Impact of Diabetes Mellitus, Its Duration, and Associated Complications on Nutritional Intake in Patients at Risk of Malnutrition: A Focused Nutritional Assessment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Parameters Studied
- Bioimpedance measurement (BIA) was performed using the NUTRILAB device (EFG, Akern, Milan, Italy) between 8:00 and 9:15, after an overnight fast and 15 min in the supine position. Resistance (R) and reactance (Xc) parameters were measured. The phase angle (PA) was calculated as: PA = ((Xc/R) × 180°/π) [13].
- Muscle ultrasound of the rectus femoris (RF) of the dominant lower extremity was performed with a 10 to 12 MHz probe and a multifrequency linear array (Mindray Z60, Madrid, Spain). The measurement was made with the patient in the supine position, without compression, at the level of the lower third from the superior pole of the patella and the anterior superior iliac spine [14]. The parameters measured to evaluate muscle mass were anteroposterior muscle thickness (Y axis), RF muscle area (RFMA), and subcutaneous fat thickness (cm).
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DRM | Disease related malnutrition |
| DM | Diabetes mellitus |
| T1D | Type 1 diabetes mellitus |
| T2D | Type 2 diabetes mellitus |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| BIA | Bioimpedance |
| RF | Rectus femoris |
| BMR | Basal metabolic rate |
| TMR | Total metabolic rate |
| SFA | Saturated fatty acids |
| MUFA | Monounsaturated fatty acids |
| PUFA | Polyunsaturated fatty acids |
References
- American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. 2. Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes: Standards of Care in Diabetes—2025. Diabetes Care 2024, 48 (Suppl. S1), S27–S49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harreiter, J.; Roden, M. Diabetes mellitus—Definition, Klassifikation, Diagnose, Screening und Prävention (Update 2023). Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2023, 135 (Suppl. S1), 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz-París, A.; García-Almeida, J.M.; Gómez-Candela, C.; Burgos-Peláez, R.; Martín, Á.; Matía-Martín, P.; Study VIDA Group. Prevalencia de desnutrición en ancianos hospitalizados con diabetes. Nutr. Hosp. 2013, 3, 592–599. [Google Scholar]
- Gómez-Candela, C.; Pérez-Fernández, L.; Sanz-París, A.; Burgos-Peláez, R.; Matía-Martín, P.; Álvarez-Recio, E.; López-Carmona, M.D.; García Almeida, J.M.; Pérez-Belmonte, L.M.; Martín Palmero, Á.; et al. Análisis del perfil de los pacientes ancianos diabéticos y hospitalizados que participaron en el estudio VIDA. Nutr. Hosp. 2016, 33, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, Y.; Omura, T.; Toyoshima, K.; Araki, A. Nutrition Management in Older Adults with Diabetes: A Review on the Importance of Shifting Prevention Strategies from Metabolic Syndrome to Frailty. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanz-Cánovas, J.; López-Sampalo, A.; Cobos-Palacios, L.; Ricci, M.; Hernández-Negrín, H.; Mancebo-Sevilla, J.J.; Bernal-López, M.; Álvarez-Recio, R.E.; López-Carmona, M.D.; Pérez-Belmonte, L.M.; et al. Management of Type 2 Diabetes mellitus in Elderly Patients with Frailty and/or Sarcopenia. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 8677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casals, C.; Suárez-Cadenas, E.; Estébanez Carvajal, F.M.; Aguilar Trujillo, M.P.; Jiménez Arcos, M.M.; Vázquez Sánchez, M.Á. Relación entre calidad de vida, actividad física, alimentación y control glucémico con la sarcopenia de adultos mayores con diabetes mellitus tipo 2. Nutr. Hosp. 2017, 34, 1198–1204. [Google Scholar]
- Volkert, D.; Beck, A.M.; Cederholm, T.; Cruz-Jentoft, A.; Goisser, S.; Hooper, L.; Kiesswetter, E.; Maggio, M.; Raynaud-Simon, A.; Sieber, C.C.; et al. ESPEN guideline on clinical nutrition and hydration in geriatrics. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 38, 10–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. 5. Facilitating Positive Health Behaviors and Well-being to Improve Health Outcomes: Standards of Care in Diabetes—2025. Diabetes Care 2024, 48 (Suppl. S1), S86–S127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. 8. Obesity and Weight Management for the Prevention and Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes: Standards of Care in Diabetes–2025. Diabetes Care 2024, 48 (Suppl. S1), S167–S180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cederholm, T.; Jensen, G.L.; Correia, M.I.T.D.; Gonzalez, M.C.; Fukushima, R.; Higashiguchi, T.; Barazzoni, R.; Blaauw, R.; Coats, A.J.S.; Crivelli, A.N.; et al. GLIM criteria for the diagnosis of malnutrition—A consensus report from the global clinical nutrition community. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 38, 1480–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Bahat, G.; Bauer, J.; Boirie, Y.; Bruyère, O.; Cederholm, T.; Zamboni, M. Sarcopenia: Revised European consensus on definition and diagnosis. Age Ageing 2019, 48, 16–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellido, D.; García-García, C.; Talluri, A.; Lukaski, H.C.; García-Almeida, J.M. Future lines of research on phase angle: Strengths and limitations. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2023, 24, 563–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Almeida, J.M.; García-García, C.; Vegas-Aguilar, I.M.; Ballesteros Pomar, M.D.; Cornejo-Pareja, I.M.; Fernández Medina, B. Nutritional ultrasound®: Conceptualisation, technical considerations and standardisation. Endocrinol. Diabetes Nutr. 2023, 70, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlidou, E.; Papadopoulou, S.K.; Seroglou, K.; Giaginis, C. Revised Harris–Benedict Equation: New Human Resting Metabolic Rate Equation. Metabolites 2023, 13, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manual de Endocrinología y Nutrición—Capítulo 151. Determinación del Gasto Energético. Requerimientos Nutricionales en la Población Sana. Valoración de la Ingesta. Available online: https://manual.seen.es/article?id=66fa615c-3690-4dd4-b231-3bc50aca0133 (accessed on 9 June 2025).
- Álvarez-Hernández, J.; Planas-Vila, M.; León-Sanz, M.; García de Lorenzo, A.; Celaya-Pérez, S.; García-Lorda, P.; Araujo, K.; Sarto-Guerri, B.; on behalf of the PREDyCES® Researches. Prevalencia y costes de la malnutrición en pacientes hospitalizados; estudio PREDyCES. Nutr. Hosp. 2012, 4, 1049–1059. [Google Scholar]
- Serrano Valles, C.; López Gómez, J.J.; García Calvo, S.; Jiménez Sahagún, R.; Torres Torres, B.; Gómez Hoyos, E.; Buigues, O.; de Luis Roman, D. Influencia del estado nutricional sobre la estancia media hospitalaria en el paciente con Diabetes mellitus tipo 2. Endocrinol. Diabetes Nutr. 2020, 67, 617–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djuricic, I.; Calder, P.C. Beneficial Outcomes of Omega-6 and Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids on Human Health: An Update for 2021. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz-Paris, A.; Álvarez Hernández, J.; Ballesteros-Pomar, M.D.; Botella-Romero, F.; León-Sanz, M.; Martín-Palmero, Á.; Olmos, M.Á.M.; Olveira, G. Evidence-based recommendations and expert consensus on enteral nutrition in the adult patient with Diabetes mellitus or hyperglycemia. Nutrition 2017, 41, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omura, T.; Araki, A. Skeletal muscle as a treatment target for older adults with diabetes mellitus: The importance of a multimodal intervention based on functional category. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2022, 22, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, Y.; Kamada, C.; Takahashi, K.; Kaimoto, T.; Iimuro, S.; Ohashi, Y.; Araki, A.; Umegaki, H.; Sakurai, T.; Ito, H.; et al. Relations of nutritional intake to age, sex and body mass index in Japanese elderly patients with type 2 diabetes: The Japanese Elderly Diabetes Intervention Trial. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2012, 12 (Suppl. S1), 9–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dent, E.; Wright, O.R.L.; Woo, J.; Hoogendijk, E.O. Malnutrition in older adults. Lancet 2023, 401, 951–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rebollo-Pérez, M.I.; Florencio Ojeda, L.; García-Luna, P.P.; Irles Rocamora, J.A.; Olveira, G.; Lacalle Remigio, J.R.; Irigoyen, C.A.; Continente, A.C.; Martín, C.C.; Soto, M.L.F.; et al. Standards for the Use of Enteral Nutrition in Patients with Diabetes or Stress Hyperglycaemia: Expert Consensus. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Boer, I.H.; Khunti, K.; Sadusky, T.; Tuttle, K.R.; Neumiller, J.J.; Rhee, C.M.; Rosas, S.E. Diabetes Management in Chronic Kidney Disease: A Consensus Report by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO). Diabetes Care 2022, 45, 3075–3090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afkarian, M.; Zelnick, L.R.; Hall, Y.N.; Heagerty, P.J.; Tuttle, K.; Weiss, N.S.; de Boer, I.H. Clinical Manifestations of Kidney Disease Among US Adults with Diabetes, 1988–2014. JAMA 2016, 316, 602–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García Almeida, J.M.; Laínez López, M.; Burgos Peláez, R.; Matía Martín, P.; Palma Milla, S.; Sanz Paris, A.; Murillo, A.Z.; Martínez, J.J.A.; Artero-Fullana, A.; Chinchetru, M.J.; et al. Malnutrition management of hospitalized patients with diabetes/hyperglycemia and sarcopenia. Nutr. Hosp. 2022, 39, 15–22. Available online: https://www.nutricionhospitalaria.org/articles/04507/show (accessed on 31 May 2025). [CrossRef]
- Purnamasari, D.; Tetrasiwi, E.N.; Kartiko, G.J.; Astrella, C.; Husam, K.; Laksmi, P.W. Sarcopenia and Chronic Complications of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Rev. Diabet. Stud. 2022, 18, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Y.S.; Chai, Y.H.; Gong, H.J.; Zhuldyz, Z.; Stehouwer, C.D.A.; Zhou, J.B.; Simó, R. The Association Between Diabetes mellitus and Risk of Sarcopenia: Accumulated Evidences from Observational Studies. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 782391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Total | DM | NoDM | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 64.7 ± 15.4 | 68.3 ± 11.8 | 63.4 ± 16.3 | 0.06 |
| Gender (%M/%W) | 34.6/65.4 | 50/50 | 29.3/70.7 | 0.01 * |
| HbA1c (%) | 5.9 ± 1.0 | 6.1 ± 1.0 | 5.8 ± 1.0 | <0.01 |
| ANTHROPOMETRY | ||||
| BMI (kg/m2) | 21.4 ± 3.7 | 22.7 ± 3.3 | 21.0 ± 3.7 | <0.01 * |
| BIOIMPEDANCIOMETRY | ||||
| Resistance/height (ohm/m) | 373 ± 73 | 351.7 ± 70 | 380 ± 72 | 0.02 * |
| Reactance/height (ohm/m) | 31.1 ± 7.3 | 28.9 ± 7.1 | 31.9 ± 7.3 | 0.02 * |
| Phase angle (°) | 4.8 ± 0.8 | 4.7 ± 1.0 | 4.8 ± 0.8 | 0.61 |
| NUTRITIONAL ULTRASOUND | ||||
| Area (cm2) | 2.9 ± 1.0 | 2.8 ± 1.0 | 2.9 ± 1.0 | 0.41 |
| Y-axis (cm) | 0.9 ± 0.3 | 0.9 ± 0.3 | 0.9 ± 0.3 | 0.40 |
| Thickness of subcutaneous fat (cm) | 0.7 ± 0.4 | 0.6 ± 0.3 | 0.8 ± 0.4 | <0.05 * |
| HANDGRIP STRENGTH | ||||
| Dynamometry (kg) | 22.0 ± 8.4 | 21.0 ± 9.1 | 22.4 ± 8.1 | 0.34 |
| OTHER DIAGNOSIS | ||||
| Oncological pathology (%) | 49.2% | 54.3% | 47.4% | 0.41 |
| Malnutrition (%) | 81 | 80.4 | 81.2 | 0.79 |
| Sarcopenia (%) | 26.8 | 39.1 | 22.6 | 0.03 * |
| Total | DM | NoDM | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BMR (kcal/day) | 1206 ± 178 | 1235 ± 182 | 1198 ± 177 | 0.24 |
| TMR (kcal/day) | 1569 ± 232 | 1605 ± 237 | 1556 ± 230 | 0.24 |
| Energy intake (kcal/day) | 1551 ± 441 | 1419 ± 382 | 1597 ± 452 | 0.02 |
| Protein intake (g of prot/day) | 69 ± 21 | 67 ± 18 | 69 ± 22 | 0.61 |
| Adjusted energy intake (kcal/kg/day) | 29.2 ± 10.0 | 24.9 ± 8.3 | 30.7 ± 10.1 | <0.01 |
| Adjusted protein intake (g of prot/kg/day) | 1.3 ± 0.5 | 1.2 ± 0.4 | 1.3 ± 0.5 | <0.05 |
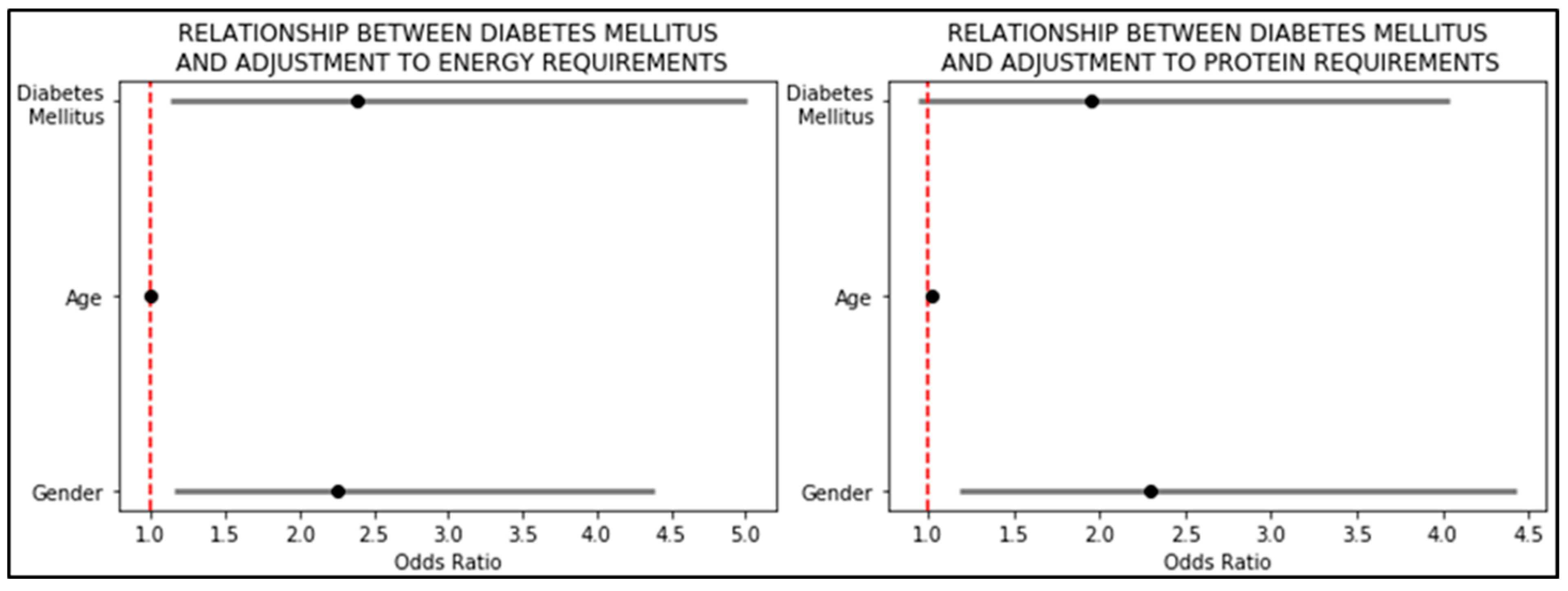
| Adjustment to energy requirements (%) | 100 ± 29 | 90 ± 25 | 104 ± 29 | <0.01 |
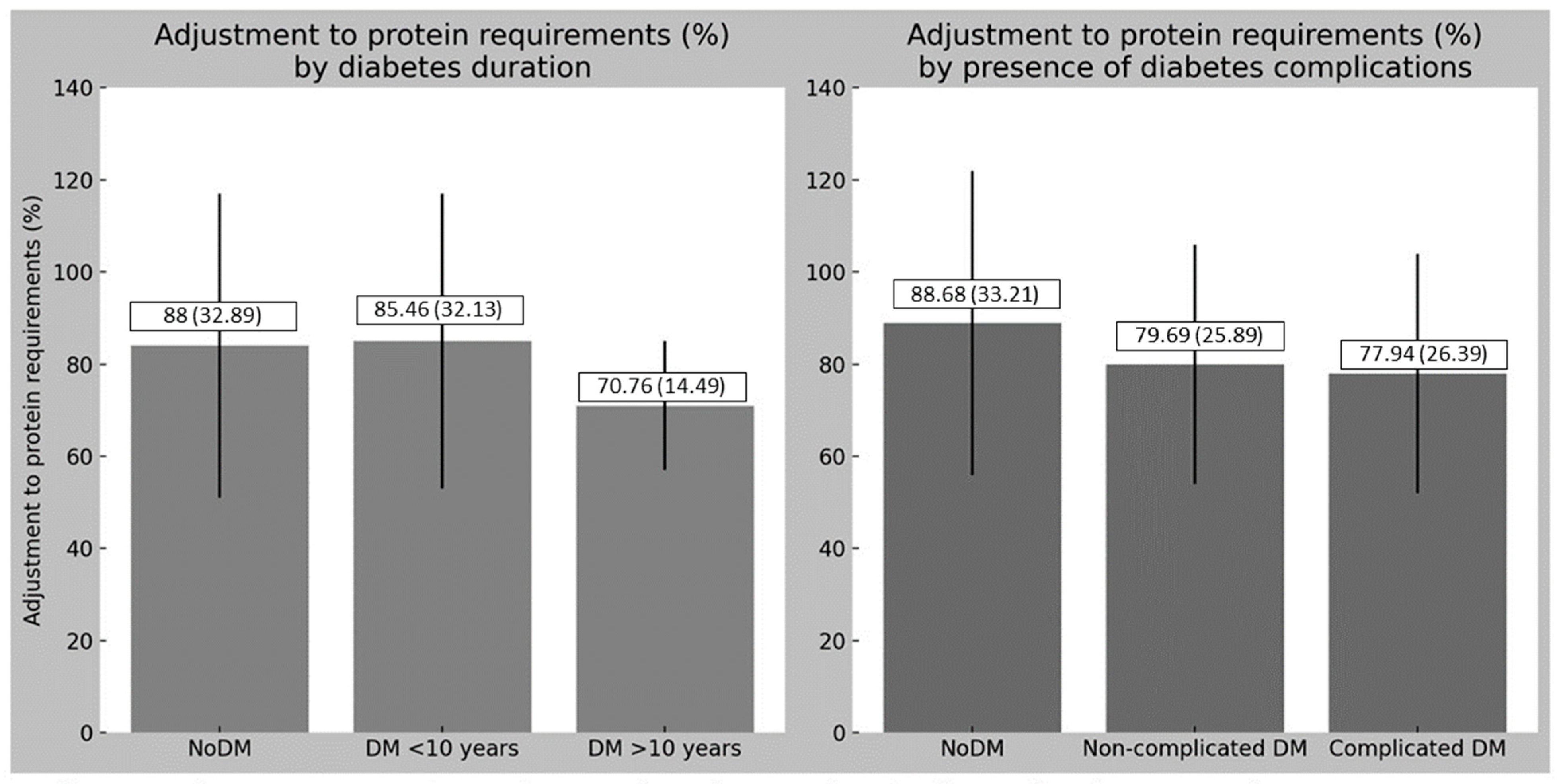
| Adjustment to protein requirements (%) | 86 ± 31 | 79 ± 25 | 88 ± 33 | <0.05 |
| %TCV Carbohydrates | 41.1 ± 8.7 | 42.4 ± 10.0 | 40.7 ± 8.2 | 0.24 |
| Fiber (g) | 13.6 ± 6.8 | 14.0 ± 6.7 | 13.5 ± 6.8 | 0.65 |
| %TCV fats | 39.6 ± 7.4 | 37.7 ± 7.0 | 40.2 ± 7.4 | <0.05 |
| SFA (g) | 20.3 ± 9.8 | 17.3 ± 8.1 | 21.4 ± 10.1 | 0.01 |
| %TCV SFA | 11.7 ± 4.1 | 10.8 ± 3.8 | 12.0 ± 4.2 | 0.08 |
| MUFA (g) | 27.7 ± 11.7 | 24.8 ± 9.0 | 28.7 ± 12.4 | 0.05 |
| %TCV MUFA | 16.1 ± 5.2 | 15.8 ± 3.9 | 16.2 ± 5.5 | 0.59 |
| PUFA (g) | 8.1 ± 5.4 | 6.4 ± 4.0 | 8.8 ± 5.6 | <0.01 |
| %TCV PUFA | 4.6 ± 2.3 | 3.9 ± 1.9 | 4.8 ± 2.5 | 0.03 |
| Cholesterol (mg) | 333 ± 154 | 283 ± 116 | 350 ± 162 | 0.01 |
| %TCV proteins | 18.1 ± 4.1 | 19.7 ± 4.9 | 17.6 ± 3.7 | <0.01 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
López, P.P.; Gutiérrez, J.G.; Asensio, L.E.; Jauregui, O.I.; Martín, D.P.; Bachiller, B.R.; Andrés, E.L.; De Luis Román, D.; Gómez, J.J.L. Impact of Diabetes Mellitus, Its Duration, and Associated Complications on Nutritional Intake in Patients at Risk of Malnutrition: A Focused Nutritional Assessment. Diabetology 2025, 6, 108. https://doi.org/10.3390/diabetology6100108
López PP, Gutiérrez JG, Asensio LE, Jauregui OI, Martín DP, Bachiller BR, Andrés EL, De Luis Román D, Gómez JJL. Impact of Diabetes Mellitus, Its Duration, and Associated Complications on Nutritional Intake in Patients at Risk of Malnutrition: A Focused Nutritional Assessment. Diabetology. 2025; 6(10):108. https://doi.org/10.3390/diabetology6100108
Chicago/Turabian StyleLópez, Paloma Pérez, Jaime González Gutiérrez, Lucía Estévez Asensio, Olatz Izaola Jauregui, David Primo Martín, Beatriz Ramos Bachiller, Eva López Andrés, Daniel De Luis Román, and Juan José López Gómez. 2025. "Impact of Diabetes Mellitus, Its Duration, and Associated Complications on Nutritional Intake in Patients at Risk of Malnutrition: A Focused Nutritional Assessment" Diabetology 6, no. 10: 108. https://doi.org/10.3390/diabetology6100108
APA StyleLópez, P. P., Gutiérrez, J. G., Asensio, L. E., Jauregui, O. I., Martín, D. P., Bachiller, B. R., Andrés, E. L., De Luis Román, D., & Gómez, J. J. L. (2025). Impact of Diabetes Mellitus, Its Duration, and Associated Complications on Nutritional Intake in Patients at Risk of Malnutrition: A Focused Nutritional Assessment. Diabetology, 6(10), 108. https://doi.org/10.3390/diabetology6100108








