Palladium Catalyzed Allylic C-H Oxidation Enabled by Bicyclic Sulfoxide Ligands
Abstract
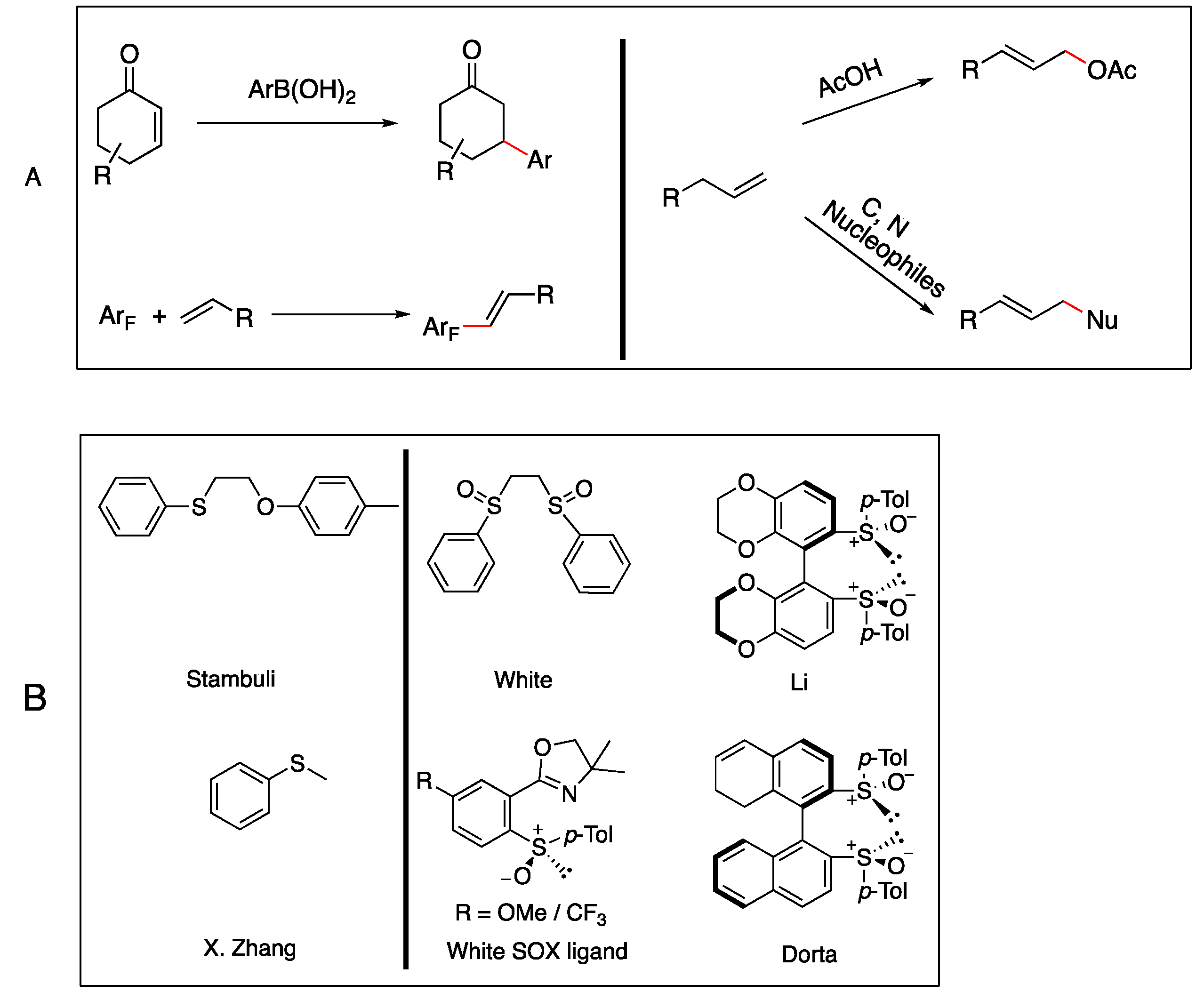
1. Introduction
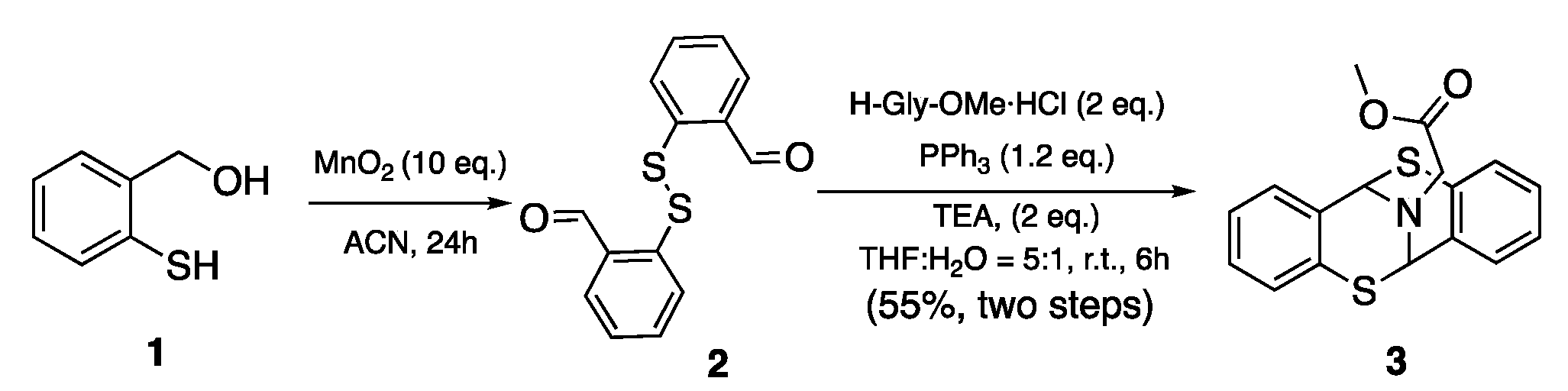
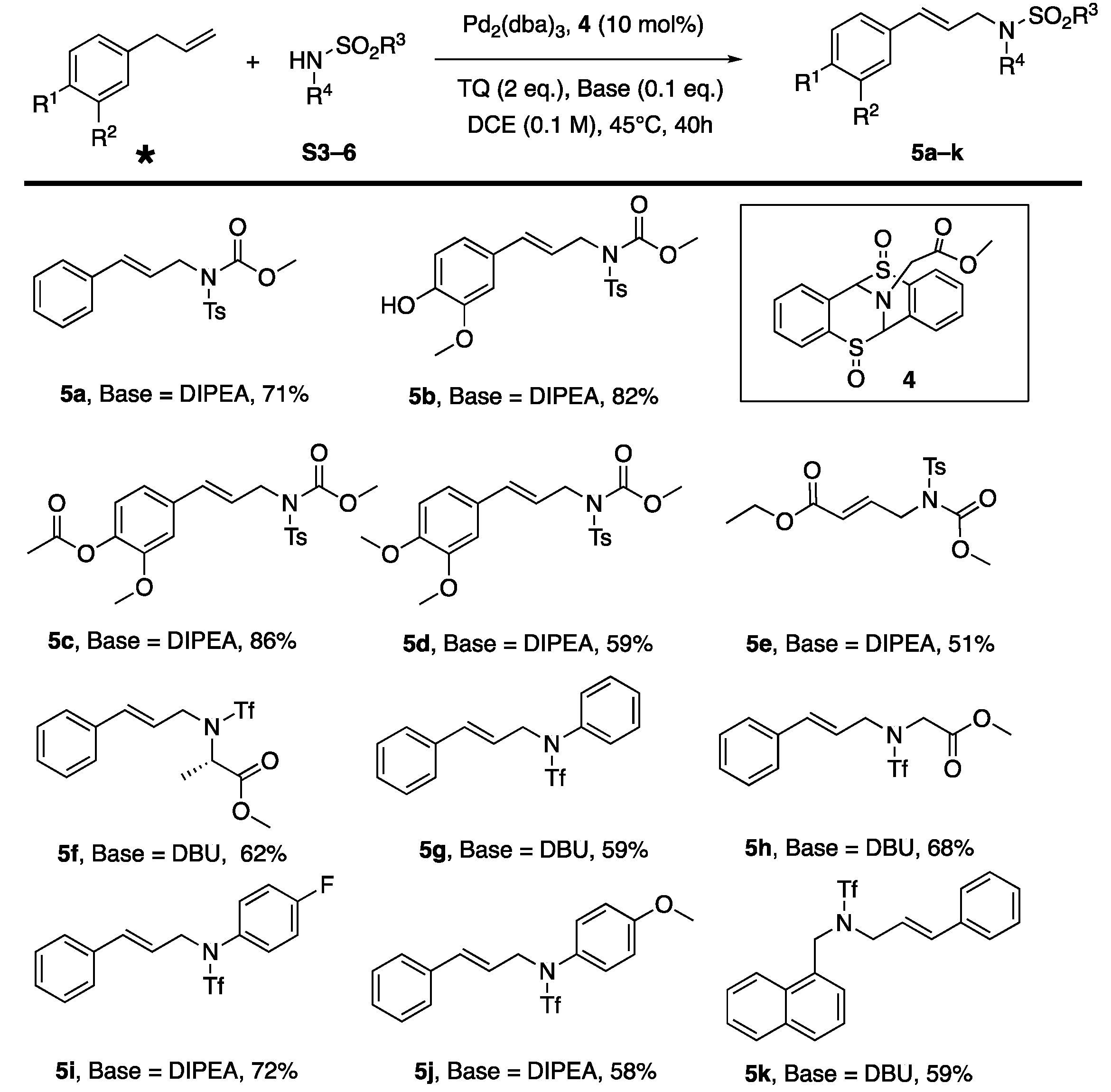
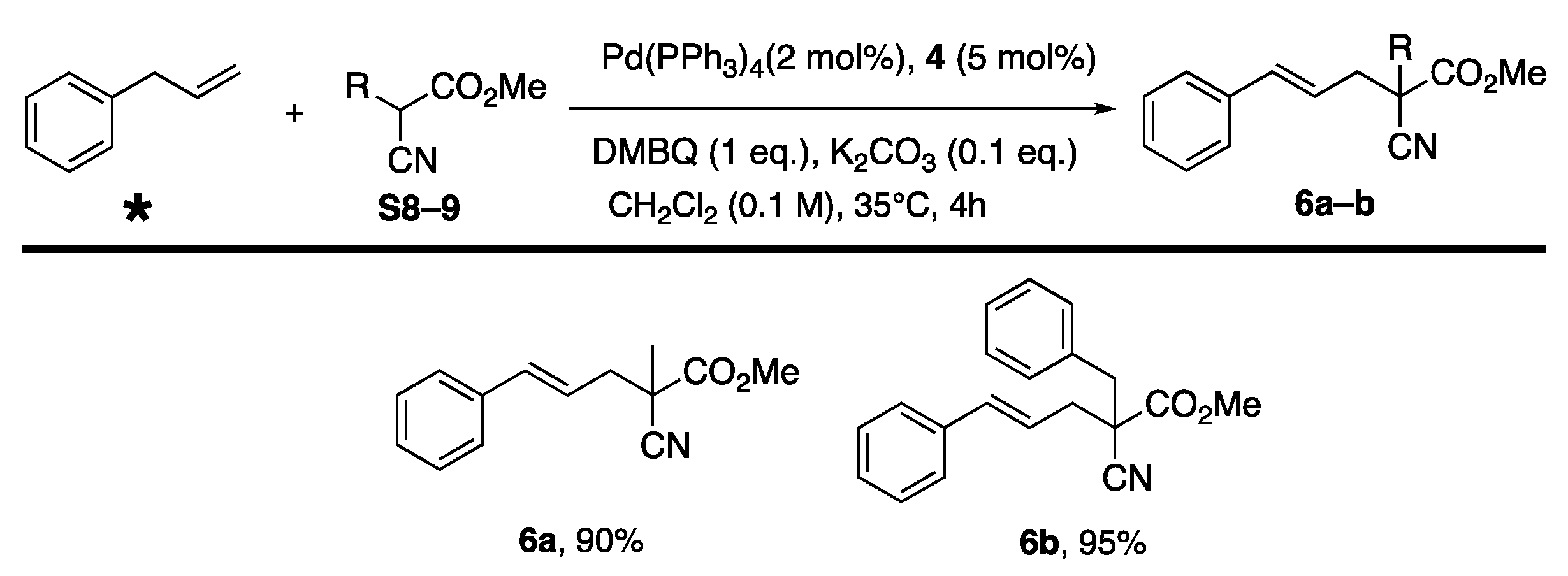
2. Material and Methods
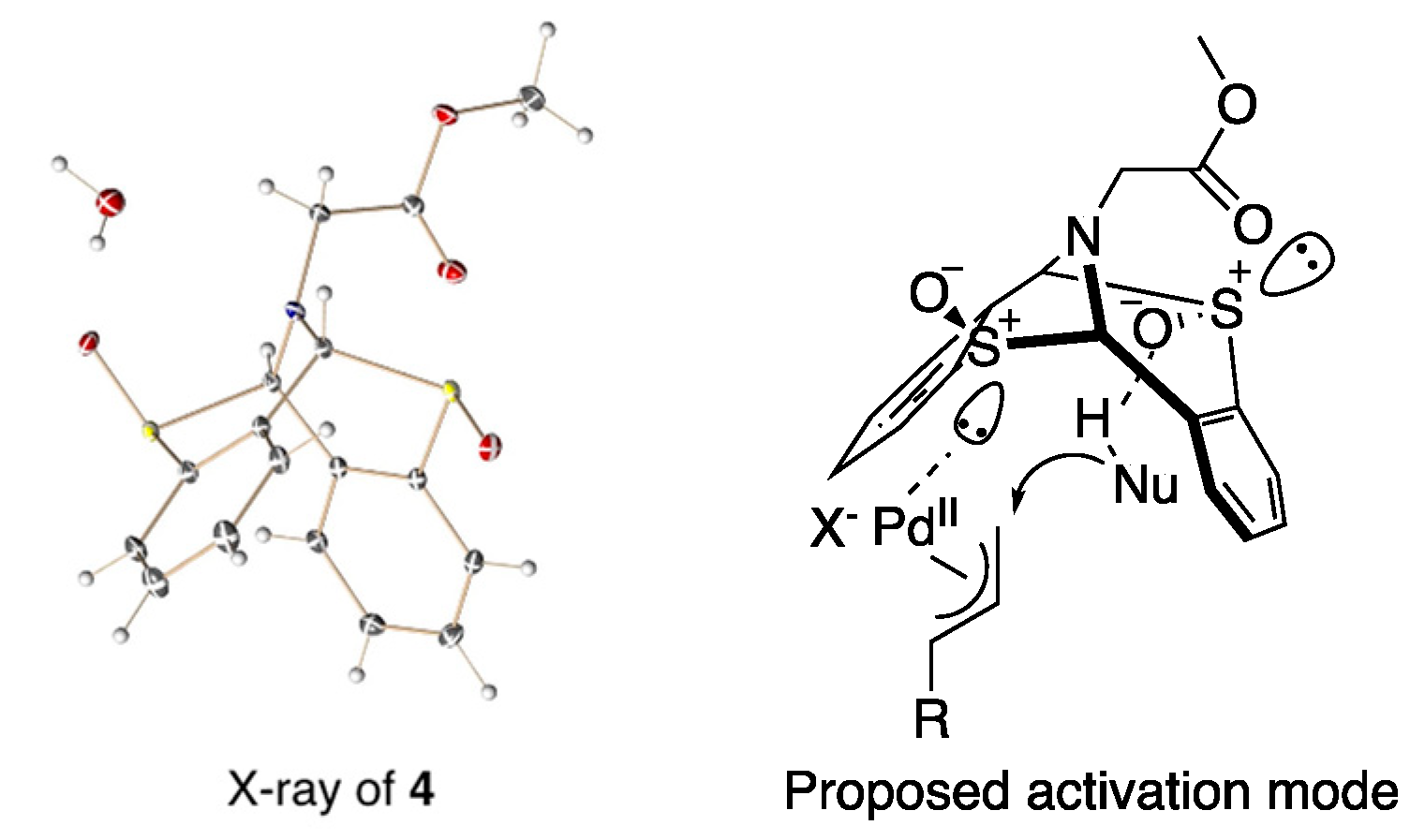
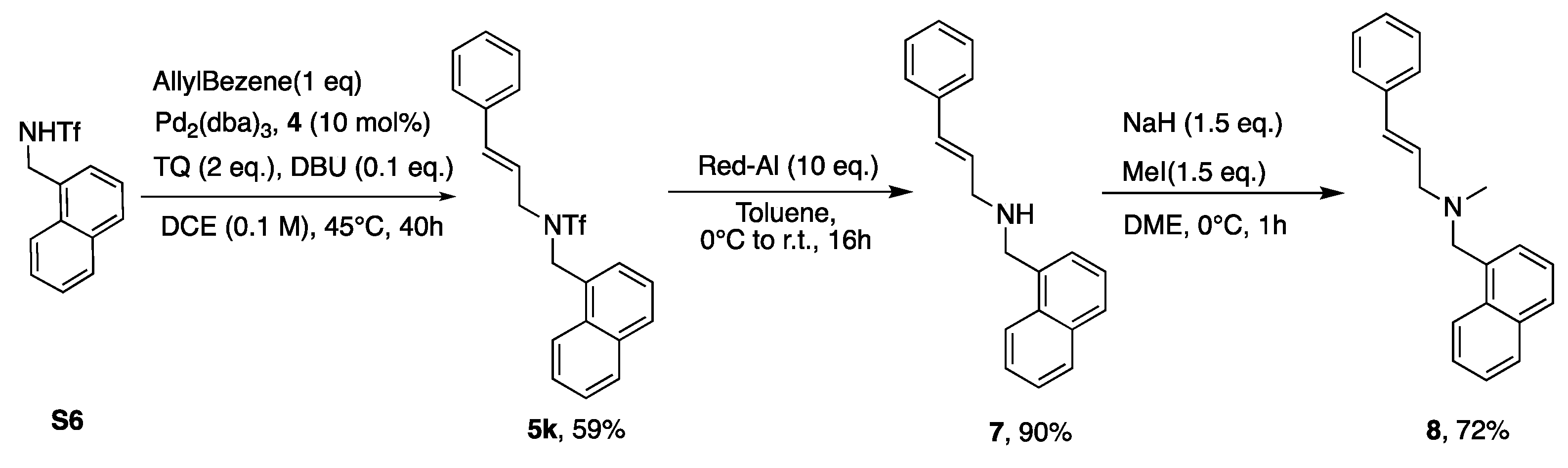
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lyons, T.W.; Sanford, M.S. Palladium-Catalyzed Ligand-Directed C−H Functionalization Reactions. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 1147–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liron, F.; Oble, J.; Lorion, M.M.; Poli, G. Direct Allylic Functionalization through Pd-Catalyzed C-H Activation. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2014, 2014, 5863–5883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sipos, G.; Drinkel, E.E.; Dorta, R. The Emergence of Sulfoxides as Efficient Ligands in Transition Metal Catalysis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 3834–3860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Wasa, M.; Chan, K.S.L.; Shao, Q.; Yu, J.-Q. Palladium-Catalyzed Transformations of Alkyl C–H Bonds. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 8754–8786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, S.A.; Mazzotti, A.R.; White, M.C. A Catalytic, Brønsted Base Strategy for Intermolecular Allylic C−H Amination. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 11701–11706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Song, C.-X.; Cai, G.-X.; Wang, W.-H.; Shi, Z.-J. Intra/Intermolecular Direct Allylic Alkylation via Pd(II)-Catalyzed Allylic C−H Activation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 12901–12903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howell, J.M.; Liu, W.; Young, A.J.; White, M.C. General Allylic C–H Alkylation with Tertiary Nucleophiles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 5750–5754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Ali, S.Z.; Ammann, S.E.; White, M.C. Asymmetric Allylic C–H Alkylation via Palladium(II)/Cis-ArSOX Catalysis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 10658–10662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; White, M.C. C–H to C–N Cross-Coupling of Sulfonamides with Olefins. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 3202–3205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, W.H.; Check, C.T.; Proust, N.; Stambuli, J.P. Allylic Oxidations of Terminal Olefins Using a Palladium Thioether Catalyst. Org. Lett. 2010, 12, 824–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.-Z.; He, C.-Y.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, X. Thioether-Promoted Direct Olefination of Polyfluoroarenes Catalyzed by Palladium. Org. Lett. 2013, 15, 5266–5269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Weng, J.; George, J.; Chen, H.; Lin, Q.; Wang, J.; Royzen, M.; Zhang, Q. Three-Component Protein Modification Using Mercaptobenzaldehyde Derivatives. Org. Lett. 2019, 21, 3828–3833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.; Ahn, S.; Kang, K.; Seo, M.-S.; Kim, Y.; Kim, W.Y.; Kim, H. Bicyclic Bridgehead Phosphoramidite (Briphos) Ligands with Tunable π-Acceptor Ability and Catalytic Activity in the Rhodium-Catalyzed Conjugate Additions. Org. Lett. 2014, 16, 5490–5493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Cao, P.; Xing, J.; Lou, Y.; Jiang, L.; Li, L.; Liao, J. Hydrogen-Bond-Promoted Palladium Catalysis: Allylic Alkylation of Indoles with Unsymmetrical 1,3-Disubstituted Allyl Acetates Using Chiral Bis(Sulfoxide) Phosphine Ligands. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 4207–4211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mariz, R.; Luan, X.; Gatti, M.; Linden, A.; Dorta, R. A Chiral Bis-Sulfoxide Ligand in Late-Transition Metal Catalysis; Rhodium-Catalyzed Asymmetric Addition of Arylboronic Acids to Electron-Deficient Olefins. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 2172–2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.-A.; Dong, X.; Chen, M.-W.; Wang, D.-S.; Zhou, Y.-G.; Li, Y.-X. Highly Effective and Diastereoselective Synthesis of Axially Chiral Bis-Sulfoxide Ligands via Oxidative Aryl Coupling. Org. Lett. 2010, 12, 1928–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaturvedi, J.; Haldar, C.; Bisht, R.; Pandey, G.; Chattopadhyay, B. Meta Selective C–H Borylation of Sterically Biased and Unbiased Substrates Directed by Electrostatic Interaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 7604–7611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, S.; Schepmann, D.; Wünsch, B. Role of the Phenolic OH Moiety of GluN2B-Selective NMDA Antagonists with 3-Benzazepine Scaffold. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 26, 889–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Ren, J.; Tan, S.M.; Tan, D.; Lee, R.; Tan, C.-H. An Enantioconvergent Halogenophilic Nucleophilic Substitution (S N 2X) Reaction. Science 2019, 363, 400–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolesnikov, P.N.; Usanov, D.L.; Barablina, E.A.; Maleev, V.I.; Chusov, D. Atom- and Step-Economical Preparation of Reduced Knoevenagel Adducts Using CO as a Deoxygenative Agent. Org. Lett. 2014, 16, 5068–5071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scattolin, T.; Deckers, K.; Schoenebeck, F. Efficient Synthesis of Trifluoromethyl Amines through a Formal Umpolung Strategy from the Bench-Stable Precursor (Me4N)SCF3. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 221–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bisz, E.; Koston, M.; Szostak, M. N -Butylpyrrolidone (NBP) as a Non-Toxic Substitute for NMP in Iron-Catalyzed C(Sp 2)–C(Sp 3) Cross-Coupling of Aryl Chlorides. Green Chem. 2021, 23, 7515–7521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SAINT. Part of Bruker APEX3 Software Package (Version 2016.9-0): Bruker AXS. 2016. Available online: https://www.brukersupport.com/ProductDetail/3177 (accessed on 6 June 2023).
- SADABS. Part of Bruker APEX3 Software Package (Version 2016.9-0): Bruker AXS. 2016. Available online: https://www.brukersupport.com/ProductDetail/3177 (accessed on 6 June 2023).
- SHELXT; Version 2014/5: G. M. Sheldrick. Acta Cryst. 2015, A71, 3–8.
- XL refinement program version 2016/6: G. M. Sheldrick. Acta Cryst. 2015, C71, 3–8.
- Das Sato, K.; Hyodo, M.; Aoki, M.; Zheng, X.-Q.; Noyori, R. Oxidation of Sulfides to Sulfoxides and Sulfones with 30% Hydrogen Peroxide under Organic Solvent- and Halogen-Free Conditions. Tetrahedron 2001, 57, 2469–2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.K.; Ryder, J.E.; Cooper, E.A. Naftifine: A Review. J. Cutan. Med. Surg. 2008, 12, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
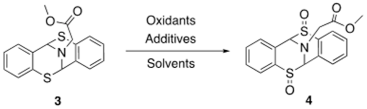 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oxidants | Solvents | Additives | Temperature | Time | Yield |
| Oxone (2 eq.) | CH2Cl2 | - | RT | O/N | N.D. |
| NaIO4 (2 eq.) | CH2Cl2 | DDQ (2 eq.) | RT | O/N | N.D. |
| MeOH | - | N.D. | |||
| PhI(OAc)2 (2 eq.) | MeOH | (NH4)2CO3(2eq.) | RT | O/N | N.D. |
| Sharpless reagents a | - | - | 0 °C | O/N | N.D. |
| DMDO (2 eq.) | - | - | 0 °C | O/N | N.D. |
| m-CPBA (2 eq.) | CH2Cl2 | - | 0 °C | 1 h | <5% |
| TBHP(0.1 eq.) | 0 °C | 1 h | N.D. | ||
| Acetone | - | 0 °C | 1 h | N.D. | |
| THF | - | 0 °C | 1 h | N.D. | |
| H2O2 (2 eq.) | HOAc | - | RT | O/N | <10% conversion |
| MeOH | - | RT | O/N | N.D. | |
| HFIP | - | RT | O/N | N.D. | |
| THF | Na2WO4·2H2O | RT | O/N | <5% | |
| Acetone:H2O b | Na2WO4·2H2O | 0 °C | 50 min | 51% | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wen, Y.; Zheng, J.; Evans, A.H.; Zhang, Q. Palladium Catalyzed Allylic C-H Oxidation Enabled by Bicyclic Sulfoxide Ligands. Organics 2023, 4, 289-296. https://doi.org/10.3390/org4020023
Wen Y, Zheng J, Evans AH, Zhang Q. Palladium Catalyzed Allylic C-H Oxidation Enabled by Bicyclic Sulfoxide Ligands. Organics. 2023; 4(2):289-296. https://doi.org/10.3390/org4020023
Chicago/Turabian StyleWen, Yuming, Jianfeng Zheng, Alex H. Evans, and Qiang Zhang. 2023. "Palladium Catalyzed Allylic C-H Oxidation Enabled by Bicyclic Sulfoxide Ligands" Organics 4, no. 2: 289-296. https://doi.org/10.3390/org4020023
APA StyleWen, Y., Zheng, J., Evans, A. H., & Zhang, Q. (2023). Palladium Catalyzed Allylic C-H Oxidation Enabled by Bicyclic Sulfoxide Ligands. Organics, 4(2), 289-296. https://doi.org/10.3390/org4020023






