Effects of Graphite Addition on Structure and Properties of CrCuFeNiTiAl1 High-Entropy Alloys
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
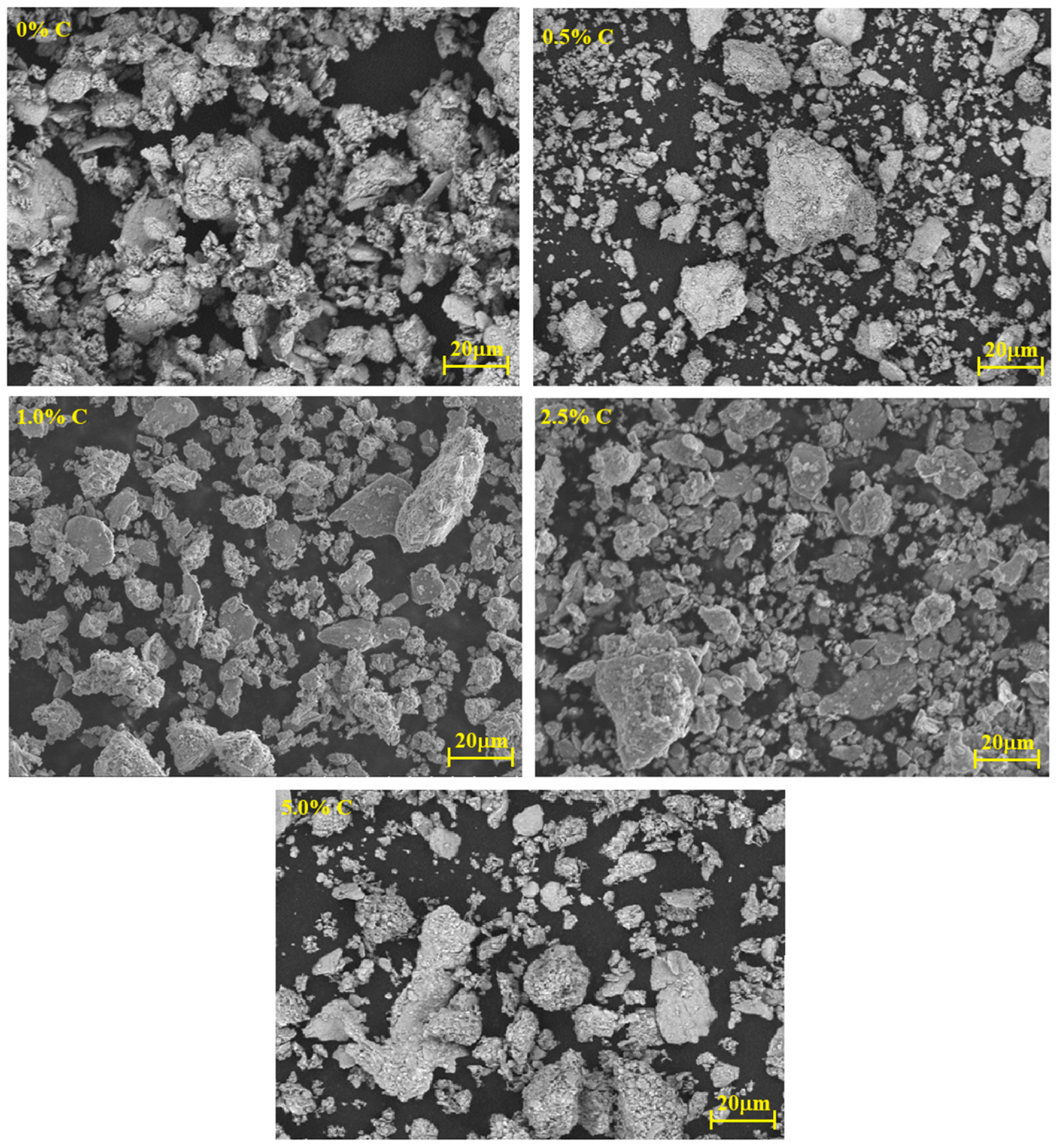
3.1. Particle Size Distribution
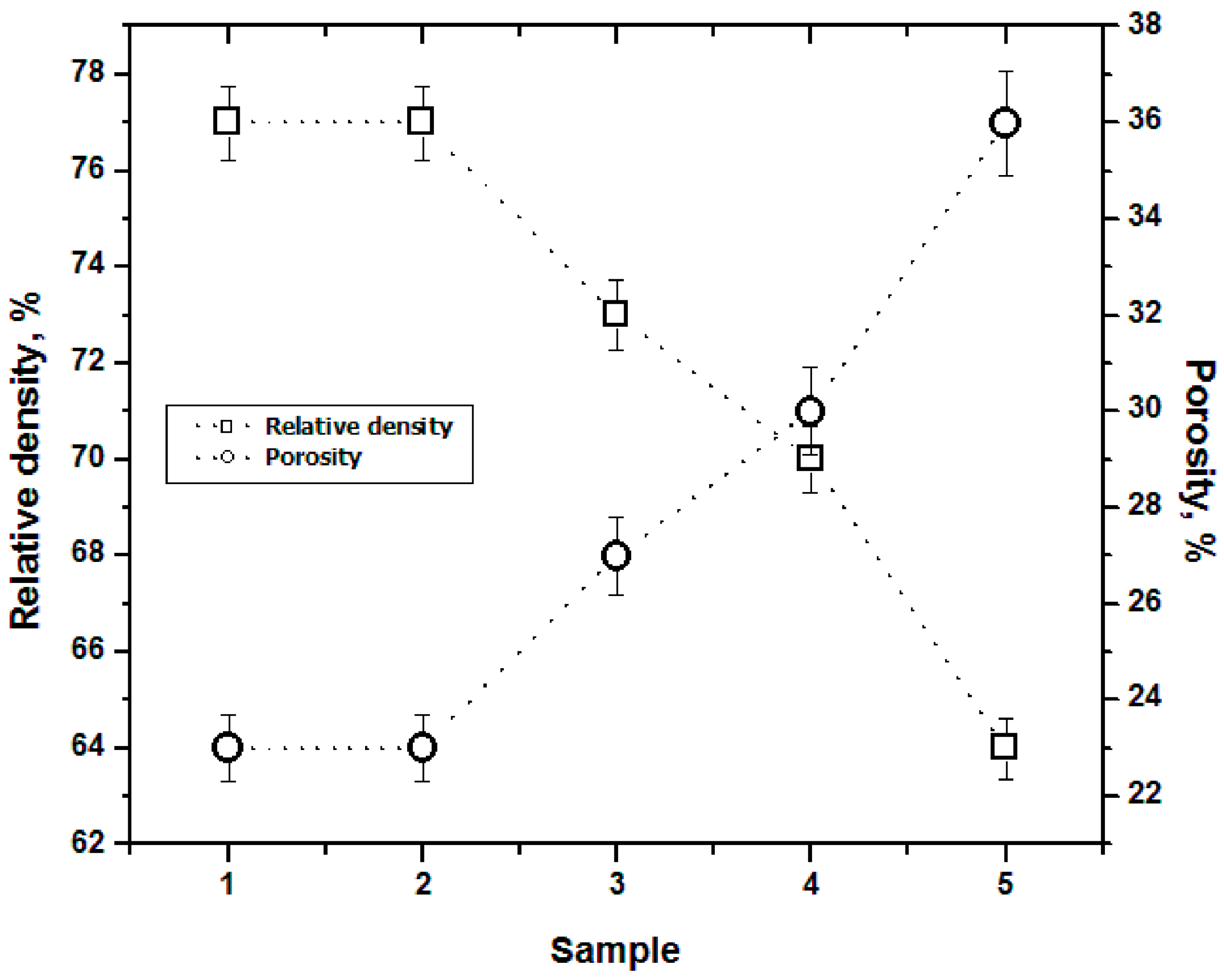
3.2. Density
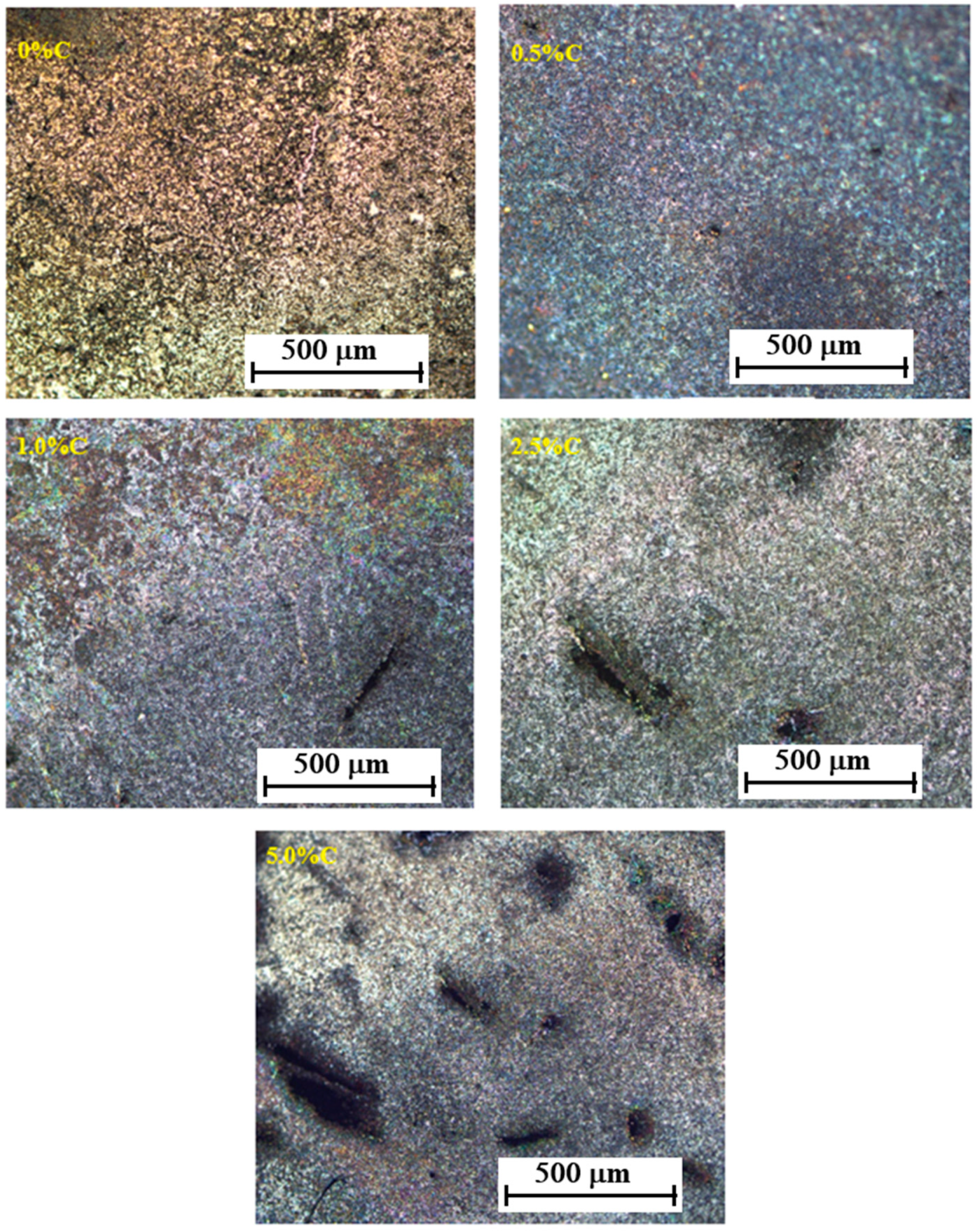
3.3. Structure
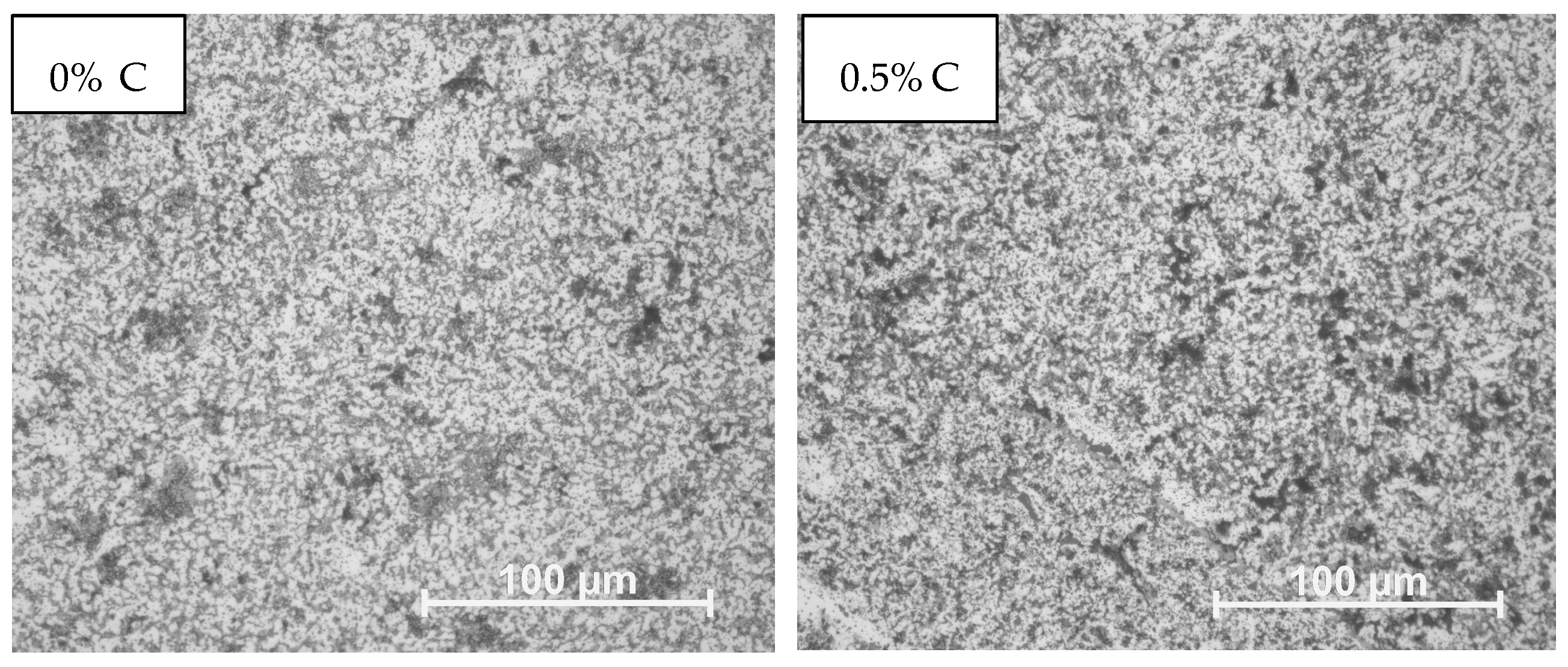
3.4. Microstructure
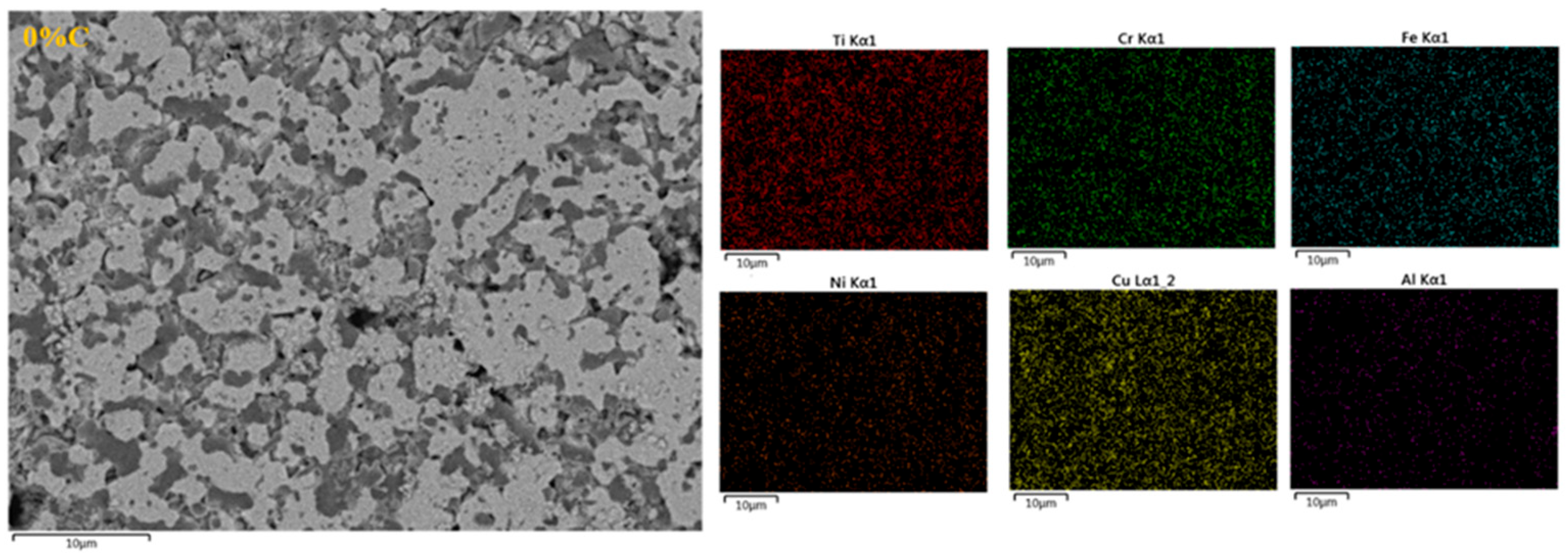
3.5. Mapping
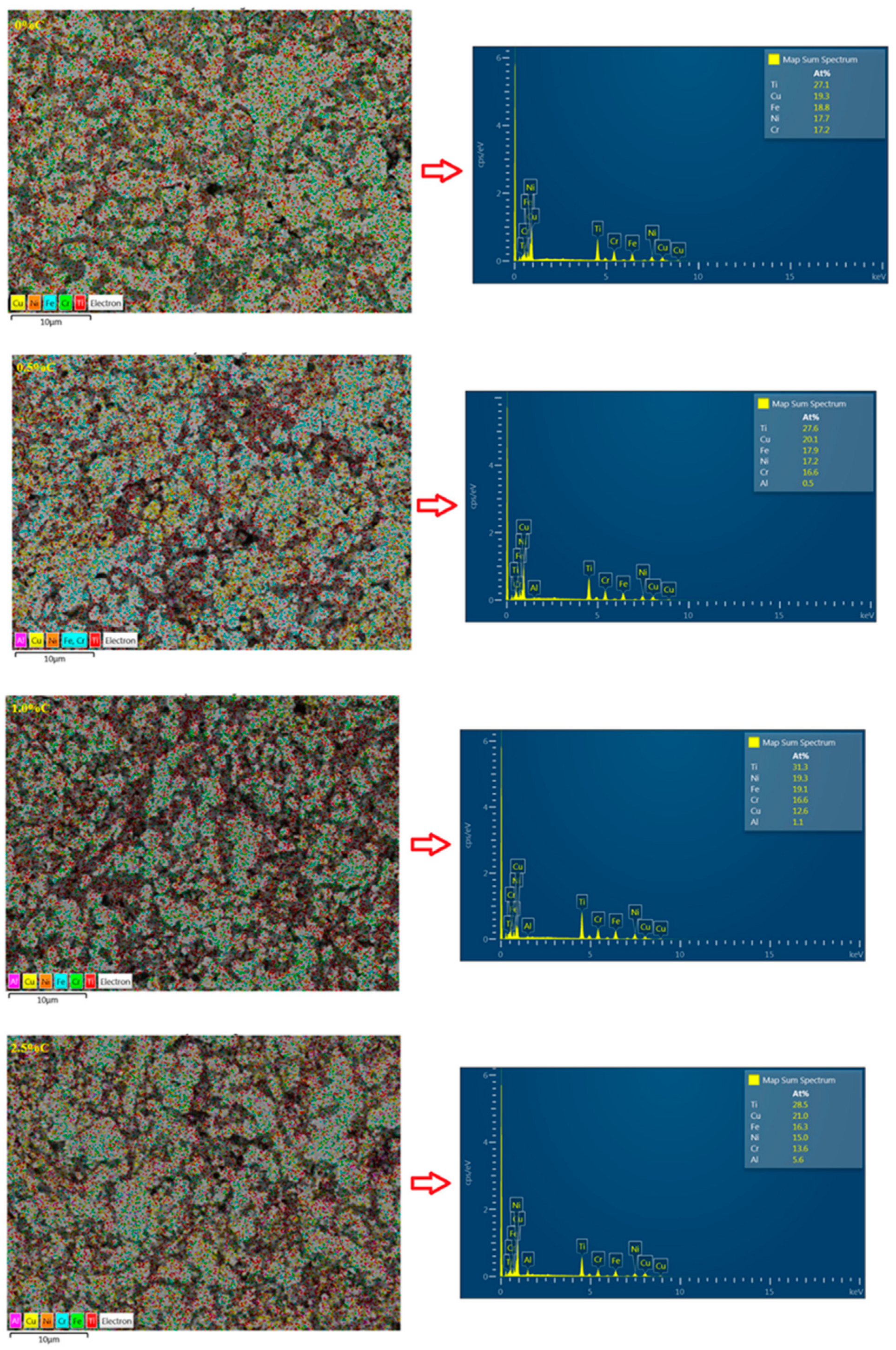
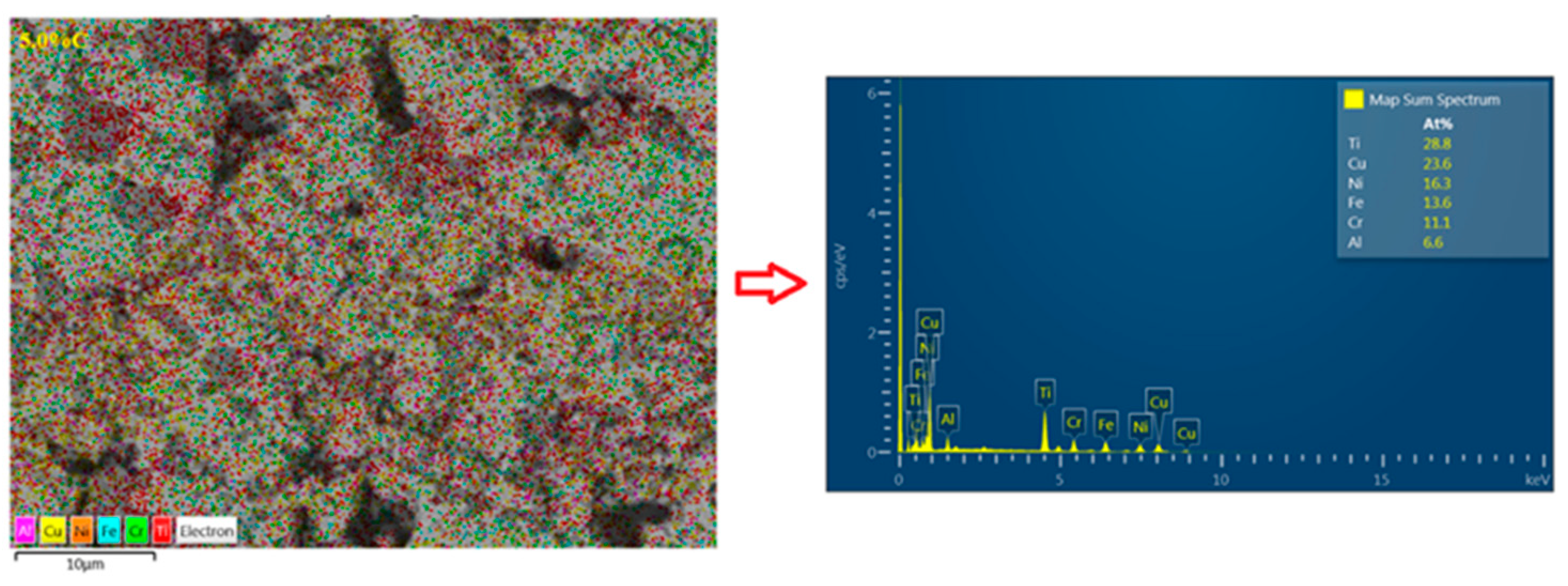
3.6. Energy-Dispersive X-Ray Spectroscopy (EDS)
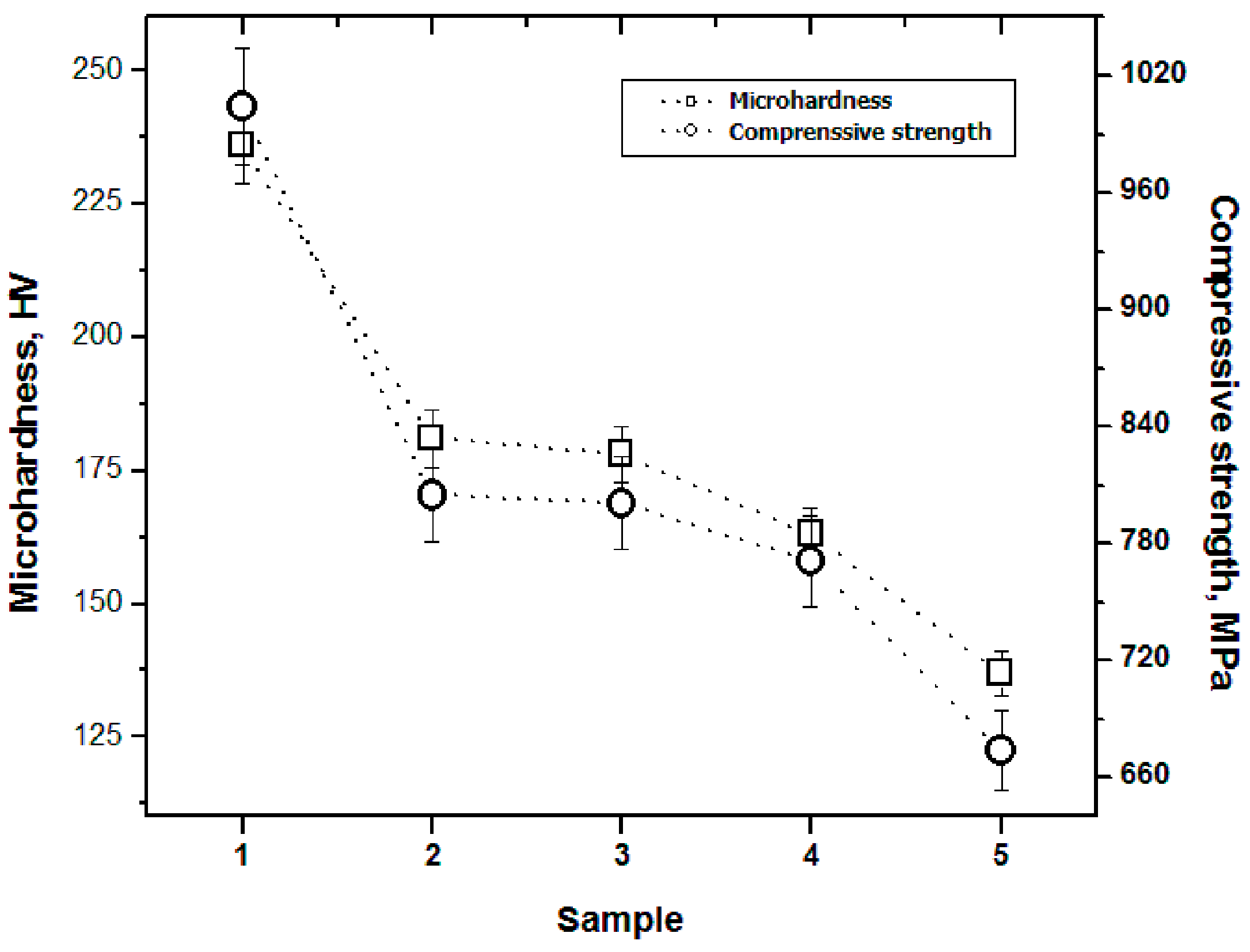
3.7. Mechanical Properties
3.7.1. Microhardness
3.7.2. Compression Strength
4. Conclusions
- ○
- With increasing C, there is agglomeration of the metal particles, which causes the generation of large agglomerates and, consequently, abnormal grain growth during sintering.
- ○
- The structure consists of cubic phases centered on the body and faces for samples with 0 and 0.5% C, while for higher C contents, a compact hexagonal structure appears due to the formation of carbides, mainly of chromium (Cr7C3).
- ○
- The microstructure is characterized by the presence of grains with a similar size distribution that do not follow a specific pattern and are disordered due to the number of elements contained in the alloy. Also, increasing the amount of the dopant element causes cracking and pore formation.
- ○
- Elemental mapping indicated that the samples with sintered CrCuFeNiTiAl1CX alloys are formed of a multi-phase microstructure, as demonstrated by the zones having different levels of contrast in the microstructure.
- ○
- The mechanical properties (microhardness and compressive strength) are negatively affected as the C content of the alloy increases.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SEM | Scanning electron microscopy |
| XRD | X-ray diffraction |
| FCC | Face-centered cubic |
| BCC | Body-centered cubic |
| HCP | Hexagonal compact |
| EDS | Energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy |
| C | Graphite |
| μHV | Vickers microhardness |
| HEAs | High-entropy alloys |
References
- Zhang, Y.; Zuo, T.T.; Tang, Z.; Gao, M.C.; Dahmen, K.A.; Liaw, P.K.; Lu, Z.P. Microstructures and properties of high entropy alloys. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2014, 61, 1–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Liaw, P.K.; Zhang, Y. Recent Progress with BCC-Structured High-Entropy Alloys. Metals 2022, 12, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, J.W.; Chen, S.K.; Lin, S.J.; Gan, J.; Chin, T.-S.; Shun, T.-T.; Tsau, C.-H.; Chang, S.-Y. Nanostructured high-entropy alloys with multiple principal elements: Novel alloy design concepts and outcomes. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2004, 6, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, H.H.; Chen, H.L.; Chen, Q. TCHEA1: A thermodynamic database not limited for “high entropy” alloys. J. Phase Equilibria Diffus. 2017, 38, 353–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, F.; Yang, Y.; Bei, H.; George, E.P. Relative effects of enthalpy and entropy on the phase stability of equiatomic high-entropy alloys. Acta Mater. 2013, 61, 2628–2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poletti, M.G.; Battezzati, L. Electronic and thermodynamic criteria for the occurrence of high-entropy alloys in metallics systems. Acta Mater. 2014, 75, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantor, B. Multicomponent high-entropy Cantor alloys. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2021, 120, 100754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Xiang, M.; Zhang, D.; Shi, J.; Wang, W.; Tang, X.; Tang, W.; Wang, Y.; Ma, X.; Chen, Z.; et al. Mechanical properties of Cantor alloys driven by additional elements: A review. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 15, 1920–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukarram, M.; Mujahid, M.; Yaqoob, K. Design and development of CoCrFeNi-Ta eutectic high entropy alloys. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 10, 1243–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzonia, A.M.; Glatzelb, U. New multiphase compositionally complex alloys driven by the high entropy alloy approach. Mater. Charact. 2019, 147, 512–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, B.E.; Fu, Z.; Zheng, B.; Fu, Z.; Zheng, B.; Chen, W.; Lin, Y.; Chen, F.; Zhang, L.; Ivanisenko, J. Recent progress in high entropy alloy research. JOM 2017, 69, 2024–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yang, H.; Wang, W.Y.; Kou, H.; Wang, J. Thermal–Mechanical Processing and Strengthen in AlxCoCrFeNi High-Entropy Alloys. Front. Mater. 2021, 7, 585602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriharitha, R.; Murty, B.S.; Kottada, R.S. Phase formation in mechanically alloyed AlxCoCrCuFeNi (x = 0.45, 1, 2.5, 5 mol) high entropy alloys. Intermetallics 2013, 32, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Jasso, G.E.; de la Torre, S.D.; Escalona-González, R.; Méndez-García, J.C.; Castillo-Robles, J.A.; Refugio-García, E.; Rocha-Rangel, E. Synthesis of CuCrFeNiTiAlx High Entropy Alloys by Means of Mechanical Alloying and Spark Plasma Sintering. Can. Metall. Q. 2021, 60, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, M.H.; Yeh, J.W. High-entropy alloys: A critical review. Mater. Res. Lett. 2014, 2, 107–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miracle, D.B.; Senkov, O.N. A critical review of high entropy alloys and related concepts. Acta Mater. 2017, 122, 448–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, C.; Rivera-Díaz-del-Castillo, P.E.J. High entropy alloy strengthening modelling. Model. Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2022, 30, 063001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Wang, T.; Xu, Z.; Liu, C.; Wu, H.; Zhao, G.; Fang, D. Effect of Ti content on microstructure and mechanical properties of CuCoFeNi high entropy alloys. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2020, 27, 1326–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Du, X.; Lu, Y.; Jiang, H.; Li, T.; Wang, T. Novel as cast AlCrFe2Ni2Ti05 high entropy alloy with excellent mechanical properties. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2020, 27, 1312–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantor, B.; Chang, I.T.; Knight, P.; Vincent, A.J.B. Microstructural development in equiatomic multicomponent alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2004, 375, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, C.; Jia, Q.; Sun, K.; Duan, D.; Jiang, H.; Li, G. Effect of carbon addition on the microstructure and corrosion resistance of the CoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy. Corros. Sci. 2024, 231, 111965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.; Feng, M.; Lian, G.; Lu, H.; Chen, C.; Huang, X. Effects of C content on the microstructure and properties of CoCrFeNiTi0.5Mo0.5Cx high-entropy alloy coatings by laser cladding. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 33, 1540–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Li, Z.; Dai, P.; Fu, P.; Chen, J.; Tang, Q. Effects of carbon addition on microstructure and mechanical properties of Fe50Mn30Co10Cr10 high-entropy alloy prepared by powder metallurgy. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 20, 73–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gromov, V.E.; Rubannikova, Y.A.; Konovalov, S.V.; Osintsev, K.A.; Vorob’ev, S.V. Generation of increased mechanical properties of Cantor high-entropy alloy. Izv. Ferr. Metall. 2021, 64, 599–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM B962-17; Standard Test Methods for Density of Compacted or Sintered Powder Metallurgy (PM) Products Using Archimedes’ Principle. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2017.
- ASTM E384–16; Standard Test Method for Microindentation Hardness of Materials. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2016.
- Available online: https://web.mit.edu/2.813/www/readings/Ellingham_diagrams.pdf (accessed on 5 May 2025).
- The Chemistry of Carbon. Available online: https://chemed.chem.purdue.edu/genchem/topicreview/bp/ch10/carbon.php (accessed on 8 March 2025).





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
García-Estrada, S.A.; Estrada-Guel, I.; Garay-Reyes, C.G.; Gómez-Esparza, C.D.; Martínez-Sánchez, R.; Castillo-Robles, J.A.; Rodríguez-García, J.A.; Calles-Arriaga, C.A.; Rocha-Rangel, E. Effects of Graphite Addition on Structure and Properties of CrCuFeNiTiAl1 High-Entropy Alloys. Eng 2025, 6, 112. https://doi.org/10.3390/eng6060112
García-Estrada SA, Estrada-Guel I, Garay-Reyes CG, Gómez-Esparza CD, Martínez-Sánchez R, Castillo-Robles JA, Rodríguez-García JA, Calles-Arriaga CA, Rocha-Rangel E. Effects of Graphite Addition on Structure and Properties of CrCuFeNiTiAl1 High-Entropy Alloys. Eng. 2025; 6(6):112. https://doi.org/10.3390/eng6060112
Chicago/Turabian StyleGarcía-Estrada, Sergio Antonio, Ivanovich Estrada-Guel, Carlos Gamaliel Garay-Reyes, Cynthia Deisy Gómez-Esparza, Roberto Martínez-Sánchez, José Adalberto Castillo-Robles, José Amparo Rodríguez-García, Carlos Adrián Calles-Arriaga, and Enrique Rocha-Rangel. 2025. "Effects of Graphite Addition on Structure and Properties of CrCuFeNiTiAl1 High-Entropy Alloys" Eng 6, no. 6: 112. https://doi.org/10.3390/eng6060112
APA StyleGarcía-Estrada, S. A., Estrada-Guel, I., Garay-Reyes, C. G., Gómez-Esparza, C. D., Martínez-Sánchez, R., Castillo-Robles, J. A., Rodríguez-García, J. A., Calles-Arriaga, C. A., & Rocha-Rangel, E. (2025). Effects of Graphite Addition on Structure and Properties of CrCuFeNiTiAl1 High-Entropy Alloys. Eng, 6(6), 112. https://doi.org/10.3390/eng6060112








