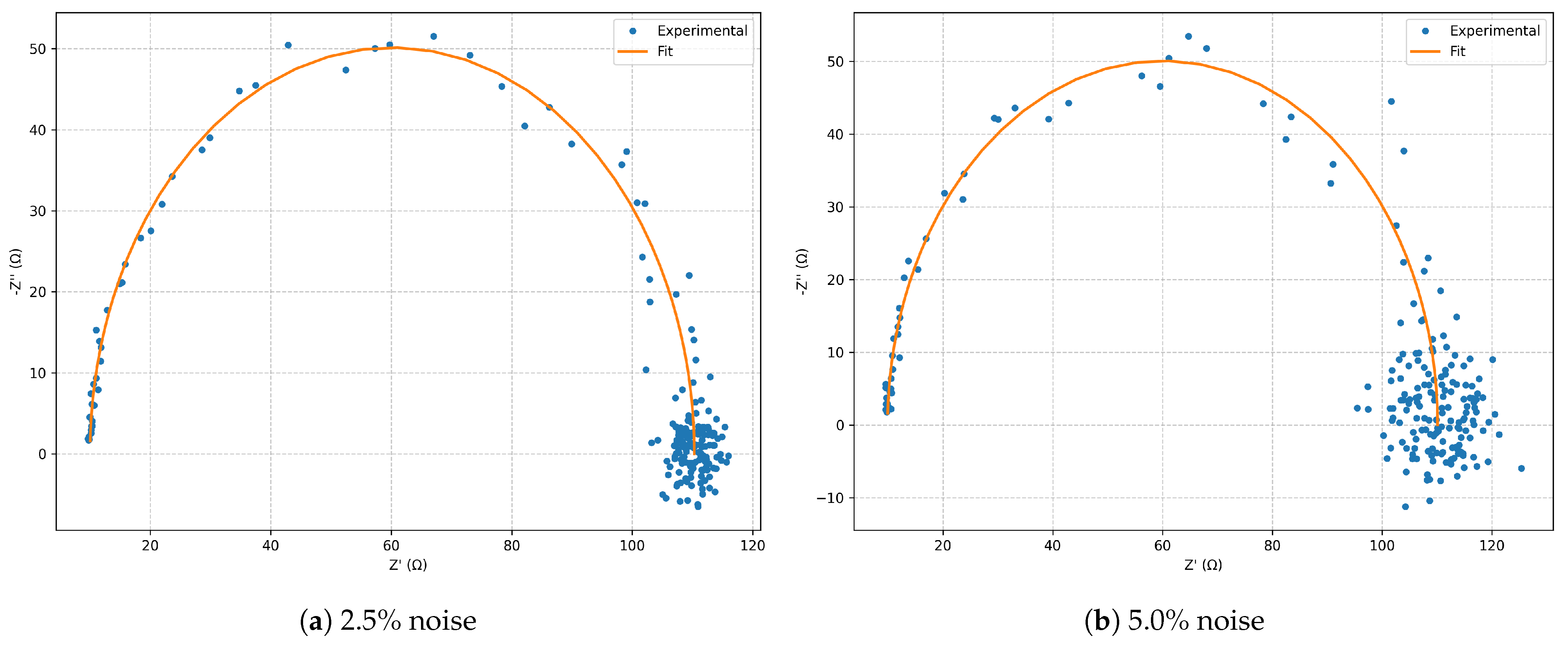
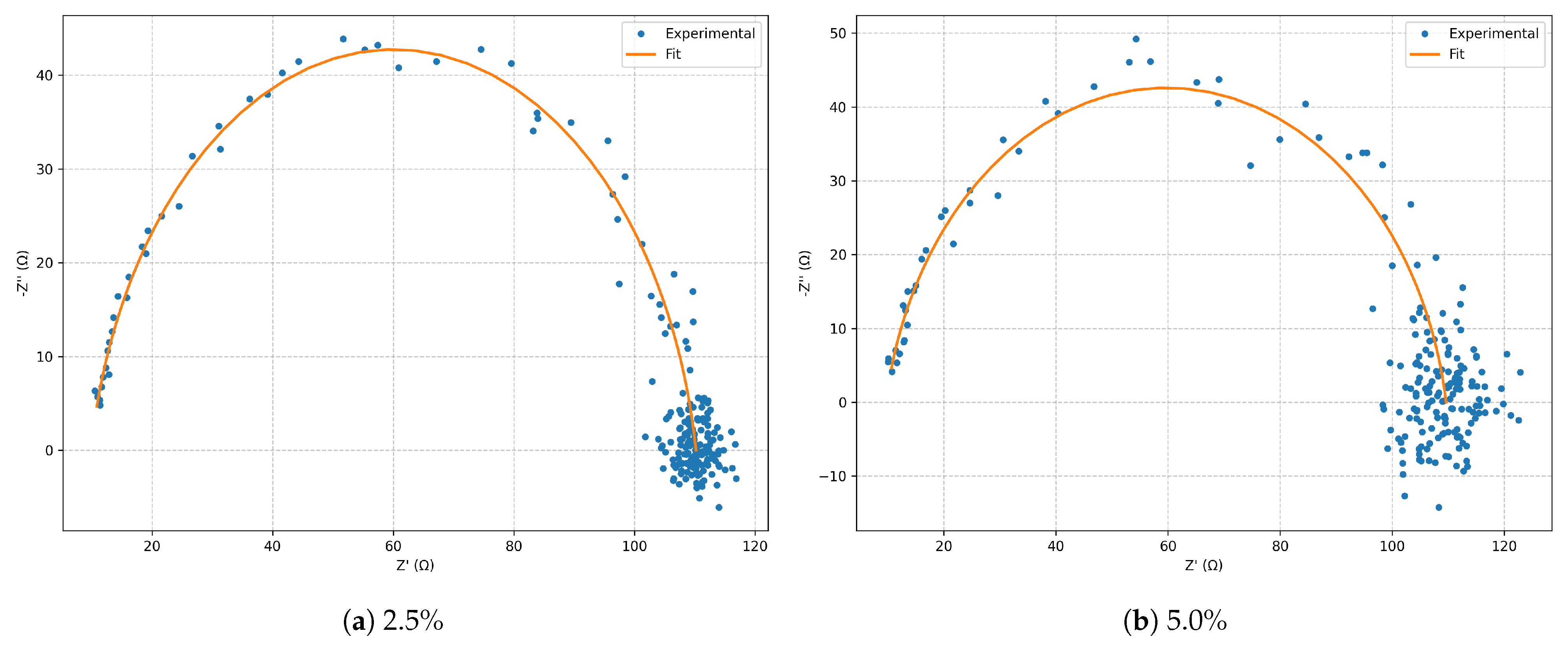
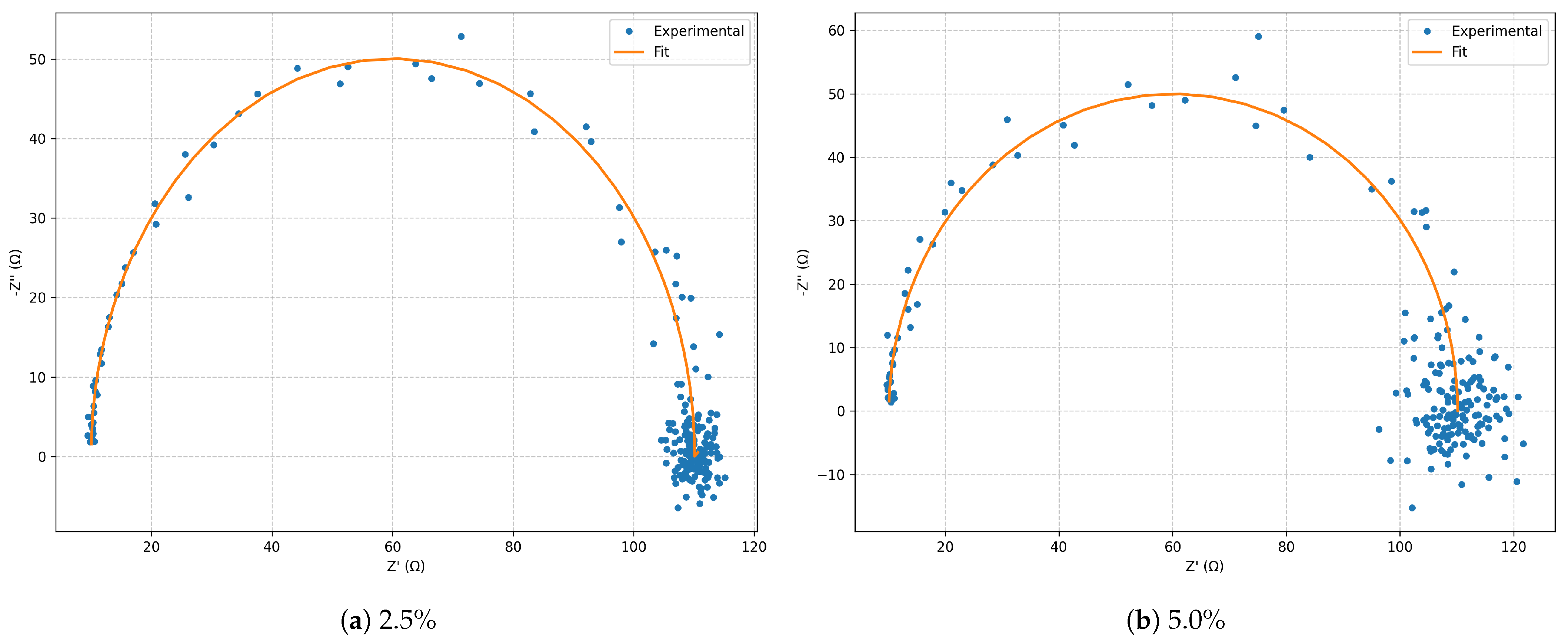
Figure 1.
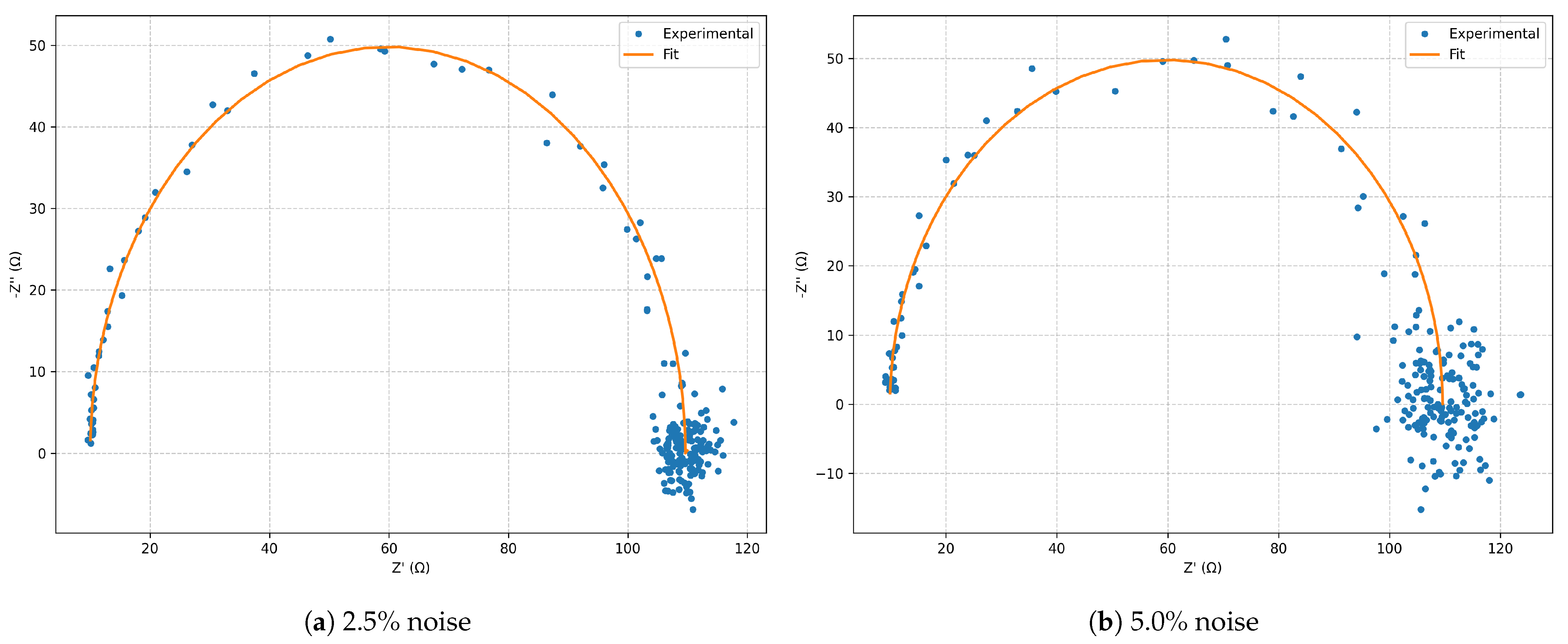
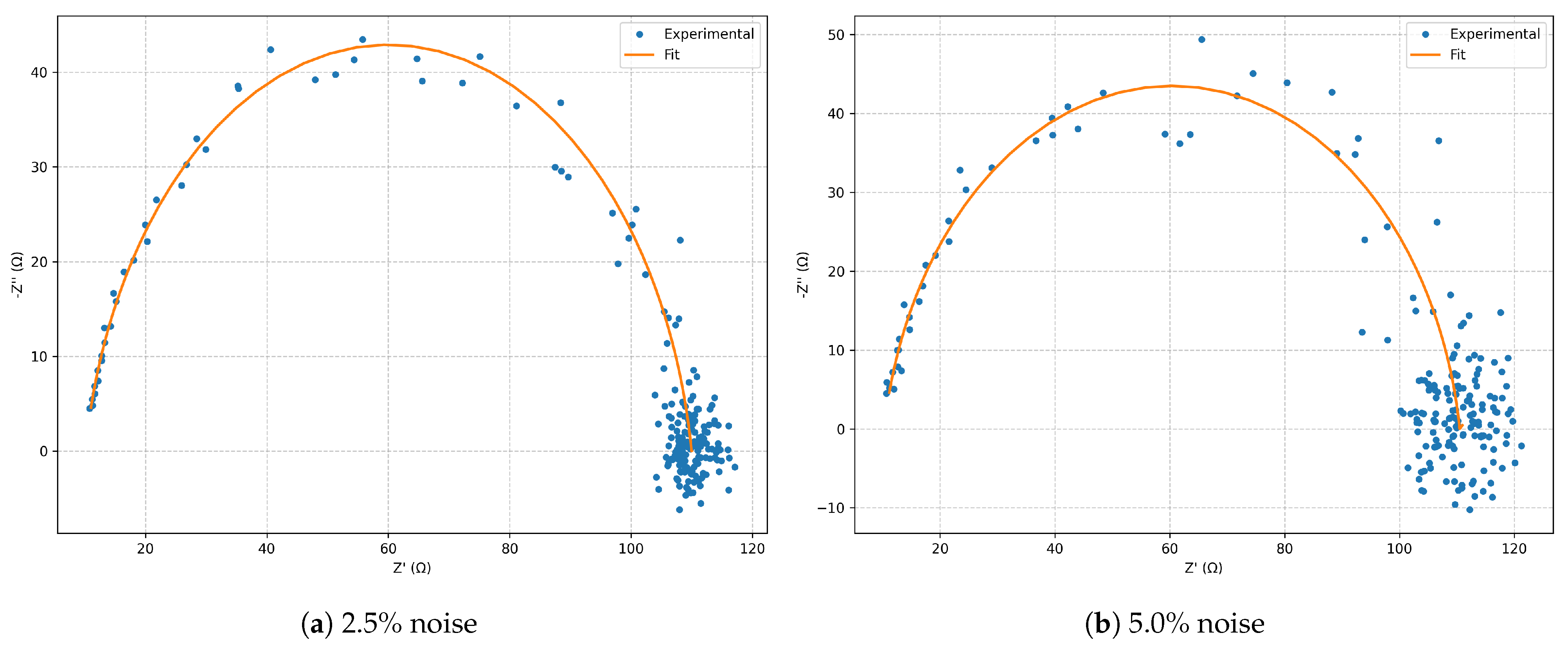
Nyquist diagrams for the series RLC model: comparison between and noise.
Figure 1.
Nyquist diagrams for the series RLC model: comparison between and noise.
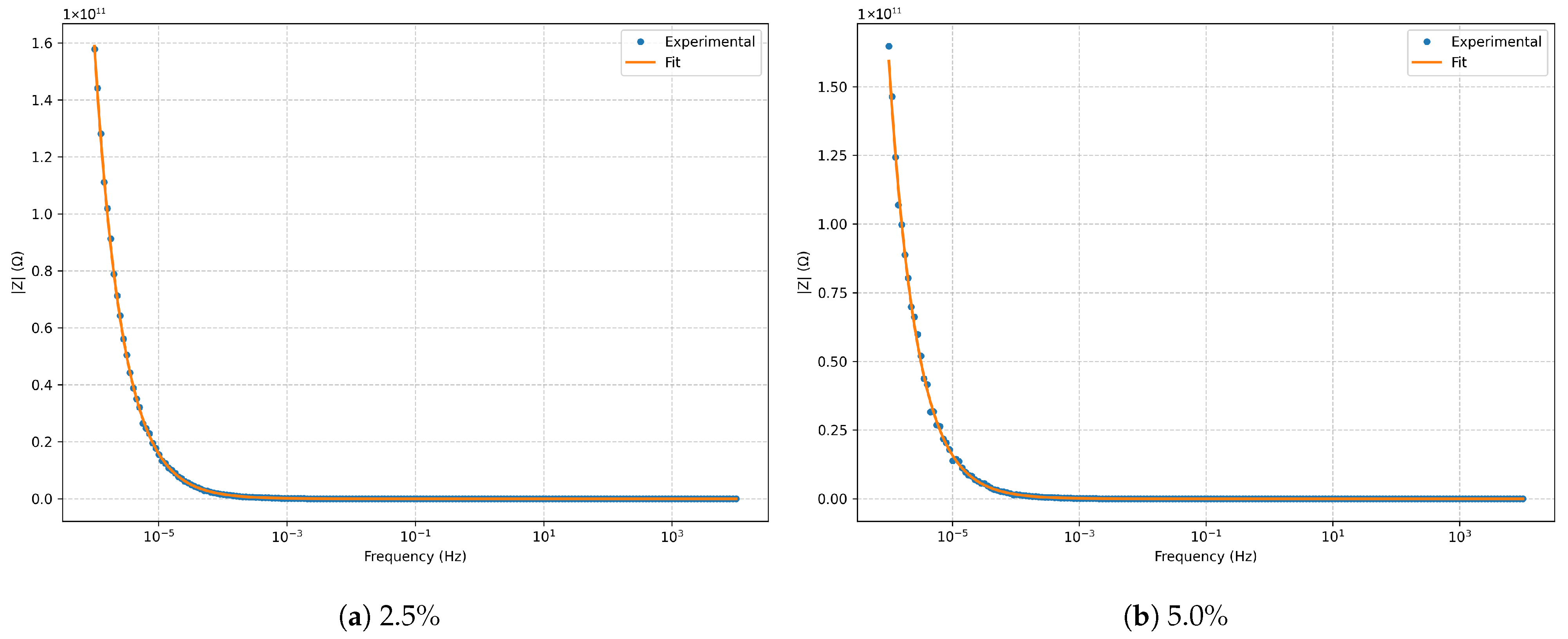
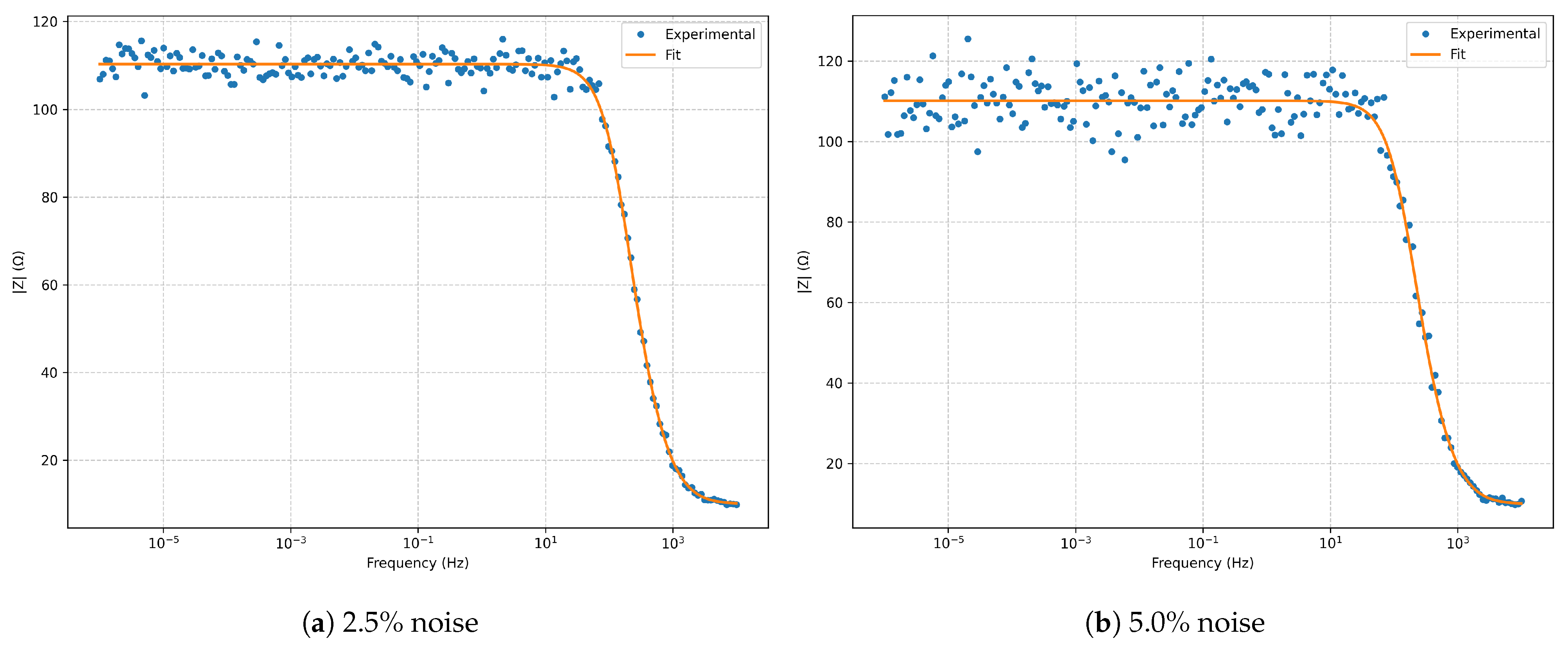
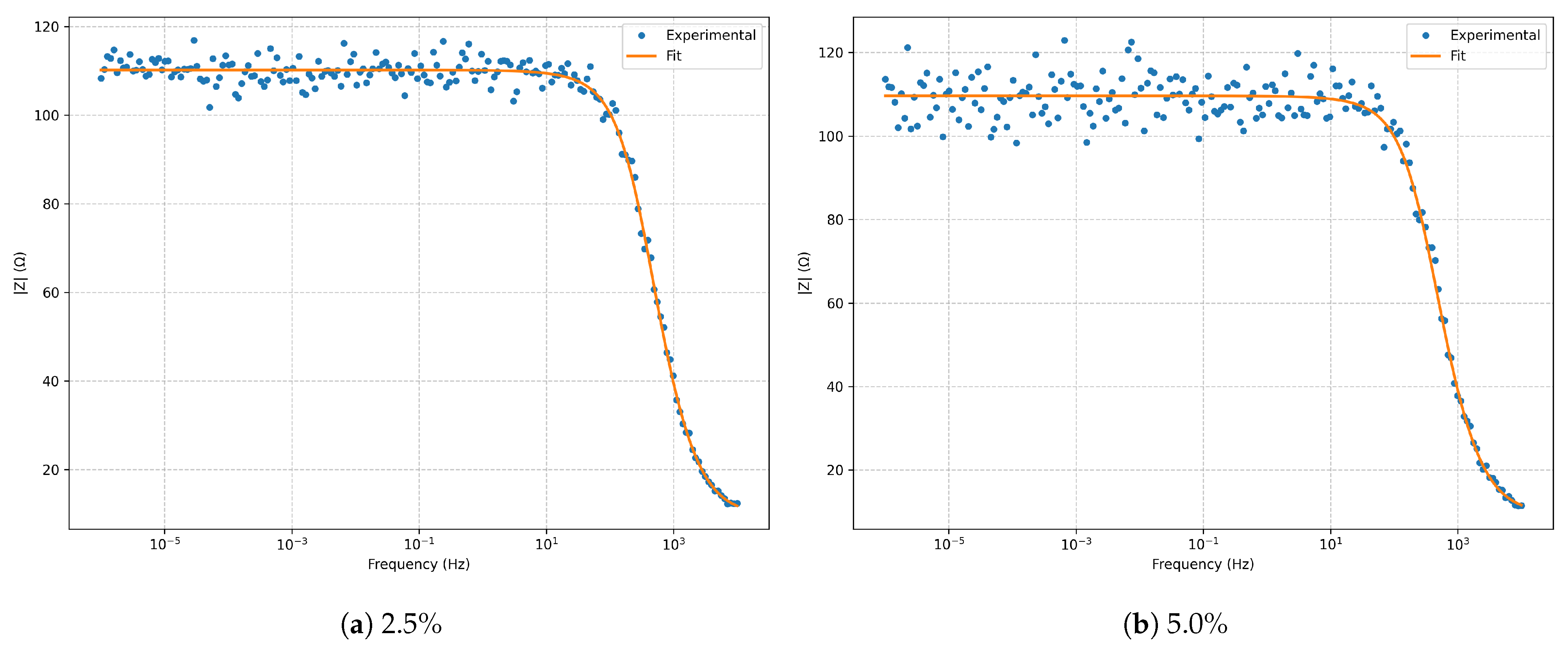
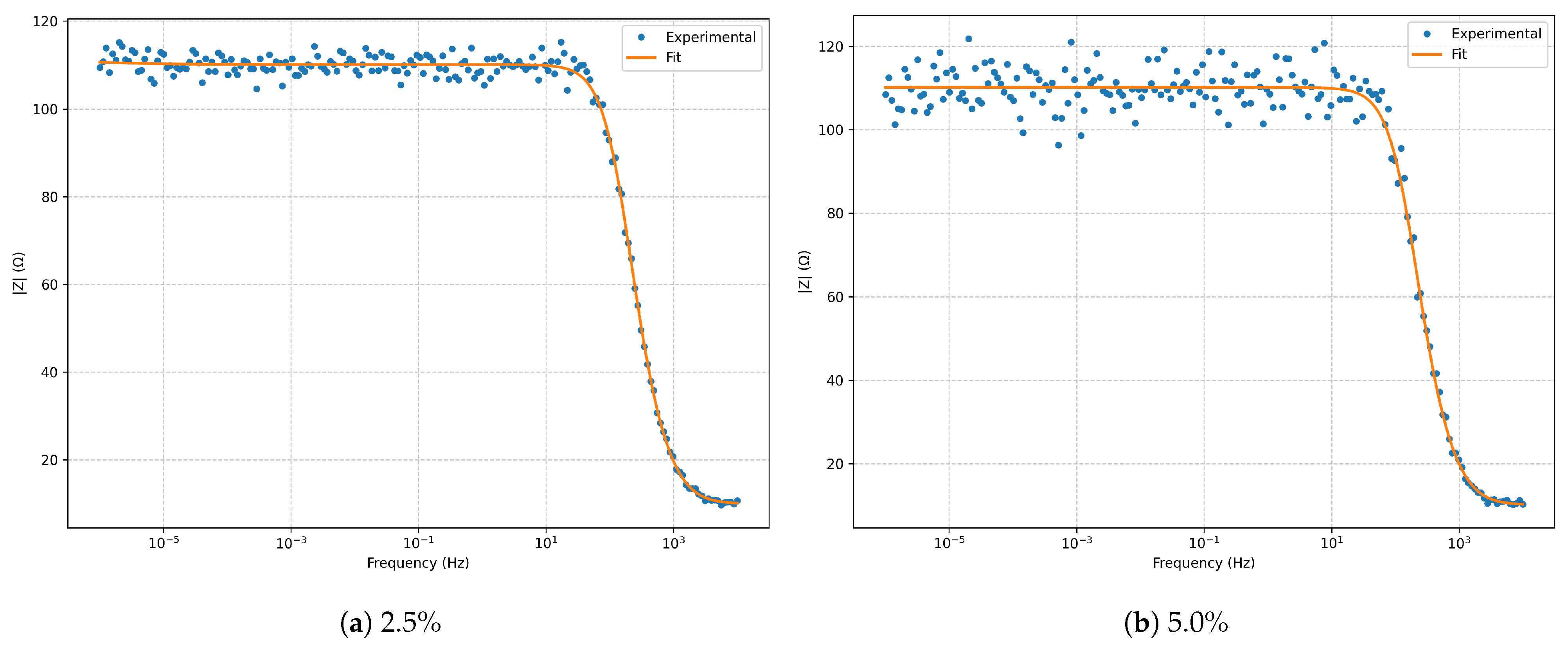
Figure 2.
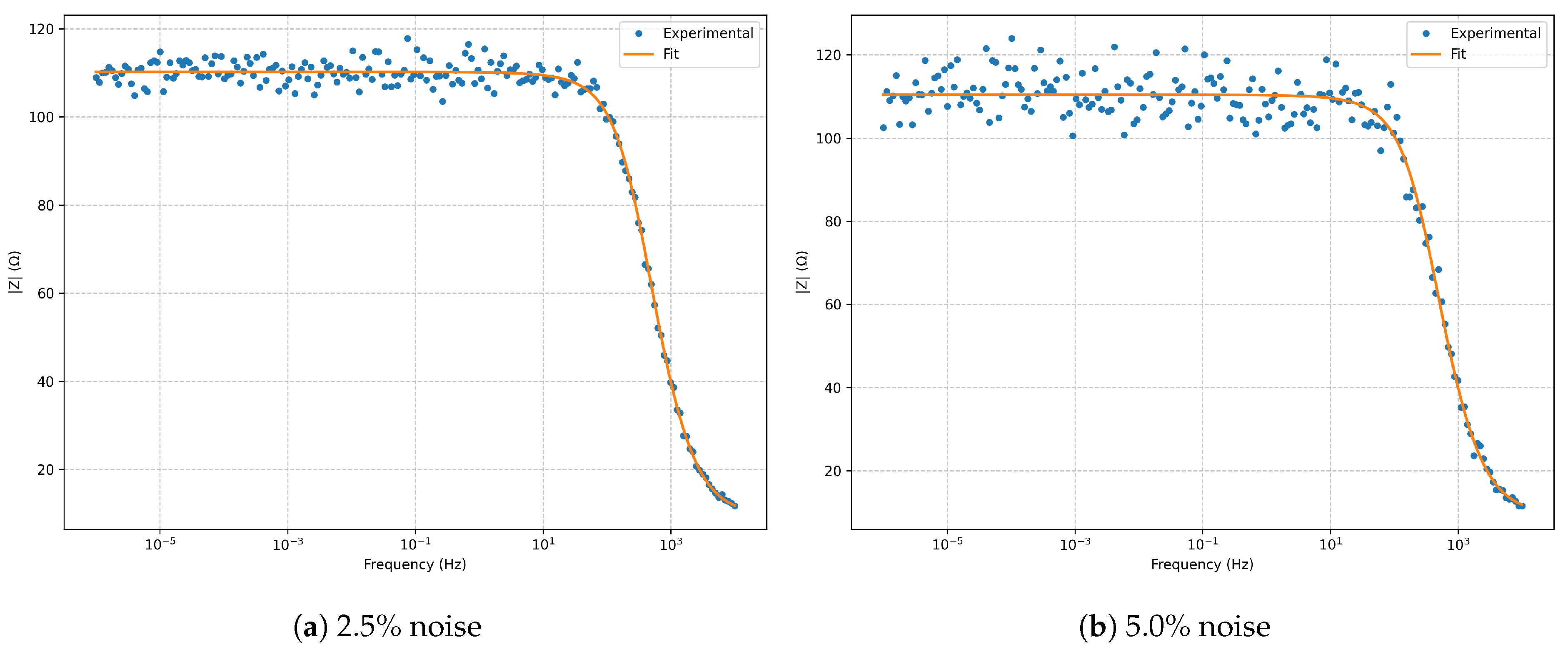
Bode magnitude for the series RLC model at and noise.
Figure 2.
Bode magnitude for the series RLC model at and noise.
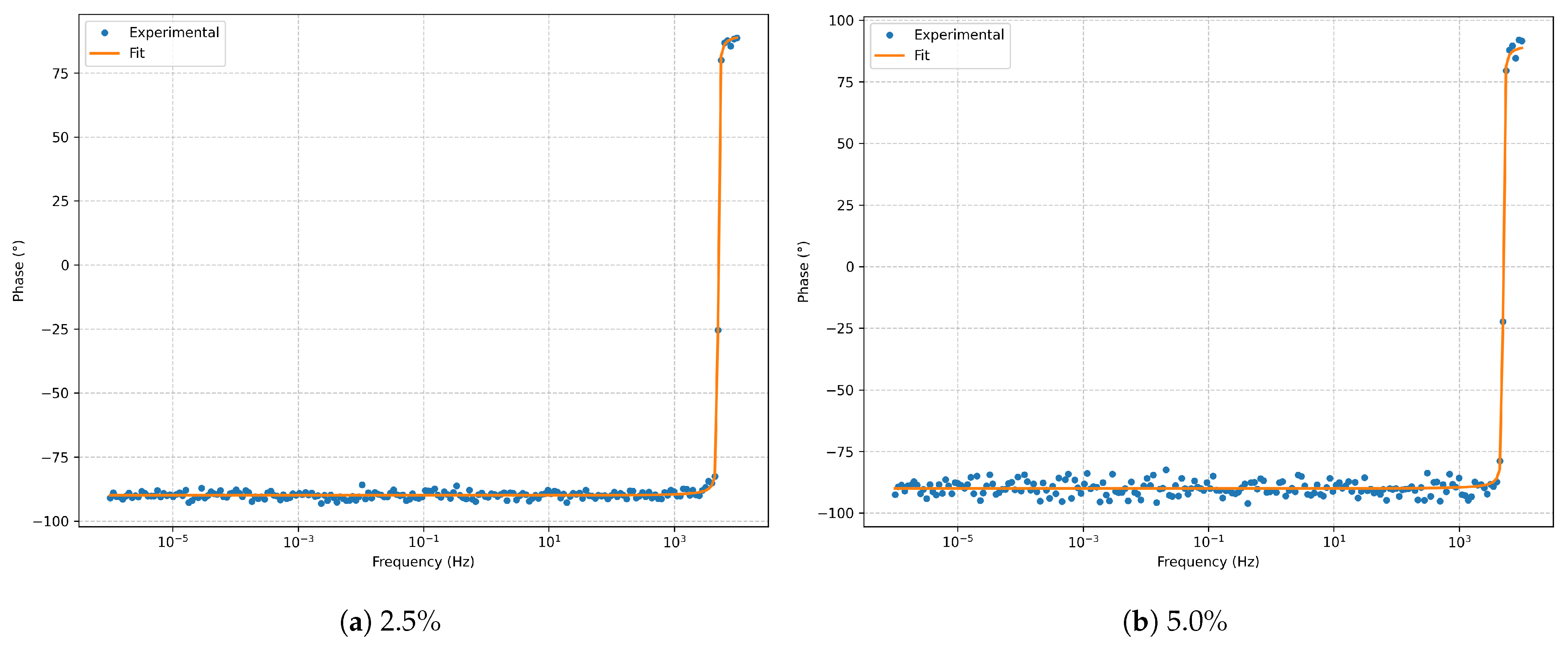
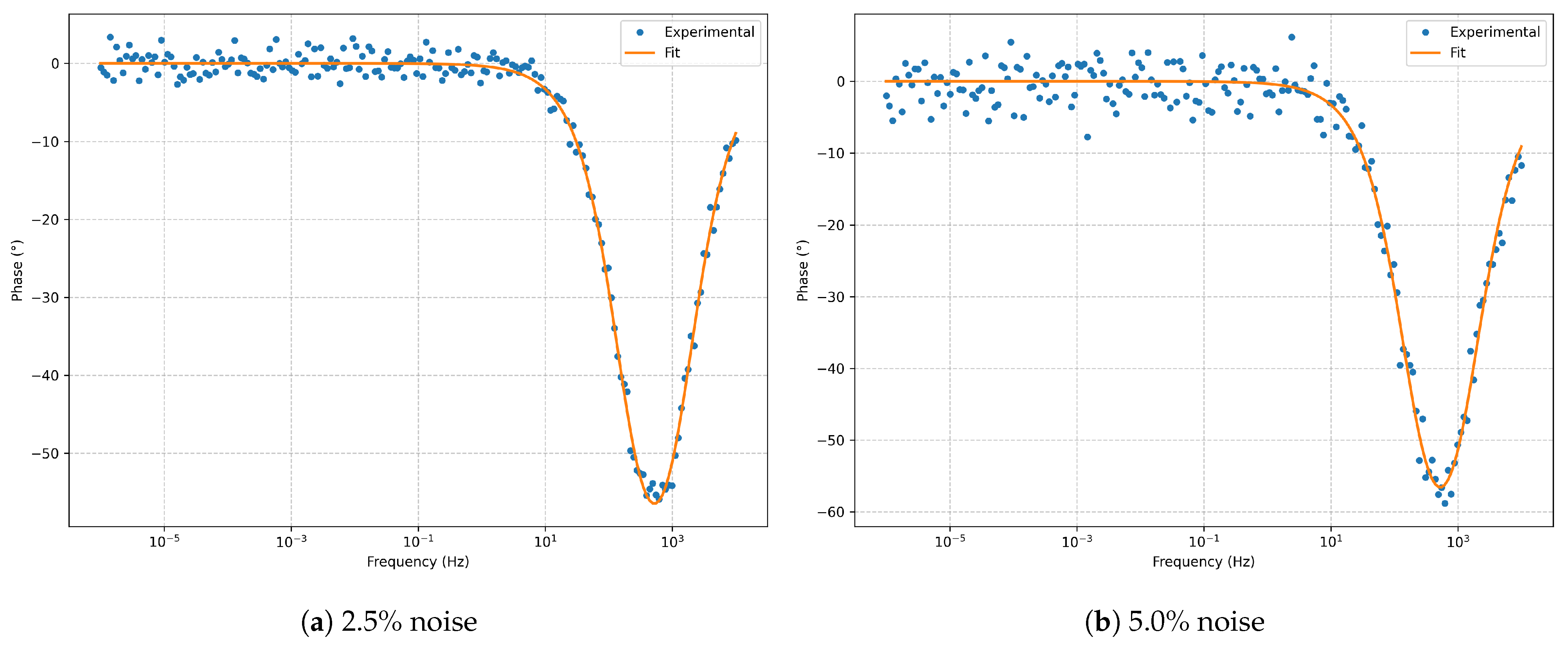
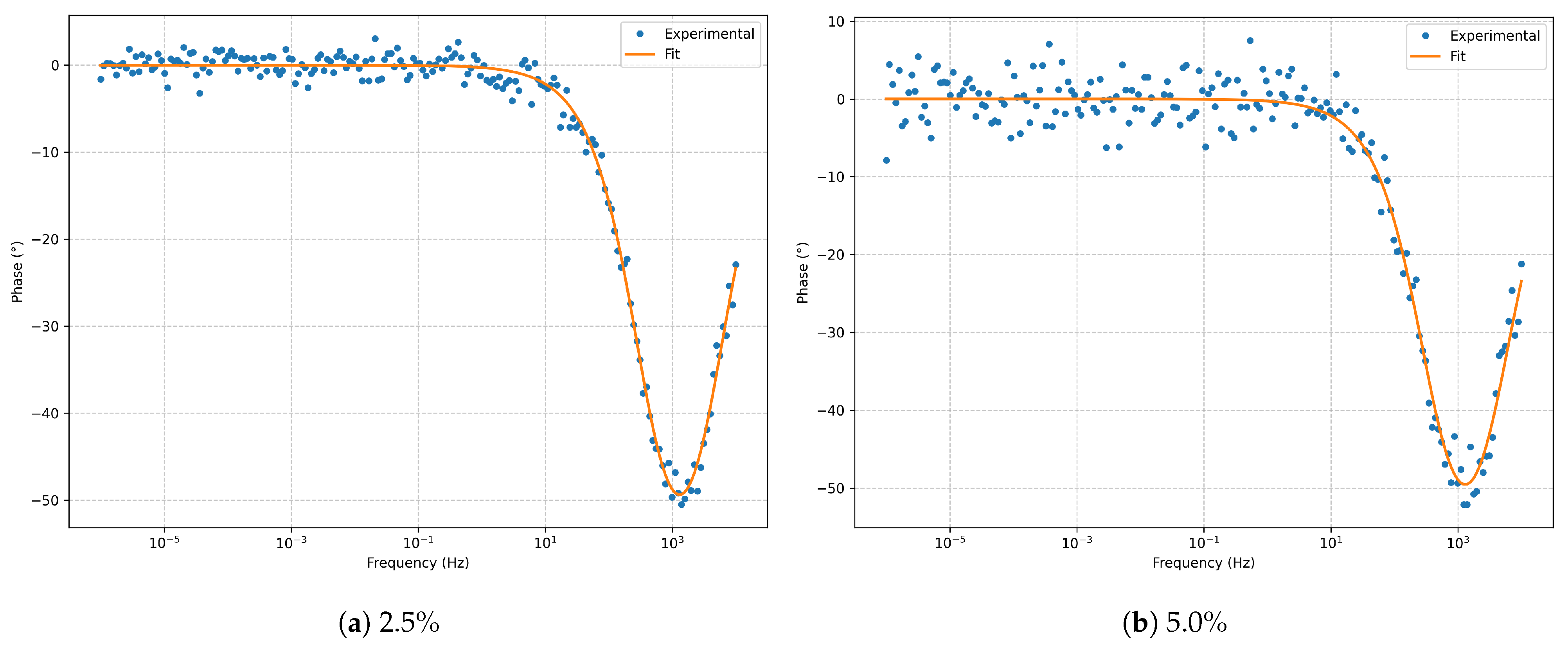
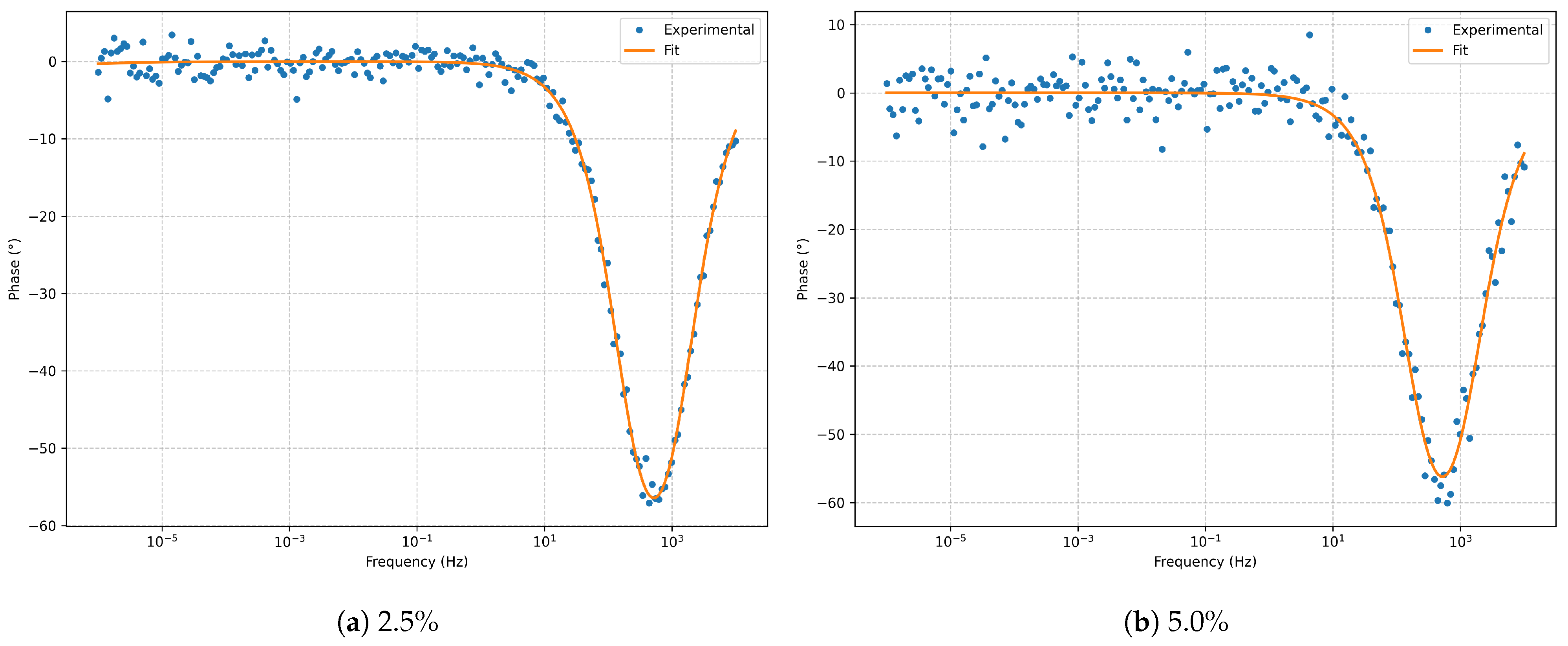
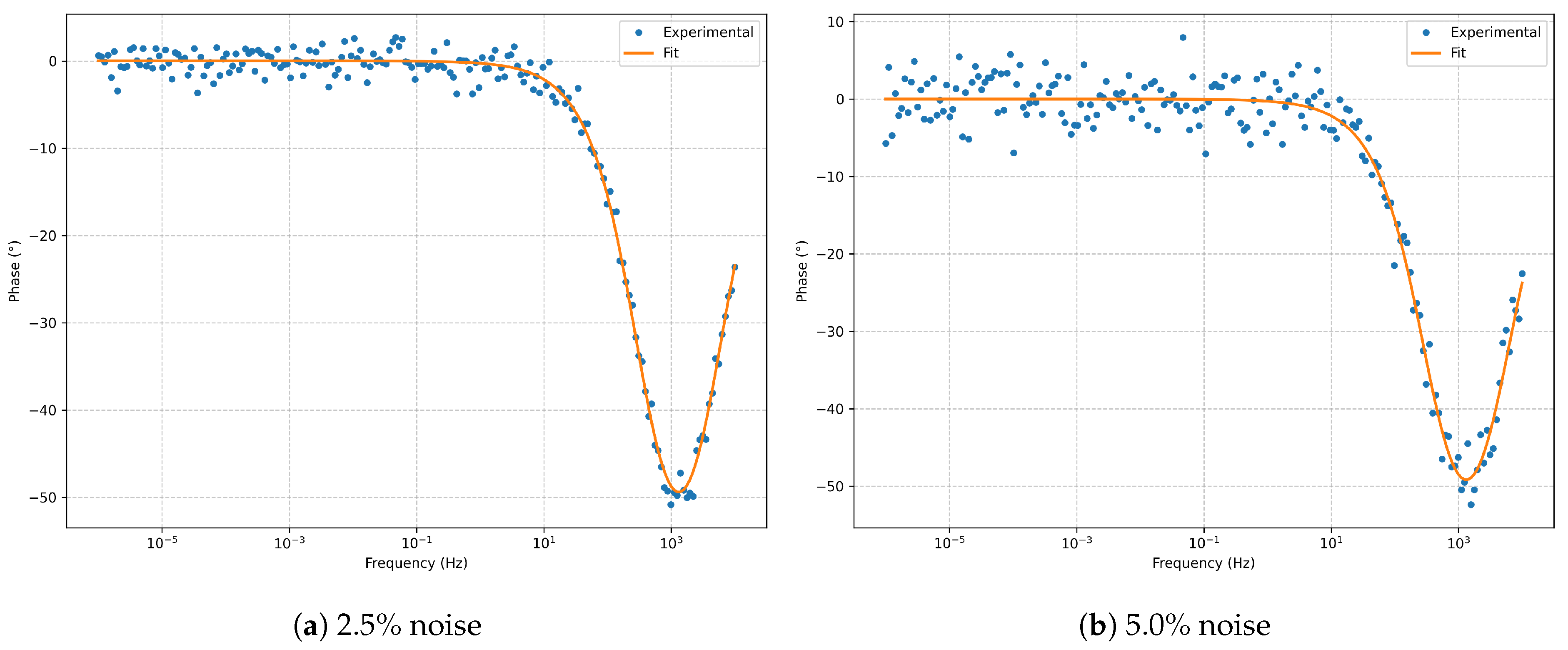
Figure 3.
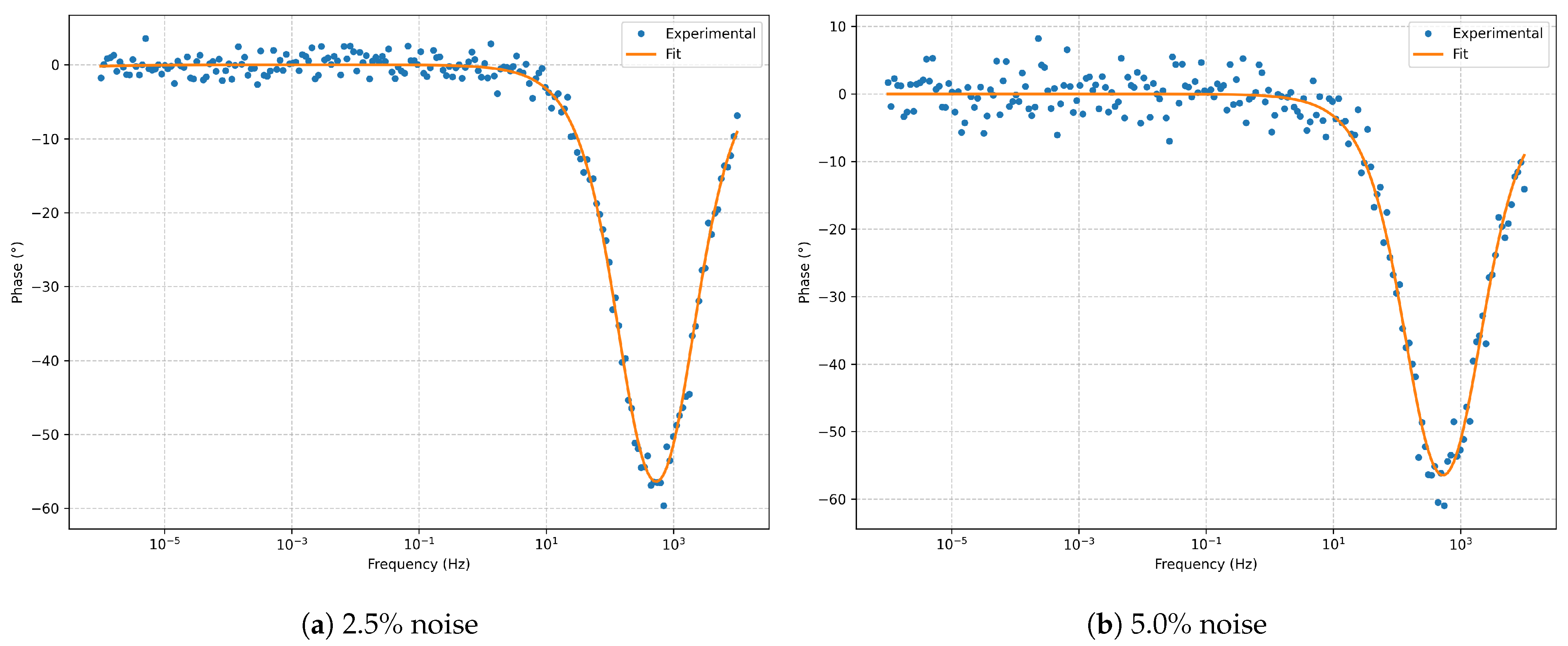
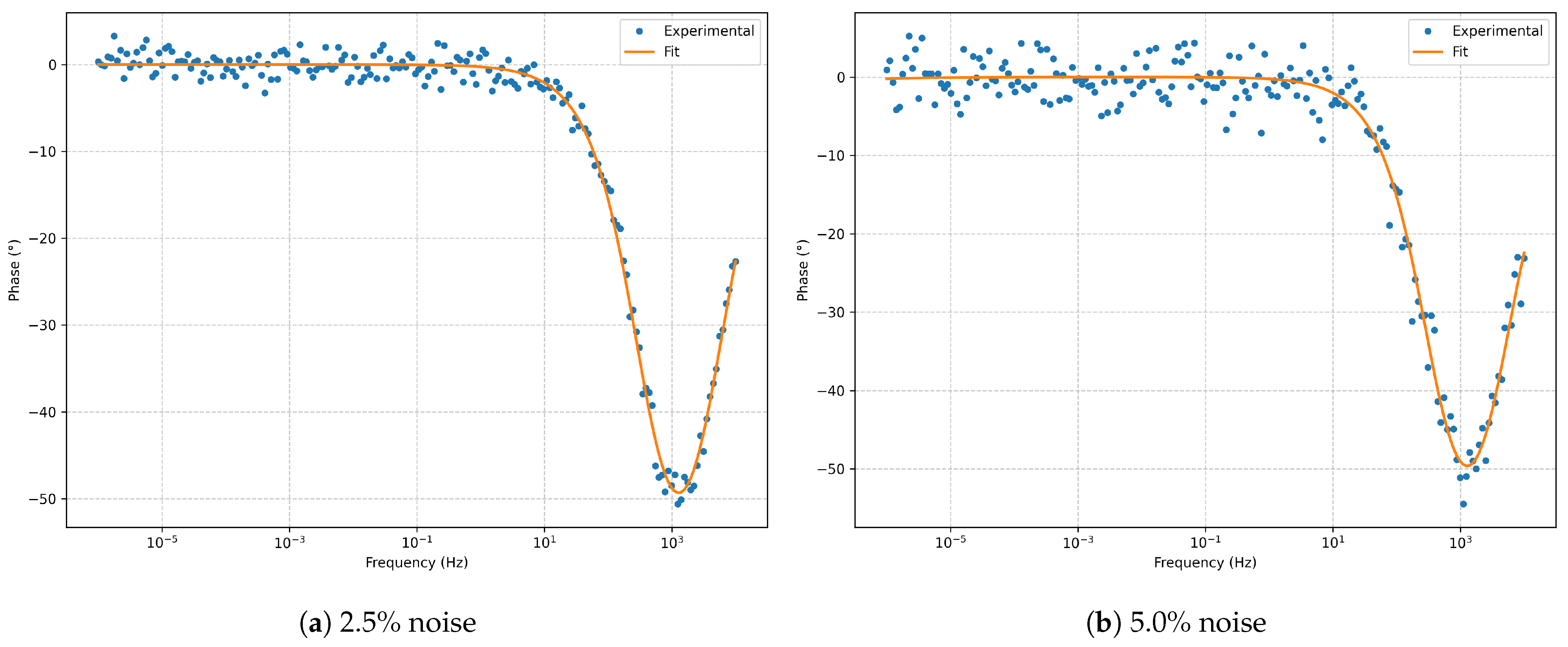
Bode phase for the series RLC model at and noise.
Figure 3.
Bode phase for the series RLC model at and noise.
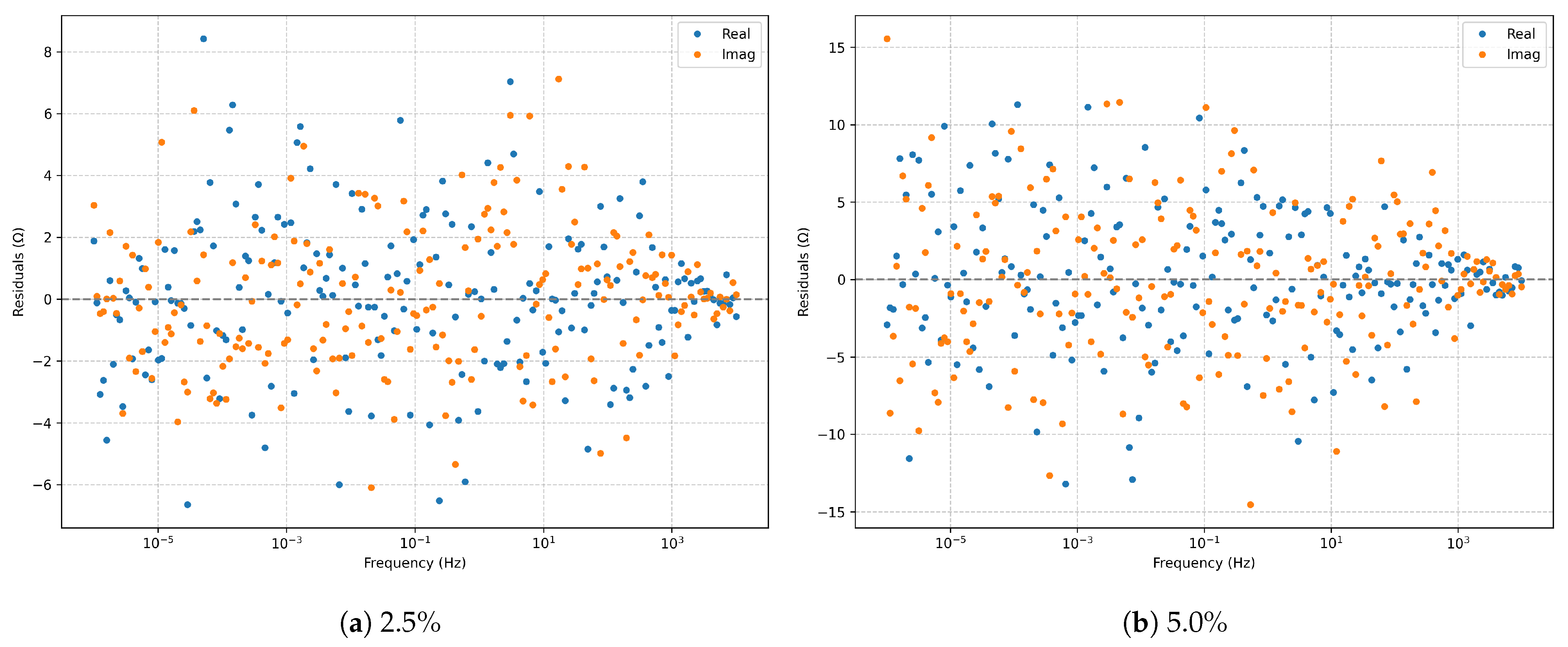
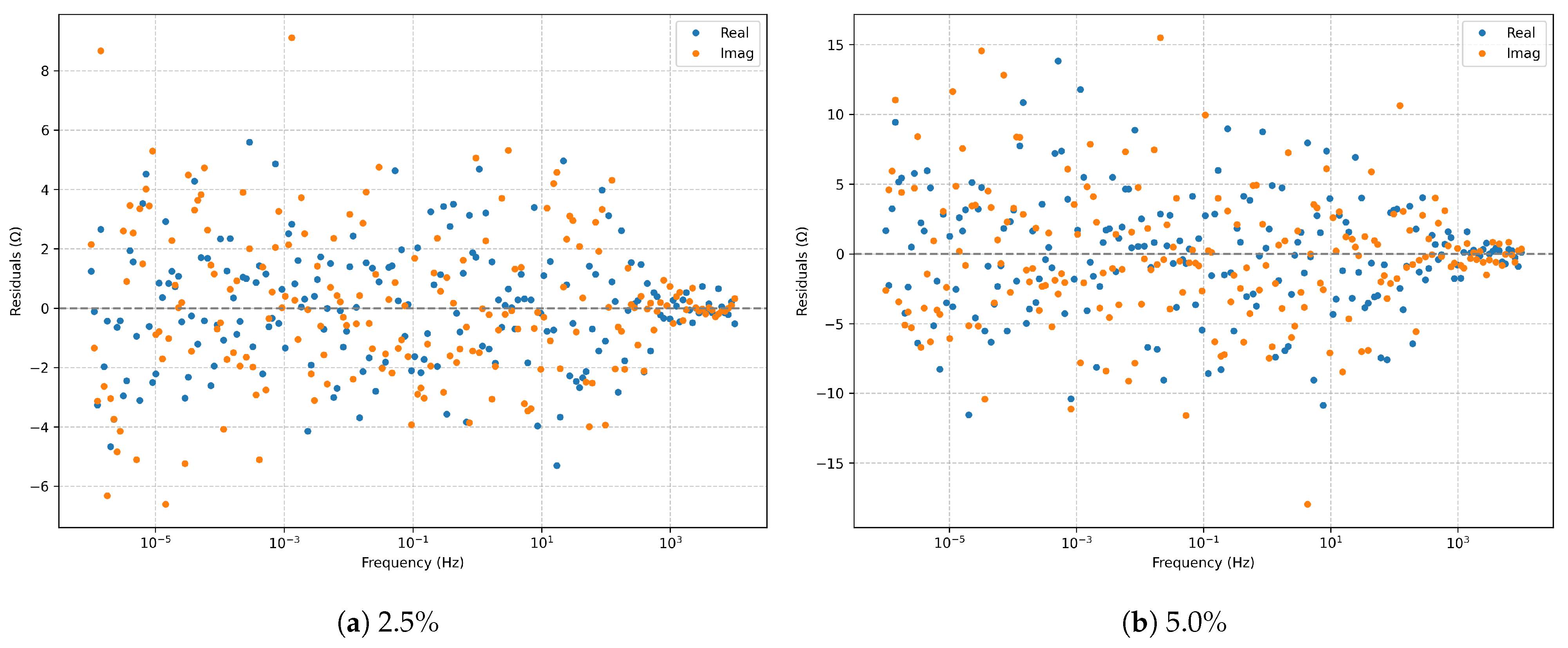
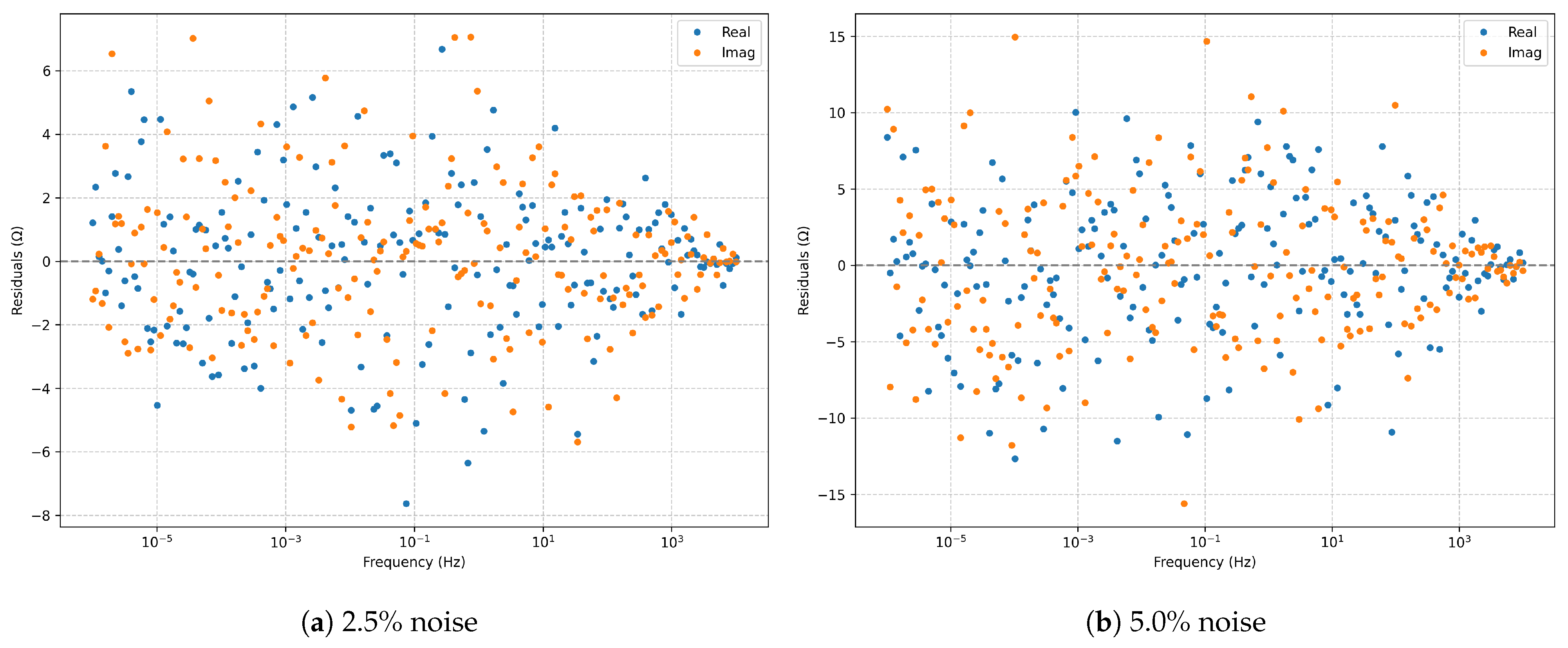
Figure 4.
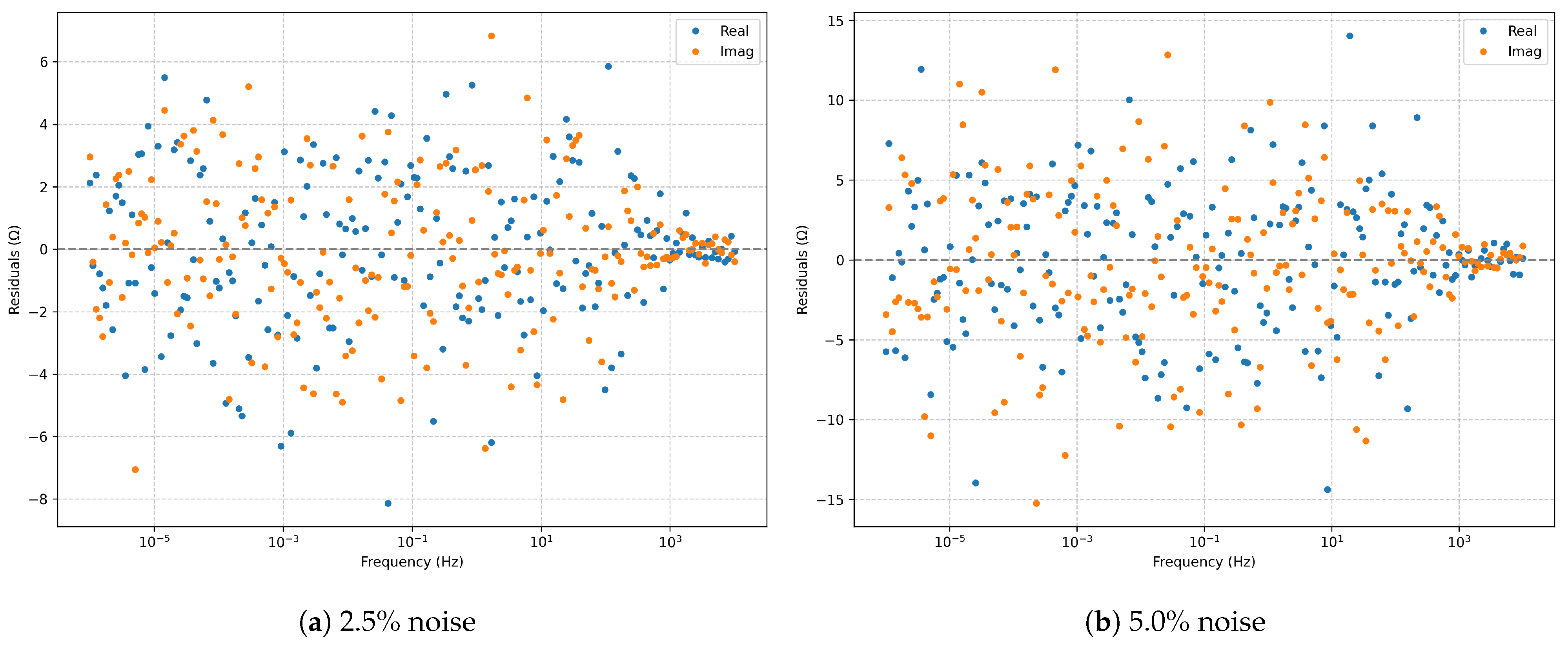
Raw complex residuals (real and imaginary parts) for the series RLC model: (a) 2.5% noise; (b) 5.0% noise.
Figure 4.
Raw complex residuals (real and imaginary parts) for the series RLC model: (a) 2.5% noise; (b) 5.0% noise.
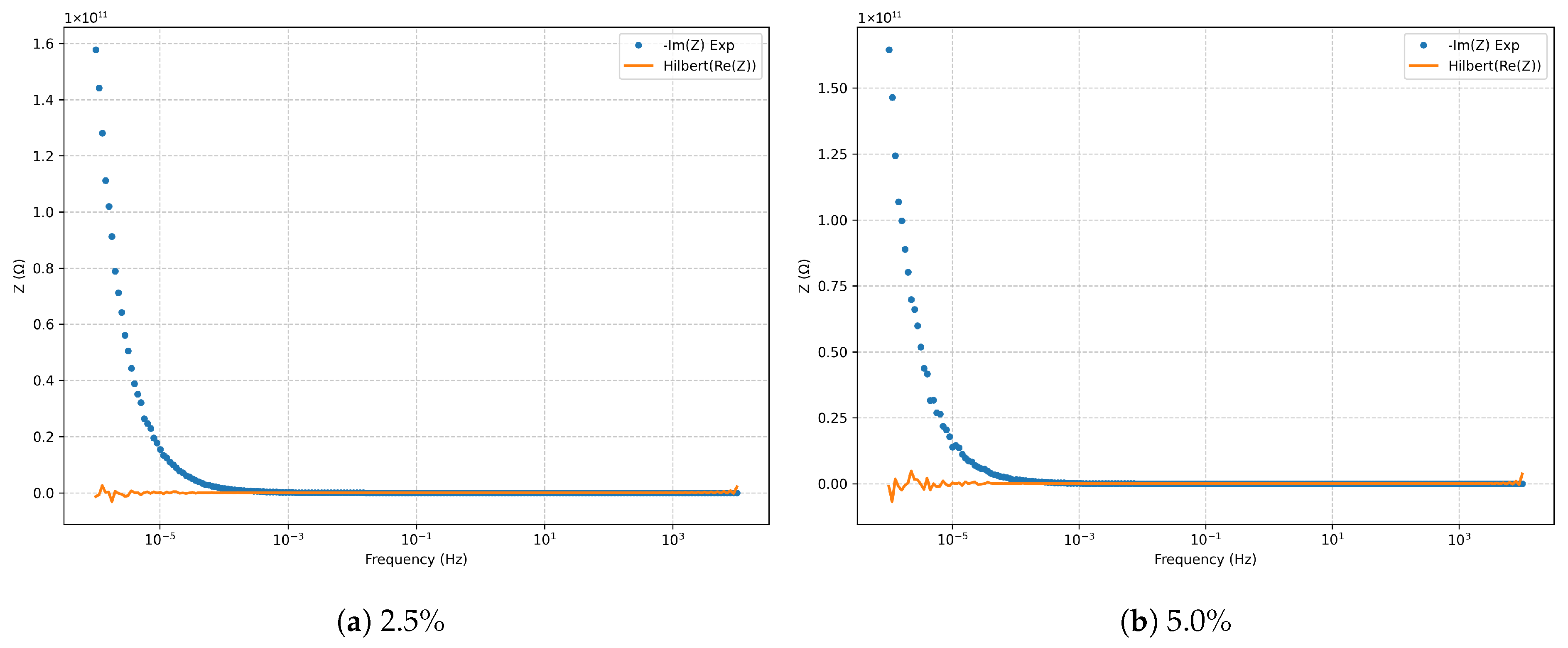
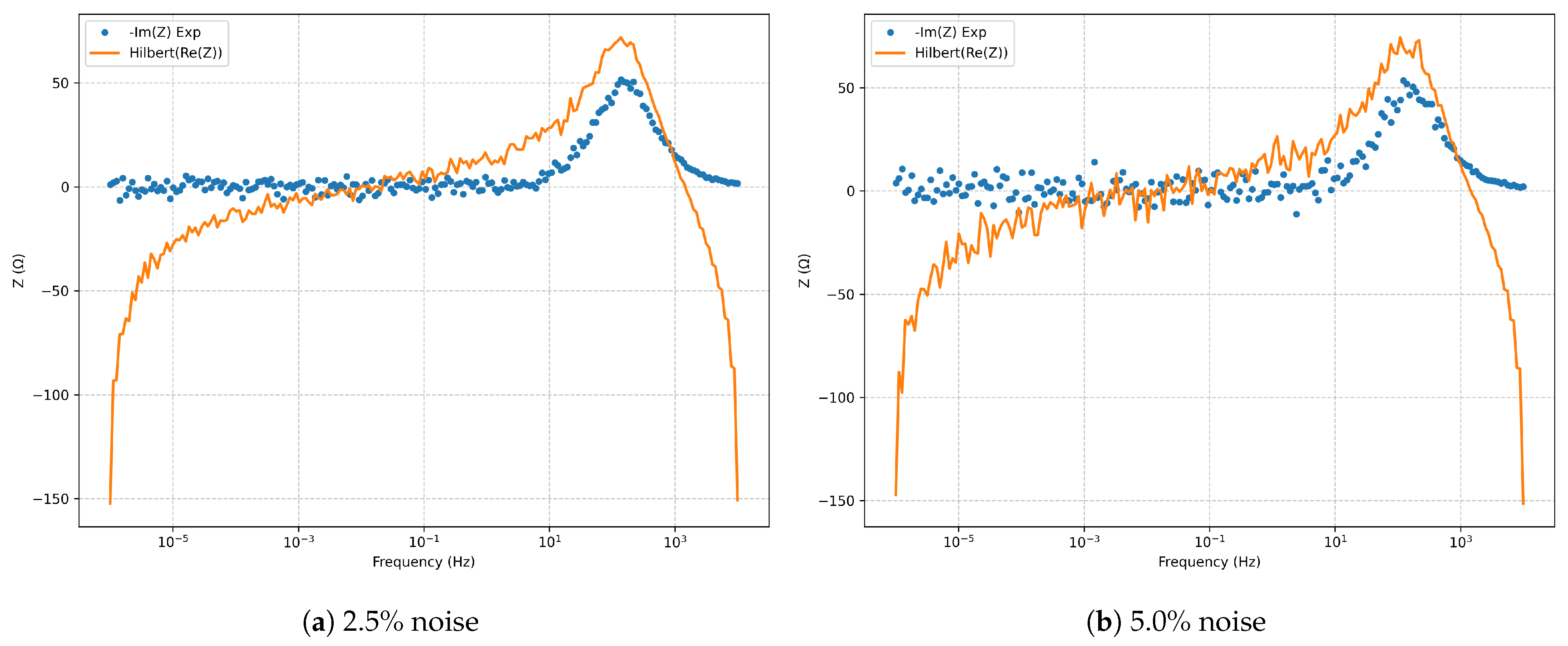
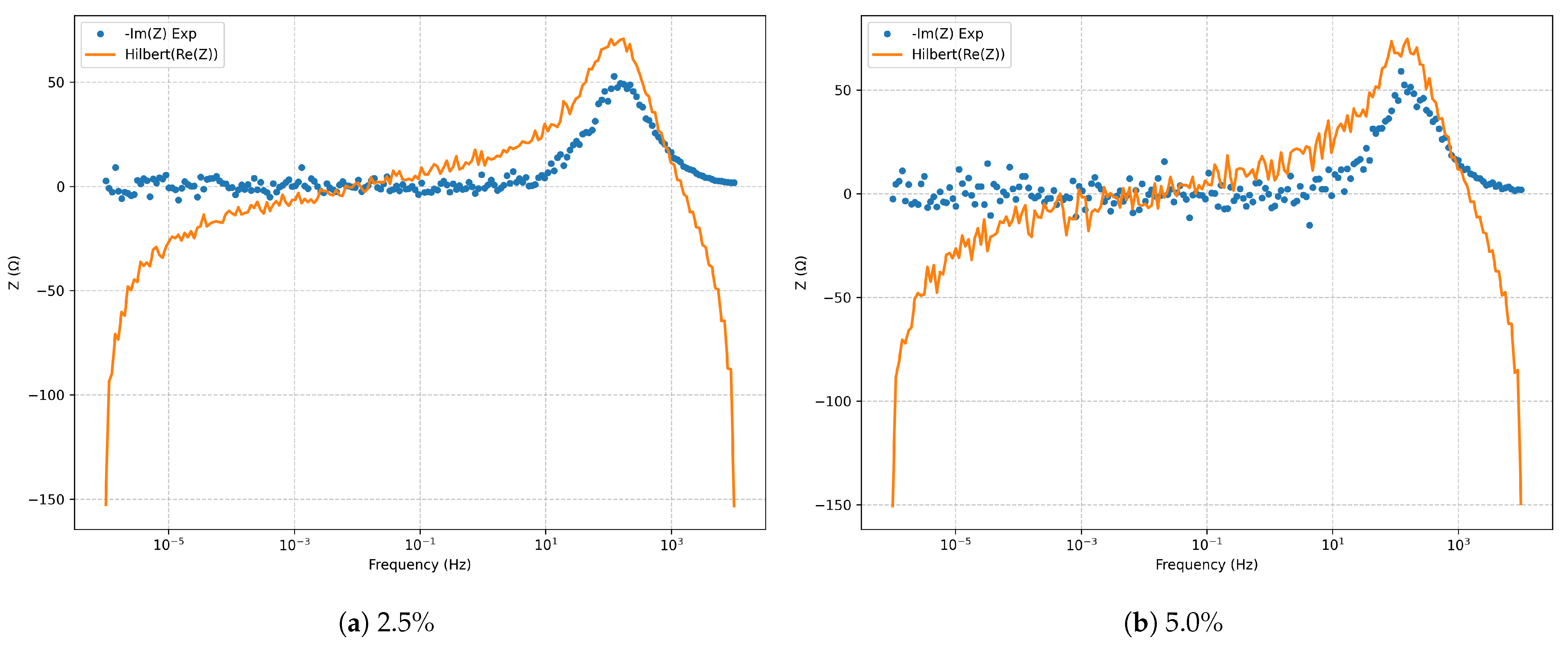
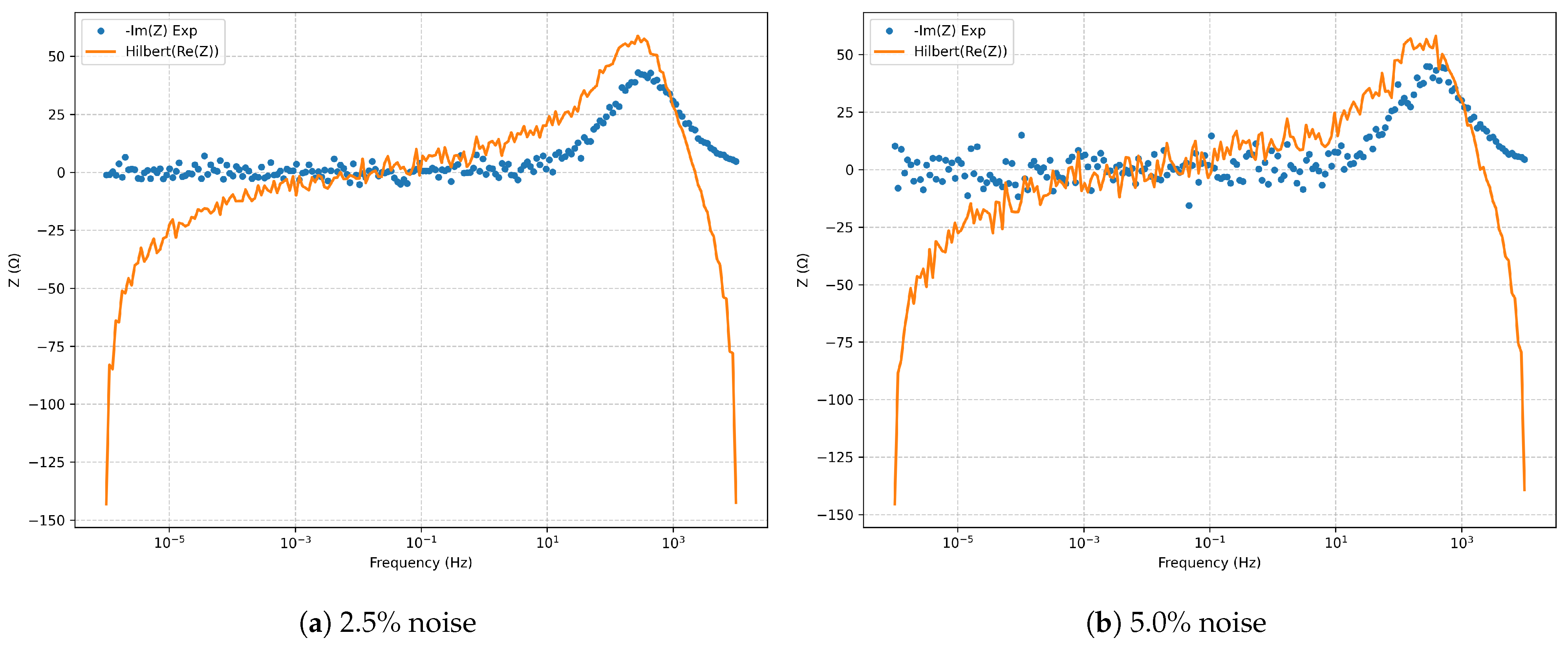
Figure 5.
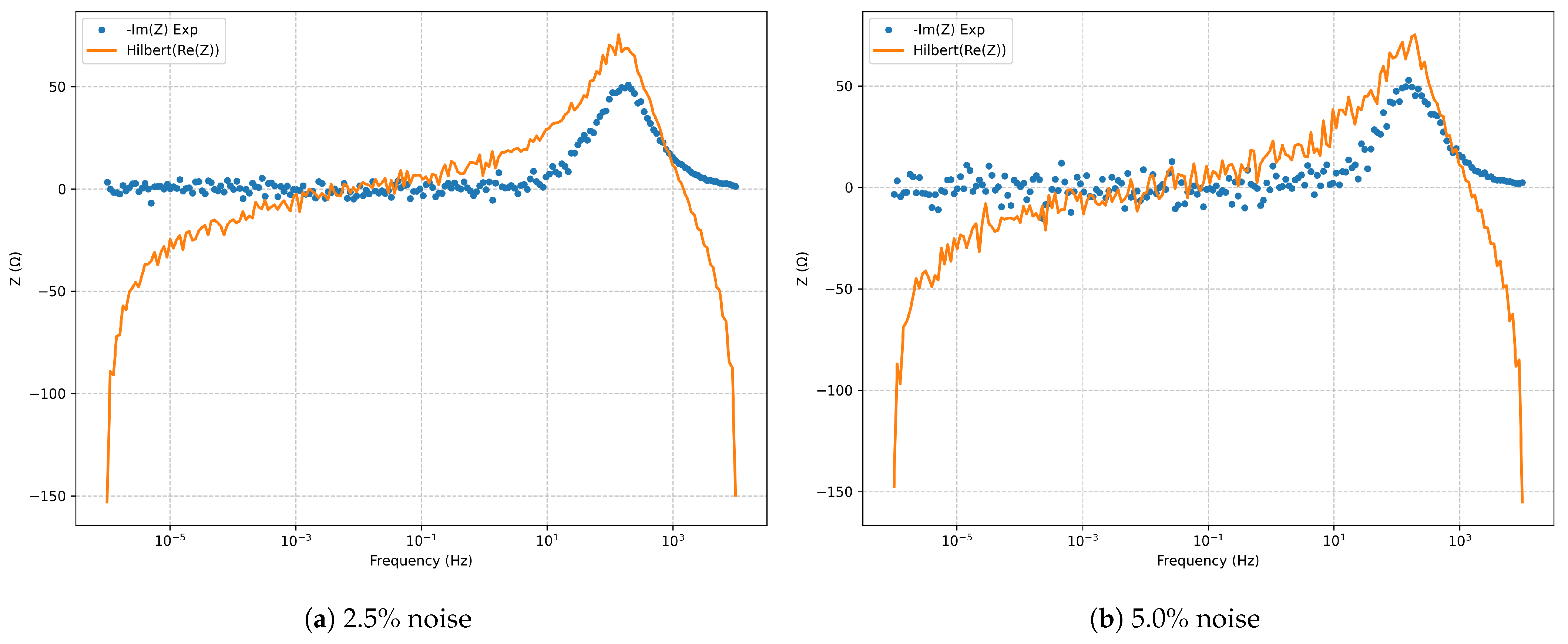
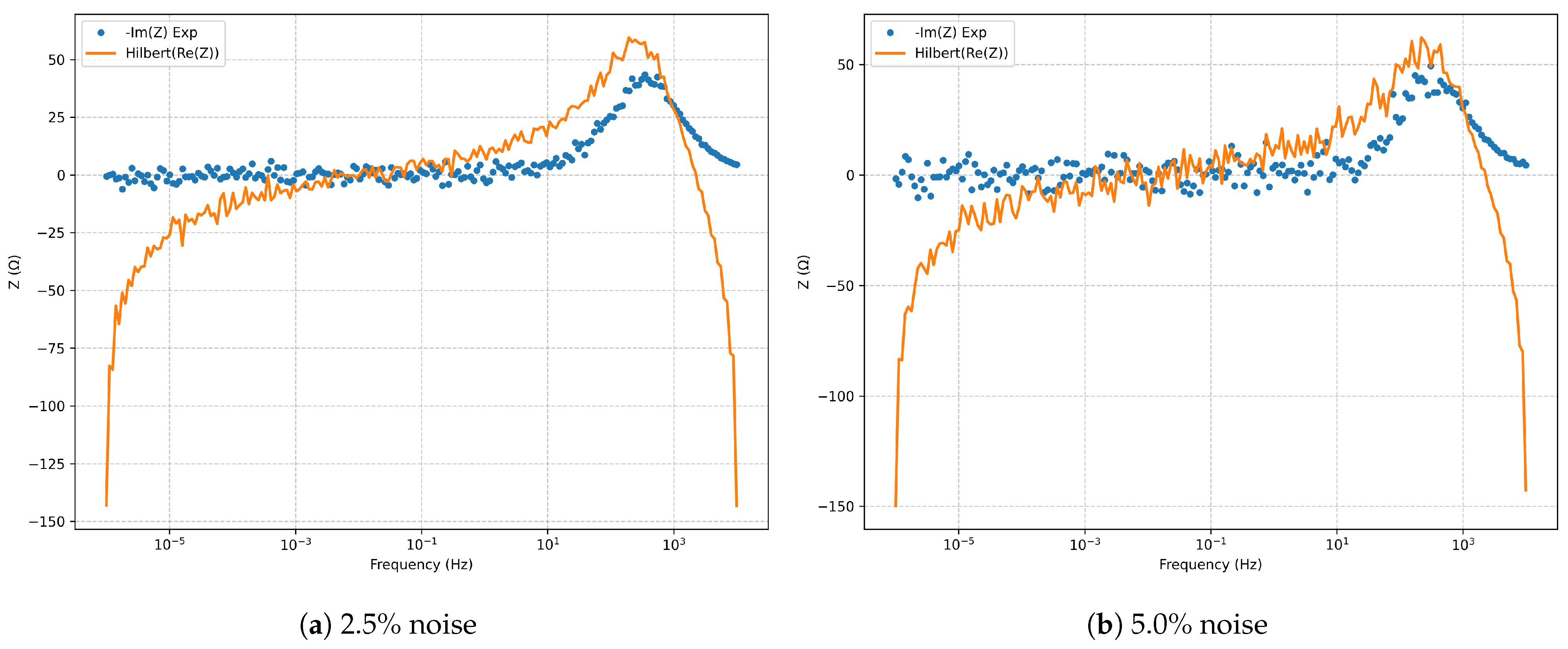
Kramers–Kronig validation (Hilbert transform) for the series RLC model.
Figure 5.
Kramers–Kronig validation (Hilbert transform) for the series RLC model.
Figure 6.
Nyquist diagrams for the classic Randles model: (a) 2.5% noise; (b) 5.0% noise.
Figure 6.
Nyquist diagrams for the classic Randles model: (a) 2.5% noise; (b) 5.0% noise.
Figure 7.
Bode magnitude for the classic Randles model at 2.5% and 5.0% noise levels.
Figure 7.
Bode magnitude for the classic Randles model at 2.5% and 5.0% noise levels.
Figure 8.
Bode phase for the classic Randles model at 2.5% and 5.0% noise levels.
Figure 8.
Bode phase for the classic Randles model at 2.5% and 5.0% noise levels.
Figure 9.
Residuals (real and imaginary parts) for the classic Randles model.
Figure 9.
Residuals (real and imaginary parts) for the classic Randles model.
Figure 10.
Kramers–Kronig validation (Hilbert transform) for the classic Randles model.
Figure 10.
Kramers–Kronig validation (Hilbert transform) for the classic Randles model.
Figure 11.
Nyquist diagrams for the Randles+CPE model: comparison between 2.5% and 5.0% noise levels.
Figure 11.
Nyquist diagrams for the Randles+CPE model: comparison between 2.5% and 5.0% noise levels.
Figure 12.
Bode magnitude for the Randles+CPE model: (a) 2.5% noise; (b) 5.0% noise.
Figure 12.
Bode magnitude for the Randles+CPE model: (a) 2.5% noise; (b) 5.0% noise.
Figure 13.
Bode phase for the Randles+CPE model at 2.5% and 5.0% noise levels.
Figure 13.
Bode phase for the Randles+CPE model at 2.5% and 5.0% noise levels.
Figure 14.
Complex residuals (real and imaginary parts) for the Randles+CPE model.
Figure 14.
Complex residuals (real and imaginary parts) for the Randles+CPE model.
Figure 15.
Kramers–Kronig validation (Hilbert transform) for the Randles+CPE model.
Figure 15.
Kramers–Kronig validation (Hilbert transform) for the Randles+CPE model.
Figure 16.
Nyquist diagrams for the Randles+Warburg model: comparison between 2.5% and 5.0% noise levels.
Figure 16.
Nyquist diagrams for the Randles+Warburg model: comparison between 2.5% and 5.0% noise levels.
Figure 17.
Bode magnitude plots for the Randles+Warburg model at 2.5% and 5.0% noise levels.
Figure 17.
Bode magnitude plots for the Randles+Warburg model at 2.5% and 5.0% noise levels.
Figure 18.
Bode phase plots for the Randles+Warburg model at 2.5% and 5.0% noise levels.
Figure 18.
Bode phase plots for the Randles+Warburg model at 2.5% and 5.0% noise levels.
Figure 19.
Complex residuals (real and imaginary parts) for the Randles+Warburg model.
Figure 19.
Complex residuals (real and imaginary parts) for the Randles+Warburg model.
Figure 20.
Kramers–Kronig validation (Hilbert transform) for the Randles+Warburg model.
Figure 20.
Kramers–Kronig validation (Hilbert transform) for the Randles+Warburg model.
Figure 21.
Nyquist plots for : comparison between 2.5% and 5.0% noise levels.
Figure 21.
Nyquist plots for : comparison between 2.5% and 5.0% noise levels.
Figure 22.
Bode magnitude plots for at 2.5% and 5.0% noise.
Figure 22.
Bode magnitude plots for at 2.5% and 5.0% noise.
Figure 23.
Bode phase plots for at 2.5% and 5.0% noise.
Figure 23.
Bode phase plots for at 2.5% and 5.0% noise.
Figure 24.
Residuals (real and imaginary parts) for .
Figure 24.
Residuals (real and imaginary parts) for .
Figure 25.
Kramers–Kronig validation (Hilbert transform) for .
Figure 25.
Kramers–Kronig validation (Hilbert transform) for .
Figure 26.
Nyquist plots for : comparison between 2.5% and 5.0% noise levels.
Figure 26.
Nyquist plots for : comparison between 2.5% and 5.0% noise levels.
Figure 27.
Bode magnitude plots for at 2.5% and 5.0% noise.
Figure 27.
Bode magnitude plots for at 2.5% and 5.0% noise.
Figure 28.
Bode phase plots for at 2.5% and 5.0% noise.
Figure 28.
Bode phase plots for at 2.5% and 5.0% noise.
Figure 29.
Residuals (real and imaginary parts) for .
Figure 29.
Residuals (real and imaginary parts) for .
Figure 30.
Kramers–Kronig validation (Hilbert transform) for .
Figure 30.
Kramers–Kronig validation (Hilbert transform) for .
Figure 31.
Nyquist plots for the full Randles model: comparison between 2.5% and 5.0% noise.
Figure 31.
Nyquist plots for the full Randles model: comparison between 2.5% and 5.0% noise.
Figure 32.
Bode magnitude for the full Randles model at 2.5% and 5.0% noise.
Figure 32.
Bode magnitude for the full Randles model at 2.5% and 5.0% noise.
Figure 33.
Bode phase for the full Randles model at 2.5% and 5.0% noise.
Figure 33.
Bode phase for the full Randles model at 2.5% and 5.0% noise.
Figure 34.
Residuals (real and imaginary parts) for the full Randles model.
Figure 34.
Residuals (real and imaginary parts) for the full Randles model.
Figure 35.
Kramers–Kronig (Hilbert transform) validation for the full Randles model.
Figure 35.
Kramers–Kronig (Hilbert transform) validation for the full Randles model.
Table 1.
Summary of metrics and parameters for series RLC (best fit at each noise level).
Table 1.
Summary of metrics and parameters for series RLC (best fit at each noise level).
| | 2.5% | 5.0% |
|---|
| RMSE | 5.494 × 108 | 1.152 × 109 |
| 3.494 × 102 | 4.018 × 102 |
| 9.9947 × 10−1 | 9.9767 × 10−1 |
| 9.9946 × 10−1 | 9.9766 × 10−1 |
| AIC | 4 × 102 | 4 × 102 |
| BIC | 4 × 102 | 4 × 102 |
| Cond# | 46 | 46 |
| [] | 1.000 [0.991, 1.295] | 1.061 [0.514, 1.257] |
| [] | 0.999 [0.994, 1.006] | 1.002 [0.982, 1.010] |
| [] | 1.002 [0.999, 1.005] | 0.999 [0.992, 1.005] |
Table 2.
Summary of metrics and parameters for classic Randles (). Best fit per noise level.
Table 2.
Summary of metrics and parameters for classic Randles (). Best fit per noise level.
| | 2.5% | 5.0% |
|---|
| RMSE | 3.2200 | 6.5700 |
| 3.5600 × 102 | 3.4700 × 102 |
| 0.9929 | 0.9709 |
| 0.9928 | 0.9707 |
| AIC | 362 | 353 |
| BIC | 374 | 365 |
| Cond# | 2.5600 × 1017 | 2.3000 × 1017 |
| [] | 10.013 [9.86, 10.14] | 9.918 [9.74, 10.14] |
| [] | 100.287 [100.00, 100.67] | 100.182 [100.00, 101.11] |
| [] | 10.047 [9.991, 10.122] | 10.013 [9.994, 10.294] |
Table 3.
Summary of metrics and parameters for Randles + CPE (). Best fit at each noise level.
Table 3.
Summary of metrics and parameters for Randles + CPE (). Best fit at each noise level.
| | 2.5% | 5.0% |
|---|
| RMSE | 3.3100 | 6.5200 |
| 3.6200 × 102 | 3.2600 × 102 |
| 0.9903 | 0.9634 |
| 0.9902 | 0.9630 |
| AIC | 370 | 334 |
| BIC | 386 | 350 |
| Cond# | 1.6700 × 1018 | 2.4100 × 1017 |
| [] | 9.862 [9.78, 10.25] | 9.688 [9.38, 10.17] |
| [] | 100.353 [100.00, 100.54] | 99.935 [99.70, 100.01] |
| [ sn−1] | 10.154 [9.351, 10.339] | 10.217 [8.436, 10.549] |
| [–] | 0.898 [0.90, 0.91] | 0.899 [0.89, 0.92] |
Table 4.
Summary of metrics and parameters for Randles + Warburg (). Best fit at each noise level.
Table 4.
Summary of metrics and parameters for Randles + Warburg (). Best fit at each noise level.
| | 2.5% | 5.0% |
|---|
| RMSE | 3.1900 | 6.3800 |
| 3.4100 × 102 | 3.400 × 102 |
| 0.9930 | 0.9725 |
| 0.9929 | 0.9723 |
| AIC | 349 | 348 |
| BIC | 365 | 364 |
| Cond# | 3.1900 × 1017 | 2.7400 × 1017 |
| [] | 9.993 [9.87, 10.13] | 10.145 [9.98, 10.34] |
| [] | 100.116 [100.00, 100.54] | 99.977 [100.00, 101.18] |
| [] | 10.059 [10.000, 10.147] | 10.015 [9.999, 10.181] |
| [] | 1.3800 × 10−3 [1.000 × 10−6, 3.5800 × 10−3] | 8.2500 × 10−6 [1.000 × 10−6, 9.4900 × 10−4] |
Table 5.
Summary of metrics and fitted parameters for with series resistance . Best fit at each noise level.
Table 5.
Summary of metrics and fitted parameters for with series resistance . Best fit at each noise level.
| | 2.5% Noise | 5.0% Noise |
|---|
| RMSE | 3.3300 | 6.4700 |
| 3.7400 × 102 | 3.4600 × 102 |
| 0.9923 | 0.9717 |
| 0.9922 | 0.9714 |
| AIC | 382 | 354 |
| BIC | 398 | 370 |
| Cond# | 7.9600 × 105 | 7.9600 × 105 |
| [] | 9.995 [9.85, 10.11] | 9.936 [9.67, 10.22] |
| [] | 99.625 [99.17, 100.03] | 99.625 [98.90, 100.30] |
| [] | 8.4700 × 10−4 [1.000 × 10−6, 3.7600 × 10−3] | 1.000 × 10−6 [1.000 × 10−6, 4.6900 × 10−3] |
| [] | 9.909 [9.801, 10.016] | 10.002 [9.711, 10.235] |
Table 6.
Summary of metrics and parameters for with series resistance . Best fit at each noise level.
Table 6.
Summary of metrics and parameters for with series resistance . Best fit at each noise level.
| | 2.5% Noise | 5.0% Noise |
|---|
| RMSE | 3.2900 | 6.4400 |
| 3.4200 × 102 | 3.2300 × 102 |
| 0.9904 | 0.9645 |
| 0.9903 | 0.9641 |
| AIC | 352 | 333 |
| BIC | 372 | 353 |
| Cond# | 2.200 × 106 | 2.2300 × 106 |
| [] | 10.103 [9.91, 10.29] | 10.274 [9.78, 10.78] |
| [] | 99.866 [99.36, 100.28] | 100.221 [99.07, 101.11] |
| [] | 1.000 × 10−6 [1.000 × 10−6, 4.8800 × 10−4] | 1.1400 × 10−3 [1.000 × 10−6, 6.0100 × 10−3] |
| [ sn−1] | 9.762 [9.151, 10.434] | 9.092 [7.652, 10.340] |
| [–] | 0.904 [0.90, 0.91] | 0.910 [0.90, 0.93] |
Table 7.
Summary of metrics and parameters for full Randles: . Best fit for each noise level.
Table 7.
Summary of metrics and parameters for full Randles: . Best fit for each noise level.
| | 2.5% | 5.0% |
|---|
| RMSE | 3.2700 | 6.6200 |
| 3.400 × 102 | 3.4600 × 102 |
| 0.9905 | 0.9625 |
| 0.9904 | 0.9620 |
| AIC | 350 | 356 |
| BIC | 369 | 376 |
| Cond# | 1.4000 × 1011 | 1.4400 × 1011 |
| [] | 9.882 [9.68, 10.02] | 9.809 [9.22, 10.30] |
| [] | 100.323 [99.96, 100.84] | 100.565 [99.71, 101.55] |
| [ sn−1] | 9.943 [9.538, 10.465] | 10.390 [9.044, 11.758] |
| [–] | 0.900 [0.89, 0.90] | 0.894 [0.88, 0.91] |
| [] | 1.0000 × 10−1 [1.0000 × 10−6, 1.0000 × 10−1] | 3.1800 × 10−4 [1.0000 × 10−6, 1.0000 × 10−1] |
Table 8.
Comparative summary of fitting metrics for all evaluated models. Bold values indicate the best performance for each metric and noise level.
Table 8.
Comparative summary of fitting metrics for all evaluated models. Bold values indicate the best performance for each metric and noise level.
| Model | 2.5% | 5.0% |
|---|
|
RMSE
|
AIC
|
BIC
|
RMSE
|
AIC
|
BIC
|
|---|
| RLC series | 4.10 | 380 | 396 | 7.20 | 385 | 402 |
| Randles classic | 3.45 | 355 | 370 | 6.80 | 362 | 379 |
| Randles + CPE | 3.30 | 352 | 369 | 6.50 | 354 | 372 |
| Randles + Warburg | 3.25 | 349 | 368 | 6.60 | 358 | 378 |
| 3.28 | 351 | 367 | 6.55 | 355 | 373 |
| 3.27 | 350 | 368 | 6.53 | 355 | 374 |
| Randles full | 3.27 | 350 | 369 | 6.62 | 356 | 376 |