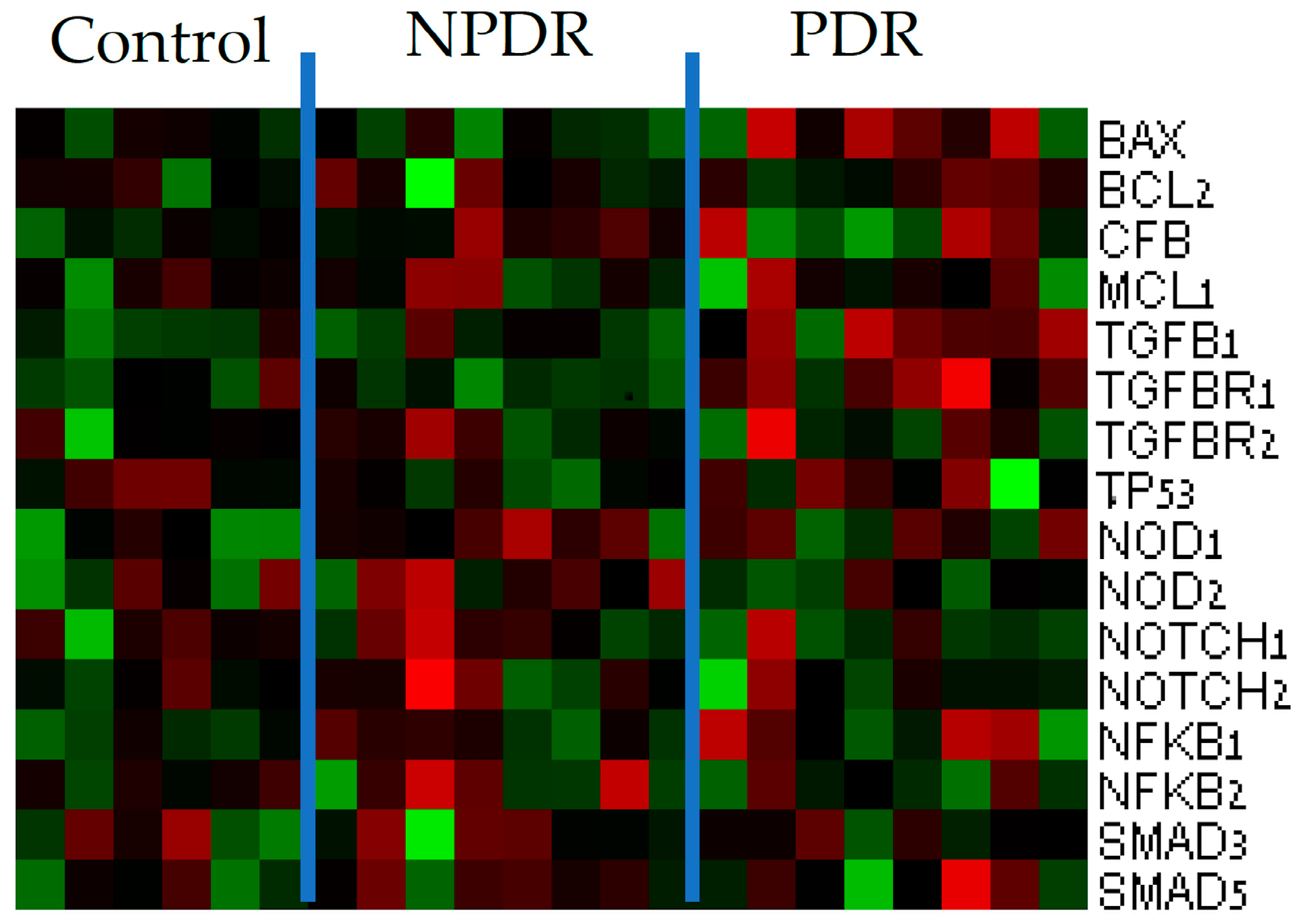
| Diagnosis | Sex | Age | Years of Diabetes | HbA1C Levels |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | Female | 66 | None | * |
| Control | Male | 79 | None | 5.4 |
| Control | Male | 43 | None | * |
| Control | Female | 38 | None | 5 |
| Control | Female | 48 | None | 5.5 |
| Control | Male | 76 | None | * |
| NPDR | Male | 71 | * | 6.8 |
| NPDR | Female | 72 | * | * |
| NPDR | Female | 85 | 6 | 6.5 |
| NPDR | Female | 91 | * | * |
| NPDR | Male | 74 | * | * |
| NPDR | Female | 62 | 17 | 6.5 |
| NPDR | Female | 85 | 18 | 6.8 |
| NPDR | Male | 67 | 24 | 7.4 |
| PDR | Male | 58 | 23 | 7.3 |
| PDR | Female | 57 | * | * |
| PDR | Male | 64 | 7 | * |
| PDR | Male | 64 | * | 6.3 |
| PDR | Female | 80 | 33 | 7.8 |
| PDR | Female | 53 | 27 | 10 |
| PDR | Male | 55 | 11 | 10.4 |
| PDR | Male | 56 | 20 | 9.3 |
| PDR | Female | 61 | 8 | 9.2 |
| GO Term | GO ID | Intersection Size | Term Size | Enrichment Ratio | Adjusted p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Peptidyl-amino acid modification | GO:0018193 | 9 | 686 | 0.013 | 1.01 × 10−2 |
| Negative regulation of natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity | GO:0045953 | 3 | 18 | 0.167 | 1.02 × 10−2 |
| Regulation of chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 2 production | GO:2000341 | 3 | 18 | 0.167 | 1.02 × 10−2 |
| Calcium mediated T cell apoptosis involved in inclusion body myositis | WP:WP5142 | 3 | 20 | 0.15 | 1.02 × 10−2 |
| Chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 2 production | GO:0072567 | 3 | 18 | 0.167 | 1.02 × 10−2 |
| Immune response | GO:0006955 | 30 | 2070 | 0.014 | 1.02 × 10−18 |
| Positive regulation of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway | GO:2001244 | 4 | 60 | 0.067 | 1.04 × 10−2 |
| Regulation of leukocyte mediated immunity | GO:0002703 | 7 | 255 | 0.027 | 1.04 × 10−3 |
| Signal transduction | GO:0007165 | 31 | 6002 | 0.005 | 1.04 × 10−6 |
| Lymphocyte differentiation | GO:0030098 | 14 | 442 | 0.032 | 1.04 × 10−10 |
| Elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate | HP:0003565 | 6 | 76 | 0.079 | 1.05 × 10−3 |
| Cell communication | GO:0007154 | 31 | 6540 | 0.005 | 1.06 × 10−5 |
| Regulation of cell population proliferation | GO:0042127 | 18 | 1685 | 0.011 | 1.06 × 10−6 |
| Negative regulation of immune system process | GO:0002683 | 8 | 515 | 0.016 | 1.07 × 10−2 |
| TAP1 binding | GO:0046978 | 2 | 4 | 0.5 | 1.07 × 10−2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zahavi, A.; Weiss, S.; Abu Dbai, J.; Salti, T.; Goldenberg-Cohen, N. Peripheral Blood Gene Expression Profiling in Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy Using NanoString Technology. Diabetology 2025, 6, 132. https://doi.org/10.3390/diabetology6110132
Zahavi A, Weiss S, Abu Dbai J, Salti T, Goldenberg-Cohen N. Peripheral Blood Gene Expression Profiling in Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy Using NanoString Technology. Diabetology. 2025; 6(11):132. https://doi.org/10.3390/diabetology6110132
Chicago/Turabian StyleZahavi, Alon, Shirel Weiss, Jawad Abu Dbai, Talal Salti, and Nitza Goldenberg-Cohen. 2025. "Peripheral Blood Gene Expression Profiling in Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy Using NanoString Technology" Diabetology 6, no. 11: 132. https://doi.org/10.3390/diabetology6110132
APA StyleZahavi, A., Weiss, S., Abu Dbai, J., Salti, T., & Goldenberg-Cohen, N. (2025). Peripheral Blood Gene Expression Profiling in Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy Using NanoString Technology. Diabetology, 6(11), 132. https://doi.org/10.3390/diabetology6110132






