Macrocyclic Azopyrrole: Synthesis, Structure and Fluoride Recognition
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Apparatuses
2.2. Preparation of Compound 2
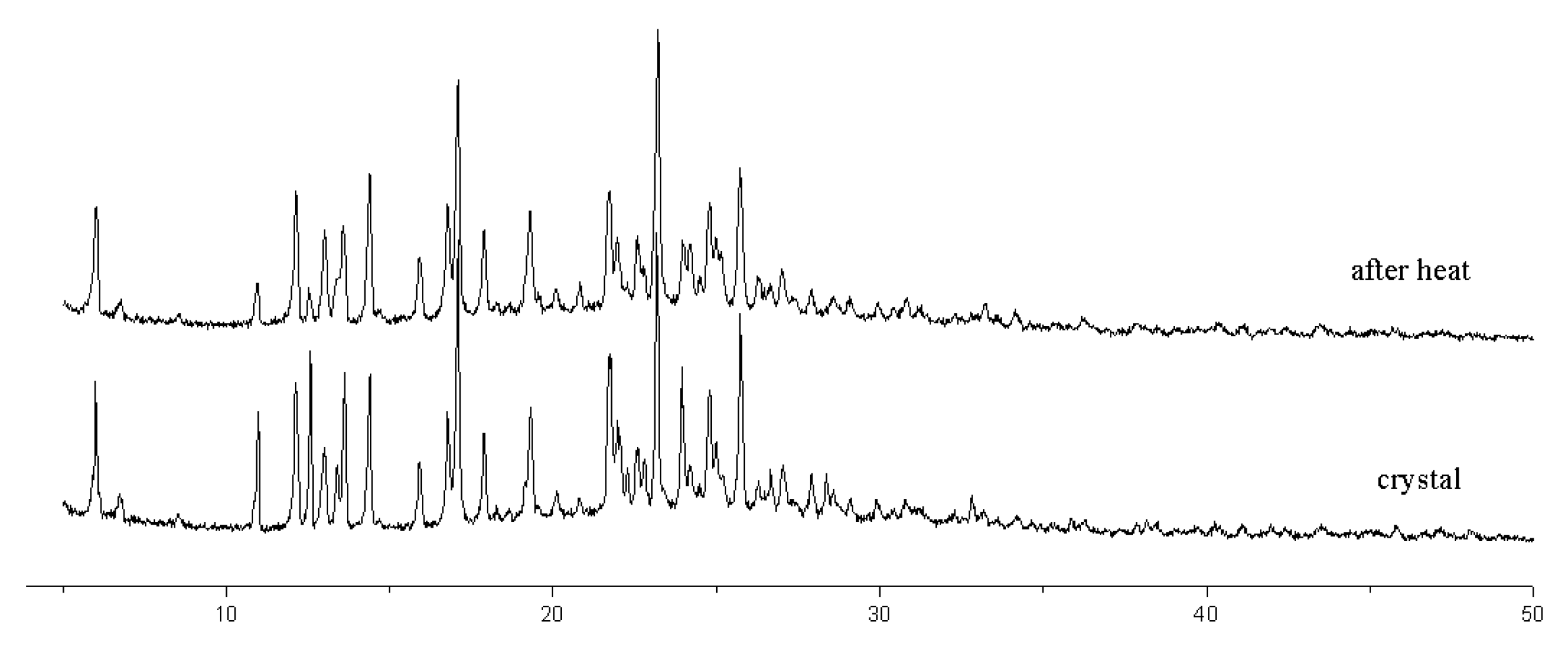
2.3. X-Ray Crystallography
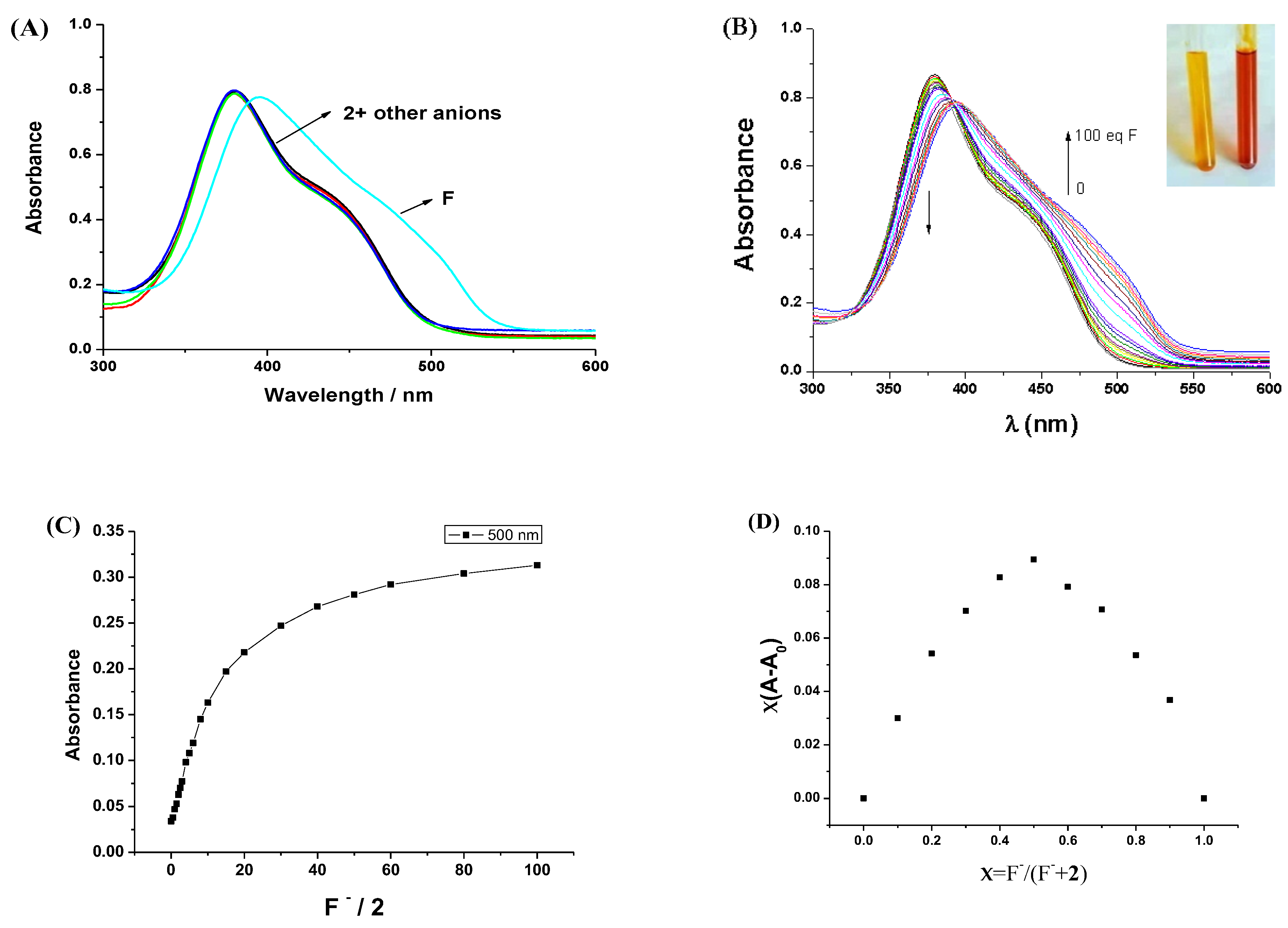
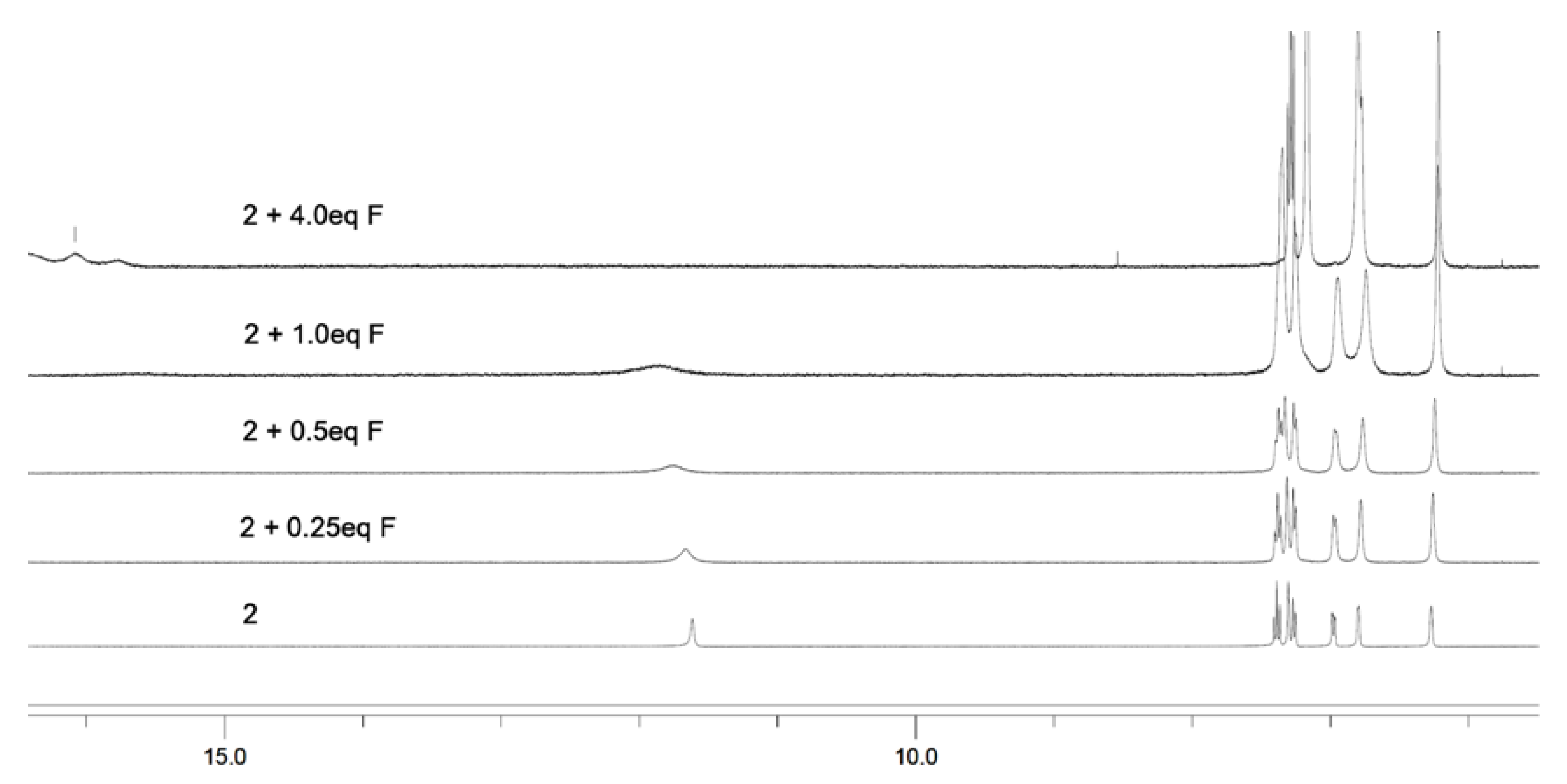
2.4. Titration Studies
3. Results
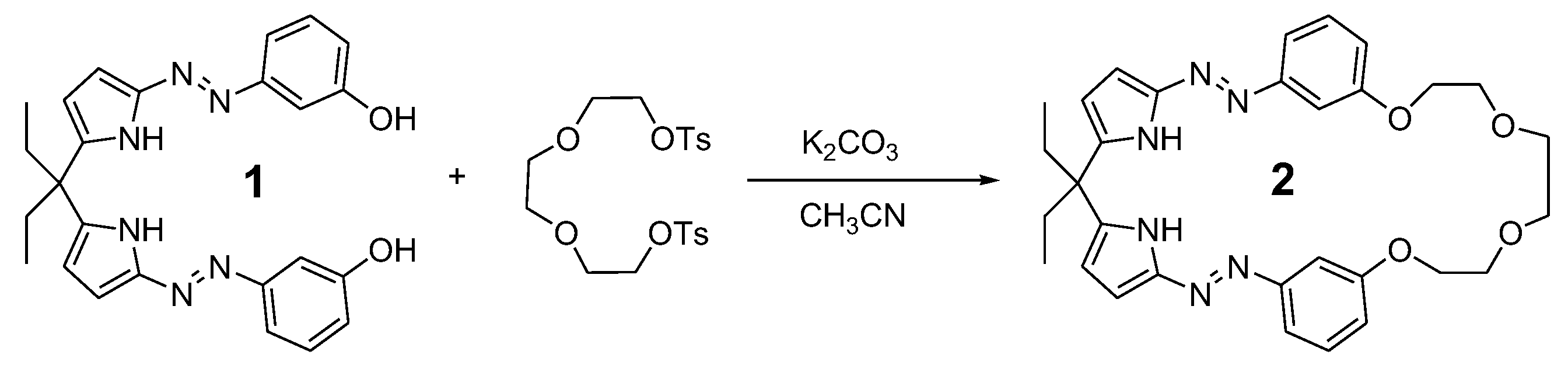
3.1. The Synthesis of Compound 2
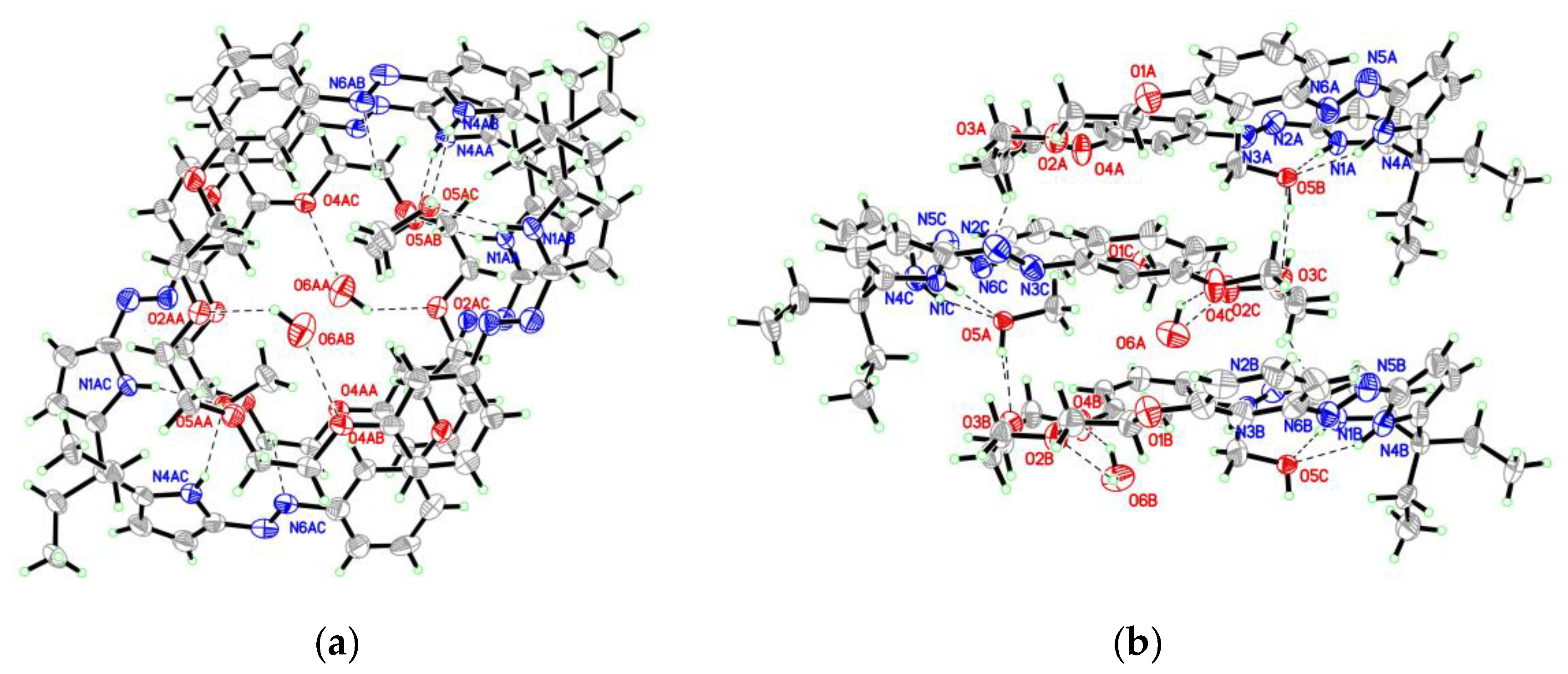
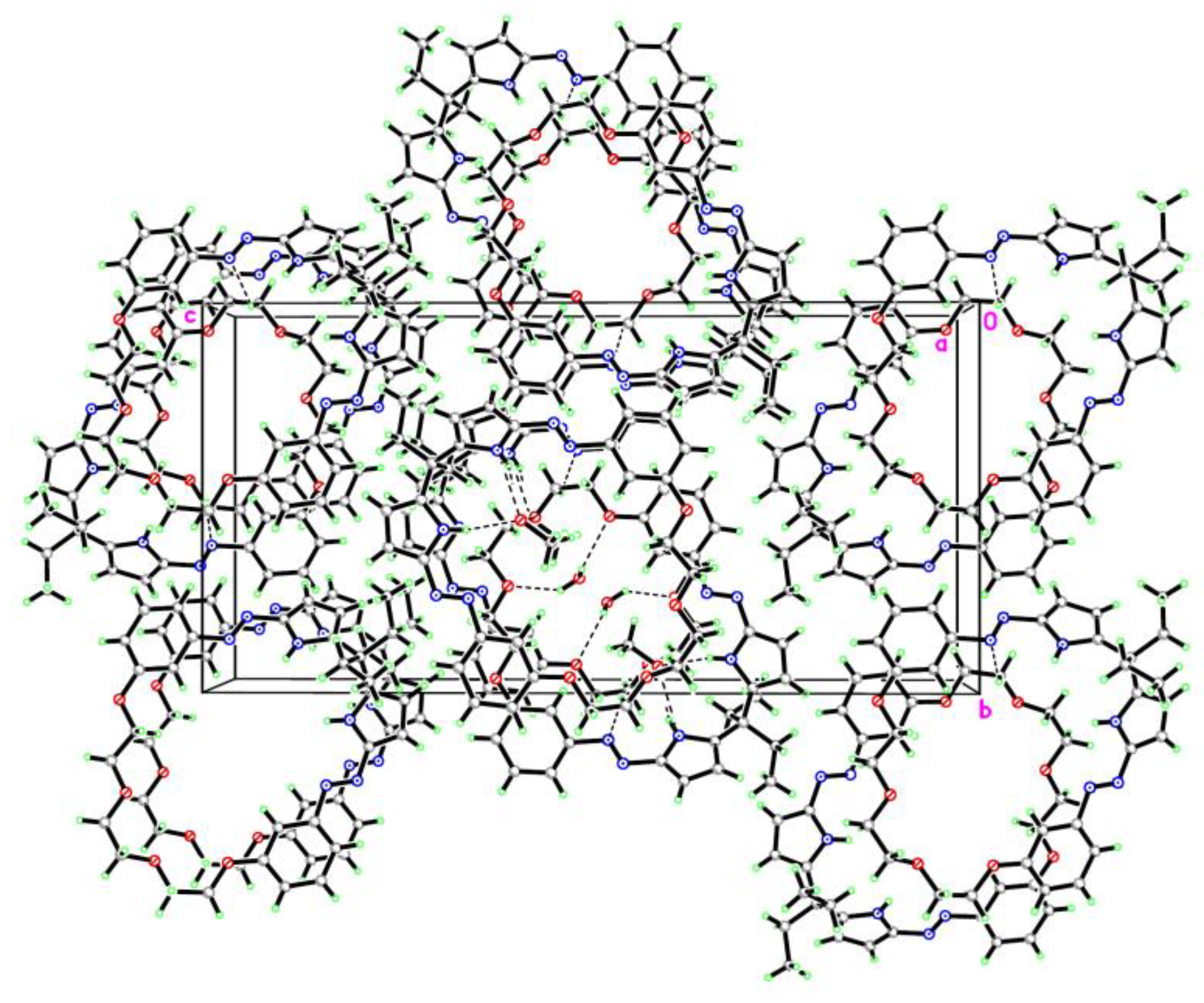
3.2. The Crystal Structure of Compound 2
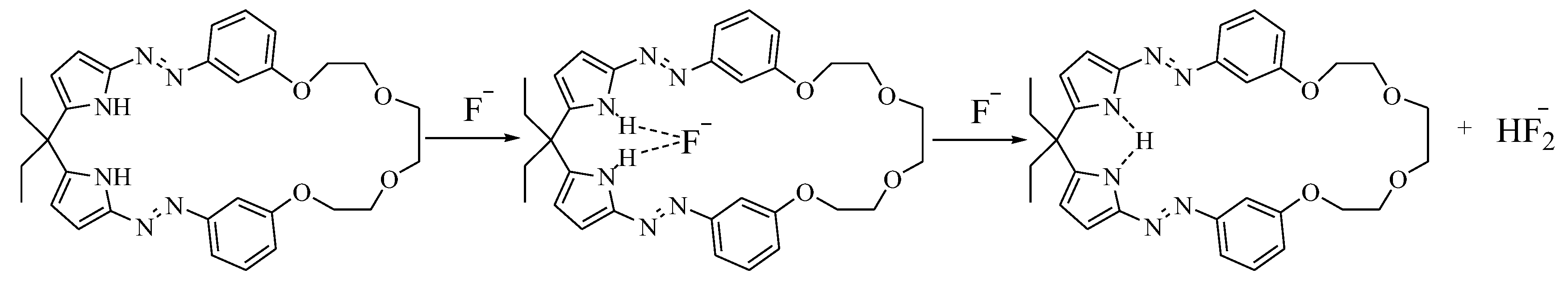
3.3. The Anions Recognition of Compound 2
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ali, Y.; Hamid, S.A.; Rashid, U. Biomedical Applications of Aromatic Azo Compounds. Mini-Rev. Med. Chem. 2018, 18, 1548–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Towns, A.D. Developments in azo disperse dyes derived from heterocyclic diazo components. Dyes Pigments 1999, 42, 3–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emanuele, L.; D’Auria, M. The Use of Heterocyclic Azo Dyes on Different Textile Materials: A Review. Organics 2024, 5, 277–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weston, C.E.; Richardson, R.D.; Haycock, P.R.; White, A.J.P.; Fuchter, M.J. Arylazopyrazoles: Azoheteroarene photoswitces offering quantitative isomerization and long thermal half-lives. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 11878–11881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calbo, J.; Weston, C.E.; White, A.J.P.; Rzepa, H.S.; Contreras-Garcia, J.; Fuchter, M.J. Tuning Azoheteroarene photoswitch performance through heteroaryl design. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 1261–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallardo-Rosas, D.; Guevara-Vela, J.M.; Rocha-Rinza, T.; Toscano, R.A.; Lopez-Cortes, J.G.; Ortega-Alfaro, M.C. Structure and isomerization behavior relationships of new push-pull azo-pyrrole photoswitches. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2024, 22, 4123–4134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, P.J.; Castro, M.C.R.; Fonseca, A.M.C.; Raposo, M.M.M. Photoswitching in azo dyes bearing thienylpyrrole and benzothiazole heterocyclic systems. Dyes Pigments 2011, 91, 745–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.Y.; Olasz, A.; Chen, C.-H.; Lee, D. Three-stage binary switching of azoaromatic polybase. Org. Lett. 2012, 14, 6286–6289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Patrick, B.O.; Dolphin, D. Near-infrared absorbing azo dyes: Synthesis and X-ray crystallographic and spectral characterization of monoazopyrroles, bisazopyrroles, and a boron-azopyrrole complex. J. Org. Chem. 2009, 74, 5237–5243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikroyannidis, J.A.; Tsagkournos, D.V.; Sharma, S.S.; Kumar, A.; Vijay, A.D.; Sharma, G.D. Efficient bulk heterojunction solar cells based on low band gap bisazo dyes containing anthracene and/or pyrrole units. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2010, 94, 2318–2327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikroyannidis, J.A.; Roy, M.S.; Sharma, G.D. Synthesis of new low band gap dyes with BF2-azopyrrole complex and their use for dye-sensitized solar cells. J. Power Sources 2010, 195, 5391–5398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Wang, W.; Guo, J.; Wang, J.; He, J.; Cheng, J.-P. Quadruple hydrogen bonded self-assemblies of 5,5′-bisdiazo-dipyrromethane. CrystEngComm 2008, 10, 957–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beer, P.D.; Gale, P.A. Anion recognition and sensing: The state of the art and future perspectives. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2001, 40, 486–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busschaert, N.; Caltagirone, C.; Rossom, W.V.; Gale, P.A. Applications of supramolecular anion recognition. Chem. Rev. 2015, 105, 8038–8155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gale, P.A.; Howe, E.N.W.; Wu, X. Anion receptor chemistry. Chem 2016, 1, 351–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Yang, D.; Yang, X.-J.; Wu, B. Anion coordination chemistry: From recognition to supramolecular assembly. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2019, 378, 415–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goshisht, M.K.; Tripathi, N. Fluorescence-based sensors as an emerging tool for anion detection: Mechanism, sensory materials and applications. J. Mater. Chem. C 2021, 9, 9820–9850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Manez, R.; Sancenon, F. Fluorogenic and chromogenic chemosensors and reagents for anions. Chem. Rev. 2003, 103, 4419–4476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dydio, P.; Lichosyt, D.; Jurezakm, J. Amide- and urea-functionalized pyrroles and benzopyrroles as synthetic, neutral anion receptors. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 2971–2978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gale, P.A.; Sessler, J.L.; Kral, V.; Lynch, V. Calix[4]pyrroles: Old yet new anion-binding agents. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1996, 118, 5140–5141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Xu, J.; Guo, Y.; Shao, S. A novel colorimetric and fluorometric anion sensor based on BODIPY-calix[4]pyrrole conjugate. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 2012, 72, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gale, P.A.; Anzenbacher, P., Jr.; Sessler, J.L. Calixpyrroles II. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2001, 222, 57–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldakov, D.; Anzenbacher, P., Jr. Sensing of aqueous phosphates by polymers with dual modes of signal transduction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 4752–4753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pohl, R.; Aldakov, D.; Kubat, P.; Jursikova, K.; Marquez, M.; Anzenbacher, P., Jr. Strategies toward improving the performance of fluorescence-based sensors for inorganic anions. Chem. Commun. 2004, 1282–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleskovic, M.; Basaric, N.; Halasz, I.; Liang, X.; Qin, W.; Mlinaric-Majerski, K. Aryl substituted adamantine-dipyrromethanes: Chromogenic and fluorescent anion sensors. Tetrahedron 2013, 69, 1725–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renic, M.; Basaric, N.; Mlinaric-Majerski, K. Adamantane-dipyrromethanes: Novel anion receptors. Tetrahedron Lett. 2007, 48, 7873–7877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gale, P.A.; Camiolo, S.; Tizzard, G.J.; Chapman, C.P.; Light, M.E.; Coles, S.J.; Hursthouse, M.B. 2-Amidopyrroles and 2,5-diamidopyrroles as simple anion binding agents. J. Org. Chem. 2001, 66, 7849–7853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Li, Z.; Yu, A.; He, J.; Cheng, J.P. o-Di-(pyrrole-2-carboxamides)-phenylene: Pseudopolymorphs and anions recognition. Tetrahedron Lett. 2004, 45, 6803–6806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damade, K.R.; More, D.H. Azo based chromogenic sensor: An approach for naked eye detection of biologically relevant anions and metal cations. Mini-Rev Org. Chem. 2024, 21, 514–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, N.; Dhaka, G.; Singh, J. Simple naked-eye ratiometric and colorimetric receptor for anions based on azo dye featuring with benzimidazole unit. Tetrahedron Lett. 2015, 56, 1162–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morsavi, H.Z.; Mohammadi, A.; Yaghoubi, S.; Khereshki, N.Z. Design and synthesis of a novel optical chemoreceptor based on naphthalene azo dye for detection cyanide ion in aqueous medium an real samples. Chem. Pap. 2024, 78, 397–407. [Google Scholar]
- Kaur, M.; Singh, H.; Kaur, N.; Singh, N. A biginelli-azophenol based robust sensor for rapid diagnosis of cyanide in real samples. Dyes Pigments 2021, 195, 109702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.M.; Saini, S.; Park, J.E.; Singh, N.; Jang, D.O. A benzothiazole-based receptor for colorimetric detection of Cu2+ and S2- ions in aqueous media. Tetrahedron Lett. 2021, 73, 153115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, S.M.S.; Bisht, T.; Garg, B. 1-Arylazo-5,5-dimethyl dipyrromethanes: Versatile chromogenic probes for anions. Sensors Actuators B 2009, 141, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Liu, L.-J.; Yin, Z. 2-(2-hydroxylphenyl)dizao-dipyrromethane: Synthesis, structure and fluoride ion detection. Chinese J. Struct. Chem. 2017, 36, 47–52. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; An, Y.; Huang, J.; Yin, Z. Bis-arylazo-naphthobipyrrole: Synthesis, structure, photophysical properties, DFT calculations and anions sensing. Dyes Pigments 2025, 236, 112661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.-X. Nitrogen and oxygen bridged calixaromatics: Synthesis, structure, fictionalization, and molecular recognition. Acc. Chem. Res. 2012, 45, 182–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogoshi, T.; Yamagishi, T.; Nakamoto, Y. Pillar-shaped macrocyclic hosts pillar[n]arenes: New key players for supramolecular chemistry. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 7937–8002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Nalluri, S.K.M.; Stoddart, J.F. Surveying macrocyclic chemistry: From flexible crown ethers to rigid cyclophanes. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 2459–2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Du, M.; Kong, L.; Cai, Y.; Hu, X. Recognition site modifiable macrocycle: Synthesis, functional group variation and structural inspection. Molecules 2023, 28, 1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, F.A.; Xiao, T.; Wang, L.; Elmes, R.B.P. Macrocyclic receptors for anion recognition. Chem. Commun. 2024, 60, 11812–11836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Z.; Wang, M.; Wang, W.; Wang, X. Solvents effects on the self-assemblies of 55-bis(3-hydroxyphenyldizao)-dipyrromethane. J. Mol. Struct. 2013, 1003, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldrick, G.M. SADABS; University of Gottingen: Gottingen, Germany, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Sheldrick, G.M. SHELXT-Integrated space-group and crystal-structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. A 2015, 71, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G.M. Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. C 2015, 71, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolomanov, O.V.; Bourhis, L.J.; Gildea, R.J.; Howard, J.A.K.; Puschmann, H. OLEX2: A complete structure solution, refinement and analysis program. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2009, 42, 339–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renny, J.S.; Tomasevich, L.L.; Tallmadge, E.H.; Collum, D.B. Method of continuous variations: Applications of Job Plots to the study of molecular associations in organometallic chemistry. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 11998–12013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connors, K.A. Binding Constants: The Measurement of Molecular Complex Stability; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Sun, J.; Yin, Z. Synthesis, crystal structrues and solvent dependent cis-trans conversion of 2-(4-hydroxylphenyl)-azopyrrole. J. Mol. Struct. 2023, 1294, 136415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Yin, Z. Cooperative intramolecular hydrogen bonding induced azo-hydrazone tautomerism of azopyrrole: Crystallographic and spectroscopic studies. Dyes Pigments 2014, 102, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Wang, W.; Du, M.; Wang, X.; Guo, J. Crystal engineering of 5,5-bisdiazo-dipyrromethane with halogen...π synthons. CrystEngComm 2009, 11, 2441–2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.-M.; Yin, Z. Synthesis and crystal structure of 55-bis(4-hydroxylphenyl)diazo-dipyrromethane. Chin. J. Struct. Chem. 2013, 32, 1093–1099. [Google Scholar]
- Spek, A.L. Single-crystal structure validation with the program PLATON. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2003, 36, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yin, Z. Discrete cage form of water hexamer in the hydrophilic channels assembled by heterocyclic azopyrrole. J. Mol. Struct. 2015, 1092, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Crystal | 2 |
|---|---|
| CCDC No. | 2117984 |
| Empirical formula | C64H82N12O11 |
| Formula weight | 1195.41 |
| Crystal system | Orthorhombic |
| Space group | P212121 |
| a(Å) | 7.6407(17) |
| b(Å) | 14.487(3) |
| c(Å) | 28.857(6) |
| α(°) | 90 |
| β(°) | 90 |
| γ(°) | 90 |
| V(Å3) | 3194.2(12) |
| Z | 2 |
| Dcalc.(g/cm3) | 1.243 |
| μ(mm−1) | 0.086 |
| F(000) | 1276.0 |
| Reflections collected | 16356 |
| Independent reflections | 5539 [Rint = 0.0676, Rsigma = 0.0865] |
| R1/wR2 [I > 2σ(I)] | 0.0752/0.1930 |
| R1/wR2 (all data) | 0.01550/0.2431 |
| GoF on F2 | 0.946 |
| Bonds | Length (Å) | Torsion Angles | Degree (°) |
|---|---|---|---|
| N2-N3 | 1.240(8) | N1-C4-N2-N3 | 0.2(11) |
| N5-N6 | 1.208(8) | C3-C4-N2-N3 | 179.4(8) |
| N1-C1 | 1.366(8) | C4-N2-N3-C14 | 179.5(6) |
| N1-C4 | 1.364(8) | C19-C14-N3-N2 | 6.1(11) |
| C1-C2 | 1.391(10) | C15-C14-N3-N2 | 172.5(7) |
| C2-C3 | 1.383(11) | N4-C8-N5-N6 | 3.5(11) |
| C3-C4 | 1.385(11) | C7-C8-N5-N6 | 174.3(8) |
| N2-C4 | 1.403(9) | C8-N5-N6-C28 | 174.4(6) |
| N3-C14 | 1.473(9) | C29-C28-N6-N5 | 21.5(10) |
| N4-C5 | 1.353(8) | C27-C28-N6-N5 | 155.9(7) |
| N4-C8 | 1.399(10) | C20-O4-C16-C17 | 12.3(11) |
| C5-C6 | 1.381(11) | O4-C20-C21-O3 | 66.0(8) |
| C6-C7 | 1.424(13) | O3-C22-C23-O2 | 67.4(7) |
| C7-C8 | 1.294(12) | O2-C24-C25-O1 | 175.5(6) |
| N5-C8 | 1.426(11) | C25-O1-C26-C27 | 8.0(11) |
| N6-C28 | 1.535(10) | N1-C1-C9-C10 | 51.6(9) |
| C16-O4 | 1.359(8) | N1-C1-C9-C5 | 71.3(9) |
| C26-O1 | 1.362(8) | N4-C5-C9-C10 | 34.7(9) |
| O4-C20 | 1.439(8) | N4-C5-C9-C1 | 87.7(8) |
| O1-C25 | 1.409(8) |
| D-H…A | D…A (Å) | H…A (Å) | ∠D-H…A (°) |
|---|---|---|---|
| N1-H1…O5 i | 3.001 (8) | 2.15 | 169 |
| N4-H4…O5 i | 2.917 (8) | 2.14 | 149 |
| O5-H5…O3 | 2.758 (8) | 1.95 | 166 |
| O6-H6A…O2 ii | 2.957 (13) | 2.31 | 133 |
| O6-H6A…O4 ii | 2.951 (13) | 2.36 | 127 |
| C21-H21B….N6 i | 3.314 (11) | 2.61 | 129 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
An, Y.; Sun, Y.; Yin, Z. Macrocyclic Azopyrrole: Synthesis, Structure and Fluoride Recognition. Organics 2025, 6, 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/org6020025
An Y, Sun Y, Yin Z. Macrocyclic Azopyrrole: Synthesis, Structure and Fluoride Recognition. Organics. 2025; 6(2):25. https://doi.org/10.3390/org6020025
Chicago/Turabian StyleAn, Ying, Ying Sun, and Zhenming Yin. 2025. "Macrocyclic Azopyrrole: Synthesis, Structure and Fluoride Recognition" Organics 6, no. 2: 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/org6020025
APA StyleAn, Y., Sun, Y., & Yin, Z. (2025). Macrocyclic Azopyrrole: Synthesis, Structure and Fluoride Recognition. Organics, 6(2), 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/org6020025







