Fractal Characterization and Quantitative Petrophysical Prediction of Low-Permeability Glutenite Reservoirs in the Qaidam Basin, NW China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Regional Geological Setting
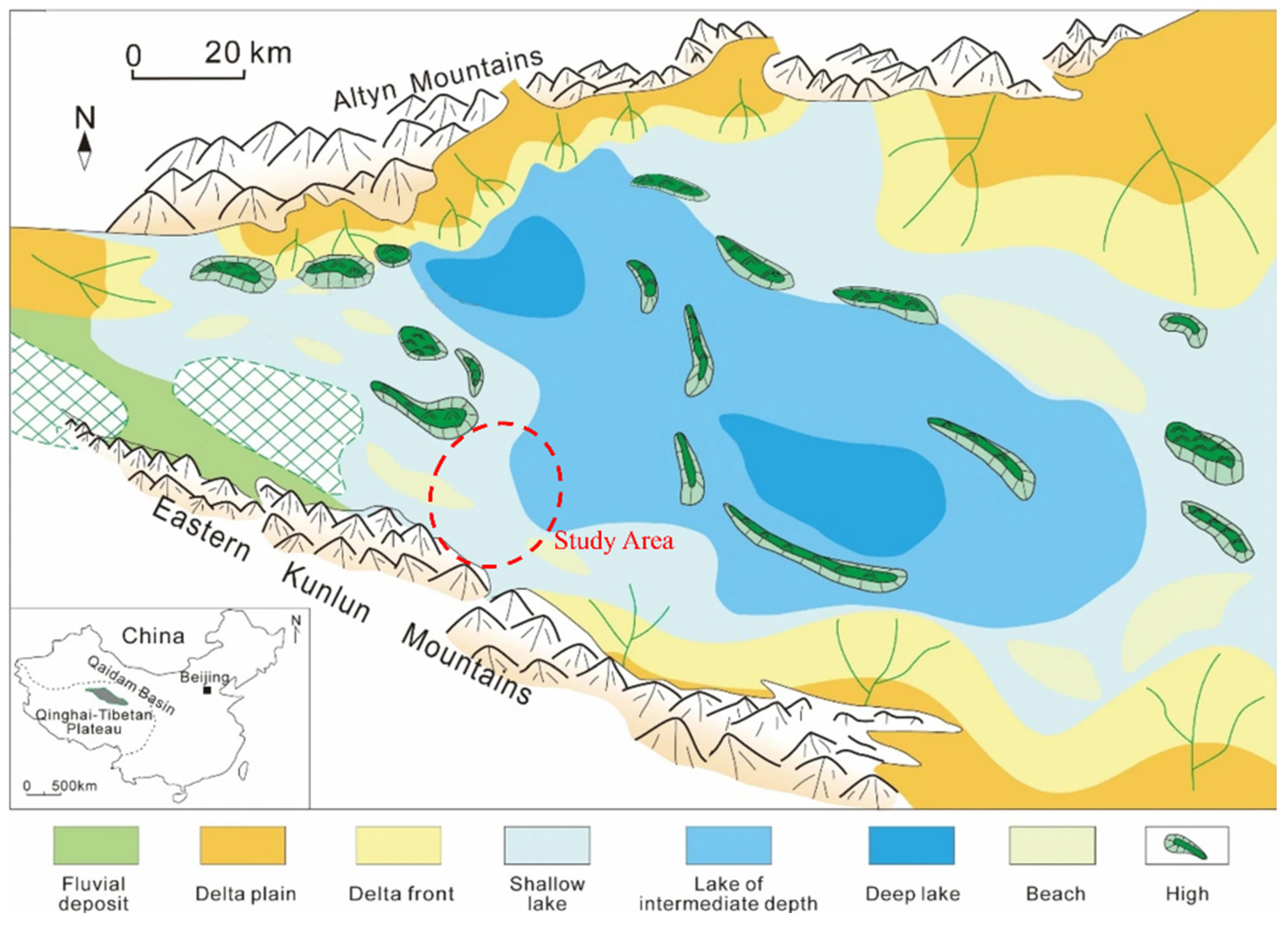

3. Petrographic and Petrophysical Characteristics
3.1. Experiments and Methods
- (1)
- Thin-section petrography and SEM imaging were used to identify mineral composition, texture, and visible porosity; a 100 µm scale bar was added to all SEM images;
- (2)
- High-pressure mercury injection (MICP) was performed to obtain capillary pressure curves and calculate pore-throat radius distributions;
- (3)
- Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) T2 spectra were acquired and divided into micro- (0.1–10 ms), meso- (10–100 ms), and macropores (100–10,000 ms);
- (4)
- Fractal dimensions were derived from ln–ln regressions of MICP and NMR data, and a total fractal dimension Dt was calculated as the porosity-weighted average.
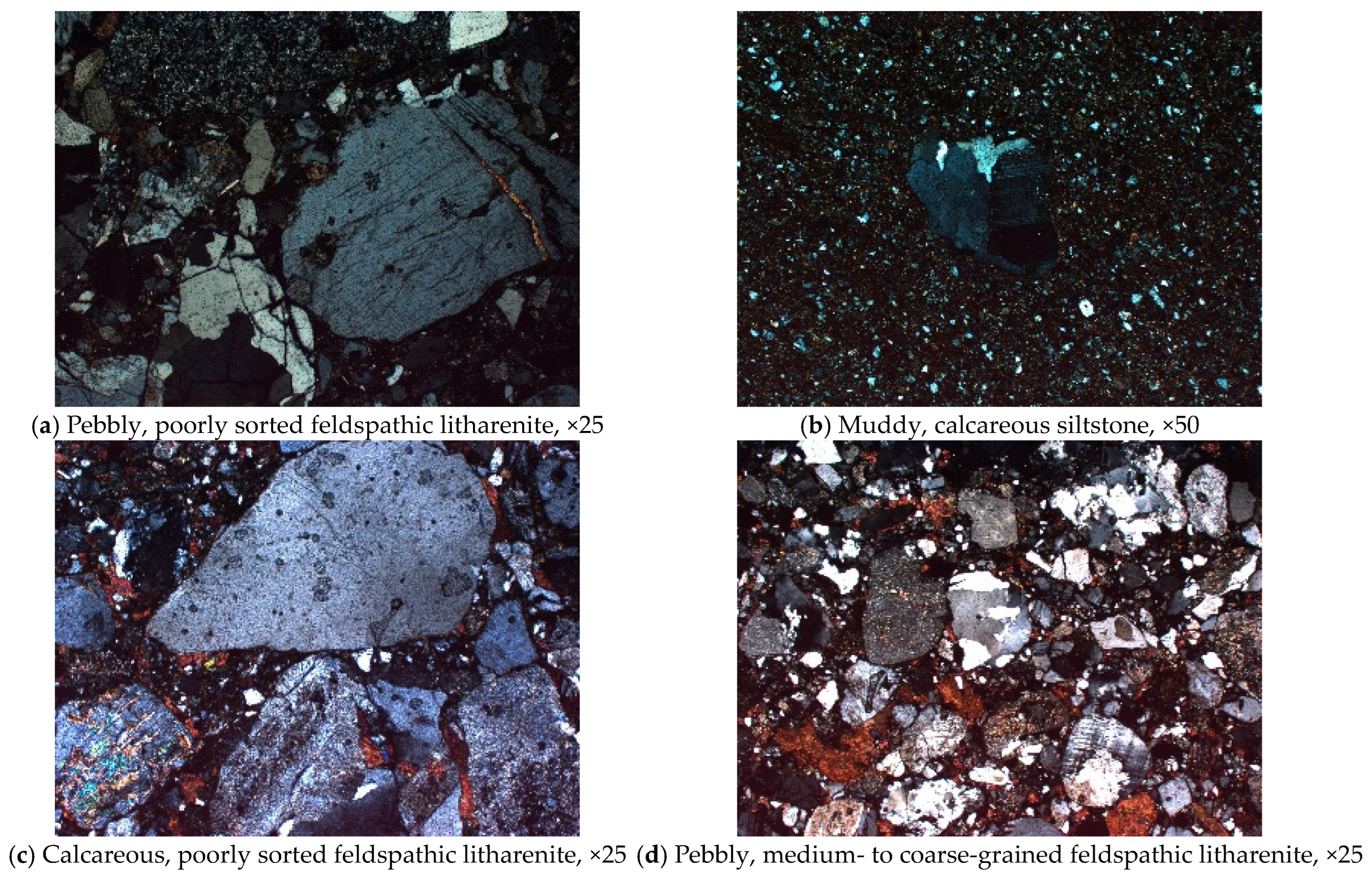
3.2. Lithofacies
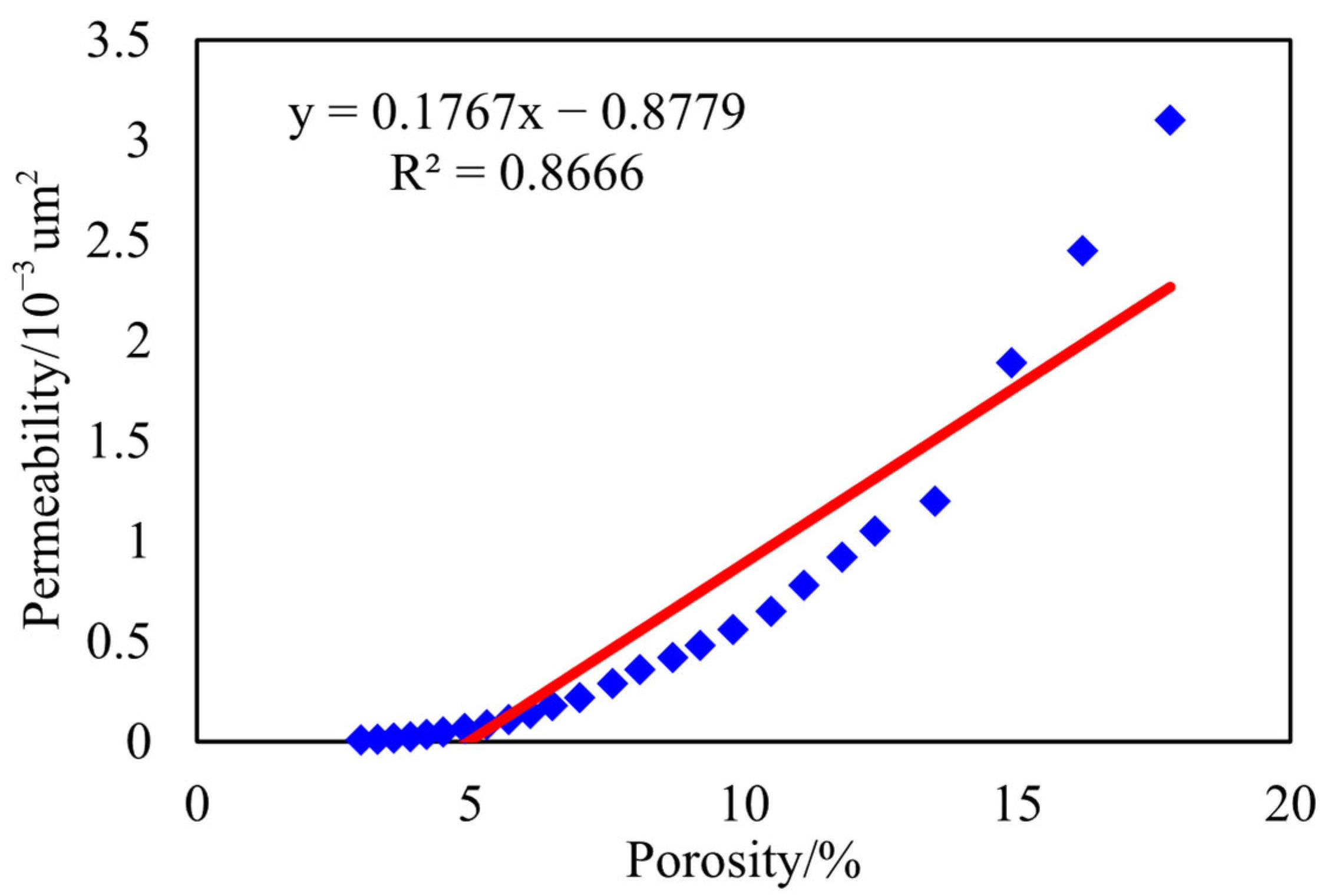
3.3. Petrophysical Analysis
3.4. Clay Minerals
4. Physical Properties and Micropore Structure
4.1. Microscopic Pore Structure
4.2. Reservoir Pore Structure Classification
| Reservoir Class | Porosity Range | Permeability Range | Sample Proportion | Description | Represent Depth/m |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Class I | >12% | >1000 mD | 29.5% | High porosity and permeability; good storage and flow capacity; favorable for hydrocarbon accumulation and movement | 2870–2930 |
| Class Ⅱ | 8–12% | 500–1000 mD | 49.2% | Moderate porosity and permeability; fair storage but lower flow capacity than Class I; stimulation measures needed for development | 3050–3180 |
| Class Ⅲ | <8% | <500 mD | 21.3% | Low porosity and permeability; poor storage and flow capacity; pose major challenges for development and require special strategies | 3320–3480 |
5. Fractal Characteristics of Reservoir Pore Structure
5.1. Fractal Characteristics of the Qaidam Basin Reservoir
5.2. Relationship Between Fractal Characteristics and Reservoir Petrophysical Parameters
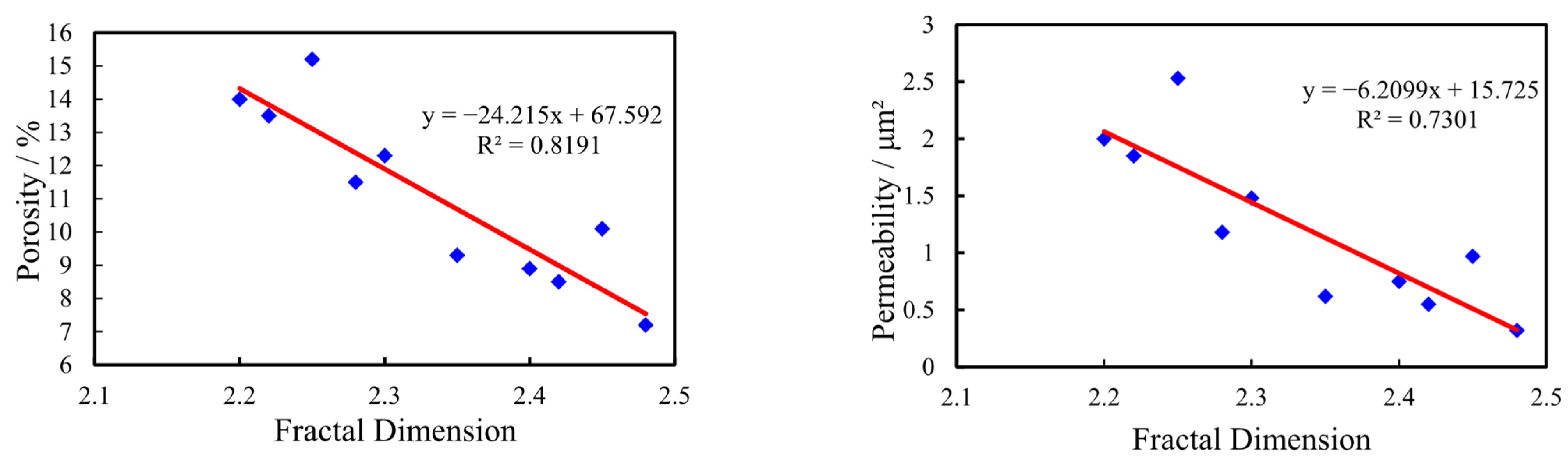
5.2.1. Relationship Between Fractal Dimension and Porosity
5.2.2. Relationship Between Fractal Dimension and Permeability
5.2.3. Model Validation and Error Analysis
| Sample ID | Measured φ/% | Predicted D | Measured k/μm2 | Predicted k/μm2 | Relative Error/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Y6-1 | 14.9 | 2.23 | 2.31 | 2.42 | 4.8 |
| Y6-2 | 10.2 | 2.42 | 0.95 | 0.92 | 3.2 |
| Y6-3 | 7.8 | 2.49 | 0.37 | 0.35 | 5.4 |
| Y6-4 | 12.7 | 2.33 | 1.55 | 1.61 | 3.9 |
| Y6-5 | 9.1 | 2.44 | 0.66 | 0.68 | 3.1 |
| Y6-6 | 6.9 | 2.51 | 0.25 | 0.24 | 4.2 |
6. Conclusions
- (1)
- The glutenite reservoirs are strongly heterogeneous, with an average porosity of 9.39% and permeability of 880 mD. Fine pores (1–10 μm) dominate; illite (up to 16.76%) forms pore-lining films that reduce permeability by 60–80%. A porosity–permeability cutoff of >12% corresponds to >1000 mD, whereas <8% porosity yields <500 mD, providing quantitative boundaries for reservoir classification;
- (2)
- The overall fractal dimension is 2.52: macropores 2.55, mesopores 2.50, and micropores 2.15. An exponential relationship (R2 = 0.88) exists between fractal dimension and permeability: higher dimensions correlate with lower mercury withdrawal efficiency and poorer connectivity. A weighted, total fractal dimension effectively integrates multi-scale pore systems and serves as a new index of reservoir quality;
- (3)
- Fractal-based porosity–permeability models exhibit prediction errors <5.4%. Reservoirs are classified into Class I (>12%, >1000 mD), Class II (8–12%, 500–1000 mD), and Class III (<8%, <500 mD). Blind well validation achieves >94% accuracy, and the classification agrees with production test data. The scheme can be directly embedded in reservoir simulators to guide well-pattern and fracturing optimization;
- (4)
- The proposed fractal-petrophysical workflow offers a transferable approach to rapidly gauge reservoir quality while drilling, informs well-placement and stimulation design in analogous deep, tight reservoirs worldwide, and thus facilitates the transition of unconventional resources to economic development.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
- (1)
- Nomenclature:
- (2)
- Quadratic model
- (3)
- Exponential model
References
- Alessa, S.; Sakhaee-Pour, A.; Sadooni, F.N.; Al-Kuwari, H.A. Comprehensive pore size characterization of Midra shale. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2021, 203, 108576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, X.L.; Tian, L.; Meng, Y.; Wang, J.Y.; Huang, C.; Wang, Z.C. Microscopic pore structure characteristics and classification of tight reservoirs in Ordos Basin. Nat. Gas Geosci. 2023, 34, 51–59. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.; Li, T.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Zhao, H. Research on fluid mobility in tight-sandstone with a NMR fractal theory pore classification method. Front. Earth Sci. 2023, 10, 1035702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhou, K.; Jiang, P.; Zhao, X.; Yao, G. Identification, characterization, and up-scaling of pore structure facies in the low permeability reservoirs: Insight into reservoir quality evaluation and sweet-spots analysis. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2024, 162, 106646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Fan, H.; Fan, T.; Gao, Y.; Wang, H.; Mu, P.; Xiao, D. Fractal research on pores in oil and gas reservoirs-Inspirations from over 700 high pressure mercury injection experiments. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2024, 170, 107086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, M.S.; Bansal, A.R.; Dimri, V.P. Scaling Laws and Fractal Geometry: Insights into Geophysical Data Interpretations. J. Geol. Soc. India 2025, 101, 983–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.Y.; Wu, S.T.; Wu, K.Y.; Shen, L.; Lei, G.; Zhang, B.; Xing, H.; Zhang, Q.; Li, G. Characteristics and hydrocarbon accumulation model of Paleogene whole petroleum system in western depression of Qaidam Basin, NW China. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2024, 51, 951–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Long, A.L.; Liu, B.; Ding, X.; Yu, H.; Song, Y. Breakthrough pressure and development strategy for gas injection in interlayers in low-permeability sandstone reservoirs: A case study of the Gasikule E31 reservoir, Qaidam Basin. Acta Pet. Sin. 2021, 42, 1364–1372. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, J.; Fan, X.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, X.; Chen, L.; Li, J. Differential impact of clay minerals and organic matter on pore structure and its fractal characteristics of marine and continental shales in China. Appl. Clay Sci. 2022, 216, 106334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H. Quantitative prediction of complex tectonic fractures in the tight sandstone reservoirs: A fractal method. Arab. J. Geosci. 2021, 14, 1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bello, A.M.; Butt, M.N.; Hussain, A.; Amao, A.O.; Olariu, C.; Koeshidayatullah, A.I.; Malik, M.H.; Al-Hashem, M.; Al-Ramadan, K. Impact of depositional and diagenetic controls on reservoir quality of syn-rift sedimentary systems: An example from Oligocene-Miocene Al Wajh Formation, northwest Saudi Arabia. Sediment. Geol. 2023, 446, 106342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, M.N.; Hussain, A.; Malik, M.H.; Amao, A.O.; Koeshidayatullah, A.; Olariu, C.; Bello, A.M.; Al-Ramadan, K. Depositional architecture of early rift non-marine systems and implications for reservoir development: Oligocene to Miocene Al Wajh Formation, Midyan Basin of Red Sea, Saudi Arabia. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2024, 168, 107033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.X.; Shi, Z.H.; Li, J.; Sha, W.; Jiang, Z.W.; Yang, L.; Yu, X.; Pu, Y.X. Reservoir formation conditions and exploration potential of Jurassic coal-rock gas in Qaidam Basin. Lithol. Reserv. 2025, 37, 17–25. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, H.; Zhang, G.Q.; Xu, L.; Li, Z.X.; Wang, H.C.; Zhao, C.Y.; Fei, Y. Characteristics and favorable area optimization of ultra-deep high-pressure basement reservoirs: A case study of Kun 2 block in Kunteyi gas reservoir, Qaidam Basin. Reserv. Eval. Dev. 2025, 15, 425–433. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.Z.; Wang, B.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, F.; Yi, L.; Zhao, Z.Y.; Wang, Z.B.; Zhang, W.J.; Hou, Y.J.; Zhu, J.; et al. Late accumulation characteristics of hydrocarbon in the Cenozoic of the western Qaidam Basin: The hydrocarbon accumulation effect of the Tibetan Plateau uplift. Chin. J. Geol. 2025, 60, 1176–1191. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, L.L.; Wang, Z.B.; Long, G.H.; Yuan, Z.L.; Zhang, T.; Liu, X.X. Source-reservoir characteristics and combination characteristics of Miocene tight reservoirs in western Qaidam Basin. Unconv. Oil Gas 2024, 11, 70–81. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, G.Y.; Xue, J.Q.; Wu, S.T.; Wu, K.Y.; Zhang, B.C.; Xing, H.T.; Zhang, N.; Pang, P.; Zhu, C. Petroleum geology and ring-shaped distribution of the Paleogene-Neogene hydrocarbon resources in western Qaidam Depression, Qaidam Basin. Oil Gas Geol. 2024, 45, 1007–1017. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, D.D.; Wang, Y.Q. New understandings and exploration discovery of Paleogene reservoirs of Kunbei fault terrace belt, Qaidam Basin, NW China. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2015, 42, 529–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Q.S.; Liu, Z.G.; Wang, B.; Zhu, C.; Song, G.Y.; Wu, J. Mechanism and Controlling Factors of Sandy Conglomerate Reservoir in Piedmont Thrust Belt: A Case of Kunbei Oilfield, Qaidam Basin, NW China. Editor. Comm. Earth Sci.-J. China Univ. Geosci. 2024, 49, 55–70. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.J.; Lu, J.G.; Ma, D.D.; Wang, L.Q.; Zhao, M.J.; Xue, J.Q.; Zhang, J.Z.; Liu, C.W.; Zhang, J. Origin and accumulation characteristics of the oil from hanging wails of Kunbei fault-terrace belt in Qaidam Basin. Acta Pet. Sin. 2012, 33, 915–924. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Wang, J.; Long, G.; Xu, L.; Cui, J.; Sun, X.; Wang, Y. Eocene lacustrine microbialites in the western Qaidam Basin, China: Implication for the sedimentary record and hydrocarbon potential. Carbonates Evaporites 2024, 39, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, Q.; Xu, S.; Hao, F. Full-scale pores and micro-fractures characterization using FE-SEM, gas adsorption, nano-CT and micro-CT: A case study of the silurian Longmaxi Formation shale in the Fuling area, Sichuan Basin, China. Fuel 2019, 253, 167–179. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Jiang, S.; Xie, C.; Chen, K.; Zhang, Z. Production performance of multiple-fractured horizontal well based on potential theory. J. Energy Resour. Technol. 2022, 144, 103005. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, D.D.; Sun, W.; Zhang, C.; Liang, X.W.; He, S.P.; Ren, D.Z.; Li, C.X. Diagenetic Facies and Micro-pore Structure of Chang 6 Reservoir in Yanchang Formation, Huaqing Area, Ordos Basin. Geoscience 2012, 26, 769–777. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.P.; Liu, C.L.; Jiang, L.W.; Feng, D.H.; Zhou, C.; Liu, F.; Li, J.J.; He, Y.B.; Dong, M.X.; Jiao, P.F. Pore microstructure and its controlling effects on gas content of deep shale reservoirs in the Wufeng-Longmaxi formations, Da’an area, western Chongqing. Oil Gas Geol. 2025, 46, 230–245. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.Z.; Liu, C.L.; Liu, W.P.; He, Y.B.; Liu, J.; Xu, L. Microporous structure of the Longmaxi Formation shale reservoirs in southern Sichuan Basin and its effect on adsorption capacity. Spec. Oil Gas Reserv. 2025, 32, 22–32. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, Q.Q.; Liu, D.D.; Xu, M.Y.; Jiang, X.Y.; Chen, W.; Feng, X.; Du, W.; Liu, J.P.; Tang, Z.J.; Zhao, S. Structure characteristics and three-dimensional reconstruction of organic matter pores in Lower Paleozoic shales of the northern Guizhou Province, Southwestern China. Shi You Ke Xue Tong Bao 2025, 10, 361–377. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Sun, Z.Y.; Tian, Y.Y.; Yang, H.; Zhang, B.; Liu, B.; Yang, T.; Huang, Q.; Li, H.L.; Tang, M.; et al. Differential evolution model of wide/narrow channel tight sandstone reservoir: A case study of tight sandstone in the Sha 1 Member of the Zitong area, Sichuan Basin. Nat. Gas Geosci. 2025, 36, 1446–1458. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Chen, R.Q.; Shang, F.; Li, L.; Bai, X. Pore structure and fractal characteristics of shale reservoirs in Jurassic Lianggaoshan Formation, northeastern Sichuan Basin. Pet. Geol. Exp. 2025, 47, 323–335. [Google Scholar]
- Ning, B.; Ren, D.Z.; Wang, H.; Zhang, H.P.; Guo, J.L.; Fu, N.H.; Li, J.J.; Li, T.; Li, Q.H. Multi-scale combination characterization of micropore structure of tight sandstone gas reservoirs. Fault-Block Oil Gas Field 2024, 31, 34–41. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.M.; Wang, Y.R.; Lin, W.; Ma, L.; Liu, D.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y. Micro-pore structure and fractal characteristics of deep shale from Wufeng Formation to Longmaxi Formation in Jingmen exploration area, Hubei Province. Nat. Gas Geosci. 2022, 33, 629–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.L.; Li, G.Y.; Liu, X.P.; Ma, Q.; Meng, L.J.; Wang, J.W.; Wei, Y.Q.; Zhuang, D.Z. Fractal Characteristics of Shale Pore Throats at Various Scales and Their Dominant Controlling Factors in the First Member of the Shahejie Formation in the Linque Sub-sag of the Nanpu Depression. Spec. Oil Gas Reserv. 2024, 31, 39–48. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Luo, T.Y.; He, P.; Sun, J.F.; Li, T. Fractal characteristics and influencing factors of tight reservoirs in Shanxi Formation in southern Ordos Basin. Unconv. Oil Gas 2024, 11, 37–45. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, W.B.; Zhang, X.H.; Zhou, D.R.; Fang, C.G.; Li, J.Q.; Huang, Z.Q. New cognition on pore structure characteristics of Permian marine shale in the Lower Yangtze Region and its implications for shale gas exploration. Nat. Gas Ind. 2021, 41, 41–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, C.Z.; Sui, Y.F.; Wang, Y.D.; Wu, Z.W.; Li, J. Relative permeability model of polymer particle dispersed phase for oil displacement based on fractal theory. Reserv. Eval. Dev. 2025, 15, 88–95. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, L.B.; Jin, Z.J.; Li, J.C.; Tang, L.J.; You, F.B.; Lei, B.Z. Fractal Characteristics of Fractural Structures and Its Relation to Oil-Gas Distribution in North Qaidam Basin. Chin. J. Geol. 2001, 36, 241–247. [Google Scholar]
- He, C.C.; Zhao, Y.Q.; Yu, L.J.; Lu, L.F.; Liu, X.W.; Pang, A.Y.; Li, C.X. Pore structure and fractal characteristics of deep shale gas reservoirs in the Permian Dalong Formation, northeastern Sichuan Basin. Pet. Geol. Exp. 2024, 46, 263–277. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, D.; Zhao, W.W.; Wu, J.; Li, H.; Xiao, Y. Pore structure and fractal characteristics of lacustrine shale in Chang 7 Member of Yanchang Formation, Yan’an area. Lujing Gongcheng 2025, 36, 137–145. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, M.Y.; Tan, C.; Shu, Z.M.; Wang, X.; Long, L.H. Mechanisms of supercritical CO2-water-rock interactions on shale micropores across sedimentary facies. Nat. Gas Geosci. 2025, 36, 1316–1329. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.B.; Du, Z.W.; Qiang, X.L.; Lei, T.; Jiang, T.T.; Wang, W.; Zhu, Y.S. Binary pore structure and fractal characteristics of tight sandstone:A case study of Chang 7 Member of Triassic Yanchang Formation in Ordos Basin. Pet. Geol. Recov. Eff. 2024, 31, 45–56. [Google Scholar]


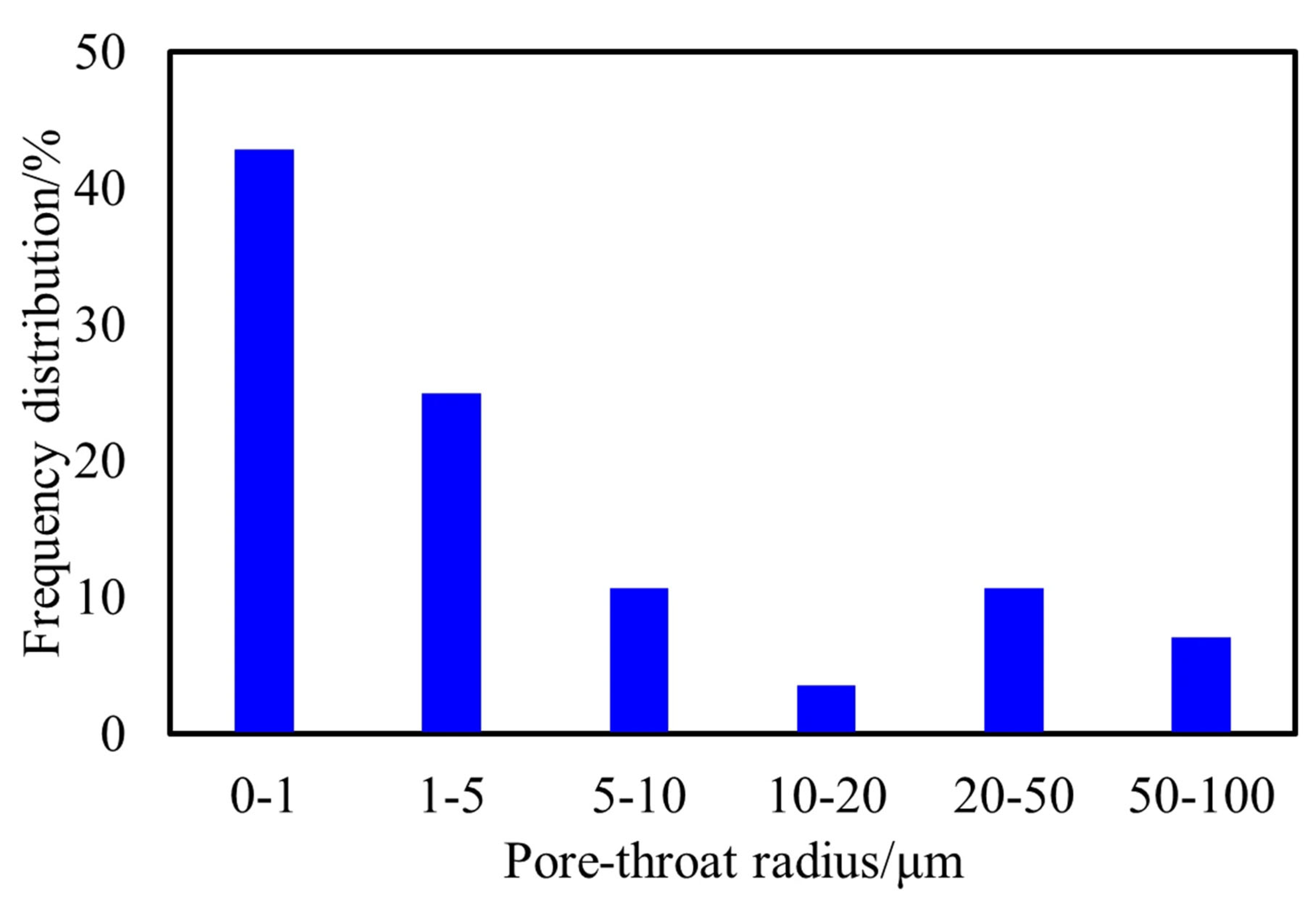

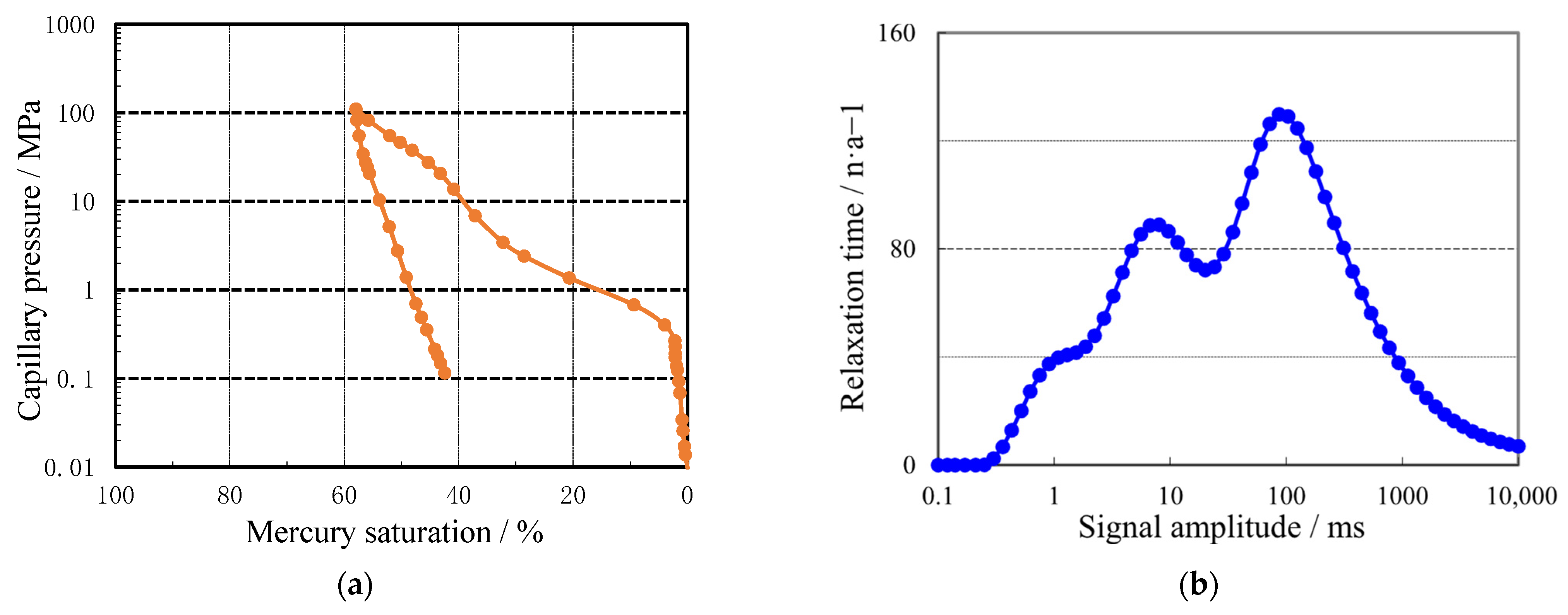

| Reservoir Class | Pore Size Interval | Fractal-Dimension Range | Mean Fractal Dimension | Fractal Coefficient a | Associated Petrophysical Character |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Class I | Macropores (>50 µm) | 2.48–2.70 | 2.55 | 0.85 | High porosity and permeability, good connectivity |
| Class II | Mesopores (10–50 µm) | 2.45–2.65 | 2.50 | 0.62 | Moderate porosity and permeability, fair connectivity |
| Class III | Micropores (<10 µm) | 2.05–2.25 | 2.15 | 0.41 | Low porosity and permeability, poor connectivity |
| Whole spectrum | 2.05–2.70 | 2.52 | Strongly heterogeneous, complex pore structure |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ren, Y.; Wu, Z.; Yang, C.; Shu, K.; Jiang, S. Fractal Characterization and Quantitative Petrophysical Prediction of Low-Permeability Glutenite Reservoirs in the Qaidam Basin, NW China. Eng 2025, 6, 311. https://doi.org/10.3390/eng6110311
Ren Y, Wu Z, Yang C, Shu K, Jiang S. Fractal Characterization and Quantitative Petrophysical Prediction of Low-Permeability Glutenite Reservoirs in the Qaidam Basin, NW China. Eng. 2025; 6(11):311. https://doi.org/10.3390/eng6110311
Chicago/Turabian StyleRen, Yuhang, Zhengbin Wu, Cheng Yang, Kun Shu, and Shu Jiang. 2025. "Fractal Characterization and Quantitative Petrophysical Prediction of Low-Permeability Glutenite Reservoirs in the Qaidam Basin, NW China" Eng 6, no. 11: 311. https://doi.org/10.3390/eng6110311
APA StyleRen, Y., Wu, Z., Yang, C., Shu, K., & Jiang, S. (2025). Fractal Characterization and Quantitative Petrophysical Prediction of Low-Permeability Glutenite Reservoirs in the Qaidam Basin, NW China. Eng, 6(11), 311. https://doi.org/10.3390/eng6110311







