Effect of Heat Treatment on Polymorphism and Particle Size Distribution of Calcium Carbonate Nanoparticle Synthesized via Mechanochemical Process
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagent
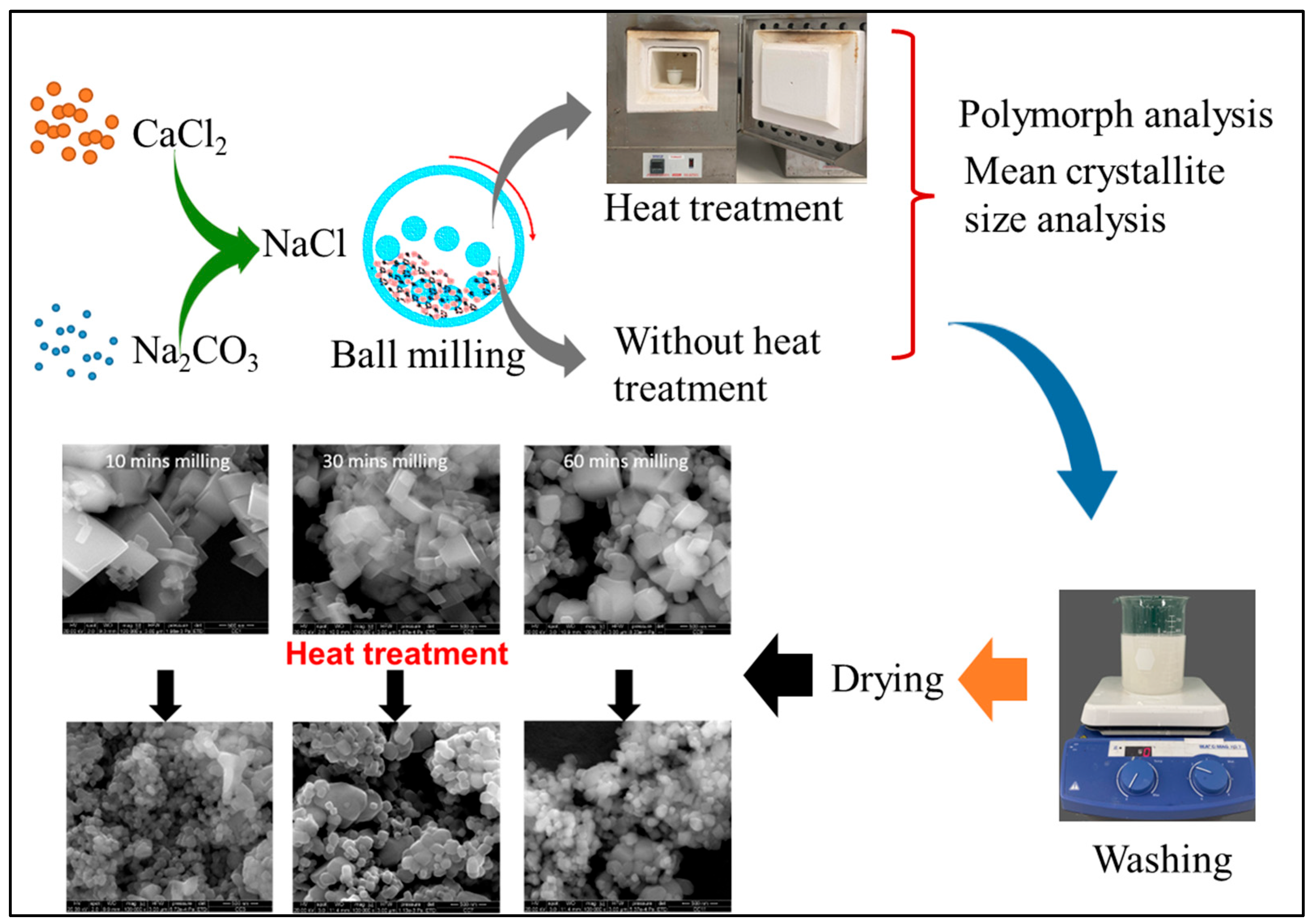
2.2. Synthesis of CaCO3 Nanoparticles
2.3. Characterization of the Milled Powder and CaCO3 Nanoparticles
2.3.1. X-Ray Diffraction Analysis and Crystallite Size Measurement
2.3.2. Thermogravimetric Analysis and Differential Scanning Calorimetry
2.3.3. Micromorphology Analysis
2.3.4. Particle Size Analysis
2.3.5. Surface Area Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
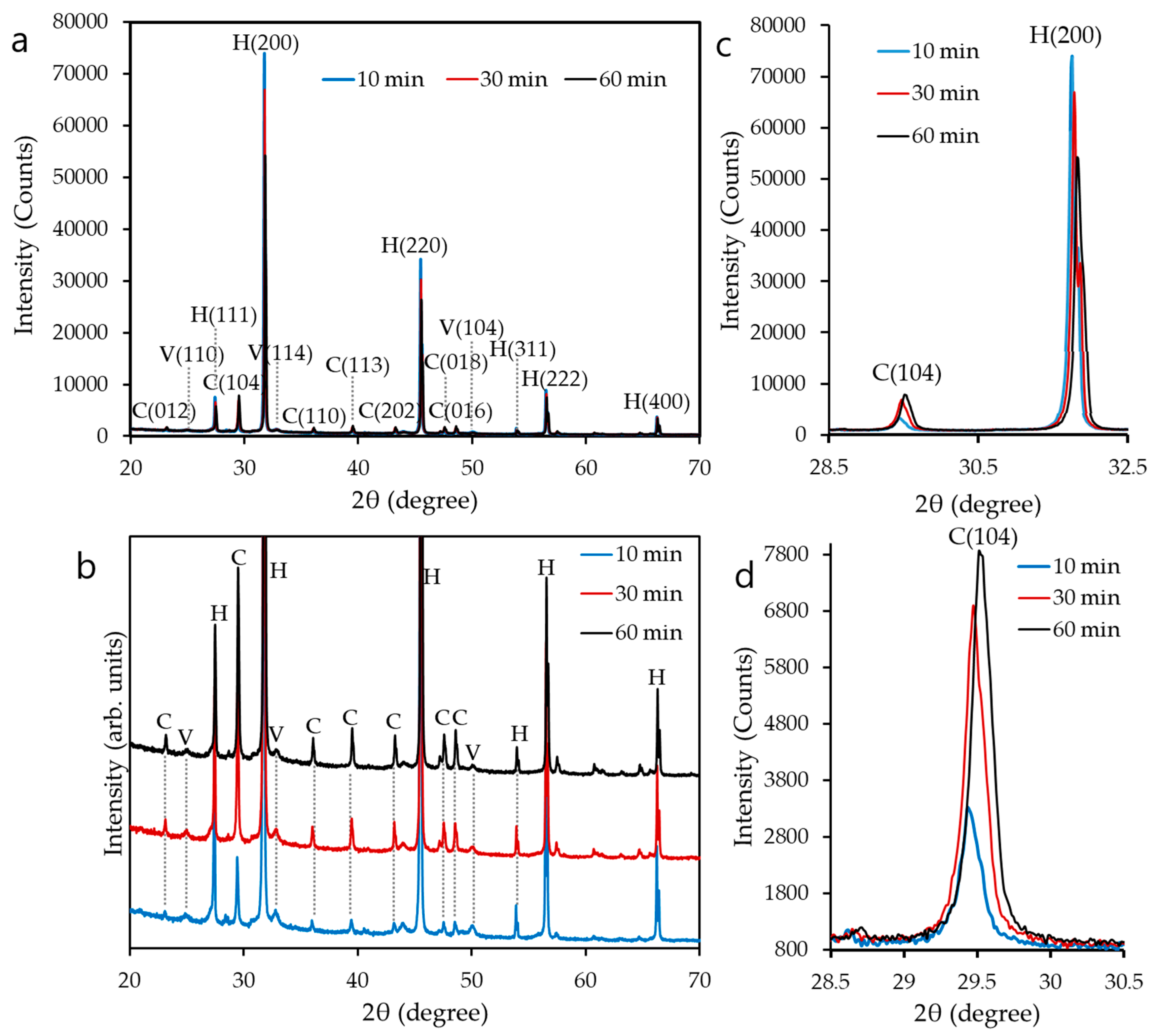
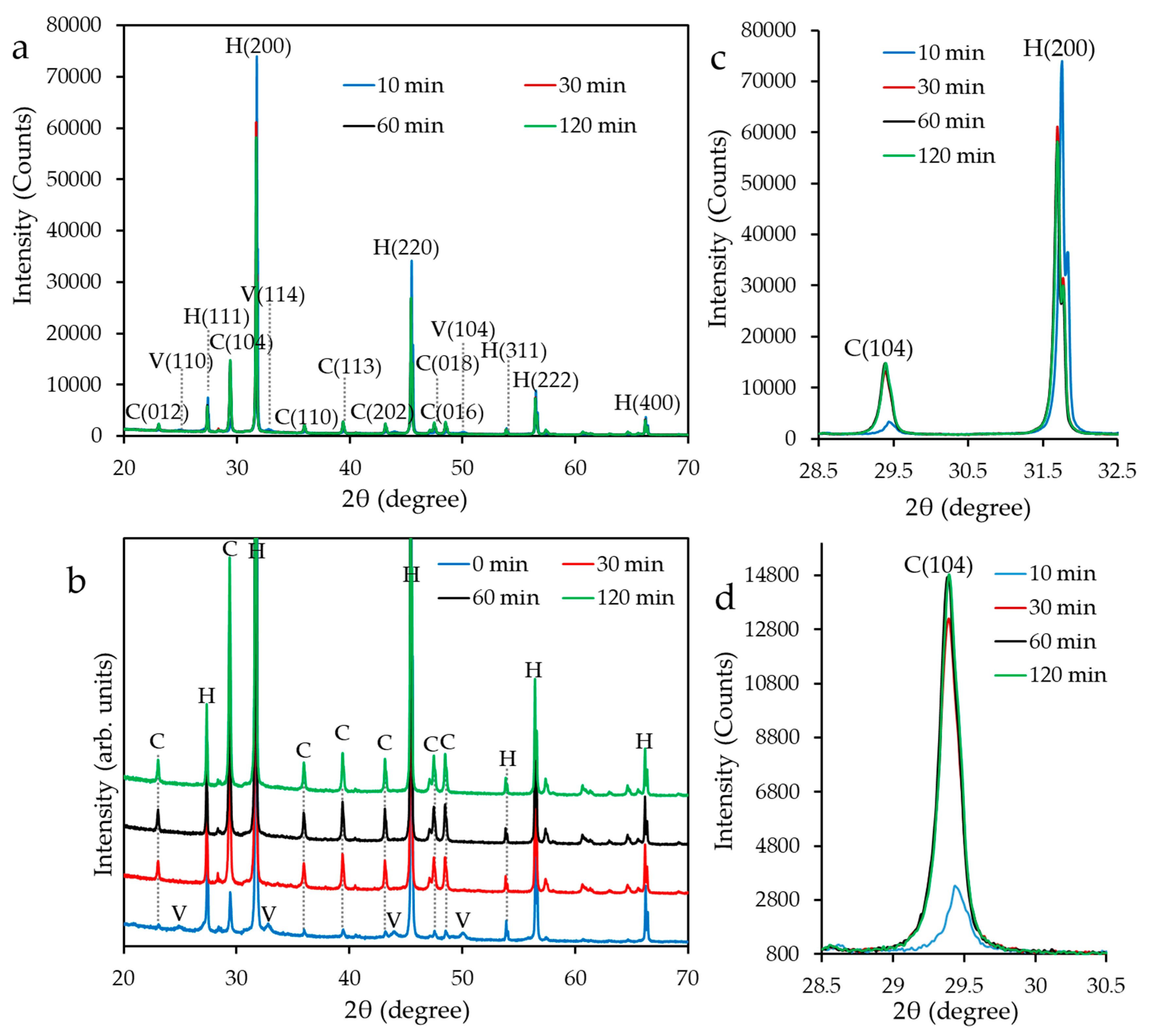
3.1. Polymorphs of CaCO3 Nanoparticles
3.2. Mean Crystallite Size
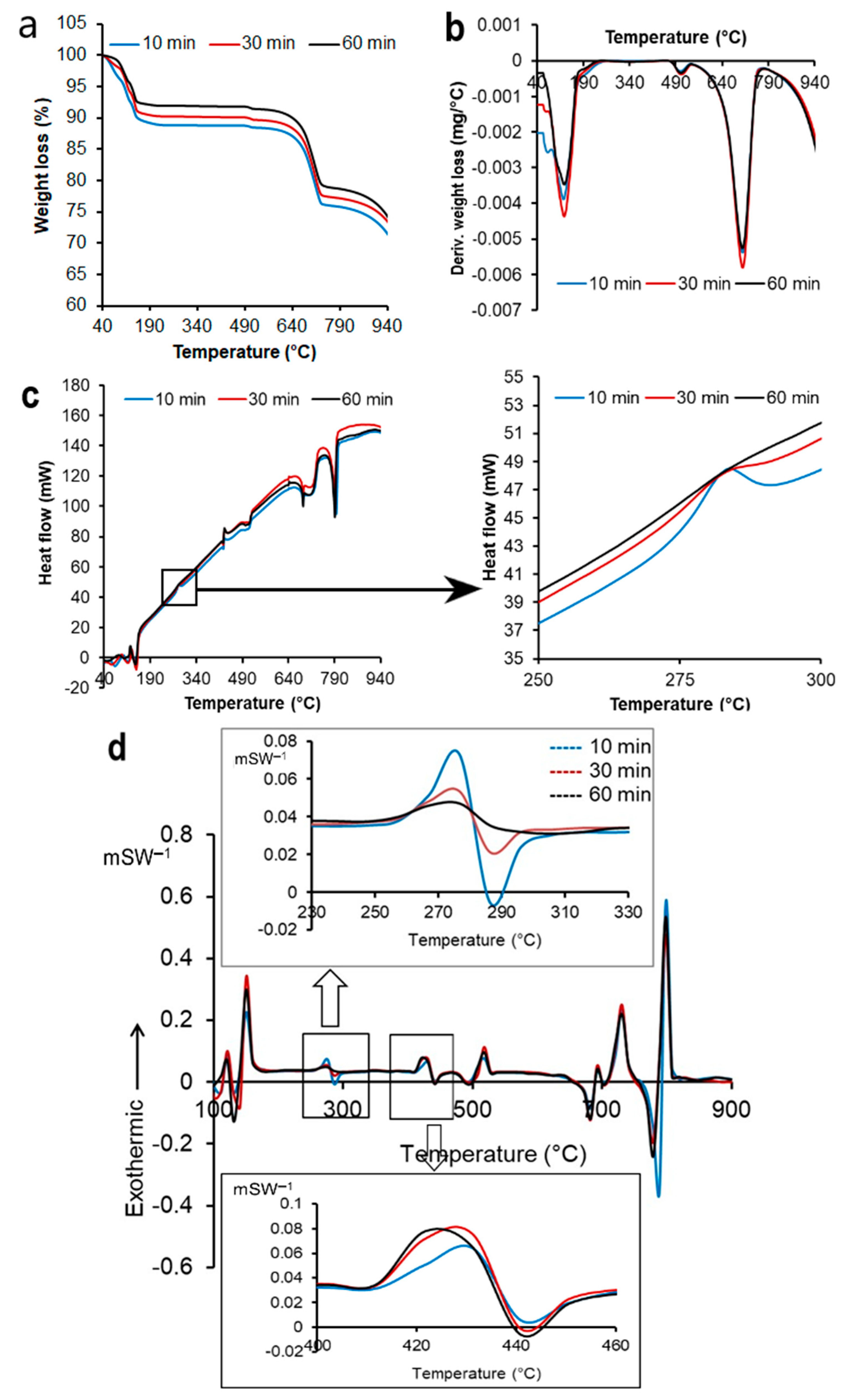
3.3. TGA and DSC Analysis
3.4. Effect of Milling and Heating Time on Particle Size Distribution
3.5. Micromorphology Analysis of Synthesized CaCO3
3.6. Surface Area
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACC | amorphous calcium carbonate |
| BET | Brunauer–Emmett–Teller |
| CaCO3 | calcium carbonate |
| DSC | differential scanning calorimetry |
| XRD | X-ray diffraction |
References
- Khosa, A.A.; Xu, T.; Xia, B.Q.; Yan, J.; Zhao, C.Y. Technological challenges and industrial applications of CaCO3/CaO based thermal energy storage system—A review. Sol. Energy 2019, 193, 618–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimoh, O.A.; Ariffin, K.S.; Hussin, H.B.; Temitope, A.E. Synthesis of precipitated calcium carbonate: A review. Carbonat. Evaporit. 2018, 33, 331–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, S.; Hsieh, J.S.; Zou, P.; Kokoszka, J. Utilization of calcium carbonate particles from eggshell waste as coating pigments for ink-jet printing paper. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 6416–6421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, W.; Liang, B.; Li, W.; Huang, H.; Shi, D.; Chen, Z.; Li, Z.; Yu, M.; Wei, G.; Huang, K. Study on the growth mechanism of porous spherical calcium carbonate synthesized by carbonization controlled by amino acids. J. Solid State Chem. 2024, 329, 124370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Zhao, X.; Cheng, B.; Zhang, Q. Controlled synthesis of calcium carbonate in a mixed aqueous solution of PSMA and CTAB. J. Solid State Chem. 2005, 178, 861–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pour, G.T.; Moghadam, S.M.M. Optimization of nano calcium carbonate production process using Taguchi method. Int. J. Mater. Mech. Manuf. 2014, 2, 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.-Q.; Liu, J.-H.; Aymonier, C.; Fermani, S.; Kralj, D.; Falini, G.; Zhou, C.-H. Calcium carbonate: Controlled synthesis, surface functionalization, and nanostructured materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2022, 51, 7883–7943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babou-Kammoe, R.; Hamoudi, S.; Larachi, F.; Belkacemi, K. Synthesis of CaCO3 nanoparticles by controlled precipitation of saturated carbonate and calcium nitrate aqueous solutions. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2012, 90, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sheikh, S.M.; El-Sherbiny, S.; Barhoum, A.; Deng, Y. Effects of cationic surfactant during the precipitation of calcium carbonate nano-particles on their size, morphology, and other characteristics. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2013, 422, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagaonkar, M.V.; Mehra, A.; Jain, R.; Heeres, H.J. Synthesis of CaCO3 nanoparticles by carbonation of lime solutions in reverse micellar systems. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2004, 82, 1438–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.H.; Hirasawa, I.; Kim, W.-S.; Choi, C.K. Morphological control of calcium carbonate crystallized in reverse micelle system with anionic surfactants SDS and AOT. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2005, 288, 496–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, K.; Shi, T.; Tang, T.; Zhang, S.; Liu, X.; Cao, Y. Preparation and characterization of nano-sized calcium carbonate as controlled release pesticide carrier for validamycin against Rhizoctonia solani. Microchim. Acta 2011, 173, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugih, A.K.; Shukla, D.; Heeres, H.J.; Mehra, A. CaCO3 nanoparticle synthesis by carbonation of lime solution in microemulsion systems. Nanotechnology 2007, 18, 035607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tai, C.Y.; Chen, C.-k. Particle morphology, habit, and size control of CaCO3 using reverse microemulsion technique. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2008, 63, 3632–3642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, M.; Stark, W.J.; Loher, S.; Maciejewski, M.; Krumeich, F.; Baiker, A. Flame synthesis of calcium carbonate nanoparticles. Chem. Commun. 2005, 648–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuzuki, T.; Pethick, K.; McCormick, P.G. Synthesis of CaCO3 nanoparticles by mechanochemical processing. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2000, 2, 375–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sargheini, J.; Ataie, A.; Salili, S.M.; Hoseinion, A.A. One-step facile synthesis of CaCO3 nanoparticles via mechano-chemical route. Powder Technol. 2012, 219, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baláž, P.; Achimovičová, M.; Baláž, M.; Billik, P.; Cherkezova-Zheleva, Z.; Criado, J.M.; Delogu, F.; Dutková, E.; Gaffet, E.; Gotor, F.J.; et al. Hallmarks of mechanochemistry: From nanoparticles to technology. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 7571–7637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takacs, L. Self-propagating reactions induced by mechanical alloying. Material Matter. 2007, 2.4, 21. [Google Scholar]
- Petrović, S.; Rožić, L.; Jović, V.; Stojadinović, S.; Grbić, B.; Radić, N.; Lamovec, J.; Vasilić, R. Optimization of a nanoparticle ball milling process parameters using the response surface method. Adv. Powder Technol. 2018, 29, 2129–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Ouyang, L.; Zeng, M.; Liu, J.; Wang, H.; Shao, H.; Zhu, M. Growth mechanism of black phosphorus synthesized by different ball milling techniques. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 784, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takacs, L.; McHenry, J.S. Temperature of the milling balls in shaker and planetary mills. J. Mater. Sci. 2006, 41, 5246–5249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, A.G.; Anandhan, S. Influence of planetary ball milling parameters on the mechano-chemical activation of fly ash. Powder Technol. 2015, 281, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suryanarayana, C. Mechanical alloying and milling. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2001, 46, 1–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deepika; Hait, S.K.; Chen, Y. Optimization of milling parameters on the synthesis of stearic acid coated CaCO3 nanoparticles. J. Coat. Technol. Res. 2014, 11, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catauro, M.; Tranquillo, E.; Dal Poggetto, G.; Pasquali, M.; Dell’Era, A.; Vecchio Ciprioti, S. Influence of the heat treatment on the particles size and on the crystalline phase of TiO2 synthesized by the sol-gel method. Materials 2018, 11, 2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopi, S.P.; Subramanian, V.K.; Palanisamy, K. Synergistic effect of EDTA and HEDP on the crystal growth, polymorphism, and morphology of CaCO3. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2015, 54, 3618–3625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, W.; Chunde, P.; Daqing, W.; Aixia, S.; Jihong, N.; Shuhua, L. An improved method for quantitative analysis of sedimentary minerals by X-ray diffraction. Powder Diffr. 1996, 11, 235–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devarajan, A.; Khadar, M.A.; Chattopadhyay, K. Effect of ball milling on chemically synthesized nanoparticles of CaCO3. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 452–453, 395–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wang, S.; Liu, Q.; Wang, X.; Zhu, J.; Luo, H.; Ji, S. Study on the efficacy of amorphous calcium carbonate as a consolidant for calcareous matrix. Herit. Sci. 2022, 10, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siva, T.; Muralidharan, S.; Sathiyanarayanan, S.; Manikandan, E.; Jayachandran, M. Enhanced polymer induced precipitation of polymorphous in calcium carbonate: Calcite aragonite vaterite phases. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2017, 27, 770–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radha, A.V.; Forbes, T.Z.; Killian, C.E.; Gilbert, P.U.P.A.; Navrotsky, A. Transformation and crystallization energetics of synthetic and biogenic amorphous calcium carbonate. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 16438–16443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuzuki, T. Mechanochemical synthesis of metal oxide nanoparticles. Commun. Chem. 2021, 4, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.X.; Chen, W.F.; Zhou, X.Z.; Gu, Z.Y.; Chen, C.M. Synthesis of CeO2 nanoparticles by mechanochemical processing and the inhibiting action of NaCl on particle agglomeration. Mater. Lett. 2005, 59, 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
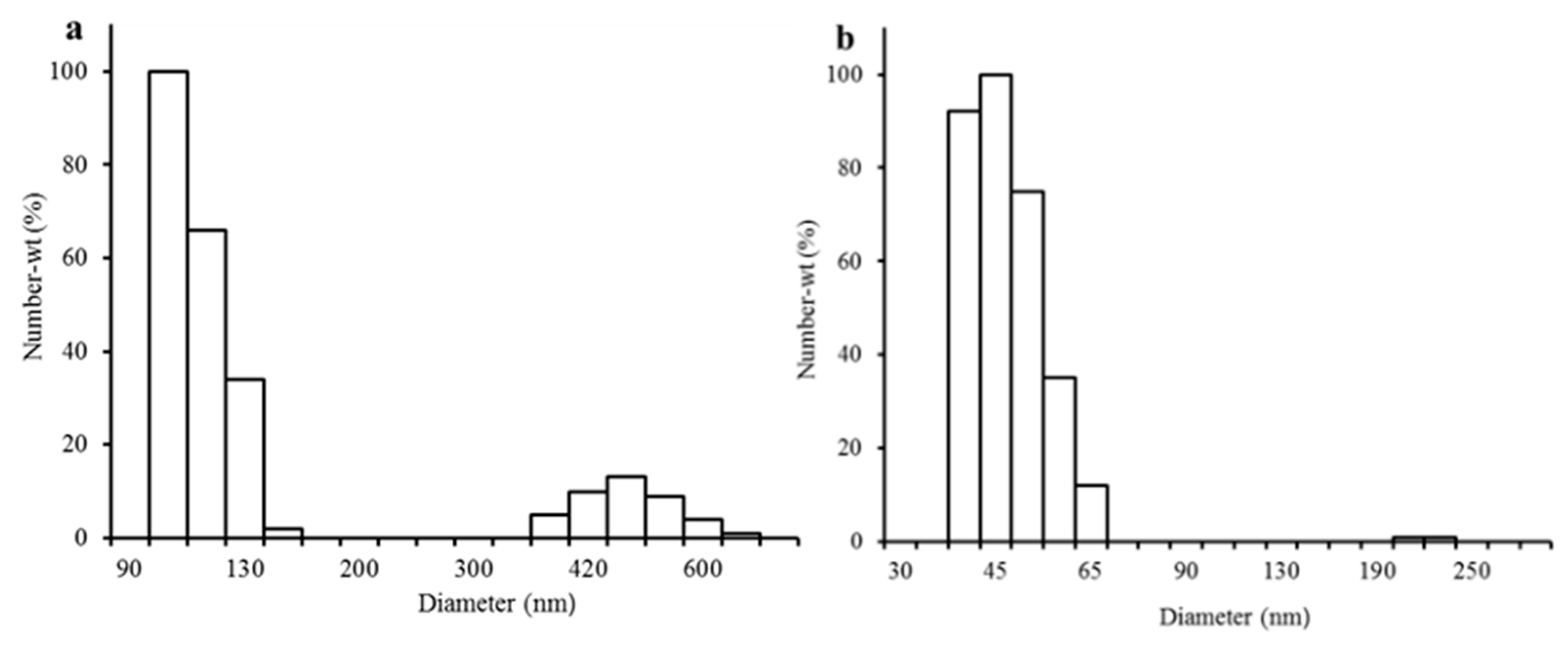
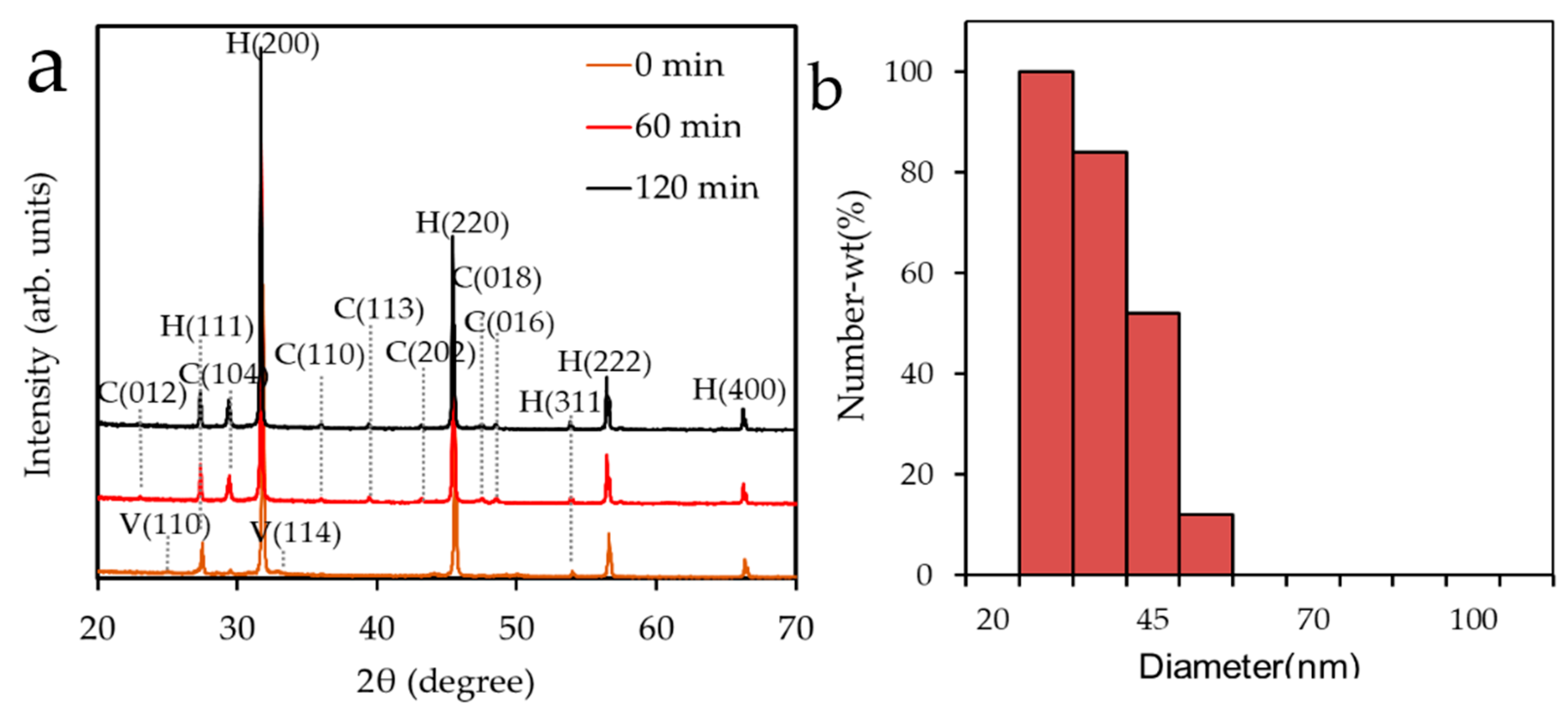

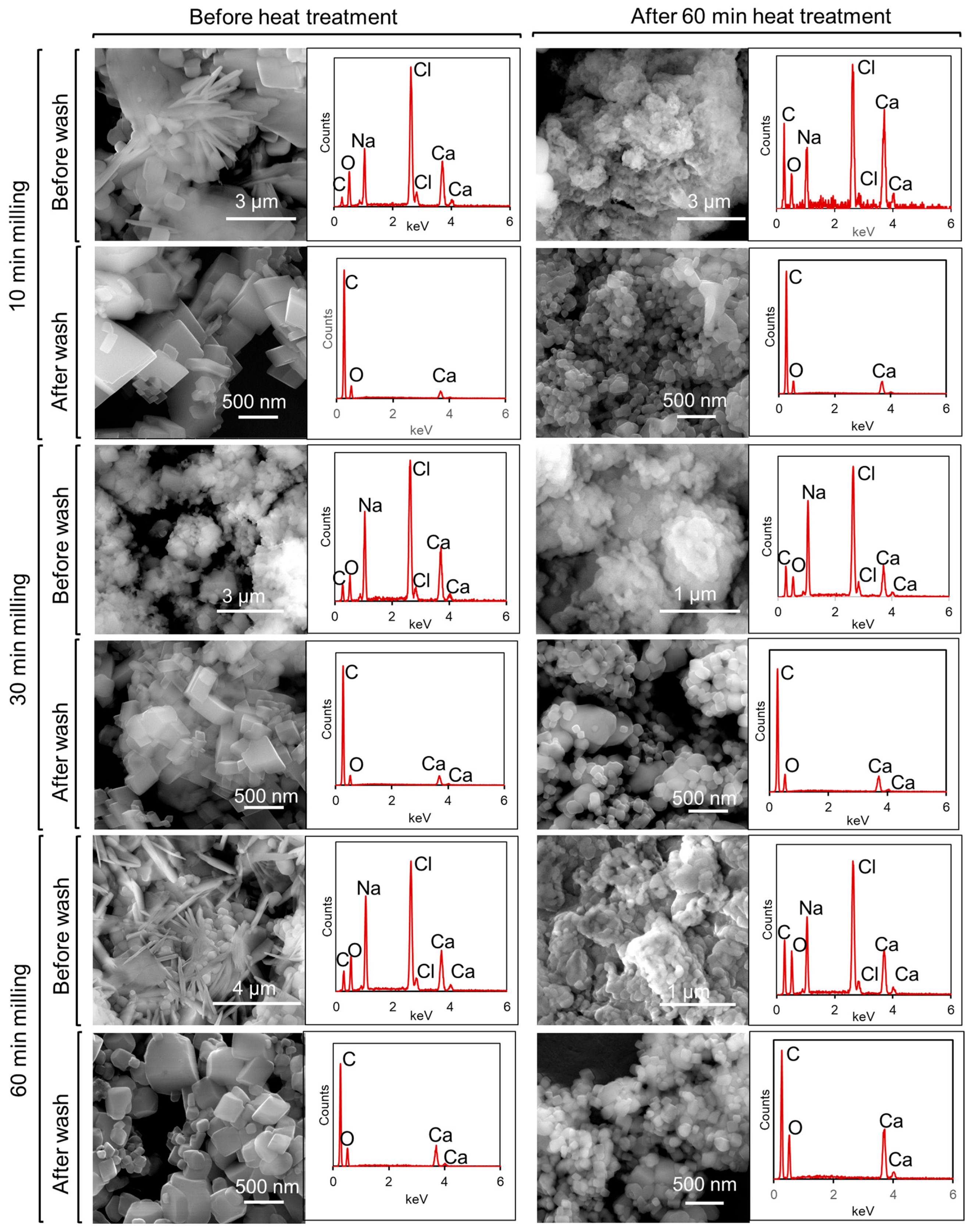
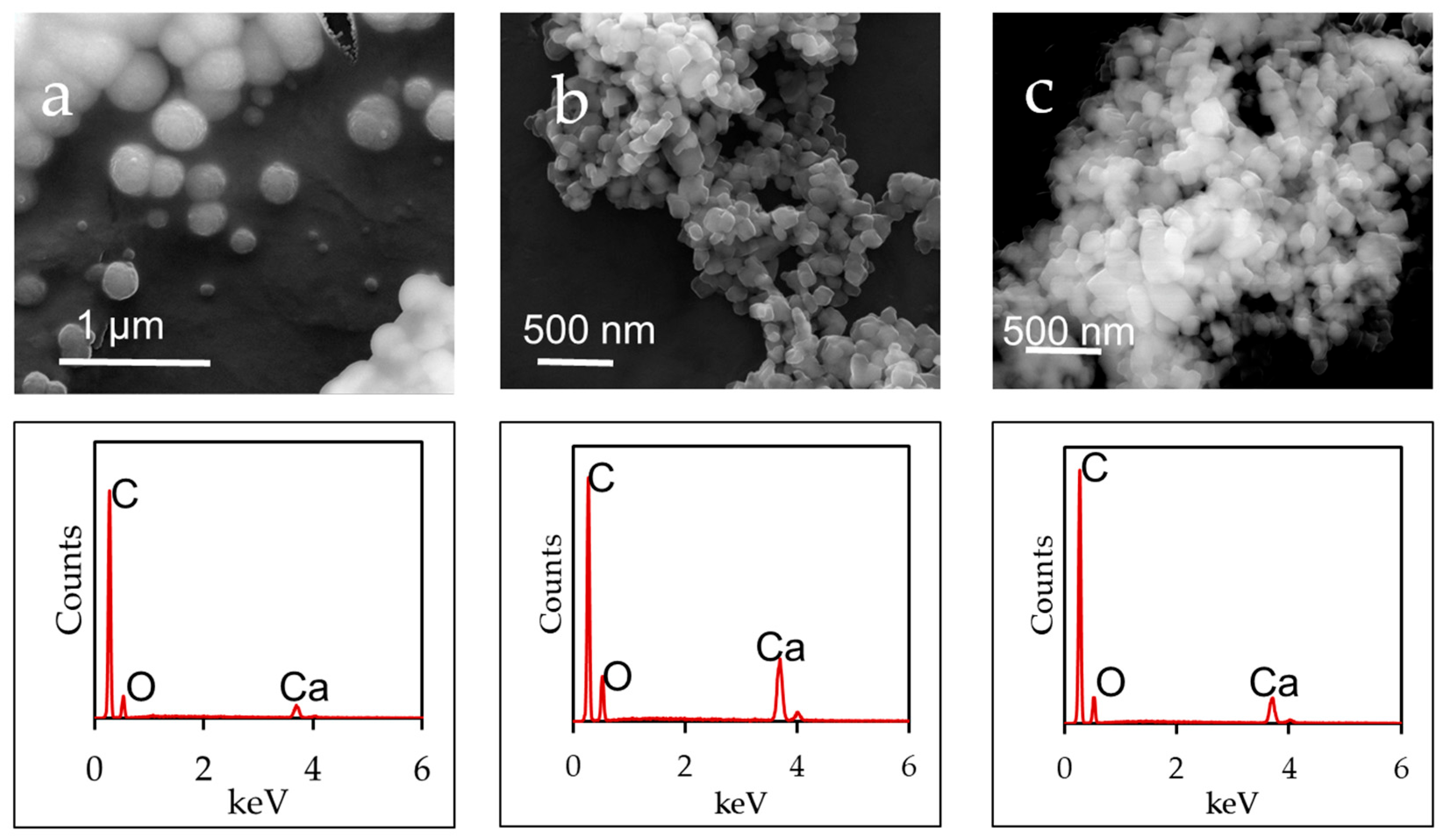
| Milling Time (min) | Heating Time | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 min (nm ± SD) | 30 min (nm ± SD) | 60 min (nm ± SD) | 120 min (nm ± SD) | |
| 10 | 56.9 ± 10.16 | 58.3 ± 4.95 | 56.4 ± 3.59 | 57.5 ± 4.03 |
| 30 | 51.2 ± 3.49 | 52.4 ± 3.42 | 56.1 ± 3.43 | 55.0 ± 2.59 |
| 60 | 51.3 ± 3.64 | 48.2 ± 2.88 | 49.1 ± 3.63 | 41.3 ± 2.05 |
| Milling Time (min) | Peak 1 | Peak 2 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Size (nm) | SD (nm) | % | Size (nm) | SD (nm) | % | |
| 0 min heat | ||||||
| 10 | 189.0 | 30.2 | 78.3 | 605.5 | 104.6 | 21.7 |
| 30 | 113.0 | 10.3 | 88.3 | 477.1 | 81.2 | 11.7 |
| 60 | 151.6 | 23.2 | 85.1 | 432.5 | 70.2 | 14.9 |
| 30 min heat | ||||||
| 10 | 88.4 | 14.9 | 94 | 247.0 | 39.7 | 5.9 |
| 30 | 64.3 | 8.6 | 98 | 247.5 | 36.7 | 1.9 |
| 60 | 66.6 | 9.6 | 99 | 277.8 | 38.8 | 0.9 |
| 60 min heat | ||||||
| 10 | 65.2 | 12.2 | 97.1 | 259.9 | 35.3 | 2.9 |
| 30 | 47.1 | 7.4 | 99.3 | 235.4 | 27.9 | 0.7 |
| 60 | 48.1 | 6.1 | 99.4 | 218.1 | 25.2 | 0.6 |
| 120 min heat | ||||||
| 10 | 68.2 | 12.9 | 98.6 | 277.8 | 45.1 | 1.4 |
| 30 | 52.6 | 7.9 | 99.6 | 249.3 | 43.5 | 0.4 |
| 60 | 52.5 | 7.1 | 99.9 | 228.0 | 12.3 | 0.1 |
| Milling Time (min) | Heating Time (min) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 30 | 60 | 120 | |
| Mean BET surface area (m2g−1) | ||||
| 10 | 3.8 | 6.9 | 6.2 | 6.6 |
| 30 | 3.9 | 7.8 | 7.5 | 7.4 |
| 60 | 6.0 | 7.8 | 7.6 | 8.6 |
| Langmuir surface area (m2g−1) | ||||
| 10 | 5.5 | 9.9 | 9.0 | 9.9 |
| 30 | 5.6 | 11.3 | 10.8 | 10.8 |
| 60 | 8.6 | 11.3 | 11.0 | 12.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nuruzzaman, M.; Liu, Y.; Rahman, M.M.; Nasif, S.O.; Naidu, R. Effect of Heat Treatment on Polymorphism and Particle Size Distribution of Calcium Carbonate Nanoparticle Synthesized via Mechanochemical Process. Appl. Nano 2025, 6, 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/applnano6020008
Nuruzzaman M, Liu Y, Rahman MM, Nasif SO, Naidu R. Effect of Heat Treatment on Polymorphism and Particle Size Distribution of Calcium Carbonate Nanoparticle Synthesized via Mechanochemical Process. Applied Nano. 2025; 6(2):8. https://doi.org/10.3390/applnano6020008
Chicago/Turabian StyleNuruzzaman, Md, Yanju Liu, Mohammad Mahmudur Rahman, Saifullah Omar Nasif, and Ravi Naidu. 2025. "Effect of Heat Treatment on Polymorphism and Particle Size Distribution of Calcium Carbonate Nanoparticle Synthesized via Mechanochemical Process" Applied Nano 6, no. 2: 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/applnano6020008
APA StyleNuruzzaman, M., Liu, Y., Rahman, M. M., Nasif, S. O., & Naidu, R. (2025). Effect of Heat Treatment on Polymorphism and Particle Size Distribution of Calcium Carbonate Nanoparticle Synthesized via Mechanochemical Process. Applied Nano, 6(2), 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/applnano6020008










