Abstract
The critical importance of effective industrial symbiosis is emphasized in the rapidly evolving landscape of manufacturing, energy, and environmental sustainability. This study employs the Decision Making Trial and Evaluation Laboratory (DEMATEL) methodology to examine and outline the complex interrelationships among critical success factors (CSFs) pivotal for the successful implementation of industrial symbiosis. Key findings indicate that leadership and technology are the most significant causal CSFs, driving positive outcomes in waste reduction, environmental impact, and economic growth, identified as primary effect factors. Leadership emerges as the predominant influence, guiding strategic alignment, fostering a collaborative and sustainable organizational culture, and affecting all other CSFs. Technological integration acts both as a direct driver of operational efficiency and as a mediator of leadership’s influence, enabling optimized resource flows and data-driven decision-making. Additional CSFs such as clear communication, enhanced training and education, and policy and regulatory support also serve as essential mediators connecting leadership to key outcomes. This research outlines an actionable pathway for stakeholders, including policymakers, engineers, and corporate executives, to strategically prioritize and utilize these CSFs to promote more resilient and sustainable industrial ecosystems.
1. Introduction
The rapidly growing population has increased daily consumption, leading to the depletion of limited resources [1]. To address these negative effects, sustainable approaches like industrial symbiosis are being adopted. Industrial symbiosis is a strategic approach that encourages collaboration among industries to enhance resource efficiency and sustainability without compromising production quality or quantity [2]. By sharing resources such as materials, water, and energy, industries can reduce waste, greenhouse gas emissions, and reliance on natural resources, while also achieving economic benefits. This strategy aligns with the principles of green, lean, and sustainable manufacturing, promoting eco-efficient operations within industrial parks [3,4]. By connecting the three pillars of sustainability—economic, environmental, and social—industrial symbiosis enhances the circular economy, contributing to both environmental sustainability and economic resilience [2,5]. The potential for industrial symbiosis implementation is extensive, covering various industries and geographic regions [6]. Despite its advantages, assessing companies’ readiness for industrial symbiosis is challenging due to complex evaluation methods [7,8].
The exploration of industrial symbiosis in the literature has been framed within the contexts of sustainable development goals [9], the circular economy [10], and regional development [11]. To quantify IS impacts, methodologies such as life cycle assessment, economic analysis, and environmental performance evaluation have been used [12]. Additionally, research themes have expanded to include waste as a resource, network development, energy innovations, and the social aspects of industrial symbiosis [7,8].
There are several factors that influence the successful implementation of industrial symbiosis, affecting both the operational capabilities and strategic sustainability decisions of manufacturing companies [8,13]. Recent studies on industrial symbiosis have employed a range of methodologies to examine its critical success factors (CSFs). Predominantly, researchers have utilized case studies [5,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22] and literature reviews [6,11,13,23,24,25], though less frequently, they have also conducted interview-based qualitative research [26,27], empirical surveys [8], and data-driven analyses [28]. However, these studies examine the CSFs for industrial symbiosis separately, overlooking their complex interconnections. Some research has explored relationships among broad CSF categories using the Analytical Network Process method [1,2,29]; however, there has been a notable lack of studies focusing on the detailed identification of cause-and-effect relationships among individual CSFs. While recent comparable studies have analyzed individual barriers to industrial symbiosis [30,31], a significant gap persists in research specifically addressing the interrelations among CSFs.
This study aims to address this gap by conducting an in-depth exploration of the CSFs for industrial symbiosis implementation. Initially, CSFs were identified through a systematic literature review and subsequently validated by industry experts to ensure their relevance and accuracy. Furthermore, using the Decision-Making Trial and Evaluation Laboratory (DEMATEL) methodology, this study systematically examined these CSFs to reveal their interconnections and assess their broader impacts. By clarifying these relationships, the study offers stakeholders—including policymakers, business leaders, and local communities—vital insights that enable the formulation of efficient, comprehensive, and innovative strategies. This contributes significantly to advancing industrial symbiosis and promoting sustainable practices within the manufacturing sector, especially in hard-to-abate industries.
The remainder of this paper is organized as follows: Section 2 offers a comprehensive review of the current literature on the CSFs for industrial symbiosis. Section 3 details the DEMATEL methodology used in this study, including information on the sample and data collection procedures. Section 4 presents the empirical findings, highlighting the identified cause-and-effect relationships among the CSFs. Section 5 discusses the research findings, provides managerial and societal implications, outlines the study’s limitations, and suggests directions for future research.
2. Literature Review
This section examines the CSFs for industrial symbiosis, based on the existing literature. A systematic methodology was adopted to create a comprehensive bibliographic dataset. The process began in July 2024 with a focused search in the Scopus database, using the keywords “industrial symbiosis” in combination with “factors”, “determinants”, “drivers”, or “enablers” in the titles of articles. This search identified 23 relevant publications, including 13 journal articles, 5 conference papers, 3 reviews, and 2 book chapters, as categorized by Scopus. Subsequently, two co-authors independently conducted a qualitative assessment to verify that these publications specifically addressed various CSFs for industrial symbiosis. All 23 publications fulfilled the inclusion criteria. Through a detailed analysis of this body of work, 11 primary CSFs for industrial symbiosis were identified and are outlined in the following subsections.
2.1. Enhanced Training and Education
Enhanced training, education, and competence validation aims to mitigate insufficient expertise and lack of awareness. Co-educational opportunities, such as collaborative training sessions among related companies, are essential for creating environments conducive to learning in areas like applying symbiosis techniques and improving waste streams [1,17]. These educational settings help to close the knowledge gap as regards appropriate technologies and reuse opportunities. For example, “speed-dating” events between companies can promote their collaboration and exchange of ideas [17]. Moreover, the involvement of universities and R&D institutions is vital, as they facilitate knowledge transfer, reinforce industry initiatives, and contribute to local coordination [29]. To address the challenges of research and innovation, it is essential to integrate the best available technologies and provide research grants that support technology development and information management [11,23]. Community awareness and educational programs are also important, as they connect industrial activities with local sustainable development goals [23]. Furthermore, public education and industry training, focusing on environmental considerations and industrial symbiosis, should be prioritized to ensure that stakeholders recognize benefits beyond profits from product sales [5]. Finally, companies can develop the organizational and technical know-how needed to use successful industrial symbiosis methods through enhanced training, education, and competence validation. [2,6,13].
2.2. Economic Growth and Profitability
Economic growth and profitability drives the financial viability and sustainability of symbiotic relationships [28]. One of the primary enablers of this growth is the increase in sales, which results from the enhanced marketability of products derived from symbiotic processes [1]. Furthermore, the expansion of raw material markets, facilitated by symbiotic relationships, allows companies to access a wider range of inputs at lower costs [1,21,26]. This growth is also supported by the creation of new ventures, where savings from symbiosis are reinvested into startups and innovative business opportunities, promoting economic diversification [1,23].
However, there are several obstacles that hinder the economic growth and profitability of industrial symbiosis. For instance, limited access to financial resources, with high processing and logistical costs, impede return on investment [11,15]. Current macroeconomic constraints further make this situation worse, forcing companies to reduce expenses and restricting financing options. To address these challenges, it is essential for companies to receive financial assistance, such as subsidies and low-interest loans with extended repayment periods [5,18]. This kind of support can enable industries to acquire the necessary equipment and technologies for successful symbiosis. Additional economic enablers include the reduction of input costs and the development of new revenue streams through the introduction of innovative products and services. Companies can also gain a competitive advantage by minimizing costs through material reuse, which can lead to increased turnover and economic sustainability. The geographical proximity of companies can further increase these benefits, through closer collaboration and reduced transportation costs [18,31]. Additionally, financial support is also crucial for social interaction platforms and public consultations, which provide business owners with opportunities to connect with potential partners and identify further synergies [5,30].
2.3. Operational Cost Reduction
Reducing operational costs significantly improves the economic viability and sustainability of industrial processes. The decrease in warehouse costs, which involves lowering expenses related to the storage and handling of materials, is a key contributor to operational costs reduction [1]. Additionally, decreasing production costs is essential, since it directly affects overall manufacturing expenditures. Efficient utilization of resources, such as water, energy, and raw materials, can help in this direction [1,29]. The reduction of logistics costs, which includes expenses associated with the transportation and storage of by-products, is another important element contributing to operational costs reduction [1,19]. Labor savings are equally crucial and can be achieved by reducing the need for a large workforce through process optimization and the implementation of automation [17,19]. Identifying opportunities for resource savings—focusing on ways to conserve water, energy, and raw materials, which are often significant cost factors in industrial processes—is also vital for operational cost reduction, especially through innovative solutions and strategic partnerships [23,29]. For example, reusing materials can lower input costs and minimize waste, further enhancing competitiveness. However, challenges such as high processing costs of by-products and the complexity of production processes in some industries can hinder progress [25].
2.4. Waste Reduction and Environmental Impact
Waste reduction and environmental impact focuses on minimizing waste generation and mitigating environmental harm. A key enabler is environmental awareness, which involves understanding the effects of industrial activities and fostering a concern for their environmental impacts. This encompasses the behavior, attitude, and mindset companies must adopt to maintain a balanced relationship with the environment [1,16]. Reducing the use of natural resources and decreasing waste output are vital for achieving sustainable industrial symbiosis [22]. Implementing efficient waste management systems and adopting eco-friendly practices, such as reusing and recycling materials, lessens environmental impact and promotes resource conservation [26]. By adopting green procurement strategies, companies can improve their environmental image, gain competitive advantages, and enter new markets [17]. Saving raw materials is also crucial for reducing waste, as it decreases the consumption of materials in production. Moreover, optimizing waste management practices, such as cutting landfill taxes and waste handling costs, can lead to significant cost reductions [29]. Additionally, fostering a culture of environmental responsibility can drive continuous improvement in waste reduction initiatives. This involves regular training and educational programs to keep employees updated on best practices and the latest advancements in sustainable technologies. By integrating these practices into their operations, companies can enhance their environmental performance and contribute to the broader objectives of industrial symbiosis [23,29].
2.5. Leadership
Effective leadership requires a strong understanding of environmental issues. This is vital for identifying the advantages and opportunities associated with industrial symbiosis [15]. In this context, proactive management is crucial for the successful implementation of industrial symbiosis [21]. Leaders must advocate for industrial symbiosis initiatives, promoting a culture of sustainability within their organizations. It is essential for them to actively incorporate industrial symbiosis into their organizations’ management frameworks and make it a fundamental aspect of their operational strategies. This includes establishing clear objectives and expectations, as well as allocating the necessary resources and support to achieve these objectives [11,31]. Additionally, leaders who embrace the concept of industrial ecology and are willing to take initiative can significantly enhance the success of industrial symbiosis efforts [29]. The insufficient awareness and support from top management is often identified as a significant obstacle to the effective implementation of industrial symbiosis [15,19]. Many managers do not understand the opportunities available or are reluctant to reuse by-products, which impedes the advancement of integrated resource utilization. This deficiency can obstruct the necessary policy and practice changes required for industrial symbiosis to succeed [21,30].
2.6. Governance and Internal Organizational Structure
Governance and Internal Organizational Structure forms the framework for symbiotic relationships to develop. Establishing formal agreements and clear guidelines that promote collaboration between different organizations is an essential part of effective governance [23]. Organizational support, effective administrative capacity, and self-organization are effective approaches that help in meeting the environmental requirements of corporations and ensure that all parties are aligned in their sustainability goals [2,15,29]. It is a fact that one of the biggest challenges to efficient governance in industrial symbiosis is the absence of administrative capacity. Lack of organizational support for integration, coordination, and communication is a common problem for organizations [2,30]. Furthermore, another frequent barrier to the adoption of symbiotic practices is unwillingness to change organizational culture. It is crucial to promote flexibility and self-organization in order to overcome these barriers [2,29,31]. The concept of industrial ecology must motivate corporations and make them want to take the lead. This requires establishing a culture of innovation and adaptability, where employees are encouraged to think creatively about how to use resources and manage waste. In this sense, organizational support is essential since it gives these endeavors the resources and support that are needed [2,11,21]. Another critical factor is the variety in traditional business approaches. Companies that embrace new business models and strategies can better integrate industrial symbiosis into their operations [21,23]. This includes retaining personnel while creating high-quality teams that are knowledgeable about symbiotic practices [11]. Finally, the level of social interaction and mental proximity within an organization might have a major effect on its ability to achieve industrial symbiosis [18].
2.7. Clear Communication and Information Sharing:
Clear communication and information sharing are critical components of industrial symbiosis, helping collaboration and maximizing the positive effects of symbiotic relationships. Establishing networks that allow companies, knowledge agents, and government institutions to communicate and exchange ideas in a shared environment is crucial [29]. By improving the flow of information, these networks allow stakeholders to identify potential partnerships and make informed decisions [2]. However, business confidentiality is one of the biggest barriers to successful communication and information sharing [11]. Companies are often hesitant to share detailed data about their raw material inputs and waste outputs, because they are concerned about disclosing sensitive business data. This lack of transparency could prevent the development of trust and collaboration among stakeholders [11,30]. Furthermore, diverse stakeholder objectives might cause conflicts, resulting in limited sharing of resources and information [31]. To overcome these challenges, it is crucial to establish good communication routes and strong connections that balance the need for confidentiality with the benefits of transparency. Establishing robust relationships is crucial for fostering confidence and eliminating unnecessary hurdles related to confidentiality. By fostering a culture of openness and cooperation, industries can enhance their ability to share information and resources effectively [5,6].
2.8. Local and Social Acceptance
One more CSF in industrial symbiosis is local and social acceptance, which ensures that local businesses and the community are involved in sustainable practices. At both the local and corporate levels, flexibility is necessary to adjust solutions to meet the particular requirements of each community. However, one of the biggest barriers is the public’s lack of trust in recycled products, which can make industrial symbiosis programs less successful and less acceptable [15,17]. Thus, it is important to implement community awareness and education programs in order to overcome these challenges [29]. These initiatives serve as bridges between industries and local communities, promoting a mutual understanding and commitment to sustainable development [11]. These initiatives can increase trust and support for industrial symbiosis by raising awareness among the community and industry regarding the importance of resource management and environmental conservation [5,26]. Furthermore, gaining social and local acceptance is made easier by social enablers like making the environment pleasant and clean, producing new job opportunities, and meeting corporate social responsibilities [11]. Finally, the social and economic stability of a country can significantly impact the success of industrial symbiosis [6].
2.9. Inter-Organizational Relationships and Geographic Proximity
In industrial symbiosis, geographic proximity and inter-organizational relationships have a major impact on the viability and success of symbiotic exchanges. Trust, transparent interaction, and a willingness to share information are the fundamentals of strong inter-organizational collaboration [2,27,29]. It is essential to establish networks that enable companies, knowledge agents, and government entities to interact and share ideas in a common area [29]. By publicizing the achievements of others and motivating businesses to follow the example, these networks promote cooperation [6,13,21].
Geographic proximity is also important for the viability of industrial symbiosis [23,29]. When synergy elements are positioned close together, transportation expenses are reduced while logistical efficiency is increased. This proximity additionally provides more frequent and effective interactions between organizations, increasing the potential for successful cooperation [2,20,23]. In addition, a region’s strategic position, particularly its industrial diversification and the availability of resources such as electricity and water, promotes the creation of symbiotic interactions, like power purchase agreements [8,20,23].
Nevertheless, a number of obstacles could get in the way of establishing strong inter-organizational relationships and experiencing the advantages of proximity. A lack of trust among those involved, insufficient prior cooperative arrangements, lack of harmonic relations, and unwillingness to engage can hinder the establishment of effective synergies [5,30,31]. Furthermore, the concern of dependency and the possibility of decreasing independence and flexibility may discourage companies from engaging in symbiosis [25]. In order to overcome these barriers, it is important to foster a culture of trust where companies are committed to transparency and are willing to share information. It is also crucial to promote active involvement of stakeholders, including local governments, organizations, and communities [18,26]. These stakeholders can have a significant role in project financing and data provision. Finally, these efforts may advance with the help of a “champion”, a significant figure who advocates for and supports industrial symbiosis [20].
2.10. Policy and Regulatory Support and Compliance
Policy and regulatory support and compliance establishes the necessary framework for sustainable practices and ensures environmental compliance. Regulatory compliance entails aligning industrial operations with environmental laws and regulations, which positively impacts economic and environmental performance and contributes to sustainable development [1,6,17]. In order to help companies participate in industrial symbiosis, clear and coherent policies are needed, as they strengthen administrative supervision and coordination [17]. The development of financial and legal support to encourage synergetic industrial activity is one of the main enablers [2,13,17,29]. The state can be helpful in encouraging businesses to participate in industrial symbiosis by providing operational subsidies, tax reductions, and other financial incentives [2,15]. It is also important to have policies that promote the use of local and national funds to support circular economy operations [26,29]. Such policies may help transform industrial complexes into synergetic parks, fostering network development between industries [17,20].
However, a number of barriers could make policy and regulatory support less effective. The regulatory environment’s complexity may hinder the adoption of new processes, making it difficult for businesses to keep up with environmental standards [2,14,20]. For example, the constraints imposed by law on the disposal of waste can be prohibitive. Often there are barriers to a waste product being considered as a by-product, blocking it from being used as a raw material by another company [6]. Furthermore, the absence of beneficial policies and insufficient public tax relief can reduce the financial motivation for companies to participate in industrial symbiosis [21,24,31]. Establishing supportive policies that allow synergies and provide good coordination between different supportive programs is crucial to addressing these challenges [18,26,30,31]. In order to encourage planning and enhance the resilience of industries with symbiotic relationships, governments need to play an active role in the initial stages of industrial symbiosis efforts [5,21]. In addition, the establishment of industrial symbiosis can be further supported by building strong networks with industries and engaging the support of local champions from companies, universities, and non-governmental groups [5].
2.11. Use of Technology and Technological Factors
The use of technology and technological factors supports the efficiency and viability of symbiotic interactions. One of the main drivers is the availability of collaborative facilities, such as specialized equipment, advanced treatment facilities, and technology labs, which improve industrial plants’ operational capabilities [2,15,29]. Moreover, an ecosystem of technology that supports the process of mimicking and combining resources is necessary [29]. This includes the digitization of these industries via the transition to Industry 4.0, which boosts accessibility to data, reduces waste, and enhances resource efficiency [23]. Modeling, optimizing, and simulating industrial symbiosis operations can provide significant insights for future development, especially for emerging and frontier countries [11]. These technological improvements help companies to adopt resource sharing initiatives and analyze material flows within a symbiotic network more effectively [11].
Nevertheless, multiple barriers may hinder the successful integration of technology in industrial symbiosis. The successful completion of interactions may be affected by a lack of the required technology or appropriate technological capacity [15,21,30]. In addition, the initial costs linked to infrastructure and equipment may be unsustainable [6,21]. There is also a demand for specific knowledge that participants gain through experience and learning within their systems, which can be a challenge if there is a lack of technological infrastructure and readiness [21,30]. To get over these challenges, it is critical to invest in well-built infrastructures that promote sustainable by-product exchange. This includes not only physical facilities but also information databases and platforms for stakeholder interactions [13,30]. Moreover, industrial symbiosis participants should gain access to cheap utilities (energy, water, etc.), logistics, and managerial resources [18]. In addition, developing a positive attitude regarding technology and ensuring safety and accessibility are both essential for encouraging its use [31].
3. Methodology
This section presents the DEMATEL methodology and the sampling and data collection procedures followed in this study.
3.1. DEMATEL Methodology
This study employs the DEMATEL approach to examine the CSFs for industrial symbiosis, based on findings from a systematic literature review. DEMATEL is recognized for its ability to analyze complex causal relationships among diverse factors [32,33,34]. Developed at the Battelle Memorial Institute in the 1970s, this method has been widely applied across various sectors [35,36,37,38,39,40]. It effectively organizes factors into cause-and-effect clusters using matrices and diagrams, enabling decision-makers to better comprehend both the direct and indirect interactions among CSFs [32,33,34,38,41]. This feature makes DEMATEL uniquely suitable for this study, as it provides a deeper insight into the interdependencies crucial for strategic planning and operational enhancements in industrial symbiosis. Unlike other methodologies like Analytical Network Process (ANP), Technique for Order Preference by Similarity to Ideal Solution (TOPSIS) or Interpretive Structural Modeling (ISM), DEMATEL offers a more straightforward visualization of complexities, which is essential for interpreting the layered relationships within industrial symbiosis. This study follows a structured five-step DEMATEL protocol [34,37,38,42], incorporating the mathematical formulations specified by Moktadir et al. [34].
3.1.1. Step 1: Calculate the Initial Average Direct Relation Matrix
In step 1 of the DEMATEL process, the Average Direct Relation Matrix is calculated to quantify the interrelationships among the identified CSFs. Experts evaluate the influence of each CSF on the others using a scale from 0 (no influence) to 4 (very high influence) [32,33,37,39]. If there are
CSFs and
experts, each expert
provides an
matrix represented as
, where
represents indicates the influence of CSF
on CSF
as evaluated by expert
. The matrices from all
experts are represented as
. The Average Direct Relation Matrix
is calculated by averaging these matrices using the formula:
This matrix consolidates expert evaluations and serves as the foundation for further analysis within the DEMATEL framework.
3.1.2. Step 2: Calculate the Normalized Direct Relation Matrix
In Step 2 of DEMATEL, the Normalized Direct Relation Matrix
is derived from the previously calculated Average Direct Relation Matrix
. This step involves normalizing
to ensure that the influence scores are on a consistent scale. The normalization factor
is calculated as the minimum of the reciprocals of the sums of the absolute values of either the row or column totals of
, given by:
The normalized matrix
is then obtained by multiplying
by
. This normalization ensures that the maximum element in
does not exceed 1, maintaining the proportional relationships essential for the subsequent DEMATEL analysis steps.
3.1.3. Step 3: Calculate the Total Relation Matrix
In Step 3 of DEMATEL, the Total Relation Matrix
is developed to capture both direct and indirect interactions among the CSFs. This matrix extends the analysis by using the Normalized Direct Relation Matrix
from Step 2. The Total Relation Matrix
is calculated using the formula
, where
is the identity matrix of the same dimensions as
, and
is the inverse of the matrix resulting from subtracting
from
. This process captures the total effects (direct and indirect) of each CSF on the others. The Total Relation Matrix
is essential for providing a comprehensive understanding of the full range of interactions, which is critical for decision-makers in managing the CSFs in subsequent DEMATEL stages.
3.1.4. Step 4: Calculate and Depict the Prominence and Net Effects of CSFs
In Step 4 of DEMATEL, the prominence and net effects of each CSF are analyzed using the Total Relation Matrix
. The process involves calculating the total influence exerted by each CSF,
, and the total influence received by each CSF,
using the following formulas:
Here,
represents the total influence exerted by the
-th CSF, and
represents the total influence received by the
-th CSF. The prominence of a CSF is determined by the sum
, indicating its overall importance in the system. The net effect is calculated as
, which reveals whether a CSF acts mainly as a cause (positive net effect) or as an effect (negative net effect) within the network.
These values are then visualized in a Prominence and Net Effect Diagram, with the prominence
plotted on the x-axis and the net effect
on the y-axis. This diagram helps decision-makers differentiate between CSFs that primarily act as causes and those that function as effects, enhancing the strategic management of their interactions.
3.1.5. Step 5: Depict the Marked Causal Relationships Among CSFs
In Step 5 of DEMATEL, the most marked causal relationships between CSFs are visually represented. These relationships are derived from the Total Relation Matrix, and only the most significant ones are highlighted. A threshold
is established to filter out less important interactions, calculated using the formula
, where μ is the mean and
is the standard deviation of the entries in the Total Relation Matrix. Interactions that exceed this threshold are considered significant and are depicted in the Diagram of Marked Causal Relationships. This selective approach, supported by studies such as those by Moktadir et al. [34], Huang et al. [42], and Kouhizadeh et al. [33], focuses on the most influential interactions, preventing less important effects from obscuring strategic decision-making.
3.2. Sample Information and Data Collection Method
Participants for DEMATEL were selected using convenience and snowball sampling, commonly applied in this research methodology [33,34,40]. The selection process specifically targeted engineers and managers who possess a deep understanding of industrial symbiosis. Inclusion criteria required participants to have significant experience in their respective fields and a demonstrable knowledge of industrial symbiosis concepts. Exclusion criteria were set to omit those lacking direct experience or relevant professional engagement with industrial symbiosis, ensuring that all participants could contribute meaningful insights based on actual practice. To further minimize potential biases in participant selection, we ensured a balance of perspectives by including professionals from various sub-sectors and roles within their industries.
Participants were tasked with assessing the interconnections between CSFs for industrial symbiosis based on their perceptions. The 11 CSFs were initially identified from the literature (refer to Section 2) and validated by two industry experts with around 20 years of experience, including a strategy head from an oil and gas company and a production manager from a high-ranking technologies firm. Participants evaluated the influence of each CSF using an 11 × 11 pairwise comparison matrix, rating the dependencies on a five-point scale from 0 (no influence) to 4 (very high influence).
A total of fourteen carefully selected responses were collected from a diverse cohort of professionals, primarily aged between 30 and 49 years, with a predominance of male participants. This sample size was intentionally chosen to balance diversity with the depth of insight essential for the DEMATEL methodology. The participants held high-level managerial or directorial roles across industries such as oil and gas, mining, manufacturing, renewable energy, and high technology. Their roles spanned areas critical to industrial symbiosis, including strategy, engineering, project management, sustainability, and business development. Most participants held advanced degrees in relevant fields like engineering, sustainability, supply chain management, and business administration. Their professional experience, ranging from 6 to 43 years with an average of 16.9 years, reflected a level of expertise and leadership that was deemed sufficient to provide the depth and quality of analysis required for this study. Comprehensive details regarding participant demographics and profiles can be found in Appendix A, Table A1.
4. Results
This section presents the key findings from the DEMATEL analysis in two parts. Section 4.1 addresses the prominence and net effects of each CSF, corresponding to stage 4 of the DEMATEL methodology, while Section 4.2 examines the most significant causal relationships among the CSFs, aligning with stage 5. The matrices used for stages 1–3 of DEMATEL—the Average Direct Relation Matrix, the Normalized Direct Relation Matrix, and the Total Relation Matrix—are detailed in Table A2 in Appendix A.
4.1. Prominence and Net Effects of CSFs
The analysis reveals the influence of various CSFs on industrial symbiosis. Table 1 contains the prominence and net effect values for each CSF, while Figure 1 plots these values, with prominence represented on the x-axis and net effect on the y-axis. Prominence quantifies the total strength of both direct and indirect influences a CSF exerts and receives within the network, reflecting its overall significance. The net effect distinguishes between CSFs that predominantly influence others (positive values) and those that are predominantly influenced (negative values). This visual representation aids in understanding which factors are drivers of change within industrial symbiosis and which are outcomes of those changes.

Table 1.
Prominence and net effect values.
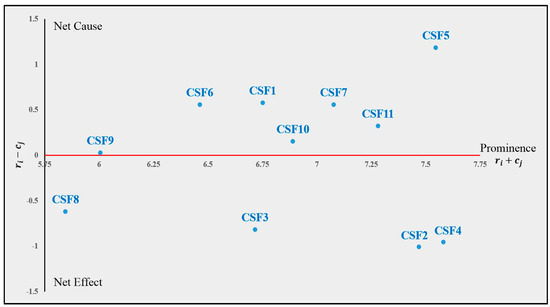
Figure 1.
Prominence and net effect diagram.
“Waste Reduction and Environmental Impact”, “Economic Growth and Profitability”, “Leadership”, and “Use of Technology and Technological Factors” received the highest prominence scores, underscoring their critical roles within the industrial symbiosis framework. Notably, the latter two factors exhibited positive net effects, identifying them as causal elements. These factors served as catalysts for change within the industrial symbiosis ecosystem, exerting more influence on other CSFs than they themselves received. In contrast, the first two factors, characterized by negative net effects, were classified as effects, meaning they were more influenced by other CSFs. This suggests that changes in these areas are typically driven by shifts in the causal factors. Conversely, CSFs such as “Local and Social Acceptance” and “Inter-organizational Relationships and Geographic Proximity” received lower prominence scores, indicating their comparatively lesser significance within the broader industrial symbiosis context.
4.2. Marked Causal Relationships Among CSFs
The Total Relation Matrix offers a comprehensive analysis of the causal relationships among the identified CSFs. In this study, a threshold was determined by calculating the sum of the mean and standard deviation of all entries in the matrix, as detailed in Section 3. This threshold was used to identify and highlight the most important relationships; only those relationships where the matrix values exceeded the threshold were considered significant, and were visually marked in red italics within the matrix (refer to Table A2 in the Appendix A for further information). These significant relationships are represented by arrows in the Marked Causal Relationships Diagram, which is depicted in Figure 2.
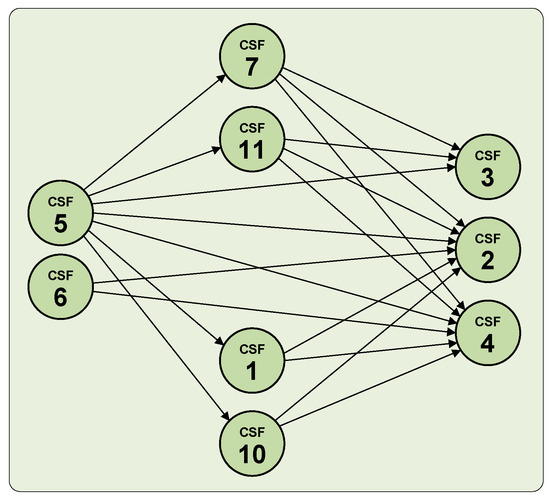
Figure 2.
Marked causal relationships.
This figure models the interconnections among the primary CSFs pertinent to industrial symbiosis, offering insights into how strategic interventions can influence the network.
The analysis identified “Waste Reduction and Environmental Impact”, “Economic Growth and Profitability”, and “Operational Cost Reduction” as the endpoints in the impact flow within the interconnected CSF model. Notably, the first two factors were more influenced by other CSFs compared to the third.
“Leadership” was identified as the most significant causal factor, exerting a predominant influence on all other key CSFs in the model. Concurrently, “Governance and Internal Organizational Structure” also influenced the network, though its impact was less pronounced than that of “Leadership”, and was primarily directed at “Waste Reduction and Environmental Impact” and “Economic Growth and Profitability”.
The model also included four CSFs that acted as channels connecting “Leadership” to the three aforementioned effect factors. “Use of Technology and Technological Factors” and “Clear Communication and Information Sharing” mediated the relationship between “Leadership” and all three effect CSFs, namely, “Waste Reduction and Environmental Impact”, “Economic Growth and Profitability”, and “Operational Cost Reduction”. Meanwhile, “Enhanced Training and Education” and “Policy and Regulatory Support and Compliance” specifically facilitated the connection between “Leadership” and the first two effect CSFs.
5. Discussion and Conclusions
This study examined the CSFs for industrial symbiosis by employing the DEMATEL methodology to analyze the cause-and-effect relationships among these factors. A systematic literature review combined with expert insights identified the significance and roles of these factors, revealing essential areas for strategic interventions to improve industrial symbiosis practices. Furthermore, this approach offered a comprehensive understanding of the interactions among different CSFs, establishing a robust basis for the study’s subsequent findings and implications.
5.1. Discussion of the Key Findings
This section presents a discussion of the study’s key findings, assessing the interactions among various CSFs that impact the implementation of industrial symbiosis.
According to the model derived in this study, “Waste Reduction and Environmental Impact” and “Economic Growth and Profitability” emerge as the most significant effect factors. This result highlights their importance as primary outcomes for organizations within industrial symbiosis settings, as also stressed in previous studies [1,23,26,29]. These factors are heavily influenced by other CSFs such as leadership, technology adoption, and effective communication, indicating that improvements in environmental performance and economic growth are driven by changes in these causal elements. “Operational Cost Reduction”, while still important (see also [29]), is less influenced by other CSFs compared to the first two factors. This relative independence suggests that cost reduction can often be achieved through direct measures like optimizing operational processes and improving resource utilization, which may not require extensive changes in leadership or significant technological investments. This distinction in influence patterns implies that while all three effect factors are essential outcomes of industrial symbiosis, they are achieved through different pathways. The first two are highly dependent on leveraging leadership, technology, governance, and other mediating factors, whereas operational cost reduction may be more readily attainable through focused internal efforts.
Leadership is identified as the most significant causal factor influencing all other CSFs in industrial symbiosis. Strong leaders drive the adoption and success of symbiotic initiatives by providing clear vision and strategic direction, aligning departments and stakeholders toward shared sustainability goals. They allocate necessary resources, foster a culture of innovation and collaboration, and motivate employees to embrace new practices. By engaging with stakeholders and addressing concerns, leaders overcome resistance to change, building trust and facilitating smooth transitions to new operational methods. They also facilitate effective communication and transparency, enhancing collaboration and informed decision-making across the organization. Additionally, leaders navigate governance and organizational structures to support symbiotic efforts, potentially restructuring teams or redefining roles as needed. Notably, the prior literature has largely overlooked the critical role of leadership in industrial symbiosis, with only a limited number of studies recognizing insufficient top management awareness and support as a significant barrier to success [4,21,30,31].
Effective governance mechanisms and well-structured organizational frameworks are crucial for supporting industrial symbiosis initiatives. While their influence on key CSFs is less pronounced than that of leadership, governance ensures alignment across departments and facilitates smooth implementation of symbiotic practices. Lately, focusing on sustainability and renewable energy has become crucial for tackling environmental, ecological, and socioeconomic issues [43]. By providing clear guidelines and defining roles and responsibilities, governance coordinates efforts toward shared sustainability goals. This alignment enhances collaboration and reduces operational silos, leading to more efficient resource utilization and waste reduction. An effective organizational structure integrates environmental objectives into the core business strategy, enabling systematic implementation of sustainable practices and reducing environmental impact. Governance also promotes innovation and continuous improvement, contributing to economic growth and profitability by identifying opportunities for cost savings and revenue generation. By institutionalizing sustainable practices and ensuring consistent application across the organization, governance enhances the effectiveness of symbiosis efforts, ultimately supporting key environmental and economic outcomes.
“Technology” and “Clear Communication and Information Sharing” are crucial both as impactful factors and as mediators connecting leadership to the key effect factors: “Waste Reduction and Environmental Impact”, “Economic Growth and Profitability”, and “Operational Cost Reduction”. Similarly, “Enhanced Training and Education” and “Policy and Regulatory Support and Compliance” serve a dual role in industrial symbiosis as both impactful causal factors and mediators between leadership and the first two of the abovementioned effect factors.
As a causal factor, the adoption of advanced technologies—such as data analytics, automation, and monitoring systems—directly enhances operational efficiency and resource optimization. These technologies enable organizations to identify new symbiotic opportunities by revealing insights and connections that might otherwise remain unnoticed. As a mediator, technology facilitates leadership’s influence on achieving desired outcomes. Leaders who prioritize technological innovation empower their organizations to implement symbiotic practices more effectively. Technology provides the tools and platforms necessary for executing leadership’s strategic vision, enhancing communication, coordination, and data-driven decision-making. By utilizing technology, organizations can streamline processes, reduce waste, and lower operational costs, all of which contribute to economic growth and improved environmental performance. These findings are consistent with previous research highlighting the critical role of technology in driving industrial symbiosis [11,23,29].
Transparent communication enhances collaboration and builds trust among stakeholders (see also [5]), ensuring that everyone is aligned with the organization’s sustainability objectives. By setting goals and strategies clearly, leadership can more effectively drive the adoption of industrial symbiosis practices. Furthermore, open communication reduces resistance to change by addressing concerns and highlighting benefits, enabling smoother implementation of industrial symbiosis initiatives. Facilitating the exchange of best practices and resource information is crucial for identifying opportunities to minimize waste, improve efficiency, and reduce operational costs. Effective information sharing also enhances the monitoring and evaluation of industrial symbiosis initiatives, providing insights for data-driven decision-making.
Organizations may also offer co-educational opportunities to enhance individual expertise and promote collaborative learning among employees. This empowers the workforce to implement symbiotic practices effectively, as also emphasized in previous studies [1,17]. Specifically, targeted training programs enable employees to become adept in resource efficiency techniques, waste minimization strategies, and innovative processes that support environmental sustainability. Moreover, education initiatives promote a culture of continuous improvement and innovation, which is vital for economic growth and profitability. Strengthening team competencies also effectively promotes organizational change toward sustainability goals. Furthermore, training and education empower employees to identify new opportunities for symbiotic relationships, optimize resource utilization, and enhance operational efficiencies. This results in reduced environmental impact and potential cost savings and revenue generation.
Compliance with environmental policies and regulations allows organizations involved in industrial symbiosis to promote sustainable practices. Furthermore, regulatory incentives, such as tax breaks, grants, or streamlined permitting processes, can facilitate the adoption of symbiotic initiatives by reducing financial and administrative barriers. This issue has been extensively explored in the literature [5,11,13,18,19,30]. Different regulatory frameworks and market conditions could affect shaping corporate strategies towards sustainable energy transitions [44]. Leadership plays a critical role in aligning organizational strategies with regulatory frameworks and utilizing available incentives. Leaders should remain informed about policy changes and advocate for supportive regulations to enhance the organization’s capacity to implement effective industrial symbiosis practices. This approach allows organizations to minimize waste and environmental impact while fostering economic growth through resource efficiency and innovation.
Finally, it is important to note that in this analysis, “Local and Social Acceptance” and “Inter-organizational Relationships and Geographic Proximity” were assigned lower prominence scores. This indicates that they are viewed as less critical than factors such as technology or regulatory compliance. This diminished focus may stem from the assumption that resolving technical and regulatory challenges will automatically lead to alignment in social and organizational dynamics. However, this perspective fails to recognize the importance of community support and strong inter-organizational collaboration in maintaining symbiotic initiatives. Insufficient local acceptance can result in public resistance, while weak relationships between organizations can lead to ineffective communication and mistrust. These oversights can hinder the establishment and resilience of symbiotic networks, ultimately affecting their success and sustainability, as also highlighted in previous studies [5,29].
5.2. Managerial Implications
This study clarifies the roles and interconnections of CSFs for industrial symbiosis, providing insights for managers seeking to improve environmental and economic performance in their organizations. Focusing initially on leadership, it is clearly identified as fundamental for initiating and guiding the successful implementation of symbiotic practices. Therefore, managers must focus on strong, visionary leadership to promote and sustain industrial symbiosis efforts. This includes establishing a clear strategic direction, aligning organizational goals, engaging in resource allocation, and promoting a culture of innovation and collaboration. Additionally, effective communication and technological advancements serve as key mediators that help translate leadership’s vision into practical execution. Prioritizing clear and transparent communication ensures alignment among stakeholders regarding the objectives and progress of symbiotic initiatives. The integration of advanced technologies improves operational efficiency and aids in identifying new symbiotic opportunities. This directly contributes to minimizing environmental impact and maximizing resource utilization. Thus, managers are advised to utilize these technologies to streamline processes, enhance data-driven decision-making, optimize resource flows, and ultimately achieve economic profitability and environmental sustainability. Furthermore, the importance of governance structures is significant. In this context, managers must ensure that their organizational frameworks support the effective implementation of industrial symbiosis by institutionalizing sustainable practices and encouraging collaboration. This structural alignment enhances resource utilization and reduces operational silos, resulting in substantial reductions in waste and operational costs.
5.3. Societal Implications
The societal implications of this study are also significant, highlighting the essential role of industrial symbiosis in promoting sustainability and enhancing community welfare. By effectively implementing CSFs such as “Waste Reduction and Environmental Impact” and “Economic Growth and Profitability”, organizations can significantly contribute to reducing environmental degradation. This approach conserves natural resources and reduces the ecological footprint, creating a healthier environment for local communities. The resulting environmental benefits, including improved air and water quality and preserved natural landscapes, directly enhance the quality of life for communities. A focus on governance and adherence to policies promotes a structured approach to sustainable development, aligning industrial activities with broader societal objectives and ensuring that economic progress does not compromise environmental or social well-being. Transparent communication and information sharing, essential to effective symbiosis practices, are vital for building trust and credibility between organizations and the communities they affect, keeping societal stakeholders informed and engaged in the symbiosis processes. These societal outcomes represent a shift towards more sustainable industrial practices and emphasize the importance of systemic thinking and the interconnectedness of industry operations and community welfare. For professionals designing and managing these systems, it is essential to understand the broader implications of their technical and operational decisions on community welfare. Such insights are critical for promoting a holistic approach to environmental management and social responsibility in industrial symbiosis projects, ultimately contributing to sustainable development on a global scale.
5.4. Limitations and Future Research Directions
The study has several limitations that can guide future research. The DEMATEL methodology, while robust in analyzing interrelationships among CSFs, is inherently subjective, relying heavily on the expertise and perceptions of participants, which may introduce bias. Additionally, the chosen sample of 14 experts may further influence the study’s reliability and generalizability, representing another potential limitation. Future research should aim to apply the DEMATEL methodology across a broader range of industries and regions to validate and potentially enhance the transferability of the results. Additionally, integrating quantitative data could complement the expert assessments, providing a more balanced view of the CSFs’ impacts and interdependencies. Research could also explore the longitudinal effects of these CSFs on industrial symbiosis outcomes, assessing how changes in one factor affect others over time. This approach would provide deeper insights into the dynamic nature of these relationships and help refine strategies for managing them more effectively in different industrial contexts.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.K.C., P.T.C., D.A.G. and A.G.L.; methodology, S.K.C. and P.T.C.; software, P.T.C.; validation, P.T.C., D.A.G. and A.G.L.; formal analysis, S.K.C. and P.T.C.; investigation, S.K.C.; resources, S.K.C.; data curation, S.K.C. and P.T.C.; writing—original draft preparation, S.K.C. and P.T.C.; writing—review and editing, P.T.C., D.A.G. and A.G.L.; visualization, P.T.C.; supervision, A.G.L.; project administration, D.A.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Appendix A

Table A1.
Participants Profile.
Table A1.
Participants Profile.
| ID | Age Range | Gender | Highest Degrees | Company Classification | Current Position | Years of Experience |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 40–49 | Male | Elec. Eng, MSc in Sustainability | Group of Companies (Oil and Gas; Refinery) | Head, Group Strategy Division | 15 |
| 2 | 40–49 | Female | Mech. Eng, MSc in Materials Science and Technology | Manufacturing Company (Cement Industry) | Digital Project Management Officer (PMO) | 20 |
| 3 | 30–39 | Male | Chem. Eng, MSc in Sustainability | Multinational Energy Corporation (Water/Waste and Energy Management) | Business Development Manager | 8 |
| 4 | 30–39 | Male | MSc in Supply Chain Management | Multinational Manufacturing Company (Refrigeration and Glass Producer) | Head, Engineering Department | 10 |
| 5 | 30–39 | Male | MBA, MSc in Supply Chain Management | Multinational Manufacturing Company (Aluminium and Copper Manufacturer) | Purchasing Category Manager | 9 |
| 6 | 40–49 | Male | Chem. Eng, MBA | Renewable energy Power Generation Company (Renewable Hydrogen) | Head of Technical Management | 20 |
| 7 | 40–49 | Female | Mech. Eng, MBA, PhD in Mechanical Engineering | Energy Company (Oil and Gas; Refinery) | Engineering and Construction Refineries Director | 14 |
| 8 | 40–49 | Male | Mech. Eng, MBA, MSc in Supply Chain Management | Group of Companies (Oil and Gas; Refinery) | Head, Group Strategy Division | 20 |
| 9 | 30–39 | Male | MSc in Maritime Management | Group of Companies (Oil and Gas; Refinery) | Head of Sustainability Reporting | 12 |
| 10 | 30–39 | Female | Chem. Eng | Group of Companies (Oil and Gas; Refinery) | Group Planning and Budgeting Advisor | 14 |
| 11 | 40–49 | Male | Elec. Eng, MSc in Electronics | High Technologies and Industrial Cooperation Company (Sensors, IoT) | Production Manager | 20 |
| 12 | 30–39 | Male | MSc in Energy and Finance | Group of Companies (Oil and Gas; Refinery) | Senior Mergers and Acquisitions Expert | 6 |
| 13 | 40–49 | Male | Mech. Eng, MBA | Multinational Energy Corporation (Oil and Gas) | Senior Charterer | 25 |
| 14 | 60–69 | Male | Min. Metall. Eng, MBA | Multinational Mining corporation (Industrial Minerals) | General Manager; Chairman of the Board of Directors | 43 |

Table A2.
DEMATEL matrices.
Table A2.
DEMATEL matrices.
| Average Direct Relation Matrix | |||||||||||
| CSFs | CSF1 | CSF2 | CSF3 | CSF4 | CSF5 | CSF6 | CSF7 | CSF8 | CSF9 | CSF10 | CSF11 |
| CSF1 | 2.786 | 2.500 | 2.571 | 2.357 | 2.143 | 2.929 | 2.143 | 1.786 | 2.429 | 3.643 | |
| CSF2 | 2.071 | 3.143 | 2.714 | 2.571 | 1.857 | 1.643 | 2.000 | 1.500 | 1.929 | 2.786 | |
| CSF3 | 1.929 | 3.429 | 2.429 | 1.929 | 1.500 | 1.643 | 1.286 | 1.786 | 1.714 | 2.500 | |
| CSF4 | 1.643 | 2.714 | 2.500 | 1.929 | 1.571 | 1.857 | 3.286 | 2.071 | 3.286 | 2.357 | |
| CSF5 | 3.429 | 3.500 | 2.786 | 3.071 | 3.571 | 3.357 | 2.500 | 3.000 | 2.571 | 2.929 | |
| CSF6 | 2.214 | 2.857 | 2.714 | 2.500 | 2.857 | 2.857 | 1.714 | 2.071 | 2.214 | 2.143 | |
| CSF7 | 2.500 | 2.929 | 2.929 | 2.286 | 2.643 | 2.692 | 2.786 | 2.857 | 2.786 | 2.357 | |
| CSF8 | 1.286 | 2.643 | 1.000 | 2.643 | 1.929 | 1.286 | 1.714 | 1.714 | 2.429 | 1.143 | |
| CSF9 | 1.429 | 2.857 | 2.714 | 2.571 | 1.714 | 1.500 | 2.357 | 2.071 | 1.929 | 1.786 | |
| CSF10 | 1.857 | 2.929 | 2.571 | 3.429 | 2.286 | 2.571 | 2.000 | 2.571 | 2.000 | 2.357 | |
| CSF11 | 2.929 | 3.214 | 3.286 | 5.786 | 1.714 | 1.714 | 2.500 | 1.786 | 1.857 | 1.929 | |
| Normalized Direct Relation Matrix | |||||||||||
| CSFs | CSF1 | CSF2 | CSF3 | CSF4 | CSF5 | CSF6 | CSF7 | CSF8 | CSF9 | CSF10 | CSF11 |
| CSF1 | 0.000 | 0.091 | 0.081 | 0.084 | 0.077 | 0.070 | 0.095 | 0.070 | 0.058 | 0.079 | 0.119 |
| CSF2 | 0.067 | 0.000 | 0.102 | 0.088 | 0.084 | 0.060 | 0.053 | 0.065 | 0.049 | 0.063 | 0.091 |
| CSF3 | 0.063 | 0.112 | 0.000 | 0.079 | 0.063 | 0.049 | 0.053 | 0.042 | 0.058 | 0.056 | 0.081 |
| CSF4 | 0.053 | 0.088 | 0.081 | 0.000 | 0.063 | 0.051 | 0.060 | 0.107 | 0.067 | 0.107 | 0.077 |
| CSF5 | 0.112 | 0.114 | 0.091 | 0.100 | 0.000 | 0.116 | 0.109 | 0.081 | 0.098 | 0.084 | 0.095 |
| CSF6 | 0.072 | 0.093 | 0.088 | 0.081 | 0.093 | 0.000 | 0.093 | 0.056 | 0.067 | 0.072 | 0.070 |
| CSF7 | 0.081 | 0.095 | 0.095 | 0.074 | 0.086 | 0.088 | 0.000 | 0.091 | 0.093 | 0.091 | 0.077 |
| CSF8 | 0.042 | 0.086 | 0.033 | 0.086 | 0.063 | 0.042 | 0.056 | 0.000 | 0.056 | 0.079 | 0.037 |
| CSF9 | 0.047 | 0.093 | 0.088 | 0.084 | 0.056 | 0.049 | 0.077 | 0.067 | 0.000 | 0.063 | 0.058 |
| CSF10 | 0.060 | 0.095 | 0.084 | 0.112 | 0.074 | 0.084 | 0.065 | 0.084 | 0.065 | 0.000 | 0.077 |
| CSF11 | 0.095 | 0.105 | 0.107 | 0.188 | 0.056 | 0.056 | 0.081 | 0.058 | 0.060 | 0.063 | 0.000 |
| Total Relation Matrix | |||||||||||
| CSFs | CSF1 | CSF2 | CSF3 | CSF4 | CSF5 | CSF6 | CSF7 | CSF8 | CSF9 | CSF10 | CSF11 |
| CSF1 | 0.238 | 0.408 | 0.365 | 0.407 | 0.315 | 0.292 | 0.337 | 0.313 | 0.284 | 0.332 | 0.375 |
| CSF2 | 0.273 | 0.287 | 0.348 | 0.371 | 0.292 | 0.256 | 0.271 | 0.279 | 0.248 | 0.287 | 0.319 |
| CSF3 | 0.250 | 0.363 | 0.234 | 0.338 | 0.255 | 0.228 | 0.251 | 0.240 | 0.238 | 0.260 | 0.291 |
| CSF4 | 0.263 | 0.375 | 0.335 | 0.297 | 0.279 | 0.252 | 0.281 | 0.322 | 0.269 | 0.331 | 0.311 |
| CSF5 | 0.383 | 0.490 | 0.428 | 0.480 | 0.291 | 0.375 | 0.397 | 0.370 | 0.362 | 0.385 | 0.406 |
| CSF6 | 0.295 | 0.397 | 0.359 | 0.388 | 0.319 | 0.218 | 0.325 | 0.291 | 0.283 | 0.315 | 0.322 |
| CSF7 | 0.321 | 0.426 | 0.388 | 0.409 | 0.333 | 0.316 | 0.260 | 0.341 | 0.324 | 0.352 | 0.349 |
| CSF8 | 0.209 | 0.310 | 0.238 | 0.312 | 0.233 | 0.202 | 0.230 | 0.179 | 0.216 | 0.259 | 0.226 |
| CSF9 | 0.239 | 0.353 | 0.319 | 0.345 | 0.253 | 0.232 | 0.275 | 0.267 | 0.188 | 0.272 | 0.274 |
| CSF10 | 0.284 | 0.399 | 0.354 | 0.415 | 0.303 | 0.294 | 0.300 | 0.316 | 0.281 | 0.249 | 0.327 |
| CSF11 | 0.331 | 0.432 | 0.397 | 0.505 | 0.305 | 0.285 | 0.332 | 0.314 | 0.294 | 0.329 | 0.278 |
Notes: Threshold value = mean + standard deviation = 0.313 + 0.063 = 0.376. Values exceeding this threshold are highlighted in red italics.
References
- Sonel, E.; Gür, Ş.; Eren, T. Analysis of Factors Affecting Industrial Symbiosis Collaboration. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 8479–8486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Pinto, M.C.B. Analyzing the Critical Success Factors for Industrial Symbiosis—A Chinese Perspective. In Advances in Industrial and Production Engineering; Phanden, R.K., Mathiyazhagan, K., Kumar, R., Paulo Davim, J., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2021; pp. 23–33. ISBN 978-981-334-319-1. [Google Scholar]
- Nyakudya, P.; Madushele, N.; Madyira, D.M. A Review of Industrial Symbiosis in Influencing Green Manufacturing. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 13th International Conference on Mechanical and Intelligent Manufacturing Technologies (ICMIMT), Cape Town, South Africa, 25–27 May 2022; pp. 80–84. [Google Scholar]
- Mileva-Boshkoska, B.; Rončević, B.; Uršič, E.D. Modeling and Evaluation of the Possibilities of Forming a Regional Industrial Symbiosis Networks. Social. Sci. 2018, 7, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teh, B.T.; Ho, C.S.; Matsuoka, Y.; Chau, L.W.; Gomi, K. Determinant Factors of Industrial Symbiosis: Greening Pasir Gudang Industrial Park. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2014, 18, 012162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves, A.; Godina, R.; Azevedo, S.G.; Pimentel, C.; Matias, J.C.O. The Potential of Industrial Symbiosis: Case Analysis and Main Drivers and Barriers to Its Implementation. Sustainability 2019, 11, 7095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agudo, F.L.; Bezerra, B.S.; Paes, L.A.B.; Gobbo, J.A., Jr. Proposal of an Assessment Tool to Diagnose Industrial Symbiosis Readiness. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2022, 30, 916–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agudo, F.L.; Bezerra, B.S.; Gobbo Júnior, J.A. Symbiotic Readiness: Factors That Interfere with the Industrial Symbiosis Implementation. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 387, 135843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cudečka-Puriņa, N.; Atstāja, D.; Koval, V.; Purviņš, M.; Nesenenko, P.; Tkach, O. Achievement of Sustainable Development Goals through the Implementation of Circular Economy and Developing Regional Cooperation. Energies 2022, 15, 4072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agudo, F.L.; Bezerra, B.S.; Gobbo, J.A.; Paes, L.A.B. Unfolding Research Themes for Industrial Symbiosis and Underlying Theories. Sustain. Dev. 2022, 30, 1682–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boom-Cárcamo, E.; Peñabaena-Niebles, R. Analysis of the Development of Industrial Symbiosis in Emerging and Frontier Market Countries: Barriers and Drivers. Sustainability 2022, 14, 4223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haq, H.; Välisuo, P.; Niemi, S. Modelling Sustainable Industrial Symbiosis. Energies 2021, 14, 1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortensen, L.; Kørnøv, L. Critical Factors for Industrial Symbiosis Emergence Process. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 212, 56–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacondini, A.; Mencherini, U.; Passarini, F.; Vassura, I.; Fanelli, A.; Cibotti, P. Feasibility of Industrial Symbiosis in Italy as an Opportunity for Economic Development: Critical Success Factor Analysis, Impact and Constrains of the Specific Italian Regulations. Waste Biomass Valor. 2015, 6, 865–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wu, J.; He, Y.; Xu, H. Which Factors Promote or Inhibit Enterprises’ Participation in Industrial Symbiosis? An Analytical Approach and a Case Study in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 244, 118600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardi, R. Non-Technical Barriers to (and Drivers for) the Circular Economy through Industrial Symbiosis: A Practical Input. Econ. Policy Energy Environ. 2017, 2017, 171–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lybæk, R.; Christensen, T.B.; Thomsen, T.P. Enhancing Policies for Deployment of Industrial Symbiosis—What Are the Obstacles, Drivers and Future Way Forward? J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 280, 124351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirata, M. Experiences from Early Stages of a National Industrial Symbiosis Programme in the UK: Determinants and Coordination Challenges. J. Clean. Prod. 2004, 12, 967–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellitto, M.A.; Murakami, F.K.; Butturi, M.A.; Marinelli, S.; Kadel, N., Jr.; Rimini, B. Barriers, Drivers, and Relationships in Industrial Symbiosis of a Network of Brazilian Manufacturing Companies. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2021, 26, 443–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simboli, A.; Taddeo, R.; Morgante, A. Analysing the Development of Industrial Symbiosis in a Motorcycle Local Industrial Network: The Role of Contextual Factors. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 66, 372–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakobsen, S.; Steinmo, M. Drivers and Barriers for Industrial Symbiosis: The Case of Mo Industrial Park. In Research Handbook of Innovation for a Circular Economy; Jakobsen, S., Lauvås, T., Quatraro, F., Rasmussen, E., Steinmo, M., Eds.; Edward Elgar Publishing: Cheltenham, UK; Northampton, MA, USA, 2021; ISBN 978-1-80037-309-9. [Google Scholar]
- Jacobsen, B.N. Do Social Factors Really Matter When Companies Engage in Industrial Symbiosis? Progress. Ind. Ecol. Int. J. 2007, 4, 440–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriques, J.; Ferrão, P.; Castro, R.; Azevedo, J. Industrial Symbiosis: A Sectoral Analysis on Enablers and Barriers. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, M.E.; Ureña, L.J.B.; Fuente, A.B.L. Key-Drivers Identification for Industrial Symbiosis Entailing Circular Economy Transition in Europe. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE European Technology and Engineering Management Summit (E-TEMS), Kaunas, Lithuania, 20–22 April 2023; pp. 39–43. [Google Scholar]
- Neves, Â.; Ferreira, H.; Lopes, F.J.; Godina, R.; Matias, J.C.O. Industrial Symbiosis Applied to Oil Refineries: Drivers and Barriers. In Quality Innovation and Sustainability; De Oliveira Matias, J.C., Oliveira Pimentel, C.M., Gonçalves Dos Reis, J.C., Costa Martins Das Dores, J.M., Santos, G., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 265–278. ISBN 978-3-031-12913-1. [Google Scholar]
- Herath, P.; Dissanayake, P.; Kumarasiri, B. Enablers to Facilitate Industrial Symbiosis for Better Waste Management of Industrial Zones in Sri Lanka. In Proceedings of the 10th World Construction Symposium 2022, Colombo, Sri Lanka, 24 June 2022; pp. 429–440. [Google Scholar]
- Rosendahl, S.; Lundkvist, K.; Haase, B.; Stemne, J.; Andersson, L.; Eriksson, R. Establishing an Industrial Symbiosis—Key Factors and Time Aspects in Steel Industry. Matériaux Tech. 2019, 107, 508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paquin, R.L.; Tilleman, S.G.; Howard-Grenville, J. Is There Cash in That Trash?: Factors Influencing Industrial Symbiosis Exchange Initiation and Completion. J. Ind. Ecol. 2014, 18, 268–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayazi, S.M.; Babgohari, A.Z.; Taghizadeh-Yazdi, M. Towards the Analysis of Industrial Symbiosis Enablers in Small and Medium Enterprises: A Hesitant Fuzzy Approach. In Decision-Making in International Entrepreneurship: Unveiling Cognitive Implications Towards Entrepreneurial Internationalisation; Jafari-Sadeghi, V., Amoozad Mahdiraji, H., Eds.; Emerald Publishing Limited: Bingley, UK, 2023; pp. 243–265. ISBN 978-1-80382-234-1. [Google Scholar]
- Bacudio, L.R.; Benjamin, M.F.D.; Eusebio, R.C.P.; Holaysan, S.A.K.; Promentilla, M.A.B.; Yu, K.D.S.; Aviso, K.B. Analyzing Barriers to Implementing Industrial Symbiosis Networks Using DEMATEL. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2016, 7, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taqi, H.M.M.; Meem, E.J.; Bhattacharjee, P.; Salman, S.; Ali, S.M.; Sankaranarayanan, B. What Are the Challenges That Make the Journey towards Industrial Symbiosis Complicated? J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 370, 133384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahuja, J.; Panda, T.K.; Luthra, S.; Kumar, A.; Choudhary, S.; Garza-Reyes, J.A. Do Human Critical Success Factors Matter in Adoption of Sustainable Manufacturing Practices? An Influential Mapping Analysis of Multi-Company Perspective. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 239, 117981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouhizadeh, M.; Saberi, S.; Sarkis, J. Blockchain Technology and the Sustainable Supply Chain: Theoretically Exploring Adoption Barriers. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2021, 231, 107831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moktadir, M.A.; Kumar, A.; Ali, S.M.; Paul, S.K.; Sultana, R.; Rezaei, J. Critical Success Factors for a Circular Economy: Implications for Business Strategy and the Environment. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2020, 29, 3611–3635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, C.; Sarkis, J. A Grey-Based DEMATEL Model for Evaluating Business Process Management Critical Success Factors. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2013, 146, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.-C.; Lee, Y.-S. Exploring the Critical Factors Influencing the Quality of Blog Interfaces Using the Decision-Making Trial and Evaluation Laboratory (DEMA℡) Method. Behav. Inf. Technol. 2014, 33, 184–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Singh, R.; Haleem, A.; Dsilva, J.; Ali, S.S. Exploration of Critical Success Factors of Logistics 4.0: A DEMATEL Approach. Logistics 2022, 6, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.-H.; Chang, S.-Y. A Case Study of Using DEMATEL Method to Identify Critical Factors in Green Supply Chain Management. Appl. Math. Comput. 2015, 256, 394–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Irfan Ahmed, R.; Ahmad, N.; Yan, C.; Usmani, M.S. Prioritizing Critical Success Factors for Sustainable Energy Sector in China: A DEMATEL Approach. Energy Strategy Rev. 2021, 35, 100635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chountalas, P.T.; Chatzifoti, N.; Alexandropoulou, A.; Georgakellos, D.A. Analyzing Barriers to Innovation Management Implementation in Sustainable Tourism Using DEMATEL Method. World 2024, 5, 1004–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.-C.; Chen, P.-Y. Analysis of Critical Factors for Social Games Based on Extended Technology Acceptance Model: A DEMA℡ Approach. Behav. Inf. Technol. 2018, 37, 774–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Zhen, L.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X. Blockchain Implementation for Circular Supply Chain Management: Evaluating Critical Success Factors. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2022, 102, 451–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrysikopoulos, S.K.; Chountalas, P.T.; Georgakellos, D.A.; Lagodimos, A.G. Green Certificates Research: Bibliometric Assessment of Current State and Future Directions. Sustainability 2024, 16, 1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrysikopoulos, S.K.; Chountalas, P.T.; Georgakellos, D.A.; Lagodimos, A.G. Decarbonization in the Oil and Gas Sector: The Role of Power Purchase Agreements and Renewable Energy Certificates. Sustainability 2024, 16, 6339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).