The Cape Gooseberry Constituent Physalin B Ameliorates Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis and Attenuates Liver Fibrosis
Abstract
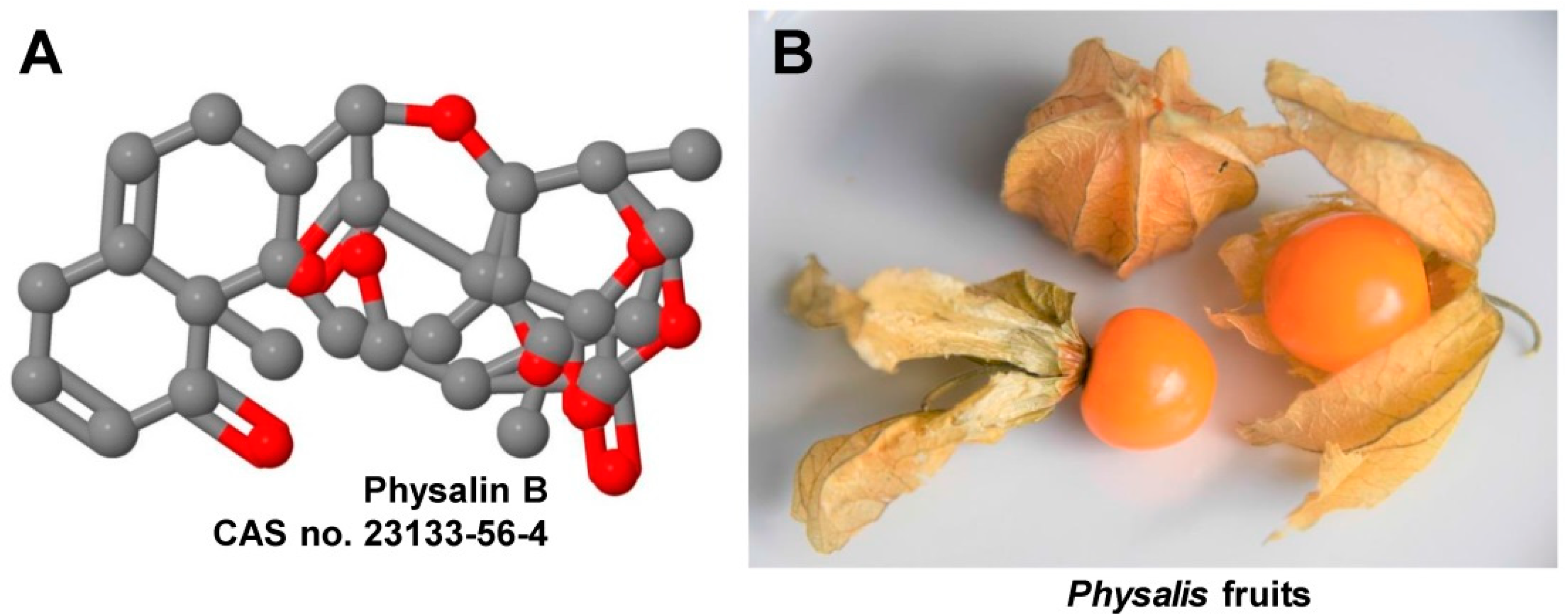
1. Introduction
2. Discussion
3. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Weiskirchen, R. Hepatoprotective and anti-fibrotic agents: It’s time to take the next step. Front. Pharmacol. 2016, 6, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.; Zhou, F.; Shen, S.; Zhang, T. Fighting liver fibrosis with naturally occurring sntioxidants. Planta Med. 2018, 84, 1318–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Oliveira, A.M.; Malunga, L.N.; Perussello, C.A.; Beta, T.; Hoffmann Ribani, R. Phenolic acids from fruits of Physalis angulata L. in two stages of maturation. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2020, 131, 448–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Wang, S.; Zhou, F.; Li, P.; Wang, Y.; Gan, L.; Lin, L. Physalin B induces cell cycle arrest and triggers apoptosis in breast cancer cells through modulating p53-dependent apoptotic pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 101, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.H.; Li, J.; Zhu, X.Y.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Ye, S.T.; Leng, Y.R.; Yang, T.; Zhang, H.; Kong, L.Y. Physalin B ameliorates nonalcoholic steatohepatitis by stimulating autophagy and NRF2 activation mediated improvement in oxidative stress. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2021, 164, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Ye, S.; Yu, D.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, M.; Leng, Y.; Yang, T.; Luo, J.; Chen, X.; et al. Physalin B attenuates liver fibrosis via suppressing LAP2α-HDAC1 mediated deacetylation of GLI1 and hepatic stellate cell activation. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.M.; Han, W.; Li, J.; Hu, L.H.; Zhou, Y.B. Physalin B not only inhibits the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway but also induces incomplete autophagic response in human colon cancer cells in vitro. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2015, 36, 517–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Xu, N.; Hu, X.; Zheng, Y. Anti-colitic effects of Physalin B on dextran sodium sulfate-induced BALB/c mice by suppressing multiple inflammatory signaling pathways. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 259, 112956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soares, M.B.; Brustolim, D.; Santos, L.A.; Bellintani, M.C.; Paiva, F.P.; Ribeiro, Y.M.; Tomassini, T.C.; Ribeiro Dos Santos, R. Physalins B, F and G, seco-steroids purified from Physalis angulata L., inhibit lymphocyte function and allogeneic transplant rejection. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2006, 6, 408–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soares, M.B.; Bellintani, M.C.; Ribeiro, I.M.; Tomassini, T.C.; Ribeiro dos Santos, R. Inhibition of macrophage activation and lipopolysaccaride-induced death by seco-steroids purified from Physalis angulata L. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2003, 459, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobo-Herrera, N.J.; Bremner, P.; Marquez, N.; Gupta, M.P.; Gibbons, S.; Muñoz, E.; Heinrich, M. Physalins from Witheringia solanacea as modulators of the NF-κB cascade. J. Nat. Prod. 2006, 69, 328–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, L.; Chai, H.B.; Castillo, J.J.; Soejarto, D.D.; Farnsworth, N.R.; Cordell, G.A.; Pezzuto, J.M.; Kinghorn, A.D. Cytotoxic constituents of Brachistus stramoniifolius. Phytother. Res. 2003, 17, 520–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Lin, M.; Hu, X.; Zhai, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Lou, Y.; ShenTu, J.; Wu, L. Simultaneous pharmacokinetics and stability studies of physalins in rat plasma and intestinal bacteria culture media using liquid chromatography with mass spectrometry. J. Sep. Sci. 2018, 41, 1781–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Chen, J.; Liu, L.; Liang, X.; Hong, D. In vivo pharmacokinetics of and tissue distribution study of physalin B after intravenous administration in rats by liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2016, 30, 1278–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doheny, D.; Manore, S.G.; Wong, G.L.; Lo, H.W. Hedgehog signaling and truncated GLI1 in cancer. Cells 2020, 9, 2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Weiskirchen, S.; Weiskirchen, R. The Cape Gooseberry Constituent Physalin B Ameliorates Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis and Attenuates Liver Fibrosis. Livers 2021, 1, 98-101. https://doi.org/10.3390/livers1020009
Weiskirchen S, Weiskirchen R. The Cape Gooseberry Constituent Physalin B Ameliorates Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis and Attenuates Liver Fibrosis. Livers. 2021; 1(2):98-101. https://doi.org/10.3390/livers1020009
Chicago/Turabian StyleWeiskirchen, Sabine, and Ralf Weiskirchen. 2021. "The Cape Gooseberry Constituent Physalin B Ameliorates Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis and Attenuates Liver Fibrosis" Livers 1, no. 2: 98-101. https://doi.org/10.3390/livers1020009
APA StyleWeiskirchen, S., & Weiskirchen, R. (2021). The Cape Gooseberry Constituent Physalin B Ameliorates Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis and Attenuates Liver Fibrosis. Livers, 1(2), 98-101. https://doi.org/10.3390/livers1020009






