Possible Involvement of miR-98 in the Regulation of PGRMC1 During Decidualization
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Endometrial Tissues
2.2. Immunohistochemistry Reagents and Antibodies
2.3. Cell Culture
2.4. Identification of MiRNAs That Regulate PGRMC1 Expression
2.5. AG-205 Treatment and siRNA/miRNA Transfection
2.6. Total RNA Extraction and Real-Time RT-PCR Analysis
2.7. Immunoblot Analysis
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
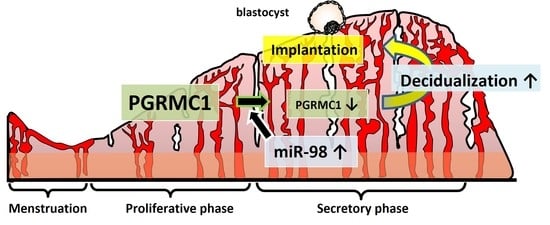
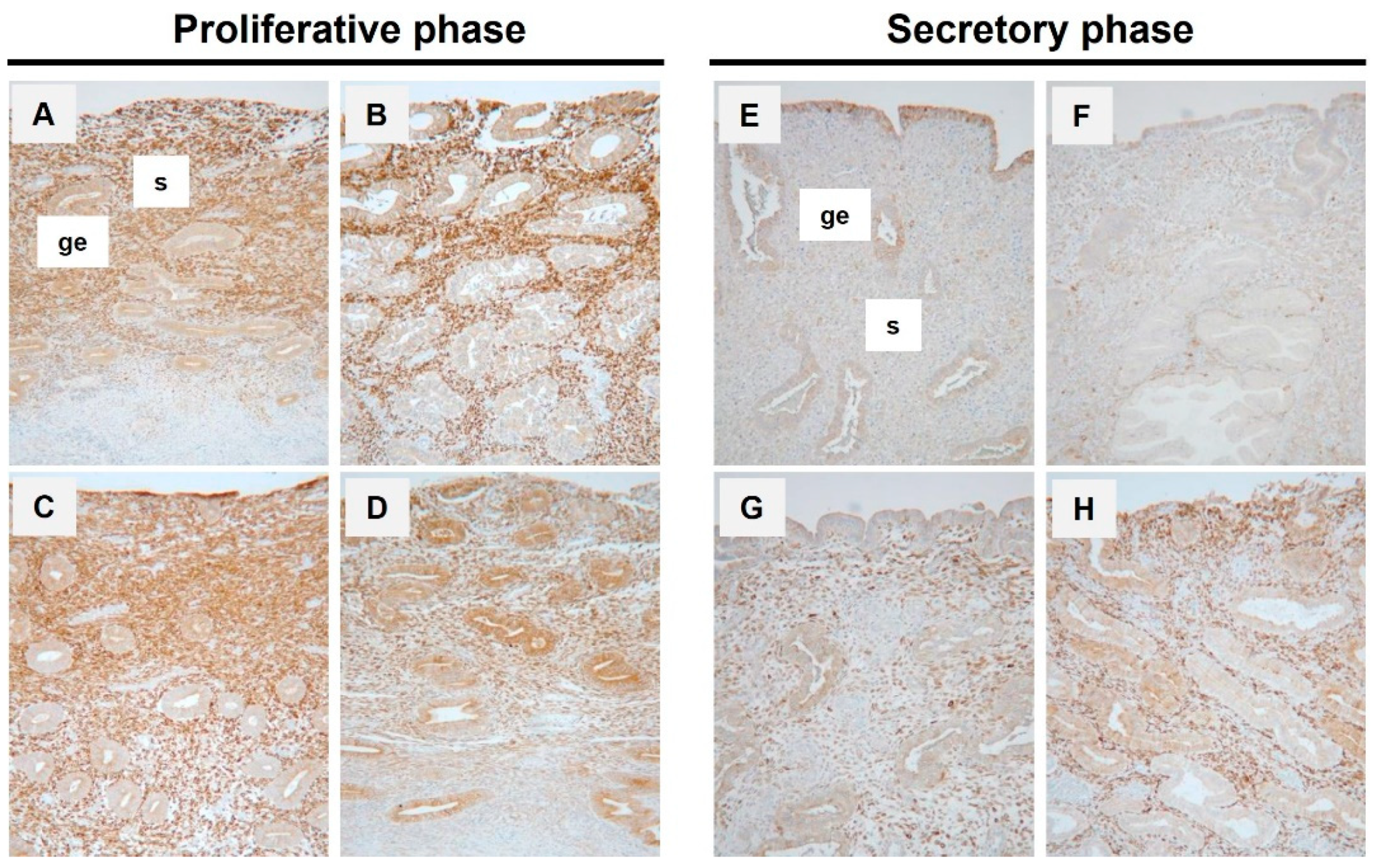
3.1. Expression of PGRMC1 in Human Endometrium Throughout the Menstrual Cycle
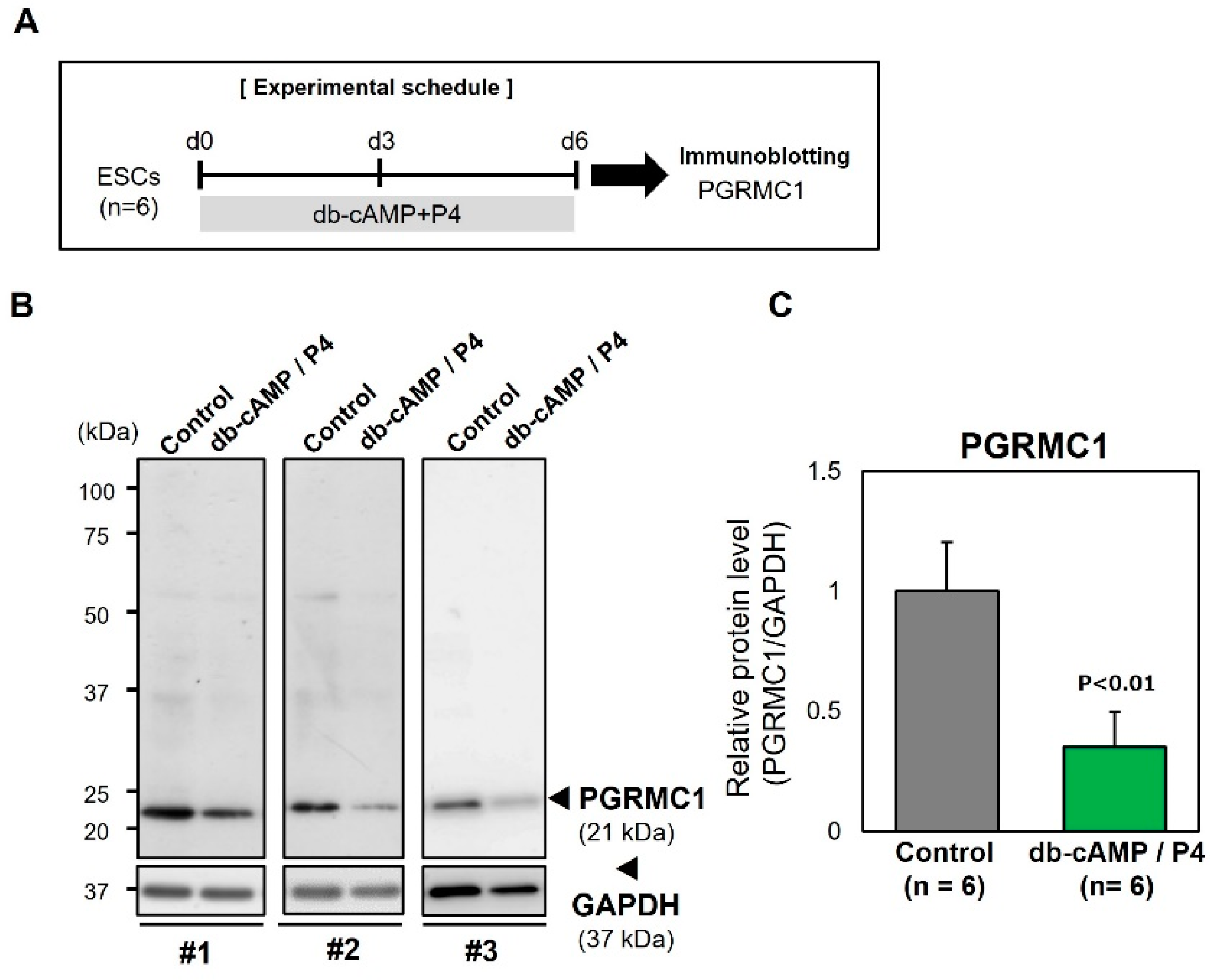
3.2. Downregulation of PGRMC1 During Decidualization of ESCs In Vitro
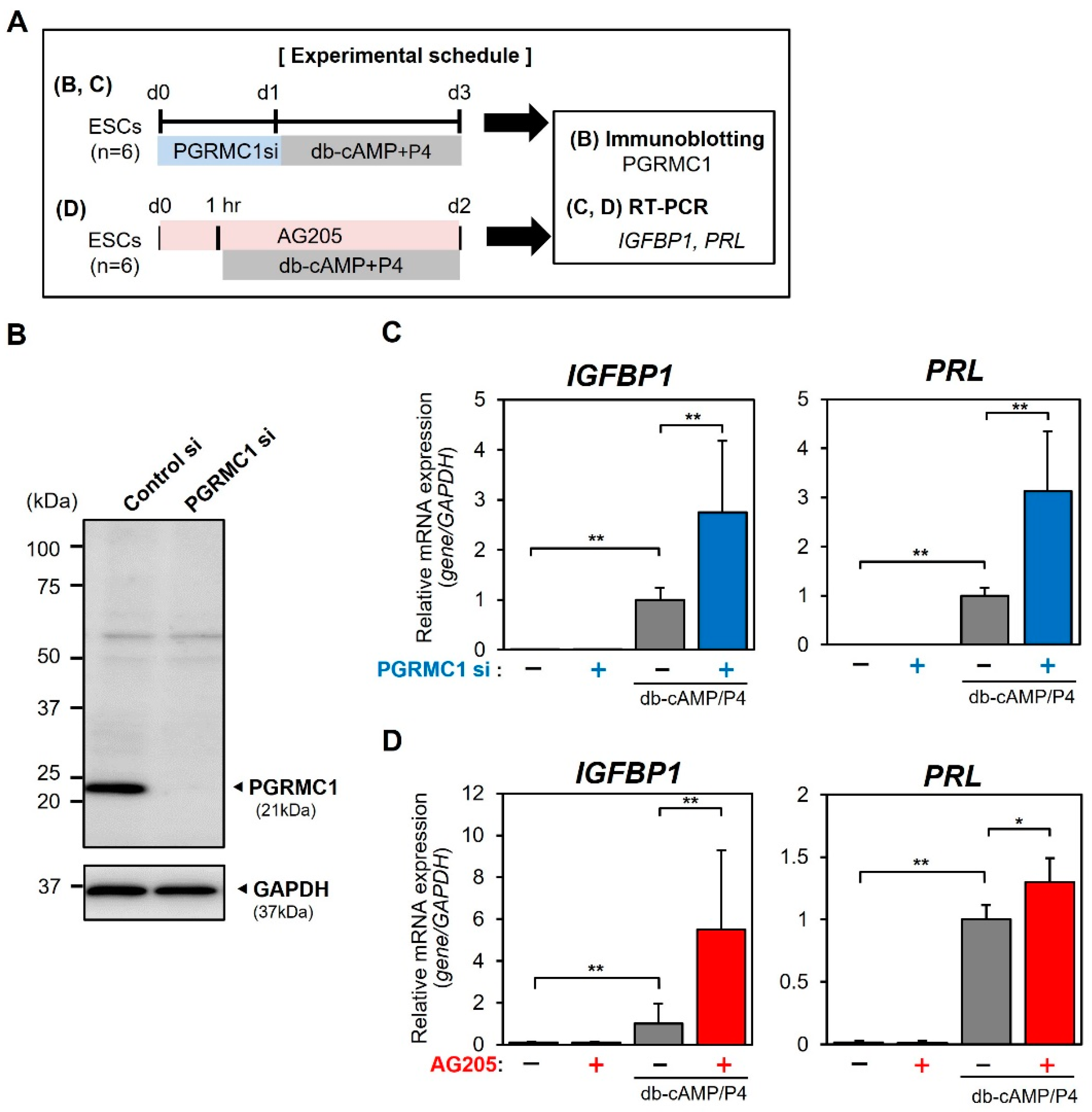
3.3. Effects of PGRMC1 Knockdown and Inhibition on Decidualization of ESCs In Vitro
3.4. MiR-98-Mediated Downregulation of PGRMC1 During Decidualization
4. Discussion
5. Strengths and Limitations of This Study
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tang, B.; Guller, S.; Gurpide, E. Cyclic adenosine 3′,5′-monophosphate induces prolactin expression in stromal cells isolated from human proliferative endometrium. Endocrinology 1993, 133, 2197–2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gellersen, B.; Brosens, J. Cyclic AMP and progesterone receptor cross-talk in human endometrium: A decidualizing affair. J. Endocrinol. 2003, 178, 357–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, B.; Guller, S.; Gurpide, E. Mechanisms involved in the decidualization of human endometrial stromal cells. Acta Eur. Fertil. 1993, 24, 221–223. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Giudice, L.C.; Dsupin, B.A.; Irwin, J.C. Steroid and peptide regulation of insulin-like growth factor-binding proteins secreted by human endometrial stromal cells is dependent on stromal differentiation. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1992, 75, 1235–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maslar, I.A.; Riddick, D.H. Prolactin production by human endometrium during the normal menstrual cycle. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 1979, 135, 751–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar, E.L.; Calzada, L. The role of progesterone in endometrial estradiol- and progesterone-receptor synthesis in women with menstrual disorders and habitual abortion. Gynecol. Endocrinol. 2007, 23, 222–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, J.D.; Clarke, C.L. Physiological action of progesterone in target tissues. Endocr. Rev. 1997, 18, 502–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshinaga, K. Progesterone and its downstream molecules as blastocyst implantation essential factors. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2014, 72, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, H.S.; Hantak, A.M.; Stubbs, L.J.; Taylor, R.N.; Bagchi, I.C.; Bagchi, M.K. Roles of progesterone receptor A and B isoforms during human endometrial decidualization. Mol. Endocrinol. 2015, 29, 882–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, B.; Elguero, S.; Thakore, S.; Dahoud, W.; Bedaiwy, M.; Mesiano, S. Role of nuclear progesterone receptor isoforms in uterine pathophysiology. Hum. Reprod. Update 2015, 21, 155–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulun, S.E.; Cheng, Y.H.; Yin, P.; Imir, G.; Utsunomiya, H.; Attar, E.; Innes, J.; Julie Kim, J. Progesterone resistance in endometriosis: Link to failure to metabolize estradiol. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2006, 248, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirota, Y.; Cha, J.; Dey, S.K. Revisiting reproduction: Prematurity and the puzzle of progesterone resistance. Nat. Med. 2010, 16, 529–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Thomas, P. Characteristics of membrane progestin receptor alpha (mPRalpha) and progesterone membrane receptor component 1 (PGMRC1) and their roles in mediating rapid progestin actions. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 2008, 29, 292–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peluso, J.J.; Pappalardo, A.; Losel, R.; Wehling, M. Progesterone membrane receptor component 1 expression in the immature rat ovary and its role in mediating progesterone’s antiapoptotic action. Endocrinology 2006, 147, 3133–3140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Meyer, C.; Schmid, R.; Scriba, P.C.; Wehling, M. Purification and partial sequencing of high-affinity progesterone-binding site(s) from porcine liver membranes. Eur. J. Biochem. 1996, 239, 726–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cahill, M.A.; Jazayeri, J.A.; Catalano, S.M.; Toyokuni, S.; Kovacevic, Z.; Richardson, D.R. The emerging role of progesterone receptor membrane component 1 (PGRMC1) in cancer biology. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1866, 339–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engmann, L.; Losel, R.; Wehling, M.; Peluso, J.J. Progesterone regulation of human granulosa/luteal cell viability by an RU486-independent mechanism. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2006, 91, 4962–4968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- McCallum, M.L.; Pru, C.A.; Niikura, Y.; Yee, S.P.; Lydon, J.P.; Peluso, J.J.; Pru, J.K. Conditional Ablation of Progesterone Receptor Membrane Component 1 Results in Subfertility in the Female and Development of Endometrial Cysts. Endocrinology 2016, 157, 3309–3319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salsano, S.; Quiñonero, A.; Pérez, S.; Garrido Gómez, T.; Simón, C.; Dominguez, F. Dynamic expression of PGRMC1 and SERBP1 in human endometrium: An implication in the human decidualization process. Fertil. Steril. 2017, 108, 832–842.e831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bushati, N.; Cohen, S.M. microRNA functions. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2007, 23, 175–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Wang, S.; Wang, Z. Role of microRNAs in embryo implantation. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2017, 15, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferlita, A.; Battaglia, R.; Andronico, F.; Caruso, S.; Cianci, A.; Purrello, M.; Pietro, C.D. Non-Coding RNAs in Endometrial Physiopathology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, A.; Jin, M.; Xie, L.; Jing, M.; Zhou, Y.; Tang, M.; Lin, T.; Wang, D. Loss of miR-29a impairs decidualization of endometrial stromal cells by TET3 mediated demethylation of Col1A1 promoter. iScience 2021, 24, 103065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshie, M.; Miyajima, E.; Kyo, S.; Tamura, K. Stathmin, a microtubule regulatory protein, is associated with hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha levels in human endometrial and endothelial cells. Endocrinology 2009, 150, 2413–2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshie, M.; Kaneyama, K.; Kusama, K.; Higuma, C.; Nishi, H.; Isaka, K.; Tamura, K. Possible role of the exchange protein directly activated by cyclic AMP (Epac) in the cyclic AMP-dependent functional differentiation and syncytialization of human placental BeWo cells. Hum. Reprod. 2010, 25, 2229–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panda, H.; Chuang, T.D.; Luo, X.; Chegini, N. Endometrial miR-181a and miR-98 expression is altered during transition from normal into cancerous state and target PGR, PGRMC1, CYP19A1, DDX3X, and TIMP3. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 97, E1316–E1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wendler, A.; Keller, D.; Albrecht, C.; Peluso, J.J.; Wehling, M. Involvement of let-7/miR-98 microRNAs in the regulation of progesterone receptor membrane component 1 expression in ovarian cancer cells. Oncol. Rep. 2011, 25, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang-Eckhardt, L.; Becker, I.; Eckhardt, M. The PGRMC1 Antagonist AG-205 Inhibits Synthesis of Galactosylceramide and Sulfatide. Cells 2021, 10, 3520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang-Eckhardt, L.; Eckhardt, M. A progesterone receptor membrane component 1 antagonist induces large vesicles independent of progesterone receptor membrane component 1 expression. Biol. Chem. 2020, 401, 1093–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thieffry, C.; Van Wynendaele, M.; Aynaci, A.; Maja, M.; Dupuis, C.; Loriot, A.; Marbaix, E.; Henriet, P. AG-205 Upregulates Enzymes Involved in Cholesterol Biosynthesis and Steroidogenesis in Human Endometrial Cells Independently of PGRMC1 and Related MAPR Proteins. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, L.C.; Tulac, S.; Lobo, S.; Imani, B.; Yang, J.P.; Germeyer, A.; Osteen, K.; Taylor, R.N.; Lessey, B.A.; Giudice, L.C. Global gene profiling in human endometrium during the window of implantation. Endocrinology 2002, 143, 2119–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, H.F.; Jin, X.H.; Cao, Z.F.; Shi, T.; Ma, X. MiR-98 is involved in rat embryo implantation by targeting Bcl-xl. FEBS Lett. 2014, 588, 574–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lv, Y.; Wang, L.; Gong, C.; Sun, J.; Chen, X.; Chen, Y.; Yang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, X.; et al. MicroRNAome in decidua: A new approach to assess the maintenance of pregnancy. Fertil. Steril. 2015, 103, 980–989.e986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salsano, S.; González-Martín, R.; Quiñonero, A.; Pérez-Debén, S.; Domínguez, F. Deciphering the Role of PGRMC1 During Human Decidualization Using an In Vitro Approach. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 106, 2313–2327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peluso, J.J.; Lodde, V.; Liu, X. Progesterone regulation of progesterone receptor membrane component 1 (PGRMC1) sumoylation and transcriptional activity in spontaneously immortalized granulosa cells. Endocrinology 2012, 153, 3929–3939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabbir, M.G. Progesterone induced Warburg effect in HEK293 cells is associated with post-translational modifications and proteasomal degradation of progesterone receptor membrane component 1. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2019, 191, 105376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brighton, P.J.; Maruyama, Y.; Fishwick, K.; Vrljicak, P.; Tewary, S.; Fujihara, R.; Muter, J.; Lucas, E.S.; Yamada, T.; Woods, L.; et al. Clearance of senescent decidual cells by uterine natural killer cells in cycling human endometrium. eLife 2017, 6, e31274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leno-Durán, E.; Ruiz-Magaña, M.J.; Muñoz-Fernández, R.; Requena, F.; Olivares, E.G.; Ruiz-Ruiz, C. Human decidual stromal cells secrete soluble pro-apoptotic factors during decidualization in a cAMP-dependent manner. Hum. Reprod. 2014, 29, 2269–2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawlings, T.M.; Makwana, K.; Taylor, D.M.; Molè, M.A.; Fishwick, K.J.; Tryfonos, M.; Odendaal, J.; Hawkes, A.; Zernicka-Goetz, M.; Hartshorne, G.M.; et al. Modelling the impact of decidual senescence on embryo implantation in human endometrial assembloids. eLife 2021, 10, e69603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusama, K.; Yoshie, M.; Tamura, K.; Nakayama, T.; Nishi, H.; Isaka, K.; Tachikawa, E. The role of exchange protein directly activated by cyclic AMP 2-mediated calreticulin expression in the decidualization of human endometrial stromal cells. Endocrinology 2014, 155, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusama, K.; Yamauchi, N.; Yoshida, K.; Azumi, M.; Yoshie, M.; Tamura, K. Senolytic treatment modulates decidualization in human endometrial stromal cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2021, 571, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menon, R.; Boldogh, I.; Hawkins, H.K.; Woodson, M.; Polettini, J.; Syed, T.A.; Fortunato, S.J.; Saade, G.R.; Papaconstantinou, J.; Taylor, R.N. Histological evidence of oxidative stress and premature senescence in preterm premature rupture of the human fetal membranes recapitulated in vitro. Am. J. Pathol. 2014, 184, 1740–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woods, J.R., Jr. Reactive oxygen species and preterm premature rupture of membranes-a review. Placenta 2001, 22 (Suppl. A), S38–S44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, L.; Allen, T.K.; Marinello, W.P.; Murtha, A.P. Roles of Progesterone Receptor Membrane Component 1 in Oxidative Stress-Induced Aging in Chorion Cells. Reprod. Sci. 2019, 26, 394–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hand, R.A.; Craven, R.J. Hpr6.6 protein mediates cell death from oxidative damage in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. J. Cell. Biochem. 2003, 90, 534–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, I.S.; Rohe, H.J.; Twist, K.E.; Craven, R.J. Pgrmc1 (progesterone receptor membrane component 1) associates with epidermal growth factor receptor and regulates erlotinib sensitivity. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 24775–24782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampton, K.K.; Anderson, K.; Frazier, H.; Thibault, O.; Craven, R.J. Insulin Receptor Plasma Membrane Levels Increased by the Progesterone Receptor Membrane Component 1. Mol. Pharmacol. 2018, 94, 665–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, A.L.; Powell, D.W.; Bard, M.; Eckstein, J.; Barbuch, R.; Link, A.J.; Espenshade, P.J. Dap1/PGRMC1 binds and regulates cytochrome P450 enzymes. Cell Metab. 2007, 5, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salsano, S.; González-Martín, R.; Quiñonero, A.; López-Martín, S.; Gómez-Escribano, A.P.; Pérez-Debén, S.; Yañez-Mo, M.; Domínguez, F. Novel nonclassic progesterone receptor PGRMC1 pulldown-precipitated proteins reveal a key role during human decidualization. Fertil. Steril. 2020, 113, 1050–1066.e1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Name | Sequence | |
|---|---|---|
| (Accession No.) | (5′–3′) | |
| IGFBP1 | S | AATGGATTTTATCACAGCAGACAG |
| (NM_000596.4) | AS | GGTAGACGCACCAGCAGAGT |
| PRL | S | AAAGGATCGCCATGGAAAG |
| (NM_000948.6) | AS | GGTCTCGAAGGGTCACCTG |
| GAPDH | S | AGCCACATCGCTCAGACA |
| (NM_002046.7) | AS | GCCCAATACGACCAAATCC |
| miR-98 | TGAGGTAGGAGGTTGTATAGTT | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tsuru, A.; Yoshie, M.; Yonekawa, R.; Kojima, J.; Azumi, M.; Kusama, K.; Nishi, H.; Tamura, K. Possible Involvement of miR-98 in the Regulation of PGRMC1 During Decidualization. Reprod. Med. 2022, 3, 189-200. https://doi.org/10.3390/reprodmed3020015
Tsuru A, Yoshie M, Yonekawa R, Kojima J, Azumi M, Kusama K, Nishi H, Tamura K. Possible Involvement of miR-98 in the Regulation of PGRMC1 During Decidualization. Reproductive Medicine. 2022; 3(2):189-200. https://doi.org/10.3390/reprodmed3020015
Chicago/Turabian StyleTsuru, Atsuya, Mikihiro Yoshie, Ryo Yonekawa, Junya Kojima, Mana Azumi, Kazuya Kusama, Hirotaka Nishi, and Kazuhiro Tamura. 2022. "Possible Involvement of miR-98 in the Regulation of PGRMC1 During Decidualization" Reproductive Medicine 3, no. 2: 189-200. https://doi.org/10.3390/reprodmed3020015
APA StyleTsuru, A., Yoshie, M., Yonekawa, R., Kojima, J., Azumi, M., Kusama, K., Nishi, H., & Tamura, K. (2022). Possible Involvement of miR-98 in the Regulation of PGRMC1 During Decidualization. Reproductive Medicine, 3(2), 189-200. https://doi.org/10.3390/reprodmed3020015