Abstract
Obesity is a chronic metabolic disease that can promote serious comorbidities as maternal complications. Thus, the objective of this study was to analyze the prevalence of overweight and obesity, and the incidence of maternal complications in pregnant women of Sinop, Mato Grosso, Brazil. It was a retrospective cohort study with clinical and epidemiological data collected from the medical records of pregnant women diagnosed in 2020. Pregnant women were subdivided into three groups: eutrophic, overweight, and obese. Data from 700 pregnant women were evaluated, 251 in the eutrophic group, in the 220 overweight group and 229 in the obese group. The percentage of pregnant women with diabetes mellitus and arterial hypertension was significantly higher in the overweight and obesity groups when compared with the eutrophic group. The incidence of gestational diabetes mellitus was significantly higher in the overweight and obese groups when compared with the eutrophic group (p < 0.0001). The incidence of gestational arterial hypertension was also significantly higher in the overweight (6.8%) and obese (12.7%) groups when compared with the eutrophic group (1.2%) (p < 0.0001). The incidence of pre-eclampsia was also higher and statistically different in the overweight and obese groups. In conclusion, it was observed that most of the pregnant women presented with overweight/obesity and that this excess body weight contributed significantly to the incidence of several maternal complications.
1. Introduction
Obesity is a complex chronic metabolic disease characterized by an excess of adipose tissue, mainly visceral white adipose tissue, and characterized by chronic low-grade inflammation, oxidative stress, insulin resistance and hyperinsulinemia [1,2].
Obesity can be classified according to body mass index (BMI), and individuals are considered overweight when they have a BMI of 25.0 to 29.9 kg/m2 and with obesity when they have BMI values above 30. Still, two other measurements such as the waist–hip ratio and the waist circumference measurement can be used to classify an individual with obesity [3].
Obesity is a multifactorial disease resulting from the interaction among inadequate diet, low physical activity, socioeconomic condition, environmental factors and the individual’s own genetic factors [3,4]. In most cases, obesity develops when dietary energy intake exceeds energy expenditure, generating an energy imbalance. Excess energy is then converted into triglycerides, which are stored in adipose tissue depots that expand in size (hypertrophy) or in number (hyperplasia), thus increasing weight gain [3,4,5].
The worldwide prevalence of overweight and obesity has doubled since 1980, and nearly one-third of the world’s population is classified as overweight or obese. Rates have increased for all ages, especially after 20 years old, and in both sexes, regardless of geographic location, ethnicity or socioeconomic status [5].
Recent data show that obesity is considered the most common nutritional disease of the century and of the modern era, making it an endemic public health problem [3]. According to estimates, in the year 2025, there will be about 2.3 billion adults worldwide who are overweight and 700 million who are obese. Currently in Brazil, the rate of overweight people is 55.7% (57.8% for men and 53.9% for women), while the general rate of individuals with obesity is 19.8%, and when analyzed by gender group, it was observed that 18.7% of men and 20.7% of women present with obesity [3,4,5,6].
Obesity is considered a major public health problem, since it affects almost all physiological functions of the body and contributes to the emergence of several other comorbidities, such as cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, dyslipidemia, anxiety, depression, various types of cancer, sleep disorders, apnea and changes in hormonal and reproductive functions [1,2,7]. In addition, with the increase in obesity rates worldwide, the number of women with overweight/obesity of reproductive age has also increased [8]. This has a detrimental effect on women’s reproductive life, women’s health during pregnancy and even fetal development, as well as the baby’s life, generating a great impact on maternity services [8,9].
Among the main maternal complications are gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM), gestational arterial hypertension (GAH), spontaneous abortion, pre-eclampsia, eclampsia, thromboembolism and intrapartum complications, including induction of labor, postpartum hemorrhage and an increased risk of cesarean section [9,10]. Fetal or neonatal complications include macrosomia, shoulder dystocia, premature birth, being large for gestational age (LGA) and neonatal death [9,11,12]. Thus, the significant impact that obesity presents to gestational period can be observed, and we can see the importance of preventing, controlling and treating this severe condition [13].
It is very important to prevent the obesity condition through changes in eating habits, having a healthier diet rich in proteins, dietary fiber, fruits and vegetables, and low consumption of carbohydrates and lipids, as well as practicing physical exercise regularly [14,15,16,17,18,19]. Furthermore, during pregnancy, it is essential to undergo medical monitoring; maintain an adequate and balanced diet; receive supplementation with some micronutrients, such as iron, folic acid and vitamins; and to carry out physical activities recommended for pregnant women.
It is well known that a healthier lifestyle, including a balanced diet and physical activity practices, reduces the risk of excessive weight gain and GDM development [19,20]. Ferrari and Joinsten, in 2021 [19], demonstrated that the practice of physical activity can increase the amount of muscle mass, and consequently myokines, which have a significantly anti-inflammatory effect, contributing decreased development of maternal complications, such as GDM and GAH.
In addition, it is important to mention that, in accordance with the review of Różańska-Walędziak et al. (2023) [21], bariatric surgery (BS) is the mainstay treatment for obesity, and the effects of the reduction in body weight significantly decrease the incidence of maternal complications during pregnancy, including GDM, GAH and macrosomia. However, pregnant women that have BS should be alert for some nutritional and vitamin deficiencies, as these deficiencies due to changes in the gastrointestinal tract are associated with increased risk of fetal growth retardation and neonates who are small for their gestational age. Furthermore, Walędziak et al. (2021) [22] demonstrated that pregnancy after bariatric surgery is associated with a higher risk of infants who are small for their gestational age (SGA) and maternal anemia, requiring greater attention during prenatal care.
Few studies have been developed in the Mato Grosso state demonstrating the impact of overweight on gestational outcomes, and, to our knowledge, no study was developed in Sinop, MT, Brazil, to demonstrate the clinical profile of pregnant women in this region, as well as the influence of excess body weight on the incidence of maternal complications in these pregnant women. Thus, the present study aimed to evaluate the clinical and epidemiological profile of pregnant women in Sinop, MT, Brazil, evaluating the prevalence of overweight and obesity in these population and the influence of this excess body weight on the incidence of maternal complications, such as GDM, GAH, pre-eclampsia and eclampsia.
2. Materials and Methods
This was a retrospective cohort study with a quantitative approach with data collected from participants diagnosed with pregnancy from 1 January 2020 to 31 December 2020 attending the UBS (Basic Health Units) and CRASM (Women’s Health Reference Center) in Sinop, Mato Grosso (MT), Brazil, via convenience sampling.
The data were obtained by reading the medical records of pregnant women attending 10 UBS and the CRASM.
The city of study, Sinop, is in the north of the state of MT and is classified as one of the 4 largest cities of MT [23]. It is located 500 km from Cuiabá, the state capital, and its economy is based on logging, agribusiness, commerce and services, and its biome is the Amazonia. Its territorial area is 3,990,870 km2 and it has an estimated population of 196,067 inhabitants [23].
All data that were collected were from patients assisted by the public health plans of Brazil (SUS, Unified Health System). Data collection occurred during weekly visits to the UBS and CRASM through readings, analyses and electronic recordings in Excel spreadsheets. The identities of the participants were kept confidential.
Given the declaration of the World Health Organization (WHO) on 30 January 2020 regarding a public health emergency, namely the outbreak of the disease caused by the new coronavirus (COVID-19), sanitary measures were adopted to avoid agglomeration, contamination and transmission of the virus.
Inclusion criteria: pregnant women diagnosed from 1 January 2020 to 31 December 2020; pregnant women attended by the 10 UBS and by CRASM in Sinop, MT; pregnant women that had information on their BMI in the medical records (the value of BMI should be referenced until 12 weeks of gestation) and pregnant women aged 18 years old or more.
Exclusion criteria: pregnancy with multiple gestation and pregnant women who were underweight (Figure 1).
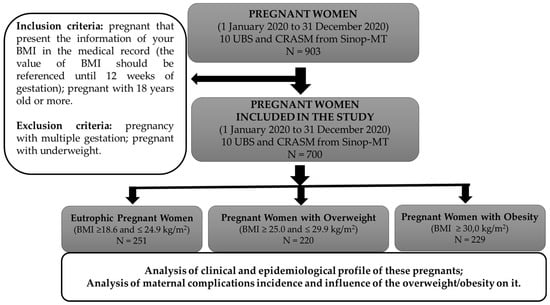
Figure 1.
Representative diagram of the study’s stages and inclusion and exclusion criteria.
From August 2021 to December 2022, data were collected by analyzing the medical records.
The following data were collected and analyzed: pregnancy age (age at which the pregnancy was diagnosed); body weight; height; BMI; marital status; ethnicity; date of last menstrual period; gestational age; single or multiple pregnancy; number of pregnancies; blood type; the presence of chronic diseases such as diabetes mellitus (DM), systemic arterial hypertension (SAH) and dyslipidemia; and the presence of maternal complications such as GDM, GAH, pre-eclampsia and eclampsia. The study also evaluated the results of laboratory exams, such as red blood count and blood glucose, to assess the presence of anemia and hyperglycemia, respectively, and evaluated the possible pharmacological treatments used by the patients.
To analyze the influence of overweight/obesity on the incidence of maternal complications, the data of patients were divided into three groups (Figure 1):
Eutrophic: pregnant women with BMI ≥ 18.6 and ≤24.9 kg/m2,
Overweight: pregnant women with BMI ≥ 25.0 and ≤29.9 kg/m2,
Obese: pregnant women with BMI ≥ 30.0 kg/m2.
The ethical aspects were considered, following Resolution 466/12 of the Ministry of Health, which stipulates regulatory ethical standards for research involving human beings. The execution of the project was carried out only after authorization was received by the Education and Service Integration Commission (CIES), as well as approval by the Ethics Committee on Research with Human Beings, process No. 4,214,565.
The data were tabulated and analyzed in Microsoft® Excel® software spreadsheets (Office 365) version 2404, using descriptive analysis evaluating the frequency and distribution. The data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation (SD) or as percentages (%). The results were statistically evaluated by one-way ANOVA test and Tukey’s post hoc test for the quantitative analysis of continuous variables, or by chi-square test (χ2) for categorical variables. Furthermore, the study used the Kruskal–Wallis test and Dunn’s post-test when the results did not assume a Gaussian curve; these results are presented as the median and interquartile range (25–75%). The analyses were carried out using the GraphPad Prism® 8 Program. The minimum acceptable significance level was p < 0.05.
3. Results
Data were collected from the medical records of 700 pregnant women (Table 1). It was observed that more than half of the evaluated pregnant women (64.1%) had overweight/obesity (BMI ≥ 25 kg/m2), while 35.9% had a normal BMI.

Table 1.
Clinical and epidemiological profile of pregnant women in Sinop, MT, according to their body mass index (BMI).
Regarding the age group, it was observed that the overweight and obese groups showed a significant difference when compared with the eutrophic group, with the median age being significantly higher in the overweight and obese groups when compared with the eutrophic group (p < 0.0001) (Table 1).
Body weight and BMI, as expected, were significantly higher in the overweight and obese groups when compared with the eutrophic group (p < 0.0001) (Table 1).
For the marital status variable, there was no statistical difference between the three groups evaluated. The highest percentage was 44.4%, which represented unavailable data, followed by those who were married or in a stable union, who represented 31.2% of the sample.
Hispanic ethnicity was the classification that presented the highest frequency distribution among the groups of pregnant women. In this regard, 37.1% of the pregnant women who belonged to the eutrophic group had this Hispanic classification, along with 32.2% who belonged to the overweight group and 24.9% of the individuals with obesity. Furthermore, there was a higher percentage of unavailable data, which can be associated with the fact that this variable is self-declaratory and many people do not know how to declare themselves.
Regarding the number of pregnancies, regarding having only one pregnancy, this had a higher rate in the eutrophic group. For two, four and more than four pregnancies, the obese group had higher rates.
Regarding blood typing, it was observed that in all groups, the most frequent type was O+ (27.0%) followed by blood Type A+ (13.6%). Still, it is important to emphasize that a significant percentage of unavailable data was observed, which is something of concern when it comes to pregnant women, as it is an important information to track the compatibility of Rh factors in maternal blood and in the blood of the fetus.
In accordance with the red blood count in the first trimester, the data showed that all analyzed groups presented with hemoglobin (Hb) and hematocrit (HCT) values within normal limits, since the reference values for hemoglobin are 12.0 to 15.0 g/dL and those for HCT are 34% to 47% [24].
Regarding glycemic levels in the first trimester, it can be observed that the glucose levels were significantly higher in the groups with overweight and obesity when compared with the eutrophic group (p < 0.001)(Table 1).
According to data from the Guidelines of the Brazilian Society of Diabetes 2019–2020, in pregnant women, a fasting blood glucose between 92 and 125 mg/dL in the first trimester of pregnancy, before completing 20 gestational weeks, is indicative of GDM or diabetes mellitus that occurs during pregnancy, requiring a new blood glucose measurement to confirm the diagnosis [25]. In relation to the frequency of the distribution of the glycemic range, it was observed that a greater number of pregnant women with a BMI above 25 (n = 28; 12.5%) had a glycemic range between 92 and 125 mg/dL, indicating GDM, whereas the number of pregnant women with a normal BMI who had this glycemic range was 12 (4.8%).
According to the variables of the clinical and laboratory data of the second and third trimesters, all analyzed groups presented Hb and HCT values within the normal range [26]. Furthermore, regarding the median glycemic levels, it was observed that there was no statistical difference among the groups, and all values were within the normal limits. The frequency of distribution of the data for glycemic range was also similar among the groups; however, the number of pregnant women who had glycemic values between 92 and 125 was higher in the group of pregnant women with a BMI above 25 (n = 6) when compared with the eutrophic pregnant group (n = 3) (Table 1). The high percentage of unavailable data (82.1%) for this variable in the second and third trimester may be due to abandonment of follow-up or due to these data not being recorded in the medical records.
As for the variables DM and SAH, before the gestational period, it was observed that there was statistical difference among the groups. The number and percentage of pregnant women who had DM were significantly higher in the overweight (n = 4; 1.8%) and obese (n = 9; 3.9%) groups when compared with the eutrophic (n = 2; 0.8%) group. The incidence of SAH was also significantly higher in the overweight (n = 7; 3.2%) and obese (n = 18; 7.9%) groups when compared with the eutrophic (n = 0; 0.0%) group. In addition, although no statistical difference was observed in the groups for the presence of dyslipidemia, only pregnant women with overweight or obesity presented with this comorbidity (Table 2).

Table 2.
Presence of pre-existing comorbidities and incidence of maternal complications in pregnant women in Sinop, MT, according to body mass index (BMI).
According to the incidence of maternal complications, the incidence of GDM and GAH were significantly higher in the groups with overweight and obesity when compared with the eutrophic group. It was observed that 6 in the eutrophic group, 14 in the overweight group and 28 in the obese group developed GDM (p < 0.0001). Moreover, only 3 pregnant women in the eutrophic group, 15 in the overweight group and 29 in the obese group developed gestational hypertension (p < 0.0001) (Table 2). The number of pregnant women who had pre-eclampsia was also higher in the groups with overweight and obesity (p = 0.003). No statistical difference was observed for eclampsia, and only one pregnant woman with obesity developed this serious maternal complication.
To confirm the association of overweight/obesity with the incidence of maternal complications the data was subdivided into two groups: eutrophic and overweight/obese. Thus, the relative risk (RR) was calculated, as demonstrated in Table 3, which showed that this condition of excess body weight significantly increases the chance of a pregnant woman presenting with maternal complications, such as GDM and GAH.

Table 3.
Presence of pre-existing comorbidities and maternal complications in pregnant women in Sinop, MT, according to body mass index (BMI): analysis of relative risk (RR).
4. Discussion
It was observed that more than half of the evaluated pregnant women had overweight/obesity (BMI ≥ 25 kg/m2). This is in line with data from the literature that demonstrated the large increase in the rates of overweight and obesity in recent years [3,5]. Silva et al. (2014) [27] demonstrated that 9 years ago, 25–30% of pregnant women in Brazil were overweight. According to our results, it can be observed that a higher percentage (64.1%) and significant portion of pregnant women living in Sinop, MT, are overweight/obese, which may have contributed to the increase in the rate of maternal and neonatal complications.
Regarding the age group, it was observed that the median age was significantly higher in the overweight and obese groups (27 (20–27) years old) when compared with the eutrophic group (23 (23–31) years old). These data suggest that increasing age increases the chance that pregnant women will have an accumulation of adipose tissue and metabolic changes resulting from this excess body weight. Data in the literature show that being aged above 30 years old is a factor that interferes with gestational weight gain [28]. However, it is important to mention that the majority of pregnant women in the present work were under 30 years old but still had high BMI values and significant maternal complications.
Regarding the number of pregnancies, when it comes to having only one pregnancy, this had a higher rate in the eutrophic group, which may be due to different maternal characteristics, as age, pre-pregnancy nutritional status, ethnic origin, socioeconomic status, drug use, physical activity and psychosocial factors [29]. Regarding having two, four or more than four pregnancies, the obese group had higher rates, leading to the hypothesis that more pregnancies increase the probability of weight gain or difficulty losing weight, since the abdominal muscle has already been distended and the abdominal region shows the natural flaccidity of the gestational state and, in the case of a lack of exercise and good nutrition, the accumulation and flaccidity tend to increase in the next pregnancy [30].
Regarding blood typing, it was observed that in all groups, the most frequent type was O+ (27.0%), followed by blood Type A+ (13.6%), these being the most common types in the Brazilian population according to results of several studies, such as [31]. Still, it is important to emphasize that a significant percentage of unavailable data was observed, which is something of concern when it comes to pregnant women, as it is an important information to track the compatibility of Rh factors in maternal blood and in the blood of the fetus.
According to the data regarding the red blood count in the first trimester, the data showed that all the analyzed groups presented hemoglobin (Hb) and hematocrit (HCT) values within normal limits, since the reference values for hemoglobin are 12.0 to 15.0 g/dL and those for HCT are 34% to 47% [24]. These results may suggest that the medical indication for the use of folic acid in prenatal care until the end of the first trimester of pregnancy is effective. Folic acid is indicated to prevent malformation of the fetus and maternal anemia; its indication is already recurrent in the SUS (Unified Health System) and in the private plans, and is very effective [32].
Regarding glycemic levels in the first trimester, it can be observed that the glucose levels were significantly higher in the groups with overweight and obesity when compared with the eutrophic group (p < 0.001). This may be directly related to the accumulation of adipose tissue in these groups. The accumulation of adipose tissue leads to chronic low-grade inflammation and insulin resistance [33]. With insulin resistance, peripheral tissues fail to respond adequately to the action of insulin, thus reducing glucose uptake and tissue storage, leading to an increase in circulating glucose levels [7,33].
In agreement with our present study, Monod et al. (2024) [34] demonstrated that both overweight and obesity were associated with several adverse maternal metabolic profiles at the beginning of pregnancy, such as insulin resistance and higher glucose levels during fasting and during the OGTT test. Furthermore, they observed that the excess body weight significantly increased the fetal subcutaneous tissue revealed by ultrasound and increased the percentages of infants who were large for their gestational age, demonstrating several maternal and neonatal complications in conditions of maternal overweight.
Although the average glucose levels in the three groups were within the reference values, the higher level of glucose in the groups with overweight and obesity can contribute to the development of other metabolic complications and pathologies in pregnant women and in newborns, such as a higher incidence of GDM and GAH.
In relation to the frequency of distribution of the glycemic range, it was observed that a greater number of pregnant women with a BMI above 25 (n = 28; 12.5%) had a glycemic range between 92 and 125 mg/dL, indicating GDM, whereas the number of pregnant women with a normal BMI who had this glycemic range was 12 (4.8%). These results are in line with data from the literature demonstrating that an increase in BMI leads to an increase in glycemic levels due to the accumulation of adipose tissue increasing the risk of the development of diabetes [25].
According to the clinical and laboratory data of the second and third trimesters of pregnancy, all analyzed groups presented Hb and HCT values within the normal range [26]. These results may be associated with iron supplementation since the beginning of pregnancy, which may have contributed to the control and prevention of anemia.
The median glycemic levels and frequency of the distribution of the data for glycemic range in the second or third trimester were similar among the groups; however, the number of pregnant women who had glycemic values between 92 and 125 was even higher in the group of pregnant women with a BMI above 25 (n = 6) when compared with the group of eutrophic pregnant women (n = 3) (Table 2). Continued prenatal care, which is recommended to ensure a pregnancy with low maternal–fetal risk or even to reduce the changes observed at the beginning of the gestational period, may have contributed to the maintenance and regularization of glycemic levels in the groups of pregnant women with overweight and obesity. The high percentage of unavailable data (82.1%) for this variable in the second and third trimesters may be due to abandonment of follow-up or through not recording these data in the medical records.
As for the variables DM and SAH, before the gestational period, it was observed that there was statistical difference between the groups. The number and percentage of pregnant women who had DM and SAH were significantly higher in pregnant women with overweight and obesity when compared to the eutrophic groups. In addition, although no statistical difference was observed in the groups for the presence of dyslipidemia, only pregnant women with overweight or obesity presented this comorbidity.
In agreement with O’Malley et al. (2020) [35], the pregnant women diagnosed with GDM were more likely to have obesity (70.4% vs. 42.6%, p < 0.001). In addition, they demonstrated that pregnant women with GDM had higher triglycerides (p = 0.023) and lower HDL cholesterol (p = 0.013) levels, as well as a higher odds ratio of increased triglycerides (odds ratio = 3.2 (1.4–6.9), p = 0.004) and lower HDL cholesterol (odds ratio = 2.2, (1.1–4.7), p = 0.036), suggesting that the association between GDM and dyslipidemia is mediated through maternal obesity.
Kivelä et al. (2021) [36] demonstrated that pregnant women with obesity had significantly higher levels of most very-low density lipoprotein-related measures, many fatty and most amino acids and a more adverse metabolic profile when compared with pregnant women with a normal weight. However, they demonstrated that most metabolic alterations during pregnancy were smaller in pregnant women with obesity when compared with pregnant women with a normal weight.
In accordance with the incidence of maternal complications, the incidence of GDM and GAH were significantly higher in the groups with overweight and obesity when compared with the eutrophic group. The number of pregnant women who had pre-eclampsia was also higher in the groups with overweight and obesity. No statistical difference was observed for eclampsia, and only one pregnant woman with obesity developed this serious maternal complication. These results confirms data from the literature that demonstrated that overweight and obesity contribute significantly to the incidence of maternal complications [10,11,37,38].
Data from a systematic review published by our group [39] also demonstrated that overweight and obesity can increase the risk of GDM, GAH and pre-eclampsia.
Saha et al. (2013) [40], in a cohort study, found that among women with an adequate weight (n = 250) or underweight (n = 150), none developed GDM; on the other hand, 6.8% of women with obesity or overweight (n = 236) developed the disease (p = 0.003). Khalak et al. (2015) [12] also found that among the 175 pregnant women who developed GDM, 78% (n = 136) were overweight or obese.
Neal et al. (2022) [41] also demonstrated that obesity significantly increased the risk of many adverse maternal and neonatal outcomes, such as GDM (22.3%), hypertensive disorder in pregnancy (11.2%) and a higher caesarean section rate (42.5%). Furthermore, they demonstrated that the condition of obesity is independently associated with the incidence of babies who are large for their gestational age (LGA), independent of maternal factors, including GDM.
Interestingly, West et al. (2020) [42] demonstrated that the risk for the development of GDM in women with srPCOS (self-reported polycystic ovary syndrome) was mostly attributed to overweight or obesity, and that women with a normal weight and srPCOS did not seem to be at higher risk of developing GDM, demonstrating the importance of weight management in reproductive-age women.
Machado et al. (2020) [11] demonstrated that the risk of GAH and pre-eclampsia increased with increasing BMI. They demonstrated that pregnant women with obesity Class III, namely pregnant women with a BMI ≥ 40.0 kg/m2, presented with a significantly higher incidence of GAH and pre-eclampsia when compared with pregnant women with obesity Class I (BMI ≥ 30.0 and ≤34.9 kg/m2) and Class II (BMI ≥ 35.0 and ≤39.9 kg/m2). Denison et al. (2014) [43] also observed that the incidence of maternal complications, such as GDM, was 30 times higher in women with BMI ≥ 40 kg/m2 (obesity Class III) when compared with women with a normal BMI (eutrophic).
According to the study by Fuchs et al. (2017) [44], the frequency of hypertensive disorders of pregnancy increases proportionally with the increase in BMI. Furthermore, the study showed that with the addition of factors such as smoking, maternal age and chronic kidney disease, among others, the relative risk increased in both groups of specific women [44]. In contrast, He et al. (2016) [45], in a retrospective case–control study analyzing 47 pregnant women with obesity (cases) and 45 eutrophic controls, observed that the incidence of GAH and pre-eclampsia were similar in both groups, showing no statistical difference.
In conclusion, we observed a higher prevalence of overweight and obesity in pregnant women in Sinop in the North of Mato Grosso state, Brazil. Furthermore, it was concluded that overweight and obesity significantly increased the incidence of maternal complications, such as GDM, GAH and pre-eclampsia, and is a serious risk factor for pregnant women and their babies.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.G.V.P. and E.A.I.F.Q.; methodology, validation and formal analysis, L.G.V.P., N.M.S., C.L.R.S., B.L.O.L., E.B.R., M.S.F., M.O.L., R.R.S., J.S.N.P., V.C.S., D.A.Q. and E.A.I.F.Q.; writing—original draft preparation, L.G.V.P. and E.A.I.F.Q.; writing—review and editing, L.G.V.P., N.M.S., C.L.R.S., B.L.O.L., E.B.R., M.S.F., M.O.L., R.R.S., J.S.N.P., V.C.S., D.A.Q. and E.A.I.F.Q.; supervision, E.A.I.F.Q.; project administration, E.A.I.F.Q.; funding acquisition, E.A.I.F.Q. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors are grateful to the Brazilian agencies CNPQ (proc. No. 001 to E.B.R.; proc. No. 002 to M.S.F.; proc. No. 003 to B.L.O.L.) and FAPEMAT (Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de Mato Grosso) (proc. No. 0001039/2022 to N.M.S.) for financial support for their scholarships.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Ethics Committee on Research with Human Beings (protocol code No. 4214565 and 15 August 2020).
Informed Consent Statement
Patient consent was waived once the study involved only the analysis of the medical records and it was dispensed by the Ethics Committee.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Universidade Federal de Mato Grosso (UFMT). The authors are grateful to the Brazilian agencies CNPQ (proc. No. 001 to E.B.R.; proc. No. 002 to M.S.F.; proc. No. 003 to B.L.O.L.) and FAPEMAT (Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de Mato Grosso) (proc. No. 0001039/2022 to N.M.S.) for financial support for their scholarships.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
References
- Kahn, B.B.; Flier, J.S. Obesity and insulin resistance. J. Clin. Investig. 2000, 106, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed-Ali, V.; Pinkney, J.; Coppack, S. Adipose tissue as an endocrine and paracrine organ. Int. J. Obes. 1998, 22, 1145–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ABESO; da obesidade, M. Assoc. Bras. Para o Estud. Da Obesidade e Da Síndrome Metabólica. 2021. Available online: https://abeso.org.br/obesidade-e-sindrome-metabolica/mapa-da-obesidade/ (accessed on 5 February 2024).
- Dhurandhar, N.V. What is obesity? Int. J. Obes. 2022, 46, 1081–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chooi, Y.C.; Ding, C.; Magkos, F. The epidemiology of obesity. Metabolism 2019, 92, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. World Heath Organization. Obes. Overweight. 2021. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight (accessed on 29 June 2022).
- Kopelman, P.G. Obesity as a medical problem. Nature 2000, 404, 635–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- David, L.S.; Lima, C.D.A.; Santos, V.M.; Pena, G.D.G.; Brito, M.F.S.F.; Silva, R.R.V.; de Pinho, L. Prevalence and associated factors on overweight/obesity in pregnant women assisted by the Family Health Strategy. Rev. Bras. Saúde Matern. Infant. 2023, 23, e20220354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timur, B.B.; Timur, H.; Tokmak, A.; Isik, H.; Eyi, E.G.Y. The Influence of Maternal Obesity on Pregnancy Complications and Neonatal Outcomes in Diabetic and Nondiabetic Women. Geburtshilfe Frauenheilkd. 2018, 78, 400–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, T.Y.; Leung, T.N.; Sahota, D.S.; Chan, O.K.; Chan, L.W.; Fung, T.Y.; Lau, T.K. Trends in maternal obesity and associated risks of adverse pregnancy outcomes in a population of Chinese women. BJOG 2008, 115, 1529–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machado, C.; Monteiro, S.; Oliveira, M.J. Impact of overweight and obesity on pregnancy outcomes in women with gestational diabetes–results from a retrospective multicenter study. Arch. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 64, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalak, R.; Cummings, J.; Dexter, S. Maternal obesity: Significance on the preterm neonate. Int. J. Obes. 2015, 39, 1433–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedell, S.; Hutson, J.; de Vrijer, B.; Eastabrook, G. Effects of Maternal Obesity and Gestational Diabetes Mellitus on the Placenta: Current Knowledge and Targets for Therapeutic Interventions. Curr. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2020, 19, 176–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.-W.; Soh, S.E.; Tint, M.-T.; Loy, S.L.; Yap, F.; Tan, K.H.; Lee, Y.S.; Shek, L.P.-C.; Godfrey, K.M.; Gluckman, P.D.; et al. Combined analysis of gestational diabetes and maternal weight status from pre-pregnancy through post-delivery in future development of type 2 diabetes. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 5021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Xie, Y.; Zhao, M.; Huang, H.; Liu, C.; Huang, F.; Zhang, Y. Effects of moderate-intensity resistance exercise on blood glucose and pregnancy outcome in patients with gestational diabetes mellitus: A randomized controlled trial. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2022, 36, 108186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kemp, B.J.; Creighton, R.M.; Cupples, G.; Kelly, B.; McAuley, E.; Fleck, O.; Wallace, H.; Graham, U.; McCance, D.R. Mothers’ experiences of a lifestyle intervention for weight reduction 12 months after gestational diabetes mellitus: Qualitative findings from the PAIGE2 study. Midwifery 2024, 129, 103911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamczak, L.; Mantaj, U.; Sibiak, R.; Gutaj, P.; Wender-Ozegowska, E. Physical activity, gestational weight gain in obese patients with early gestational diabetes and the perinatal outcome—A randomised–controlled trial. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2024, 24, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basu, A.; Feng, D.; Planinic, P.; Ebersole, J.L.; Lyons, T.J.; Alexander, J.M. Dietary Blueberry and Soluble Fiber Supplementation Reduces Risk of Gestational Diabetes in Women with Obesity in a Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Nutr. 2021, 151, 1128–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrari, N.; Joisten, C. Impact of physical activity on course and outcome of pregnancy from pre- to postnatal. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 75, 1698–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muktabhant, B.; Lawrie, T.A.; Lumbiganon, P.; Laopaiboon, M. Diet or exercise; or both, for preventing excessive weight gain in pregnancy. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2015, CD007145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Różańska-Walędziak, A.; Walędziak, M.; Mierzejewska, A.; Skopińska, E.; Jędrysik, M.; Chełstowska, B. Nutritional Implications of Bariatric Surgery on Pregnancy Management—A Narrative Review of the Literature. Medicina 2023, 59, 1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walędziak, M.; Kacperczyk-Bartnik, J.; Bartnik, P.; Czajkowski, K.; Kwiatkowski, A.; Różańska-Walędziak, A. The influence of gestational weight gain after bariatric procedures on selected pregnancy outcomes: A single center study. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 21120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IBGE. IBGE (INSTITUTO Bras. Geogr. E ESTATÍSTICA)/Cid.|Mato Grosso|Sinop|História Fotos. 2023. Available online: https://cidades.ibge.gov.br/brasil/mt/sinop/historico (accessed on 16 October 2023).
- Frick, M.N.; Frizzo, G.G. Prevalência de anemia e seus fatores determinantes em gestantes de município do Estado do RS. Rev. Contexto Saúde 2018, 18, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SBD–Sociedade Brasileira de Diabetes, Diretrizes Sociedade Brasileira de Diabetes 2019–2020., São Paulo, 2020. Available online: https://www.saude.ba.gov.br/wp-content/uploads/2020/02/Diretrizes-Sociedade-Brasileira-de-Diabetes-2019-2020.pdf (accessed on 5 February 2024).
- Sortica, G.H.; Cardozo, A.C.; Silva, G.L.; Azevedo, M.; Lemos, N.A. Guia do Pré-Natal na Atenção Básica, 1st ed.; Secretaria de Estado da Saúde do Rio Grande do Sul-Departamento de Ações em Saúde/Departamento de Assistência Hospitalar e Ambulatorial/Assessoria Técnica de Planejamento: Porto Alegre, Brazil, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, J.C.; do Amaral, A.R.; Ferreira, B.D.S.; Willeman, I.K.M.; e Silva, M.R.; Salles, W.B. Obesidade materna e suas consequências na gestação e no parto: Uma revisão sistemática. FEMINA 2014, 42, 135–140. [Google Scholar]
- Nomura, R.M.Y.; Paiva, L.V.; Costa, V.N.; Liao, A.W.; Zugaib, M. Influência do estado nutricional materno, ganho de peso e consumo energético sobre o crescimento fetal, em gestações de alto risco. Rev. Bras. Ginecol. Obstet. 2012, 34, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konno, S.C.; Benicio, M.H.D.A.; Barros, A.J.D. Fatores associados à evolução ponderal de gestantes: Uma análise multinível. Rev. Saúde Pública 2007, 41, 995–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leite, A.C.D.N.M.T.; Araújo, K.K.B.C. Diástase dos retos abdominais em puérperas e sua relação com variáveis obstétricas. Fisioter. Mov. 2012, 25, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, C.K.L. Frequência da Classificação Sanguínea no Laboratório de Análises Clínicas (LAC) do Hospital Distrital de Itaporanga (HDI); Trabalho de Conclusão de Curso (Graduação em Farmácia)—Universidade Esatdual da Paraíba, Centro de Ciências Biológicas e da Saúde: Campina Grande-Paraíba, Brazil, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- BRASIL. Manual Técnico. Pré-Natal e Puerpério: Atenção Qualificada e Humanizada; Ministério da Saúde: Brasília, Brazil, 2005.
- Tilg, H.; Moschen, A.R. Adipocytokines: Mediators linking adipose tissue, inflammation and immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2006, 6, 772–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monod, C.; Kotzaeridi, G.; Linder, T.; Yerlikaya-Schatten, G.; Wegener, S.; Mosimann, B.; Henrich, W.; Tura, A.; Göbl, C.S. Maternal overweight and obesity and its association with metabolic changes and fetal overgrowth in the absence of gestational diabetes mellitus: A prospective cohort study. Acta Obstet. Gynecol. Scand. 2024, 103, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Malley, E.G.; Reynolds, C.M.E.; Killalea, A.; O’Kelly, R.; Sheehan, S.R.; Turner, M.J. Maternal obesity and dyslipidemia associated with gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM). Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2020, 246, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kivelä, J.; Sormunen-Harju, H.; Girchenko, P.V.; Huvinen, E.; Stach-Lempinen, B.; Kajantie, E.; Villa, P.M.; Reynolds, R.M.; Hämäläinen, E.K.; Lahti-Pulkkinen, M.; et al. Longitudinal Metabolic Profiling of Maternal Obesity, Gestational Diabetes, and Hypertensive Pregnancy Disorders. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 106, e4372–e4388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callaway, L.K.; Chang, A.M.; McIntyre, H.D.; Prins, J.B. The prevalence and impact of overweight and obesity in an Australian obstetric population. Med. J. Aust. 2006, 184, 56–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Shen, Z.; Zhan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ma, S.; Zhang, S.; Liu, J.; Wu, S.; Feng, Y.; Chen, Y.; et al. Effects of pre-pregnancy body mass index and gestational weight gain on maternal and infant complications. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2020, 20, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinheiro, L.G.V.; Soares, C.L.R.; Lima, B.L.O.; Sanches, N.M.; Oliveira, R.K.; de Queiroz, D.A.; de Queiroz, E.A.I.F. Obesidade, gestação e complicações maternas e neonatais: Uma revisão sistemática. Sci. Electron. Arch. 2023, 16, 68–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, D.; Roy, P.; Koley, A.K.; Saha, A.; Dey, B.C.; Ari, M.; Ganguly, T.K.; Mukhopadhyaya, A.K. Maternal bmi—How it affect obstetric behaviour and pregnancy outcome. J. Evol. Med. Dent. Sci. 2013, 2, 6622–6630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neal, K.; Ullah, S.; Glastras, S.J. Obesity Class Impacts Adverse Maternal and Neonatal Outcomes Independent of Diabetes. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 832678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, S.; Ollila, M.; Franks, S.; Piltonen, T.; Jokelainen, J.; Nevalainen, J.; Puukka, K.; Ruokonen, A.; Järvelin, M.; Auvinen, J.; et al. Overweight, obesity and hyperandrogenemia are associated with gestational diabetes mellitus: A follow-up cohort study. Acta Obstet. Gynecol. Scand. 2020, 99, 1311–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denison, F.; Norwood, P.; Bhattacharya, S.; Duffy, A.; Mahmood, T.; Morris, C.; Raja, E.; Norman, J.; Lee, A.; Scotland, G. Association between maternal body mass index during pregnancy, short-term morbidity, and increased health service costs: A population-based study. BJOG Int. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2014, 121, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, F.; Senat, M.-V.; Rey, E.; Balayla, J.; Chaillet, N.; Bouyer, J.; Audibert, F. Impact of maternal obesity on the incidence of pregnancy complications in France and Canada. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Curran, P.; Raker, C.; Martin, S.; Larson, L.; Bourjeily, G. Placental findings associated with maternal obesity at early pregnancy. Pathol.-Res. Pract. 2016, 212, 282–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).