Liver Cirrhosis: Evolving Definitions, and Recent Advances in Diagnosis, Prevention and Management
Abstract
1. Liver Cirrhosis—Causes, Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, Natural History, Clinical Complications, and Prognostic Scores
1.1. Novel Concepts of Decompensation of Liver Cirrhosis
1.2. Causes of Cirrhosis
1.3. Burden of Liver Cirrhosis
1.4. Pathophysiology of Liver Cirrhosis
1.5. Diagnosing Cirrhosis
| (A) Imaging-based non-invasive liver disease assessment of hepatic fibrosis, steatosis, and portal hypertension | |||||
| Imaging Modality | Components | Aetiology of Liver Disease | Evidence | Comments | |
| Ultrasonography | Hepatic nodularity, signs of portal hypertension | All | Well-validated |
| |
| CT/MRI | Hepatic nodularity, signs of portal hypertension | All | Well-validated |
| |
| Transient elastography (FibroScan) | Liver stiffness measurement | All | Well-validated but exact cut-offs for specific fibrosis stages and causes not established. |
| |
| Acoustic radiation force impulse imaging | Liver stiffness measurement | All | Moderate validation in single etiology CLD with histology as reference standard |
| |
| Magnetic resonance elastography (MRE) | Liver stiffness measurement | All | Limited validation in single etiology CLD with histology as reference standard |
| |
| (B) Blood-based biomarker algorithms for fibrosis | |||||
| Indirect serum non-invasive fibrosis tests | Component | Etiology of liver disease | Model algorithm | year | Comments |
| Fibroindex [112] | Indirect markers: AST, platelets, gamma globulin | HCV | 1.738 − 0.064 (platelet [×104/mm3]) + 0/005 (AST IU/L) + 0.463 (gamma globulin [g/Dl]) | 2007 |
|
| King’s Score [113] | Indirect markers: AST, INR, platelets. Clinical variable: Age | HCV | Age × AST × INR/[platelet count (109/L)] | 2009 |
|
| APRI [114] | Indirect markers: AST, platelets | HBV, HCV | [(AST level/ULN)/platelet count (109/L)] × 100 | 2003 |
|
| Fibrosis-4 Index (FIB-4) [106] | Indirect markers: AST, ALT, platelets; clinical variable: age | HBV, HCV, MASLD | Age (y) × AST (U/L) Platelet count (109/L) × √ALT (U/L) | 2006 |
|
| NAFLD Fibrosis Score (NFS) [115] | Indirect markers: AST, ALT, platelets, albumin, Clinical variables: Age, BMI, IFG/diabetes | MASLD | −1.675 + (0.037 × age) + (0.094 × BMI) + 1.13 × IFG/diabetes (yes = 1, no = 0) + 0.99 × (AST/ALT ratio) − (0.013 × platelets) − (0.66 × albumin) | 2007 |
|
| Easy Liver Fibrosis Test (eLIFT) [116] | Indirect markers: GGT, AST, platelets, prothrombin index | HBV, HCV, MASLD, ALD | Component weighted scores (0–4) | 2017 |
|
| AST/ALT [117,118,119] | Indirect markers: AST, ALT | HBV, HCV, MASLD, ALD | (AST/AST upper limit of normal)/Platelet count × 100 | - |
|
| Forns Index [120] | Indirect markers: GGT, Cholesterol, platelets | HBV, HCV | 7.811 − 3.131 × ln [platelets (mm3)/1000] + 0.781 × ln [GGT (IU/L)] + 3.467 × ln [age] − 0.014 × [cholesterol (mg/dL)] | 2002 |
|
| (C) Proprietary blood-based NILDA | |||||
| FibroSureTM/FibroTest® [121] | Indirect markers: α2M, GGT, total bilirubin, haptoglobin, ApoA-I | HBV, HCV, MASLD, ALD | Proprietary Biopredictive, France | 2001 |
|
| ELFTM [122] | Direct markers: HA, PIIINP, TIMP-1, Clinical variable: Age | HBV, HCV, MASLD | Proprietary Siemens, UK | 2004 |
|
| HepascoreTM [123,124] | Direct marker: HA, TIMP-1, Clinical variable: α2M | HCV, MASLD | Proprietary Pathwest, Australia | 2005 |
|
| Fibrospect IITM [124,125] | Direct marker: HA, Indirect markers: Total bilirubin, α2M, GGT, Clinical variable: Age, Sex | HCV | Proprietary Prometheus, USA | 2004 |
|
| FibroMeterTM [124] | Direct marker: HA, Indirect marker: Platelets, prothrombin index, urea, AST, α2M, Clinical variable: Age | HBV, HCV, MASLD, ALD | Proprietary BioLiveScale, France | 2005 |
|
| Test | Rule Out Fibrosis | Rule in Fibrosis Stage 2 | Rule in Fibrosis Stage 3 or 4 |
|---|---|---|---|
| FIB-4 | <1.3 | 2.67–3.25 | >3.25 |
| NAFLD cirrhosis score (NFS) | <1.455 | Not established | >0.676 |
| Fibro test | <0.31 | 0.48–0.72 | >0.72 |
| ELF | <7.7 | 9.8–10.5 | 10.5 |
| Transient elastography | <6 kPa | 8 kPa–12 kPa | >12 kPa |
| AST/ALT ratio | <0.5 (F0–F1) | 0.5–1.0 | >1.0 |
1.6. Special Considerations: Impact of COVID-19 Pandemic and Cirrhosis
1.7. Diagnosing Clinically Significant Portal Hypertension
1.8. Screening for HCC
1.9. Prognostic Scores
1.10. ACLF and ACLF Scores and FIPS
2. Management of Liver Cirrhosis
2.1. General Considerations
2.2. Portal Hypertension Complications and Management
3. The Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt
3.1. TIPS
3.2. Physiological Effects of TIPS
4. Cirrhosis Complications and Management
4.1. Ascites
4.1.1. Albumin in Refractory Ascites
4.1.2. TIPS and LT in Refractory Ascites
4.2. Muscle Cramps
4.3. Hyponatraemia
4.4. Bacterial Infections and Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis
4.5. Portal Hypertension-Related Bleeding
Approach to Variceal Bleeding
4.6. Hepatic Encephalopathy
4.7. Acute Kidney Injury and Hepatorenal Syndrome
4.8. Sarcopenia
4.9. Hepatopulmonary Syndrome
5. Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
List of Abbreviations
| ACLF | Acute-on-chronic-liver failure |
| AD | Acute decompensation of cirrhosis |
| AFP | Alpha-fetoprotein |
| AKD | Acute kidney disease |
| AKI | Acute kidney injury |
| ALD | Alcohol related liver disease |
| ALT | Alanine aminotransferase |
| APoA-1 | Apolipoprotein A-1 |
| AST | Aspartate aminotransferase |
| AUD | Alcohol use disorder |
| AVB | Acute variceal bleeding |
| BATO | Balloon-occluded antegrade transvenous obliteration |
| BRTO | Balloon-occluded RTO |
| cACLD | Compensated advanced chronic liver disease |
| CKD | Chronic kidney disease |
| CLD | Chronic liver disease |
| CLIF-C ACLF | Chronic Liver Failure Consortium Acute-on-chronic liver failure |
| CLIF-C AD | Chronic Liver Failure-Consortium Acute Decompensation |
| COVID-19 | Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) |
| CSPH | Clinically significant portal hypertension |
| CTP | Child–Turcotte–Pugh |
| eLIFT | Easy liver fibrosis |
| EV | Esophageal varices |
| EVL | Endoscopic variceal ligation |
| FIB-4 | Fibrosis-4 index |
| FIPS | The Freiburg index of post-TIPS survival |
| GasD | Gasdermin D |
| GEV | Gastroesophageal varices |
| HA | Hyaluronic acid |
| HBV | Hepatitis B virus |
| HCC | Hepatocellular carcinoma |
| HCV | Hepatitis C virus |
| HE | Hepatic encephalopathy |
| HPS | Hepatopulmonary syndrome |
| HRS | Hepatorenal syndrome |
| HVPG | Hepatic venous pressure gradient |
| IFG | Impaired fasting glucose |
| IGF-1 | Insulin-like growth factor-1 |
| IGV1 | Isolated gastric varices type 1 |
| IGV2 | Isolated gastric varices type 2 |
| INCPH | Idiopathic non-cirrhotic portal hypertension |
| INR | Internationalized normal ratio (also known as prothrombin time) |
| kPa | Kilopascal |
| LT | Liver transplantation |
| LVP | Large volume paracentesis |
| MASH | Metabolic-associated steatohepatitis |
| MASLD | Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease |
| MELD | Model for End-Stage Liver Disease |
| MELD-Na | Model for End-Stage Liver Disease-Sodium |
| MRI | Magnetic resonance imaging |
| NFS | NAFLD fibrosis score |
| NSBBs | Non-selective beta-blockers |
| OLT | Orthotopic liver transplantation |
| PBC | Primary biliary cirrhosis |
| PH | Portal hypertension |
| PHES | Psychometric hepatic encephalopathy score |
| PICD | Paracentesis-induced circulatory dysfunction |
| PIIINP | Amino-terminal propeptide of type III procollagen |
| POPH | Portopulmonary hypertension |
| PPI | Proton pump inhibitors |
| PT | Prothrombin time |
| RA | Refractory ascites |
| RIPK3 | Receptor-interacting serine/threonine protein kinase 3 |
| SBP | Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis |
| sCr | Serum creatinine |
| TE | Transient elastography |
| TIMP-1 | Tissue inhibitor matrix metalloproteinase 1 |
| TIPS | Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt |
| VCTE | Vibration-controlled transient elastography |
| α2M | α2-macroglobulin |
References
- Devarbhavi, H.; Asrani, S.K.; Arab, J.P.; Nartey, Y.A.; Pose, E.; Kamath, P.S. Global burden of liver disease: 2023 update. J. Hepatol. 2023, 79, 516–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GCoD Collaborators. Global, regional, and national age-sex-specific mortality for 282 causes of death in 195 countries and territories, 1980–2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet 2018, 392, 1736–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, D.Q.; Terrault, N.A.; Tacke, F.; Gluud, L.L.; Arrese, M.; Bugianesi, E.; Loomba, R. Global epidemiology of cirrhosis—Aetiology, trends and predictions. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 20, 388–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalo, E.; Read, S.; Ahlenstiel, G. Targeting Gut–Liver Axis for Treatment of Liver Fibrosis and Portal Hypertension. Livers 2021, 1, 147–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papavramidou, N.; Fee, E.; Christopoulou-Aletra, H. Jaundice in the Hippocratic Corpus. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2007, 11, 1728–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginès, P.; Krag, A.; Abraldes, J.G.; Solà, E.; Fabrellas, N.; Kamath, P.S. Liver cirrhosis. Lancet 2021, 398, 1359–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’AMico, G.; Morabito, A.; D’AMico, M.; Pasta, L.; Malizia, G.; Rebora, P.; Valsecchi, M.G. Clinical states of cirrhosis and competing risks. J. Hepatol. 2018, 68, 563–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Tsao, G.; Friedman, S.; Iredale, J.; Pinzani, M. Now there are many (stages) where before there was one: In search of a pathophysiological classification of cirrhosis. Hepatology 2010, 51, 1445–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Franchis, R.; Bosch, J.; Garcia-Tsao, G.; Reiberger, T.; Ripoll, C. Baveno VII—Renewing consensus in portal hypertension. J. Hepatol. 2022, 76, 959–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trebicka, J.; Fernandez, J.; Papp, M.; Caraceni, P.; Laleman, W.; Gambino, C.; Giovo, I.; Uschner, F.E.; Jimenez, C.; Mookerjee, R.; et al. The PREDICT study uncovers three clinical courses of acutely decompensated cirrhosis that have distinct pathophysiology. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 842–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’AMico, G.; Garcia-Tsao, G.; Pagliaro, L. Natural history and prognostic indicators of survival in cirrhosis: A systematic review of 118 studies. J. Hepatol. 2006, 44, 217–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ginés, P.; Quintero, E.; Arroyo, V.; Terés, J.; Bruguera, M.; Rimola, A.; Caballería, J.; Rodés, J.; Rozman, C. Compensated cirrhosis: Natural history and prognostic factors. Hepatology 1987, 7, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arroyo, V.; Moreau, R.; Jalan, R. Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 2137–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goble, S.R.; Ismail, A.S.; Debes, J.D.; Leventhal, T.M. Critical care outcomes in decompensated cirrhosis: A United States national inpatient sample cross-sectional study. Crit. Care 2024, 28, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughn-Sandler, V.; Sherman, C.; Aronsohn, A.; Volk, M.L. Consequences of Perceived Stigma Among Patients with Cirrhosis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2013, 59, 681–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valery, P.C.; Clark, P.J.; Pratt, G.; Bernardes, C.M.; Hartel, G.; Toombs, M.; Irvine, K.M.; Powell, E.E. Hospitalisation for cirrhosis in Australia: Disparities in presentation and outcomes for Indigenous Australians. Int. J. Equity Health 2020, 19, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’aMico, G.; Morabito, A.; D’aMico, M.; Pasta, L.; Malizia, G.; Rebora, P.; Valsecchi, M.G. New concepts on the clinical course and stratification of compensated and decompensated cirrhosis. Hepatol. Int. 2017, 12, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonon, M.; D’aMbrosio, R.; Calvino, V.; Tosetti, G.; Barone, A.; Incicco, S.; Gambino, C.; Gagliardi, R.; Borghi, M.; Zeni, N.; et al. A new clinical and prognostic characterization of the patterns of decompensation of cirrhosis. J. Hepatol. 2023, 80, 603–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreau, R.; Jalan, R.; Gines, P.; Pavesi, M.; Angeli, P.; Cordoba, J.; Durand, F.; Gustot, T.; Saliba, F.; Domenicali, M.; et al. Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure Is a Distinct Syndrome That Develops in Patients With Acute Decompensation of Cirrhosis. Gastroenterology 2013, 144, 1426–1437.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farias, A.Q.; Vilalta, A.C.; Zitelli, P.M.; Pereira, G.; Goncalves, L.L.; Torre, A.; Diaz, J.M.; Gadano, A.C.; Mendes, L.S.; Alvares-Da-Silva, M.R.; et al. Genetic Ancestry, Race, and Severity of Acutely Decompensated Cirrhosis in Latin America. Gastroenterology 2023, 165, 696–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, N.; Kaur, P.; Garg, P.; Ranjan, V.; Ralmilay, S.; Rathi, S.; De, A.; Premkumar, M.; Taneja, S.; Roy, A.; et al. Clinical and Pathophysiological Characteristics of Non-Acute Decompensation of Cirrhosis. J. Hepatol. 2025, in press. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GBD 2019 Diseases and Injuries Collaborators. Global burden of 369 diseases and injuries in 204 countries and territories, 1990–2019: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet 2020, 396, 1204–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Australian Bureau of Statistics. Causes of Death, Australia, 2023. 2024. Available online: https://www.abs.gov.au/statistics/health/causes-death/causes-death-australia/2023 (accessed on 25 May 2025).
- Asrani, S.K.; Devarbhavi, H.; Eaton, J.; Kamath, P.S. Burden of liver diseases in the world. J. Hepatol. 2019, 70, 151–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GBDD Collaborators. Global age-sex-specific fertility, mortality, healthy life expectancy (HALE), and population estimates in 204 countries and territories, 1950–2019: A comprehensive demographic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet 2020, 396, 1160–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jepsen, P.; Younossi, Z.M. The global burden of cirrhosis: A review of disability-adjusted life-years lost and unmet needs. J. Hepatol. 2021, 75, S3–S13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.-N.; Xue, F.; Zhang, N.; Zhang, W.; Hou, J.-J.; Lv, Y.; Xiang, J.-X.; Zhang, X.-F. Global burden of liver cirrhosis and other chronic liver diseases caused by specific etiologies from 1990 to 2019. BMC Public Health 2024, 24, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. WHO Sounds Alarm on Viral Hepatitis Infections Claiming 3500 Lives Each Day. 2024. Available online: https://www.who.int/news/item/09-04-2024-who-sounds-alarm-on-viral-hepatitis-infections-claiming-3500-lives-each-day (accessed on 15 April 2025).
- World Health Organization. Global Hepatitis Report 2024: Action for Access in Low- and Middle-Income Countries; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, V.L.; Yeh, M.; Le, A.K.; Jun, M.; Saeed, W.K.; Yang, J.D.; Huang, C.; Lee, H.Y.; Tsai, P.; Lee, M.; et al. Anti-viral therapy is associated with improved survival but is underutilised in patients with hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma: Real-world east and west experience. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 48, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, D.-Y.; Li, J.-M.; Lin, S.; Dong, X.; You, J.; Xing, Q.-Q.; Ren, Y.-D.; Chen, W.-M.; Cai, Y.-Y.; Fang, K.; et al. Global burden of acute viral hepatitis and its association with socioeconomic development status, 1990–2019. J. Hepatol. 2021, 75, 547–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghany, M.G.; Morgan, T.R.; Panel, A.-I.H.C.G. Hepatitis C Guidance 2019 Update: American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases-Infectious Diseases Society of America Recommendations for Testing, Managing, and Treating Hepatitis C Virus Infection. Hepatology 2020, 71, 686–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver. Electronic address eee, Clinical Practice Guidelines Panel C, representative EGB, Panel m. EASL recommendations on treatment of hepatitis C: Final update of the series(☆). J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 1170–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Global Status Report on Alcohol and Health; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Arab, J.P.; Addolorato, G.; Mathurin, P.; Thursz, M.R. Alcohol-Associated Liver Disease: Integrated Management With Alcohol Use Disorder. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 21, 2124–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narro, G.E.C.; Díaz, L.A.; Ortega, E.K.; Garín, M.F.B.; Reyes, E.C.; Delfin, P.S.M.; Arab, J.P.; Bataller, R. Alcohol-related liver disease: A global perspective. Ann. Hepatol. 2024, 29, 101499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avila, M.A.; Dufour, J.F.; Gerbes, A.L.; Zoulim, F.; Bataller, R.; Burra, P.; Cortez-Pinto, H.; Gao, B.; Gilmore, I.; Mathurin, P.; et al. Recent advances in alcohol-related liver disease (ALD): Summary of a Gut round table meeting. Gut 2019, 69, 764–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, E.; Cruz-Lemini, M.; Altamirano, J.; Ndugga, N.; Couper, D.; Abraldes, J.G.; Bataller, R. Heavy daily alcohol intake at the population level predicts the weight of alcohol in cirrhosis burden worldwide. J. Hepatol. 2016, 65, 998–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslam, M.; Sanyal, A.J.; George, J.; on behalf of theInternational Consensus Panel. MAFLD: A Consensus-Driven Proposed Nomenclature for Metabolic Associated Fatty Liver Disease. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 1999–2014.e1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Koenig, A.B.; Abdelatif, D.; Fazel, Y.; Henry, L.; Wymer, M. Global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease-Meta-analytic assessment of prevalence, incidence, and outcomes. Hepatology 2016, 64, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riazi, K.; Azhari, H.; Charette, J.H.; Underwood, F.E.; King, J.A.; Afshar, E.E.; Swain, M.G.; Congly, S.E.; Kaplan, G.G.; Shaheen, A.A. The prevalence and incidence of NAFLD worldwide: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 7, 851–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas, 10th ed.; International Diabetes Federation: Brussels, Belgium, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Obesity and Overweight; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Anstee, Q.M.; Marietti, M.; Hardy, T.; Henry, L.; Eslam, M.; George, J.; Bugianesi, E. Global burden of NAFLD and NASH: Trends, predictions, risk factors and prevention. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 15, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estes, C.; Razavi, H.; Loomba, R.; Younossi, Z.; Sanyal, A.J. Modeling the epidemic of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease demonstrates an exponential increase in burden of disease. Hepatology 2018, 67, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Australian Institute of Health Welfare (AIHW). Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Health Performance Framework 2010 Report; AIHW: Canberra, Australia, 2011.
- European Association for the Study of the Liver (EASL); European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD); European Association for the Study of Obesity (EASO). EASL-EASD-EASO Clinical Practice Guidelines on the management of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD). J. Hepatol. 2024, 81, 492–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, P.J.; Bowlus, C.L.; Yimam, K.K.; Razavi, H.; Estes, C. Epidemiology, Natural History, and Outcomes of Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis: A Systematic Review of Population-based Studies. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 20, 1687–1700.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barberio, B.; Massimi, D.; Cazzagon, N.; Zingone, F.; Ford, A.C.; Savarino, E.V. Prevalence of Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis in Patients With Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Gastroenterology 2021, 161, 1865–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izquierdo-Sanchez, L.; Lamarca, A.; La Casta, A.; Buettner, S.; Utpatel, K.; Klümpen, H.-J.; Adeva, J.; Vogel, A.; Lleo, A.; Fabris, L.; et al. Cholangiocarcinoma landscape in Europe: Diagnostic, prognostic and therapeutic insights from the ENSCCA Registry. J. Hepatol. 2022, 76, 1109–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boonstra, K.; Weersma, R.K.; van Erpecum, K.J.; Rauws, E.A.; Spanier, B.W.; Poen, A.C.; van Nieuwkerk, K.M.; Drenth, J.P.; Witteman, B.J.; Tuynman, H.A.; et al. Population-based epidemiology, malignancy risk, and outcome of primary sclerosing cholangitis. Hepatology 2013, 58, 2045–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boonstra, K.; Beuers, U.; Ponsioen, C.Y. Epidemiology of primary sclerosing cholangitis and primary biliary cirrhosis: A systematic review. J. Hepatol. 2012, 56, 1181–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grønbæk, L.; Vilstrup, H.; Jepsen, P. Autoimmune hepatitis in Denmark: Incidence, prevalence, prognosis, and causes of death. A nationwide registry-based cohort study. J. Hepatol. 2014, 60, 612–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, M.D.; Jepsen, P.; Vilstrup, H.; Grønbæk, L. Increased Cancer Risk in Autoimmune Hepatitis: A Danish Nationwide Cohort Study. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 117, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Verna, E.C.; Simon, T.G.; Söderling, J.; Hagström, H.; Green, P.H.R.; Ludvigsson, J.F. Cancer Risk in Patients With Autoimmune Hepatitis: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study With Histopathology. Am. J. Epidemiology 2021, 191, 298–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleming, K.M.; Aithal, G.P.; Card, T.R.; West, J. All-cause mortality in people with cirrhosis compared with the general population: A population-based cohort study. Liver Int. 2011, 32, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jepsen, P.; Ott, P.; Andersen, P.K.; Sørensen, H.T.; Vilstrup, H. Clinical Course of Alcoholic Liver Cirrhosis: A Danish Population-Based Cohort Study. Hepatology 2010, 51, 1675–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleming, K.M.; Aithal, G.P.; Card, T.R.; West, J. The rate of decompensation and clinical progression of disease in people with cirrhosis: A cohort study. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2010, 32, 1343–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuppan, D.; Afdhal, N.H. Liver Cirrhosis. Lancet 2008, 371, 838–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aggarwal, A.; Biswas, S.; Arora, U.; Vaishnav, M.; Shenoy, A.; Swaroop, S.; Agarwal, A.; Elhence, A.; Kumar, R.; Goel, A.; et al. Definitions, Etiologies, and Outcomes of Acute on Chronic Liver Failure: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024, 22, 2199–2210.e25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mezzano, G.; Juanola, A.; Cardenas, A.; Mezey, E.; Hamilton, J.P.; Pose, E.; Graupera, I.; Ginès, P.; Solà, E.; Hernaez, R. Global burden of disease: Acute-on-chronic liver failure, a systematic review and meta-analysis. Gut 2021, 71, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, A.; Sawhney, R. Australasian Insights and Perspectives on the Burden of Chronic Liver Disease. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 22, 907–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howell, J.M.; Majumdar, A.M.; Fink, M.M.; Byrne, M.; McCaughan, G.M.; Strasser, S.I.M.; Crawford, M.M.; Hodgkinson, P.M.; Stuart, K.A.M.; Tallis, C.M.; et al. The Hidden Epidemic: The Prevalence and Impact of Concurrent Liver Diseases in Patients Undergoing Liver Transplantation in Australia and New Zealand. Transplant. Direct 2022, 8, e1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanless, I.R.; Wong, F.; Blendis, L.M.; Greig, P.; Heathcote, J.E.; Levy, G. Hepatic and portal vein thrombosis in cirrhosis: Possible role in development of parenchymal extinction and portal hypertension. Hepatology 1995, 21, 1238–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsochatzis, E.A.; Bosch, J.; Burroughs, A.K. Liver cirrhosis. Lancet 2014, 383, 1749–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, M.; Semela, D.; Bruix, J.; Colle, I.; Pinzani, M.; Bosch, J. Angiogenesis in liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2009, 50, 604–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLeve, L.D. Liver sinusoidal endothelial cells in hepatic fibrosis. Hepatology 2014, 61, 1740–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanless, I.R. The Role of Vascular Injury and Congestion in the Pathogenesis of Cirrhosis: The Congestive Escalator and the Parenchymal Extinction Sequence. Curr. Hepatol. Rep. 2020, 19, 40–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tschumperlin, D.J.; Ligresti, G.; Hilscher, M.B.; Shah, V.H. Mechanosensing and fibrosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trautwein, C.; Friedman, S.L.; Schuppan, D.; Pinzani, M. Hepatic fibrosis: Concept to treatment. J. Hepatol. 2015, 62, S15–S24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramachandran, P.; Dobie, R.; Wilson-Kanamori, J.R.; Dora, E.F.; Henderson, B.E.P.; Luu, N.T.; Portman, J.R.; Matchett, K.P.; Brice, M.; Marwick, J.A.; et al. Resolving the fibrotic niche of human liver cirrhosis at single-cell level. Nature 2019, 575, 512–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turco, L.; Garcia-Tsao, G. Portal Hypertension: Pathogenesis and Diagnosis. Clin. Liver Dis. 2019, 23, 573–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhathal, P.S.; Grossman, H.J. Reduction of the increased portal vascular resistance of the isolated perfused cirrhotic rat liver by vasodilators. J. Hepatol. 1985, 1, 325–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwakiri, Y. Endothelial dysfunction in the regulation of cirrhosis and portal hypertension. Liver Int. 2011, 32, 199–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiest, R.; Groszmann, R.J. The paradox of nitric oxide in cirrhosis and portal hypertension: Too much, not enough. Hepatology 2002, 35, 478–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAvoy, N.C.; Semple, S.; Richards, J.M.J.; Robson, A.J.; Patel, D.; Jardine, A.G.M.; Leyland, K.; Cooper, A.S.; Newby, D.E.; Hayes, P.C. Differential visceral blood flow in the hyperdynamic circulation of patients with liver cirrhosis. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 43, 947–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, P.-Y.; Ginès, P.; Schrier, R.W.; Epstein, F.H. Nitric Oxide as a Mediator of Hemodynamic Abnormalities and Sodium and Water Retention in Cirrhosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998, 339, 533–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arroyo, V.; Angeli, P.; Moreau, R.; Jalan, R.; Clària, J.; Trebicka, J.; Fernández, J.; Gustot, T.; Caraceni, P.; Bernardi, M. The systemic inflammation hypothesis: Towards a new paradigm of acute decompensation and multiorgan failure in cirrhosis. J. Hepatol. 2021, 74, 670–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gines, P.; Sola, E.; Angeli, P.; Wong, F.; Nadim, M.K.; Kamath, P.S. Hepatorenal syndrome. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2018, 4, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turco, L.; Garcia-Tsao, G.; Magnani, I.; Bianchini, M.; Costetti, M.; Caporali, C.; Colopi, S.; Simonini, E.; De Maria, N.; Banchelli, F.; et al. Cardiopulmonary hemodynamics and C-reactive protein as prognostic indicators in compensated and decompensated cirrhosis. J. Hepatol. 2018, 68, 949–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haj, M.; Rockey, D.C. Ammonia Levels Do Not Guide Clinical Management of Patients With Hepatic Encephalopathy Caused by Cirrhosis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 115, 723–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraldes, J.G.; Tarantino, I.; Turnes, J.; Garcia-Pagan, J.C.; Rodés, J.; Bosch, J. Hemodynamic Response to Pharmacological Treatment of Portal Hypertension and Long–Term Prognosis of Cirrhosis. Hepatology 2003, 37, 902–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwenger, K.J.; Clermont-Dejean, N.; Allard, J.P. The role of the gut microbiome in chronic liver disease: The clinical evidence revised. JHEP Rep. 2019, 1, 214–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierce, A.M.; Gustin, M.S. Development of a Particulate Mass Measurement System for Quantification of Ambient Reactive Mercury. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 51, 436–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trebicka, J.; Bork, P.; Krag, A.; Arumugam, M. Utilizing the gut microbiome in decompensated cirrhosis and acute-on-chronic liver failure. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 18, 167–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trebicka, J.; Macnaughtan, J.; Schnabl, B.; Shawcross, D.L.; Bajaj, J.S. The microbiota in cirrhosis and its role in hepatic decompensation. J. Hepatol. 2021, 75, S67–S81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelmann, C.; Clària, J.; Szabo, G.; Bosch, J.; Bernardi, M. Pathophysiology of decompensated cirrhosis: Portal hypertension, circulatory dysfunction, inflammation, metabolism and mitochondrial dysfunction. J. Hepatol. 2021, 75, S49–S66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, A.; Debelius, J.; Brenner, D.A.; Karin, M.; Loomba, R.; Schnabl, B.; Knight, R. The gut–liver axis and the intersection with the microbiome. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 15, 397–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.-X.; Schwabe, R.F. The gut microbiome and liver cancer: Mechanisms and clinical translation. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 14, 527–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiest, R.; Lawson, M.; Geuking, M. Pathological bacterial translocation in liver cirrhosis. J. Hepatol. 2014, 60, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, C.; Bajaj, J.S. Chronic Liver Diseases and the Microbiome—Translating Our Knowledge of Gut Microbiota to Management of Chronic Liver Disease. Gastroenterology 2020, 160, 556–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solé, C.; Guilly, S.; Da Silva, K.; Llopis, M.; Le-Chatelier, E.; Huelin, P.; Carol, M.; Moreira, R.; Fabrellas, N.; De Prada, G.; et al. Alterations in Gut Microbiome in Cirrhosis as Assessed by Quantitative Metagenomics: Relationship With Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure and Prognosis. Gastroenterology 2021, 160, 206–218.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajaj, J.S.; Heuman, D.M.; Hylemon, P.B.; Sanyal, A.J.; White, M.B.; Monteith, P.; Noble, N.A.; Unser, A.B.; Daita, K.; Fisher, A.R.; et al. Altered profile of human gut microbiome is associated with cirrhosis and its complications. J. Hepatol. 2014, 60, 940–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines for the management of patients with decompensated cirrhosis. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 406–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapper, E.B.; Parikh, N.D. Diagnosis and Management of Cirrhosis and Its Complications. JAMA 2023, 329, 1589–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udell, J.A.; Wang, C.S.; Tinmouth, J.; FitzGerald, J.M.; Ayas, N.T.; Simel, D.L.; Schulzer, M.; Mak, E.; Yoshida, E.M. Does This Patient With Liver Disease Have Cirrhosis? JAMA 2012, 307, 832–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanting, R.; Broekstra, D.C.M.; Werker, P.M.N.M.; Heuvel, E.R.v.D. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis on the Prevalence of Dupuytren Disease in the General Population of Western Countries. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2014, 133, 593–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandel, L.; Baurmash, H. Parotid Enlargement Due to Alcoholism. J. Am. Dent. Assoc. 1971, 82, 369–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagström, H.; Nasr, P.; Ekstedt, M.; Hammar, U.; Stål, P.; Hultcrantz, R.; Kechagias, S. Fibrosis stage but not NASH predicts mortality and time to development of severe liver disease in biopsy-proven NAFLD. J. Hepatol. 2017, 67, 1265–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekstedt, M.; Hagström, H.; Nasr, P.; Fredrikson, M.; Stål, P.; Kechagias, S.; Hultcrantz, R. Fibrosis stage is the strongest predictor for disease-specific mortality in NAFLD after up to 33 years of follow-up. Hepatology 2015, 61, 1547–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, C.H.; Lim, W.H.; Lim, G.E.H.; Tan, D.J.H.; Syn, N.; Muthiah, M.D.; Huang, D.Q.; Loomba, R. Mortality Outcomes by Fibrosis Stage in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 21, 931–939.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Axley, P.; Mudumbi, S.; Sarker, S.; Kuo, Y.-F.; Singal, A.; Lin, W. Patients with stage 3 compared to stage 4 liver fibrosis have lower frequency of and longer time to liver disease complications. PLOS ONE 2018, 13, e0197117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterling, R.K.; Patel, K.; Duarte-Rojo, A.; Asrani, S.K.; Alsawas, M.; Dranoff, J.A.; Fiel, M.I.; Murad, M.H.; Leung, D.H.; Levine, D.; et al. AASLD Practice Guideline on blood-based noninvasive liver disease assessment of hepatic fibrosis and steatosis. Hepatology 2025, 81, 321–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterling, R.K.; Asrani, S.K.; Levine, D.; Duarte-Rojo, A.; Patel, K.; Fiel, M.I.; Leung, D.H.; Taouli, B.; Alsawas, M.; Murad, M.H.; et al. AASLD Practice Guideline on noninvasive liver disease assessment of portal hypertension. Hepatology 2024, 81, 1060–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterling, R.K.; Duarte-Rojo, A.; Patel, K.; Asrani, S.K.; Alsawas, M.; Dranoff, J.A.; Fiel, M.I.; Murad, M.H.; Leung, D.H.; Levine, D.; et al. AASLD Practice Guideline on imaging-based noninvasive liver disease assessment of hepatic fibrosis and steatosis. Hepatology 2025, 81, 672–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterling, R.K.; Lissen, E.; Clumeck, N.; Sola, R.; Correa, M.C.; Montaner, J.; Sulkowski, M.S.; Torriani, F.J.; Dieterich, D.T.; Thomas, D.L.; et al. Development of a simple noninvasive index to predict significant fibrosis in patients with HIV/HCV coinfection. Hepatology 2006, 43, 1317–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, D.N.; Thiele, M.; Johansen, S.; Kjærgaard, M.; Lindvig, K.P.; Israelsen, M.; Antonsen, S.; Detlefsen, S.; Krag, A.; Anastasiadou, E.; et al. Prognostic performance of 7 biomarkers compared to liver biopsy in early alcohol-related liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2021, 75, 1017–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinella, M.E.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A.; Siddiqui, M.S.; Abdelmalek, M.F.; Caldwell, S.; Barb, D.; Kleiner, D.E.; Loomba, R. AASLD Practice Guidance on the clinical assessment and management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2023, 77, 1797–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, J.; Loomba, R.R.; Imajo, K.; Madamba, E.; Gandhi, S.; Bettencourt, R.; Singh, S.; Hernandez, C.; Valasek, M.A.; Behling, C.; et al. MRE combined with FIB-4 (MEFIB) index in detection of candidates for pharmacological treatment of NASH-related fibrosis. Gut 2020, 70, 1946–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniels, S.J.; Leeming, D.J.; Eslam, M.; Hashem, A.M.; Nielsen, M.J.; Krag, A.; Karsdal, M.A.; Grove, J.I.; Neil Guha, I.; Kawaguchi, T.; et al. ADAPT: An Algorithm Incorporating PRO-C3 Accurately Identifies Patients With NAFLD and Advanced Fibrosis. Hepatology 2019, 69, 1075–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stift, J.; Semmler, G.; Walzel, C.; Mandorfer, M.; Schwarzer, R.; Schwabl, P.; Paternostro, R.; Scheiner, B.; Wöran, K.; Pinter, M.; et al. Transjugular aspiration liver biopsy performed by hepatologists trained in HVPG measurements is safe and provides important diagnostic information. Dig. Liver Dis. 2019, 51, 1144–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koda, M.; Matunaga, Y.; Kawakami, M.; Kishimoto, Y.; Suou, T.; Murawaki, Y. Fibroindex, a practical index for predicting significant fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology 2007, 45, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cross, T.J.; Rizzi, P.; Berry, P.A.; Bruce, M.; Portmann, B.; Harrison, P.M. Kingʼs Score: An accurate marker of cirrhosis in chronic hepatitis C. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2009, 21, 730–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wai, C.-T.; Greenson, J.K.; Fontana, R.J.; Kalbfleisch, J.D.; Marrero, J.A.; Conjeevaram, H.S.; Lok, A.S.-F. A simple noninvasive index can predict both significant fibrosis and cirrhosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology 2003, 38, 518–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angulo, P.; Hui, J.M.; Marchesini, G.; Bugianesi, E.; George, J.; Farrell, G.C.; Enders, F.; Saksena, S.; Burt, A.D.; Bida, J.P.; et al. The NAFLD fibrosis score: A noninvasive system that identifies liver fibrosis in patients with NAFLD. Hepatology 2007, 45, 846–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boursier, J.; de Ledinghen, V.; Leroy, V.; Anty, R.; Francque, S.; Salmon, D.; Lannes, A.; Bertrais, S.; Oberti, F.; Fouchard-Hubert, I.; et al. A stepwise algorithm using an at-a-glance first-line test for the non-invasive diagnosis of advanced liver fibrosis and cirrhosis. J. Hepatol. 2017, 66, 1158–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.-H.; Xin, Y.-N.; Dong, Q.-J.; Wang, Q.; Jiang, X.-J.; Zhan, S.-H.; Sun, Y.; Xuan, S.-Y. Performance of the Aspartate Aminotransferase-to-Platelet Ratio Index for the Staging of Hepatitis C-Related Fibrosis: An Updated Meta-Analysis §Δ. Hepatology 2010, 53, 726–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallatah, H.I. Noninvasive Biomarkers of Liver Fibrosis: An Overview. Adv. Hepatol. 2014, 2014, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McPherson, S.; Stewart, S.F.; Henderson, E.; Burt, A.D.; Day, C.P. Simple non-invasive fibrosis scoring systems can reliably exclude advanced fibrosis in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Gut 2010, 59, 1265–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forns, X.; Ampurdanès, S.; Llovet, J.M.; Aponte, J.; Quintó, L.; Martínez-Bauer, E.; Bruguera, M.; Sánchez-Tapias, J.M.; Rodés, J. Identification of chronic hepatitis C patients without hepatic fibrosis by a simple predictive model. Hepatology 2002, 36, 986–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imbert-Bismut, F.; Ratziu, V.; Pieroni, L.; Charlotte, F.; Benhamou, Y.; Poynard, T.; MULTIVIRC Group. Biochemical markers of liver fibrosis in patients with hepatitis C virus infection: A prospective study. Lancet 2001, 357, 1069–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, W.M.C.; Voelker, M.; Thiel, R.; Becka, M.; Burt, A.; Schuppan, D.; Hubscher, S.; Roskams, T.; Pinzani, M.; Arthur, M.J. Serum markers detect the presence of liver fibrosis: A cohort study. Gastroenterology 2004, 127, 1704–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, L.A.; Bulsara, M.; Rossi, E.; DeBoer, B.; Speers, D.; George, J.; Kench, J.; Farrell, G.; McCaughan, G.W.; Jeffrey, G.P. Hepascore: An Accurate Validated Predictor of Liver Fibrosis in Chronic Hepatitis C Infection. Clin. Chem. 2005, 51, 1867–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calès, P.; Oberti, F.; Michalak, S.; Hubert-Fouchard, I.; Rousselet, M.; Konaté, A.; Gallois, Y.; Ternisien, C.; Chevailler, A.; Lunel, F. A novel panel of blood markers to assess the degree of liver fibrosis†. Hepatology 2005, 42, 1373–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, K.; Gordon, S.C.; Jacobson, I.; Hézode, C.; Oh, E.; Smith, K.M.; Pawlotsky, J.-M.; McHutchison, J.G. Evaluation of a panel of non-invasive serum markers to differentiate mild from moderate-to-advanced liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis C patients. J. Hepatol. 2004, 41, 935–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, A.M.; Barritt, A.S. Elevated Liver Enzymes in Patients with COVID-19: Look, but Not Too Hard. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2021, 66, 1767–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marjot, T.; Moon, A.M.; Cook, J.A.; Abd-Elsalam, S.; Aloman, C.; Armstrong, M.J.; Pose, E.; Brenner, E.J.; Cargill, T.; Catana, M.-A.; et al. Outcomes following SARS-CoV-2 infection in patients with chronic liver disease: An international registry study. J. Hepatol. 2021, 74, 567–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultan, S.; Altayar, O.; Siddique, S.M.; Davitkov, P.; Feuerstein, J.D.; Lim, J.K.; Falck-Ytter, Y.; El-Serag, H.B. AGA Institute Rapid Review of the Gastrointestinal and Liver Manifestations of COVID-19, Meta-Analysis of International Data, and Recommendations for the Consultative Management of Patients with COVID-19. Gastroenterology 2020, 159, 320–334.e27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioannou, G.N.; Liang, P.S.; Locke, E.; Green, P.; Berry, K.; O’hAre, A.M.; Shah, J.A.; Crothers, K.; Eastment, M.C.; Fan, V.S.; et al. Cirrhosis and Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Infection in US Veterans: Risk of Infection, Hospitalization, Ventilation, and Mortality. Hepatology 2020, 74, 322–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranieri, V.M.; Giunta, F.; Suter, P.M.; Slutsky, A.S. Mechanical ventilation as a mediator of multisystem organ failure in acute respiratory distress syndrome. JAMA 2000, 284, 43–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Global Progress Report on HIV, Viral Hepatitis and Sexually Transmitted Infections 2021. Accountability for the Global Health Sector Strategies 2016–2021: Actions for Impact; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Kujawski, S.A.; Yao, L.; Wang, H.E.; Carias, C.; Chen, Y.-T. Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on pediatric and adolescent vaccinations and well child visits in the United States: A database analysis. Vaccine 2022, 40, 706–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pley, C.M.; McNaughton, A.L.; Matthews, P.C.; Lourenço, J. The global impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the prevention, diagnosis and treatment of hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection. BMJ Glob. Health 2021, 6, e004275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blach, S.; Kondili, L.A.; Aghemo, A.; Cai, Z.; Dugan, E.; Estes, C.; Gamkrelidze, I.; Ma, S.; Pawlotsky, J.-M.; Razavi-Shearer, D.; et al. Impact of COVID-19 on global HCV elimination efforts. J. Hepatol. 2021, 74, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalo, E.; Read, S.; Meller, M.; Ahlenstiel, G. The Impact of the COVID-19 Epidemic on Hospital Admissions for Alcohol-related Liver Disease and Pancreatitis in Western Sydney. Gastro Hep Adv. (AGA) 2023, 2, 424–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.Q.; Mathurin, P.; Cortez-Pinto, H.; Loomba, R. Global epidemiology of alcohol-associated cirrhosis and HCC: Trends, projections and risk factors. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 20, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapper, E.B.; Asrani, S.K. The COVID-19 pandemic will have a long-lasting impact on the quality of cirrhosis care. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 441–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosch, J.; Abraldes, J.G.; Berzigotti, A.; García-Pagan, J.C. The clinical use of HVPG measurements in chronic liver disease. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2009, 6, 573–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ripoll, C.; Groszmann, R.; Garcia–Tsao, G.; Grace, N.; Burroughs, A.; Planas, R.; Escorsell, A.; Garcia–Pagan, J.C.; Makuch, R.; Patch, D.; et al. Hepatic Venous Pressure Gradient Predicts Clinical Decompensation in Patients With Compensated Cirrhosis. Gastroenterology 2007, 133, 481–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, W.; Al-Karaghouli, M.; Stach, J.; Sung, S.; Matheson, G.J.; Abraldes, J.G. Test-Retest Reliability and Consistency of HVPG and Impact on Trial Design: A Study in 289 Patients from 20 Randomized Controlled Trials. Hepatology 2021, 74, 3301–3315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jachs, M.; Hartl, L.; Simbrunner, B.; Semmler, G.; Balcar, L.; Hofer, B.S.; Schwarz, M.; Bauer, D.; Stättermayer, A.F.; Pinter, M.; et al. Prognostic performance of non-invasive tests for portal hypertension is comparable to that of hepatic venous pressure gradient. J. Hepatol. 2024, 80, 744–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abraldes, J.G.; Bureau, C.; Stefanescu, H.; Augustin, S.; Ney, M.; Blasco, H.; Procopet, B.; Bosch, J.; Genesca, J.; Berzigotti, A.; et al. Noninvasive tools and risk of clinically significant portal hypertension and varices in compensated cirrhosis: The “Anticipate” study. Hepatology 2016, 64, 2173–2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, D.E.; Ripoll, C.; Thiele, M.; Fortune, B.E.; Simonetto, D.A.; Garcia-Tsao, G.; Bosch, J. AASLD Practice Guidance on risk stratification and management of portal hypertension and varices in cirrhosis. Hepatology 2023, 79, 1180–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Tsao, G.; Abraldes, J.G.; Berzigotti, A.; Bosch, J. Portal hypertensive bleeding in cirrhosis: Risk stratification, diagnosis, and management: 2016 practice guidance by the American Association for the study of liver diseases. Hepatology 2017, 65, 310–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stafylidou, M.; Paschos, P.; Katsoula, A.; Malandris, K.; Ioakim, K.; Bekiari, E.; Haidich, A.-B.; Akriviadis, E.; Tsapas, A. Performance of Baveno VI and Expanded Baveno VI Criteria for Excluding High-Risk Varices in Patients With Chronic Liver Diseases: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 17, 1744–1755.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Re, G.; Casali, A.M.; Cavalli, D.; Guida, G.; Cau, R.; Cavalli, G. Histometric analysis of white pulp arterial vessels in congestive splenomegaly. Appl. Pathol. 1986, 4, 98–103. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, P.; Mishra, S.R.; Kumar, M.; Sharma, B.C.; Sarin, S.K. Liver and Spleen Stiffness in Patients with Extrahepatic Portal Vein Obstruction. Radiology 2012, 263, 893–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paternostro, R.; Reiberger, T.; Bucsics, T. Elastography-based screening for esophageal varices in patients with advanced chronic liver disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 308–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, J.-J.; Maeng, S.A.; Chang, Y.; Lee, S.H.; Jeong, S.W.; Jang, J.Y.; Cheon, G.J.; Kim, Y.S.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, S.G. Enhancing liver cirrhosis varices and CSPH risk prediction with spleen stiffness measurement using 100-Hz probe. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jachs, M.; Odriozola, A.; Turon, F.; Moga, L.; Téllez, L.; Fischer, P.; Saltini, D.; Kwanten, W.J.; Grasso, M.; Llop, E.; et al. Spleen stiffness measurement by vibration-controlled transient elastography at 100 Hz for non-invasive predicted diagnosis of clinically significant portal hypertension in patients with compensated advanced chronic liver disease: A modelling study. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024, 9, 1111–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rigamonti, C. Spleen stiffness in portal hypertension algorithms: The next advance. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024, 9, 1067–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioannou, G.N.; Splan, M.F.; Weiss, N.S.; McDonald, G.B.; Beretta, L.; Lee, S.P. Incidence and Predictors of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Patients With Cirrhosis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2007, 5, 938–945.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanwal, F.; Tapper, E.B.; Ho, C.; Asrani, S.K.; Ovchinsky, N.; Poterucha, J.; Flores, A.; Ankoma-Sey, V.; Luxon, B.; Volk, M. Development of Quality Measures in Cirrhosis by the Practice Metrics Committee of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology 2018, 69, 1787–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrero, J.A.; Kulik, L.M.; Sirlin, C.B.; Zhu, A.X.; Finn, R.S.; Abecassis, M.M.; Roberts, L.R.; Heimbach, J.K. Diagnosis, Staging, and Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: 2018 Practice Guidance by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology 2018, 68, 723–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singal, A.G.; Zhang, E.; Narasimman, M.; Rich, N.E.; Waljee, A.K.; Hoshida, Y.; Yang, J.D.; Reig, M.; Cabibbo, G.; Nahon, P.; et al. HCC surveillance improves early detection, curative treatment receipt, and survival in patients with cirrhosis: A meta-analysis. J. Hepatol. 2022, 77, 128–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayob, N.; Kanwal, F.; Alsarraj, A.; Hernaez, R.; El-Serag, H.B. The Performance of AFP, AFP-3, DCP as Biomarkers for Detection of Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC): A Phase 3 Biomarker Study in the United States. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 21, 415–423.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singal, A.G.; Llovet, J.M.; Yarchoan, M.; Mehta, N.; Heimbach, J.K.; Dawson, L.A.; Jou, J.H.; Kulik, L.M.; Agopian, V.G.; Marrero, J.A.; et al. AASLD Practice Guidance on prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2023, 78, 1922–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durand, F.; Valla, D. Assessment of the prognosis of cirrhosis: Child–Pugh versus MELD. J. Hepatol. 2005, 42, S100–S107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Child, C.G.; Turcotte, J.G. Surgery and portal hypertension. Major Probl. Clin. Surg. 1964, 1, 1–85. [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan, D.E.; Dai, F.; Skanderson, M.; Aytaman, A.; Baytarian, M.; D’aDdeo, K.; Fox, R.; Hunt, K.; Knott, A.; the VOCAL Study Group. Recalibrating the Child–Turcotte–Pugh Score to Improve Prediction of Transplant-Free Survival in Patients with Cirrhosis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2016, 61, 3309–3320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malinchoc, M.; Kamath, P.S.; Gordon, F.D.; Peine, C.J.; Rank, J.; ter Borg, P.C. A model to predict poor survival in patients undergoing transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunts. Hepatology 2000, 31, 864–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, I.; Nababan, S.H.H.; Handayu, A.D.; Aprilicia, G.; Gani, R.A. Scoring system for predicting 90-day mortality of in-hospital liver cirrhosis patients at Cipto Mangunkusumo Hospital. BMC Gastroenterol. 2023, 23, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biggins, S.W.; Kim, W.R.; Terrault, N.A.; Saab, S.; Balan, V.; Schiano, T.; Benson, J.; Therneau, T.; Kremers, W.; Wiesner, R.; et al. Evidence-Based Incorporation of Serum Sodium Concentration Into MELD. Gastroenterology 2006, 130, 1652–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriksen, J.H.; Parving, H.H.; Christiansen, L.; Winkler, K.; Lassen, N.A. Increased transvascular escape rate of albumin during experimental portal and hepatic venous hypertension in the pig. Relation to findings in patients with cirrhosis of the liver. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Investig. 1981, 41, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godfrey, E.L.; Malik, T.H.; Lai, J.C.; Mindikoglu, A.L.; Galván, N.T.N.; Cotton, R.T.; O’mAhony, C.A.; Goss, J.A.; Rana, A. The decreasing predictive power of MELD in an era of changing etiology of liver disease. Am. J. Transplant. 2019, 19, 3299–3307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latt, N.L.; Niazi, M.; Pyrsopoulos, N.T. Liver transplant allocation policies and outcomes in United States: A comprehensive review. World J. Methodol. 2022, 12, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francoz, C.; Prié, D.; AbdelRazek, W.; Moreau, R.; Mandot, A.; Belghiti, J.; Valla, D.; Durand, F. Inaccuracies of creatinine and creatinine-based equations in candidates for liver transplantation with low creatinine: Impact on the model for end-stage liver disease score. Liver Transplant. 2010, 16, 1169–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, T.; Hsu, C.; Lin, H.; Lee, P.; Lee, J.; Lee, F.; Hou, M.; Lee, S. Selecting an optimal cutoff value for creatinine in the model for end-stage liver disease equation. Clin. Transplant. 2010, 24, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundaram, V.; Shah, P.; Mahmud, N.; Lindenmeyer, C.C.; Klein, A.S.; Wong, R.J.; Karvellas, C.J.; Asrani, S.K.; Jalan, R. Patients with severe acute-on-chronic liver failure are disadvantaged by model for end-stage liver disease-based organ allocation policy. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 52, 1204–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, W.R.; Mannalithara, A.; Heimbach, J.K.; Kamath, P.S.; Asrani, S.K.; Biggins, S.W.; Wood, N.L.; Gentry, S.E.; Kwong, A.J. MELD 3.0: The Model for End-Stage Liver Disease Updated for the Modern Era. Gastroenterology 2021, 161, 1887–1895.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kjaergard, L.L.; Liu, J.; Als-Nielsen, B.; Gluud, C. Artificial and bioartificial support systems for acute and acute-on-chronic liver failure: A systematic review. JAMA 2003, 289, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernaez, R.; Sola, E.; Moreau, R.; Gines, P. Acute-on-chronic liver failure: An update. Gut 2017, 66, 541–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laleman, W.; Claria, J.; Van der Merwe, S.; Moreau, R.; Trebicka, J. Systemic Inflammation and Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure: Too Much, Not Enough. Can. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 2018, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laleman, W.; Verbeke, L.; Meersseman, P.; Wauters, J.; van Pelt, J.; Cassiman, D.; Wilmer, A.; Verslype, C.; Nevens, F. Acute-on-chronic liver failure: Current concepts on definition, pathogenesis, clinical manifestations and potential therapeutic interventions. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011, 5, 523–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajaj, J.S.; O’Leary, J.G.; Reddy, K.R.; Wong, F.; Biggins, S.W.; Patton, H.; Fallon, M.B.; Garcia-Tsao, G.; Maliakkal, B.; Malik, R.; et al. Survival in Infection-Related Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure Is Defined by Extrahepatic Organ Failures. Hepatology 2014, 60, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalan, R.; Pavesi, M.; Saliba, F.; Amorós, A.; Fernandez, J.; Holland-Fischer, P.; Sawhney, R.; Mookerjee, R.; Caraceni, P.; Moreau, R.; et al. The CLIF Consortium Acute Decompensation score (CLIF-C ADs) for prognosis of hospitalised cirrhotic patients without acute-on-chronic liver failure. J. Hepatol. 2015, 62, 831–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalo, E.; Sturm, L.; Schultheiss, M.; Moore, O.; Kurup, R.; Gahm, C.; Read, S.; Reincke, M.; Huber, J.P.; Müller, L.; et al. The Freiburg Index of Post-TIPS Survival accurately predicts mortality in patients with acute decompensation of cirrhosis. Liver Int. 2024, 44, 3229–3237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturm, L.; Schultheiss, M.; Stöhr, F.; Labenz, C.; Maasoumy, B.; Tiede, A.; Praktiknjo, M.; Seifert, L.L.; Auer, T.A.; Fehrenbach, U.; et al. Freiburg index of post-TIPS survival (FIPS) identifies patients at risk of further decompensation and ACLF after TIPS. J. Hepatol. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsochatzis, E.; Papatheodoridis, G.V.; Manesis, E.K.; Kafiri, G.; Tiniakos, D.G.; Archimandritis, A.J. Metabolic syndrome is associated with severe fibrosis in chronic viral hepatitis and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2007, 27, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stepanova, M.; Rafiq, N.; Younossi, Z.M. Components of metabolic syndrome are independent predictors of mortality in patients with chronic liver disease: A population-based study. Gut 2010, 59, 1410–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines on nutrition in chronic liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2019, 70, 172–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tandon, P.; Ismond, K.P.; Riess, K.; Duarte-Rojo, A.; Al-Judaibi, B.; Dunn, M.A.; Holman, J.; Howes, N.; Haykowsky, M.J.F.; Josbeno, D.A.; et al. Exercise in cirrhosis: Translating evidence and experience to practice. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 1164–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijarnpreecha, K.; Thongprayoon, C.; Ungprasert, P. Coffee consumption and risk of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 29, e8–e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, S.C.; Wolk, A. Coffee Consumption and Risk of Liver Cancer: A Meta-Analysis. Gastroenterology 2007, 132, 1740–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayat, U.; Siddiqui, A.A.; Okut, H.; Afroz, S.; Tasleem, S.; Haris, A. The effect of coffee consumption on the non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and liver fibrosis: A meta-analysis of 11 epidemiological studies. Ann. Hepatol. 2021, 20, 100254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Gottardi, A.; Berzigotti, A.; Seijo, S.; D’Amico, M.; Thormann, W.; Abraldes, J.G.; García-Pagán, J.C.; Bosch, J. Postprandial effects of dark chocolate on portal hypertension in patients with cirrhosis: Results of a phase 2, double-blind, randomized controlled trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 96, 584–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Guerra, M.; García-Pagán, J.C.; Turnes, J.; Bellot, P.; Deulofeu, R.; Abraldes, J.G.; Bosch, J. Ascorbic acid improves the intrahepatic endothelial dysfunction of patients with cirrhosis and portal hypertension. Hepatology 2006, 43, 485–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elia, C.; Graupera, I.; Barreto, R.; Solà, E.; Moreira, R.; Huelin, P.; Ariza, X.; Solé, C.; Pose, E.; Baiges, A.; et al. Severe acute kidney injury associated with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in cirrhosis: A case-control study. J. Hepatol. 2015, 63, 593–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosch, J.; Gracia-Sancho, J.; Abraldes, J.G. Cirrhosis as new indication for statins. Gut 2020, 69, 953–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turco, L.; Reiberger, T.; Vitale, G.; La Mura, V. Carvedilol as the new non-selective beta-blocker of choice in patients with cirrhosis and portal hypertension. Liver Int. 2023, 43, 1183–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasool, M.F.; Khalil, F.; Läer, S. Optimizing the Clinical Use of Carvedilol in Liver Cirrhosis Using a Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Modeling Approach. Eur. J. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 2016, 42, 383–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zacharias, A.P.; Jeyaraj, R.; Hobolth, L.; Bendtsen, F.; Gluud, L.L.; Morgan, M.Y. Cochrane Hepato-Biliary Group Carvedilol versus traditional, non-selective beta-blockers for adults with cirrhosis and gastroesophageal varices. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2018, 2018, CD011510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serper, M.; Kaplan, D.E.; Taddei, T.H.; Tapper, E.B.; Cohen, J.B.; Mahmud, N. Nonselective beta blockers, hepatic decompensation, and mortality in cirrhosis: A national cohort study. Hepatology 2022, 77, 489–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villanueva, C.; Torres, F.; Sarin, S.K.; Shah, H.A.; Tripathi, D.; Brujats, A.; Rodrigues, S.G.; Bhardwaj, A.; Azam, Z.; Hayes, P.C.; et al. Carvedilol reduces the risk of decompensation and mortality in patients with compensated cirrhosis in a competing-risk meta-analysis. J. Hepatol. 2022, 77, 1014–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Téllez, L.; Ibáñez-Samaniego, L.; del Villar, C.P.; Yotti, R.; Martínez, J.; Carrión, L.; de Santiago, E.R.; Rivera, M.; González-Mansilla, A.; Pastor, Ó.; et al. Non-selective beta-blockers impair global circulatory homeostasis and renal function in cirrhotic patients with refractory ascites. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 1404–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colapinto, R.; Stronell, R.; Gildiner, M.; Ritchie, A.; Langer, B.; Taylor, B.; Blendis, L. Formation of intrahepatic portosystemic shunts using a balloon dilatation catheter: Preliminary clinical experience. Am. J. Roentgenol. 1983, 140, 709–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Pagan, J.C.; Saffo, S.; Mandorfer, M.; Garcia-Tsao, G. Where does TIPS fit in the management of patients with cirrhosis? JHEP Rep. 2020, 2, 100122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomier-Layrargues, G.; Bouchard, L.; Lafortune, M.; Bissonnette, J.; Guérette, D.; Perreault, P. The Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt in the Treatment of Portal Hypertension: Current Status. Int. J. Hepatol. 2012, 2012, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossle, M. TIPS: 25 years later. J. Hepatol. 2013, 59, 1081–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Busk, T.M.; Bendtsen, F.; Poulsen, J.H.; Clemmesen, J.O.; Larsen, F.S.; Goetze, J.P.; Iversen, J.S.; Jensen, M.T.; Møgelvang, R.; Pedersen, E.B.; et al. Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt: Impact on systemic hemodynamics and renal and cardiac function in patients with cirrhosis. Am. J. Physiol. Liver Physiol. 2018, 314, G275–G286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribera, J.; Córdoba-Jover, B.; Portolés, I.; Morales-Ruiz, M. The Role of Hepatic and Splanchnic Lymphatic System in Portal Hypertension and Ascites. Curr. Hepatol. Rep. 2019, 18, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riggio, O.; Angeloni, S.; Salvatori, F.M.; De Santis, A.; Cerini, F.; Farcomeni, A.; Attili, A.F.; Merli, M. Incidence, Natural History, and Risk Factors of Hepatic Encephalopathy After Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt With Polytetrafluoroethylene-Covered Stent Grafts. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 103, 2738–2746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Planas, R.; Montoliu, S.; Ballesté, B.; Rivera, M.; Miquel, M.; Masnou, H.; Galeras, J.A.; Giménez, M.D.; Santos, J.; Cirera, I.; et al. Natural History of Patients Hospitalized for Management of Cirrhotic Ascites. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2006, 4, 1385–1394.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biggins, S.W.; Angeli, P.; Garcia-Tsao, G.; Ginès, P.; Ling, S.C.; Nadim, M.K.; Wong, F.; Kim, W.R. Diagnosis, Evaluation, and Management of Ascites, Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis and Hepatorenal Syndrome: 2021 Practice Guidance by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology 2021, 74, 1014–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, K.P.; Wong, F.; Gines, P.; Bernardi, M.; Ochs, A.; Salerno, F.; Angeli, P.; Porayko, M.; Moreau, R.; Garcia-Tsao, G.; et al. The Management of Ascites in Cirrhosis: Report on the Consensus Conference of the International Ascites Club. Hepatology 2003, 38, 258–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arroyo, V.; Ginès, P.; Gerbes, A.L.; Dudley, F.J.; Gentilini, P.; Laffi, G.; Reynolds, T.B.; Ring-Larsen, H.; Schölmerich, J. Definition and diagnostic criteria of refractory ascites and hepatorenal syndrome in cirrhosis. Hepatology 1996, 23, 164–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimola, A.; García-Tsao, G.; Navasa, M.; Piddock, L.J.; Planas, R.; Bernard, B.; Inadomi, J.M. Diagnosis, treatment and prophylaxis of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis: A consensus document. J. Hepatol. 2000, 32, 142–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, K. Large animal practitioners grapple with fluid shortage. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2015, 246, 825–826. [Google Scholar]
- Runyon, B.A.; Canawati, H.N.; Akriviadis, E.A. Optimization of ascitic fluid culture technique. Gastroenterology 1988, 95, 1351–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Runyon, B.A.; Montano, A.A.; Akriviadis, E.A.; Antillon, M.R.; Irving, M.A.; McHutchison, J.G. The Serum-Ascites Albumin Gradient Is Superior to the Exudate-Transudate Concept in the Differential Diagnosis of Ascites. Ann. Intern. Med. 1992, 117, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerbes, A.L.; Jüngst, D.; Xie, Y.; Permanetter, W.; Paumgartner, G. Ascitic fluid analysis for the differentiation of malignancy-related and nonmalignant ascites. Proposal of a diagnostic sequence. Cancer 1991, 68, 1808–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardi, M.; Laffi, G.; Salvagnini, M.; Azzena, G.; Bonato, S.; Marra, F.; Trevlsani, F.; Gasbarrini, G.; Naccarato, R.; Gentillni, P. Efficacy and safety of the stepped care medical treatment of ascites in liver cirrhosis: A randomized controlled clinical trial comparing two diets with different sodium content. Liver Int. 1993, 13, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.; Planas, R.; Pardo, A.; Durández, R.; Cabré, E.; Morillas, R.M.; Granada, M.L.; Jiménez, J.A.; Quintero, E.; Gassull, M.A. Spironolactone alone or in combination with furosemide in the treatment of moderate ascites in nonazotemic cirrhosis. A randomized comparative study of efficacy and safety. J. Hepatol. 2003, 39, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, A.V.; Kumar, P.; Sharma, M.; Sowmya, T.R.; Talukdar, R.; Rao, P.N.; Reddy, D.N. Pathophysiology and Prevention of Paracentesis-induced Circulatory Dysfunction: A Concise Review. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2020, 8, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, Y.J.; Kumar, R.; Chua, Y.J.J.; Ang, T.L. Long-term albumin infusion in decompensated cirrhosis: A review of current literature. World J. Hepatol. 2021, 13, 421–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caraceni, P.; Riggio, O.; Angeli, P.; Alessandria, C.; Neri, S.; Foschi, F.G.; Levantesi, F.; Airoldi, A.; Boccia, S.; Svegliati-Baroni, G.; et al. Long-term albumin administration in decompensated cirrhosis (ANSWER): An open-label randomised trial. Lancet 2018, 391, 2417–2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Pascoli, M.; Fasolato, S.; Piano, S.; Bolognesi, M.; Angeli, P. Long-term administration of human albumin improves survival in patients with cirrhosis and refractory ascites. Liver Int. 2018, 39, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saab, S.; Nieto, J.M.; Lewis, S.K.; Runyon, B.A. Cochrane Hepato-Biliary Group TIPS versus paracentesis for cirrhotic patients with refractory ascites. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2006, 2010, CD004889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bañares, R.A.-O.; Bernardi, M.A.-O. Long-term albumin administration in patients with decompensated cirrhosis. It is time for a reappraisal. Liver Int. 2019, 39, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’aMico, G.; Luca, A.; Morabito, A.; Miraglia, R.; D’aMico, M. Uncovered Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt for Refractory Ascites: A Meta-Analysis. Gastroenterology 2005, 129, 1282–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deltenre, P.; Mathurin, P.; Dharancy, S.; Moreau, R.; Bulois, P.; Henrion, J.; Pruvot, F.R.; Ernst, O.; Paris, J.C.; Lebrec, D. Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt in refractory ascites: A meta-analysis. Liver Int. 2005, 25, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salerno, F.; Cammà, C.; Enea, M.; Rössle, M.; Wong, F. Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt for Refractory Ascites: A Meta-analysis of Individual Patient Data. Gastroenterology 2007, 133, 825–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, M.; Qi, X.S.; Yang, Z.P.; Yang, M.; Fan, D.M.; Han, G.H. TIPS improves liver transplantation-free survival in cirrhotic patients with refractory ascites: An updated meta-analysis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 2704–2714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bureau, C.; Thabut, D.; Oberti, F.; Dharancy, S.; Carbonell, N.; Bouvier, A.; Mathurin, P.; Otal, P.; Cabarrou, P.; Péron, J.M.; et al. Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunts With Covered Stents Increase Transplant-Free Survival of Patients With Cirrhosis and Recurrent Ascites. Gastroenterology 2017, 152, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benmassaoud, A.; Roccarina, D.; Arico, F.; Leandro, G.; Yu, B.; Cheng, F.; Yu, D.; Patch, D.; Tsochatzis, E. Sarcopenia Does Not Worsen Survival in Patients With Cirrhosis Undergoing Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt for Refractory Ascites. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 115, 1911–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahangiri, Y.; Pathak, P.; Tomozawa, Y.; Li, L.; Schlansky, B.L.; Farsad, K. Muscle Gain after Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt Creation: Time Course and Prognostic Implications for Survival in Cirrhosis. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2019, 30, 866–872.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsien, C.; Shah, S.N.; McCullough, A.J.; Dasarathy, S. Reversal of sarcopenia predicts survival after a transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic stent. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 25, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhogal, H.K.; Sanyal, A.J. Using Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunts for Complications of Cirrhosis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011, 9, 936–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardelli, S.; Lattanzi, B.; Torrisi, S.; Greco, F.; Farcomeni, A.; Gioia, S.; Merli, M.; Riggio, O. Sarcopenia Is Risk Factor for Development of Hepatic Encephalopathy After Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt Placement. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 15, 934–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosch, J. Small diameter shunts should lead to safe expansion of the use of TIPS. J. Hepatol. 2021, 74, 230–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macken, L.; Hashim, A.; Mason, L.; Verma, S. Permanent indwelling peritoneal catheters for palliation of refractory ascites in end-stage liver disease: A systematic review. Liver Int. 2019, 39, 1594–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aagaard, N.K.; Malago, M.; De Gottardi, A.; Thomas, M.; Sauter, G.; Engelmann, C.; Aranovich, D.; Cohen, M.; Thévenot, T.; Ehmann, T.; et al. Consensus care recommendations for alfapump® in cirrhotic patients with refractory or recurrent ascites. BMC Gastroenterol. 2022, 22, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotopoulou, C.; Berg, T.; Hausen, A.; Hennig, R.; Jalan, R.; Malagó, M.; Capel, J.; De Gottardi, A.; Stirnimann, G. Continuous low flow ascites drainage through the urinary bladder via the Alfapump system in palliative patients with malignant ascites. BMC Palliat. Care 2019, 18, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bureau, C.; Adebayo, D.; de Rieu, M.C.; Elkrief, L.; Valla, D.; Peck-Radosavljevic, M.; McCune, A.; Vargas, V.; Simon-Talero, M.; Cordoba, J.; et al. Alfapump® system vs. large volume paracentesis for refractory ascites: A multicenter randomized controlled study. J. Hepatol. 2017, 67, 940–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellot, P.; Welker, M.-W.; Soriano, G.; von Schaewen, M.; Appenrodt, B.; Wiest, R.; Whittaker, S.; Tzonev, R.; Handshiev, S.; Verslype, C.; et al. Automated low flow pump system for the treatment of refractory ascites: A multi-center safety and efficacy study. J. Hepatol. 2013, 58, 922–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solbach, P.; zu Siederdissen, C.H.; Wellhöner, F.; Richter, N.; Heidrich, B.; Lenzen, H.; Kerstin, P.; Hueper, K.; Manns, M.P.; Wedemeyer, H.; et al. Automated low-flow ascites pump in a real-world setting: Complications and outcomes. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 30, 1082–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, F.; Bendel, E.; Sniderman, K.; Frederick, T.; Haskal, Z.J.; Sanyal, A.; Asrani, S.K.; Capel, J.; Kamath, P.S. Improvement in Quality of Life and Decrease in Large-Volume Paracentesis Requirements With the Automated Low-Flow Ascites Pump. Liver Transplant. 2020, 26, 651–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heuman, D.M.; Abou-Assi, S.G.; Habib, A.; Williams, L.M.; Stravitz, R.T.; Sanyal, A.J.; Fisher, R.A.; Mihas, A.A. Persistent ascites and low serum sodium identify patients with cirrhosis and low MELD scores who are at high risk for early death. Hepatology 2004, 40, 802–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somsouk, M.; Kornfield, R.; Vittinghoff, E.; Inadomi, J.M.; Biggins, S.W. Moderate ascites identifies patients with low model for end-stage liver disease scores awaiting liver transplantation who have a high mortality risk. Liver Transplant. 2010, 17, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biggins, S.W. Use of serum sodium for liver transplant graft allocation: A decade in the making, now is it ready for primetime? Liver Transplant. 2015, 21, 279–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angeli, P.; Albino, G.; Carraro, P.; Dalla Pria, M.; Merkel, C.; Caregaro, L.; De Bei, E.; Bortoluzzi, A.; Plebani, M.; Gatta, A. Cirrhosis and muscle cramps: Evidence of a causal relationship. Hepatology 1996, 23, 264–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elfert, A.A.; Ali, L.A.; Soliman, S.; Zakaria, S.; El-Din, I.S.; Elkhalawany, W.; Abd-Elsalam, S. Randomized placebo-controlled study of baclofen in the treatment of muscle cramps in patients with liver cirrhosis. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 28, 1280–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-Elsalam, S.; Arafa, M.; Elkadeem, M.; Elfert, A.; Soliman, S.; Elkhalawany, W.; Badawi, R. Randomized-controlled trial of methocarbamol as a novel treatment for muscle cramps in cirrhotic patients. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 31, 499–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-Elsalam, S.; El-Kalla, F.; Ali, L.A.; Mosaad, S.; Alkhalawany, W.; Elemary, B.; Badawi, R.; Elzeftawy, A.; Hanafy, A.; Elfert, A. Pilot study of orphenadrine as a novel treatment for muscle cramps in patients with liver cirrhosis. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2017, 6, 422–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, F.-Y.; Lee, S.-D.; Tsai, Y.-T.; Lai, K.-H.; Chao, Y.; Lin, H.-C.; Wang, S.-S.; Lo, K.-J. A randomized controlled trial of quinidine in the treatment of cirrhotic patients with muscle cramps. J. Hepatol. 1991, 12, 236–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapper, E.B.; Salim, N.; Baki, J.; Zhao, Z.; Sundaram, V.; Patwardhan, V.; Nikirk, S.J. Pickle Juice Intervention for Cirrhotic Cramps Reduction: The PICCLES Randomized Controlled Trial. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 117, 895–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidot, H.; Cvejic, E.; Carey, S.; Strasser, S.I.; McCaughan, G.W.; Allman-Farinelli, M.; Shackel, N.A. Randomised clinical trial: Oral taurine supplementation versus placebo reduces muscle cramps in patients with chronic liver disease. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 48, 704–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angeli, P.; Wong, F.; Watson, H.; Ginès, P. CAPPS Investigators Hyponatremia in cirrhosis: Results of a patient population survey. Hepatology 2006, 44, 1535–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sersté, T.; Gustot, T.; Rautou, P.-E.; Francoz, C.; Njimi, H.; Durand, F.; Valla, D.; Lebrec, D.; Moreau, R. Severe hyponatremia is a better predictor of mortality than MELDNa in patients with cirrhosis and refractory ascites. J. Hepatol. 2012, 57, 274–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, W.R.; Biggins, S.W.; Kremers, W.K.; Wiesner, R.H.; Kamath, P.S.; Benson, J.T.; Edwards, E.; Therneau, T.M. Hyponatremia and Mortality among Patients on the Liver-Transplant Waiting List. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 1018–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, F. Clinical Consequences of Infection in Cirrhosis: Organ Failures and Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure. Clin. Liver Dis. 2019, 14, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piano, S.; Brocca, A.; Mareso, S.; Angeli, P. Infections complicating cirrhosis. Liver Int. 2018, 38 (Suppl. S1), 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piano, S.; Singh, V.; Caraceni, P.; Maiwall, R.; Alessandria, C.; Fernandez, J.; Soares, E.C.; Kim, D.J.; Kim, S.E.; Marino, M.; et al. Epidemiology and Effects of Bacterial Infections in Patients With Cirrhosis Worldwide. Gastroenterology 2019, 156, 1368–1380.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalan, R.; Fernandez, J.; Wiest, R.; Schnabl, B.; Moreau, R.; Angeli, P.; Stadlbauer, V.; Gustot, T.; Bernardi, M.; Canton, R.; et al. Bacterial infections in cirrhosis: A position statement based on the EASL Special Conference 2013. J. Hepatol. 2014, 60, 1310–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, J.; Acevedo, J.; Castro, M.; Garcia, O.; de Lope, C.R.; Roca, D.; Pavesi, M.; Sola, E.; Moreira, L.; Silva, A.; et al. Prevalence and risk factors of infections by multiresistant bacteria in cirrhosis: A prospective study. Hepatology 2011, 55, 1551–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piano, S.; Bartoletti, M.; Tonon, M.; Baldassarre, M.; Chies, G.; Romano, A.; Viale, P.; Vettore, E.; Domenicali, M.; Stanco, M.; et al. Assessment of Sepsis-3 criteria and quick SOFA in patients with cirrhosis and bacterial infections. Gut 2017, 67, 1892–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajaj, J.S.; Kamath, P.S.; Reddy, K.R.; Longo, D.L. The Evolving Challenge of Infections in Cirrhosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 2317–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.L.; Holroyd-Leduc, J.; Thorpe, K.E.; Straus, S.E. Does This Patient Have Bacterial Peritonitis or Portal Hypertension? How Do I Perform a Paracentesis and Analyze the Results? JAMA 2008, 299, 1166–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dever, J.B.; Sheikh, M.Y. Editorial: Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis—Bacteriology, diagnosis, treatment, risk factors and prevention. Authors’ reply. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 41, 1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández, J.; Tandon, P.; Mensa, J.; Garcia-Tsao, G. Antibiotic prophylaxis in cirrhosis: Good and bad. Hepatology 2016, 63, 2019–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernard, B.; Grangé, J.-D.; Khac, E.N.; Amiot, X.; Opolon, P.; Poynard, T. Antibiotic Prophylaxis for the Prevention of Bacterial Infections in Cirrhotic Patients With Gastrointestinal Bleeding: A Meta–Analysis. Hepatology 1999, 29, 1655–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llach, J.; Rimola, A.; Navasa, M.; Ginès, P.; Salmerón, J.M.; Ginès, A.; Arroyo, V.; Rodés, J. Incidence and Predictive Factors of First Episode of Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis in Cirrhosis With Ascites: Relevance of Ascitic Fluid Protein Concentration. Hepatology 1992, 16, 724–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreau, R.; Elkrief, L.; Bureau, C.; Perarnau, J.-M.; Thévenot, T.; Saliba, F.; Louvet, A.; Nahon, P.; Lannes, A.; Anty, R.; et al. Effects of Long-term Norfloxacin Therapy in Patients With Advanced Cirrhosis. Gastroenterology 2018, 155, 1816–1827.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escorsell, A.; Bordas, J.; Feu, F.; Garcia-Pagan, J.; Gines, A.; Bosch, J.; Rodes, J. Endoscopic assessment of variceal volume and wall tension in cirrhotic patients: Effects of pharmacological therapy. Gastroenterology 1997, 113, 1640–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reverter, E.; Tandon, P.; Augustin, S.; Turon, F.; Casu, S.; Bastiampillai, R.; Keough, A.; Llop, E.; González, A.; Seijo, S.; et al. A MELD-Based Model to Determine Risk of Mortality Among Patients With Acute Variceal Bleeding. Gastroenterology 2014, 146, 412–419.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moitinho, E.; Escorsell, À.; Bandi, J.; Salmerón, J.; García–Pagán, J.; Rodés, J.; Bosch, J. Prognostic value of early measurements of portal pressure in acute variceal bleeding. Gastroenterology 1999, 117, 626–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraldes, J.G.; Villanueva, C.; Bañares, R.; Aracil, C.; Catalina, M.V.; García-Pagán, J.C.; Bosch, J. Hepatic venous pressure gradient and prognosis in patients with acute variceal bleeding treated with pharmacologic and endoscopic therapy. J. Hepatol. 2007, 48, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortune, B.E.; Garcia-Tsao, G.; Ciarleglio, M.; Deng, Y.; Fallon, M.B.; Sigal, S.; Chalasani, N.P.; Lim, J.K.; Reuben, A.; Vargas, H.E.; et al. Child-Turcotte-Pugh Class is Best at Stratifying Risk in Variceal Hemorrhage: Analysis of a US Multicenter Prospective Study. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2017, 51, 446–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augustin, S.; González, A.; Genescà, J. Acute esophageal variceal bleeding: Current strategies and new perspectives. World J. Hepatol. 2010, 2, 261–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merli, M.; Nicolini, G.; Angeloni, S.; Rinaldi, V.; De Santis, A.; Merkel, C.; Attili, A.F.; Riggio, O. Incidence and natural history of small esophageal varices in cirrhotic patients. J. Hepatol. 2003, 38, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Northup, P.G.; Garcia-Pagan, J.C.; Garcia-Tsao, G.; Intagliata, N.M.; Superina, R.A.; Roberts, L.N.; Lisman, T.; Valla, D.C. Vascular Liver Disorders, Portal Vein Thrombosis, and Procedural Bleeding in Patients With Liver Disease: 2020 Practice Guidance by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology 2020, 73, 366–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripathi, D.; Ferguson, J.W.; Kochar, N.; Leithead, J.A.; Therapondos, G.; Mcavoy, N.C.; Stanley, A.J.; Forrest, E.H.; Hislop, W.S.; Mills, P.R.; et al. Randomized controlled trial of carvedilol versus variceal band ligation for the prevention of the first variceal bleed # †. Hepatology 2009, 50, 825–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, P.B.; Benjamin, J.; Tripathi, H.; Patidar, Y.; Maiwall, R.; Kumar, G.; Joshi, Y.K.; Sarin, S.K. Post-transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt Hepatic Encephalopathy: Sarcopenia Adds Insult to Injury. Turk. J. Gastroenterol. 2023, 34, 406–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Singh, S.; Desai, V.; Shah, V.H.; Kamath, P.S.; Murad, M.H.; Simonetto, D.A. Comparison of Therapies for Primary Prevention of Esophageal Variceal Bleeding: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-analysis. Hepatology 2019, 69, 1657–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villanueva, C.; Colomo, A.; Bosch, A.; Concepción, M.; Hernandez-Gea, V.; Aracil, C.; Graupera, I.; Poca, M.; Alvarez-Urturi, C.; Gordillo, J.; et al. Transfusion Strategies for Acute Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, J.Y.; Yu, Y.; Tang, R.S.; Chan, H.C.; Yip, H.-C.; Chan, S.M.; Luk, S.W.; Wong, S.H.; Lau, L.H.; Lui, R.N.; et al. Timing of Endoscopy for Acute Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1299–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bañares, R.; Albillos, A.; Rincón, D.; Alonso, S.; González, M.; Ruiz-Del-Arbol, L.; Salcedo, M.; Molinero, L.-M. Endoscopic treatment versus endoscopic plus pharmacologic treatment for acute variceal bleeding: A meta-analysis. Hepatology 2002, 35, 609–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavez-Tapia, N.C.; Barrientos-Gutierrez, T.; Tellez-Avila, F.; Soares-Weiser, K.; Mendez-Sanchez, N.; Gluud, C.; Uribe, M. Meta-analysis: Antibiotic prophylaxis for cirrhotic patients with upper gastrointestinal bleeding - an updated Cochrane review. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2011, 34, 509–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Pagán, J.C.; Caca, K.; Bureau, C.; Laleman, W.; Appenrodt, B.; Luca, A.; Abraldes, J.G.; Nevens, F.; Vinel, J.P.; Mössner, J.; et al. Early Use of TIPS in Patients with Cirrhosis and Variceal Bleeding. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 2370–2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boike, J.R.; Thornburg, B.G.; Asrani, S.K.; Fallon, M.B.; Fortune, B.E.; Izzy, M.J.; Verna, E.C.; Abraldes, J.G.; Allegretti, A.S.; Bajaj, J.S.; et al. North American Practice-Based Recommendations for Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunts in Portal Hypertension. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 20, 1636–1662.e36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, E.W.; Eghtesad, B.; Garcia-Tsao, G.; Haskal, Z.J.; Hernandez-Gea, V.; Jalaeian, H.; Kalva, S.P.; Mohanty, A.; Thabut, D.; Abraldes, J.G. AASLD Practice Guidance on the use of TIPS, variceal embolization, and retrograde transvenous obliteration in the management of variceal hemorrhage. Hepatology 2023, 79, 224–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castellanos, E.R.; Seron, P.; Gisbert, J.P.; Cosp, X.B. Cochrane Hepato-Biliary Group Endoscopic injection of cyanoacrylate glue versus other endoscopic procedures for acute bleeding gastric varices in people with portal hypertension. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2015, 2015, CD010180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Xiang, T.; Wu, J.; Wang, X.; Zhu, Y.; Xi, X.; Yan, Y.; Yang, J.; García-Pagán, J.C.; Yang, L. Endoscopic Cyanoacrylate Injection Versus Balloon-Occluded Retrograde Transvenous Obliteration for Prevention of Gastric Variceal Bleeding: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Hepatology 2021, 74, 2074–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanagawa, H.; Mima, S.; Kouyama, H.; Gotoh, K.; Uchida, T.; Okuda, K. Treatment of gastric fundal varices by balloon-occluded retrograde transvenous obliteration. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 1996, 11, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, C.F.; Amodio, P.; Bajaj, J.S.; Dhiman, R.K.; Montagnese, S.; Taylor-Robinson, S.D.; Vilstrup, H.; Jalan, R. Hepatic encephalopathy: Novel insights into classification, pathophysiology and therapy. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 1526–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louissaint, J.; Deutsch-Link, S.; Tapper, E.B. Changing Epidemiology of Cirrhosis and Hepatic Encephalopathy. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 20, S1–S8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilstrup, H.; Amodio, P.; Bajaj, J.; Cordoba, J.; Ferenci, P.; Mullen, K.D.; Weissenborn, K.; Wong, P. Hepatic encephalopathy in chronic liver disease: 2014 practice guideline by the European Association for the Study of the Liver and the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology 2014, 60, 715–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapper, E.B.; Parikh, N.D.; Waljee, A.K.; Volk, M.; Carlozzi, N.E.; Lok, A.S.-F. Diagnosis of Minimal Hepatic Encephalopathy: A Systematic Review of Point-of-Care Diagnostic Tests. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 113, 529–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campagna, F.; Montagnese, S.; Ridola, L.; Senzolo, M.; Schiff, S.; De Rui, M.; Pasquale, C.; Nardelli, S.; Pentassuglio, I.; Merkel, C.; et al. The animal naming test: An easy tool for the assessment of hepatic encephalopathy. Hepatology 2017, 66, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Román, E.; Córdoba, J.; Torrens, M.; Torras, X.; Villanueva, C.; Vargas, V.; Guarner, C.; Soriano, G. Minimal Hepatic Encephalopathy Is Associated With Falls. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 106, 476–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labenz, C.; Baron, J.S.; Toenges, G.; Schattenberg, J.M.; Nagel, M.; Sprinzl, M.F.; Nguyen-Tat, M.; Zimmermann, T.; Huber, Y.; Marquardt, J.U.; et al. Prospective evaluation of the impact of covert hepatic encephalopathy on quality of life and sleep in cirrhotic patients. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 48, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajaj, J.S.; Hafeezullah, M.; Hoffmann, R.G.; Varma, R.R.; Franco, J.; Binion, D.G.; Hammeke, T.A.; Saeian, K. Navigation skill impairment: Another dimension of the driving difficulties in minimal hepatic encephalopathy. Hepatology 2008, 47, 596–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wijdicks, E.F. Hepatic Encephalopathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1660–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kircheis, G.; Nilius, R.; Held, C.; Berndt, H.; Buchner, M.; Gortelmeyer, R.; Hendricks, R.; Kruger, B.; Kuklinski, B.; Meister, H.; et al. Therapeutic efficacy of L-ornithine-L-aspartate infusions in patients with cirrhosis and hepatic encephalopathy: Results of a placebo-controlled, double-blind study. Hepatology 1997, 25, 1351–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, T.; Qiu, J.H.; Qiao, L. Rifaximin treatment in hepatic encephalopathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 2424, author reply 2424–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bureau, C.; Thabut, D.; Jezequel, C.; Archambeaud, I.; D’Alteroche, L.; Dharancy, S.; Borentain, P.; Oberti, F.; Plessier, A.; De Ledinghen, V.; et al. The Use of Rifaximin in the Prevention of Overt Hepatic Encephalopathy After Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Ann. Intern. Med. 2021, 174, 633–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, A.; Sharma, B.C.; Sharma, P.; Sarin, S.K. Secondary Prophylaxis of Hepatic Encephalopathy in Cirrhosis: An Open-Label, Randomized Controlled Trial of Lactulose, Probiotics, and No Therapy. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 107, 1043–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajaj, J.S.; Fagan, A.; Gavis, E.A.; Kassam, Z.; Sikaroodi, M.; Gillevet, P.M. Long-term Outcomes of Fecal Microbiota Transplantation in Patients With Cirrhosis. Gastroenterology 2019, 156, 1921–1923.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, Y.R.; Ali, H.; Tiwari, A.; Guevara-Lazo, D.; Nombera-Aznaran, N.; Pinnam, B.S.M.; Gangwani, M.K.; Gopakumar, H.; Sohail, A.H.; Kanumilli, S.; et al. Role of fecal microbiota transplant in management of hepatic encephalopathy: Current trends and future directions. World J. Hepatol. 2024, 16, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bloom, A.; Bloom, S.; Silva, H.; Nicoll, A.J.; Sawhney, R. Zinc supplementation and its benefits in the management of chronic liver disease: An in-depth literature review. Ann. Hepatol. 2021, 25, 100549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grüngreiff, K.; Reinhold, D.; Wedemeyer, H. The role of zinc in liver cirrhosis. Ann. Hepatol. 2016, 15, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, M.K.; Zhou, Z.; Cave, M.; Barve, A.; McClain, C.J. Zinc and Liver Disease. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2012, 27, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badal, B.D.; Fagan, A.; Tate, V.; Mousel, T.; Gallagher, M.L.; Puri, P.; Davis, B.; Miller, J.; Sikaroodi, M.; Gillevet, P.; et al. Substitution of One Meat-Based Meal with Vegetarian and Vegan Alternatives Generates Lower Ammonia and Alters Metabolites in Cirrhosis: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2024, 15, 10–14309. [Google Scholar]
- Laleman, W.; Simon-Talero, M.; Maleux, G.; Perez, M.; Ameloot, K.; Soriano, G.; Villalba, J.; Garcia-Pagan, J.; Barrufet, M.; Jalan, R.; et al. Embolization of large spontaneous portosystemic shunts for refractory hepatic encephalopathy: A multicenter survey on safety and efficacy. Hepatology 2013, 57, 2448–2457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynn, A.M.; Singh, S.; Congly, S.E.; Khemani, D.; Johnson, D.H.; Wiesner, R.H.; Kamath, P.S.; Andrews, J.C.; Leise, M.D. Embolization of portosystemic shunts for treatment of medically refractory hepatic encephalopathy. Liver Transplant. 2016, 22, 723–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huelin, P.; Piano, S.; Solà, E.; Stanco, M.; Solé, C.; Moreira, R.; Pose, E.; Fasolato, S.; Fabrellas, N.; de Prada, G.; et al. Validation of a Staging System for Acute Kidney Injury in Patients With Cirrhosis and Association With Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 15, 438–445.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, A.P.; Knapp, S.M.; Orman, E.S.; Ghabril, M.S.; Nephew, L.D.; Anderson, M.; Ginès, P.; Chalasani, N.P.; Patidar, K.R. Changing epidemiology and outcomes of acute kidney injury in hospitalized patients with cirrhosis – a US population-based study. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 1092–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fede, G.; D’aMico, G.; Arvaniti, V.; Tsochatzis, E.; Germani, G.; Georgiadis, D.; Morabito, A.; Burroughs, A.K. Renal failure and cirrhosis: A systematic review of mortality and prognosis. J. Hepatol. 2012, 56, 810–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angeli, P.; Gines, P.; Wong, F.; Bernardi, M.; Boyer, T.D.; Gerbes, A.; Moreau, R.; Jalan, R.; Sarin, S.K.; Piano, S.; et al. Diagnosis and management of acute kidney injury in patients with cirrhosis: Revised consensus recommendations of the International Club of Ascites. Gut 2015, 64, 531–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomson, M.J.; Taylor, A.; Sharma, P.; Lok, A.S.; Tapper, E.B. Limited Progress in Hepatorenal Syndrome (HRS) Reversal and Survival 2002–2018: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2019, 65, 1539–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martín–Llahí, M.; Guevara, M.; Torre, A.; Fagundes, C.; Restuccia, T.; Gilabert, R.; Solá, E.; Pereira, G.; Marinelli, M.; Pavesi, M.; et al. Prognostic Importance of the Cause of Renal Failure in Patients With Cirrhosis. Gastroenterology 2011, 140, 488–496.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davenport, A.; Cholongitas, E.; Xirouchakis, E.; Burroughs, A.K. Pitfalls in assessing renal function in patients with cirrhosis--potential inequity for access to treatment of hepatorenal failure and liver transplantation. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2011, 26, 2735–2742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huelin, P.; Solà, E.; Elia, C.; Solé, C.; Risso, A.; Moreira, R.; Carol, M.; Fabrellas, N.; Bassegoda, O.; Juanola, A.; et al. Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin for Assessment of Acute Kidney Injury in Cirrhosis: A Prospective Study. Hepatology 2019, 70, 319–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiwall, R.; Kumar, A.; Bhardwaj, A.; Kumar, G.; Bhadoria, A.S.; Sarin, S.K. Cystatin C predicts acute kidney injury and mortality in cirrhotics: A prospective cohort study. Liver Int. 2017, 38, 654–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, K.; Bhurwal, A.; Law, C.; Ventre, S.; Minacapelli, C.D.; Kabaria, S.; Li, Y.; Tait, C.; Catalano, C.; Rustgi, V.K. Acute kidney injury and hepatorenal syndrome in cirrhosis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 27, 3984–4003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, F.; Pappas, S.C.; Curry, M.P.; Reddy, K.R.; Rubin, R.A.; Porayko, M.K.; Gonzalez, S.A.; Mumtaz, K.; Lim, N.; Simonetto, D.A.; et al. Terlipressin plus Albumin for the Treatment of Type 1 Hepatorenal Syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 818–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Yang, C.; Yan, S.; Liu, X.; Zhou, L.; Yuan, X. Sarcopenia in cirrhosis: From pathophysiology to interventional therapy. Exp. Gerontol. 2024, 196, 112571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyas, F.; Aloor, F.Z.; Satapathy, S.K. Sarcopenia and Frailty in Advanced Liver Disease Patients: A Comprehensive Review. Curr. Hepatol. Rep. 2024, 23, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tandon, P.; Montano-Loza, A.J.; Lai, J.C.; Dasarathy, S.; Merli, M. Sarcopenia and frailty in decompensated cirrhosis. J. Hepatol. 2021, 75 (Suppl. S1), S147–S162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuhrmann, V.; Krowka, M. Hepatopulmonary syndrome. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 744–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raevens, S.; Boret, M.; Fallon, M.B. Hepatopulmonary syndrome. JHEP Rep. 2022, 4, 100527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fallon, M.B.; Krowka, M.J.; Brown, R.S.; Trotter, J.F.; Zacks, S.; Roberts, K.E.; Shah, V.H.; Kaplowitz, N.; Forman, L.; Wille, K.; et al. Impact of Hepatopulmonary Syndrome on Quality of Life and Survival in Liver Transplant Candidates. Gastroenterology 2008, 135, 1168–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, F.P.; Martínez-Pallí, G.; Barberà, J.A.; Roca, J.; Navasa, M.; Rodríguez-Roisin, R. Gas exchange mechanism of orthodeoxia in hepatopulmonary syndrome. Hepatology 2004, 40, 660–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krowka, M.J.; Fallon, M.B.; Kawut, S.M.; Fuhrmann, V.; Heimbach, J.K.; Ramsay, M.A.; Sitbon, O.; Sokol, R.J. International Liver Transplant Society Practice Guidelines: Diagnosis and Management of Hepatopulmonary Syndrome and Portopulmonary Hypertension. Transplantation 2016, 100, 1440–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, M.S.; Angeli, P.; Trebicka, J. Acute and non-acute decompensation of liver cirrhosis (47/130). Liver Int. 2024, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
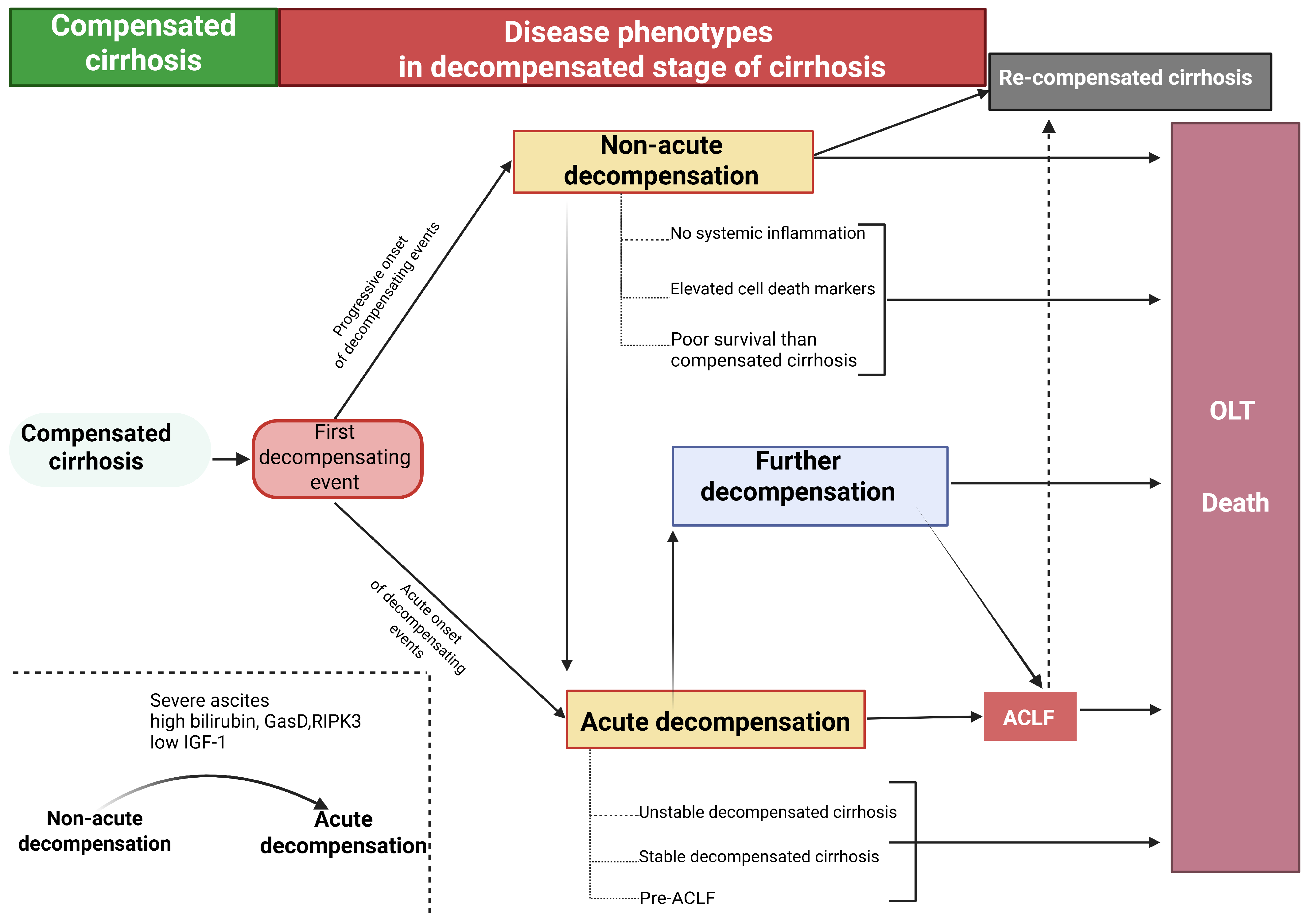
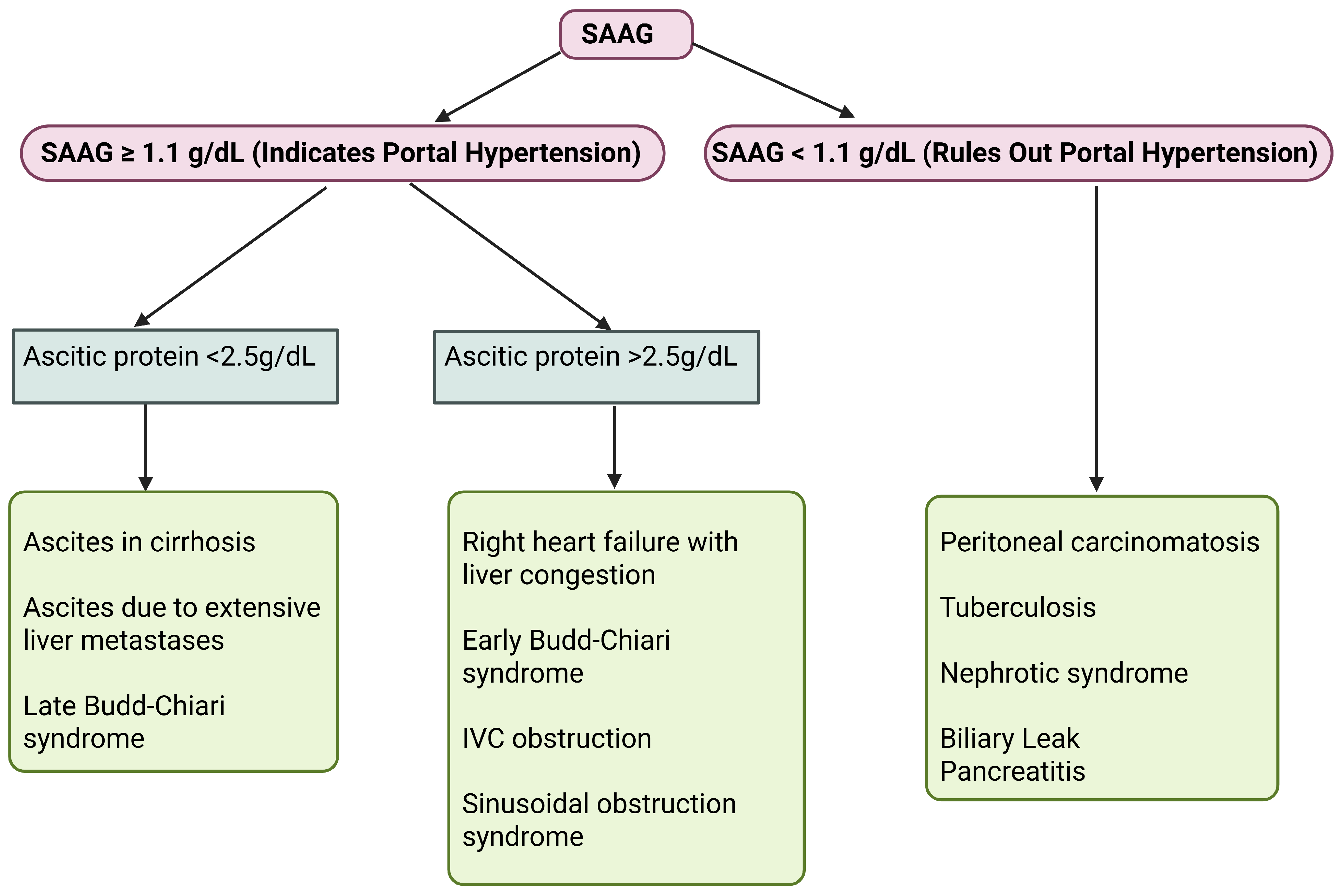
| 1. Alcohol-related liver disease 2. Metabolic and genetic MASLD Haemochromatosis Wilson’s disease al-antitryp sin deficiency Cystic fibrosis Progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis Lysosomal acid lipase deficiency Tyrosinemia type 1 Type IV glycogen storage disease 3. Auto-immune Autoimmune hepatitis Primary biliary cholangitis 4. Biliary Biliary atresia (paediatrics patients) Biliary strictures Primary sclerosing cholangitis 5. Vascular Budd-Chiari syndrome Veno-occlusive disease Fontan-associated liver disease Cardiac cirrhosis/Right sided heart failure 6. Drugs and toxins (long tenn use) Methotrexate Isoniazid Amiodarone Methyldopa Vitamin A Allopurinol Valproic Acid Vinyl chloride Aflatoxin Herbs like kava and comfrey 7. Cryptogenic cirrhosis 8. Infections Viral hepatitis B Viral hepatitis C Viral hepatitis D (typically superimposed on hepatitis B infection) Schistosomiasis |
| Points | 1 | 2 | 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Encephalopathy | None | Minimal | Advanced (coma) |
| Ascites | Absent | Controlled | Refractory |
| Bilirubin (μmol/L) | <34 | 34–51 | >51 |
| Albumin (g/L) | >35 | 28–35 | <28 |
| Prothrombin (s) a | <4 | 4–6 | >6 |
| Target | Treatments |
|---|---|
| Etiological therapy | Antiviral therapy (HCV, HBV), immunosuppression (AIH), sustained alcohol abstinence, and therapeutic relapse management |
| Adoption of healthy lifestyle | Reduction and cessation of alcohol consumption, regular moderate aerobic exercise, and dietary counseling aimed at maintaining a BMI between 18 and 29 kg/m2. Ensuring adequate protein intake (exceeding 1.2–1.5 g/kg/day), avoiding processed foods, high-sugar and high-fructose corn syrup-sweetened products, excessive salt, and tobacco use, as well as incorporating a nocturnal high-protein snack |
| Elevated hepatic vascular resistance | Carvedilol, TIPS |
| Activated hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) | Antifibrotic agents (experimental), anticoagulants |
| Liver sinusoidal endothelial cell (LSEC) dedifferentiation | Statins |
| Hepatocellular damage | Antioxidant Therapy |
| Splanchnic vasodilation | Nonselective beta-blockers, Carvedilol, Somatostatin, Terlipressin, and analogs |
| Gut-liver axis | Nonselective beta-blockers, Carvedilol, probiotics, prebiotics, fecal microbiota transplantation, antibiotics |
| Collaterals and varices | Nonselective beta-blockers, Carvedilol, antiangiogenics (experimental), endoscopic therapy, collateral embolisation, BRTO, PARTO, esophageal stents, balloon tamponade |
| Endothelial dysfunction and NO imbalance | NO donors (experimental), phosphodiesterase inhibitors (sildenafil, tadalafil) |
| Microbiome modulation | Prebiotics, postbiotics (experimental), dietary fiber interventions |
| Renal dysfunction and hepatorenal syndrome | Terlipressin, albumin, norepinephrine |
| Liver transplantation | Liver transplantation (advanced decompensated cirrhosis) |
| Therapy | Mechanism of Action | Initial Dose | Titration Strategy | Maximum Dose | Therapeutic Goal | Common Side Effects | Duration of Therapy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Propranolol | Reduces cardiac output through beta-1 receptor blockade, which lowers heart rate and contractility; it also decreases portal pressure. | 20–40 mg twice daily | Titrate gradually every 2–3 days until therapeutic goal is achieved. | No ascites: 320 mg/day; with ascites: 160 mg/day | Target heart rate of 55–60 bpm; maintain SBP ≥ 90 mm Hg | Fatigue, bradycardia, difficulty breathing, low blood pressure, constipation | Therapy should be maintained long-term—or until placement of a TIPS or liver transplantation—no routine surveillance via upper endoscopy recommended |
| Nadolol | Induces constriction of splanchnic arteries by blocking beta-2 receptors, leading to unopposed alpha-adrenergic vasoconstrictive activity. | 20–40 mg at bedtime | Adjust dose as required | No ascites: 160 mg/day; with ascites: 80 mg/day | Target heart rate of 55–60 bpm; maintain SBP ≥ 90 mm Hg | Tiredness, slow heart rate, low blood pressure | Therapy should be maintained long-term—or until placement of a TIPS or liver transplantation—no routine surveillance via upper endoscopy recommended |
| Carvedilol | In addition to beta-1 and beta-2 receptor blockade, reduces intrahepatic vascular resistance via alpha-adrenergic activity. | 6.25 mg one time daily | Rise to 6.25 mg two times daily after 3 days | 12.5 mg/day (higher doses possible for non-liver conditions) | No specific heart rate target; maintain SBP ≥ 90 mm Hg | Low blood pressure, dizziness, fatigue | Therapy should be maintained long-term—or until placement of a TIPS or liver transplantation—no routine surveillance via upper endoscopy recommended |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Battle, A.; Mudd, J.; Ahlenstiel, G.; Kalo, E. Liver Cirrhosis: Evolving Definitions, and Recent Advances in Diagnosis, Prevention and Management. Livers 2025, 5, 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/livers5030028
Battle A, Mudd J, Ahlenstiel G, Kalo E. Liver Cirrhosis: Evolving Definitions, and Recent Advances in Diagnosis, Prevention and Management. Livers. 2025; 5(3):28. https://doi.org/10.3390/livers5030028
Chicago/Turabian StyleBattle, Andrew, Julie Mudd, Golo Ahlenstiel, and Eric Kalo. 2025. "Liver Cirrhosis: Evolving Definitions, and Recent Advances in Diagnosis, Prevention and Management" Livers 5, no. 3: 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/livers5030028
APA StyleBattle, A., Mudd, J., Ahlenstiel, G., & Kalo, E. (2025). Liver Cirrhosis: Evolving Definitions, and Recent Advances in Diagnosis, Prevention and Management. Livers, 5(3), 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/livers5030028







