Evaluation of N,N,N′,N′-Tetramethylethylenediamine (TMEDA) as an Alternative Fuel for a Hypergolic Bipropellant Rocket Engine
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Lab Synthesis of WFNA
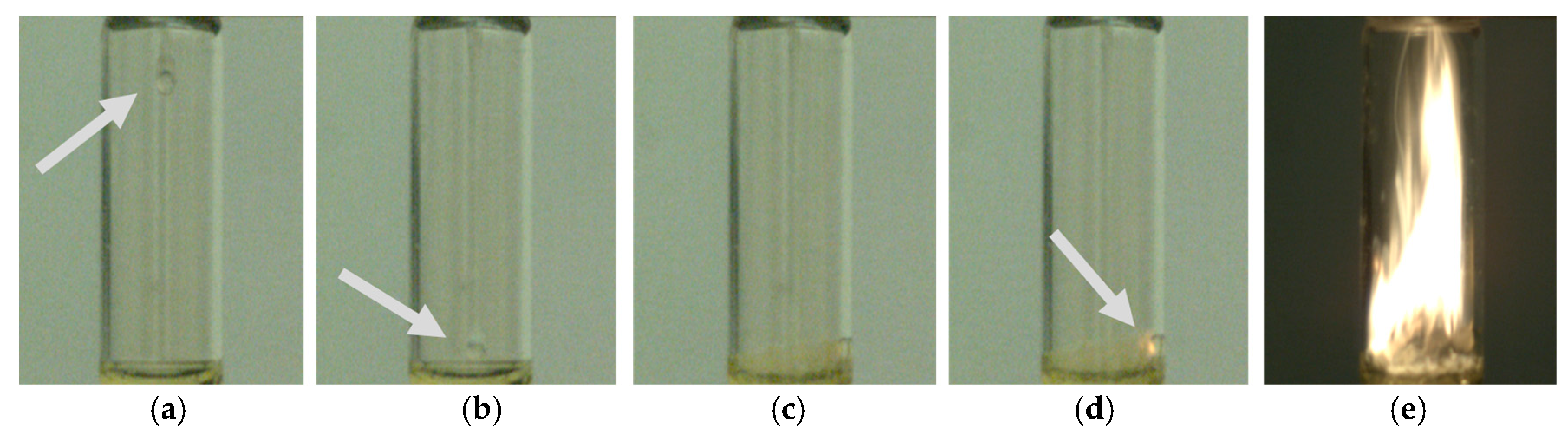
2.2. WFNA Droplet Testing Setup with TMEDA Fuel
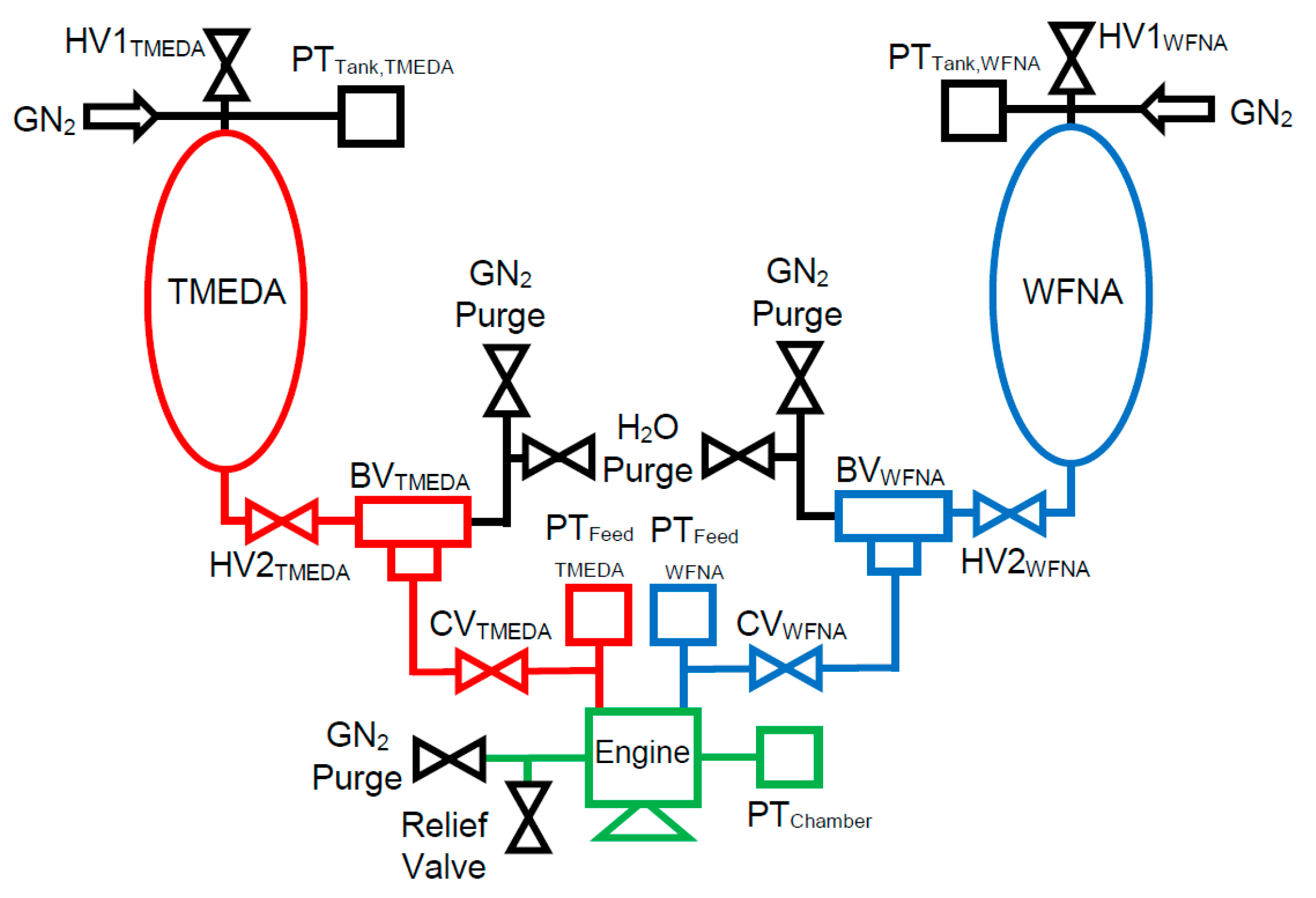
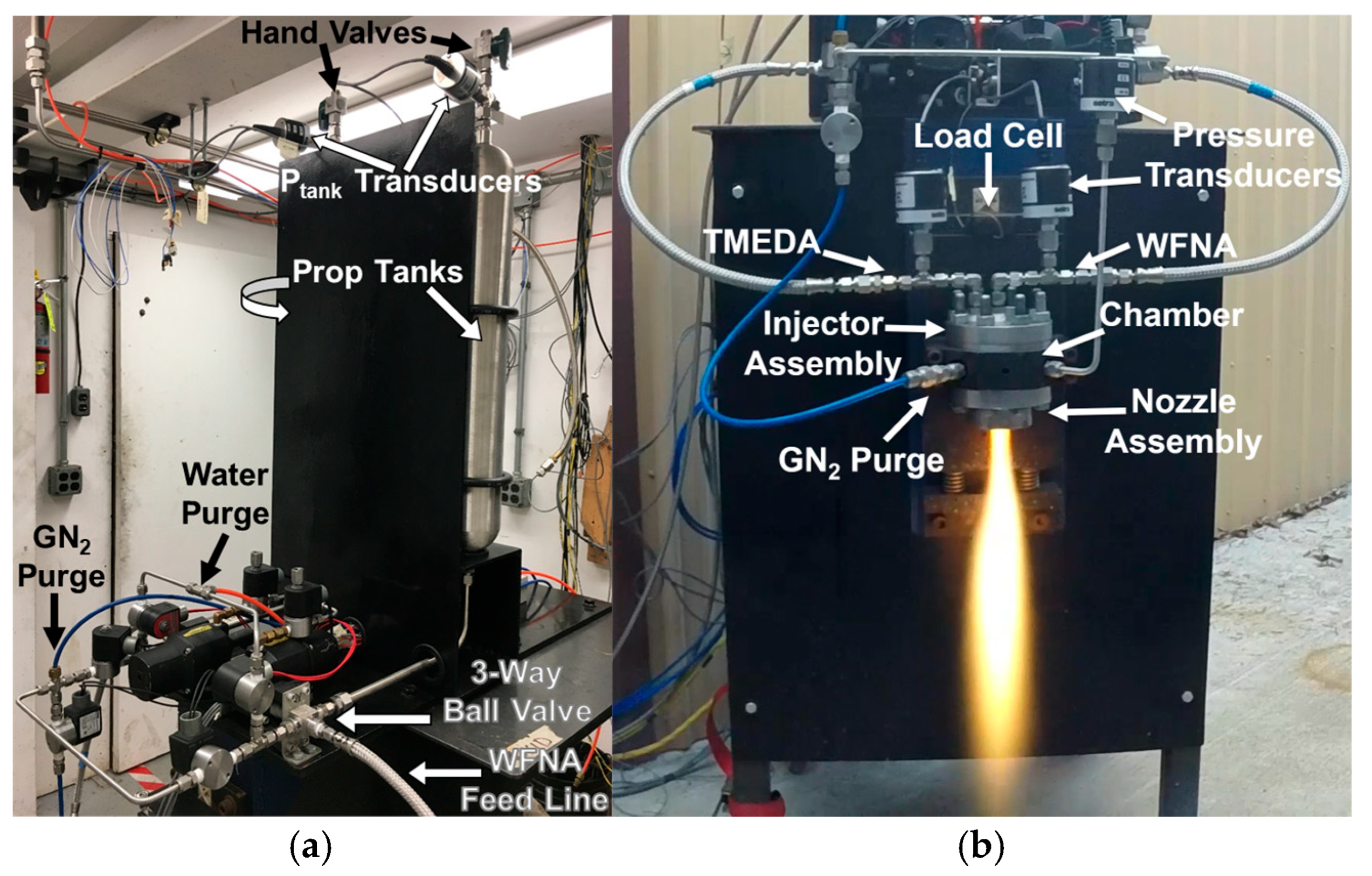
2.3. TMEDA/WFNA Hypergolic Bipropellant Rocket Engine Test Setup
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. WFNA Droplet Testing with TMEDA Fuel
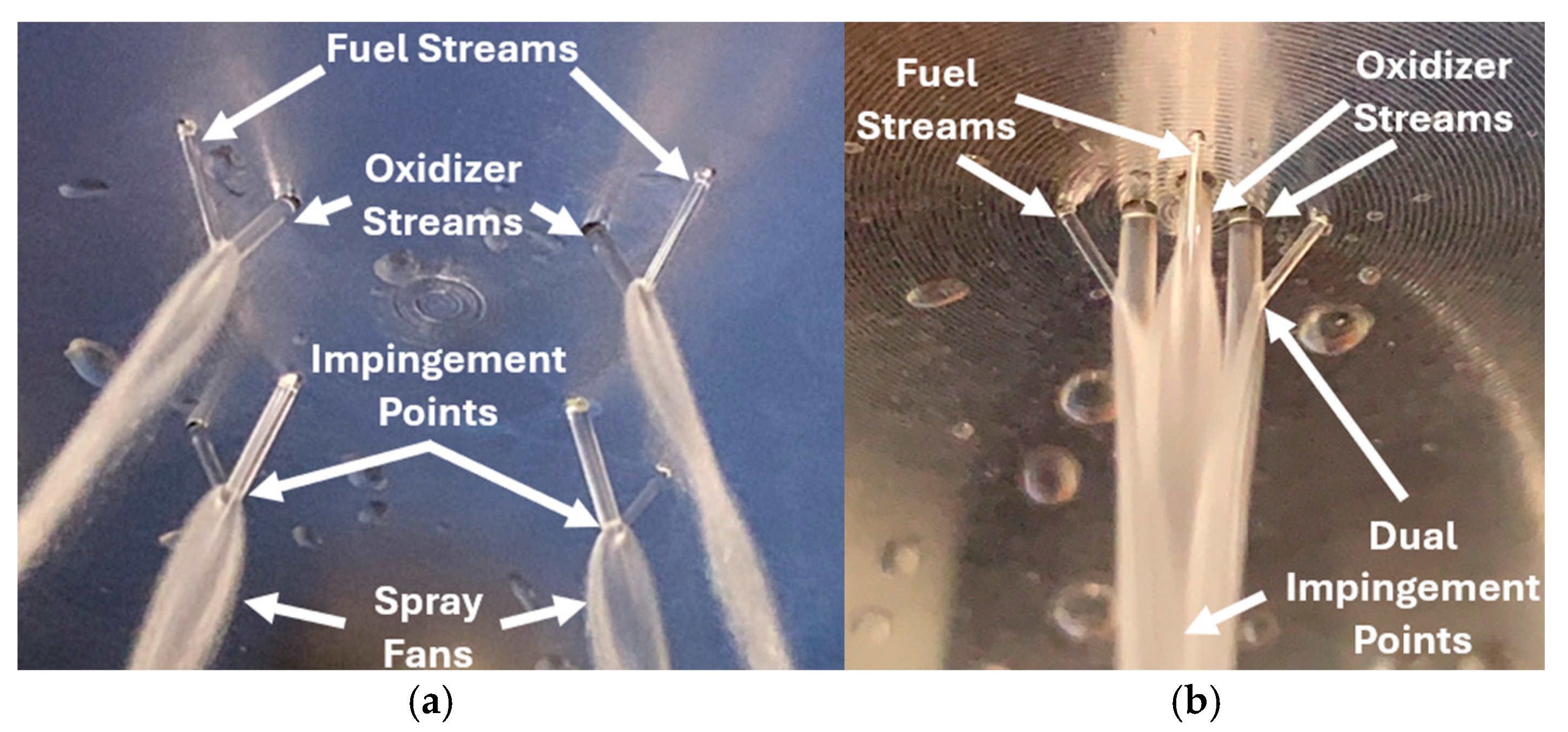
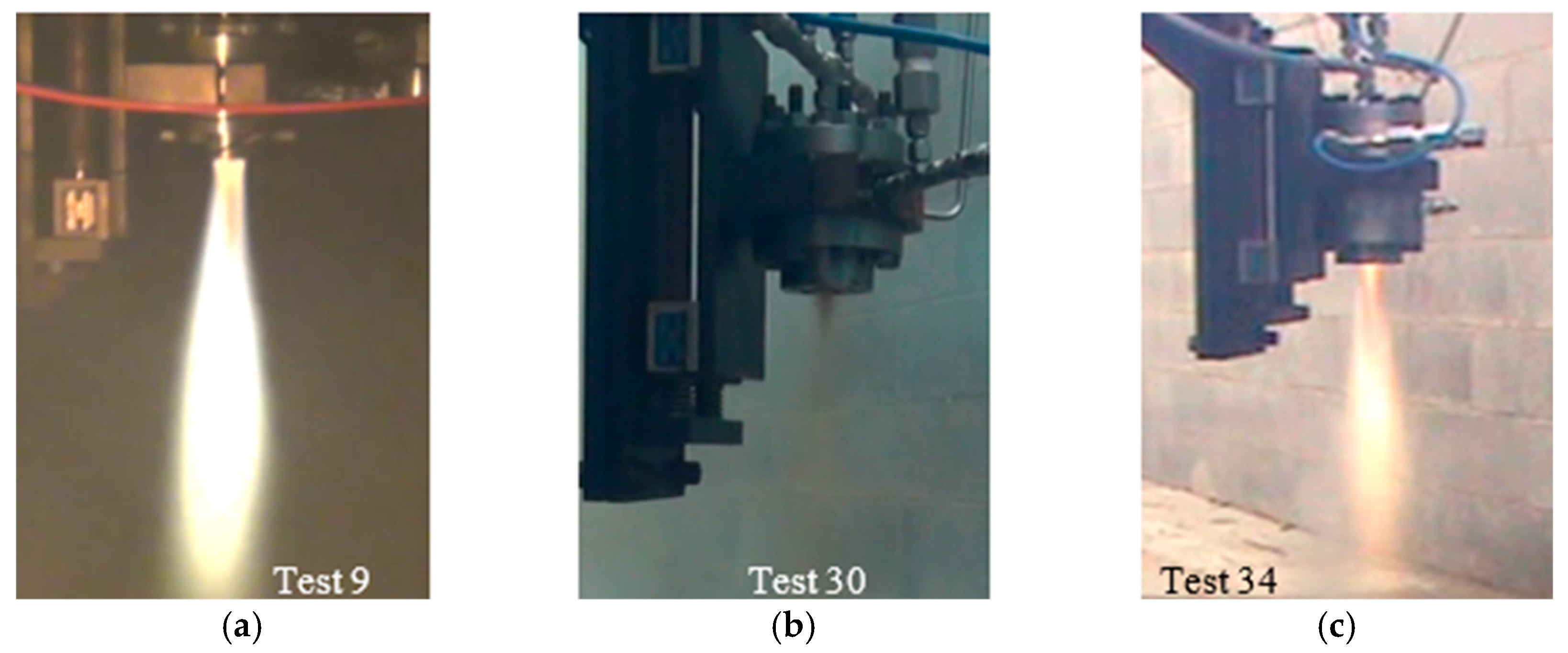
3.2. TMEDA/WFNA Hypergolic Bipropellant Rocket Engine Testing
3.3. Future Directions
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BV | Ball valve |
| CRES | Corrosion-resistant stainless steel |
| c* | Characteristic velocity [m/s] |
| D | Diameter [mm] |
| DMAZ | 2-N,N-dimethylaminoethylazide |
| F | Thrust [N] |
| GN2 | Gaseous nitrogen |
| HV | Hand valve |
| HNO3 | Nitric acid |
| H2SO4 | Sulfuric acid |
| ID | Inner diameter [mm] |
| Isp | Specific impulse [s] |
| KNO3 | Potassium nitrate |
| L | Length [mm] |
| L/D | Length-to-diameter ratio of injector orifice |
| L* | Characteristic length [m] |
| m | Mass [g] |
| MMH | Monomethylhydrazine |
| MON | Mixed oxides of nitrogen |
| MR | Oxidizer-to-fuel mixture ratio |
| NaNO3 | Sodium nitrate |
| NaOH | Sodium hydroxide |
| N2H4 | Hydrazine |
| NO2 | Nitrogen dioxide |
| N2O4 | Nitrogen tetroxide |
| OD | Outer diameter [mm] |
| PC | Chamber pressure [MPa] |
| Pfeed | Reactant feed pressure [MPa] |
| PT | Pressure transducer |
| RFNA | Red fuming nitric acid |
| t0 | Time oxidizer and fuel streams initiate impingement [ms] |
| tign | Time of first light subsequent impingement [ms] |
| TMEDA | N,N,N′,N′-tetramethylethylenediamine |
| TST | Twin split triplet |
| UD | Unlike doublet |
| V | Volume [mL] |
| WFNA | White fuming nitric acid |
| ηc* | c* efficiency |
| ϕ | Equivalence ratio |
| ρ | Density [g/mL] |
References
- Clark, J.D. Ignition! An Informal History of Liquid Rocket Propellants; Rutgers University Press: New Brunswick, NJ, USA, 1972; pp. 7–73. [Google Scholar]
- Schalla, R.L.; Fletcher, E.A. The Ignition Behavior of Various Amines with White Fuming Nitric Acid; Lewis Research Center, NASA: Cleveland, OH, USA, 1959.
- Coil, M.A. Hypergolic Ignition of a Gelled Ionic Liquid Fuel. In Proceedings of the 46th AIAA/ASME/SAE/ASEE Joint Propulsion Conference & Exhibit, Nashville, TN, USA, 25–28 July 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huzel, D.K.; Huang, D.H. Modern Engineering for Design of Liquid-Propellant Rocket Engines; Progress in Astronautics and Aeronautics; American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics, Inc.: Reston, VA, USA, 1992; Volume 147, pp. 1–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, G.P.; Biblarz, O. Rocket Propulsion Elements, 7th ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2001; pp. 234–235. [Google Scholar]
- Sutton, G.P. History of Liquid Propellant Rocket Engines; American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics, Inc.: Alexandria, VA, USA, 2006; pp. 5–21. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Thynell, S.T.; Chowdhury, A. Experimental Study on Hypergolic Interaction between N,N,N′,N′-Tetramethylethylenediamine and Nitric Acid. Energy Fuels 2010, 24, 5320–5330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Shreeve, J.M. Ionic Liquid Propellants: Future Fuels for Space Propulsion. Chem. Eur. J. 2013, 19, 15446–15451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AIAA SP-084-1999; Fire, Explosion, Compatibility, and Safety Hazards of Hypergols—Hydrazine. American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics, Inc.: Reston, VA, USA, 1999; pp. 1–150.
- Gohardani, A.S.; Stanojev, J.; Demaire, A.; Anflo, K.; Persson, M.; Wingborg, N.; Nilsson, C. Green Space Propulsion: Opportunities and Prospects. Prog. Aerosp. Sci. 2014, 71, 128–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.; Kwon, S. Experiment and Speculations on Nontoxic Hypergolic Propulsion with Hydrogen Peroxide. Spacecr. Rocket. 2018, 55, 1230–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.J.; Lee, E.K.; Kwon, S.J. Suppression of Hard Start for Nontoxic Hypergolic Thruster Using H2O2 Oxidizer. J. Propuls. Power 2017, 33, 1111–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sackheim, R.L.; Masse, R.K. Green Propulsion Advancement: Challenging the Maturity of Monopropellant Hydrazine. J. Propuls. Power 2014, 30, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, A.; Wingborg, N. Green Propellants Based on Ammonium Dinitramide (ADN). In Advances in Spacecraft Technologies; Hall, J., Ed.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2011; pp. 139–156. [Google Scholar]
- Spores, R.A.; Masse, R.L.; Kimbrel, S.; McLean, C. GPIM AF-M315E Propulsion System. In Proceedings of the 49th AIAA/ASME/SAE/ASEE Joint Propulsion Conference, San Jose, CA, USA, 14–17 July 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambreau, S.D.; Schneider, S.; Rosander, M.; Hawkins, T.; Gallegos, C.J.; Pastewait, M.F.; Vaghjiani, G.L. Fourier Transform Infrared Studies in Hypergolic Ignition of Ionic Liquids. J. Phys. Chem. A 2008, 112, 7816–7824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, S.; Hawkins, T.; Rosander, M.; Vaghjiani, G.; Chambreau, S.; Drake, G. Ionic Liquids as Hypergolic Fuels. Energy Fuels 2008, 22, 2871–2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Tao, G.H.; Parrish, D.A.; Shreeve, J.M. Nitrocyanamide-Based Ionic Liquids and Their Potential Applications as Hypergolic Fuels. Chem. Eur. J. 2010, 16, 5736–5743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, D.M. Tertiary Amine Azides in Hypergolic Liquid or Gel Fuels Propellant Systems. U.S. Patent 6013143A, 11 January 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson, W.H.; Felton, L.D.; Wang, Z.S. Hypergolic Liquid or Gel Fuel Mixtures. U.S. Patent 0,127,551A1, 5 June 2008. [Google Scholar]
- McQuaid, M.J.; Stevenson, W.H.; Thompson, D.M. Computationally Based Design and Screening of Hypergolic Multiamines; Technical Report, NTIS No. ADA433347; US Army Research Laboratory: Aberdeen Proving Ground, MD, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson, W.H.; Felton, L.D.; Wang, Z.S. Hypergolic Liquid or Gel Fuel Mixtures. U.S. Patent 0272071, 10 November 2011. [Google Scholar]
- McQuaid, M.J. Computational Characterization of 2-Azidocycloalkanamines: Notional Variations on the Hypergol 2-Azido-N,N-Dimethylethanamine (DMAZ); ARL-TR-2806; Army Research Laboratory: Aberdeen Proving Ground, MD, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Bittner, D.E.; Sell, J.L.; Risha, G.A. Effect of Jet Momentum Ratio and Equivalence Ratio on the Ignition Process of TMEDA and White Fuming Nitric Acid (WFNA). In Proceedings of the 49th AIAA/ASME/SAE/ASEE Joint Propulsion Conference, San Jose, CA, USA, 14–17 July 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.J.; Kwon, S.J. Green Hypergolic Combination: Diethylenetriamine-Based Fuel and Hydrogen Peroxide. Acta Astronaut. 2017, 137, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.; Park, S.; Park, Y.; Lee, J. Ignition-Delay Measurement for Drop Test with Hypergolic Propellants: Reactive Fuels and Hydrogen Peroxide. Combust. Flame 2020, 217, 306–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.; Jang, D.; Kwon, S. Demonstration of 500 N Scale Bipropellant Thruster using Non-Toxic Hypergolic Fuel and Hydrogen Peroxide. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2016, 49, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connell, T.L.; Risha, G.A.; Yetter, R.A.; Natan, B. Ignition of Hydrogen Peroxide with Gel Hydrocarbon Fuels. J. Propuls. Power 2018, 34, 170–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourpoint, T.L.; Anderson, W.E. Hypergolic Reaction Mechanisms of Catalytically Promoted Fuels with Rocket Grade Hydrogen Peroxide. Combust. Sci. Technol. 2007, 179, 2107–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sell, J.L.; Bittner, D.E.; Koeck, J.J.; Risha, G.A. Design, Fabrication, and Ground Test of a Hydrocarbon Rocker Engine. In Proceedings of the 49th AIAA/ASME/SAE/ASEE Joint Propulsion Conference, San Jose, CA, USA, 14–17 July 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupe, J.H. A Correlation Between the Dynamic Properties of a Pair of Impinging Streams and the Uniformity of Mixture-Ratio Distribution in the Resulting Spray; Progress Report No.20-209; Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology: Pasadena, CA, USA, 1956. [Google Scholar]
- Nusca, M.J.; Mathis, N.P.; Michaels, R.S. Reacting Flow CFD Model of Throttling in the Army’s Impinging Stream Vortex Engine. In Proceedings of the 44th AIAA/ASME/SAE/ASEE Joint Propulsion Conference, Hartford, CT, USA, 21–23 July 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McBride, B.J.; Gordon, S. Computer Program for Calculation of Complex Chemical Equilibrium Compositions and Applications; NASA Reference Publication 1311; Lewis Research Center, NASA: Cleveland, OH, USA, 1994.
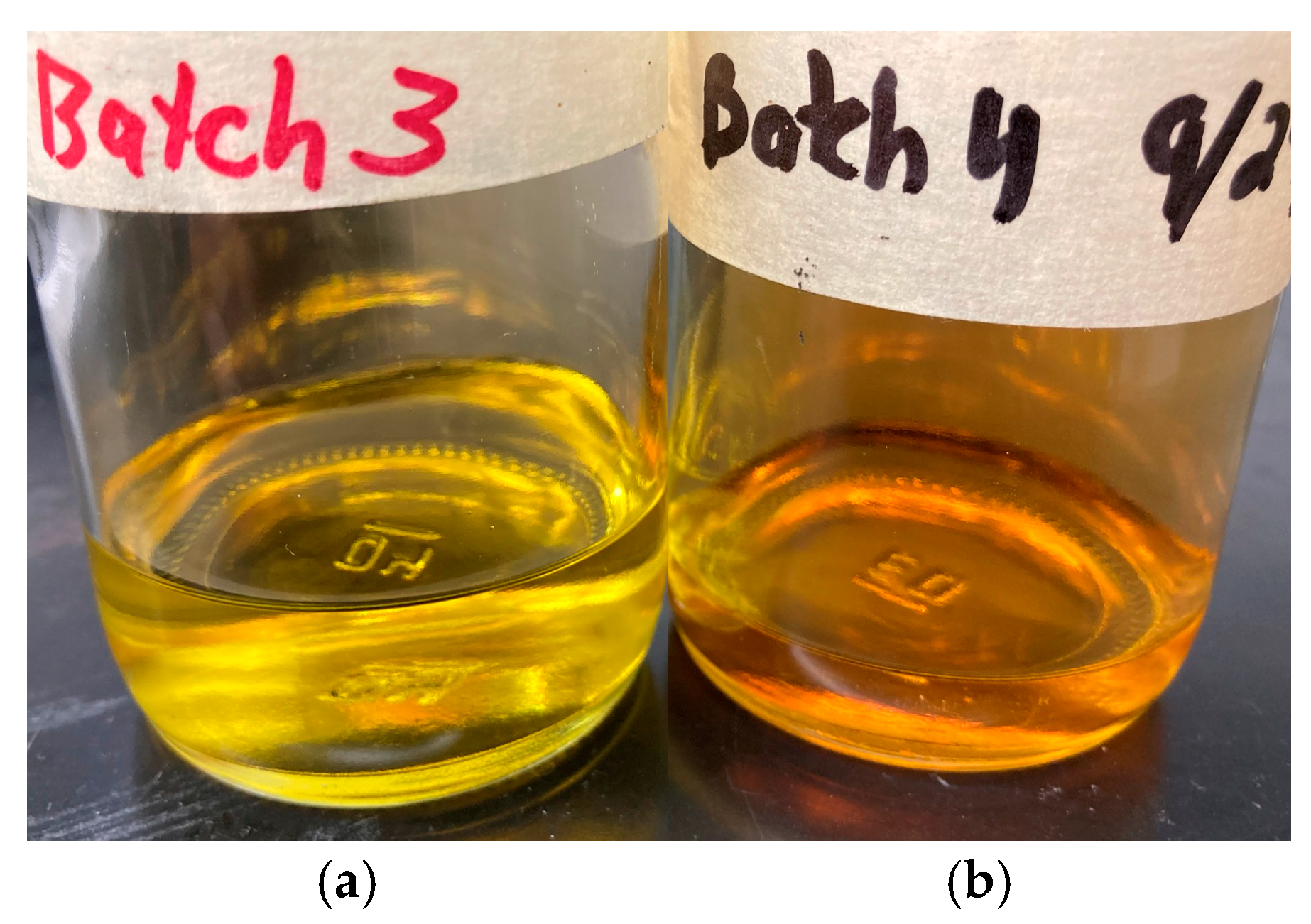
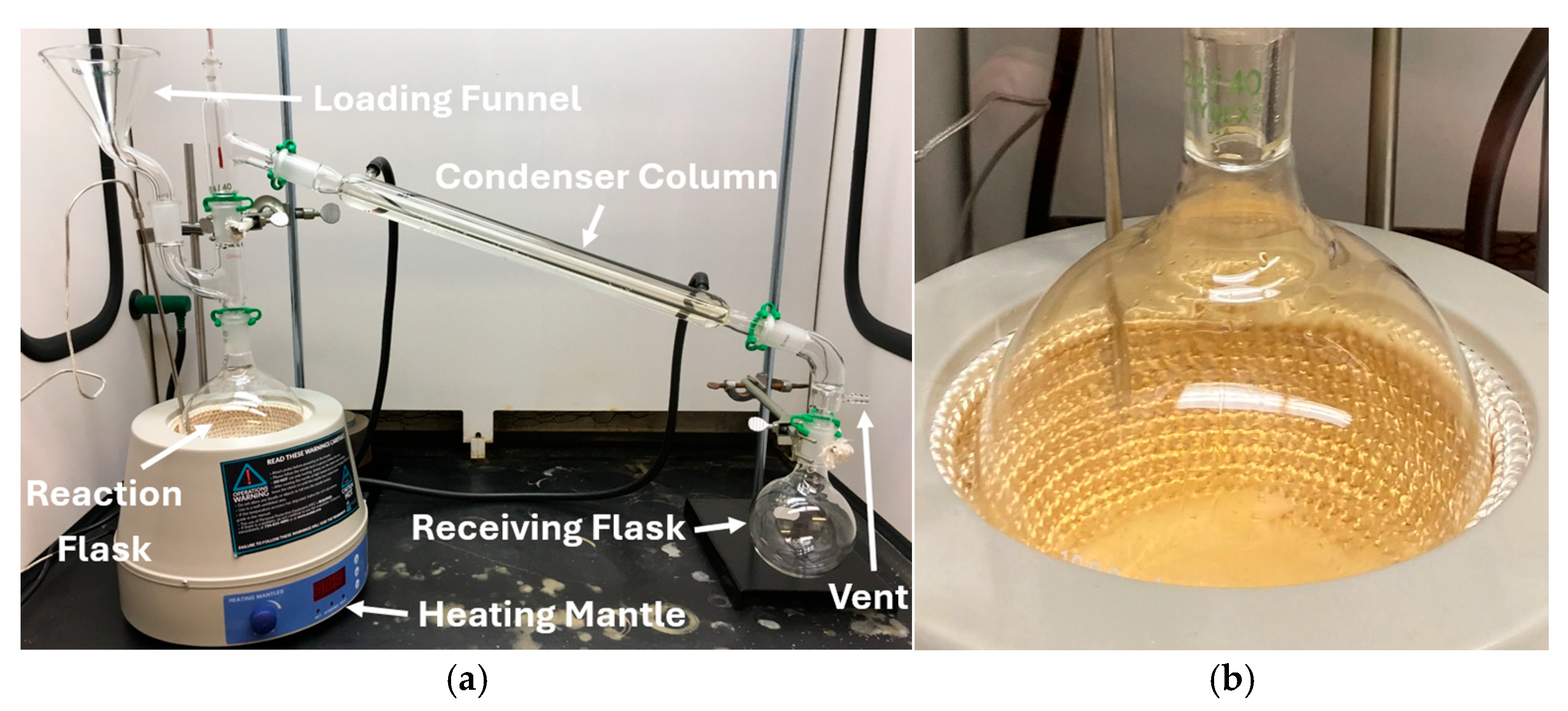
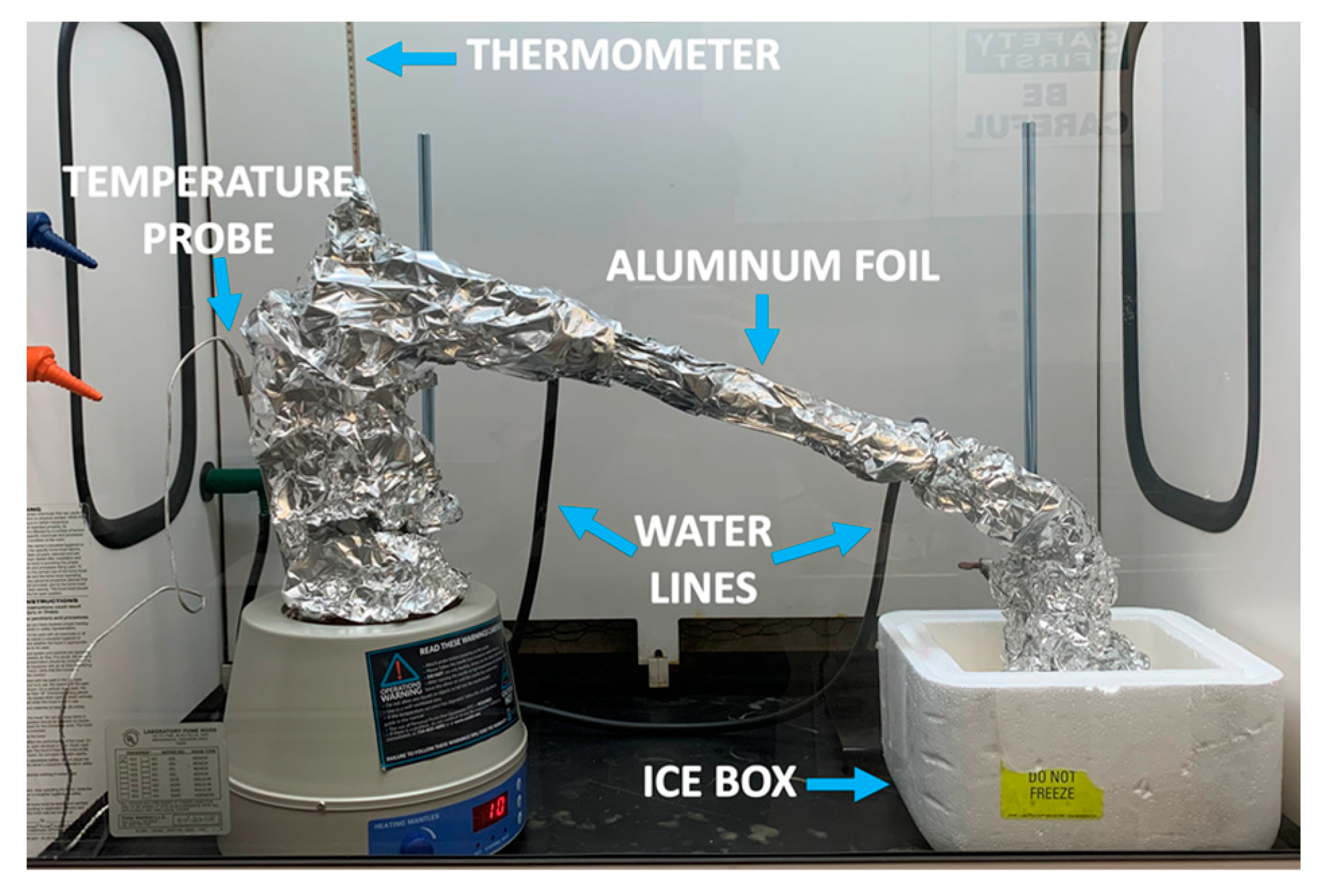

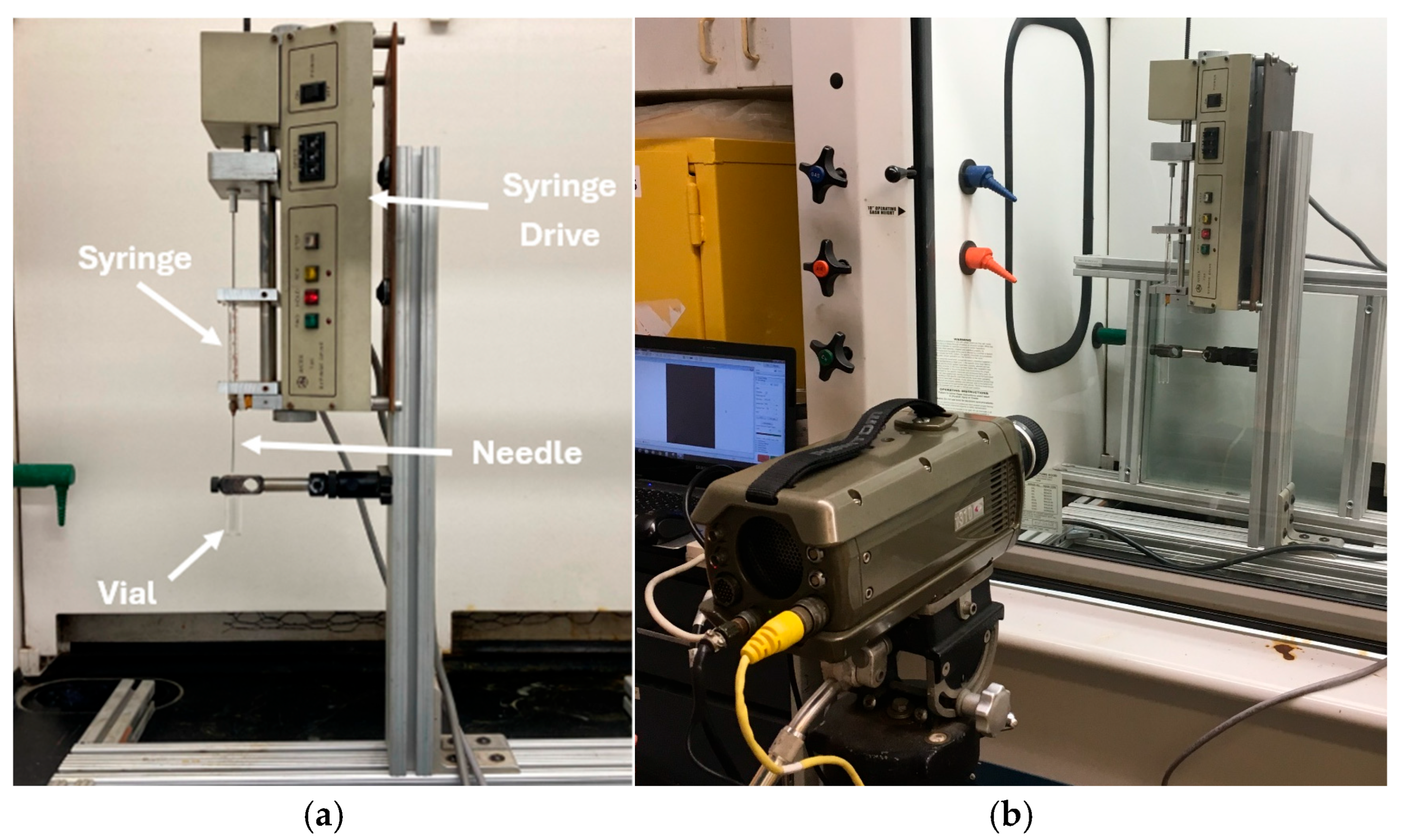

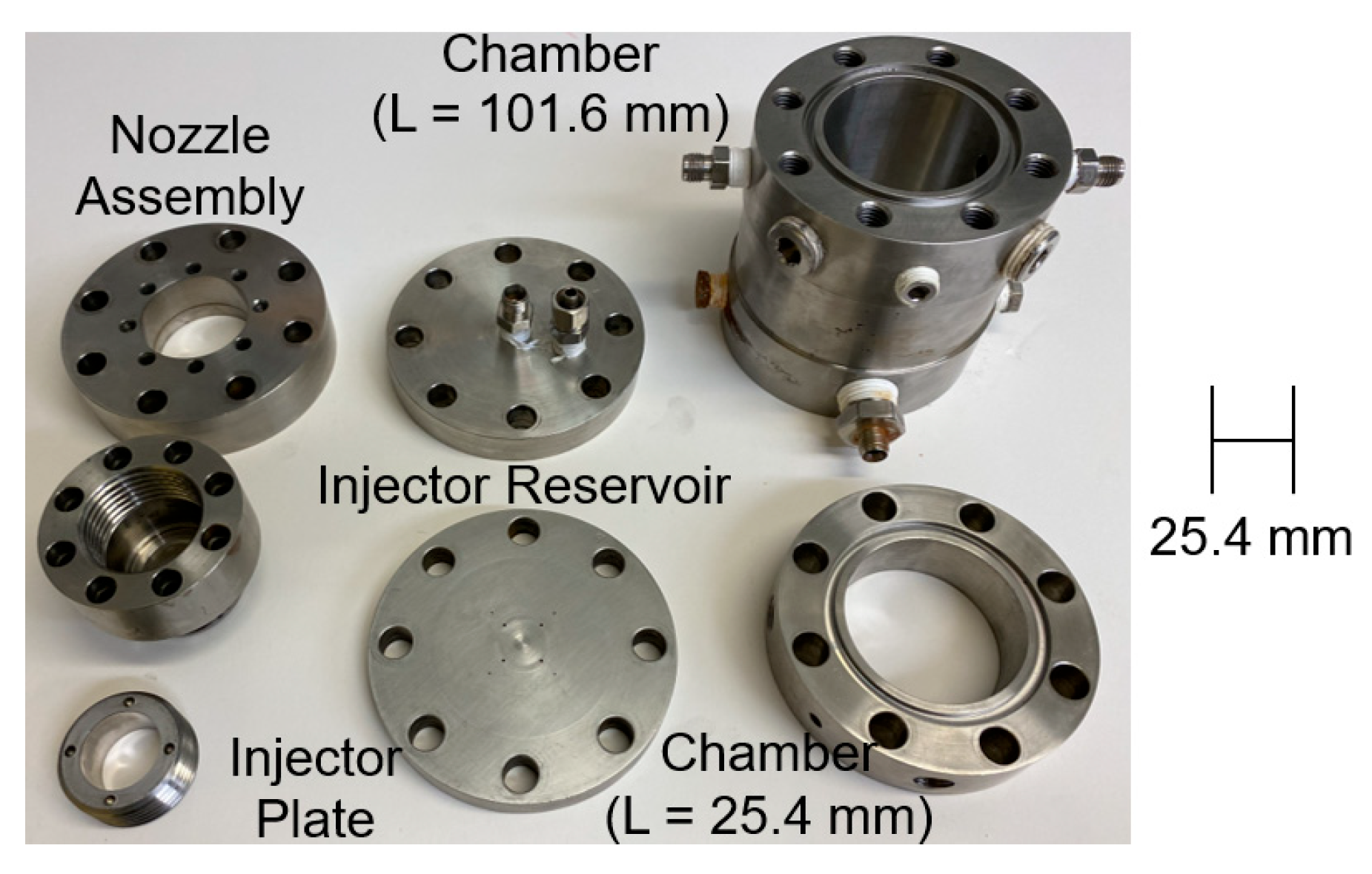


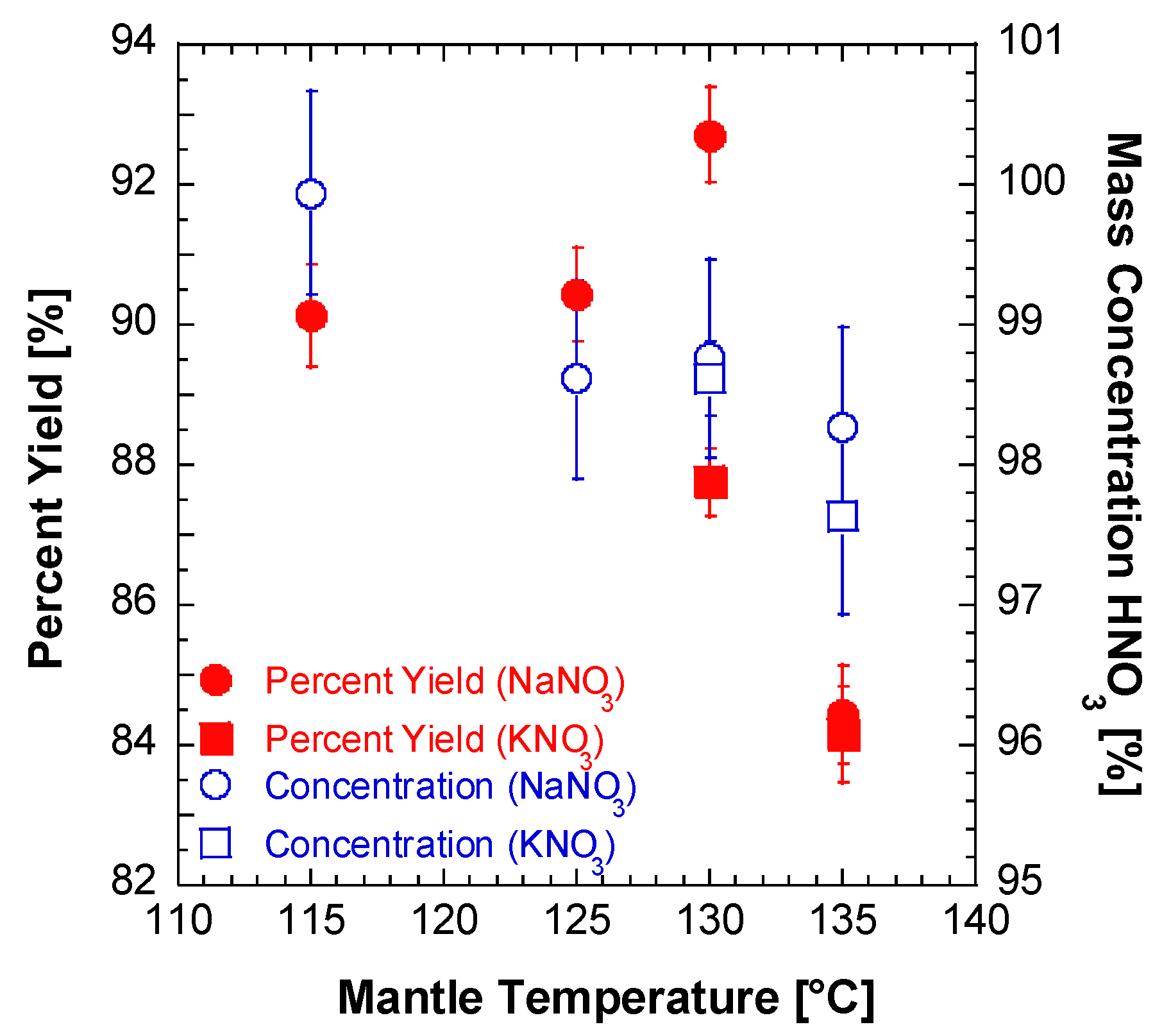
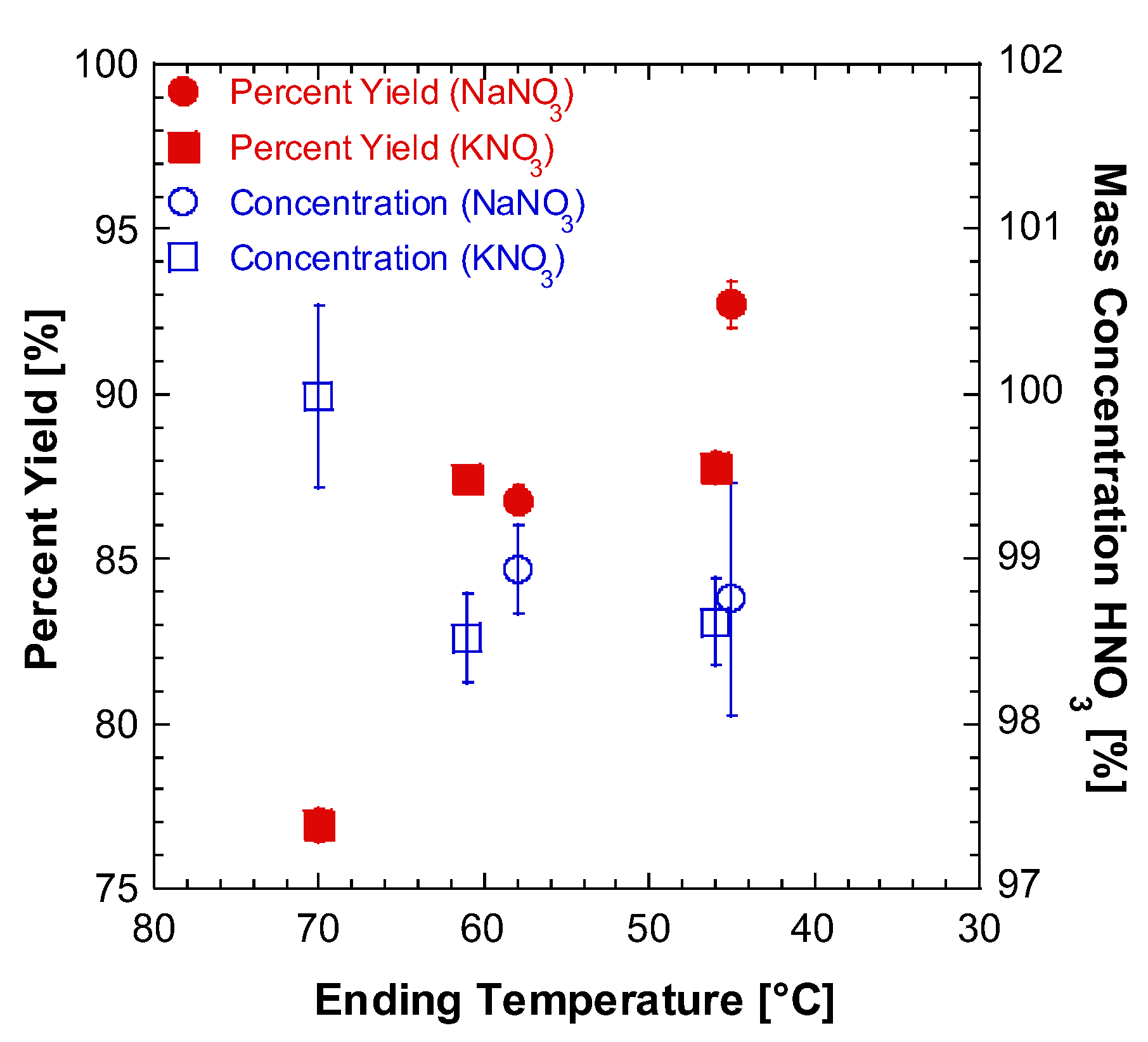
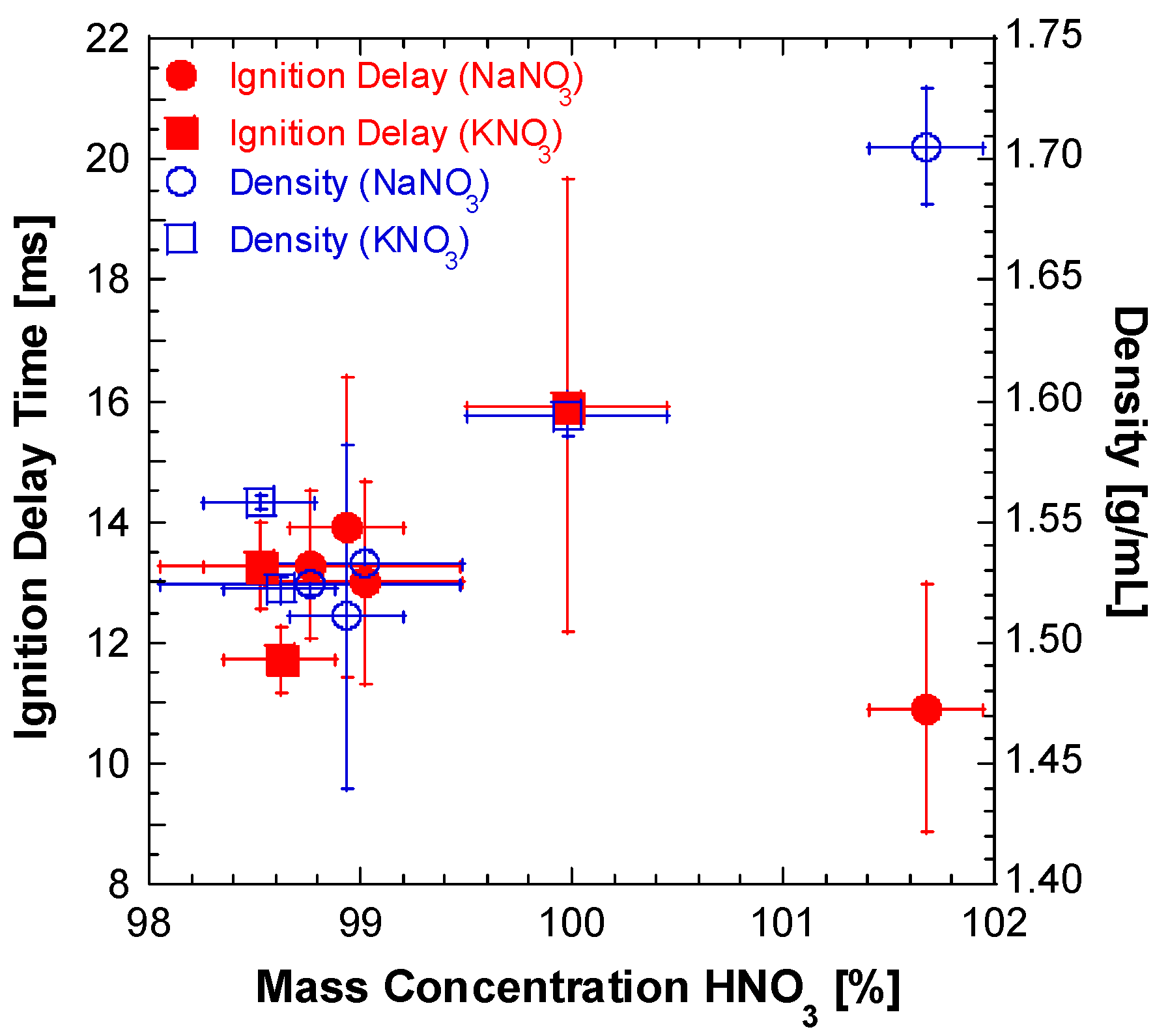



| Batch | mNO3 Salt [g] | VH2SO4 [mL] | Mantle Temp. [°C] | Stop Temp. [°C] | Distill Time [min] | myield [g] | Vyield [mL] | ρ [g/mL] | Percent Yield [%] | Ignition Delay [ms] | ±Ign. Delay Standard Deviation [ms] | wt./wt. Conc. [%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 85.010 | 70 | 130 | --- | 180 | 51.57 | 33.00 | 1.513 | 75.97 | 27.56 | 2.229 | 92.11 |
| 2 | 85.000 | 70 | 130 | 58.0 | 63 | 54.85 | 36.30 | 1.511 | 86.80 | 13.92 | 2.484 | 98.94 |
| 3 | 170.000 | 140 | 120 | 60.0 | 271 | 72.05 | 47.00 | 1.533 | 57.06 | 13.00 | 1.673 | 99.02 |
| 4 | 166.660 | 140 | 85 | 48.0 | 171 | 22.16 | 13.00 | 1.705 | 18.38 | 10.92 | 2.050 | 101.67 |
| 5 | 85.004 | 70 | 130 | 70.0 | 63 | 40.64 | 25.50 | 1.594 | 76.93 | 15.92 | 3.741 | 99.98 |
| 6 | 85.039 | 70 | 130 | 46.0 | 107 | 47.02 | 30.89 | 1.522 | 87.76 | 11.72 | 0.546 | 98.62 |
| 7 | 170.102 | 140 | 130 | 61.0 | 127 | 93.79 | 60.20 | 1.558 | 87.42 | 13.28 | 0.711 | 98.52 |
| 8 | 170.316 | 140 | 130 | 45.0 | 104 | 117.60 | 76.00 | 1.547 | 92.72 | 13.28 | 1.230 | 98.76 |
| 9 | 101.098 | 70 | 135 | 45.0 | 118 | 54.15 | 34.20 | 1.583 | 84.16 | 16.52 | 2.145 | 97.63 |
| 10 | 170.022 | 140 | 125 | 45.0 | 140 | 114.68 | 74.00 | 1.550 | 90.44 | 14.00 | 1.351 | 98.61 |
| 11 | 85.000 | 70 | 105 | 38.0 | 187 | 23.74 | 15.19 | 1.563 | 27.44 | 14.56 | 0.941 | 72.25 |
| 12 | 85.025 | 72 | 135 | 45.0 | 80 | 53.73 | 35.00 | 1.535 | 84.44 | 14.32 | 1.557 | 98.27 |
| 13 | 340.484 | 290 | 130 | 64.0 | 221 | 223.80 | 148.00 | 1.512 | 89.08 | 14.08 | 1.510 | 99.67 |
| 14 | 85.036 | 70 | 115 | 45.0 | 65 | 56.41 | 31.00 | 1.529 | 90.14 | 15.96 | 0.528 | 99.94 |
| Test | Injector Design | PC [MPa] | Total Flow [g/s] | F [N] | ϕ | ηc* [%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | UD #1 | 1.04 | 65.72 | - | 1.15 | 71.1 |
| 9 | UD #1 | 0.98 | 91.86 | 51.52 | 0.92 | 49.3 |
| 19 | UD #2 | 0.90 | 50.76 | 49.22 | 1.21 | 79.7 |
| 20 | UD #2 | 0.92 | 60.37 | 61.31 | 0.90 | 71.0 |
| 23 | TST | 0.81 | 77.53 | 51.60 | 0.96 | 48.0 |
| 24 | TST | 0.84 | 86.60 | 53.73 | 0.77 | 46.9 |
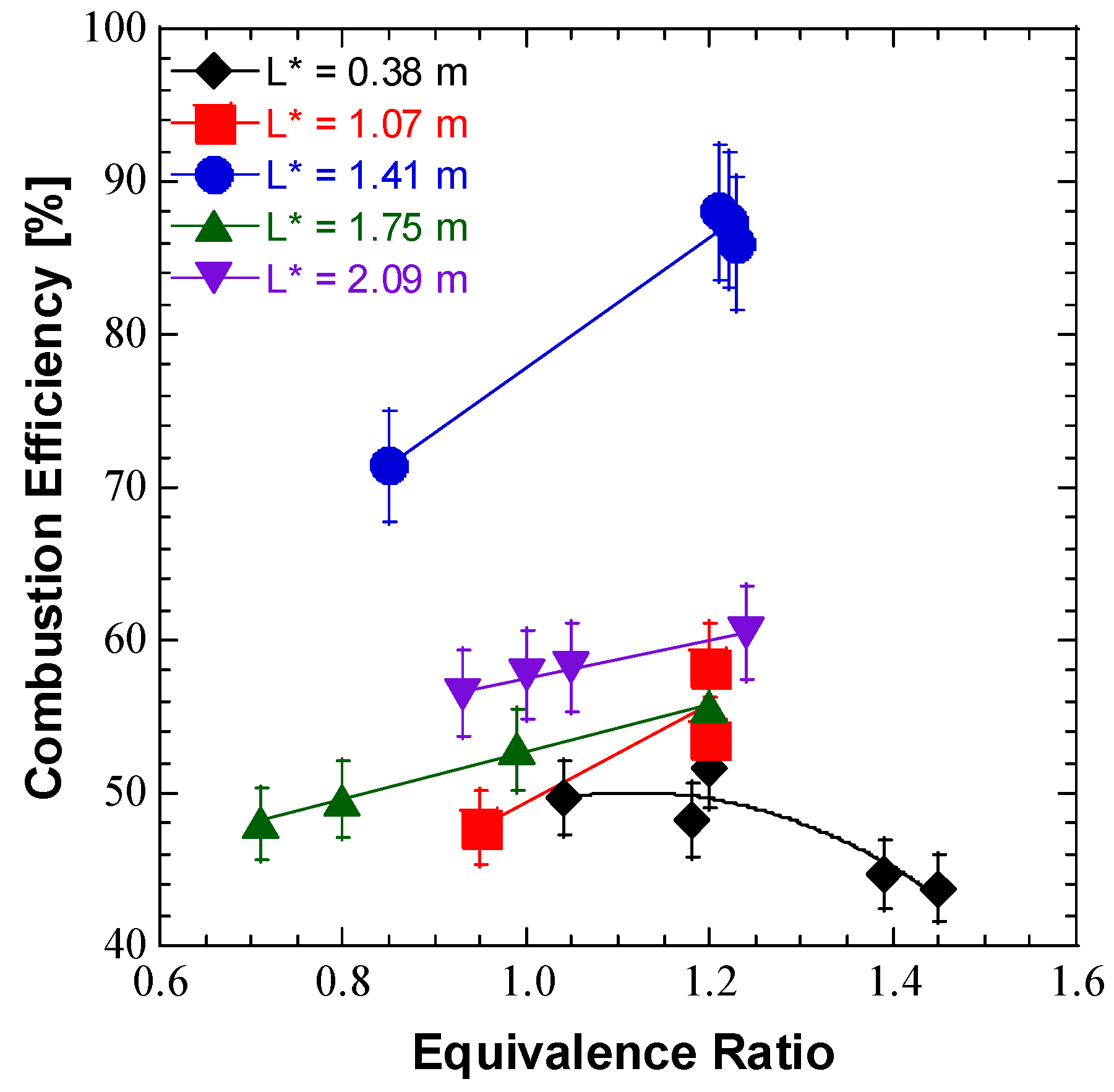
| Test | Injector Design | L* [m] | PC [MPa] | Total Flow [g/s] | F [N] | ϕ | ηc* [%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 27 | UD #1 | 0.38 | 0.84 | 88.36 | 36.35 | 1.45 | 43.8 |
| 28 | UD #1 | 0.38 | 0.88 | 89.93 | 37.03 | 1.39 | 44.7 |
| 29 | UD #1 | 0.38 | 0.85 | 80.49 | 35.98 | 1.18 | 48.2 |
| 30 | UD #1 | 0.38 | 0.94 | 87.58 | 43.89 | 1.04 | 49.7 |
| 31 | UD #1 | 0.38 | 0.97 | 85.55 | 47.41 | 1.20 | 51.6 |
| 32 | UD #1 | 1.41 | 0.97 | 51.50 | - | 1.23 | 86.0 |
| 33 | UD #1 | 1.41 | 0.97 | 50.44 | - | 1.22 | 87.5 |
| 34 | UD #1 | 1.41 | 0.96 | 50.19 | 34.79 | 1.21 | 88.0 |
| 35 | UD #1 | 1.41 | 0.96 | 65.02 | 41.90 | 0.85 | 71.4 |
| 37 | UD #1 | 1.07 | 0.85 | 73.83 | 29.69 | 1.20 | 53.6 |
| 38 | UD #1 | 1.07 | 0.86 | 70.17 | 31.01 | 1.20 | 58.2 |
| 39 | UD #1 | 1.07 | 0.86 | 85.07 | 30.73 | 0.95 | 47.8 |
| 40 | UD #1 | 2.09 | 0.88 | 66.18 | 65.64 | 1.24 | 60.5 |
| 41 | UD #1 | 2.09 | 0.89 | 70.94 | 66.69 | 1.05 | 58.2 |
| 42 | UD #1 | 2.09 | 0.91 | 72.91 | 68.60 | 1.00 | 57.7 |
| 43 | UD #1 | 2.09 | 0.91 | 76.26 | 67.14 | 0.93 | 56.5 |
| 45 | UD #1 | 1.75 | 0.86 | 70.10 | 75.59 | 1.20 | 55.6 |
| 46 | UD #1 | 1.75 | 0.88 | 77.50 | 77.86 | 0.99 | 52.9 |
| 47 | UD #1 | 1.75 | 0.89 | 87.81 | 78.53 | 0.80 | 49.6 |
| 48 | UD #1 | 1.75 | 0.90 | 94.98 | 79.15 | 0.71 | 48.0 |
| 49 | UD #2 | 1.41 | 0.82 | 59.16 | 86.49 | 1.40 | 63.5 |
| 50 | UD #2 | 1.41 | 0.85 | 60.46 | 89.47 | 1.12 | 64.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hollingshead, J.M.; Ianuzzi, M.L.L.; Moore, J.D.; Risha, G.A. Evaluation of N,N,N′,N′-Tetramethylethylenediamine (TMEDA) as an Alternative Fuel for a Hypergolic Bipropellant Rocket Engine. Fuels 2025, 6, 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/fuels6030058
Hollingshead JM, Ianuzzi MLL, Moore JD, Risha GA. Evaluation of N,N,N′,N′-Tetramethylethylenediamine (TMEDA) as an Alternative Fuel for a Hypergolic Bipropellant Rocket Engine. Fuels. 2025; 6(3):58. https://doi.org/10.3390/fuels6030058
Chicago/Turabian StyleHollingshead, Joshua M., Makayla L. L. Ianuzzi, Jeffrey D. Moore, and Grant A. Risha. 2025. "Evaluation of N,N,N′,N′-Tetramethylethylenediamine (TMEDA) as an Alternative Fuel for a Hypergolic Bipropellant Rocket Engine" Fuels 6, no. 3: 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/fuels6030058
APA StyleHollingshead, J. M., Ianuzzi, M. L. L., Moore, J. D., & Risha, G. A. (2025). Evaluation of N,N,N′,N′-Tetramethylethylenediamine (TMEDA) as an Alternative Fuel for a Hypergolic Bipropellant Rocket Engine. Fuels, 6(3), 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/fuels6030058







