Abstract
X-linked hypophosphatemia (XLH) is the most common genetic form of rickets and osteomalacia and is characterized by growth retardation, deformities of the lower limbs, and bone and muscular pain. Spontaneous dental abscesses caused by endodontic infections due to dentin dysplasia are well-known dental manifestations. When dentin affected by microcracks or attrition of the enamel is exposed to oral fluids, oral bacteria are able to invade the hypomineralized dentin and pulp space, leading to pulp necrosis, followed by the formation of a periapical gingival abscess. Without appropriate dental management, this dental manifestation results in early loss of teeth and deterioration in the patient’s quality of life. Early specific dental intervention and oral management in collaboration with medical personnel are strongly recommended for XLH patients. Importantly, dental manifestations sometimes appear before the diagnosis of XLH. Dentists should be alert for this first sign of XLH and refer affected children to a pediatrician for early diagnosis. A humanized monoclonal antibody for FGF23 (burosumab) is a promising new treatment for XLH; however, the effects on the dental manifestations remain to be elucidated. The establishment of fundamental dental therapy to solve dental problems is still underway and is eagerly anticipated.
1. Introduction
X-linked hypophosphatemia (XLH; OMIM# 307800) is the most common genetic form of rickets and osteomalacia and is characterized by growth retardation, deformities of the lower limbs, and bone and muscular pain [1,2,3]. Sequence variations in the phosphate regulating endopeptidase homolog X-linked (PHEX) gene lead to overproduction of fibroblast growth factor 23 (FGF23), resulting in renal phosphate wasting and impaired skeletal mineralization [4]. The incidence of XLH is estimated to be approximately 1 in 20,000 [5].
Spontaneous dental abscesses caused by endodontic infections due to dentin dysplasia are well-known dental manifestations [6,7,8]. Without appropriate dental management, this dental manifestation of XLH finally results in early loss of teeth and reduced quality of life [9,10]. Early specific dental intervention and ongoing oral management in collaboration with medical professionals are strongly recommended for XLH patients [9,11]. Moreover, this dental manifestation sometimes appears before the diagnosis of XLH [12,13,14]; dentists should be aware of this first sign of XLH and refer affected children to a pediatrician for early diagnosis.
A combination of active vitamin D and phosphate salts is the conventional medical therapy for patients with XLH [15,16]. A humanized monoclonal antibody for FGF23 (burosumab) is a new and promising treatment for XLH [15,16,17].
This review summarizes the manifestations and management of XLH from a dental perspective.
2. Dental Manifestations of XLH
Harris and Sullivan first described dental findings in 1960, after XLH was first reported in 1930 [18]. XLH is caused by loss-of-function sequence variations in PHEX [1,2,3]. PHEX sequence variations cause hypophosphatemia indirectly, through the increased expression of FGF23 [4]. A high serum FGF23 concentration impairs renal phosphate reabsorption, thereby increasing phosphate excretion. FGF23 also decreases phosphate absorption in the intestine by suppressing serum 1,25-dyhydroxyvitamin D [1,25(OH)2D] levels. The lack of phosphate leads to a mineralization defect of bone and teeth [7,8,19,20]. PHEX protein is also expressed in osteoblasts, osteocytes, and odontoblasts in addition to the kidney [19]. PHEX has been proposed to dynamically regulate FGF-23 expression in bone and teeth [20]. The hard mineralized tissue of teeth is composed of enamel, dentin, and cementum [21], and is supported by alveolar bone. Dentin is produced by the mineralization of the organic matrix synthesized and secreted by odontoblasts [22]. Inorganic phosphate and calcium are essential for the mineralization of teeth and bone. Abnormal mineralization of dentin is the main cause of dental problems in XLH patients [23,24,25,26,27,28].
A spontaneous formation of a periapical gingival abscess or fistula around a visibly healthy tooth with no evidence of dental caries or trauma is a typical dental manifestation of XLH (Figure 1) [6,7,8]. Owing to microcracks or attrition of the enamel, dentin is exposed to the bacteria abundant in the oral cavity, which invade the hypomineralized dentin and pulp space leading to pulp necrosis and periapical gingival abscess formation (Figure 2) [6,7,8]. Abscess formation is more commonly found in primary teeth than in permanent teeth [6], possibly because the enamel of primary teeth is half as thick as that of permanent teeth, and less hard, so the dentin is more easily exposed [29,30]. The frequency of occurrence of dental abscesses in children with XLH is reported to range from 25% to 70% [6,19,31,32,33]. Primary incisors are affected more often than canines, and first and second molars are occasionally involved [6,9]. Teeth in the mandible and maxilla are equally likely to develop an abscess [31]. For XLH, the different expression in the two sexes is not as well-established. The features of XLH are the same in males and females [34]. On the other hand, some reports indicate that XLH is an X-linked dominant disorder and symptoms are mediated by lyonization, and dental manifestations are more severe in male than female individuals, as they also are in bone [7,31]. The dental phenotype is associated with the severity of the disease [35]. The younger the patient when the first abscess appears, the more severe the dental manifestations [13]. An abscess on one tooth indicates that at least one other tooth is likely to be affected [31].
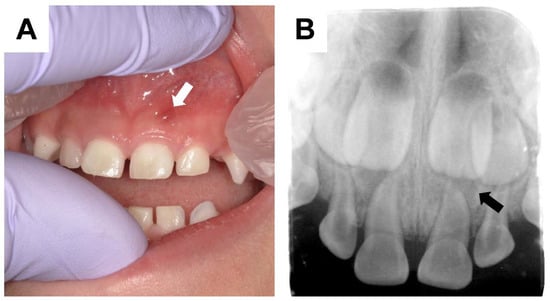
Figure 1.
Clinical and radiographic dental manifestations of X-linked hypophosphatemia (XLH). (A) Oral photograph of male patient aged 4 years 4 months showing a periapical gingival abscess (white arrow) corresponding to the primary maxillary left central incisor. (B) Periapical radiograph showing radiolucency (black arrow) around the periapical region of the primary maxillary left central incisor.
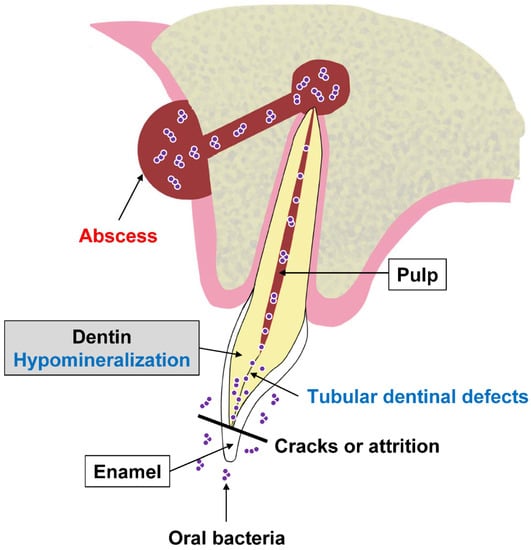
Figure 2.
Illustration of the mechanism of gingival abscess formation in a tooth of an X-linked hypophosphatemia (XLH) patient.
The principal dental defects are seen in dentin both radiographically and histologically. Prominent pulp horns, a large pulp chamber suggesting taurodontism, and thin dentin are recognized radiographically (Figure 3) [6,7,8,13]. A wide predentin layer (the first layer of the non-mineralized matrix), interglobular dentin, and tubular dentinal defects extending from the pulp to the enamel are detected histologically (Figure 4) [6,23,24,25]. The pulp color can sometimes be observed on the lingual side of the primary incisors due to the thin dentin (Figure 5) [14]. Additionally, an absence of secondary dentin formation in the wall of the pulp chamber after root formation has been reported [36].
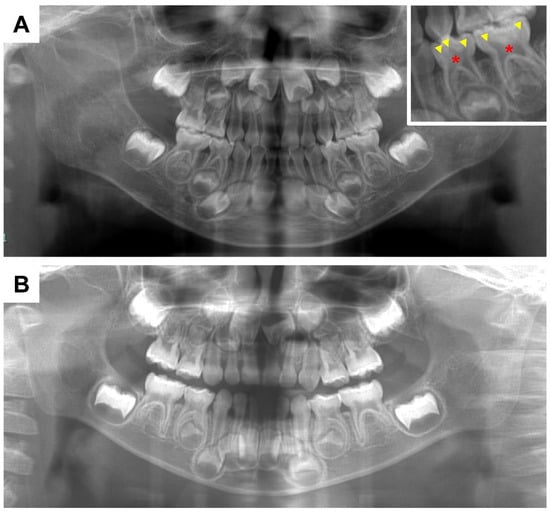
Figure 3.
Panoramic radiographs. (A) Female X-linked hypophosphatemia (XLH) patient aged 3 years 11 months. The square on the upper right is an enlargement of the primary mandibular left molar region. Wide pulp chambers (asterisks) and prominent pulp horns (arrowheads) can be seen. (B) Healthy age-matched female.
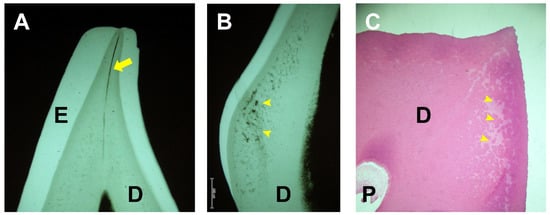
Figure 4.
(A) Contact microradiograph of a ground section of a primary tooth of a patient with X-linked hypophosphatemia (XLH) showing a tubular defect from the enamel–dentin junction to the pulp (arrow). (B) Contact microradiograph of a ground section of a primary tooth of a patient with XLH showing interglobular dentin (arrowheads). (C) Histopathological image of a decalcified section of a permanent tooth of a patient with XLH aged 20 years (H-E staining) showing interglobular dentin (arrowheads). E: enamel; D: dentin; P: pulp.
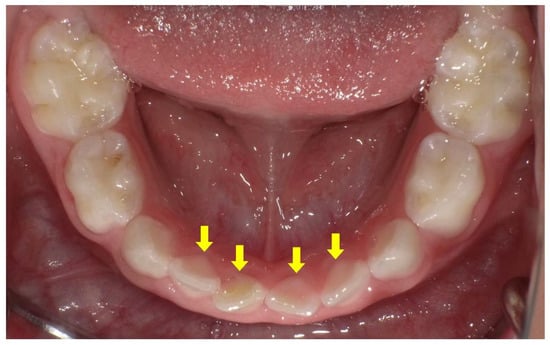
Figure 5.
Intraoral photograph of the mandibular arch of a male X-linked hypophosphatemia (XLH) patient aged 3 years 3 months. The pink color of the pulp can be seen through the enamel on the lingual side of the primary mandibular incisors (arrows).
The dentin defects found in XLH patients are sometimes accompanied by a thinner layer of enamel [8], although the structure of enamel is normal [7,26]. The thin enamel tends to wear faster and expose the poorly mineralized dentin, leading to pulpal infection [7]. Additionally, delayed eruption, short roots, root resorption, a poorly defined lamina dura, and a hypoplastic alveolar ridge were recognized in a patient with XLH [7]. Whether caries activity is higher in children with XLH compared with healthy subjects is unknown; however, caries progresses easily via the thin enamel and poorly mineralized dentin [7]. Children with XLH often present with delayed dental development, abnormal eruption patterns, and increased frequency of specific malocclusions (Figure 6). An open bite or impacted or ectopic eruption of maxillary canines due to delayed maxillary growth in relation to mandibular growth has been reported [37,38,39].
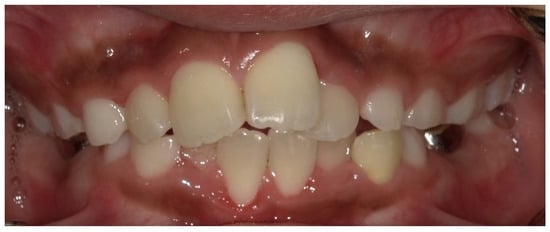
Figure 6.
Crowding in the anterior region of a male X-linked hypophosphatemia (XLH) patient aged 10 years 1 month.
Endodontic infections due to poor dentin mineralization are also recognized in permanent teeth [40] (Figure 7). However, maxillofacial cellulitis is rare in adults with XLH [8]. Endodontically affected teeth are common in XLH patients, and the number of affected teeth increases significantly with age [41]. More than 60% of adults with XLH have experienced more than five dental abscesses [42]. The most commonly affected teeth are incisors and canines, followed by molars and premolars [41]. The order in which teeth are affected is determined not only by the time of eruption but also by the rate of natural attrition as a result of mastication [7]. High prevalence and severity of periodontitis are often recognized in adult patients with XLH [43]. Nearly 80% of adult XLH patients are reported to have moderate or severe periodontitis [44]. Periodontitis is a major cause of tooth loss in adults with XLH [8].
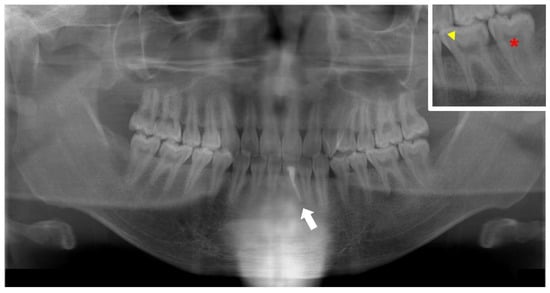
Figure 7.
Panoramic radiograph of the permanent dentition of a male X-linked hypophosphatemia (XLH) patient aged 21 years who underwent root canal treatment of the mandibular left central incisor associated with a cystic swelling (arrow). The square on the upper right is an enlargement of the primary mandibular left molar region. Wide pulp chambers (asterisks) and prominent pulp horns (arrowheads) can be seen.
3. Oral Management of XLH
There is no fundamental treatment for dentin dysplasia in XLH. Early detection and management of pulp infection improve the prognosis of the tooth [7,8]. Short-term periodical dental check-ups are required for XLH patients [19,45,46,47]. The consensus statement of XLH recommends twice-yearly dentist visits [2]. The principle of dental management in XLH patients is to preserve pulp vitality [7]. Professional tooth cleaning, application of topical fluoride, and fissure sealing are recommended [7,13,19,33,45]. Pit and fissure sealing of the enamel is effective in preventing the invasion of oral bacteria [7,8,13,19,45]. Exposed dentin due to attrition or cracking of the enamel should be repaired as soon as possible [14]. The bonding strength of adhesive composite restorations is assumed to be reduced due to mineralization defects in the dentin. Prolonged etching times or a total etch system increases the risk of pulp irritation; therefore, a self-etch system is recommended [13,45].
The crucial purpose of oral management of XLH is to protect vital pulp from being infected by oral bacteria. The vitality of the tooth should be carefully monitored [7]. Early coronal restoration of teeth at high risk is strongly recommended, especially in patients who are diagnosed early with many abscesses [35]. Composite resin crowns in the anterior region, stainless steel crowns for primary teeth and immature permanent teeth, and permanent crowns for permanent teeth in the posterior region are recommended [35,48,49]. Full ceramic crowns should be avoided because of the extensive tooth reduction required when compared with metal crowns [7]. Large pulp chambers and prominent pulp horns should be considered during the preparation of the tooth to prevent exposure or irritation of the pulp [7,13].
When apical periodontitis is detected, a periapical radiograph is taken, and the dentist must decide whether to perform endodontic treatment or extract the tooth. Systemic antibiotics are used in cases of acute abscess [8]. Primary teeth play an important role as space maintainers for permanent successors, and dentists should preserve them for as long as possible until replacement [50]. Early extraction before replacement leads to loss of space for the eruption of permanent teeth [50]. Space maintenance is necessary after the extraction of primary teeth before replacement [50]. Obturation of the root canal system in XLH patients should aim to fill any voids to achieve maximal density, due to the increased risk of reinfection of the root canal because of dentin dysplasia [7]. The use of thermoplasticized techniques using a virtually insoluble sealer is recommended for permanent teeth [7]. Working length should be determined accurately, taking into account the short roots commonly found in XLH patients [7]. In contrast, for primary teeth, the use of calcium hydroxide and iodoform (Ca(OH)2/iodoform), which are absorbed during root resorption, is recommended [51]. Additionally, for permanent teeth undergoing root formation, Ca(OH)2 or mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA) is recommended before obturation to promote apexification [7,52,53].
Once the pulp starts to become necrotic, the blood supply stops, and the devitalized tooth tends to break down [54]. Teeth with broken roots are indicated for extraction [55]. Prosthetic crowns are necessary for teeth that have undergone root canal treatment (Figure 8). The thin dentin perforates easily and does not support restorative posts for prosthetic crowns in permanent teeth [7,13]. The application of posts in the roots should be avoided to prevent root fracture [7,13].
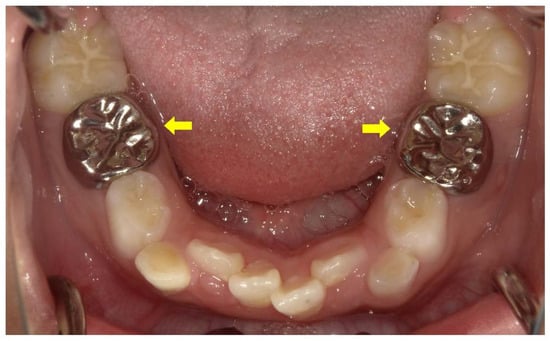
Figure 8.
Treatment of a male X-linked hypophosphatemia (XLH) patient aged 8 years 3 months involved full coverage of the primary mandibular second molars with stainless steel crowns (arrows) after root canal treatment associated with a cystic swelling.
There is no established orthodontic treatment for XLH patients [56]. Traumatic orthodontic forces sometimes cause pulp necrosis [46]. It is important to prevent traumatic forces during orthodontic treatment of XLH patients. Orthodontic treatment involves the movement of teeth and extensive remodeling of the alveolar bone [8]. This treatment sometimes results in the loss of permanent teeth in XLH patients with uncontrolled rickets of the jaw [57]. Optimizing conventional medical treatment of XLH is considered mandatory before the initiation of orthodontic treatment [2,8]. A longer period of retention and observation is necessary in cases with abnormal bone remodeling to confirm the stability of the resulting occlusion [58]. The high frequency of permanent tooth loss secondary to endodontic infections or periodontitis often leads to the need for dental implants [2]. Several reports have described cases of XLH patients who have had dental implants [46,59]. Standard surgical protocols in adults with XLH who are not receiving conventional therapy resulted in a decreased success rate compared with healthy control individuals [2]. Some studies reported that the interruption of conventional therapy in XLH may have a negative influence on bone healing around implants [8]. Dental implant surgery should be performed after 3–6 months of medical treatment, which should be continued for 6 months following the implant surgery [2]. The healing time should be extended up to 6 months [2].
4. Dental Effects of Conventional Therapy or Burosumab in XLH
The conventional medical therapy of XLH has consisted of oral phosphate and active vitamin D supplementation [15,16]. However, this therapy has certain limitations related to efficacy and safety [15]. A humanized monoclonal antibody for FGF23 (burosumab) was recently approved as a promising treatment for XLH [15,16,17].
Early intervention with conventional therapy is reported to have a beneficial effect on dental status [60,61,62,63,64,65,66]. The missing and filled teeth index of patients treated since early childhood is similar to that of the healthy, age-matched controls [62]. This therapy improves dentin mineralization and formation, reducing the size of the dental pulp canal and chamber in both the primary and permanent dentitions [8,62]. Dentin mineralization of permanent teeth especially, which mineralize after birth, can be restored by the treatment [65]. The primary dentition usually shows more severe symptoms than the permanent dentition [64]. This can also be explained by the low levels of calcium and phosphorus during odontogenesis of the primary dentition [64]. However, this therapy cannot completely eliminate dentin dysplasia [67]. Remaining defects may result from the early exposure of odontoblasts and the surrounding osteoblasts to hypophosphatemia before the commencement of conventional therapy, and from intrinsic cell disturbances linked to the genetic alteration [62]. Additionally, unlike bone, dentin is not remodeled and is not involved in the regulation of calcium and phosphate metabolism [22]. The effects of burosumab on the dentition of XLH patients has not yet been reported. A post hoc analysis of a 64-week, open-label, randomized controlled study of 61 children with XLH aged 1–12 years revealed that dental abscesses occurred in 3 of 12 (25%) younger (<5 years) children in the conventional therapy group, while 0 of 20 (0%) younger children from the burosumab group developed dental abscesses [68]. However, in older children (5–12 years) with XLH, dental abscesses presented more frequently with burosumab (8/15, 53%) than with conventional therapy (0/20, 0%). Dental caries, which were reported more frequently in the burosumab group (9/29, 31%) than the conventional therapy group (2/32, 6%), occurred slightly more often in older than younger children who received conventional therapy (2/20, 10% vs. 0/12, 0%), and slightly more often in younger than older children who received burosumab (5/14, 36% vs. 4/15, 27%). On the basis of the results of this study, the protective effects of burosumab seem to be weaker, or at least not more intense, against the development of dental abscesses compared with conventional therapy; however, a longer duration study is needed.
5. Importance of Medical and Dental Collaboration in XLH
Without appropriate dental management, spontaneous periapical gingival abscess formation in XLH patients finally leads to early loss of teeth and a reduced quality of life [10,32]. Early oral management soon after diagnosis and follow-up throughout life by dentists are recommended for XLH patients [19,45,46,47]. There is a need for a system in which medical doctors explain the importance of oral care to parents of children with XLH and ensure they find appropriate dental care [2]. The alveolar bone status is particularly important when XLH patients receive orthodontic treatment or dental implants [2]. Dentists should consult with the patient’s medical doctor about the status of rickets control with medical treatment [2,8].
Primary incisors emerge into the oral cavity at around 6 months of age, and the primary dentition is complete by the age of 2 years [69]. Most XLH patients are diagnosed at approximately 1–2 years of age when their delayed walking or bowed legs are observed by pediatricians [3,70]. Spontaneous periapical abscesses sometimes lead to an XLH diagnosis [12,13,14]. Pediatric dentists must never overlook dental abscesses in teeth that appear to be intact. A system should be established by which dentists can immediately refer patients to pediatricians when this first dental sign of XLH is observed.
6. Conclusions
Renal phosphate wasting in XLH leads to a mineralization defect of teeth, but not bone [1,2,3]. The main dental manifestations are periapical gingival abscesses, which are derived from endodontic infections caused by poorly mineralized dentin [6,7,8]. Medical and dental collaboration is important in the treatment of XLH, and dental symptoms should be followed-up as the patient ages [1,2,3,8,9]. The establishment of fundamental dental therapy to treat dental manifestations is still underway and is eagerly anticipated.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Written informed consent has been obtained from the parents of patients or patients to publish the accompanying images.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Carpenter, T.O.; Imel, E.A.; Holm, I.A.; Jan de Beur, S.M.; Insogna, K.L. A clinician’s guide to X-linked hypophosphatemia. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2011, 26, 1381–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haffner, D.; Emma, F.; Eastwood, D.M.; Duplan, M.B.; Bacchetta, J.; Schnabel, D.; Wicart, P.; Bockenhauer, D.; Santos, F.; Levtchenko, E.; et al. Clinical practice recommendations for the diagnosis and management of X-linked hypophosphataemia. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2019, 15, 435–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahir, K.; Roberts, M.S.; Krolczyk, S.; Simmons, J.H. X-Linked Hypophosphatemia: A New Era in Management. J. Endocr. Soc. 2020, 4, bvaa151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakanishi, T.; Michigami, T. Pathogenesis of FGF23-Related Hypophosphatemic Diseases Including X-linked Hypophosphatemia. Endocrines 2022, 3, 303–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo, I.; Fukumoto, S.; Ozono, K.; Namba, N.; Inoue, D.; Okazaki, R.; Yamauchi, M.; Sugimoto, T.; Minagawa, M.; Michigami, T.; et al. Nationwide survey of fibroblast growth factor 23 (FGF23)-related hypophosphatemic diseases in Japan: Prevalence, biochemical data and treatment. Endocr. J. 2015, 62, 811–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, J.R.; Gelbier, M.J.; Bennett, J.H.; Winter, G.B. Dental problems associated with hypophosphataemic vitamin D resistant rickets. Int. J. Paediatr. Dent. 1998, 8, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabandal, M.M.; Robotta, P.; Bürklein, S.; Schäfer, E. Review of the dental implications of X-linked hypophosphataemic rickets (XLHR). Clin. Oral Investig. 2015, 19, 759–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duplan, M.B.; Norcy, E.L.; Courson, F.; Chaussain, C. Dental and periodontal features and management in XLH children and adults. Int. J. Bone Frag. 2021, 1, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baroncelli, G.I.; Mora, S. X-Linked Hypophosphatemic Rickets: Multisystemic Disorder in Children Requiring Multidisciplinary Management. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 688309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, C.; Celestin, E.; Chambolle, D.; Linglart, A.; Biosse Duplan, M.; Chaussain, C.; Friedlander, L. Oral health-related quality of life in patients with X-linked hypophosphatemia: A qualitative exploration. Endocr. Connect. 2022, 11, e210564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trombetti, A.; Al-Daghri, N.; Brandi, M.L.; Cannata-Andía, J.B.; Cavalier, E.; Chandran, M.; Chaussain, C.; Cipullo, L.; Cooper, C.; Haffner, D.; et al. Interdisciplinary management of FGF23-related phosphate wasting syndromes: A Consensus Statement on the evaluation, diagnosis and care of patients with X-linked hypophosphataemia. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2022, 18, 366–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Archard, H.O.; Witkop, C.J. Hereditary hypophosphatemia (vitamin D-resistant rickets) presenting primary dental manifestations. Oral Surg. 1966, 22, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batra, P.; Tejani, Z.; Mars, M. X-linked hypophosphatemia: Dental and histologic findings. J. Can. Dent. Assoc. 2006, 72, 69–72. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wato, K.; Okawa, R.; Matayoshi, S.; Ogaya, Y.; Nomura, R.; Nakano, K. X-linked hypophosphatemia diagnosed after identification of dental symptoms. Ped. Dent. J. 2020, 30, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinoshita, Y.; Fukumoto, S. X-Linked Hypophosphatemia and FGF23-Related Hypophosphatemic Diseases: Prospect for New Treatment. Endocr. Rev. 2018, 39, 274–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajima, T.; Hasegawa, Y. Treatment of X-Linked Hypophosphatemia in Children. Endocrines 2022, 3, 522–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukumoto, S. FGF23-related hypophosphatemic rickets/osteomalacia: Diagnosis and new treatment. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2021, 66, R57–R65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, R.; Sullivan, H.R. Dental Sequelae in Deciduous Dentition in Vitamin D Resistant Rickets. Aust. Dent. J. 1960, 5, 200–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baroncelli, G.I.; Angiolini, M.; Ninni, E.; Galli, V.; Saggese, R.; Giuca, M.R. Prevalence and pathogenesis of dental and periodontal lesions in children with X-linked hypophosphatemic rickets. Eur. J. Paediatr. Dent. 2006, 7, 61–66. [Google Scholar]
- Robinson, M.E.; AlQuorain, H.; Murshed, M.; Rauch, F. Mineralized tissues in hypophosphatemic rickets. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2020, 35, 1843–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavez, M.B.; Kramer, K.; Chu, E.Y.; Thumbigere-Math, V.; Foster, B.L. Insights into dental mineralization from three heritable mineralization disorders. J. Struct. Biol. 2020, 212, 107597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vital, S.O.; Gaucher, C.; Bardet, C.; Rowe, P.S.; George, A.; Linglart, A.; Chaussain, C. Tooth dentin defects reflect genetic disorders affecting bone mineralization. Bone 2012, 50, 989–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abe, K.; Ooshima, T.; Lily, T.S.; Yasufuku, Y.; Sobue, S. Structural deformities of deciduous teeth in patients with hypophosphatemic vitamin D-resistant rickets. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. 1988, 65, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, K.; Ooshima, T.; Sobue, S.; Moriwaki, Y. The crystallinity of human deciduous teeth in hypophosphataemic vitamin D-resistant rickets. Arch. Oral Biol. 1989, 34, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, K.; Ooshima, T.; Masatomi, Y.; Sobue, S.; Moriwaki, Y. Microscopic and crystallographic examinations of the teeth of the X-linked hypophosphatemic mouse. J. Dent. Res. 1989, 68, 1519–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, T.R.; Costa, F.W.; Soares, E.C.; Williams, J.R., Jr.; Fonteles, C.S. Enamel and dentin mineralization in familial hypophosphatemic rickets: A micro-CT study. Dentomaxillofac. Radiol. 2015, 44, 20140347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coyac, B.R.; Falgayrac, G.; Penel, G.; Schmitt, A.; Schinke, T.; Linglart, A.; McKee, M.D.; Chaussain, C.; Bardet, C. Impaired mineral quality in dentin in X-linked hypophosphatemia. Connect. Tissue Res. 2018, 59, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clayton, D.; Chavez, M.B.; Tan, M.H.; Kolli, T.N.; Giovani, P.A.; Hammersmith, K.J.; Bowden, S.A.; Foster, B.L. Mineralization Defects in the Primary Dentition Associated With X-Linked Hypophosphatemic Rickets. JBMR Plus 2021, 5, e10463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Menezes Oliveira, M.A.; Torres, C.P.; Gomes-Silva, J.M.; Chinelatti, M.A.; De Menezes, F.C.; Palma-Dibb, R.G.; Borsatto, M.C. Microstructure and mineral composition of dental enamel of permanent and deciduous teeth. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2010, 73, 572–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, A.K.; Sorvari, R.; Birkhed, D.; Meurman, J.H. Dental erosion in deciduous teeth—An in vivo and in vitro study. J. Dent. 2001, 29, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McWhorter, A.G.; Seale, N.S. Prevalence of dental abscess in a population of children with vitamin D-resistant rickets. Pediatr. Dent. 1991, 13, 91–96. [Google Scholar]
- Baroncelli, G.I.; Zampollo, E.; Manca, M.; Toschi, B.; Bertelloni, S.; Michelucci, A.; Isola, A.; Bulleri, A.; Peroni, D.; Giuca, M.R. Pulp chamber features, prevalence of abscesses, disease severity, and PHEX mutation in X-linked hypophosphatemic rickets. J. Bone Miner. Metab. 2021, 39, 212–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marin, A.; Morales, P.; Jiménez, M.; Borja, E.; Ivanovic-Zuvic, D.; Collins, M.T.; Florenzano, P. Characterization of Oral Health Status in Chilean Patients with X-Linked Hypophosphatemia. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2021, 109, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruppe, M.D. X-Linked Hypophosphatemia. GeneReviews®, 9 Feberuary 2012. University of Washington, Seattle, 1993–2022. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK83985/ (accessed on 13 April 2017).
- Seow, W.K.; Romaniuk, K.; Sclavos, S. Micromorphologic features of dentin in vitamin D-resistant rickets: Correlation with clinical grading of severity. Pediatr. Dent. 1989, 11, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rakocz, M.; Keating, J.; Johnson, R. Management of the primary dentition in vitamin D-resistant rickets. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. 1982, 54, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seow, W.K.; Needleman, H.L.; Holm, I.A. Effect of familial hypophosphatemic rickets on dental development: A controlled, longitudinal study. Pediatr. Dent. 1995, 17, 346–350. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Jundi, S.H.; Dabous, I.M.; Al-Jamal, G.A. Craniofacial morphology in patients with hypophosphataemic vitamin-D-resistant rickets: A cephalometric study. J. Oral Rehabil. 2009, 36, 483–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, M.A.; Junior, L.A.S.; Santos, M.A.; Vaisbich, M.H. Dental abnormalities and oral health in patients with Hypophosphatemic rickets. Clinics 2010, 65, 1023–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murayama, T.; Iwatsubo, R.; Akiyama, S.; Amano, A.; Morisaki, I. Familial hypophosphatemic vitamin D-resistant rickets: Dental findings and histologic study of teeth. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 2000, 90, 310–316. [Google Scholar]
- Andersen, M.G.; Beck-Nielsen, S.S.; Haubek, D.; Hintze, H.; Gjørup, H.; Poulsen, S. Periapical and endodontic status of permanent teeth in patients with hypophosphatemic rickets. J. Oral Rehabil. 2012, 39, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connor, J.; Olear, E.A.; Insogna, K.L.; Katz, L.; Baker, S.; Kaur, R.; Simpson, C.A.; Sterpka, J.; Dubrow, R.; Zhang, J.H.; et al. Conventional Therapy in Adults With X-Linked Hypophosphatemia: Effects on Enthesopathy and Dental Disease. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 100, 3625–3632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, L.; Liu, R.; White, N.; Alon, U.S.; Cobb, C.M. Periodontal status of patients with hypophosphatemic rickets: A case series. J. Periodontol. 2011, 82, 1530–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duplan, M.B.; Coyac, B.R.; Bardet, C.; Zadikian, C.; Rothenbuhler, A.; Kamenicky, P.; Briot, K.; Linglart, A.; Chaussain, C. Phosphate and Vitamin D Prevent Periodontitis in X-Linked Hypophosphatemia. J. Dent. Res. 2017, 96, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douyere, D.; Joseph, C.; Gaucher, C.; Chaussain, C.; Courson, F. Familial hypophosphatemic vitamin D-resistant rickets—Prevention of spontaneous dental abscesses on primary teeth: A case report. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 2009, 107, 525–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, B.N.; Jung, H.Y.; Chang, H.S.; Hwang, Y.C.; Hwang, I.N.; Oh, W.M. Dental management of patients with X-linked hypophosphatemia. Restor. Dent. Endod. 2017, 42, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akif, D.; Tuba, A.A.; Esra, E.; Tulga, Ö.F. Dental Management of Hypophosphatemic Vitamin D Resistant Rickets. J. Pediatr. Res. 2018, 5, 221–224. [Google Scholar]
- Breen, G.H. Prophylactic dental treatment for a patient with vitamin D-resistant rickets: Report of case. ASDC J. Dent. Child. 1986, 53, 38–43. [Google Scholar]
- Seow, W.K.; Latham, S.C. The spectrum of dental manifestations in vitamin D-resistant rickets: Implications for management. Pediatr. Dent. 1986, 8, 245–250. [Google Scholar]
- Laing, E.; Ashley, P.; Farhad, B.N.; Dalgit, S.G. Space maintenance. Int. J. Pediatr. Dent. 2009, 19, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortazavi, M.; Mesbahi, M. Comparison of zinc oxide and eugenol, and Vitapex for root canal treatment of necrotic primary teeth. Int. J. Pediatr. Dent. 2004, 14, 417–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S. Ca(OH)2 apexification of pulp necroses of the permanent incisors in a case of X-linked hypophosphataemic rickets—The 60-month check-up: A case report. Ped. Dent. J. 2021, 31, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, H.; Dutta, A.; Philpott, R. Presentation and non-surgical endodontic treatment of two patients with X-linked hypophosphatemia: A case report. Int. Endod. J. 2021, 54, 1403–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosen, E.; Beitlitum, I.; Tsesis, I. The preservation of teeth with root-originated fractures. Evid. Based Endod. 2018, 3, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshino, K.; Ito, K.; Kuroda, M.; Sugihara, N. Prevalence of vertical root fracture as the reason for tooth extraction in dental clinics. Clin. Oral Investig. 2015, 19, 1405–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makrygiannakis, M.A.; Dastoori, M.; Athanasiou, A.E. Orthodontic treatment of a nine-year-old patient with hypophosphatemic rickets diagnosed since the age of two: A case report. Int. Orthod. 2020, 18, 648–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibson, C.; Mubeen, S.; Evans, R. X-linked hypophosphatemic rickets: Orthodontic considerations and management. A case report. J. Orthod. 2022, 49, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawakami, M.; Takano-Yamamoto, T. Orthodontic treatment of a patient with hypophosphatemic vitamin D-resistant rickets. ASDC J. Dent. Child. 1997, 64, 395–399. [Google Scholar]
- Resnick, D. Implant placement and guided tissue regeneration in a patient with congenital vitamin D-resistant rickets. J. Oral Implantol. 1998, 24, 214–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larmas, M.; Hietala, E.L.; Similä, S.; Pajari, U. Oral manifestations of familial hypophosphatemic rickets after phosphate supplement therapy: A review of the literature and report of case. ASDC J. Dent. Child. 1991, 58, 328–334. [Google Scholar]
- Seow, W.K. The effect of medical therapy on dentin formation in vitamin D-resistant rickets. Pediatr. Dent. 1991, 13, 97–102. [Google Scholar]
- Chaussain-Miller, C.; Sinding, C.; Wolikow, M.; Lasfargues, J.J.; Godeau, G.; Garabédian, M. Dental abnormalities in patients with familial hypophosphatemic vitamin D-resistant rickets: Prevention by early treatment with 1-hydroxyvitamin D. J. Pediatr. 2003, 142, 324–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaussain-Miller, C.; Sinding, C.; Septier, D.; Wolikow, M.; Goldberg, M.; Garabedian, M. Dentin structure in familial hypophosphatemic rickets: Benefits of vitamin D and phosphate treatment. Oral Dis. 2007, 13, 482–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beltes, C.; Zachou, E. Endodontic management in a patient with vitamin D-resistant Rickets. J. Endod. 2012, 38, 255–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linglart, A.; Biosse-Duplan, M.; Briot, K.; Chaussain, C.; Esterle, L.; Guillaume-Czitrom, S.; Kamenicky, P.; Nevoux, J.; Prié, D.; Rothenbuhler, A.; et al. Therapeutic management of hypophosphatemic rickets from infancy to adulthood. Endocr. Connect. 2014, 3, R13–R30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Econs, M.J. Conventional Therapy in Adults With XLH Improves Dental Manifestations, But Not Enthesopathy. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 100, 3622–3624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okawa, R.; Hamada, M.; Takagi, M.; Matayoshi, S.; Nakano, K. A Case of X-Linked Hypophosphatemic Rickets with Dentin Dysplasia in Mandibular Third Molars. Children 2022, 9, 1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, L.M.; Glorieux, F.H.; Whyte, M.P.; Munns, C.F.; Portale, A.A.; Högler, W.; Simmons, J.H.; Gottesman, G.S.; Padidela, R.; Namba, N.; et al. Effect of Burosumab Compared With Conventional Therapy on Younger vs Older Children With X-linked Hypophosphatemia. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 107, e3241–e3253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schour, I.; Massler, M. The development of the human dentition. J. Am. Dent. Assoc. 1941, 28, 1153–1160. [Google Scholar]
- Petje, G.; Meizer, R.; Radler, C.; Aigner, N.; Grill, F. Deformity correction in children with hereditary hypophosphatemic rickets. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2008, 466, 3078–3085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).