Abstract
Background: Prior to year 2000, the majority of pancreas transplants (PTx) were performed as simultaneous pancreas-kidney transplants (SPKTs) in Caucasian adults with end stage renal failure secondary to type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) who were middle-aged. In the new millennium, improving outcomes have led to expanded recipient selection that includes patients with a type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) phenotype, which excessively affects minority populations. Methods: Using PubMed® to identify appropriate citations, we performed a literature review of PTx in minorities and in patients with a T2DM phenotype. Results: Mid-term outcomes with SPKT in patients with uremia and circulating C-peptide levels (T2DMphenotype) are comparable to those patients with T1DM although there may exist a selection bias in the former group. Excellent outcomes with SPKT suggests that the pathophysiology of T2DM is heterogeneous with elements consisting of both insulin deficiency and resistance related to beta-cell failure. As a result, increasing endogenous insulin (Cp) production following PTx may lead to freedom checking blood sugars or taking insulin, better metabolic counter-regulation, and improvements in quality of life and life expectancy compared to other available treatment options. Experience with solitary PTx for T2DM or in minorities is limited but largely mirrors the trends reported in SPKT. Conclusions: PTx is a viable treatment option in patients with pancreas endocrine failure who are selected appropriately regardless of diabetes type or recipient race. This review will summarize data that unconventional patient populations with insulin-requiring diabetes may gain value from PTx with an emphasis on contemporary experiences and appropriate selection in minorities in the new millennium.
1. Introduction: Scope of Diabetes Mellitus
Chronic glucose hyperlability and dysmetabolism because of deficiencies in insulin action, secretion, or both are characteristics of diabetes mellitus (DM). Historically, type 2 DM (T2DM) was categorized as primarily a disease of insulin action (“insulin resistance”) whereas type 1 DM (T1DM) was defined by insulin deficiency or absence. The phenotype of DM was also determined not only by the supposed pathophysiology but also by clinical manifestations and epidemiologic features [1]. The determinants of DM consist of a matrix of genetic, environmental, lifestyle, and cultural factors. DM is linked to diet, physical exercise, obesity, and disproportionately affects minority populations. The expanding prevalence of DM has become a global pandemic and poses a formidable healthcare challenge for virtually every country. In 2021, 537 million people were living with DM worldwide, which represented 10% of the global adult population [2]. It is estimated that 77% of the global DM population live in low or middle-income countries, and for those in high-income countries, many live in lower socio-economic groups.
Of the estimated 37.3 million patients with DM in the United States (US; 11.3% of the total population), approximately 28.7 million have an established diagnosis, 4.5 million require insulin, and an estimated 1.4 million incident cases occur annually in those aged 20 years or older [3,4]. Moreover, it is estimated that another 96 million US adults (38.0% of the total population) have prediabetes (because of elevated hemoglobin A1c [HbA1c] and fasting serum glucose levels). In 2017, indirect and direct costs attributed to DM care in the US were estimated at $327 billion [5]. In people of Hispanic origin and non-Hispanic Blacks, new cases of diabetes cases are higher compared to non-Hispanic Whites and non-Hispanic Asians [2,3,4]. In the US, the prevalence of DM was highest among Alaska Natives and Native American Indians (14.7%), then Hispanics (12.5%) and non-Hispanic Blacks (11.7%), and lower in Asians (9.2%) and Whites (7.5%). DM also disproportionately affects those with the lowest levels of education and income. It is estimated that 25% of individuals with DM have chronic kidney disease secondary to diabetes and this risk increases with age [4]. For example, the risk of diabetic kidney disease in patients ≥ 60 years of age is 5 times higher than those aged 20–39 years [6]. In 2017, 50,000 incident cases (44%) of kidney failure occurred in the US secondary to DM, making it the most common cause of end stage renal disease (ESRD) [6]. The proportion of candidates with DM on the kidney waiting list in the US is >40%. At present, >250,000 patients with DM and kidney failure are alive either with a functioning kidney transplant or on chronic dialysis [4,6]. The prevalence of ESRD is 3.7 times greater in African Americans (AA), 1.6 times greater in Hispanics, 1.4 times greater in Native Americans, and 1.5 times greater in Asians compared to non-Hispanic Whites in the US. [4,6] DM and kidney disease remain among the top ten causes of death in the US and contribute substantially to the number one cause of death in the US, which is heart disease.
2. Methods
Using PubMed® to identify appropriate citations, we performed a literature review of PTx in minorities and in patients with a T2DM phenotype. In addition, both authors have >30 years of experience in the field of PTx, are well-published in these areas, and relied upon their personal experience and literature accumulated over the past 3 decades to augment this endeavor. The purpose of this review is to summarize data that unconventional patient populations with insulin-requiring diabetes may gain value from PTx with an emphasis on contemporary experiences and appropriate selection in minorities in the new millennium.
3. Status of Pancreas Transplantation (PTx)
The first successful vascularized pancreas transplant (PTx) was performed in 1966. The goal of PTx is to provide complete islet cell replacement that responds to internal feedback controls and is therefore auto-regulating. A functioning PTx re-establishes both endogenous glucagon and insulin (C-peptide [Cp]) production, which releases the patient from the need to either administer exogenous insulin or check blood sugar levels [7]. However, removing the daily burden and stigma of DM comes at a price, namely the risks associated with a major abdominal surgical procedure and the need for chronic daily immunosuppression. In reviewing the International Pancreas Transplant Registry (IPTR), as of 2022, >65,000 PTxs were performed worldwide, including >36,000 in the US in the past 50+ years [8,9,10,11]. Most PTxs (>80–85%) are performed as simultaneous pancreas-kidney transplants (SPKTs) in patients with either kidney failure or advanced chronic kidney disease and insulin-requiring DM. In 2021, 818 SPKTs were performed in the US [8,9,10,11]. A discussion of PTx in minorities and the elderly is closely intertwined with T2DM and obesity, so we will begin with a review of PTx in patients with a T2DM phenotype.
4. Pancreas Transplantation in Patients with T2DM
Entering the new millennium, according to the IPTR, Caucasian patients received 90% of SPKTs and >95% of SPKT recipients were identified as having T1DM [12]. However, in the new millennium in the US, the annual proportion of SPKT recipients with a T2DM phenotype rose from 6% to 27% (Figure 1). Concurrently, the annual proportion of SPKTs performed in AA recipients tripled from 10% to nearly 30% (Figure 2) [8,9,10,11]. During this same period, the number of Hispanic and Asian SPKT recipients increased as well (Figure 3). For SPKT recipients with T1DM, 58% were Caucasian, 26% AA, 14% Hispanic, and 2% of Asian/other origin (Figure 4). For SPKT recipients with T2DM, 24% were Caucasian, 44% AA, 22% Hispanic, 8% Asian, and 2% other descent [8,9,10,11].
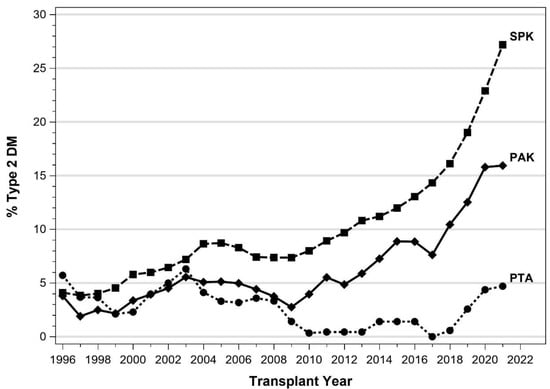
Figure 1.
Proportion of recipients identified as having T2DM by year according to PTx category for US cases as reported to the IPTR.
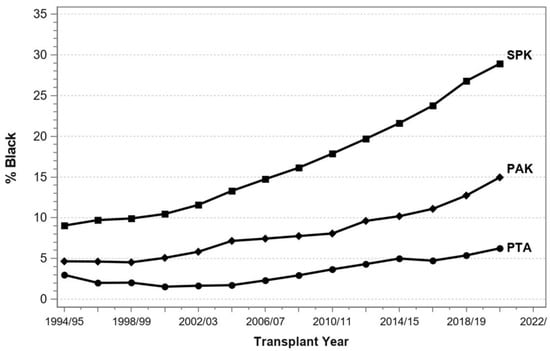
Figure 2.
Proportion of African American recipients by year according to PTx category for US cases as reported to the IPTR.
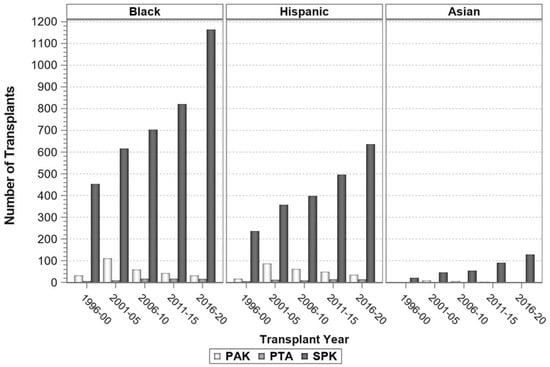
Figure 3.
Number of minority recipients by PTx category in 5-year increments for US cases as reported to the IPTR.
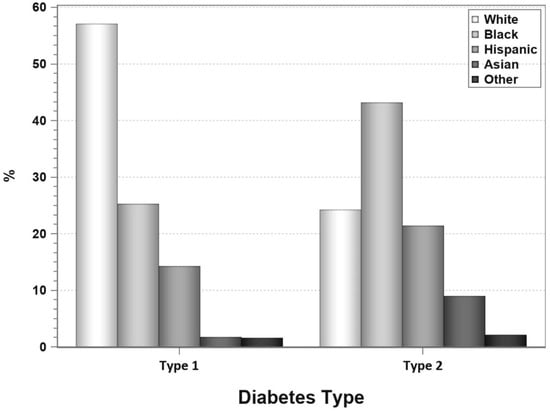
Figure 4.
Proportion of SPKT recipients by race according to diabetes type in the latest era (1 January 2017–31 December 2021) for US cases as reported to the IPTR.
Approximately 90–95% of cases of DM are related to T2DM, which is associated with the metabolic syndrome and characterized by both relative insulin deficiency and insulin resistance [1]. However, tremendous overlap in the clinical presentations of T2DM versus T1DM can occur. The epidemic of obesity has also changed the timing and presentation of DM. The development of bariatric surgery has provided remarkable insights regarding T2DM as a complication of obesity. Nevertheless, the role of SPKT in patients with ESRD and T2DM is less well defined compared to those patients with T1DM [13,14]. Because the primary pathophysiology of T2DM was thought to be exclusive to insulin resistance, it was not intuitive that PTx would be effective in this setting. However, initial reports of SPKT in patients with a T2DM phenotype and detectable pretransplant Cp levels clearly showed that outcomes were quite similar to those achieved in patients with T1DM as characterized by improved quality and quantity of life, effective counter-regulation of glucose levels, and absence of the need for exogenous insulin therapy [13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25]. The success of SPKT in patients irrespective of diabetes “type” provided evidence that T2DM exhibited a heterogeneous pathophysiology comprised of elements of both insulin deficiency and deficiency due to beta-cell failure or dysfunction. Therefore, it is now believed that T2DM and T1DM may represent a spectrum of disorders that develop in patients with a genetic predisposition to selective beta-cell deficiency [26]. The influence of behavioral and environmental factors on a predisposed genetic milieu may actually determine the severity of onset, timing, and manifestations of DM.
In patients who underwent kidney transplantation from 2000–2016, according to a Scientific Registry of Transplant Recipients (SRTR) analysis, only 641/35,849 (1.8%) with T2DM underwent SPKT [27]. Clearly, the proportion of SPKTs performed in patients with T2DM and ESRD should be higher if the procedure was generally recognized and accepted as a preferred treatment in selected patients. The etiology for SPKT underutilization (and under-appreciation) in T2DM is multifactorial and may be due to disparities in race, access, age, body size, co-morbidities, type of insurances, support networks, and perceived lower outcomes in SPKT recipients with T2DM compared to those with T1DM. Prior studies of SPKT in T2DM (defined by detectable pretransplant Cp levels) compared to T1DM have been limited to either larger registry or smaller single center reports without a suitable control group [8,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57,58]. In the US, for every 1000 patients with ESRD and T1DM, only three will receive an SPKT in their lifetime. Because of the overlapping clinical presentations between T1DM and T2DM, detectable Cp has become less of a factor in establishing the “type” of diabetes [59,60,61].
Moreover, the administration of immunosuppressive medications following transplantation may result in “new onset” or “post-transplant” DM, which may be a variant of T2DM [62,63,64]. It is important to note that immunosuppressive regimens and dosing are similar following SPKT regardless of diabetes “type”. Although SPKT in T2DM may be associated with a selection bias, outcomes are equivalent to patients with T1DM who undergo SPKT [8,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57,58]. In the US, for every 1000 patients with ESRD and T2DM, only one will receive an SPKT.
5. SPKT Outcomes in T2DM
5.1. IPTR Data
In the mid-1990s, the IPTR began reporting on outcomes in patients identified as having either T1DM or T2DM [12]. In these annual reports, SPKT recipients with T2DM rose from 4% prior to 2002 to 8% from 2002–2011 to 27% in 2021. At present, T2DM accounts for 16% of sequential pancreas after kidney (PAK) transplant cases and 4–5% of pancreas transplant alone (PTA) cases (Figure 1) [8,9,10,11,12,65,66,67]. The percentage of PTA recipients with T2DM has not changed substantially in the past 20 years whereas the proportion of PAK recipients with T2DM has increased from 4% to 16% [8,9,10,11,12]. Shared characteristics of patients with T2DM (versus T1DM) include older age at PTx and at the time of diagnosis of DM, absence of autoantibodies and absence of need for insulin at time of initial DM diagnosis, higher body mass index (BMI), more frequently minority (not Caucasian) and male, and shorter duration of insulin therapy. In the most recent IPTR era, survival outcomes in SPKT are slightly inferior in patients with T2DM compared to those categorized as T1DM (Figure 5, Figure 6 and Figure 7) [8,9,10,11]. This is the first time that IPTR data has shown any differences in SPKT outcomes according to type of diabetes.
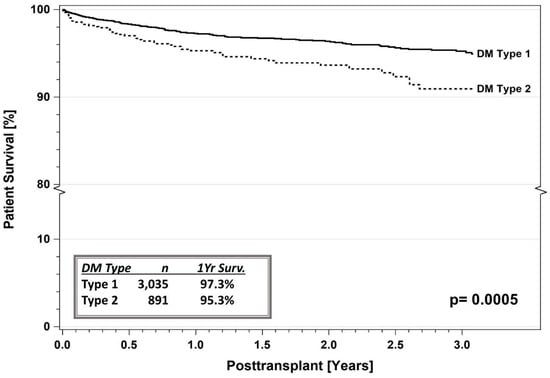
Figure 5.
SPKT patient survival according to diabetes type in the latest era (1 January 2017–31 December 2021) for US cases as reported to the IPTR. Surv. = Survival.
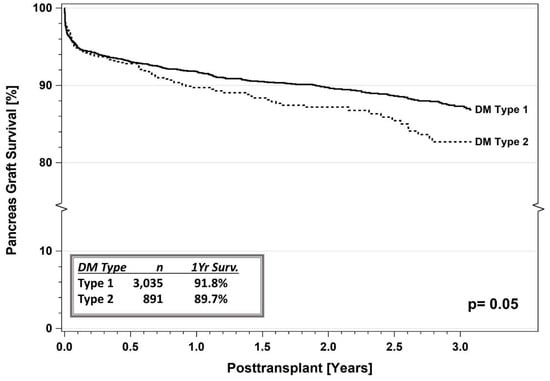
Figure 6.
SPKT pancreas graft survival according to diabetes type in the latest era (1 January 2017–31 December 2021) for US cases as reported to the IPTR. Surv. = Survival.
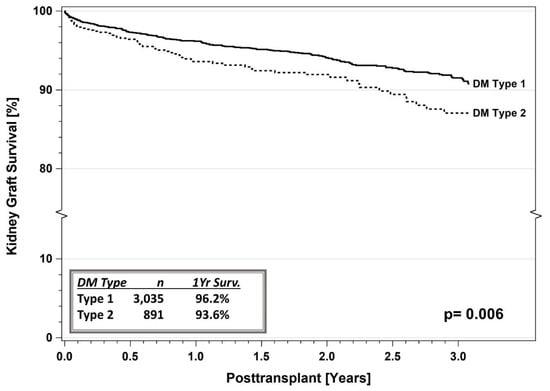
Figure 7.
SPKT kidney graft survival according to diabetes type in the latest era (1 January 2017–31 December 2021) for US cases as reported to the IPTR. Surv. = Survival.
In 2017, Gruessner et al., reported outcomes of PTx in patients with T2DM in three eras: era 1, 1995–2001; era 2, 2002–2008; and era 3, 2009–2015 [46]. Of the 1512 cases analyzed, 1322 were primary SPKT and the remaining 190 were PTA or PAK recipients. When comparing the 3 eras, an increasing number of SPKTs were performed in patients with T2DM relative to those with T1DM. There was an improvement in survival outcomes in each successive era along with a reduction in early pancreas graft losses. Risk factors for patient death were either a failed kidney and/or pancreas graft, recipient age > 43 years, and being AA. Death with a functioning graft was the major cause for either pancreas or kidney graft failure even though mortality decreased in each successive era. Notably, DM recurrence was rare except in the setting of excessive posttransplant weight gain (Figure 8) [46]. However, in 70% of male and 75% of female recipients, substantial weight gain did occur. Multivariate risk analysis for pancreas graft loss in the first 36 months posttransplant demonstrated that recipient BMI > 28 kg/m2 (compared to those < 25 kg/m2) and donor age > 30 years were the most predictive factors. However, there was no difference in pancreas graft failure for overweight or obese recipients (BMI > 28 kg/m2) compared to recipients with a normal BMI (25–28 kg/m2). This finding was corroborated by Al-Qaoud et al., in a study of SPKT in non-obese recipients (BMI < 30 kg/m2, n = 500) compared to obese recipients (BMI > 30 kg/m2, n = 88) from 2004 to 2014 using the United Network for Organ Sharing (UNOS) database [49,68]. In this study, 5-year pancreas survival rates were 76.3% in the low BMI compared to 74.2% in the high BMI cohorts and the majority of high BMI recipients clustered within a BMI range of 30–33 kg/m2.
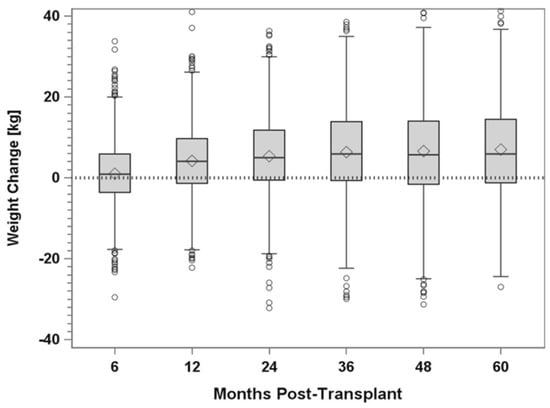
Figure 8.
Weight change over time in PTx recipients identified as having T2DM for US cases as reported to the IPTR.
In a more recent era (January 2017 through December 2021), current 1- and 3-year patient survival rates are 97.3% versus 95.3% and 94.8% versus 90.5%, respectively, for SPKT recipients with T1DM versus T2DM (Figure 5, p = 0.0005) [8,9,10,11]. Corresponding 1- and 3-year pancreas graft survival rates (91.8% versus 89.7% and 87.4% versus 83.2%, p = 0.05, Figure 6) and kidney graft survival rates (96.2% versus 93.6% and 90.5% versus 87.0%, p = 0.006, Figure 7) are slightly inferior for SPKT recipients with T1DM versus T2DM, respectively. In the other PTx categories, the number of recipients with T2DM is too small for comparative analyses. When comparing successive eras, patient and graft survival rates continue to increase and early technical graft failures and immunologic graft losses continue to decrease regardless of DM type. Posttransplant weight gain has been identified as being problematic, particularly in SPKT recipients with a T2DM phenotype (Figure 8) [46,54]. In addition to defining diabetes “type” established by Cp levels, the IPTR has also reported survival outcomes based on age of onset of DM (according to decade), which has demonstrated similar trends. Complete autonomy from administering exogenous insulin is the most common definition of pancreas graft survival in studies to date.
5.2. Single Center Studies
There currently does not exist any randomized studies comparing SPKT to alternative treatment options in patients with either T2DM or T1DM. However, comparable functional and survival outcomes have been documented in SPKT recipients with either DM type in multiple retrospective cohort studies [18,19,23,24,25,28,29,30,36,37,38,43,48,50,51,52,54,55,56,57]. Early reports of successful SPKT from 1996 to 2004 included cases identified as “maturity-onset” DM of the young, “lean” or adult onset DM, and “unrecognized” non-insulin dependent DM [15,16,17,20,21,22]. In each of these studies, outcomes and the clinical course mirrored those observed in concurrent SPKT recipients with T1DM.
However, a series of landmark publications from the Washington Hospital Center chronicles the true genesis of the controversial application of SPKT to patients with T2DM [18,19,23,30]. In 2013, Light et al., reported their 20-year longitudinal experience with 173 SPKT recipients with either T1DM (n = 115) or T2DM (n = 58) defined by random pretransplant Cp levels either <0.8 ng/mL or ≥0.8 ng/mL, respectively [30]. Pretransplant Cp levels were not a consideration with respect to recipient selection. The group with higher Cp levels was older at the time of SPKT (mean age 42.8 versus 38.5 years) and older at the time of DM diagnosis (mean age 24.2 versus 15.4 years, both p < 0.0001). The T2DM group was also characterized as being mostly AA (68.9% versus 41.7%, p = 0.007), had a higher BMI pre- and posttransplant (both p < 0.0001), and had shorter duration of insulin use (mean 19.2 versus 22.6 years, p = 0.01) compared to the T1DM group. Death-censored graft survival was slightly higher (p = 0.064) in the T2DM group whereas patient survival was superior (p = 0.019) in the T1DM group. Race of the donors or recipients did not affect survival outcomes. Moreover, nearly 40% of patients identified as having T2DM had Cp levels < 0.8 ng/mL whereas 17% of patients with T1DM based on clinical criteria actually had pretransplant Cp levels > 0.8 ng/mL. A number of conclusions were gained from this seminal study: (1) Patients identified as having either T2DM or T1DM can benefit equally from SPKT although stratification may overlap; (2) In patients who were not insulinopenic pretransplant, beta cell exhaustion did not occur posttransplant; (3) Excellent outcomes were observed in patients with a T2DM phenotype independent of pretransplant random Cp levels or race; and (4) Classifying DM and basing selection for SPKT on Cp levels is not useful in determining candidacy and of limited value.
The University of Minnesota, in 2005, studied 17 PTxs (7 SPKT, 4 PAK, 6 PTA) performed in patients with T2DM without using Cp levels including three patients who were not on insulin [24]. At 12-month follow-up, both pancreas and patient survival rates were 94%. Survival rates at 4+ years follow-up were 65% and 71%, respectively. This study is unique because it reported outcomes in not only SPKT but also following solitary PTx in T2DM as well as in patients who were not insulin-dependent at the time of transplant.
In 2008, Singh et al., published the initial Wake Forest experience in SPKT patients with (≥2.0 ng/mL, n = 7) versus without (<2.0 ng/mL, n = 67) detectable Cp levels at the time of SPKT [25]. A higher Cp threshold was chosen to better distinguish between T2DM and T1DM because it had been proposed that a fasting Cp level > 3.0 ng/mL is a contraindication to PTx and that T2DM patients with baseline Cp levels > 1.8 ng/mL may not actually require insulin therapy [60,69]. In a subsequent study from the same group published in 2015, data were presented on 162 SPKTs including 30 (18.5%) with Cp levels ≥ 2.0 ng/mL pretransplant (Cp positive group, mean Cp level 5.7 ng/mL, range 2.1–12.4) and 132 in patients with absent or low Cp levels (<2.0 ng/mL, Cp “negative”) [43]. Cp positive patients had a later age at diagnosis of DM (mean age 30 versus 15 years) and shorter period of pretransplant insulin need (mean 15 versus 28 years), higher proportion that were age ≥ 50 years (37% versus 23 and had a BMI ≥ 28 kg/m2 (40% versus 14%) at the time of SPKT, and had more AAs proportionately (43% versus 17%, all p ≤ 0.05) compared to Cp negative patients. Patient, kidney and pancreas graft (insulin-free) rates were comparable in Cp positive and negative patients, as were death-censored kidney and pancreas graft survival rates after a mean follow-up of 5.6 years. In AA patients, survival rates in Cp positive (n = 14) and Cp negative (n = 22) patients were similar as were outcomes when comparing Cp positive (n = 14) AA patients compared to Cp positive non-AA (n = 16) patients. There were no differences in outcomes in Cp positive patients undergoing SPKT with either systemic- or portal-enteric drainage or in patients with a BMI ≥ 28 or <28 kg/m2. With medium-term survival outcomes comparable between groups, this study determined that elevated pretransplant Cp levels are helpful in characterizing a T2DM phenotype but are not helpful in predicting outcomes following SPKT.
In 2010, Chakkera et al., compared outcomes after SPKT in 70 patients with T1DM versus 10 with T2DM [28]. A composite of the following clinical factors was used to define T2DM: History of being treated with oral anti-diabetic medications prior to needing insulin; presence of detectable Cp levels; lack of detectable anti-GAD65 antibody; and absence of ketoacidosis history. A daily insulin requirement > 1 unit/kg/day or a BMI > 30 kg/m2 were exclusions for SPKT. With a median follow-up of 16 months, the two groups had comparable outcomes according to a Cox regression survival analysis. Importantly, some patients with T2DM had low Cp levels whereas some patients with T1DM had higher detectable Cp levels. Using a Cp level of ≥ or <0.8 ng/mL as a target for determining type of DM would have misclassified 8% of patients with T1DM and 30% of patients with T2DM.
A 9-year single center cohort study was reported by Margreiter et al., in 2013 comparing outcomes in 32 T2DM patients undergoing deceased donor kidney transplant alone versus SPKT in 195 T1DM and 21 T2DM patients [36]. Survival outcomes were lowest in T2DM patients undergoing kidney transplant alone, intermediate in T2DM patients with SPKT, and highest after SPKT in T1DM patients. However, there were no differences in outcomes amongst the two SPKT groups in the multivariable analysis mode. The authors concluded that T2DM candidates who are <55 years of age and have a low coronary risk should be considered for SPKT.
At the International Pancreas and Islet Transplant Association meeting in 2013, the California Pacific Medical Center reported their SPKT experience in 164 T1DM patients versus 55 T2DM patients (defined as pretransplant Cp level > 2.0 ng/mL) spanning 11 years [37,38]. Five-year pancreas graft survival rates were 86% and 78% in patients with T1DM versus T2DM, respectively. In addition, having a BMI either > or <30 kg/m2 did not influence outcomes. In 2017, Shin and colleagues compared long-term metabolic outcomes following PTx in 151 patients with T1DM and 42 patients with T2DM (classification based on older age of onset of DM, no history of diabetic ketoacidosis, not on insulin at time of DM diagnosis, and body weight > 115% of ideal body weight) and did not identify any significant differences in survival or functional outcomes in a Korean population at 5 years [48].
In 2018, Gondolesi et al., reported their single center retrospective experience at a Latin-American center (Argentina) spanning an 8-year period from 2008–2016 with 45 SPKTs and 1 PTA, including 11 in patients with T2DM based on older age (>age 30 years) of onset of DM, higher body weight, Cp > 1.0 in 8 cases (mean 2.1 ng/mL), and absence of autoimmune markers [50]. At 5-year follow-up, there were no significant differences in survival or functional outcomes and 79% of patients were insulin-free. In 2019, Rohan et al., reported their single center retrospective experience from the Medical University of South Carolina in 112 patients (91 SPKT, 19 PAK, 2 PTA) with pre-operative Cp testing, including 63 with no measurable Cp and 49 with detectable Cp levels (T2DM group, mean Cp level 1.57 ng/mL) [51]. Patients in the T2DM were more likely to be male, AA, had a previous transplant, and had a shorter duration of DM. With follow-up out to 5 years, no differences in survival, metabolic, or functional outcomes were noted although patients in the T2DM group tended to have higher measurable Cp levels posttransplant as well as having a trend toward more pancreas rejection and polyomavirus nephropathy compared to the T1DM group. No differences in weight gain or other complications were identified, and the authors concluded that the two groups had similar posttransplant courses. Furthermore, in 2019, the Georgetown group reported their experience with PTx in 38 patients with T1DM (27 SPKT, 7 PAK, 4 PTA) compared to 11 with T2DM (9 SPK, 2 PAK) [52]. Patients were classified at T1DM or T2DM based on pretransplant Cp levels > 2.0 ng/mL and other clinical factors including estimated age at onset of DM, BMI, presence of ketoacidosis, and timing of initiation of insulin therapy. Patients in the T2DM cohort were older, had a shorter duration and later age at diagnosis of DM, and had higher pretransplant Cp levels (mean 4.1 ng/mL); race was not reported. With 2-year follow-up, there were no differences in survival or functional outcomes, complications, or resource utilization. However, the T1DM group experienced trends toward higher mortality and re-intervention rates, while the T2DM group had trends toward higher rates of pancreas rejection, short-term postoperative insulin requirement, graft failure, and increasing BMI. The authors concluded that DM classification based on Cp levels is neither accurate nor essential for patient selection in PTx and that distinguishing between insulin resistance and metabolic resistance is of the utmost importance.
In 2020, Torabi et al., performed a retrospective, single center analysis of 25 patients (21 SPKT, 4 PAK) with T1DM compared to 12 with T2DM (11 SPKT, 1 PAK) based on a pretransplant Cp level either ≤ or >0.1 (mean 3.2 ng/mL) [54]. At follow-up out to 3 years, similar outcomes were reported although the T2DM cohort was noted to be particularly susceptible to rapid weight gain posttransplant that continued for the duration of the study. The authors concluded that these patients might benefit from aggressive nutritional management and dietary counselling. In addition, in 2020, Hau et al., from Leipzig, Germany, performed a single center retrospective study comparing 89 SPKT recipients with T1DM, 12 with T2DM (mean pretransplant Cp level 3.2), and 26 patients with T2DM undergoing kidney transplantation alone [55]. At 5 years follow-up, the two SPKT groups had superior (and similar) survival and functional outcomes compared to the patients undergoing kidney transplant alone. In a multivariate Cox regression analysis, significant risk factors for death in the SPKT cohorts were donor age > 45 years and preemptive transplantation. Risk factors for pancreas graft failure were recipient age > 45 years, recipient BMI > 25 kg/m2, donor BMI > 25 kg/m2, cold ischemia time > 12 h, and surgical complications.
In the most recent experience from Wake Forest, outcomes in SPKT recipients according to presence (Cp+, ≥2.0 ng/mL) or absence (Cp-) of pretransplant Cp were analyzed in a case–control fashion [70]. A total of 215 SPKTs were performed between August 2002 and May 2019; 41 patients were identified who were Cp+ pretransplant (mean level 5.4 ng/mL) and compared to 41 Cp- (level undetectable) case–controls matched for recipient age, gender, race, and date of transplant. This is one of the first studies that attempts to identify a matched control group. The two groups were well matched for a number of pertinent characteristics. After a mean follow-up of 7 years, 5-year patient survival (93% vs. 95%), kidney graft survival (73% vs. 85%), and pancreas graft survival (68% vs. 85%, p = 0.11) rates were slightly lower in Cp+ versus Cp- patients, respectively. Death-censored kidney (69% vs. 73%) and pancreas graft survival (59% vs. 81%, p = 0.07) rates were also slightly lower in Cp+ vs. Cp- patients, respectively. The Cp+ group had fewer deaths with functioning grafts (9.8% vs. 19.5% Cp-, p = NS) but more pancreas graft failures (9.8% vs. 0 Cp-, p = 0.12) due to either insulin resistance (in patients with normal Cp levels and excessive weight gain) or rejection (19.5% vs. 12% Cp-, p = NS). There were no differences in outcomes according to donor or recipient race or sex. Posttransplant weight gain > 5 kg occurred in 76% of Cp+ vs. 32% of Cp- patients (p = 0.0001). Mean posttransplant weight gain was 15 kg in Cp+ vs. 6.5 kg in Cp- patients (p < 0.001). In patients with functioning grafts, mean posttransplant Cp (4.9 vs. 2.6 ng/mL), HbA1c (5.5 vs. 5.2%) and serum creatinine (1.4 vs. 1.2 mg/dL) levels were slightly higher in Cp+ patients whereas mean estimated glomerular filtration rate levels (61 vs. 66 mL/min/1.73 m2) were slightly lower compared to Cp- patients. In this matched case–control study, survival and functional outcomes in Cp+ patients were somewhat inferior following SPKT, with posttransplant weight gain and graft failure due to insulin resistance or rejection accounting for the differences in medium-term outcomes.
In 2021, Pham and colleagues reported on the University of Wisconsin experience with SPKT in patients with T2DM [56]. A total of 39 SPKT recipients identified as having T2DM were compared to 284 concurrent SPKT recipients with T1DM. No differences in survival outcomes were noted between the two groups although patients with T2DM and a BMI > 28 kg/m2 and patients with T1DM and a total pretransplant daily insulin requirement > 75 units/day experienced a higher incidence of post-transplant DM. Furthermore, in 2021, Fu et al., reported superior metabolic outcomes and renal function in 71 patients with T2DM undergoing SPKT compared to 85 with T2DM undergoing kidney transplantation alone [57]. In 2022, Cao et al., performed a systematic review of the literature and meta-analysis that included 9 cohort studies with respect to SPKT in patients with T2DM. When comparing the treatment effect, survival estimates were comparable between patients with either T1DM or T2DM undergoing SPKT whereas SPKT conferred a survival advantage compared to kidney transplantation alone [58].
5.3. Registry Studies
In 2011, a UNOS database study analyzed a total of 6756 primary SPKTs performed between 2000 and 2007; 6141 patients were identified as having T1DM and 582 (8.6%) as having T2DM [31]. Compared to recipients with T1DM, recipients with T2DM were more often either AA or Hispanic, obese, and male. In patients with T2DM, the incidences of kidney primary nonfunction (1.03% T2DM versus 0.47% T1DM, p = 0.03) and delayed kidney graft function (11.7% T2DM versus 7.8% T1DM p < 0.001) were both higher compared to recipients with T1DM. There were no differences in 5-year patient and pancreas survival rates in the two groups. However, 5-year overall and death-censored kidney graft survival rates were lower in patients with T2DM but after adjustment for multiple characteristics, kidney survival outcomes in SPKT recipients with T2DM were comparable to those with T1DM. In this study, the major co-variates influencing survival outcomes (independent of DM type) were older recipient and donor age, obesity, AA race, duration of dialysis, and cardiovascular disease. An associated editorial highlighted the importance of recipient selection, in particular because the greatest risk factors for mortality after SPKT in this study were recipient age > 45 years and co-morbidities such as peripheral vascular and coronary artery disease irrespective of DM type [32]. In addition, they emphasized that T2DM patients who had a BMI < 30 kg/m2 and who were <50 years of age would be rendered insulin-free and have acceptable outcomes after SPKT. Notably, lower pancreas survival rates because of beta-cell exhaustion developing in patients with T2DM are only a theoretical concern and not an actual event if the above selection criteria are endorsed.
In a study of the SRTR database published in 2012 and spanning 2000–2008, outcomes were compared in patients with T2DM (who had a BMI of 18–30 kg/m2 and an age range of 18–59 years) who received either a deceased donor kidney transplant (n = 4005), a living donor kidney transplant (n = 1987), or an SPKT (n = 424) [33]. Patient and kidney graft survival rates were lowest with a deceased donor kidney transplant, in-between with an SPKT, and highest with a living donor kidney transplant. When a living donor kidney transplant is not available, the authors concluded that SPKT is a good option in this population if patients are selected carefully. In an editorial that accompanied this study, Cohen and Ratner [34] stressed the key role of kidney quality on influencing outcomes, which endorses greater application of SPKT in patients with ESRD and T2DM within the limits of the UNOS kidney and pancreas allocation policies.
In another UNOS database study published in 2020 by Alhamad et al., outcomes were analyzed in 35,849 patients with T2DM and chronic kidney disease including 641 SPKT, 10,888 living donor kidney, and 24,320 deceased donor kidney transplants performed between 2000 and 2016 [27]. Because the study purpose was to analyze the effect of 3-month pancreas allograft function on long-term outcomes, early deaths and kidney graft losses were excluded. A total of 40 patients (6.2%) experienced early pancreas graft loss in the SPKT group. SPKT recipients were more likely to have a lower BMI and a lower PRA level, be male and younger, but less likely to receive a zero-human leukocyte antigen (HLA) mismatch organ than kidney alone recipients. Deceased donor kidney transplant alone recipients had longer dialysis times and higher PRA levels compared to SPKT and living donor kidney alone recipients. Donors for deceased donor kidney alone recipients were older, more commonly obese or hypertensive, and had longer cold ischemia times compared SPKT and living donor kidney alone recipients. The highest long-term (up to 10 years) kidney and patient survival rates occurred in SPKT recipients with both kidney and pancreas grafts functioning at 3 months. However, in those SPKT recipients with early pancreas graft loss, the beneficial long-term survival effect of SPKT compared to either living or deceased donor kidney transplant alone was no longer apparent. The authors speculated that the survival advantage of SPKT is a consequence of not only long-term euglycemia but also differences in donor and recipient characteristics as well as possibly a reduced waiting time and selection bias. During the period of study, for patients identified as having T2DM, only 2% underwent SPKT and the remaining received a kidney alone transplant. Similar to previous studies in T1DM, the authors concluded that T2DM patients also experience a similar survival benefit with SPKT compared to kidney transplant alone if pancreas graft failure does not occur in the first 3 months posttransplant. Moreover, SPKT as a treatment option for patients with T2DM and ESRD may be underutilized.
6. Recipient Selection for T2DM
Literature to date demonstrate comparable intermediate-term survival and functional outcomes reported for SPKT in T1DM and T2DM individuals along with the lack of strict diagnostic criteria to differentiate between the two groups of patients. T2DM and T1DM can be difficult to distinguish because of clinical overlap related to the heterogeneity of glucose dysmetabolism. Studies of SPKT in T2DM patients with ESRD have suggested a clinical course that mirrors that of T1DM patients undergoing SPKT. Moreover, a T2DM recipient phenotype has been identified that includes an increased proportion of AA and other minority recipients. Selection criteria for PTx in patients with either T2DM or T1DM are listed in Table 1 [44]. Because SPKT is associated with improved renal function preservation, better donor quality, and decreased waiting time compared to deceased donor kidney alone transplantation, characterization of DM “type” may not be necessary. Consequently, DM patients on insulin need only be evaluated for SPKT based on their predicted ability to manage the requisite immunosuppression, adhere to a more intense posttransplant follow-up schedule, and tolerate the surgical procedure (with a higher inherent complication rate) independent of pre-existing Cp levels [8,9,10,11,13,14,23,24,25,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57,58,71]. The belief that patients with T2DM should not qualify for PTx is not corroborated by available data, nor is the concern that the pool of available organs for patients awaiting kidney alone transplantation will be reduced by offering SPKT to these patients. From 2000 to 2021, the proportion of kidneys utilized for SPKTs decreased from 11% to 5% of all deceased donor kidney transplant activity in the US in spite of liberalization of PTx recipient selection criteria to include older patients, minorities, and patients with a T2DM phenotype.

Table 1.
Selection Criteria for PTx in Patients with either T1DM or T2DM.
UNOS approved new eligibility allocation criteria for PTx candidacy in November 2011, which went into effect on 31 October 2014. SPKT criteria included patients on insulin who either have a Cp level < 2.0 ng/mL or have a BMI < 28 kg/m2 if their Cp level is ≥2.0 ng/mL. Subsequently, the BMI threshold was increased to ≤30 kg/m2. Patients meeting these criteria will receive allocation priority ahead of patients on the kidney wait list when a potential kidney-pancreas donor is identified. Interestingly, these criteria were implemented without any studies suggesting that either higher recipient BMI or Cp levels have a direct adverse effect on outcomes following SPKT in T2DM patients although recipient selection bias probably prevents adequate study of these factors.
Candidate selection is determined by a multidisciplinary team that performs a comprehensive medical, psychosocial, and financial evaluation (Table 2). This evaluation process verifies the presence and severity of insulin-requiring DM, determines whether the patient can tolerate the operative procedure and chronic immunosuppression, confirms that exclusion criteria are not present (Table 1), and documents end-organ complications for future monitoring after transplantation [44,71]. Main elements of recipient selection include inadequately controlled glycemic excursions, ongoing microvascular complications, degree of nephropathy (which determines type of transplant), cardiovascular reserve, overall performance and functional status, and satisfactory social support. We do not view active smoking as an absolute contraindication to PTx unless the candidate is a heavy smoker or has evidence for smoking related morbidity. However, we strongly encourage smoking cessation in all patients. Marijuana use is not considered a contraindication unless it is associated with other addictive behaviors that are uncontrolled. Importantly, we recommend performing duplex ultrasonography of the iliac vessels in combination with abdominal and pelvic computerized tomographic imaging to assess the severity of peripheral vascular disease.

Table 2.
Recipient Evaluation.
Quality of life is a multi-dimensional construct reflecting an individual’s perception of health, well-being, and happiness. Conceptual aspects include physical, social, and psychological function, the burden of symptoms and treatments, and sense of well-being. Various questionnaires and survey instruments are available that assess indices of well-being, affect, satisfaction, activities and daily living, and health-care burden. Quality of life surveys do not specifically address any particular physiological consequence, but they do take into account various factors that are important to the transplant recipient. These factors include opportunities for social interaction, ability to return to work or maintain employment, overall energy level, and psychological adjustment. There is no question that impaired or poor quality of life is a “secondary complication” of diabetes, particularly in IDDM patients with ESRD.
Qualitative assessment of the impact of DM on the patient is helpful. For example, if the presence of DM is self-perceived to be causing a significant impairment in overall quality of life or if a patient believes that DM is controlling their life more than they are controlling DM, then PTx is a reasonable treatment option to consider. It is important to comprehend the relationship between the patient and their diabetes because most patients are able to articulate if/when they lost control of their diabetes management. Numerous studies have demonstrated that successful SPKT results in improvements in physical function, activities and daily living, energy level, mobility, vocational rehabilitation, social well-being, communication, role function, health perception, self-image, psychological function, future expectations, sense of well-being, overall satisfaction, diet flexibility, diabetes-related concerns, time to manage health, health impact on family, and autonomy [72,73,74,75,76,77,78,79,80,81,82]. The major benefits of PTx are an enhanced quality of life characterized by the following: (a) rehabilitation to “normal” living with physical, social and psychological well-being with near normal activities and daily living and a self-perception of normality; (b) global improvement in quality of life with the perception of being healthy and having control over one’s destiny; and (c) fewer restrictions and enhanced capacities leading to an improved sense of well-being and independence [72,73,74,75,76,77,78,79,80,81,82].
Freedom from daily insulin injections and blood glucose monitoring are important advantages for patients with a successful PTX. In addition, the elimination not only of hyperglycemia but hypoglycemia as well is a dramatic benefit, particularly for those patients with hypoglycemia unawareness. In this setting, improvement in quality of life following PTx is not only an endpoint but also a “turning point” in their overall well-being and health. In addition to dysmetabolism and progressive diabetic complications, significant psycho-emotional or physical difficulties with insulin therapy are another indication for PTx. However, the most important part of recipient selection is the overall evaluation of cardiovascular disease burden, risk, and functional reserve [44,71,83,84,85,86,87,88,89,90,91].
Because significant (and silent) coronary artery disease may occur in this population, the cardiac evaluation includes initially a non-invasive functional examination (echocardiography in combination with either an exercise or a pharmacological stress test) [44,71,84,85,86,87,88,89,90]. Cardiac catheterization may be required at some centers in all potential SPKT candidates whereas others may reserve it for selected indications [84,85,86,87,88,89,90]. Prior cardiac interventions or history of cardiac events are not necessarily contraindications for PTx because excellent outcomes can still be achieved in these patients [83,88,89,90,91]. However, in the absence of discernible structural heart disease, sudden cardiac death continues to be a cause of mortality in PTx recipients [84,85,86,87,88,89,90,91,92,93,94]. However, because the majority of patients have identifiable peripheral vascular or cardiac disease, candidacy is determined by the severity of cardiovascular disease and whether it can be adequately treated pretransplant.
Contraindications for PTx are listed in Table 1 [44,71]. Most patients < 45 years of age are considered to be acceptable medical candidates for PTx if they are not obese and have no history of major peripheral vascular or cardiac disease. Patients > 55 years of age are not considered to be acceptable medical candidates for SPKT until proven otherwise; a detailed cardiovascular and peripheral vascular evaluation is required [44,71,95,96,97,98,99,100,101,102,103,104,105]. Because of a higher rate of surgical complications in obese patients, BMI > 35 kg/m2 is usually considered a contraindication for SPKT unless the individual either has a favorable body habitus (no central obesity) or is able to lose weight [106,107,108,109,110,111,112,113]. Patients who have had prior bariatric surgery and lost weight can have successful outcomes following SPKT. In 2012, Porubsky et al., reported four patients with T1DM who underwent successful PTx following bariatric surgery [114]. In light of the obesity epidemic, staged bariatric surgery as a bridge to transplantation should be considered in obese DM patients who are morbidly obese or fail nonoperative weight loss strategies. Pretransplant weight loss as a result of metabolic surgery may not only improve access and outcomes but in some cases may even prevent the need for PTx if the patient becomes insulin independent. Alternatively, the development of T2DM associated with excessive weight gain following SPKT may be treated with bariatric surgery, thus preserving pancreas allograft function [115,116,117]. Successful robotic PTx has also been reported in obese patients as a means of expanding criteria and improving access in patients with either T1DM or T2DM [118,119,120].
7. Pancreas Transplantation in Minorities
As previously noted, since year 2000 in the US, the annual percentage of patients with T2DM undergoing SPKT has steadily risen from 6% to 27% (Figure 1) concomitant with a progressive rise in the yearly percentage of AA SPKT recipients from 10% to nearly 30% (Figure 2) [8,9,10,11]. During this same period, the number of Hispanic and Asian SPKT recipients increased as well (Figure 3). For SPKT recipients with T1DM, approximately 56% were Caucasian, 25% AA, 15% Hispanic, 2% Asian, and 2% other ethnicity. On the other hand, for SPKT recipients with T2DM, 24% were Caucasian, 44% AA, 22% Hispanic, 8% Asian, and 2% other descent (Figure 4). Based on epidemiology and the prevalence of end stage diabetic nephropathy, however, non-Caucasian SPKT recipients should be proportionately greater if the procedure was performed objectively in different ethnic groups [121,122,123,124]. This discrepancy is multifactorial and probably due to disparities in insurance coverage, healthcare access and resources, social and caregiver support, health literacy, and the perception that minority SPKT patients (especially those with T2DM) have inferior outcomes versus Caucasian patients. According to data from 2017–2018, the age-adjusted prevalence of diagnosed T1DM is greater among minorities versus Caucasian adults [4]. Additionally, studies suggest that there is inferior metabolic control and an increased incidence of ESRD and other end organ injury in AA patients with T1DM compared to Caucasian patients [125,126]. Moreover, minority patients have decreased access to SPKT, which may be related in part to lack of referral because of concerns regarding inferior outcomes for non-Caucasian patients undergoing SPKT [121,122,123,124]. When reviewing prior literature (which is conflicting), compared to non-Hispanic Caucasian patients, AA SPKT recipients may have inferior patient and graft survival rates in both registry and single center reports [19,23,127,128,129,130,131,132,133,134,135,136,137,138,139,140,141,142].
Following kidney transplantation, a number of studies have reported lower graft survival with higher rates of acute rejection and immunologic graft loss in AA versus non-AA recipients [122,123,143]. However, following SPKT, the data regarding the impact of recipient race is less clear. In 1997, Douzdjian et al., performed a dual center retrospective analysis of outcomes in 99 SPKT (13 Black) recipients. There were no significant differences in graft survival or rejection rates although Black patients experienced numerically higher pancreas and kidney graft survival rates [127]. Douzdjian et al., in 1997, using South-Eastern Organ Procurement Foundation data, also performed one of the first registry analyses of the effect of race on SPKT outcomes [128]. They found no differences in pancreas or patient survival rates at 1 and 5 years between Caucasian and AA (n = 98) SPKT patients, with the AA group representing only 12% of recipients. However, Black patients in this study had decreased kidney graft survival following kidney transplantation alone compared to non-Hispanic White kidney alone recipients.
In 2000, a case–control study by Lo et al., reported lower pancreas and kidney survival rates and a higher incidence of acute rejection in 10 AA versus 10 Caucasian SPKT patients at the University of Tennessee-Memphis [130]. In 2001, the Washington Hospital Center experience with SPKT in 49 AA patients (40% characterized as “type 2” based on pretransplant Cp levels) was reviewed by Light et al. [19,23]. Ten-year survival rates were similar irrespective of diabetes type or race. In a follow-up report on their 20-year experience, Light and Tucker studied 173 SPKT recipients, of which 51% (n = 88) were AA [30]. Death-censored pancreas and kidney graft survival rates were better in T2DM recipients whereas patient survival was greater in patients with T1DM. The authors concluded that candidacy for SPKT should be based on clinical criteria (such as age, BMI, and comorbidities), not on race or diabetes type.
Conversely, in 2003, Rogers et al., at the Medical University of South Carolina, reported worse outcomes in 33 AA SPKT recipients based on more acute rejection episodes and a lower pancreas survival rate versus a contemporary control group of 63 Caucasian SPKT patients [131]. Interestingly, five-year kidney and patient survival rates were comparable in the two groups. In 2005, an ad hoc analysis was performed of a prospective randomized multicenter trial of two-dose or five-dose induction with daclizumab versus no antibody induction in 298 SPKT recipients including 37 AA patients compared to 261 non-AA patients [132]. At a follow-up of three years, no differences were discerned in pancreas, kidney, or patient survival rates when comparing 261 non-AA to 37 AA SPKT recipients. However, metabolic and functional differences were identified as AA patients had higher serum creatinine and HbA1c levels, a lower glomerular filtration rate, higher diastolic blood pressure, and greater need for oral hypoglycemic agents compared to the non-AA group [133]. In a single center study conducted at Tulane University, Zhang et al., reported five- and then seven-year outcomes in 73 Caucasian (55 underwent SPKT, 18 solitary PTxs) and 45 AA (36 underwent SPKT, 9 solitary PTx) recipients who received two-dose induction therapy with basiliximab from 1998 to 2005 [134,135]. The cumulative incidence of acute rejection was slightly higher (36% AA compared to 31% Caucasian) in the AA group but no differences were noted in patient or graft survival rates.
In 2010, an SRTR database study was performed by Luan and colleagues for SPKTs performed in the US from 2000 through 2007 [136]. A total of 931/6585 (14.1%) SPKTs occurred in AA recipients. In the first three months following SPKT, no racial differences in outcomes were noted. Subsequently, AA SPKT recipients had a 47% and 38% greater risk for death-censored pancreas and kidney graft failure, respectively, compared to the non-AA group. Additionally, the risk of either pancreas or kidney graft loss due to rejection was twice as high in AA versus non-AA SPKT recipients. Another retrospective UNOS database analysis was conducted by Brooks and co-authors in 2018 that included SPKTs performed from 1989 through 2014 [137]. The study group included 20,196 SPKT recipients, of which 2708 were AA (13.4%), 199 Asian (1%), 1456 Hispanic (7.2%), and the remaining 15,833 (78.4%) were Caucasian. Asians and Hispanics had the highest overall ten-year graft and patient survival rates compared to the two other groups. At one-year, AA SPKT recipients had superior pancreas and kidney graft survival rates compared to non-Hispanic Caucasians. However, AA patients had significantly lower graft and patient and survival outcomes versus Caucasian patients with follow-up beyond three-years. In 2020, the group at the University of Alabama-Birmingham analyzed their SPKT experience spanning 1999 to 2014 including 68 AA and 120 Caucasian recipients [138]. Although they reported “equivalent” outcomes in AA versus Caucasian SPKT patients, their data showed a 15% higher risk of pancreas loss, a 27% higher risk of kidney loss, and a 17% higher risk of death in AA versus Caucasian recipients.
In 2022, Gonzales et al., performed a retrospective longitudinal cohort analysis of 287 PTxs (217 SPKT) including 162 in non-AA and 125 in AA recipients (107 SPKT) at Medical University of South Carolina [139]. This study represents the largest single center experience with AA in SPKT to date, surpassing the 88 AA SPKT recipients reported by Light and Tucker [30]. AA patients had higher rates of kidney rejection, post-operative bleeding, pancreatic leaks, and higher mean HbA1c levels long-term. However, pancreas and patient survival rates were comparable to the non-AA group. Furthermore, in 2022, Li and colleagues performed a retrospective analysis of the SRTR database including 28,797 primary PTxs performed from 1989 to 2018, including 3828 (13.3%) in AA recipients. Prior to 2009, the hazard ratio for pancreas graft failure at 3 years follow-up was 1.16 (16% increased risk) for AA recipients, who experienced more pancreas graft loss secondary to rejection. After 2009, the hazard ratio for AA recipients dropped to 1.01 (no excessive risk of pancreas graft loss). However, from 1998 to 2018, univariate analysis in SPKT recipients demonstrated that AA patients had a significantly increased risk of kidney graft failure (hazard ratio 1.45).
According to the latest IPTR data [10], for patients identified as having T1DM, there are no differences at 3 years follow-up in Blacks, Hispanics, and Whites with respect to either patient survival (Figure 9) or pancreas graft survival rates (Figure 10). However, AA SPKT recipients with T1DM have a significant lower kidney graft survival rate (Figure 11) compared to either Hispanics or Whites at 3 years follow-up. For patients identified as having T2DM, there are no differences in three-year patient (Figure 12), pancreas (Figure 13), or kidney graft survival rates (Figure 14) according to race.
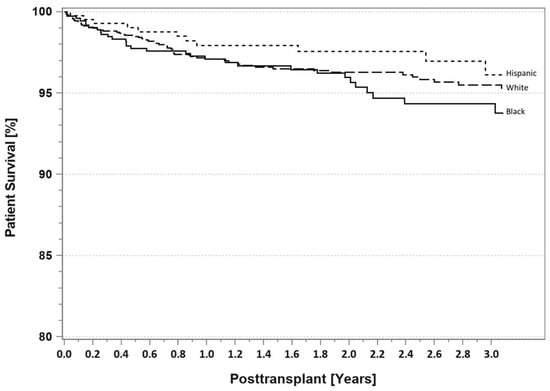
Figure 9.
SPKT patient survival according to recipient race in patients identified as having T1DM in the latest era (1 January 2017–31 December 2021).
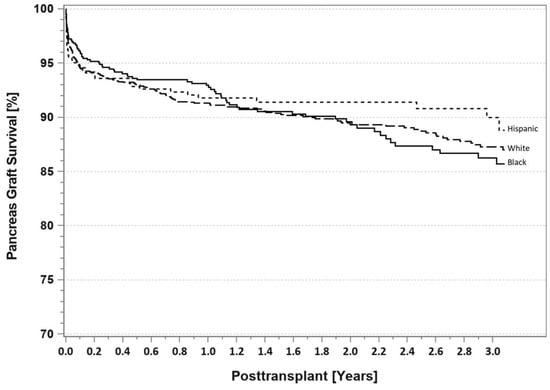
Figure 10.
SPKT pancreas graft survival according to recipient race in patients identified as having T1DM in the latest era (1 January 2017–31 December 2021).
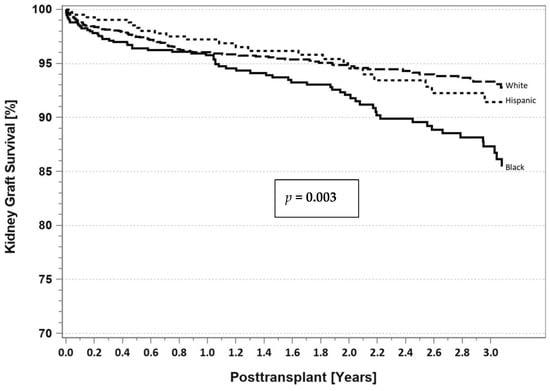
Figure 11.
SPKT kidney graft survival according to recipient race in patients identified as having T1DM in the latest era (1 January 2017–31 December 2021).
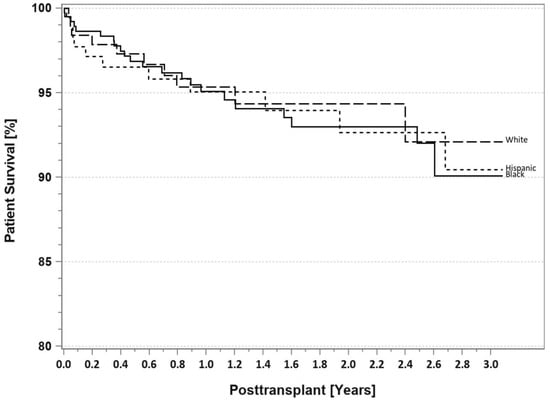
Figure 12.
SPKT patient survival according to recipient race in patients identified as having T2DM in the latest era (1 January 2017–31 December 2021).
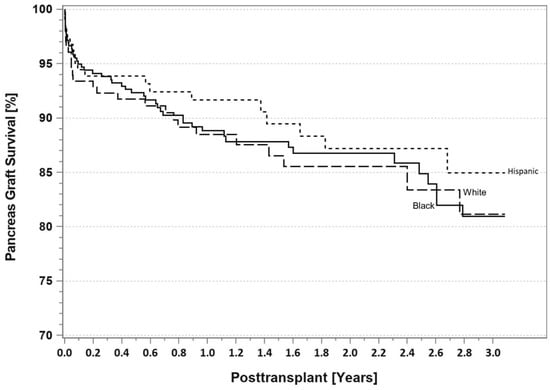
Figure 13.
SPKT pancreas graft survival according to recipient race in patients identified as having T2DM in the latest era (1 January 2017–31 December 2021).
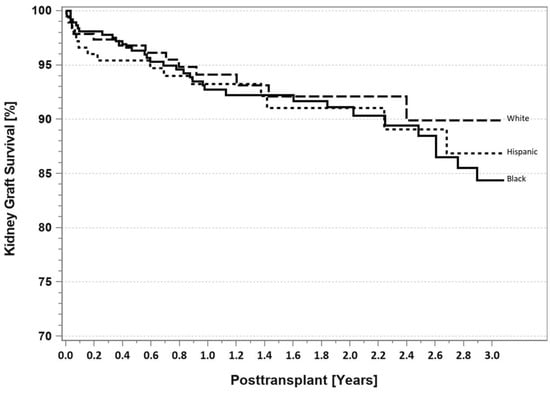
Figure 14.
SPKT kidney graft survival according to recipient race in patients identified as having T2DM in the latest era (1 January 2017–31 December 2021).
At Wake Forest, from November 2001 to January 2019, we performed a single center retrospective experience in 57 AA versus 158 non-Hispanic Caucasian SPKT recipients [142]. There were no differences in preservation and donor factors other than younger donor age in the AA group (mean age 23.0 AA versus 27.2 Caucasian, p = 0.01). Mean follow-up was 8.9 years Caucasian versus 8.4 years AA; 87% of Caucasian and 84% of AA patients had follow-up of 4 years or more. Mean recipient age (40 years AA versus 44 Caucasian, p = 0.02), similar to donor age, was 4 years younger in the AA group. The AA group had more patients with a longer duration (≥20 months) of dialysis (51% AA versus 24% Caucasian), fewer patients on peritoneal dialysis (14% AA versus 30% Caucasian), more sensitized (PRA ≥ 20%) patients (21% AA versus 6% Caucasian), and more 5–6 HLA mismatches (67% AA versus 51% Caucasian, all p < 0.05). In addition, the AA group had more patients with T2DM based on pretransplant Cp levels ≥ 2.0 ng/mL (35% AA versus 11% Caucasian), more patients with a shorter need for insulin use (<20 years, 47% AA versus 23% Caucasian), and more patients with onset of DM at a later age (≥age 24; 30% AA versus 13% Caucasian, all p < 0.05). With a minimum follow-up of 15 months, one-year patient (97%), kidney (95%), and pancreas (89%) graft survival rates were comparable in both groups. Length of initial hospitalization and the incidences of acute rejection, early thrombosis, and relaparotomy were similar in both groups. Overall patient survival rates (77% AA versus 65% Caucasian, p = 0.098) were higher in the AA group, whereas kidney (55% AA versus 59.6% Caucasian) and pancreas (54.4% AA versus 47.5% Caucasian) graft survival rates were comparable. Death-censored kidney (68% AA versus 71% Caucasian) and pancreas (both 62%) graft survival rates demonstrated that death with a functioning graft was nearly twice as often in Caucasian (23.4%) versus AA patients (12%, p = 0.086). Cumulative acute rejection rates were 27% C versus 33% AA and rates of early graft loss (usually secondary to thrombosis) were 5% AA versus 7% Caucasian. Death-censored dual graft loss, ascribed to acute and chronic rejection, was three times more likely in AA (21%) versus Caucasian patients (7%, p = 0.0055).
However, starting at four years post-SPKT, kidney survival rates were higher in Caucasians because the AA group experienced more medium-term graft loss secondary to acute and chronic rejection. Potential reasons for this finding in the AA group include lack of transplant center follow-up, greater intrinsic risk for immunological graft loss or noncompliance, or loss of Medicare coverage for immunosuppressant medications after 3 years. Conversely, the risk of late mortality was four times higher in the Caucasian group and death with a functioning graft was two times more common in Caucasians. Consequently, the AA group had improved patient survival after eight years compared to the Caucasian group. Although long-term pancreas and kidney survival rates were comparable in Caucasian and AA patients, the disparate causes of graft loss and divergent timelines may provide insight as to how to achieve better long-term outcomes according to race. In our limited experience with SPKT in other minorities (6 Hispanic, 4 Asian), patient survival is 100% and both pancreas and kidney survival rates are 80%.
Several single center studies from South America have reported good outcomes in a predominantly Hispanic population, while other studies from China, Korea, India, and Japan have reported excellent outcomes in a predominantly Asian population [48,50,144,145,146,147,148]. In 1997, the University of Miami group published one of the first reports of successful SPKT in Hispanic recipients with T1DM [144]. In a 2016 IPTR study of long-term (5-year) outcomes following PTx, Black race was associated with reduced pancreas and kidney and survival rates and “other” race with better graft survival rates versus patients identified as White [149]. In the IPTR report published in 2018, race was grouped as White, Black, Hispanic, Asian, and multiracial/other [8,9]. In the non-White groups, the number of SPKTs has increased in successive eras (Figure 3) whereas the number of SPKTs in Whites has remained static. A multivariate risk factor analysis demonstrated no effect of race on patient survival but Black race had a negative effect and Hispanic race a positive effect on both pancreas and kidney survival rates compared to Whites in the SPKT category.
Exploring the interaction between recipient and donor and recipient variables and their impact on pancreas technical failure rates independent of race or diabetes type is another important consideration. Older donor age, particularly above age 45 years, has been correlated with worse outcomes, including pancreas failure and inferior glycemic control [150,151,152,153,154,155,156,157,158,159,160,161]. A composite risk model, used to predict technical pancreas failure, was developed by Finger et al., at the University of Minnesota after reviewing 1115 PTXs at their center. While donor age was predictive of technical pancreas failure, recipient age was not [156]. Independent of recipient age, race, diabetes type, or BMI, recent studies have investigated functional or performance status and the effects of sarcopenia on SPKT outcomes [162,163,164,165]. There exists a relationship between frailty, sarcopenia and DM because of the excess accumulation of advanced glycation end products and intramyocellular lipids in combination with the catabolic effects of insulin deficiency [166]. As seen in other solid organ transplant groups, reduced functional status, sarcopenia, and frailty are highly predictive of survival following SPKT independent of age or race.
8. Summary
In the previous century, vascularized PTx occurred primarily in middle-aged, Caucasian adults with T1DM, usually as an SPKT in patients with ESRD. With steadily improving outcomes in the past 20 years, recipient selection for PTx has become liberalized to include minorities, obese, and older patients, all of whom disproportionately display a T2DM phenotype. In the past, because the pathophysiology of T2DM was believed to be related to insulin resistance, the presence of a T2DM phenotype was considered a contraindication for SPKT. However, considerable overlap may exist in the clinical manifestations of T2DM versus T1DM. “Type” of DM can no longer be reliably ascertained based on detectable Cp levels. Successful SPKT in uremic patients with detectable Cp levels and a type 2 diabetes phenotype (no autoantibodies or history of ketoacidosis, DM onset and transplant at an older age, shorter need for insulin use, use of oral anti-diabetic agents initially when DM first diagnosed, higher body weight/BMI, higher proportion of African Americans and other minorities) is now being achieved. Intermediate-term SPKT outcomes are near equivalent in patients with either T2DM or T1DM although clearly a selection bias occurs in patients with presumed T2DM. This finding suggests that a heterogeneous pathophysiology of T2DM that consists of elements of both insulin deficiency and insulin resistance due to beta-cell failure. Consequently, escalation of endogenous insulin (Cp) production following successful SPKT may result in improved life expectancy and quality of life, enhanced glucose counter-regulation, and total freedom from exogenous insulin therapy or the need to monitor serum glucose levels compared to other treatment options available to these patients. Experience with solitary PTx in patients with T2DM or minorities is limited but largely mirrors the trends reported in SPKT.
At present, PTx is an effective treatment option in appropriately selected patients with pancreas endocrine failure regardless of diabetes type or recipient race. Limitations in the current data include the lack of granular information in registry data, the low number of patients studied in single center retrospective analyses, and the absence of a randomized trial comparing pancreas transplantation to state of the art diabetes management. Improvements in PTx outcomes are related to modifications in both donor and recipient selection. The transplant community continues to provide viable options to patients with DM in the setting of improved medical management, which has resulted in a changing referral population. A consequence of improvements in care has been providing candidate evaluation and transplantation in situations that were previously considered exclusionary. As a result, there has been an increase number of PTxs performed in unconventional patients including minorities and patients with a T2DM phenotype. Analogous to kidney transplantation, SPKT may provide both a quality of life and survival advantage to appropriately selected patients independent of age, race, or phenotype [167,168,169,170,171].
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.J.S. and A.G.; methodology, R.J.S. and A.G.; software, A.G.; validation, R.J.S. and A.G.; formal analysis, R.J.S. and A.G.; investigation, R.J.S.; resources, R.J.S. and A.G.; data curation, R.J.S. and A.G.; writing—original draft preparation, R.J.S.; writing—review and editing, R.J.S. and A.G.; visualization, R.J.S.; supervision, R.J.S.; project administration, R.J.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This analysis received approval as exempt by the Wake Forest Baptist Health Institutional Review Board and is in accordance with the guidelines of the 1975 Declaration of Helsinki.
Informed Consent Statement
Because this is primarily a review article, informed consent was not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data available on request from the authors due to privacy/ethical issues.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
| AA | African American |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| Cp | C-peptide |
| DM | Diabetes mellitus |
| ESRD | End stage renal disease |
| HbA1c | Hemoglobin A1c |
| HLA | Human leukocyte antigen |
| IPTR | International Pancreas Transplant Registry |
| PAK | Pancreas after kidney |
| PRA | Panel reactive antibody |
| PTA | Pancreas transplant alone |
| PTx | Pancreas transplant |
| SPKT | Simultaneous pancreas-kidney transplant |
| SRTR | Scientific Registry of Transplant Recipients |
| T1DM | Type 1 diabetes mellitus |
| T2DM | Type 2 diabetes mellitus |
| UNOS | United Network for Organ Sharing |
| US | United States |
References
- American Diabetes Association. Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care 2009, 32 (Suppl. S1), S62–S67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IDF. 10th Edition. Available online: Diabetesatlas.org (accessed on 1 July 2022).
- Available online: http://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/data/statistics-report/index.html?CDC_AA_refVal (accessed on 1 July 2022).
- Duru, O.K.; Middleton, T.; Tewari, M.K.; Norris, K. The landscape of diabetic kidney disease in the United States. Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2018, 18, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Diabetes Association. Economic costs of diabetes in the US in 2017. Diabetes Care 2018, 41, 917–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saran, R.; Robinson, B.; Abbott, K.C.; Bragg-Gresham, J.; Chen, X.; Gipson, D.; Gu, H.; Hirth, R.A.; Hutton, D.; Jin, Y.; et al. US Renal Data System 2019 Annual Data Report: Epidemiology of kidney disease in the United States. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2020, 75 (Suppl. S1), A6–A7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, J.L. Pancreas transplantation: Indications and consequences. Endocr. Rev. 2004, 25, 919–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruessner, A.C.; Gruessner, R.W.G. Pancreas Transplantation for Patients with Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in the USA Registry Report. Gastroenterol. Clin. N. Am. 2018, 47, 417–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruessner, A.C.; Gruessner, R.W.G. The Current State of Pancreas Transplantation in the USA—A Registry Report. Curr. Transplant. Rep. 2018, 5, 304–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Updated International Pancreas Transplant Registry (IPTR) Data, Angelika Gruessner (Personal Communication). United Network for Organ Sharing (UNOS) Data. Available online: https://optn.transplant.hrsa.gov/data/view-data-reports/national-data/ (accessed on 27 July 2022).
- Kandaswamy, R.; Stock, P.G.; Miller, J.; White, S.E.; Booker, S.E.; Israni, A.K.; Snyder, J.J. OPTN/SRTR 2020 Annual Data Report: Pancreas. Am. J. Transplant. 2022, 22 (Suppl. S2), 137–203. Available online: https://srtr.transplant.hrsa.gov (accessed on 1 July 2022). [CrossRef]
- Gruessner, A.C.; Sutherland, D.E. Pancreas Transplant Outcomes for United States (US) Cases Reported to the United Network for Organ Sharing (UNOS) and Non-US Cases Reported to the International Pancreas Transplant Registry (IPTR) as of October, 2000; Cecka, J.M., Terasaki, P.I., Eds.; UCLA Tissue Typing Laboratory: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2001; pp. 45–72. [Google Scholar]
- Sener, A.; Cooper, M.; Bartlett, S.T. Is there a role for pancreas transplantation in type 2 diabetes mellitus? Transplantation 2010, 90, 121–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlando, G.; Stratta, R.J.; Light, J. Pancreas transplantation for type 2 diabetes mellitus. Curr. Opin. Organ. Transplant. 2011, 16, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantarovich, D.; Murat, A.; Krempf, M.; Paineau, J.; Soulillou, J.P. Simultaneous pancreas and kidney transplantation in a type II (non-insulin-dependent) diabetic uremic patient requiring pregraft insulin therapy. Transplant. Proc. 1990, 22, 662. [Google Scholar]
- Ratner, R.E.; Gray, R.S.; Sasaki, T.; Light, J.A. Combined kidney-pancreas transplantation in patients with unrecognized NIDDM. Diabetologia 1996, 39 (Suppl. S1), 500. [Google Scholar]
- Stegall, M.; Wachs, M.; Kam, I. Successful pancreas transplantation in adult-onset diabetes mellitus (AODM). Diabetes 1997, 46 (Suppl. S1), A64. [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki, T.M.; Gray, R.S.; Ratner, R.E.; Currier, C.; Aquino, A.; Barhyte, D.Y.; Light, J.A. Successful long-term kidney-pancreas transplants in diabetic patients with high C-peptide levels. Transplantation 1998, 65, 1510–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Light, J.A.; Sasaki, T.M.; Currier, C.B.; Barhyte, D.Y. Successful long term kidney-pancreas transplants regardless of C-peptide status and race. Transplantation 2001, 71, 152–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pox, C.; Ritzel, R.; Büsing, M.; Meier, J.; Klempnauer, J.; Schmiegel, W.; Nauck, M. Combined pancreas and kidney transplantation in a lean type 2 diabetic patient. Effects on insulin secretion and sensitivity. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2002, 110, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, A.L.; Friedman, E.A. Pancreas transplantation for type 2 diabetes at U.S. transplant centers. Diabetes Care 2002, 25, 1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saudek, F.; Pruhova, S.; Boucek, P.; Lebl, J.; Adamec, M.; Ek, J.; Pedersen, O.; Hansen, T. Maturity-onset diabetes of the young with end-stage nephropathy: A new indication for simultaneous pancreas and kidney transplantation? Transplantation 2004, 77, 1298–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Light, J.A.; Barhyte, D.Y. Simultaneous pancreas-kidney transplants in type I and type II diabetic patients with end-stage renal disease: Similar 10-year outcomes. Transplant. Proc. 2005, 37, 1283–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, D.S.; Gruessner, A.C.; Kandaswamy, R.; Gruessner, R.W.; Sutherland, D.E.; Humar, A. Outcomes of pancreas transplants for patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Clin. Transplant. 2005, 19, 792–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.P.; Rogers, J.; Farney, A.C.; Hartmann, E.L.; Reeves-Daniel, A.; Doares, W.; Ashcraft, E.; Adams, P.L.; Stratta, R.J. Do pretransplant C-peptide levels influence outcomes in simultaneous kidney-pancreas transplantation? Transplant. Proc. 2008, 40, 510–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkin, T.J. The accelerator hypothesis: A review of the evidence for insulin resistance as the basis for type I as well as type II diabetes. Int. J. Obes. 2009, 33, 716–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alhamad, T.; Kunjai, R.; Wellen, J.; Brennan, D.C.; Wiseman, A.; Ruano, K.; Hicks, V.; Wang, M.; Schnitzler, M.A.; Chang, S.-H.; et al. Three-month pancreas graft function significantly influences survival following simultaneous pancreas-kidney transplantation in type 2 diabetes patients. Am. J. Transplant. 2020, 20, 788–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakkera, H.; Bodner, J.; Heilman, R.; Mulligan, D.; Moss, A.; Mekeel, K.; Mazur, M.; Hamawi, K.; Ray, R.; Beck, G.; et al. Outcomes after simultaneous pancreas and kidney transplantation and the discriminative ability of the C-peptide measurement pretransplant among type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Transplant. Proc. 2010, 42, 2650–2652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knight, R.J.; Lawless, A.; Patel, S.J.; Gaber, A.O. Simultaneous kidney-pancreas transplantation for end-stage renal disease patients with insulin-dependent diabetes and detectable C-peptide. Transplant. Proc. 2010, 42, 4195–4196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Light, J.; Tucker, M. Simultaneous pancreas kidney transplants in diabetic patients with end-stage renal disease: The 20-yr experience. Clin. Transplant. 2013, 27, E256–E263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampaio, M.S.; Kuo, H.T.; Bunnapradist, S. Outcomes of simultaneous pancreas-kidney transplantation in type 2 diabetic recipients. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 6, 1198–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, D.B.; Sutherland, D.E.R. Simultaneous pancreas-kidney transplants are appropriate in insulin-treated candidates with uremia regardless of diabetes type. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 6, 957–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wiseman, A.C.; Gralla, J. Simultaneous pancreas kidney transplant versus other kidney transplant options in patients with type 2 diabetes. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2012, 7, 656–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, D.J.; Ratner, L.E. Type 2 diabetes: The best transplant option is still uncertain. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2012, 7, 530–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scalea, J.R.; Cooper, M. Surgical strategies for type II diabetes. Transplant. Rev. 2012, 26, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Margreiter, C.; Resch, T.; Oberhuber, R.; Aigner, F.; Maier, H.; Sucher, R.; Schneeberger, S.; Ulmer, H.; Bösmüller, C.; Margreiter, R.; et al. Combined pancreas-kidney transplantation for patients with end-stage nephropathy caused by type-2 diabetes mellitus. Transplantation 2013, 95, 1030–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, P.; Bohannon, L.; Bry, W. 11 year experience with simultaneous pancreas and kidney transplantation in patients with type 1 and type 1 diabetes at a single center. Transplantation 2013, 96 (Suppl. S74), A382. [Google Scholar]
- Bry, W.; Mahanty, H.; Patel, P.; Peddi, V.R.; Hassoun, A.; Neidlinger, N.; Katznelson, S. Elevated BMI does not affect outcome in type II diabetics undergoing whole organ pancreas transplantation. Transplantation 2013, 96 (Suppl. S84), A419. [Google Scholar]
- Wiseman, A.C. Kidney transplant options for the diabetic patient. Transplant. Rev. 2013, 27, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciancio, G.; Burke, G.W. Type 2 diabetes: Is pancreas transplantation an option? Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2014, 14, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weems, P.; Cooper, M. Pancreas transplantation in type II diabetes mellitus. World J. Transplant. 2014, 4, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, S.; Gough, S.C. Pancreas transplantation: A treatment option for people with diabetes. Diabet. Med. 2014, 31, 512–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stratta, R.J.; Rogers, J.; Farney, A.C.; Orlando, G.; El-Hennawy, H.; Gautreaux, M.D.; Reeves-Daniel, A.; Palanisamy, A.; Iskandar, S.S.; Bodner, J.K. Pancreas transplantation in C-peptide positive patients: Does type of diabetes really matter? J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2015, 22, 716–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stratta, R.J.; Farney, A.C.; Orlando, G.; Rogers, J. Pancreas transplantation for type 2 diabetes mellitus: Who and why? Curr. Transpl. Rep. 2015, 2, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fourtounas, C. Transplant options for patients with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease. World J. Transplant. 2014, 4, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruessner, A.C.; Laftavi, M.R.; Pankewycz, O.; Gruessner, R.W.G. Simultaneous pancreas and kidney transplantation—Is it a treatment option for patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus? An analysis of the International Pancreas Transplant Registry. Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2017, 17, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, D.J.; Sayed, B.A.; Turgeon, N.A. Pancreas transplantation in unconventional recipients. Curr. Opin. Organ. Transplant. 2016, 21, 393–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, S.; Jung, C.H.; Choi, J.Y.; Kwon, H.W.; Jung, J.H.; Kim, Y.H.; Han, D.J. Long-term metabolic outcomes of functioning pancreas transplants in Type 2 diabetic recipients. Transplantation 2017, 101, 1254–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Qaoud, T.; Odorico, J.S.; Redfield, R.R., III. Pancreas transplantation in type 2 diabetes: Expanding the criteria. Curr. Opin. Organ. Transplant. 2018, 23, 454–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gondolesi, G.E.; Aguirre, N.F.; Ramisch, D.A.; Mos, F.; Pedraza, N.; Fortunato, M.; Gutiérrez, L.; Fraguas, H.; Marrugat, R.; Rabin, G.; et al. Pancreas transplantation at a single Latin-American center: Overall results with type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Transplant. Proc. 2018, 50, 1475–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohan, V.; Taber, D.; Palanisamy, A.; Mcgillicuddy, J.; Chavin, K.; Baliga, P.; Bratton, C. Impact of type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus on pancreas transplant outcomes. Exp. Clin. Transplant. 2019, 6, 796–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andacoglu, O.M.; Himmler, A.; Geng, X.; Ahn, J.; Ghasemian, S.; Cooper, M.; Abrams, P. Comparison of glycemic control after pancreas transplantation for type 1 and type 2 diabetic recipients at a high volume center. Clin. Transplant. 2019, 33, e13656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenssen, T.; Hartmann, A. Post-transplant diabetes mellitus in patients with solid organ transplants. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2019, 15, 172–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torabi, J.; Rocca, J.P.; Kestenbaum, E.; Ajaimy, M.; DeFeo, M.; Konicki, A.; Liriano-Ward, L.; Azzi, Y.; Pynadath, C.; Akalin, E.; et al. Preoperative C-peptide predicts weight gain after pancreas transplantation. Prog. Transplant. 2020, 39, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hau, H.M.; Jahn, N.; Brunotte, M.; Lederer, A.A.; Sucher, E.; Rasche, F.M.; Seehofer, D.; Sucher, R. Short and long-term metabolic outcomes in patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes receiving a simultaneous pancreas kidney transplant. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2020, 20, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pham, P.H.; Stalter, L.N.; Martinez, E.J.; Wang, J.F.; Welch, B.M.; Leverson, G.; Marka, N.; Al-Qaoud, T.; Mandelbrot, D.; Parajuli, S.; et al. Single center results of simultaneous pancreas-kidney transplantation in patients with type 2 diabetes. Am. J. Transplant. 2021, 21, 2810–2823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.; Cao, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhao, J.; Wang, Z.; Mo, C.; Shi, X.; Feng, G.; Song, W. Metabolic outcomes and renal function after simultaneous kidney/pancreas transplantation compared with kidney transplantation alone for type 2 diabetes mellitus. Transplant. Int. 2021, 34, 1198–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.; Liu, X.; Lan, X.; Ni, K.; Li, L.; Fu, Y. Simultaneous pancreas and kidney transplantation for end-stage kidney disease patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Langenbecks Arch. Surg. 2022, 2, 660–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covic, A.M.C.; Schelling, J.R.; Constantiner, M.; Iyengar, S.K.; Sedor, J.R. Serum C-peptide concentrations poorly phenotype type 2 diabetic end-stage renal disease patients. Kidney Int. 2000, 58, 1742–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmatjes, E.; Fernandez, C.; Rueda, S.; Nicolau, J.; Chiganer, G.; Ricart, M.J.; Junca, E.; Fernández-Cruz, L. The utility of the C-peptide in the phenotyping of patient candidates for pancreas transplantation. Clin. Transplant. 2007, 21, 358–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Lovejoy, N.F.; Faustman, D.L. Persistence of prolonged C-peptide production in Type 1 diabetes as measured with an ultrasensitive C-peptide assay. Diabetes Care 2012, 35, 465–470. [Google Scholar]
- Dean, P.G.; Kudva, R.; Larson, T.S.; Kremers, W.K.; Stegall, M.D. Postransplant diabetes mellitus after pancreas transplantation. Am. J. Transplant. 2008, 8, 175–182. [Google Scholar]
- Egidi, M.F.; Lin, A.; Bratton, C.F.; Baliga, P.K. Prevention and management of hyperglycemia after pancreas transplantation. Curr. Opin. Organ. Transplant. 2008, 13, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neidlinger, N.; Singh, N.; Klein, C.; Odorico, J.; Del Rio, A.M.; Becker, Y.; Sollinger, H.; Pirsch, J. Incidence of and risk factors for posttransplant diabetes mellitus after pancreas transplantation. Am. J. Transplant. 2010, 10, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandaswamy, R.; Stock, P.G.; Skeans, M.A.; Gustafson, S.K.; Sleeman, E.F.; Wainright, J.L.; Carrico, R.J.; Ghimire, V.; Snyder, J.J.; Israni, A.K.; et al. OPTN/SRTR 2011 Annual Data Report: Pancreas. Am. J. Transplant. 2013, 13 (Suppl. S1), 47–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruessner, A.C. 2011 update on pancreas transplantation: Comprehensive trend analysis of 25,000 cases followed up over the course of twenty-four years at the International Pancreas Transplant Registry (IPTR). Rev. Diabet. Stud. 2011, 8, 6–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruessner, A.C.; Gruessner, R.W. Pancreas Transplantation of US and Non-US Cases from 2005 to 2014 as Reported to the United Network for Organ Sharing (UNOS) and the International Pancreas Transplant Registry (IPTR). Rev. Diabet. Stud. 2016, 13, 35–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Qaoud, T.; Redfield, R.; Odorico, J. The case for simultaneous pancreas and kidney (SPK) transplantation for obese T2DM patients. Rev. Diabet. Stud. 2017, 14, 103, IPITA Congress abstracts (PO1.4). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzanares, J.; Conget, I.; Gonzalez-Clemente, J.; Vidal, J.; Rodríguez-Villar, C.; Rojas, I.; Fernández-Fernández, F.; Casamitjana, R.; Gomis, R. Insulin treatment in diabetes mellitus type II: The usefulness of the breakfast test. Med. Clin. 1995, 104, 761–765. [Google Scholar]
- Gurram, V.; Gurung, K.; Rogers, J.; Farney, A.C.; Orlando, G.; Jay, C.; Reeves-Daniel, A.; Mena-Gutierrez, A.; Sakhovskaya, N.; Doares, W.; et al. Do pretransplant C-peptide levels influence outcomes in simultaneous pancreas-kidney transplantation? A matched case-control study. Clin. Transplant. 2021, 35, e14498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stratta, R.J.; Taylor, R.J.; Wahl, T.O.; Duckworth, W.C.; Gallagher, T.F.; Knight, T.F.; Fischer, J.L.; Neumann, T.V.; Miller, S.; Langnas, A.N.; et al. Recipient selection and evaluation for vascularized pancreas transplantation. Transplantation 1993, 55, 1090–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gross, C.R.; Limwattananon, C.; Matthees, B.J. Quality of life after pancreas transplantation: A review. Clin. Transplant. 1998, 12, 351–361. [Google Scholar]
- Sureshkumar, K.K.; Mubin, T.; Mikhael, N.; Kashif, M.A.; Nghiem, D.D.; Marcus, R.J. Assessment of quality of life after simultaneous pancreas-kidney transplantation. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2002, 39, 1300–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, J.T.; Baines, L.S.; Morris, M.C.; Jindal, R.M. Quality of life after kidney and pancreas transplantation: A review. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2003, 42, 431–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stratta, R.J. Pancreas transplantation: Long-term aspects and effect on quality of life. In Pancreas and Islet Transplantation; Hakim, N.S., Stratta, R.J., Gray, D., Eds.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2002; p. 229. [Google Scholar]
- Pera, P.I.; Vasallo, J.M.; Rabasa, A.T.; Salinas, F.O.; Pérez, L.F.C.; Brulles, M.J.R. Quality of life in simultaneous pancreas-kidney transplant recipients. Clin. Transplant. 2009, 23, 600–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, L.; Outerelo, C.; Malheiro, J.; Fonseca, I.M.; Henriques, A.C.; Dias, L.S.; Rodrigues, A.S.; Cabrita, A.M.; Noronha, I.L. Health-related quality of life may improve after transplantation in pancreas-kidney recipients. Clin. Transplant. 2015, 29, 242–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanlon, M.; Cooper, M.; Abrams, P. Quality of life after pancreas transplantation: Time to look again. Curr. Opin. Organ. Transplant. 2019, 24, 451–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Posegger, K.; Linhares, M.; Mucci, S.; Romano, T.M.; Gonzalez, A.M.; Netto, A.A.S.; Rangel, B.; Filho, G.D.J.L.; Silva-Junior, H.T.; Medina-Pestana, J. The quality of life in type 1 diabetic patients with end-stage kidney disease before and after simultaneous pancreas-kidney transplantation: A single center prospective study. Transplant. Int. 2020, 33, 330–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibbons, A.; Cinnirella, M.; Bayfield, J.; Watson, C.J.E.; Oniscu, G.C.; Draper, H.; Tomson, C.R.V.; Ravanan, R.; Johnson, R.J.; Forsythe, J.; et al. Changes in quality of life, health status and other patient-reported outcomes following simultaneous pancreas and kidney transplantation (SPKT): A quantitative and qualitative analysis within a UK-wide programme. Transplant. Int. 2020, 33, 1230–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nijhoff, M.; Hovens, J.G.F.M.; Huisman, S.D.; Ringers, J.; Rabelink, T.; de Fijter, H.J.; van der Boog, P.J.; de Koning, E.J. Psychological symptoms and quality of life after simultaneous kidney and pancreas transplantation. Transplant. Direct 2020, 6, e552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shingde, R.; Calis, V.; Craig, J.C.; Chapman, J.R.; Webster, A.C.; Pleass, H.; O’Connell, P.J.; Allen, R.; Robertson, P.; Yuen, L.; et al. Relative survival and quality of life benefits of pancreas-kidney transplantation, deceased kidney transplantation and dialysis in type 1 diabetes mellitus—A probabilistic simulation model. Transplant. Int. 2020, 33, 1393–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutherland, D.E.R.; Gruessner, R.W.G.; Dunn, D.L.; Matas, A.J.; Humar, A.; Kandaswamy, R.; Mauer, S.M.; Kennedy, W.R.; Goetz, F.C.; Robertson, R.P.; et al. Lessons learned from more than 1000 pancreas transplants at a single institution. Ann. Surg. 2001, 233, 463–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manske, C.L.; Thomas, W.; Wang, Y.; Wilson, R.F. Screening diabetic transplant candidates for coronary artery disease: Identification of a low risk subgroup. Kidney Int. 1993, 44, 617–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, K.; Stewart, D.; Cooper, S.; Davis, C.L. Pre-transplant cardiac testing for kidney-pancreas transplant candidates and association with cardiac outcomes. Clin. Transplant. 2001, 15, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, I.W.Y.; Valantine, H.A.; Shibata, A.; Waskerwitz, J.; Dafoe, D.C.; Alfrey, E.J.; Tan, J.C.; Millan, M.; Busque, S.; Scandling, J.D. Validation of a screening protocol for identifying low-risk candidates with type 1 diabetes mellitus for kidney with or without pancreas transplantation. Clin. Transplant. 2006, 20, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eller, K.; Kniepeiss, D.; Rosenkranz, A.R. Preoperative risk evaluation: Where is the limit for recipients of a pancreatic graft? Curr. Opin. Organ. Transplant. 2013, 18, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.W.; Masson, P.; Turner, R.M.; Lord, S.W.; Baines, L.A.; Craig, J.C.; Webster, A.C. Prognostic value of cardiac tests in potential kidney transplant recipients: A systematic review. Transplantation 2015, 99, 731–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knapper, J.T.; Raval, Z.; Harinstein, M.E.; Friedewald, J.J.; Skaro, A.I.; Abecassis, M.I.; Ali, Z.A.; Gheorghiade, M.; Flaherty, J.D. Assessment and management of coronary artery disease in kidney and pancreas transplant candidates. J. Cardiovasc. Med. 2019, 20, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangus, R.S.; Powelson, J.; Kinsella, S.B.; Farar, D.T.; Creal, C.A.; Fridell, J.A. Pretransplant coronary artery disease associated with worse clinical outcomes in pancreas transplantation. Clin. Transplant. 2013, 27, E442–E447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurence, J.M.; Barbas, A.S.; Sapisochin, G.; Marquez, M.A.; Bazerbachi, F.; Selzner, M.; Norgate, A.; McGilvray, I.D.; Schiff, J.; Ross, H.; et al. The significance of pre-operative coronary interventions on outcome after pancreas transplantation. Clin. Transplant. 2016, 30, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Schulman-Marcus, J.; Watkins, A.C.; Feldman, D.N.; Swaminathan, R.; Lee, J.B.; Muthukumar, T.; Serur, D.; Kim, L.; Hartono, C. In-hospital cardiovascular complications after pancreas transplantation in the United States from 2003 to 2012. Am. J. Cardiol. 2017, 129, 682–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hathaway, D.K.; El-Gebely, S.; Cardoso, S.; Elmer, D.S.; Gaber, A.O. Autonomic cardiac dysfunction in diabetic transplant recipients succumbing to sudden cardiac death. Transplantation 1995, 59, 634–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stratta, R.J. Mortality after vascularized pancreas transplantation. Surgery 1998, 124, 823–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freise, C.E.; Stock, P.G.; Melzer, J.S. Increased morbidity and mortality of simultaneous pancreas-renal transplantation in patients over 49 years of age. Transplant. Proc. 1998, 30, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ablorsu, E.; Ghazanfar, A.; Mehra, S.; Campbell, B.; Riad, H.; Pararajasingam, R.; Parrott, N.; Picton, M.; Augustine, T.; Tavakoli, A. Outcome of pancreas transplantation in recipients older than 50 years: A single-centre experience. Transplantation 2008, 86, 1511–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schenker, P.; Vonend, O.; Krüger, B.; Klein, T.; Michalski, S.; Wunsch, A.; Krämer, B.K.; Viebahn, R. Long-term results of pancreas transplantation in patients older than 50 years. Transplant. Int. 2011, 24, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afaneh, C.; Rich, B.S.; Aull, M.J.; Hartono, C.; Leeser, D.B.; Kapur, S. Pancreas transplantation: Does age increase morbidity? J. Transplant. 2011, 2011, 596801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.P.; Mangus, R.S.; Powelson, J.A.; Samy, K.P.; Taber, T.E.; Goble, M.L.; Fridell, J.A. Impact of recipient age on whole organ pancreas transplantation. Clin. Transplant. 2013, 27, E49–E55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siskind, E.; Maloney, C.; Akerman, M.; Alex, A.; Ashburn, S.; Barlow, M.; Siskind, T.; Bhaskaran, M.; Ali, N.; Basu, A.; et al. An analysis of pancreas transplantation outcomes based on age groupings—An update of the UNOS database. Clin. Transplant. 2014, 28, 990–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurence, J.M.; Marquez, M.A.; Seal, J.B.; Sapisochin, G.; Bazerbachi, F.; Selzner, M.; Norgate, A.; Greig, P.D.; McGilvray, I.; Schiff, J.; et al. The effect of recipient age on outcome after pancreas transplantation. Transplantation 2015, 99, e13–e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scalea, J.R.; Redfield, R.R., III; Arpali, E.; Leverson, G.; Sollinger, H.W.; Kaufman, D.B.; Odorico, J.S. Pancreas transplantation in older patients is safe, but patient selection is paramount. Transplant. Int. 2016, 29, 810–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schenker, P. The elderly pancreas transplant recipient. Transplant. Int. 2016, 29, 807–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, S.; Smilevska, R.; Franklin, R.; Hammer, C.; Knight, S.; Vrakas, G.; Reddy, S.; Gilbert, J.; Quiroga, I.; Sharples, E.; et al. An analysis of the association between older recipient age and outcomes after whole-organ pancreas transplantation—A single-centre retrospective study. Transplant. Int. 2020, 33, 529–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurung, K.; Alejo, J.; Rogers, J.; Farney, A.C.; Orlando, G.; Jay, C.; Reeves-Daniel, A.; Mena-Gutierrez, A.; Sakhovskaya, N.; Doares, W.; et al. Recipient age and outcomes following simultaneous pancreas-kidney transplantation in the new millennium: Single-center experience and review of the literature. Clin. Transplant. 2021, 38, e14302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bumgardner Gl Henry, M.L.; Elkhammas, E.; Wilson, G.A.; Tso, P.; Davies, E.; Qiu, W.; Ferguson, R.M. Obesity as a risk factor after combined pancreas/kidney transplantation. Transplantation 1995, 60, 1426–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, J.; Chavin, K.D.; Baliga, P.K.; Lin, A.; Emovon, O.; Afzal, F.; Ashcraft, E.E.; Baillie, G.M.; Taber, D.J.; Rajagopalan, P.R. Influence of mild obesity on outcome of simultaneous pancreas and kidney transplantation. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2003, 7, 1096–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanish, S.I.; Petersen, R.P.; Collins, B.H.; Tuttle-Newhall, J.; Marroquin, C.E.; Kuo, P.C.; Butterly, D.W.; Smith, S.R.; Desai, D.M. Obesity predicts increased overall complications following pancreas transplantation. Transplant. Proc. 2005, 37, 3564–3566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampaio, M.S.; Reddy, P.N.; Kuo, H.T.; Poommipanit, N.; Cho, Y.W.; Shah, T.; Bunnapradist, S. Obesity was associated with inferior outcomes in simultaneous pancreas kidney transplant. Transplantation 2010, 89, 1117–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afaneh, C.; Rich, B.; Aull, M.J.; Hartono, C.; Kapur, S.; Leeser, D.B. Pancreas transplantation considering the spectrum of body mass indices. Clin. Transplant. 2011, 25, E520–E529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fridell, J.A.; Mangus, R.S.; Tabor, T.E.; Goble, M.L.; Milgrom, M.L.; Good, J.; Vetor, R.; Powelson, J.A. Growth of a nation part II: Impact of recipient obesity on whole-organ pancreas transplantation. Clin. Transplant. 2011, 25, E366–E374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurence, J.M.; Marquez, M.A.; Bazerbachi, F.; Seal, J.B.; Selzner, M.; Norgate, A.; McGilvray, I.D.; Schiff, J.; Cattral, M.S. Optimizing pancreas transplantation outcomes in obese recipients. Transplantation 2015, 99, 1282–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedat, B.; Niclauss, N.; Jannot, A.S.; Andres, A.; Toso, C.; Morel, P.; Berney, T. Impact of recipient body mass index on short-term and long-term survival of pancreatic grafts. Transplantation 2015, 99, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porubsky, M.; Powelson, J.A.; Selzer, D.J.; Mujtaba, M.A.; Taber, T.; Carnes, K.L.; Fridell, J.A. Pancreas transplantation after bariatric surgery. Clin. Transplant. 2012, 26, E1–E6. [Google Scholar]
- Bonatti, H.; Schmitt, T.; Northup, J.; Schirmer, B.; Swenson, B.; Pruett, T.; Sawyer, R.; Brayman, K. Laparoscopic gastric banding in a kidney-pancreas transplant recipient with new onset type II diabetes mellitus associated with morbid obesity. Clin. Transplant. 2008, 22, 829–832. [Google Scholar]
- Zelones, J.; Biswas, O.; Mehran, A. Laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy after simultaneous pancreas-kidney transplant. Am. Surg. 2012, 78, 613–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elli, E.F.; Gonzalez-Heredia, R.; Sanchez-Johnsen, L.; Patel, N.; Garcia-Roca, R.; Oberholzer, J. Sleeve gastrectomy surgery in obese post-organ transplantation. Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. 2016, 12, 528–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boggi, U.; Signori, S.; Vistoli, F.; Amorese, G.; Consani, G.; De Lio, N.; Perrone, V.; Croce, C.; Marchetti, P.; Cantarovich, D.; et al. Current perspectives on laparoscopic robot-assisted pancreas and pancreas-kidney transplantation. Rev. Diabet. Stud. 2011, 8, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeh, C.C.; Spaggiari, M.; Tzvetanov, I.; Oberholzer, J. Robotic pancreas transplantation in a type 1 diabetic patient with morbid obesity: A case report. Medicine 2017, 96, e5847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantrell, L.A.; Oberholzer, J. Robotic pancreas transplantation: The state of the art. Curr. Opin. Organ. Transplant. 2018, 23, 423–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaacs, R.; Lobo, P.I.; Nock, S.L.; Hanson, J.A.; Ojo, A.O.; Pruett, T.L. Racial disparities in access to simultaneous pancreas-kidney transplantation. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2000, 36, 526–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, C.Y.; Gaston, R.S. Renal transplantation in Black Americans. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 343, 1545–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, C.Y.; Kew, C. Health disparities in transplantation: Focus on complexity and challenge of renal transplantation in African Americans. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2005, 89, 1003–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melancon, J.K.; Kucirka, L.M.; Boulware, L.E.; Powe, N.R.; Locke, J.E.; Montgomery, R.A.; Segev, D.L. Impact of Medicare coverage on disparities in access to simultaneous pancreas and kidney transplantation. Am. J. Transplant. 2009, 9, 2785–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Crook, E.D.; Patel, S.R. Diabetic nephropathy in African-American patients. Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2004, 4, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirk, J.K.; D’Agostino, R.B., Jr.; Bell, R.A.; Passmore, L.V.; Bonds, D.E.; Karter, A.J.; Narayan, K.M. Disparities in HbA1c levels between African-American and non-Hispanic White adults with diabetes: A meta-analysis. Diabetes Care 2006, 29, 2130–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douzdjian, V.; Bhaskar, S.S.; Baliga, P.K.; Gugliuzza, K.; Rajagopalan, P.R. Effect of race on outcome after kidney and kidney-pancreas transplantation in type 1 diabetic patients. Diabetes Care 1997, 20, 1310–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douzdjian, V.; Thacker, L.R.; Blanton, J.W. Effect of race on outcome following kidney-pancreas transplantation in type 1 diabetics: The South-Eastern Organ Procurement Foundation experience. Clin. Transplant. 1997, 11, 470–475. [Google Scholar]
- Burke, G.W.; Ciancio, G.; Colona, J.; Roth, D.; Miller, J. African-Americans with type 1 insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus and end stage renal disease: Results after simultaneous pancreas kidney transplantation. Transplant. Proc. 1997, 29, 3715–3716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, A.; Stratta, R.J.; Egidi, M.F.; Shokouh-Amiri, M.H.; Grewal, H.P.; Kizilisik, A.T.; Alloway, R.R.; Gaber, L.W.; Gaber, A.O. Outcome of simultaneous kidney-pancreas transplantation in African-American recipients: A case control study. Transplant. Proc. 2001, 33, 1675–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, J.; Baliga, P.K.; Chavin, K.D.; Lin, A.; Emovon, O.; Afzal, F.; Baillie, G.M.; Ashcraft, E.E.; Rajagopalan, P.R. Effect of ethnicity on outcome of simultaneous pancreas and kidney transplantation. Am. J. Transplant. 2003, 3, 1278–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, J.; Stratta, R.J.; Alloway, R.R.; Lo, A.; Hodge, E. African-American ethnicity is no longer a risk factor for early adverse outcomes in simultaneous kidney-pancreas transplantation with contemporary immunosuppression. Transplant. Proc. 2004, 36, 1055–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, J.; Stratta, R.J.; Lo, A.; Alloway, R.R. Inferior late functional and metabolic outcomes in African American simultaneous kidney-pancreas recipients. Transplant. Proc. 2005, 37, 3552–3554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Florman, S.; Devidoss, S.; Zarifian, A.; Yau, C.L.; Paramesh, A.; Killackey, M.; Alper, B.; Fonseca, V.; Slakey, D. A comparison of long-term survivals of simultaneous pancreas-kidney transplant between African American and Caucasian recipients with basiliximab induction therapy. Am. J. Transplant. 2007, 7, 1815–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Florman, S.; Paramesh, A.; Islam, T.; Zarifian, A.; Simon, E.; Hamm, L.L.; Slakey, D. Pancreas transplantation in African American patients undergoing basiliximab induction. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2009, 337, 307–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, F.L.; Kommareddi, M.; Cibrik, D.M.; Samaniego, M.; Ojo, A.O. Influence of recipient race on the outcome of simultaneous pancreas and kidney transplantation. Am. J. Transplant. 2010, 10, 2074–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooks, J.T.; Liu, R.; Oliver, M.; DeLeonibus, A.; Mei, J.; White, D.; Siskind, E.; Ortiz, J. Simultaneous pancreas and kidney transplantation is associated with inferior long-term outcomes in African Americans. Pancreas 2018, 47, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, C.J.; MacLennan, P.A.; Mannon, E.C.; Reed, R.D.; Shelton, B.A.; Hanaway, M.J.; Agarwal, G.; Gaston, R.S.; Julian, B.A.; Kew, C.E.; et al. Redefining the influence of ethnicity on simultaneous kidney-pancreas transplantation outcomes. Ann. Surg. 2020, 271, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzales, H.M.; Taber, D.J.; Nadig, S.; Patel, N.; Lin, A.; Baliga, P.K.; Rohan, V.S. The impact of race on metabolic, graft, and patient outcomes after pancreas transplantation. Am. J. Surg. 2022, 223, 812–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Xiang, J.; Liu, J.; Wang, L. Race does not predict pancreas graft failure after pancreas transplantation in the modern era. Clin. Transplant. 2022, 36, e14576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McElroy, L.; Fridell, J. Impact of race on pancreas transplant outcomes in the current era: It is not all black and white. Clin. Transplant. 2022, 36, e14615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, J.; Jay, C.J.; Farney, A.C.; Orlando, G.; Jacobs, M.L.; Harriman, D.; Gurram, V.; Sharda, B.; Gurung, K.; Reeves-Daniel, A.; et al. Simultaneous pancreas-kidney transplantation in Caucasian versus African-American patients: Does recipient race influence outcomes. Clin. Transplant. 2022, 36, e14599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feyssa, E.; Jones-Burton, C.; Ellison, G.; Philosophe, B.; Howell, C. Racial-ethnic disparity in kidney transplantation outcomes: Influence of donor and recipient characteristics. J. Natl. Med. Assoc. 2009, 101, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciancio, G.; Burke, G.W.; Gomez, C.; Olson, L.; Esquenazi, V.; Miller, J. Simultaneous pancreas-kidney transplantation in Hispanic recipients with type 1 diabetes mellitus and end-stage renal disease. Transplant. Proc. 1997, 29, 3717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perosa, M.; Boggi, U.; Cantarovich, D.; Robertson, P. Pancreas transplantation outside the USA: An update. Curr. Opin. Organ. Transplant. 2011, 16, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishibashi, M.; Ito, T.; Sugitani, A.; Furukawa, H.; Sekiguchi, S.; Gotoh, M.; Teraoka, S.; Sato, Y.; Matsuno, N.; Kenmochi, S.; et al. Present status of pancreas transplantation in Japan: Donation predominantly from marginal donors and modified surgical technique—Report of Japan pancreas transplantation registry. Transplant. Proc. 2008, 40, 486–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perosa, M.; Crescentini, F.; Noujaim, H.; Mota, L.T.; Branez, J.R.; Ianhez, L.E.; Ferreira, G.; de Oliveira, R.A.; Genzini, T. Over 500 pancreas transplants by a single team in Sao Paulo, Brazil. Clin. Transplant. 2011, 25, E422–E429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.Y.; Jung, J.H.; Shin, S.; Kim, Y.H.; Han, D.J. Association between the pancreas transplantation and survival of patients with diabetes: A single center experience. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0186827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruessner, A.C.; Gruessner, R.W.G. Long-term outcome after pancreas transplantation: A registry analysis. Curr. Opin. Organ. Transplant. 2016, 21, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odorico, J.S.; Heisey, D.M.; Voss, B.J.; Steiner, D.; Knechtle, S.; D’Alessandro, A.; Hoffmann, R.; Sollinger, H. Donor factors affecting outcome after pancreas transplantation. Transplant. Proc. 1998, 30, 276–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boggi, U.; Del Chiaro, M.; Signori, S.; Vistoli, F.; Amorese, G.; Croce, C.; Morelli, L.; Bartolo, T.V.; Pietrabissa, A.; Barsotti, M.; et al. Pancreas transplants from donors aged 45 years or older. Transplant. Proc. 2005, 37, 1265–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvalaggio, P.R.; Schnitzler, M.A.; Abbott, K.C.; Brennan, D.C.; Irish, W.; Takemoto, S.K.; Axelrod, D.; Santos, L.S.; Kocak, B.; Willoughby, L.; et al. Patient and graft survival implications of simultaneous pancreas kidney transplantation from old donors. Am. J. Transplant. 2007, 7, 1561–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schenker, P.; Wunsch, A.; Ertas, N.; Schaeffer, M.; Rump, L.; Viebahn, R.; Vonend, O. Long-term results after simultaneous pancreas-kidney transplantation using donors aged 45 years or older. Transplant. Proc. 2008, 40, 923–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fridell, J.A.; Rogers, J.; Stratta, R.J. The Pancreas Allograft Donor: Current Status, Controversies, and Challenges for the Future. Clin. Transplant. 2010, 24, 433–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Axelrod, D.A.; Sung, R.S.; Meyer, K.H.; Wolfe, R.A.; Kaufman, D.B. Systematic evaluation of pancreas allograft quality, outcomes and geographic variation in utilization. Am. J. Transplant. 2010, 10, 837–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finger, E.B.; Radosevich, D.M.; Dunn, T.B.; Chinnakotla, S.; Sutherland, D.E.; Matas, A.J.; Pruett, T.L.; Kandaswamy, R. A composite risk model for predicting technical failure in pancreas transplantation. Am. J. Transplant. 2013, 13, 1840–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kayler, L.K.; Wen, X.; Zachariah, M.; Casey, M.; Schold, J.; Magliocca, J. Outcomes and survival analysis of old-to-old simultaneous pancreas and kidney transplantation. Transplant. Int. 2013, 26, 963–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arenas-Bonilla, A.J.; Campos-Hernandez, J.P.; Carrasco-Valiente, J.; Márquez-López, F.; Ruiz-García, J.; Sánchez-Gónzalez, A.; Salamanca-Bustos, J.; Regueiro-López, J.; Navarro-Cabello, M.; Requena-Tapia, M. Influence of donor and recipient ages in survival of simultaneous pancreas-kidney transplantation. Transplant. Proc. 2016, 48, 3033–3036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proneth, A.; Schnitzbauer, A.A.; Schenker, P.; Wunsch, A.; Rauchfuss, F.; Arbogast, H.; Manekeller, S.; Nadalin, S.; Heise, M.; Ströhlein, M.A.; et al. Extended pancreas donor program—The EXPAND study: A prospective multicenter trial testing the use of pancreas donors older than 50 years. Transplantation 2018, 102, 1330–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mensink, J.W.; de Vries, K.M.; Huurman, V.A.L.; Pol, R.A.; Alwayn, I.P.; Braat, A.E. Risk analysis of extended pancreas donor selection criteria. Pancreatology 2019, 19, 994–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, T.; Kenmochi, T.; Aida, N.; Kurihara, K.; Asaoka, T.; Ito, T. Are the outcomes of Japanese pancreas transplantation utilizing extended-criteria donors acceptable? A propensity score matching analysis for donors < 50 or ≥50 years old. Transplant. Int. 2020, 33, 1046–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruessner, A.; Laftavi, M.; Pankewycz, O.; Gruessner, R. Pancreas transplants in the elderly patient: Should it be done? Am. J. Transplant. 2018, 18 (Suppl. S4), 391. [Google Scholar]
- Meier, R.P.H.; Noguchi, H.; Kelly, Y.M.; Sarwal, M.; Conti, G.; Ward, C.; Halleluyan, R.; Tavakol, M.; Stock, P.G.; Freise, C.E. Impact of sarcopenia on simultaneous pancreas and kidney transplantation outcomes: A retrospective observational cohort study. Transplant. Direct 2020, 6, e610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lentine, K.L.; Alhamad, T.; Cheungpasitporn, W.; Tan, J.C.; Chang, S.H.; Cooper, M.; Dadhania, D.M.; Axelrod, D.A.; Schnitzler, M.A.; Ouseph, R.; et al. Impact of functional status on outcomes of simultaneous pancreas-kidney transplantation: Risks and opportunities for patient benefit. Transplant. Direct 2020, 6, e599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuda, Y.; Asaoka, T.; Eguchi, H.; Sasaki, K.; Iwagami, Y.; Yamada, D.; Noda, T.; Kawamoto, K.; Gotoh, K.; Kobayashi, S.; et al. Clinical impact of preoperative sarcopenia on the postoperative outcomes after pancreas transplantation. World J. Surg. 2018, 42, 3364–3371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landi, F.; Onder, G.; Bernabei, R. Sarcopenia and diabetes: Two sides of the same coin. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2013, 14, 540–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rana, A.; Gruessner, A.; Agopian, V.G.; Khalpey, Z.; Riaz, I.B.; Kaplan, B.; Halazun, K.J.; Busuttil, R.W.; Gruessner, R.W.G. Survival benefit of solid-organ transplant in the United States. JAMA Surg. 2015, 150, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parajuli, S.; Mandelbrot, D.A. One more time, emphasizing the advantage of simultaneous pancreas and kidney transplantation for patients with type 1 diabetes and end-stage renal disease. Transplant. Int. 2020, 33, 1384–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunn, T.B. Life after pancreas transplantation: Reversal of diabetic lesions. Curr. Opin. Organ. Transplant. 2014, 19, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Dellen, D.; Worthington, J.; Mitu-Pretorian, O.M.; Ghazanfar, A.; Forgacs, B.; Pararajasingam, R.; Campbell, B.; Parrott, N.R.; Augustine, T.; Tavakoli, A. Mortality in diabetes: Pancreas transplantation is associated with significant survival benefit. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2013, 28, 1315–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, B.N.; Brazy, P.C.; Becker, Y.T.; Odorico, J.S.; Pintar, T.J.; Collins, B.H.; Pirsch, J.D.; Leverson, G.E.; Heisey, D.M.; Sollinger, H.W. Simultaneous pancreas-kidney transplantation reduces excess mortality in type 1 diabetic patients with end-stage renal disease. Kidney Int. 2000, 57, 2129–2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).