A Practical Guide to Manual and Semi-Automated Neurosurgical Brain Lesion Segmentation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics
2.2. Hardware
2.3. Software
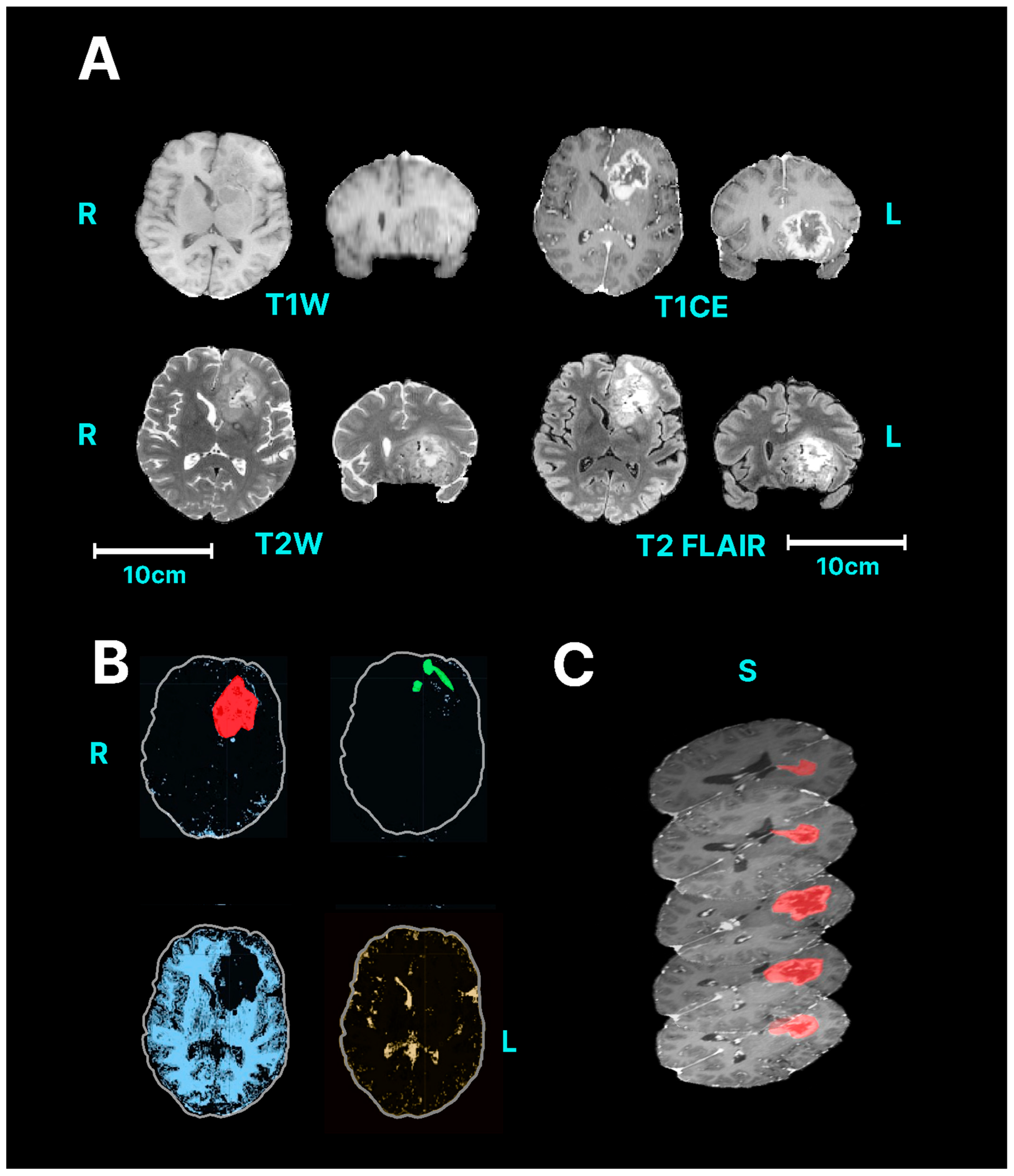
2.4. Image Acquisition
2.5. Training
2.6. Segmentation
2.7. Methods of Quality Control
2.7.1. Expertly Defined Segmentations and the Imaging Ground Truth
2.7.2. Error Metrics
2.8. Post-Segmentation Processing and Radiomics
3. Results and Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pham, D.L.; Xu, C.; Prince, J.L. Current methods in medical image segmentation. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2000, 2, 315–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kauke, M.; Safi, A.F.; Stavrinou, P.; Krischek, B.; Goldbrunner, R.; Timmer, M. Does Meningioma Volume Correlate With Clinical Disease Manifestation Irrespective of Histopathologic Tumor Grade? J. Craniofac. Surg. 2019, 30, e799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helland, R.H.; Ferles, A.; Pedersen, A.; Kommers, I.; Ardon, H.; Barkhof, F.; Bello, L.; Berger, M.S.; Dunås, T.; Nibali, M.C.; et al. Segmentation of glioblastomas in early post-operative multi-modal MRI with deep neural networks. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 18897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simi, V.R.; Joseph, J. Segmentation of Glioblastoma Multiforme from MR Images—A comprehensive review. Egypt. J. Radiol. Nucl. Med. 2015, 46, 1105–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Li, M.; Liu, J.; Wang, F.; Weng, Q.; Wang, X.; Cao, D. Machine learning-based radiomics analysis in predicting the meningioma grade using multiparametric MRI. Eur. J. Radiol. 2020, 131, 109251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cepeda, S.; Pérez-Nuñez, A.; García-García, S.; García-Pérez, D.; Arrese, I.; Jiménez-Roldán, L.; García-Galindo, M.; González, P.; Velasco-Casares, M.; Zamora, T.; et al. Predicting Short-Term Survival after Gross Total or Near Total Resection in Glioblastomas by Machine Learning-Based Radiomic Analysis of Preoperative MRI. Cancers 2021, 13, 5047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pemberton, H.G.; Wu, J.; Kommers, I.; Müller, D.M.J.; Hu, Y.; Goodkin, O.; Vos, S.B.; Bisdas, S.; Robe, P.A.; Ardon, H.; et al. Multi-class glioma segmentation on real-world data with missing MRI sequences: Comparison of three deep learning algorithms. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 18911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trimpl, M.J.; Primakov, S.; Lambin, P.; Stride, E.P.J.; Vallis, K.A.; Gooding, M.J. Beyond automatic medical image segmentation-the spectrum between fully manual and fully automatic delineation. Phys. Med. Biol. 2022, 67, 12TR01. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGrath, H.; Li, P.; Dorent, R.; Bradford, R.; Saeed, S.; Bisdas, S.; Ourselin, S.; Shapey, J.; Vercauteren, T. Manual segmentation versus semi-automated segmentation for quantifying vestibular schwannoma volume on MRI. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2020, 15, 1445–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacKeith, S.; Das, T.; Graves, M.; Patterson, A.; Donnelly, N.; Mannion, R.; Axon, P.; Tysome, J. A comparison of semi-automated volumetric vs linear measurement of small vestibular schwannomas. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2018, 275, 867–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaidyanathan, A.; van der Lubbe, M.F.J.A.; Leijenaar, R.T.H.; van Hoof, M.; Zerka, F.; Miraglio, B.; Primakov, S.; Postma, A.A.; Bruintjes, T.D.; Bilderbeek, M.A.L.; et al. Deep learning for the fully automated segmentation of the inner ear on MRI. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 2885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ann, C.N.; Luo, N.; Pandit, A.S. Letter: Image Segmentation in Neurosurgery: An Undervalued Skill Set? Neurosurgery 2022, 91, e31–e32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, H.; Witanto, J.N.; Pratama, K.; Lee, D.; Choi, K.S.; Choi, S.H.; Kim, K.; Kim, M.; Kim, J.W.; Kim, Y.H.; et al. Fully Automated MRI Segmentation and Volumetric Measurement of Intracranial Meningioma Using Deep Learning. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2023, 57, 871–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Street, J.S.; Pandit, A.S.; Toma, A.K. Predicting vasospasm risk using first presentation aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage volume: A semi-automated CT image segmentation analysis using ITK-SNAP. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0286485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziegelitz, D.; Hellström, P.; Björkman-Burtscher, I.M.; Agerskov, S.; Stevens-Jones, O.; Farahmand, D.; Tullberg, M. Evaluation of a fully automated method for ventricular volume segmentation before and after shunt surgery in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. World Neurosurg. 2023, 181, e303–e311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitfield, P.; Thomson, S.; Brown, J.; Kitchen, N.; Edlmann, E. Neurosurgery Curriculum 2021. Published 4 August 2021. Available online: https://www.gmc-uk.org/-/media/documents/neurosurgery-curriculum-2021---minor-changes-approved-feb22_pdf-89622738.pdf (accessed on 7 October 2023).
- Buffinton, C.M.; Baish, J.W.; Ebenstein, D.M. An Introductory Module in Medical Image Segmentation for BME Students. Biomed. Eng. Educ. 2023, 3, 95–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yushkevich, P.A.; Piven, J.; Hazlett, H.C.; Smith, R.G.; Ho, S.; Gee, J.C.; Gerig, G. User-guided 3D active contour segmentation of anatomical structures: Significantly improved efficiency and reliability. NeuroImage 2006, 31, 1116–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fedorov, A.; Beichel, R.; Kalpathy-Cramer, J.; Finet, J.; Fillion-Robin, J.-C.; Pujol, S.; Bauer, C.; Jennings, D.; Fennessy, F.; Sonka, M.; et al. 3D Slicer as an image computing platform for the Quantitative Imaging Network. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2012, 30, 1323–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rorden, C.; Brett, M. Stereotaxic display of brain lesions. Behav. Neurol. 2000, 12, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The MathWorks Inc. MATLAB, Version: 9.13.0 (R2022b); Version: 9.13.0 (R2022b); The MathWorks Inc.: Natick, MA, USA, 2022. Available online: https://www.mathworks.com (accessed on 8 November 2023).
- Baid, U.; Ghodasara, S.; Mohan, S.; Bilello, M.; Calabrese, E.; Colak, E.; Farahani, K.; Kalpathy-Cramer, J.; Kitamura, F.C.; Pati, S.; et al. The RSNA-ASNR-MICCAI BraTS 2021 Benchmark on Brain Tumor Segmentation and Radiogenomic Classification. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2107.02314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menze, B.H.; Jakab, A.; Bauer, S.; Kalpathy-Cramer, J.; Farahani, K.; Kirby, J.; Burren, Y.; Porz, N.; Slotboom, J.; Wiest, R.; et al. The Multimodal Brain Tumor Image Segmentation Benchmark (BRATS). IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2015, 34, 1993–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakas, S.; Akbari, H.; Sotiras, A.; Bilello, M.; Rozycki, M.; Kirby, J.S.; Freymann, J.B.; Farahani, K.; Davatzikos, C. Advancing The Cancer Genome Atlas glioma MRI collections with expert segmentation labels and radiomic features. Sci. Data 2017, 4, 170117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakas, S.; Akbari, H.; Sotiras, A.; Bilello, M.; Rozycki, M.; Kirby, J.; Freymann, J.; Farahani, K.; Davatzikos, C. Segmentation Labels for the Pre-Operative Scans of the TCGA-GBM Collection; National Institutes of Health: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakas, S.; Akbari, H.; Sotiras, A.; Bilello, M.; Rozycki, M.; Kirby, J.; Freymann, J.; Farahani, K.; Davatzikos, C. Segmentation Labels for the Pre-Operative Scans of the TCGA-LGG Collection; National Institutes of Health: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakas, S.; Reyes, M.; Jakab, A.; Bauer, S.; Rempfler, M.; Crimi, A.; Shinohara, R.T.; Berger, C.; Ha, S.M.; Rozycki, M.; et al. Identifying the Best Machine Learning Algorithms for Brain Tumor Segmentation, Progression Assessment, and Overall Survival Prediction in the BRATS Challenge. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1811.02629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.-H.; Lee, H.; Choi, K.S.; Nam, J.G.; Park, C.-K.; Park, S.-H.; Chung, J.W.; Choi, S.H. Validation of MRI-Based Models to Predict MGMT Promoter Methylation in Gliomas: BraTS 2021 Radiogenomics Challenge. Cancers 2022, 14, 4827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsson, W.; Aspelin, P.; Bergquist, M.; Hillergård, K.; Jacobsson, B.; Lindsköld, L.; Wallberg, J.; Lundberg, N. The effects of PACS on radiographer’s work practice. Radiography 2007, 13, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Morgan, P.S.; Ashburner, J.; Smith, J.; Rorden, C. The first step for neuroimaging data analysis: DICOM to NIfTI conversion. J. Neurosci. Methods 2016, 264, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atkinson, D. Geometry in Medical Imaging: DICOM and NIfTI Formats. Zenodo 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, J.; Box, G.; Galvin, A.; Brotchie, P.; Trost, N.; Sutherland, T. Magnetic resonance imaging of meningiomas: A pictorial review. Insights Imaging 2014, 5, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallinan, J.T.P.D.; Hegde, A.N.; Lim, W.E.H. Dilemmas and diagnostic difficulties in meningioma. Clin. Radiol. 2013, 68, 837–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ginsberg, L.E. Radiology of meningiomas. J. Neurooncol. 1996, 29, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Lu, Y.; Xiong, J.; Wang, D.; She, D.; Kuai, X.; Geng, D.; Yin, B. Presurgical differentiation between malignant haemangiopericytoma and angiomatous meningioma by a radiomics approach based on texture analysis. J. Neuroradiol. 2019, 46, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saad, A.F.; Chaudhari, R.; Fischbein, N.J.; Wintermark, M. Intracranial Hemorrhage Imaging. Semin. Ultrasound CT MRI 2018, 39, 441–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Provenzale, J.M.; Hacein-Bey, L. CT evaluation of subarachnoid hemorrhage: A practical review for the radiologist interpreting emergency room studies. Emerg. Radiol. 2009, 16, 441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abd-Elghany, A.A.; Naji, A.A.; Alonazi, B.; Aldosary, H.; Alsufayan, M.A.; Alnasser, M.; Mohammad, E.A.; Mahmoud, M.Z. Radiological characteristics of glioblastoma multiforme using CT and MRI examination. J. Radiat. Res. Appl. Sci. 2019, 12, 289–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, G.; Alexander, G.S.; Bakas, S.; Nikam, R.; Talekar, K.; Palmer, J.D.; Shi, W. Advanced magnetic resonance imaging in glioblastoma: A review. Chin. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 6, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fournel, J.; Bartoli, A.; Bendahan, D.; Guye, M.; Bernard, M.; Rauseo, E.; Khanji, M.Y.; Petersen, S.E.; Jacquier, A.; Ghattas, B. Medical image segmentation automatic quality control: A multi-dimensional approach. Med. Image Anal. 2021, 74, 102213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monereo-Sánchez, J.; de Jong, J.J.; Drenthen, G.S.; Beran, M.; Backes, W.H.; Stehouwer, C.D.; Schram, M.T.; Linden, D.E.; Jansen, J.F. Quality control strategies for brain MRI segmentation and parcellation: Practical approaches and recommendations—Insights from the Maastricht study. NeuroImage 2021, 237, 118174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lebovitz, S.; Levina, N.; Lifshitz-Assaf, H. Is AI Ground Truth Really True? The Dangers of Training and Evaluating AI Tools Based on Experts’ Know-What. MIS Q. 2021, 45, 1501–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eelbode, T.; Bertels, J.; Berman, M.; Vandermeulen, D.; Maes, F.; Bisschops, R.; Blaschko, M.B. Optimization for Medical Image Segmentation: Theory and Practice When Evaluating With Dice Score or Jaccard Index. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2020, 39, 3679–3690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCague, C.; Ramlee, S.; Reinius, M.; Selby, I.; Hulse, D.; Piyatissa, P.; Bura, V.; Crispin-Ortuzar, M.; Sala, E.; Woitek, R. Introduction to radiomics for a clinical audience. Clin. Radiol. 2023, 78, 83–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yu, J.; Lv, X.; Ju, X.; Shi, Z.; Chen, L.; Chen, Z. Sparse Representation-Based Radiomics for the Diagnosis of Brain Tumors. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2018, 37, 893–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Ou, X.; Wang, J.; Guo, W.; Ma, X. Radiomics-Based Machine Learning in Differentiation Between Glioblastoma and Metastatic Brain Tumors. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razek, A.A.K.A.; Alksas, A.; Shehata, M.; AbdelKhalek, A.; Baky, K.A.; El-Baz, A.; Helmy, E. Clinical applications of artificial intelligence and radiomics in neuro-oncology imaging. Insights Imaging 2021, 12, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, S.; Wiest, R.; Nolte, L.P.; Reyes, M. A survey of MRI-based medical image analysis for brain tumor studies. Phys. Med. Biol. 2013, 58, R97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaus, M.R.; Warfield, S.K.; Nabavi, A.; Black, P.M.; Jolesz, F.A.; Kikinis, R. Automated Segmentation of MR Images of Brain Tumors. Radiology 2001, 218, 586–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilke, M.; de Haan, B.; Juenger, H.; Karnath, H.-O. Manual, semi-automated, and automated delineation of chronic brain lesions: A comparison of methods. NeuroImage 2011, 56, 2038–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laukamp, K.R.; Pennig, L.; Thiele, F.; Reimer, R.; Görtz, L.; Shakirin, G.; Zopfs, D.; Timmer, M.; Perkuhn, M.; Borggrefe, J. Automated Meningioma Segmentation in Multiparametric MRI. Clin. Neuroradiol. 2021, 31, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LaBella, D.; Adewole, M.; Alonso-Basanta, M.; Altes, T.; Anwar, S.M.; Baid, U.; Bergquist, T.; Bhalerao, R.; Chen, S.; Chung, V.; et al. The ASNR-MICCAI Brain Tumor Segmentation (BraTS) Challenge 2023: Intracranial Meningioma. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2305.07642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaBella, D.; Khanna, O.; McBurney-Lin, S.; Mclean, R.; Nedelec, P.; Rashid, A.S.; Tahon, N.H.; Altes, T.; Baid, U.; Bhalerao, R.; et al. A multi-institutional meningioma MRI dataset for automated multi-sequence image segmentation. Sci. Data 2024, 11, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barros, R.S.; van der Steen, W.E.; Boers, A.M.; Zijlstra, I.; Berg, R.v.D.; El Youssoufi, W.; Urwald, A.; Verbaan, D.; Vandertop, P.; Majoie, C.; et al. Automated segmentation of subarachnoid hemorrhages with convolutional neural networks. Inform. Med. Unlocked 2020, 19, 100321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akkus, Z.; Galimzianova, A.; Hoogi, A.; Rubin, D.L.; Erickson, B.J. Deep Learning for Brain MRI Segmentation: State of the Art and Future Directions. J. Digit. Imaging 2017, 30, 449–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Directive 95/46/EC (General. Data Protection Regulation). Regulation EU (2016) 2016/679 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 27 April 2016 on the Protection of Natural Persons with Regard to the Processing of Personal. Data and on the Free Movement of Such. Data, and Repealing. Off. J. Eur. Union 2016, 119. [Google Scholar]
- Avrin, D. HIPAA privacy and DICOM anonymization for research. Acad. Radiol. 2008, 15, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lotan, E.; Tschider, C.; Sodickson, D.K.; Caplan, A.L.; Bruno, M.; Zhang, B.; Lui, Y.W. Medical Imaging and Privacy in the Era of Artificial Intelligence: Myth, Fallacy, and the Future. J. Am. Coll. Radiol. JACR 2020, 17, 1159–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Lyu, J.; Wang, R.; Wen, Q.; Zhao, L.; Chen, W.; Bi, S.; Meng, J.; Mao, K.; Xiao, Y.; et al. A digital mask to safeguard patient privacy. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 1883–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Planells, H.; Parmar, V.; Marcus, H.J.; Pandit, A.S. From theory to practice: What is the potential of artificial intelligence in the future of neurosurgery? Expert. Rev. Neurother. 2023, 23, 1041–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Lesion | Sequences for Segmentations | Radiological Features |
|---|---|---|
| Meningioma | T1w T1w + contrast T2w | Meningiomas have isointensity to slight hypointensity with T1 weighting. With T2-weighted sequences, meningiomas have isointensity to slight hyperintensity [32]. Two basic morphologies of meningioma include en plaque with a sheet-like dural extension and globose with a broad dural attachment [33]. The thick extended dura (commonly referred to as a dural tail) tends to extend away from the meningioma, which can be easily missed [34]. Bone changes may be visible, such as hyperostosis, osteolysis, enlargement of the skull base foramina and meningioma calcification [35]. |
| Subarachnoid Haemorrhage (SAH) | CT non-contrast | Acute haemorrhage will be present with 15–25 Hounsfield Units (HU) of greater density than normal grey and white matter on a CT scan [36]. Anatomically, SAH is typically found present in the interpeduncular cistern, the Sylvian fissure, the occipital horns of the lateral ventricles and the deep sulci on each side of the medial longitudinal fissure [37]. |
| Glioblastoma (GBM) | T1w T1w + contrast T2w T2 FLAIR/TIRM | GBMs are generally hyperintense on T2-weighted images but are hypo- or isointense on T1-weighted images [38]. GBM often have enhancing and non-enhancing components. Necrosis is typically visible as a low signal intensity (SI) on T1-enhanced MRI and located at the centre of the lesion [39]. Cystic components of a GBM are typically T2W hyperintense and T1 hypointense, with a well-defined thin wall. There can also an area of oedema surrounding the tumour that is visible in T2 FLAIR scans [38]. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jain, R.; Lee, F.; Luo, N.; Hyare, H.; Pandit, A.S. A Practical Guide to Manual and Semi-Automated Neurosurgical Brain Lesion Segmentation. NeuroSci 2024, 5, 265-275. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurosci5030021
Jain R, Lee F, Luo N, Hyare H, Pandit AS. A Practical Guide to Manual and Semi-Automated Neurosurgical Brain Lesion Segmentation. NeuroSci. 2024; 5(3):265-275. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurosci5030021
Chicago/Turabian StyleJain, Raunak, Faith Lee, Nianhe Luo, Harpreet Hyare, and Anand S. Pandit. 2024. "A Practical Guide to Manual and Semi-Automated Neurosurgical Brain Lesion Segmentation" NeuroSci 5, no. 3: 265-275. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurosci5030021
APA StyleJain, R., Lee, F., Luo, N., Hyare, H., & Pandit, A. S. (2024). A Practical Guide to Manual and Semi-Automated Neurosurgical Brain Lesion Segmentation. NeuroSci, 5(3), 265-275. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurosci5030021






