Metabolic Syndrome and Pharmacological Interventions in Clinical Development
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Atherogenic Dyslipidemia
1.2. Arterial Hypertension
1.3. Management of Hyperglycemia
1.4. Weight Management
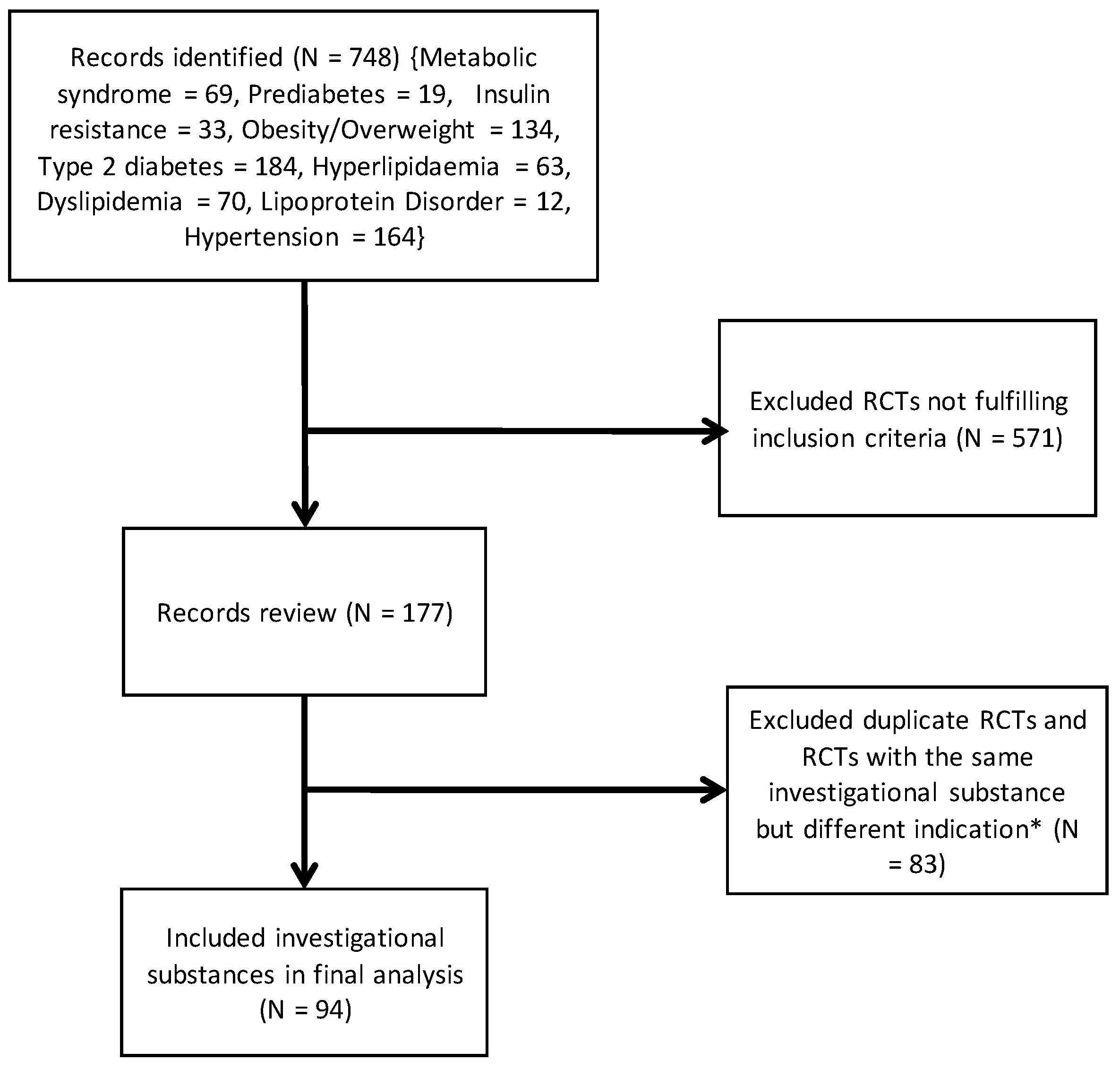
2. Material and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Type 2 Diabetes, Obesity and/or Overweight
3.2. Dyslipidemia and Lipoprotein Disorder
3.3. Hypertension
3.4. Metabolic Syndrome and Insulin Resistance
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Grundy, S.M.; Cleeman, J.I.; Daniels, S.R.; Donato, K.A.; Eckel, R.H.; Franklin, B.A.; Gordon, D.J.; Krauss, R.M.; Savage, P.J.; Smith, S.C., Jr.; et al. Diagnosis and management of the metabolic syndrome: American Heart Association/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Scientific Statement: Executive summary. Circulation 2005, 112, e285–e290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rask Larsen, J.; Dima, L.; Correll, C.U.; Manu, P. The pharmacological management of metabolic syndrome. Expert Rev. Clin. Pharmacol. 2018, 11, 397–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alberti, K.G.M.M.; Eckel, R.H.; Grundy, S.M.; Zimmet, P.Z.; Cleeman, J.I.; Donato, K.A.; Fruchart, J.-C.; James, W.P.T.; Loria, C.M.; Smith, S.C., Jr.; et al. Harmonizing the metabolic syndrome: A joint interim statement of the International Diabetes Federation Task Force on Epidemiology and Prevention; National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; American Heart Association; World Heart Federation; International Atherosclerosis Society; and International Association for the Study of Obesity. Circulation 2009, 120, 1640–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ford, E.S.; Giles, W.H.; Mokdad, A.H. Increasing prevalence of the metabolic syndrome among u.s. Adults. Diabetes Care 2004, 27, 2444–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Athyros, V.G.; Bouloukos, V.I.; Pehlivanidis, A.N.; Papageorgiou, A.A.; Dionysopoulou, S.G.; Symeonidis, A.N.; Petridis, D.I.; Kapousouzi, M.I.; Satsoglou, E.A.; Mikhailidis, D.P. The prevalence of the metabolic syndrome in Greece: The MetS-Greece Multicentre Study. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2005, 7, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batsis, J.A.; Romero-Corral, A.; Collazo-Clavell, M.L.; Sarr, M.G.; Somers, V.K.; Lopez-Jimenez, F. Effect of bariatric surgery on the metabolic syndrome: A population-based, long-term controlled study. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2008, 83, 897–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Agostino, R.B.; Vasan, R.S.; Pencina, M.J.; Wolf, P.A.; Cobain, M.; Massaro, J.M.; Kannel, W.B. General cardiovascular risk profile for use in primary care: The Framingham heart study. Circulation 2008, 117, 743–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grundy, S.M.; Stone, N.J.; Bailey, A.L.; Beam, C.; Birtcher, K.K.; Blumenthal, R.S.; Braun, L.T.; de Ferranti, S.; Faiella-Tommasino, J.; Forman, D.E.; et al. 2018 AHA/ACC/AACVPR/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/ADA/AGS/APhA/ASPC/NLA/PCNA guideline on the management of blood cholesterol: American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association on clinical practice guidelines. Circulation 2019, 139, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaddoura, R.; Orabi, B.; Salam, A.M. PCSK9 monoclonal antibodies: An overview. Heart Views 2020, 21, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, H.; Hong, L.; Wang, H.; Li, B.; Zhang, M.; Li, J.; Yang, L.; Liu, F. Inclisiran: A new generation of lipid-lowering siRNA therapeutic. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1260921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, S.; Wu, B.J.; Guiney, L.; Barter, P.J.; Rye, K.A. Cholesteryl ester transfer protein and its inhibitors. J. Lipid Res. 2018, 59, 772–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiorentino, R.; Chiarelli, F. Treatment of dyslipidaemia in children. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nissen, S.E.; Lincoff, A.M.; Brennan, D.; Ray, K.K.; Mason, D.; Kastelein, J.J.P.; Thompson, P.D.; Libby, P.; Cho, L.; Plutzky, J.; et al. Bempedoic acid and cardiovascular outcomes in statin-intolerant patients. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 1353–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancia, G.; Kreutz, R.; Brunström, M.; Burnier, M.; Grassi, G.; Januszewicz, A.; Muiesan, M.L.; Tsioufis, K.; Agabiti-Rosei, E.; Algharably, E.A.; et al. 2023 ESH guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension the task force for the management of arterial hypertension of European Society of Hypertension: Endorsed by the International Society of Hypertension (ISH) and the European Renal Association (ERA). J. Hypertens. 2023, 41, 1874–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, M.J.; Aroda, V.R.; Collins, B.S.; Gabbay, R.A.; Green, J.; Maruthur, N.M.; Rosas, S.E.; Del Prato, S.; Mathieu, C.; Mingrone, G.; et al. Management of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes, 2022. A consensus report by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD). Diabetes Care 2022, 45, 2753–2786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Diabetes Association. 3. Prevention or delay of type 2 diabetes: Standards of medical care in diabetes—2021. Diabetes Care 2021, 44, S34–S39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spector, R. A revolution in the treatment of obesity. Am. J. Med. 2024, 22, S0002934324003346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ElSayed, N.A.; Aleppo, G.; Aroda, V.R.; Bannuru, R.R.; Brown, F.M.; Bruemmer, D.; Collins, B.S.; Hilliard, M.E.; Isaacs, D.; Johnson, E.L.; et al. 8. Obesity and weight management for the prevention and treatment of type 2 diabetes: Standards of care in diabetes—2023. Diabetes Care 2023, 46, S128–S139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). FDA Approves New Medication for Chronic Weight Management. 2023. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-approves-new-medication-chronic-weight-management (accessed on 28 June 2024).
- Grundy, S.M. Drug therapy of the metabolic syndrome: Minimizing the emerging crisis in polypharmacy. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2006, 5, 295–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matfin, G. Developing therapies for the metabolic syndrome: Challenges, opportunities, and… the unknown. Ther. Adv. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 1, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Global Observatory on Health Research and Development. Clinical Trials. Available online: https://www.who.int/observatories/global-observatory-on-health-research-and-development/resources/databases/databases-on-processes-for-r-d/clinical-trials (accessed on 28 May 2024).
- Wong, C.H.; Siah, K.W.; Lo, A.W. Estimation of clinical trial success rates and related parameters. Biostatistics 2019, 20, 273–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, D.; Qin, H.H.; Zheng, Q.; Ning, J.; Zhu, Z.; Mengying, G.; Bu, Y.; Jones, C.; Fenaux, M.; Xu, S.; et al. 755-p: A phase 2 evaluation of a novel GLP-1 analog ecnoglutide (Xw003) for glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 2023, 72, 755-P. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, L.; Jiang, H.; An, P.; Deng, H.; Liu, M.; Li, L.; Feng, L.; Song, B.; Han-Zhang, H.; Ma, Q.; et al. IBI362 (LY3305677), a weekly-dose GLP-1 and glucagon receptor dual agonist, in Chinese adults with overweight or obesity: A randomised, placebo-controlled, multiple ascending dose phase 1b study. EClinicalMedicine 2021, 39, 101088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmermann, T.; Thomas, L.; Baader-Pagler, T.; Haebel, P.; Simon, E.; Reindl, W.; Bajrami, B.; Rist, W.; Uphues, I.; Drucker, D.J.; et al. BI 456906: Discovery and preclinical pharmacology of a novel GCGR/GLP-1R dual agonist with robust anti-obesity efficacy. Mol. Metab. 2022, 66, 101633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nauck, M.A.; D‘Alessio, D.A. Tirzepatide, a dual GIP/GLP-1 receptor co-agonist for the treatment of type 2 diabetes with unmatched effectiveness regrading glycaemic control and body weight reduction. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2022, 21, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jastreboff, A.M.; Kaplan, L.M.; Frías, J.P.; Wu, Q.; Du, Y.; Gurbuz, S.; Coskun, T.; Haupt, A.; Milicevic, Z.; Hartman, M.L.; et al. Triple–hormone-receptor agonist retatrutide for obesity—A phase 2 trial. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 389, 514–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frias, J.P.; Deenadayalan, S.; Erichsen, L.; Knop, F.K.; Lingvay, I.; Macura, S.; Mathieu, C.; Pedersen, S.D.; Davies, M. Efficacy and safety of co-administered once-weekly cagrilintide 2·4 mg with once-weekly semaglutide 2·4 mg in type 2 diabetes: A multicentre, randomised, double-blind, active-controlled, phase 2 trial. Lancet 2023, 402, 720–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopelman, P.G.; Grace, C. New thoughts on managing obesity. Gut 2004, 53, 1044–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niethammer, A.G.; Zheng, Z.; Timmer, A.; Lee, T.L. First-in-human evaluation of oral denatonium acetate (ARD-101), a potential bitter taste receptor agonist: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 1 trial in healthy adults. Clin. Pharmacol. Drug Dev. 2022, 11, 997–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Teng, P.; Montgomery, N.T.; Li, X.; Tang, W. Development of triantennary N-Acetylgalactosamine conjugates as degraders for extracellular proteins. ACS Cent. Sci. 2021, 7, 499–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutierrez, J.A.; Liu, W.; Perez, S.; Xing, G.; Sonnenberg, G.; Kou, K.; Blatnik, M.; Allen, R.; Weng, Y.; Vera, N.B.; et al. Pharmacologic inhibition of ketohexokinase prevents fructose-induced metabolic dysfunction. Mol. Metab. 2021, 48, 101196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heymsfield, S.B.; Coleman, L.A.; Miller, R.; Rooks, D.S.; Laurent, D.; Petricoul, O.; Praestgaard, J.; Swan, T.; Wade, T.; Perry, R.G.; et al. Effect of bimagrumab vs placebo on body fat mass among adults with type 2 diabetes and obesity: A phase 2 randomized clinical trial. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e2033457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Xing, B.; Cao, Y.; He, X.; Bennett, K.E.; Tong, C.; An, C.; Hojnacki, T.; Feng, Z.; Deng, S.; et al. Menin-regulated Pbk controls high fat diet-induced compensatory beta cell proliferation. EMBO Mol. Med. 2021, 13, e13524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, H.P.; Xiong, Y. Learn from failures and stay hopeful to GPR40, a GPCR target with robust efficacy, for therapy of metabolic disorders. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 1043828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neary, N.M.; Small, C.J.; Druce, M.R.; Park, A.J.; Ellis, S.M.; Semjonous, N.M.; Dakin, C.L.; Filipsson, K.; Wang, F.; Kent, A.S.; et al. Peptide YY3-36 and glucagon-like peptide-17-36 inhibit food intake additively. Endocrinology 2005, 146, 5120–5127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benichou, O.; Coskun, T.; Gonciarz, M.D.; Garhyan, P.; Adams, A.C.; Du, Y.; Dunbar, J.D.; Martin, J.A.; Mather, K.J.; Pickard, R.T.; et al. Discovery, development, and clinical proof of mechanism of LY3463251, a long-acting GDF15 receptor agonist. Cell Metab. 2023, 35, 274–286.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, T.L.; Vissing, J.; Krag, T.O. Antimyostatin treatment in health and disease: The story of great expectations and limited success. Cells 2021, 10, 533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ProKidney Corp. (Nasdaq: PROK). ProKidney Receives Allowance from the UK Medicines and Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency (MHRA) for proact 1 (REGEN-006) and EMA Scientific Advice on Phase 3 Protocols of REACT for Diabetic Chronic Kidney Disease. 2022. Available online: https://investors.prokidney.com/news-releases/news-release-details/prokidney-receives-allowance-uk-medicines-and-healthcare (accessed on 28 June 2024).
- Enkhmaa, B.; Berglund, L. Non-genetic influences on lipoprotein(A) concentrations. Atherosclerosis 2022, 349, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasas, S.; Azizad, M.; Clifton, P.; Gaudet, D.; Goldenberg, R.; Modesto, K.; Chang, T.; Melquist, S.; Fu, R.; San Martin, J.; et al. Abstract 17091: ARO-APOC3, an investigational RNAi therapeutic, silences APOC3 and reduces atherosclerosis-associated lipoproteins in patients with mixed dyslipidemia: MUIR study results. Circulation 2023, 148, A17091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaudet, D.; Pall, D.; Watts, G.F.; Nicholls, S.J.; Rosenson, R.S.; Modesto, K.; San Martin, J.; Hellawell, J.; Ballantyne, C.M. Plozasiran (ARO-APOC3) for severe hypertriglyceridemia: The SHASTA-2 randomized clinical trial. JAMA Cardiol. 2024, 9, 620–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergmark, B.A.; Marston, N.A.; Prohaska, T.A.; Alexander, V.J.; Zimerman, A.; Moura, F.A.; Murphy, S.A.; Goodrich, E.L.; Zhang, S.; Gaudet, D.; et al. Olezarsen for hypertriglyceridemia in patients at high cardiovascular risk. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 390, 1770–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nissen, S.E.; Linnebjerg, H.; Shen, X.; Wolski, K.; Ma, X.; Lim, S.; Michael, L.F.; Ruotolo, G.; Gribble, G.; Navar, A.M.; et al. Lepodisiran, an extended-duration short interfering RNA targeting lipoprotein(A): A randomized dose-ascending clinical trial. JAMA 2023, 330, 2075–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenson, R.S.; Gaudet, D.; Hegele, R.A.; Ballantyne, C.M.; Nicholls, S.J.; Lucas, K.J.; San Martin, J.; Zhou, R.; Muhsin, M.A.; Chang, T.; et al. Zodasiran, an RNAi therapeutic targeting ANGPTL3, for mixed hyperlipidemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, NEJMoa2404147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nissen, S.E.; Wolski, K.; Watts, G.F.; Koren, M.J.; Fok, H.; Nicholls, S.J.; Rider, D.A.; Cho, L.; Romano, S.; Melgaard, C.; et al. Single ascending and multiple-dose trial of zerlasiran, a short interfering RNA targeting lipoprotein(A): A randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2024, 331, 1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicholls, S.J.; Nissen, S.E.; Fleming, C.; Urva, S.; Suico, J.; Berg, P.H.; Linnebjerg, H.; Ruotolo, G.; Turner, P.K.; Michael, L.F.; et al. Muvalaplin, an oral small molecule inhibitor of lipoprotein(A) formation: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2023, 330, 1042–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballantyne, C.M.; Ditmarsch, M.; Kastelein, J.J.P.; Nelson, A.J.; Kling, D.; Hsieh, A.; Curcio, D.L.; Maki, K.C.; Davidson, M.H.; Nicholls, S.J. Obicetrapib plus ezetimibe as an adjunct to high-intensity statin therapy: A randomized phase 2 trial. J. Clin. Lipidol. 2023, 17, 491–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokote, K.; Yamashita, S.; Arai, H.; Araki, E.; Suganami, H.; Ishibashi, S. Long-term efficacy and safety of pemafibrate, a novel selective peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-α modulator (SPPARMα), in dyslipidemic patients with renal impairment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freeman, M.W.; Halvorsen, Y.D.; Marshall, W.; Pater, M.; Isaacsohn, J.; Pearce, C.; Murphy, B.; Alp, N.; Srivastava, A.; Bhatt, D.L.; et al. Phase 2 trial of baxdrostat for treatment-resistant hypertension. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 395–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Presented by Bhatt, D.L. Results from a Phase 2, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial Evaluating the Efficacy and Safety of Baxdrostat in Patients with Uncontrolled Hypertension; Session 403-08; ACC Scientific Session: New Orleans, LA, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laffin, L.J.; Rodman, D.; Luther, J.M.; Vaidya, A.; Weir, M.R.; Rajicic, N.; Slingsby, B.T.; Nissen, S.E. Aldosterone synthase inhibition with lorundrostat for uncontrolled hypertension: The Target-HTN randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2023, 330, 1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, E.; Duran, J.M.; Weinland, J.; Lin, T.; Mullick, A.E.; Geary, R.; Tsimikas, S. Abstract 17395: Effect ION904, an antisense inhibitor of angiotensinogen production: Results of phase 1 and phase 2 pilot studies. Circulation 2023, 148, A17395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakris, G.L.; Yang, Y.F.; McCabe, J.M.; Liu, J.R.; Tan, X.J.; Benn, V.J.; Pitt, B. Efficacy and safety of ocedurenone: Subgroup analysis of the BLOCK-CKD study. Am. J. Hypertens. 2023, 36, 612–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Presented by Bakris, G.L. Zilebesiran in Combination with a Standard-of-Care Antihypertensive in Patients with Inadequately Controlled Hypertension—KARDIA-2. 2024. Available online: https://www.acc.org/Latest-in-Cardiology/Clinical-Trials/2024/04/05/04/26/kardia-2 (accessed on 28 May 2024).
- Tokudome, T.; Otani, K.; Mao, Y.; Jensen, L.J.; Arai, Y.; Miyazaki, T.; Sonobe, T.; Pearson, J.T.; Osaki, T.; Minamino, N.; et al. Endothelial natriuretic peptide receptor 1 play crucial role for acute and chronic blood pressure regulation by atrial natriuretic peptide. Hypertension 2022, 79, 1409–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.L.; Wu, X.; Serra Roma, A.; Markiewicz, M.; Healy, E.; Yan, J.-H.; Bitsaktsis, C.; Kulmatycki, K.; Kinhikar, A.; Zhang, T.; et al. 23281: Safety and Blood Pressure Lowering Effects of a Novel and Long-Acting Natriuretic Peptide Receptor 1 Agonist in Healthy Participants: A First-in-Human Clinical Study. Late-breaking science abstracts and featured science abstracts from the American Heart Association’s scientific sessions 2023 and late-breaking abstracts in resuscitation science from the resuscitation science symposium 2023. Circulation 2023, 148, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, P.W.; Pieske, B.; Anstrom, K.J.; Ezekowitz, J.; Hernandez, A.F.; Butler, J.; Lam, C.S.P.; Ponikowski, P.; Voors, A.A.; Jia, G.; et al. Vericiguat in patients with heart failure and reduced ejection fraction. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1883–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crater, G.D.; Lalonde, K.; Ravenelle, F.; Harvey, M.; Després, J.P. Effects of CB1R inverse agonist, INV-202, in patients with features of metabolic syndrome. A randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind phase 1b study. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2024, 26, 642–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, A. Neuropsychiatric adverse effects signal the end of the line for rimonabant. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2010, 7, 602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glund, S.; Schoelch, C.; Thomas, L.; Niessen, H.G.; Stiller, D.; Roth, G.J.; Neubauer, H. Inhibition of acetyl-CoA carboxylase 2 enhances skeletal muscle fatty acid oxidation and improves whole-body glucose homeostasis in db/db mice. Diabetologia 2012, 55, 2044–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijayakumar, A.; Murakami, E.; Huss, R.S.; Sroda, N.; Shimazaki, A.; Kashiwagi, Y.; Myers, R.P.; Subramanian, M.; Shulman, G.I. 849-P: Antidiabetic effects of TLC-3595, a selective ACC2 inhibitor, in ZDF rats. Diabetes 2023, 72, 849-P. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Roux, C.W.; Steen, O.; Lucas, K.J.; Startseva, E.; Unseld, A.; Hennige, A.M. Glucagon and GLP-1 receptor dual agonist survodutide for obesity: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-finding phase 2 trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2024, 12, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naeem, M.; Imran, L.; Banatwala, U.E.S.S. Unleashing the power of retatrutide: A possible triumph over obesity and overweight: A correspondence. Health Sci. Rep. 2024, 7, e1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asrih, M.; Wei, S.; Nguyen, T.T.; Yi, H.S.; Ryu, D.; Gariani, K. Overview of growth differentiation factor 15 in metabolic syndrome. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2023, 27, 1157–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stavas, J.; Silva, A.L.; Wooldridge, T.D.; Aqeel, A.; Saad, T.; Prakash, R.; Bakris, G. Rilparencel (Renal autologous cell therapy-REACT®) for chronic kidney disease and type 1 and type 2 diabetes: Phase 2 trial design evaluating bilateral kidney dosing and redosing triggers. Am. J. Nephrol. 2024, 55, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Renal Association. 61st ERA Congress, Congress Review. 2024. Available online: https://www.era-online.org/wp-content/uploads/2024/06/ERA24-Congress-Review.pdf (accessed on 28 June 2024).
- Bejar, N.; Tat, T.T.; Kiss, D.L. RNA therapeutics: The next generation of drugs for cardiovascular diseases. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2022, 24, 307–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Measure | Categorical Cut Points |
|---|---|
| Elevated waist circumference * | Population- and country-specific definitions |
| Elevated triglycerides (drug treatment for elevated triglycerides is an alternate indicator **) | ≥150 mg/dL (1.7 mmol/L) |
| Reduced HDL-C (drug treatment for reduced HDL-C is an alternate indicator **) | <40 mg/dL (1.0 mmol/L) in males; <50 mg/dL (1.3 mmol/L) in females |
| Elevated blood pressure (antihypertensive drug treatment in a patient with a history of hypertension is an alternate indicator) | Systolic ≥ 130 and/or diastolic ≥ 85 mm Hg |
| Elevated fasting glucose *** (drug treatment of elevated glucose is an alternate indicator) | ≥100 mg/dL |
| N | Investigational Drug | Mechanism of Action | Indication | Main Site Location | Phase | NCT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 6-bromotryptophan (6-BT) | Endogenous plasma microbiome-derived tryptophan metabolite | Metabolic Syndrome | USA and/or Europe | Phase 1 Phase 2 | NCT05971524 |
| 2 | AD-209 | N/A | Essential Hypertension | South Korea | Phase 2 | NCT05631990 |
| 3 | AD-218 | N/A | Dyslipidemia | South Korea | Phase 3 | NCT05631990 |
| 4 | AD-221 and AD-221A | N/A | Primary Hypercholesterolemia | China | Phase 3 | NCT05131997 |
| 5 | AD-223 | N/A | Essential Hypertension | South Korea | Phase 3 | NCT06052748 |
| 6 | ALN-KHK | RNAi targeting ketohexokinase | Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus with Obesity | USA and/or Europe | Phase 1 Phase 2 | NCT05761301 |
| 7 | ALT-801 (SP-1373) | Dual GCGR and GLP-1 receptor agonist | Obesity | USA and/or Europe | Phase 2 | NCT05295875 |
| 8 | AP-325 | Binds and modulates the GABAA receptor (an ionotropic receptor and ligand-gated ion channel) | Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus | USA and/or Europe | Phase 2 | NCT05160272 |
| 9 | APHD-012 | Distal jejunal-release dextrose | Obesity | USA and/or Europe | Phase 2 | NCT05385978 |
| 10 | ATB-1011 and ATB-1012 | N/A | Essential Hypertension and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus | China | Phase 3 | NCT05573477 |
| 11 | AZD0780 | Oral PCSK9 Inhibitor | Dyslipidemia | USA and/or Europe | Phase 2 | NCT06173570 |
| 12 | AZD8233 | ASO targeting PCSK9 | Hyperlipidaemia | USA and/or Europe | Phase 2 | NCT04964557, NCT06173570 |
| 13 | AZD9550 | Dual GCGR and GLP-1 receptor agonist | Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus with Overweight or Obesity | USA and/or Europe | Phase 1 Phase 2 | NCT06151964 |
| 14 | Baxdrostat (CIN-107) | Aldosterone synthase inhibitors | Uncontrolled Hypertension and Resistant Hypertension; Uncontrolled Hypertension and Chronic Kidney Disease | USA and/or Europe | Phase 2 Phase 3 | NCT06344104, NCT05432167 |
| 15 | BC Lispro (THDB0206) | Insulin | Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus | China | Phase 3 | NCT05834868 |
| 16 | Berlim 25/2 | N/A | Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Dyslipidemia | Brazil | Phase 3 | NCT04602754 |
| 17 | Bimagrumab | mAb inhibitor of ActRII | Overweight or Obesity | USA and/or Europe | Phase 2 | NCT05616013 |
| 18 | BMF-219 | Oral irreversible covalent inhibitor of menin | Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus | USA and/or Europe | Phase 1 Phase 2 | NCT05731544 |
| 19 | BR1017A and BR1017B | N/A | Essential Hypertension and Primary Hypercholesterolemia | South Korea | Phase 3 | NCT05930028 |
| 20 | BR1018B and BR1018C | N/A | Essential Hypertension and Primary Hypercholesterolemia | South Korea | Phase 3 | NCT06165250 |
| 21 | Cagrilintide | Amylin receptor agonist | Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus; Overweight or Obesity | USA and/or Europe | Phase 2 Phase 3 | NCT05813925, NCT04982575 |
| 22 | CKD-391 and CKD-331 | N/A | Primary Hypercholesterolemia | China, South Korea | Phase 3 | NCT05657574 |
| 23 | CPL207280 | GPR40 (also known as FFA receptor 1) agonist | Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus | USA and/or Europe | Phase 2 | NCT05248776 |
| 24 | D064 and D702 | N/A | Essential Hypertension | South Korea | Phase 3 | NCT06121518 |
| 25 | D150, D745 and D759 | N/A | Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus | South Korea | Phase 3 | NCT05566028 |
| 26 | Dapiglutide | Dual GLP-1R/GLP-2R agonist | Obesity | USA and/or Europe | Phase 2 | NCT05788601 |
| 27 | Denatonium Acetate (ARD-101) | Oral potential TAS2R agonist | Obesity | USA and/or Europe | Phase 2 | NCT05121441 |
| 28 | DW1125 and DW1125A | N/A | Primary Hypercholesterolemia or Dyslipidemia | South Korea | Phase 3 | NCT05970679 |
| 29 | DWP16001 | SGLT2 inhibitor | Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus | China, South Korea | Phase 3 | NCT05376930, NCT05505994 |
| 30 | Ecnoglutide (XW003) | Long-acting cAMP Signaling Biased GLP-1 Analog | Obesity; Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus | USA and/or Europe, China | Phase 2 Phase 3 | NCT05111912, NCT05813795, NCT05680155, NCT05680129 |
| 31 | Efsitora Alfa (BIF, LY3209590, or insulin efsitora alfa) | Basal Insulin Fc | Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus | USA and/or Europe | Phase 3 | NCT05462756 |
| 32 | GLY-200 | Mucin-complexing polymer | Obesity; Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus | USA and/or Europe | Phase 2 | NCT06259981, NCT05478525 |
| 33 | GSBR-1290 | Oral GLP-1 receptor agonist | Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus, and Overweight or Obesity | USA and/or Europe | Phase 1 Phase 2 | NCT05762471 |
| 34 | GZR18 | GLP-1 receptor agonist | Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus; Overweight or Obesity | China | Phase 1 Phase 2 | NCT06256523, NCT06256536, NCT06256562 |
| 35 | GZR4 | INSR agonist | Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus | China | Phase 2 | NCT06202079 |
| 36 | HCP1803 | N/A | Essential Hypertension | South Korea | Phase 3 | NCT05362110 |
| 37 | HCP1904-3 | N/A | Essential Hypertension | South Korea | Phase 3 | NCT05199129 |
| 38 | HCP2102 | N/A | Essential Hypertension | South Korea | Phase 3 | NCT05450601 |
| 39 | HD-6277 | Selective GPR40 agonist | Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus | South Korea | Phase 2 | NCT05666128 |
| 40 | HEC88473 | Dual FGF21 receptor and GLP-1 receptor agonist | Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus | China | Phase 2 | NCT06148649 |
| 41 | HRS9531 | Dual GIP and GLP-1 receptor agonist | Obesity; Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus | China | Phase 2 | NCT05881837, NCT05966272 |
| 42 | HS-20094 | Dual GIP and GLP-1 receptor agonist | Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus; Overweight or Obesity | China | Phase 2 | NCT06118008, NCT06118021 |
| 43 | HSG4112 | Analog of glabridin | Overweight or Obesity | South Korea | Phase 2 | NCT05197556 |
| 44 | iGlarLixi vs. IDegAsp | Insulins | Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus | China | Phase 3 | NCT05413369 |
| 45 | INS068 | Long-acting insulin analog | Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus | South Korea | Phase 3 | NCT05702073, NCT05699408 |
| 46 | Insulin Efsitora Alfa (LY3209590) | Basal Insulin Fc (BIF) | Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus | USA and/or Europe | Phase 3 | NCT05662332, NCT05275400 |
| 47 | INV-202 | CB1R inverse agonist | Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome; Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus | USA and/or Europe | Phase 2 | NCT05891834, NCT05514548 |
| 48 | ION904 (IONIS-AGT-LRx) | Hepatocyte-directed ASO targeting AGT mRNA | Uncontrolled Hypertension | USA and/or Europe | Phase 2 | NCT05314439 |
| 49 | JS002 | Humanized anti-PCSK9 mAb | Hyperlipidaemia | China | Phase 3 | NCT05532800 |
| 50 | JW0101+C2101 | Livalo (pitavastatin) | Dyslipidemia and Hypertension | South Korea | Phase 3 | NCT05331014 |
| 51 | JW0201 | N/A | Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus | South Korea | Phase 3 | NCT05814393 |
| 52 | Lepodisiran (LY3819469) | siRNA (binds to the hepatic asialoglycoprotein receptor) targeting Lp(a) | Elevated Lipoprotein(a) | USA and/or Europe | Phase 2 Phase 3 | NCT05565742, NCT06292013 |
| 53 | Lerodalcibep (LIB003) | PCSK9 Inhibitor | Hyperlipidaemia and High risk Cardiovascular Disease (CVD) | USA and/or Europe | Phase 3 | NCT05004675, NCT05234775 |
| 54 | Lorundrostat (MLS-101) | Aldosterone synthase inhibitor | Resistant Hypertension; Uncontrolled Hypertension | USA and/or Europe | Phase 2 Phase 3 | NCT06153693, NCT05968430, NCT05001945 |
| 55 | Eloralintide (LY3841136) | Amylin receptor agonist | Overweight or Obesity | USA and/or Europe | Phase 2 | NCT06230523 |
| 56 | MAR001 | Maresin 1 (MaR1) specialised pro-resolving lipid mediator | Metabolic dysfunction at screening (triglyceride levels > 2.8 mmol/L) | USA and/or Europe | Phase 1 Phase 2 | NCT05896254 |
| 57 | Maridebart cafraglutide (AMG 133) | Dual GIP and GLP-1 receptor agonist | Overweight or Obesity With or Without Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus | USA and/or Europe | Phase 2 | NCT05669599 |
| 58 | Mazdutide (IBI362, LY3305677) | Dual GCGR and GLP-1 receptor agonist | Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus with Obesity; Overweight or Obesity | USA and/or Europe, China | Phase 2 Phase 3 | NCT06184568, NCT06143956, NCT04904913 |
| 59 | MBL949 | GDF15 agonist (agonist at the GFRAL/RET receptor) | Obesity with or without Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus | USA and/or Europe | Phase 2 | NCT05199090 |
| 60 | MK-0616 | Oral PCSK9 inhibitor | Hyperlipidaemia | USA and/or Europe | Phase 3 | NCT05952856 |
| 61 | Muvalaplin (LY3473329) | Orally active inhibitor of Lp(a) | Elevated Lipoprotein(a) at High Risk for Cardiovascular Events | USA and/or Europe | Phase 2 | NCT05563246 |
| 62 | NNC0165-1875 | NPY2R or Y2R agonist | Obesity | USA and/or Europe | Phase 2 | NCT04969939 |
| 63 | NNC0480-0389 | N/A | Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus | USA and/or Europe | Phase 2 | NCT05144984 |
| 64 | NNC0519-0130 | Dual GIP and GLP-1 receptor agonist | Overweight or Obesity, Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus | USA and/or Europe | Phase 2 | NCT06326060, NCT06326047 |
| 65 | NST-1024 (SEFA-1024) | CETP inhibitor | Hypertriglyceridemia | USA and/or Europe | Phase 2 | NCT05889156 |
| 66 | Obicetrapib (AMG-899, DEZ-001, TA-8995) | CETP inhibitor | Hyperlipidaemia; Heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia (HeFH) and/or atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) or multiple ASCVD risk factors | USA and/or Europe | Phase 2 Phase 3 | NCT05421078, NCT06005597, NCT05266586 |
| 67 | Ocedurenone(KBP-5074) | Third-generation non-steroidal MRA | Uncontrolled Hypertension and Moderate or Severe Chronic Kidney Disease | USA and/or Europe | Phase 3 | NCT04968184 |
| 68 | Olezarsen (ISIS 678354, AKCEA-APOCIII-LRx) | ASO targeting mRNA for APOC3 | Hypertriglyceridemia and Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease, or With Severe Hypertriglyceridemia; Severe Hypertriglyceridemia | USA and/or Europe | Phase 3 | NCT05552326, NCT05079919, NCT05610280 |
| 69 | Olpasiran (AMG-890, ARO-LPA) | siRNA (binds to the hepatic asialoglycoprotein receptor) targeting Lp(a) | Atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) and elevated Lipoprotein(a). | USA and/or Europe | Phase 3 | NCT05581303 |
| 70 | Orforglipron (LY3502970) | Non-peptide GLP-1 receptor agonist | Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus with Overweight or Obesity; Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus; Overweight or Obesity and related comorbidities, Overweight or Obesity | USA and/or Europe | Phase 3 | NCT05803421, NCT06010004, NCT05869903, NCT05872620, NCT05051579, NCT05048719 |
| 71 | PB-201 | Glucokinase activator (partial, pancreas- and liver-dual activator of glucokinase) | Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus | China | Phase 3 | NCT05102149 |
| 72 | Pegozafermin (BIO89-100) | FGF21 analog | Severe Hypertriglyceridemia | USA and/or Europe | Phase 3 | NCT05852431 |
| 73 | Pelacarsen (IONIS-APO(a)-LRx, AKCEA-APO(a)-LRx, or TQJ230) | Apo(a) inhibitor, hepatocyte-directed ASO targeting mRNA transcribed from the LPA gene | Hyperlipoproteinemia(a) and Established Cardiovascular Disease | USA and/or Europe | Phase 3 | NCT05305664, NCT05900141 |
| 74 | Pemafibrate (K-877, LY3473329) | Selective peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR)-α modulator (SPPARM) | Hypercholesterolemia and statin intolerance; Elevated Lipoprotein(a) | USA and/or Europe | Phase 2 Phase 3 | NCT05923281, NCT05563246 |
| 75 | Plozasiran (ARO-APOC3) | siRNA targeting mRNA for APOC3 | Hypertriglyceridemia; Severe Hypertriglyceridemia; Dyslipidemia | USA and/or Europe | Phase 2 Phase 3 | NCT06347133, NCT06347016, NCT05413135, NCT04720534, NCT04998201 |
| 76 | RAY1225 | Dual GIP and GLP-1 receptor agonist | Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus; Obesity | China | Phase 2 | NCT06254274, NCT06254261 |
| 77 | Recaticimab (SHR-1209) | mAb against PCSK9 | Hyperlipidaemia | China | Phase 3 | NCT04885218 |
| 78 | Rilparencel (Renal Autologous Cell Therapy-REACT®) | Renal Autologous Cell Therapy | Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Chronic Kidney Disease | USA and/or Europe | Phase 3 | NCT05099770 |
| 79 | Retatrutide (LY3437943) | Triple GIP, GLP-1 and GCGR receptor agonist | Overweight or Obesity and Chronic Kidney Disease With or Without Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus; Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus; Overweight or Obesity; Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus with Overweight or Obesity; Overweight or Obesity with Cardiovascular Disease | USA and/or Europe | Phase 2 Phase 3 | NCT05936151, NCT06297603, NCT05929066, NCT05929079, NCT05882045, NCT04881760 |
| 80 | RGT-075 | Oral GLP-1 receptor agonist | Overweight or Obesity | USA and/or Europe | Phase 2 | NCT06277934 |
| 81 | Solbinsiran (LY3561774) | siRNA that targets ANGPTL3 | Dyslipidemia | USA and/or Europe | Phase 2 | NCT05256654 |
| 82 | SPC1001 | N/A | Essential Hypertension | South Korea | Phase 2 | NCT06212648 |
| 83 | SPH3127 | Renin inhibitor (direct) | Essential Hypertension | China | Phase 3 | NCT05359068 |
| 84 | Supaglutide | GLP-1 receptor agonist | Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus | China | Phase 2 Phase 3 | NCT04994288, NCT04998032 |
| 85 | Survodutide (BI 456906) | Dual GCGR and GLP-1 receptor agonist | Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus with Overweight or Obesity; Obesity; Overweight or Obesity | USA and/or Europe | Phase 3 | NCT06066528, NCT06176365, NCT06066515, NCT06077864 |
| 86 | TLC-3595 (S-723595) | Allosteric inhibitor of acetyl-CoA carboxylase 2 (ACC2) | Insulin Resistance | USA and/or Europe | Phase 2 | NCT05665751 |
| 87 | Trevogrumab (REGN1033) and Garetosmab (REGN2477) | Trevogrumab is GFD8 fully humanized mAb, Garetosmab (REGN2477) Act-A mAb | Obesity | USA and/or Europe | Phase 2 | NCT06299098 |
| 88 | Vericiguat | Stimulator of soluble guanylate cyclase (sGC) | Metabolic Syndrome and Coronary Vascular Dysfunction | USA and/or Europe | Phase 2 | NCT05711719 |
| 89 | VK2735 | Dual GIP and GLP-1 receptor agonist | Overweight or Obesity | USA and/or Europe | Phase 2 | NCT06068946 |
| 90 | XXB750 | mAb, NPR1 agonist | Resistant Hypertension | USA and/or Europe | Phase 2 | NCT05562934 |
| 91 | Yogliptin | DPP-4 inhibitor | Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus | China | Phase 3 | NCT05318326 |
| 92 | Zerlasiran (SLN360) | siRNA (binds to the hepatic asialoglycoprotein receptor) targeting Lp(a) | Elevated lipoprotein(a) at high risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease events | USA and/or Europe | Phase 2 | NCT05537571 |
| 93 | Zilebesiran (ALN-AGT) | siRNA targeting AGT mRNA | High cardiovascular risk and Uncontrolled Hypertension; Hypertension | USA and/or Europe | Phase 2 | NCT06272487, NCT04936035, NCT05103332 |
| 94 | Zodasiran (ARO-ANG3) | siRNA that targets ANGPTL3 | Dyslipidemia | USA and/or Europe | Phase 2 | NCT04832971 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Javor, E.; Šarčević, D.; Rešić, A. Metabolic Syndrome and Pharmacological Interventions in Clinical Development. Diabetology 2024, 5, 300-320. https://doi.org/10.3390/diabetology5030023
Javor E, Šarčević D, Rešić A. Metabolic Syndrome and Pharmacological Interventions in Clinical Development. Diabetology. 2024; 5(3):300-320. https://doi.org/10.3390/diabetology5030023
Chicago/Turabian StyleJavor, Eugen, David Šarčević, and Arnes Rešić. 2024. "Metabolic Syndrome and Pharmacological Interventions in Clinical Development" Diabetology 5, no. 3: 300-320. https://doi.org/10.3390/diabetology5030023
APA StyleJavor, E., Šarčević, D., & Rešić, A. (2024). Metabolic Syndrome and Pharmacological Interventions in Clinical Development. Diabetology, 5(3), 300-320. https://doi.org/10.3390/diabetology5030023






