Novel, Simple, and Environmentally Friendly Methodology for the Determination of Urinary Iodide by Colorimetry Based on Silver Nanoplates
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Instruments
2.2. Reagents and Solutions
2.3. Sandell–Kolthoff Determination
2.4. Standards and Sample Preparation
2.5. Synthesis and Characterization of AgTNPs
2.6. Characterization of AgTNP Behavior with Iodide Standards
2.7. Urine Interferent Assays
2.8. SPE Sample Preparation Optimization
2.9. Statistics
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of AgTNPs After Their Modification by Iodide
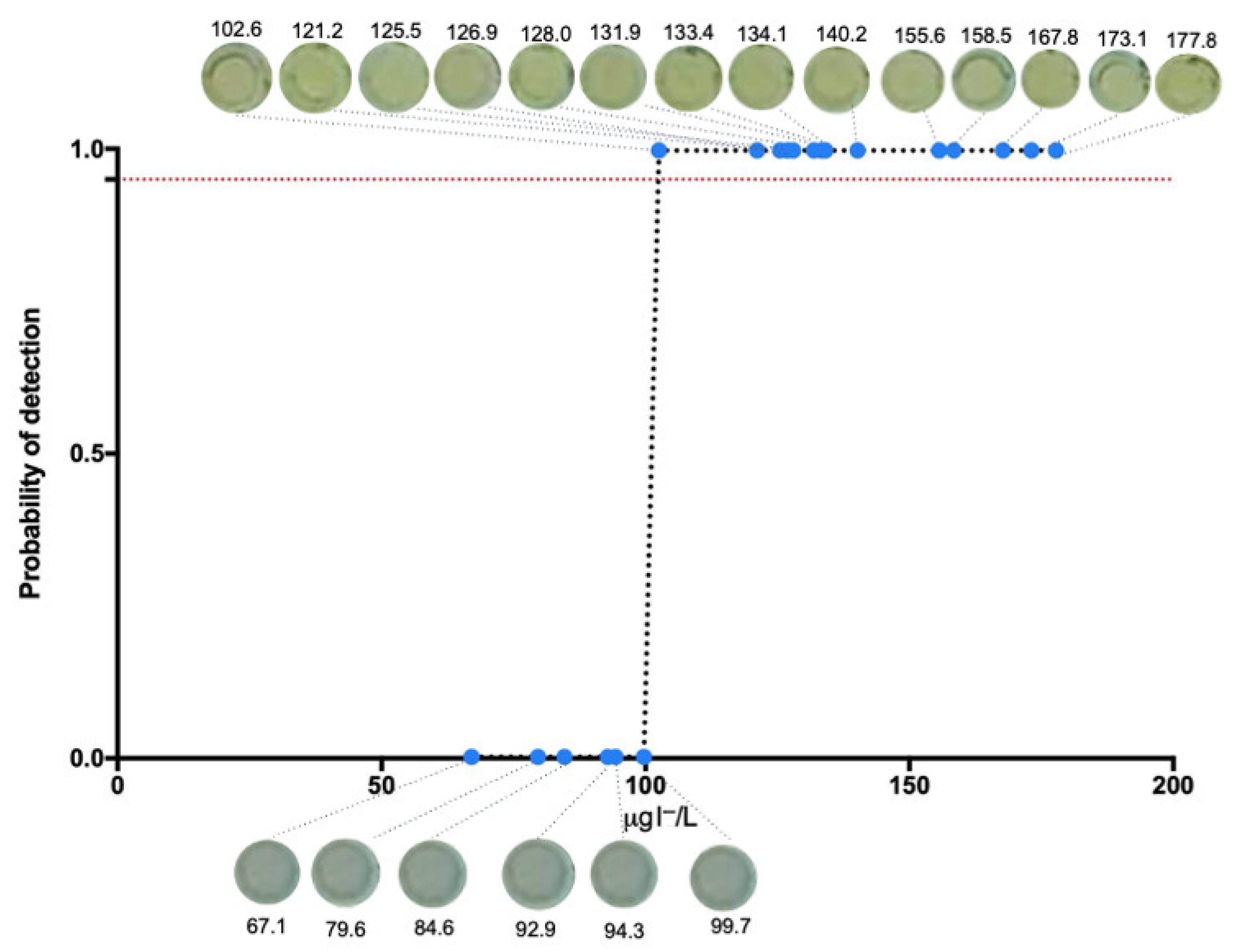
3.2. Limit of Detection of the Colorimetric Methodology
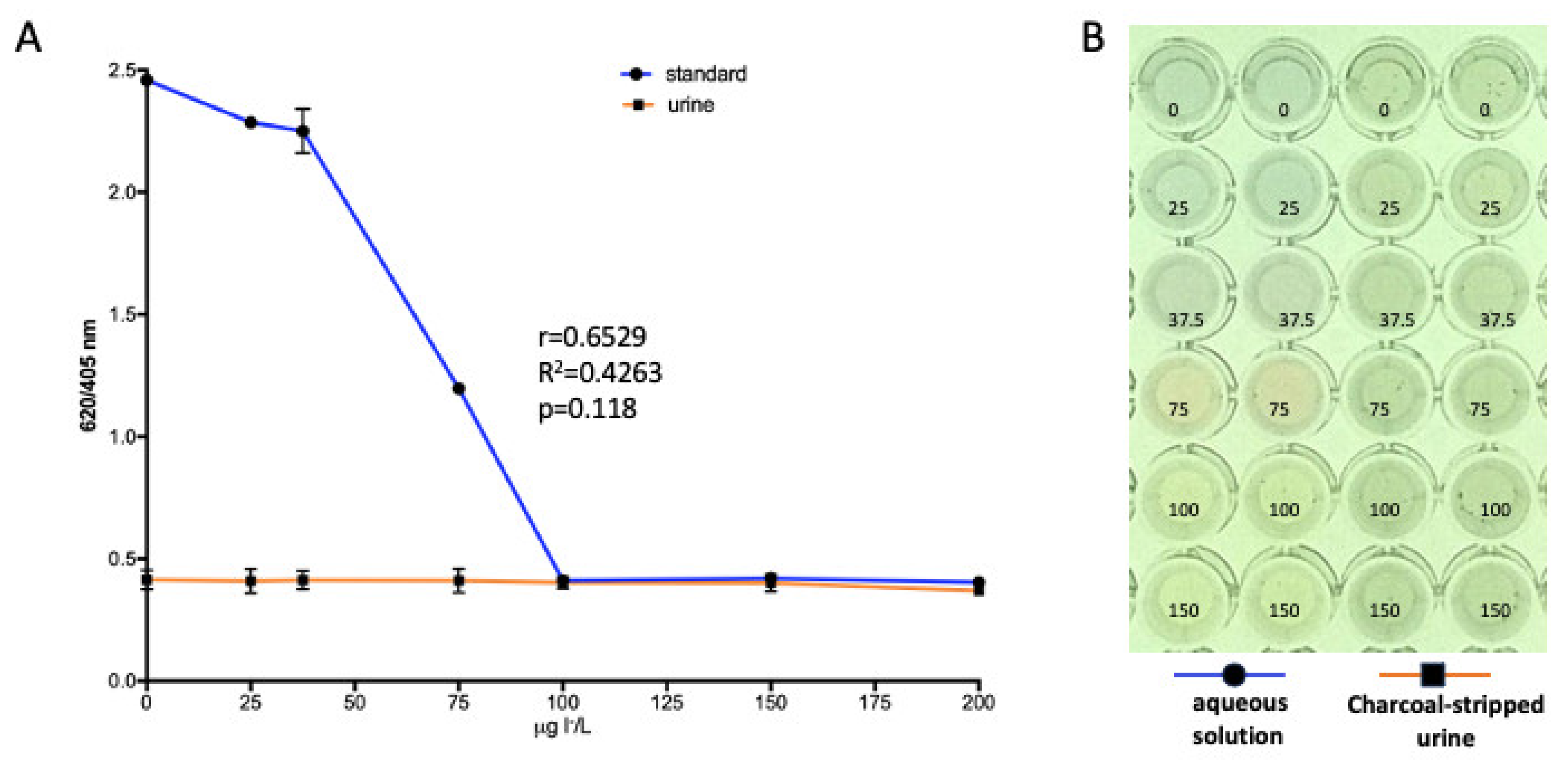
3.3. Effect of Charcoal-Stripped Urine Spikes with Iodide on AgTNPs
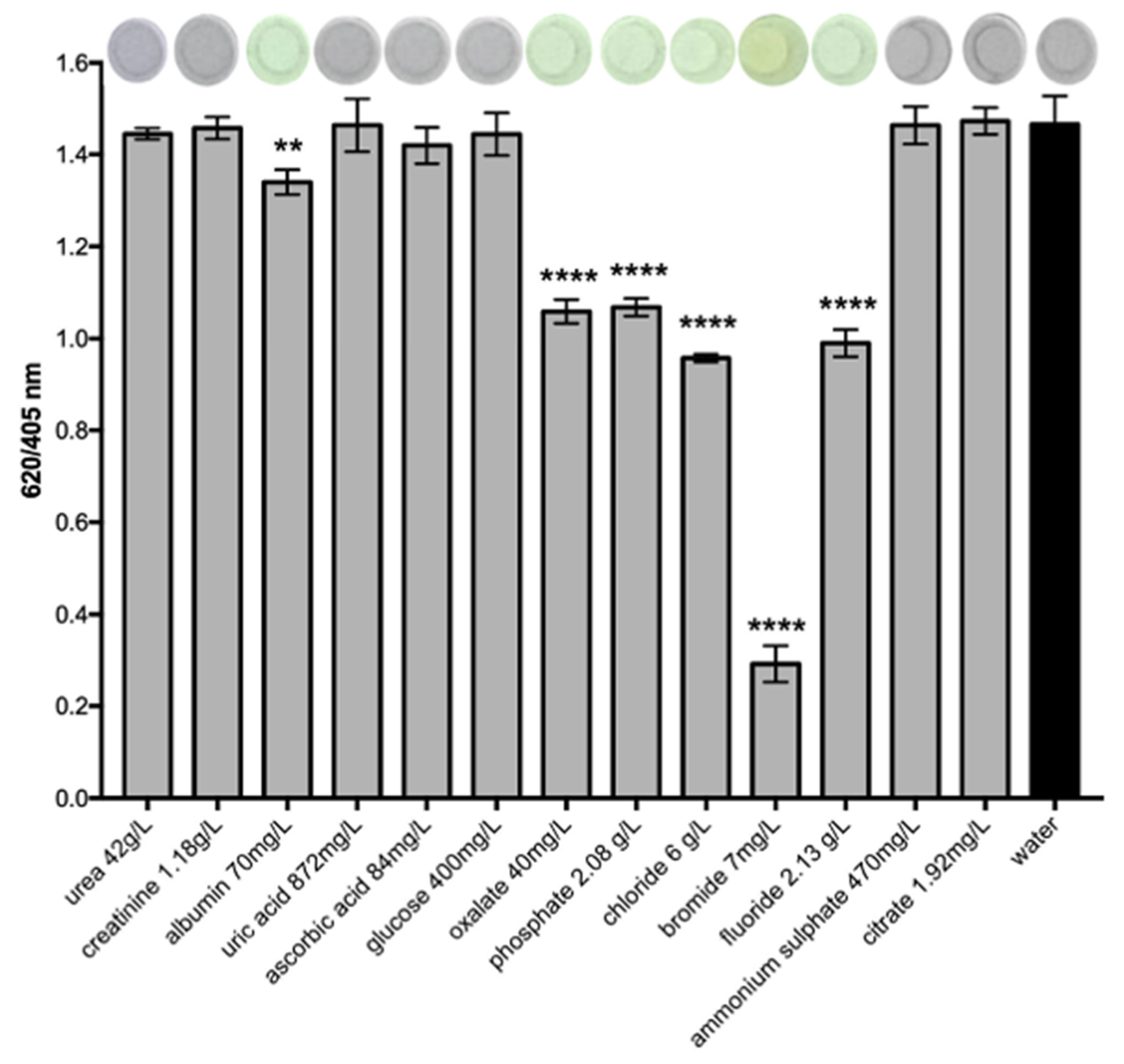
3.4. Effect of Common Urine Interferent Molecules and Ions on AgTNP SPR Band
3.5. Optimization of SPE Protocol for the Recovery of Iodide from Urine
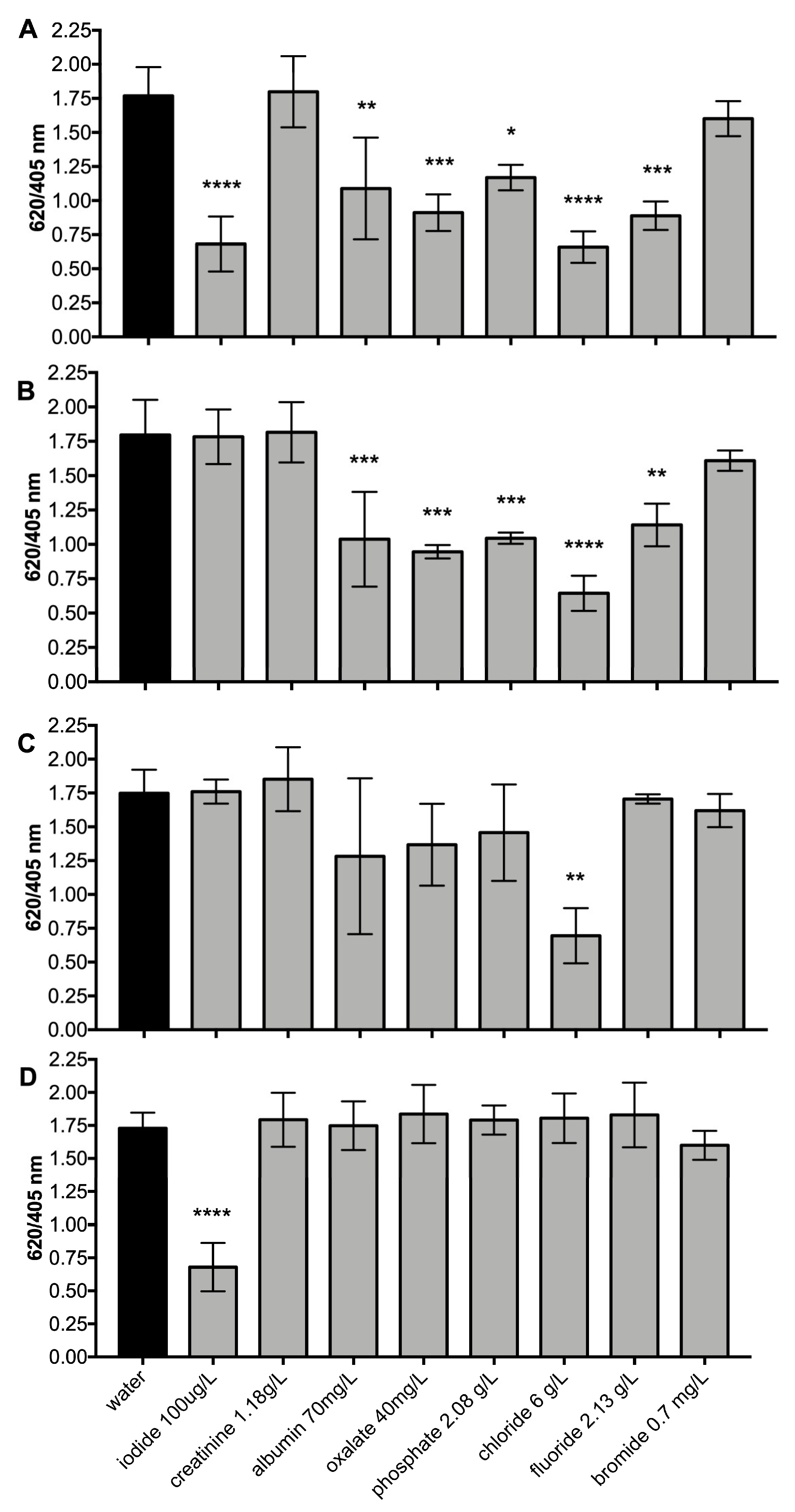
3.6. Efficiency of the SPE Protocol for the Elimination of Common Urine Interferences
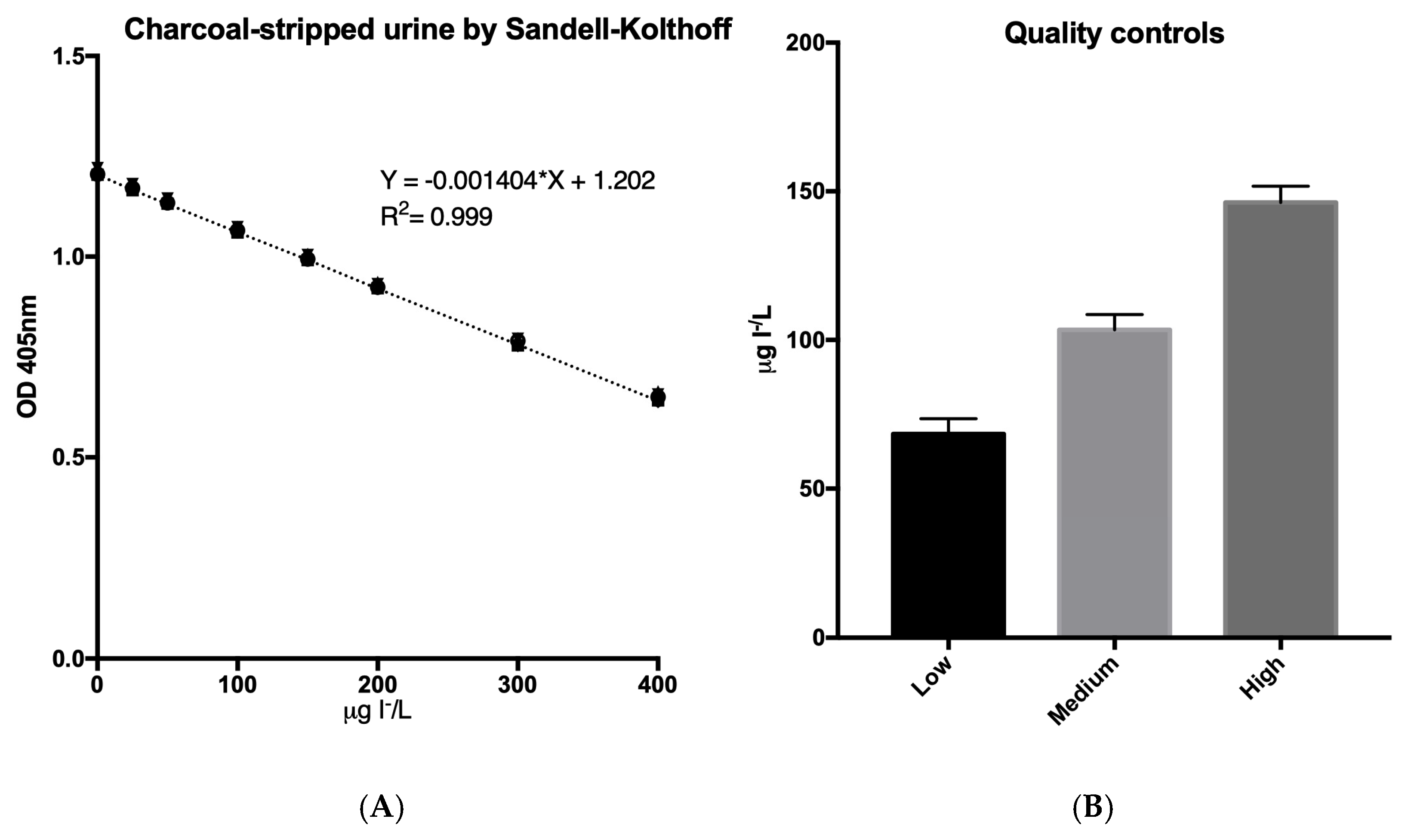
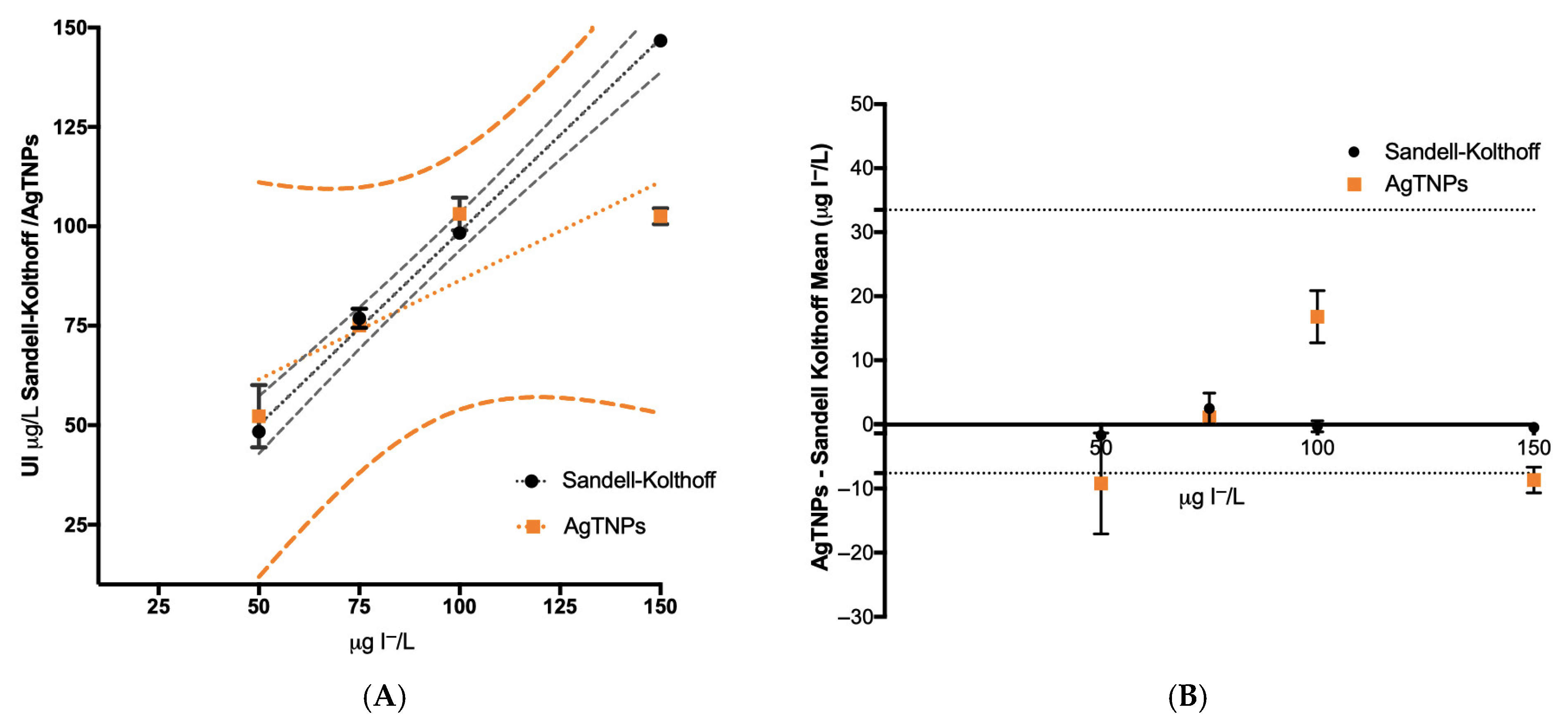
3.7. Comparison of Urine Iodide Determination Using Sandell–Kolthoff and AgTNPs After the SPE Protocol for the Elimination of Urine Interferences
3.8. Qualitative Urine Iodide Determination Using AgTNPs After SPE Protocol
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ID | Iodine Deficiency |
| IDDs | Iodine Deficiency Disorders |
| UI | Urinary Iodine |
| AgTNPs | Silver Triangular Nanoplates |
| SPE | Solid-Phase Extraction |
| TEM | Transmission Electron Microscopy |
| UV–vis | UV–vis spectroscopy |
| ζ potential | Zeta Potential |
| ICP-MS | Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry |
| AgNPs | Silver Nanoparticles |
| SPR | Surface Plasmon Resonance |
| LSPR | Localized Surface Plasmon Resonance |
| DoE | Design of Experiment |
| Urine QC | Urine Quality Control |
| LOD | Limit of detection |
References
- Hetzel, B. Iodine Deficiency Disorders (IDD) and Their Eradication. Lancet 1983, 322, 1126–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertinato, J.; Qiao, C.; L’Abbé, M.R. Iodine Status of Canadian Children, Adolescents, and Women of Childbearing Age. J. Nutr. 2021, 151, 3710–3717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pretell, E.A.; Pearce, E.N.; Moreno, S.A.; Dary, O.; Kupka, R.; Gizak, M.; Gorstein, J.; Grajeda, R.; Zimmermann, M.B. Elimination of Iodine Deficiency Disorders from the Americas: A Public Health Triumph. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2017, 5, 412–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Council for Control Of Iodine Deficiency Disorders; UNICEF; World Health Organization. Assessment of Iodine Deficiency Disorders and Monitoring Their Elimination: A Guide for Programme Managers, 3rd ed.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Delange, F. Optimal Iodine Nutrition During pregnancy, lactation and the neonatal period. Int. J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2004, 2, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Jooste, P.L.; Strydom, E. Methods for Determination of Iodine in Urine and Salt. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 24, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allain, P.; Mauras, Y.; Dougé, C.; Jaunault, L.; Delaporte, T.; Beaugrand, C. Determination of Iodine and Bromine in Plasma and Urine by Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry. Analyst 1990, 115, 813–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haldimann, M.; Zimmerli, B.; Als, C.; Gerber, H. Direct Determination of Urinary Iodine by Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry Using Isotope Dilution with Iodine-129. Clin. Chem. 1998, 44, 817–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macours, P.; Aubry, J.C.; Hauquier, B.; Boeynaems, J.M.; Goldman, S.; Moreno-Reyes, R. Determination of Urinary Iodine by Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2008, 22, 162–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandell, E.B.; Kolthoff, I.M. Micro Determination of Iodine by a Catalytic Method. Mikrochim. Acta 1937, 1, 9–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pino, S.; Fang, S.L.; Braverman, L.E. Ammonium Persulfate: A New and Safe Method for Measuring Urinary Iodine by Ammonium Persulfate Oxidation. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2009, 106, S22–S27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunn, J.T.; Crutchfield, H.E.; Gutekunst, R.; Dunn, A.D. Two Simple Methods for Measuring Iodine in Urine. Thyroid. Off. J. Am. Thyroid. Assoc. 1993, 3, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Tan, H.-L.; Ge, H. Global, Regional, and National Burden of Iodine Deficiency in Reproductive Women from 1990 to 2019, and Projections to 2035: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study in 2019. Int. J. Womens Health 2025, 17, 1863–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peeling, R.W.; Holmes, K.K.; Mabey, D.; Ronald, A. Rapid Tests for Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs): The Way Forward. Sex. Transm. Infect. 2006, 82 (Suppl. S5), v1–v6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rick, J.; Tsai, M.C.; Hwang, B. Biosensors Incorporating Bimetallic Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 2015, 6, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayanthi, V.S.P.K.S.; Das, A.B.; Saxena, U. Recent Advances in Biosensor Development for the Detection of Cancer Biomarkers. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 91, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Hagen, J.A.; Papautsky, I. Point-of-Care Colorimetric Detection with a Smartphone. Lab A Chip 2012, 12, 4240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Du, Y.; Dong, S. DNA Based Gold Nanoparticles Colorimetric Sensors for Sensitive and Selective Detection of Ag(I) Ions. Anal. Chim. Acta 2009, 644, 78–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, J.; Sang, Y.; Huang, C.Z. Visual Colorimetric Detection of Berberine Hydrochloride with Silver Nanoparticles. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2008, 47, 860–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, M.; Cao, Y.; Wang, H.; Pan, Y.; Lee, B.; Huang, C. Time-Dependent Surface Plasmon Resonance Spectroscopy of Silver Nanoprisms in the Presence of Halide Ions. ChemPhysChem A Eur. J. Chem. Phys. Phys. Chem. 2010, 11, 1742–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao , C.; Lu , Z.; Liu , Y.; Zhang, Q.; Chi, M.; Cheng, Q.; Yin, Y. Highly Stable Silver Nanoplates for Surface Plasmon Resonance Biosensing. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2012, 51, 5629–5633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.H.; Ling, J.; Peng, J.; Cao, Q.E.; Ding, Z.T.; Bian, L.C. A Colorimetric Method for Highly Sensitive and Accurate Detection of Iodide by Finding the Critical Color in a Color Change Process Using Silver Triangular Nanoplates. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 798, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maruthupandi, M.; Chandhru, M.; Rani, S.K.; Vasimalai, N. Highly Selective Detection of Iodide in Biological, Food, and Environmental Samples Using Polymer-Capped Silver Nanoparticles: Preparation of a Paper-Based Testing Kit for On-Site Monitoring. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 11372–11379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niaz, A.; Bibi, A.; Huma, N.; Zaman, M.I.; Khan, M.; Rahim, A. Highly Selective and Ecofriendly Colorimetric Method for the Detection of Iodide Using Green Tea Synthesized Silver Nanoparticles. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 249, 1047–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaghazchi, T.; Kolur, N.A.; Sabet, R.H. Recovery of Iodine with Activated Carbon from Dilute Aqueous Solutions. Afinidad 2009, 66, 338–343. [Google Scholar]
- Ohashi, T.; Yamaki, M.; Pandav, C.S.; Karmarkar, M.G.; Irie, M. Simple Microplate Method for Determination of Urinary Iodine. Clin. Chem. 2000, 46, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 Years of Image Analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarigul, N.; Korkmaz, F.; Kurultak, İ. A New Artificial Urine Protocol to Better Imitate Human Urine. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 20159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, E.N.; Curhan, G.C. Body Size and 24-Hour Urine Composition. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2006, 48, 905–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouatra, S.; Aziat, F.; Mandal, R.; Guo, A.C.; Wilson, M.R.; Knox, C.; Bjorndahl, T.C.; Krishnamurthy, R.; Saleem, F.; Liu, P.; et al. The Human Urine Metabolome. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuenca, R.E.; Pories, W.J.; Bray, J. Bromine Levels in Human Serum, Urine, Hair. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 1988, 16, 151–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.-Y.; Liu, D.; Zhong, C.-C.; Hu, Y.-H.; Zhao, F.; Guo, H.-L.; Chen, F. Rapid Determination of Urinary Oxalic Acid Concentration Aids in the Screening and Monitoring of Kidney Diseases: An LC-ESI-MS/MS Method That Does Not Require Complex Derivatization, Acidification Treatment, or Large-Volume Sample Consumption. Microchem. J. 2025, 210, 112909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torra, M.; Rodamilans, M.; Corbella, J. Serum and Urine Fluoride Concentration: Relationships to Age, Sex and Renal Function in a Non-Fluoridated Population. Sci. Total Environ. 1998, 220, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrido, B.C.; Gustavo; Gomes, S.; Barrabin, J.S.; Padilha, M.C.; Gualberto, M. Assessing Limits of Detection in Qualitative Methods: A Simple Implementation of Logistic Regression in a Web-Based R Shiny Application Environment and Its Potential in Toxicology and Doping Control. Drug Test. Anal. 2022, 15, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López, I.A.; Gómez, I. Halide Ion Effect in Shape Transformation from Silver Triangular Nanoprisms to Silver Nanodisks. Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 2012, 1371, imrc11-1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivieri, A.C. Practical Guidelines for Reporting Results in Single- and Multi-Component Analytical Calibration: A Tutorial. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 868, 10–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.C.; Yu, A.B. Silver Nanoplates: A Highly Sensitive Material toward Inorganic Anions. Langmuir 2008, 24, 4300–4309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basharzad, P.F.; Farhadi, K.; Forough, M.; Molaei, R. Silver Nanoparticles as a New Colorimetric Probe for Determination of Oxalic Acid in Urine. Sens. Lett. 2016, 14, 906–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravindran, A.; Singh, A.; Raichur, A.M.; Chandrasekaran, N.; Mukherjee, A. Studies on Interaction of Colloidal Ag Nanoparticles with Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA). Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2010, 76, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Variable 1 | Variable 2 | Variable 3 | Variable 4 | Response | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Run | A: Charcoal Solution Volume (μL) | B: Absorption Time (min) | C: Eluent pH | D: Eluent’s Equilibration Time (min) | Iodide Recovery (%) |
| 1 | 2750 | 36 | 9.5 | 180 | 89.41 |
| 2 | 2500 | 12 | 11.5 | 300 | 74.39 |
| 3 | 3000 | 60 | 11.5 | 60 | 93.51 |
| 4 | 3000 | 60 | 7.5 | 60 | 13.43 |
| 5 | 2750 | 2 | 9.5 | 180 | 90.98 |
| 6 | 2500 | 12 | 11.5 | 60 | 72.23 |
| 7 | 3000 | 12 | 11.5 | 60 | 95.31 |
| 8 | 3000 | 60 | 11.5 | 300 | 96.39 |
| 9 | 2750 | 36 | 9.5 | 180 | 93.21 |
| 10 | 2500 | 12 | 7.5 | 300 | 13.79 |
| 11 | 2500 | 60 | 11.5 | 300 | 72.59 |
| 12 | 3000 | 12 | 7.5 | 300 | 16.32 |
| 13 | 2750 | 70 | 9.5 | 180 | 88.46 |
| 14 | 2500 | 12 | 7.5 | 60 | 12.35 |
| 15 | 2750 | 36 | 9.5 | 350 | 59.24 |
| 16 | 3000 | 12 | 11.5 | 300 | 97.11 |
| 17 | 3104 | 36 | 9.5 | 180 | 92.82 |
| 18 | 2500 | 60 | 7.5 | 300 | 11.99 |
| 19 | 2750 | 36 | 6.67 | 180 | 1.17 |
| 20 | 2396 | 36 | 9.5 | 180 | 74.75 |
| 21 | 2500 | 60 | 11.5 | 60 | 70.78 |
| 22 | 2750 | 36 | 9.5 | 180 | 92.79 |
| 23 | 2500 | 60 | 7.5 | 60 | 10.55 |
| 24 | 2750 | 36 | 9.5 | 10 | 27.50 |
| 25 | 2750 | 36 | 12.33 | 180 | 95.31 |
| 26 | 3000 | 60 | 7.5 | 300 | 14.87 |
| 27 | 2750 | 36 | 9.5 | 180 | 92.80 |
| 28 | 3000 | 12 | 7.5 | 60 | 15.23 |
| Quality Controls After SPE Concentration (µg I−/L) | Intraday (n = 3) | Interday (n = 6) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD (µg I−/L) | CV (%) | Mean ± SD (µg I−/L) | CV (%) | |
| Low | 68.40 ± 3.10 | 4.5 | 68.39 ± 1.09 | 1.6 |
| Medium | 102.59 ± 3.10 | 3.0 | 103.45 ± 0.65 | 0.6 |
| High | 146.03 ± 4.67 | 3.2 | 146.25 ± 0.88 | 0.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ortiz, I.T.; Balod, M.; Antezana, P.E.; Ortiz, G.N.; Desimone, M.F.; Gamarra-Luques, C.; Altamirano, J.C.; Hapon, M.B. Novel, Simple, and Environmentally Friendly Methodology for the Determination of Urinary Iodide by Colorimetry Based on Silver Nanoplates. Sustain. Chem. 2025, 6, 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/suschem6030029
Ortiz IT, Balod M, Antezana PE, Ortiz GN, Desimone MF, Gamarra-Luques C, Altamirano JC, Hapon MB. Novel, Simple, and Environmentally Friendly Methodology for the Determination of Urinary Iodide by Colorimetry Based on Silver Nanoplates. Sustainable Chemistry. 2025; 6(3):29. https://doi.org/10.3390/suschem6030029
Chicago/Turabian StyleOrtiz, Irina Tamara, Maia Balod, Pablo Edmundo Antezana, Gisel Nadin Ortiz, Martin Federico Desimone, Carlos Gamarra-Luques, Jorgelina Cecilia Altamirano, and María Belén Hapon. 2025. "Novel, Simple, and Environmentally Friendly Methodology for the Determination of Urinary Iodide by Colorimetry Based on Silver Nanoplates" Sustainable Chemistry 6, no. 3: 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/suschem6030029
APA StyleOrtiz, I. T., Balod, M., Antezana, P. E., Ortiz, G. N., Desimone, M. F., Gamarra-Luques, C., Altamirano, J. C., & Hapon, M. B. (2025). Novel, Simple, and Environmentally Friendly Methodology for the Determination of Urinary Iodide by Colorimetry Based on Silver Nanoplates. Sustainable Chemistry, 6(3), 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/suschem6030029









