Ternary Nickel-Iron-Phosphorus (NiFeP) Electrocatalysts for Alkaline Water Splitting
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Preparation of Coatings
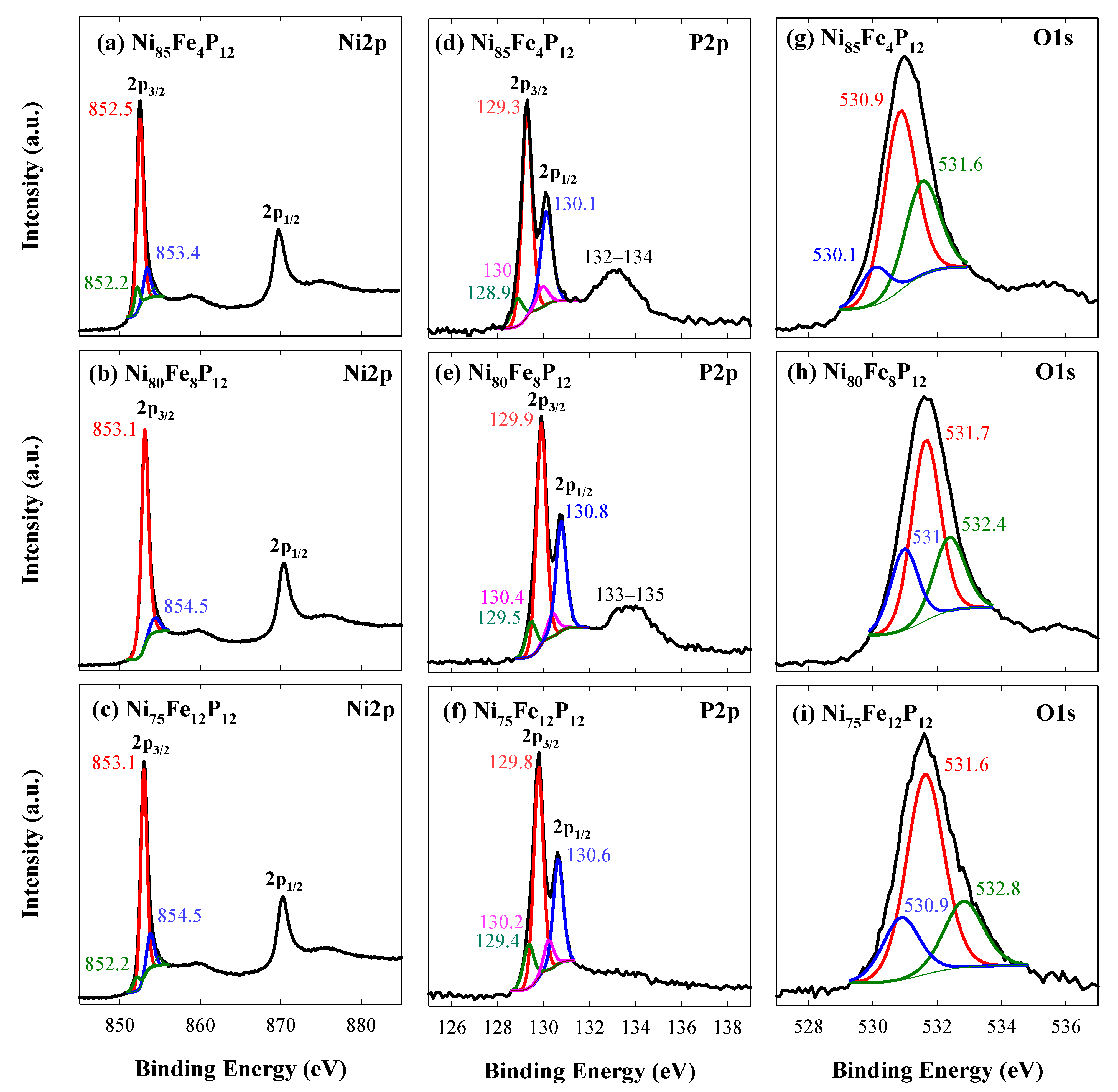
2.3. Characterization of Coatings
2.4. Electrochemical Measurements
3. Results and Discussion
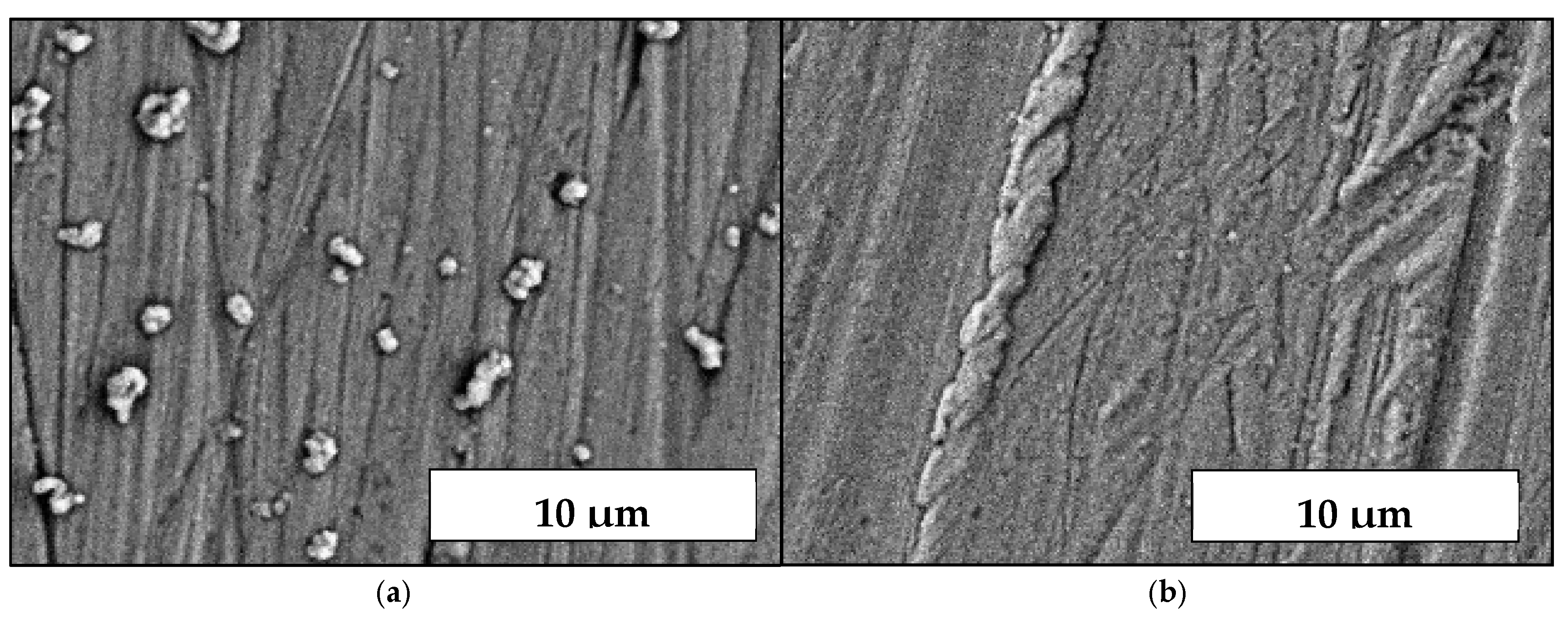
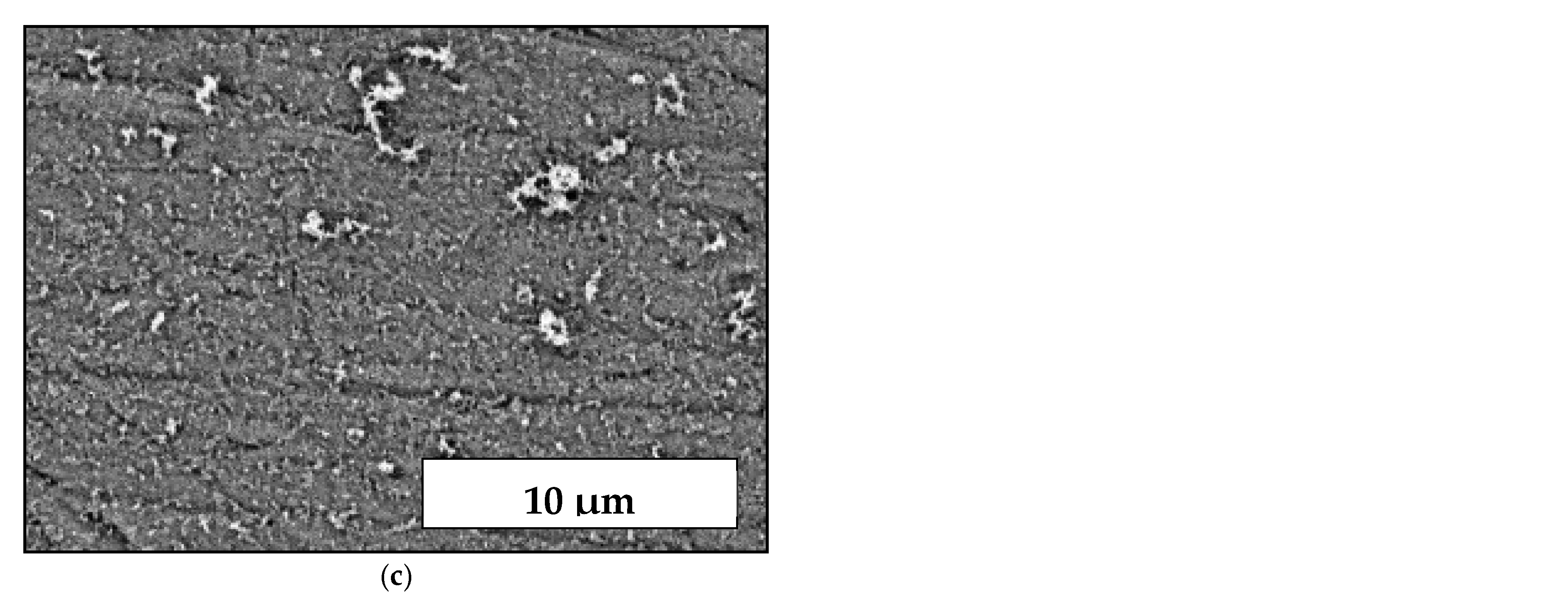
3.1. Coatings, Microstructure and Morphology Studies
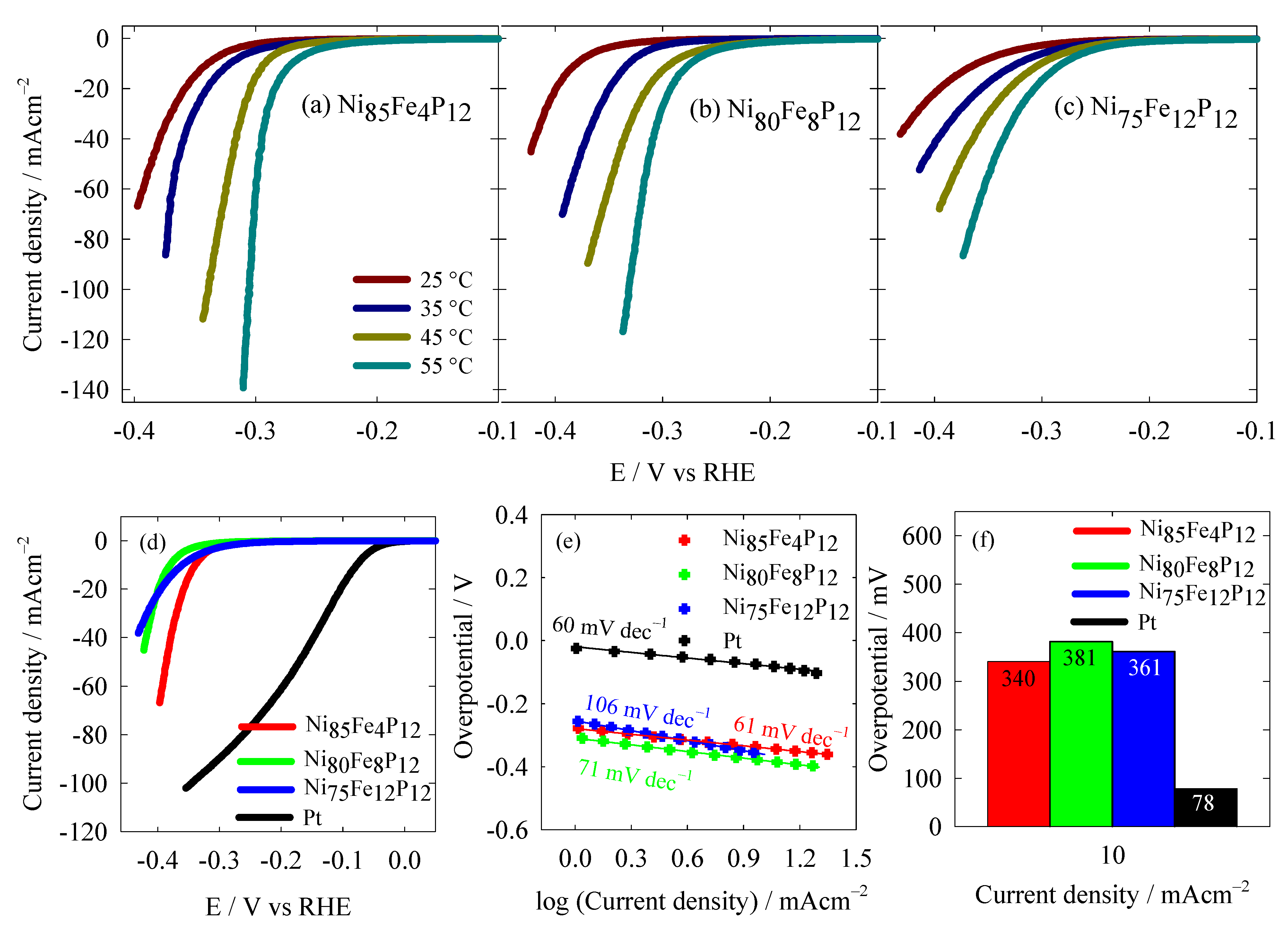
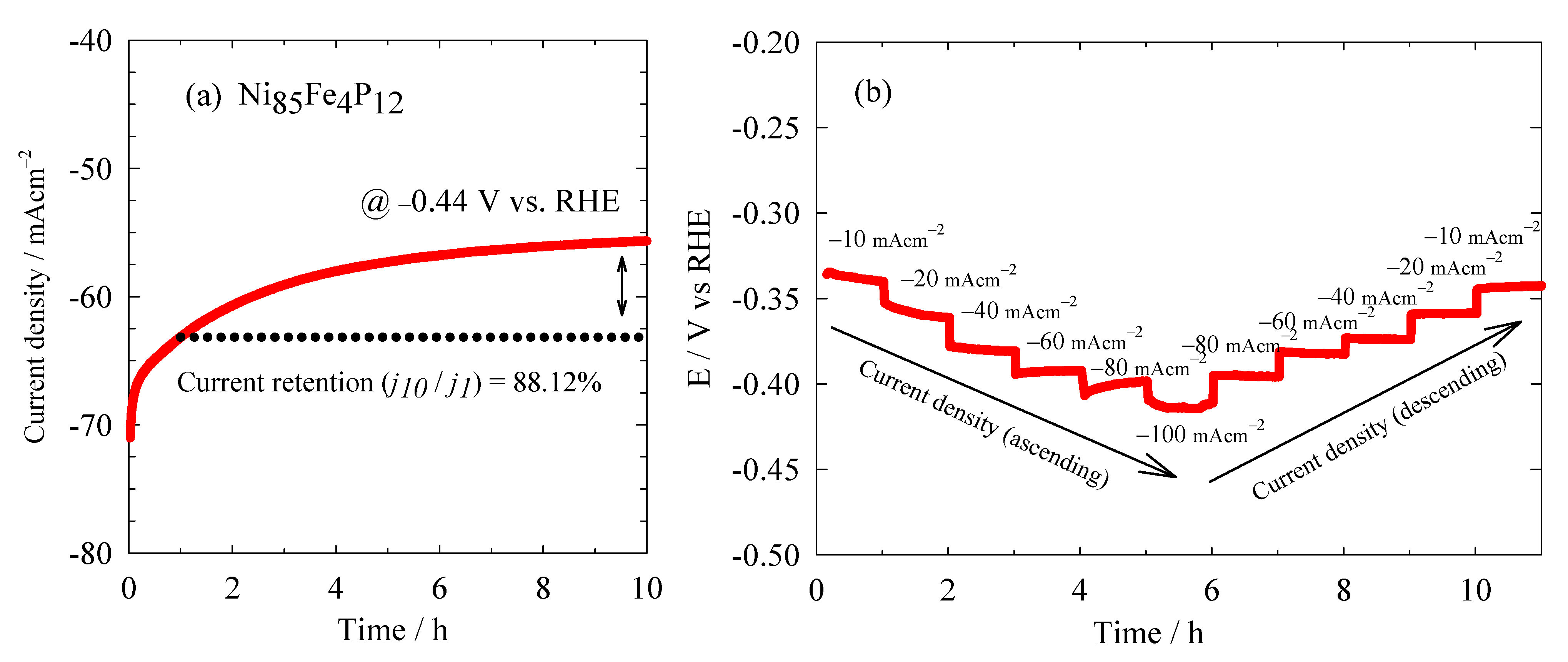
3.2. Hydrogen Evolution Reaction Study
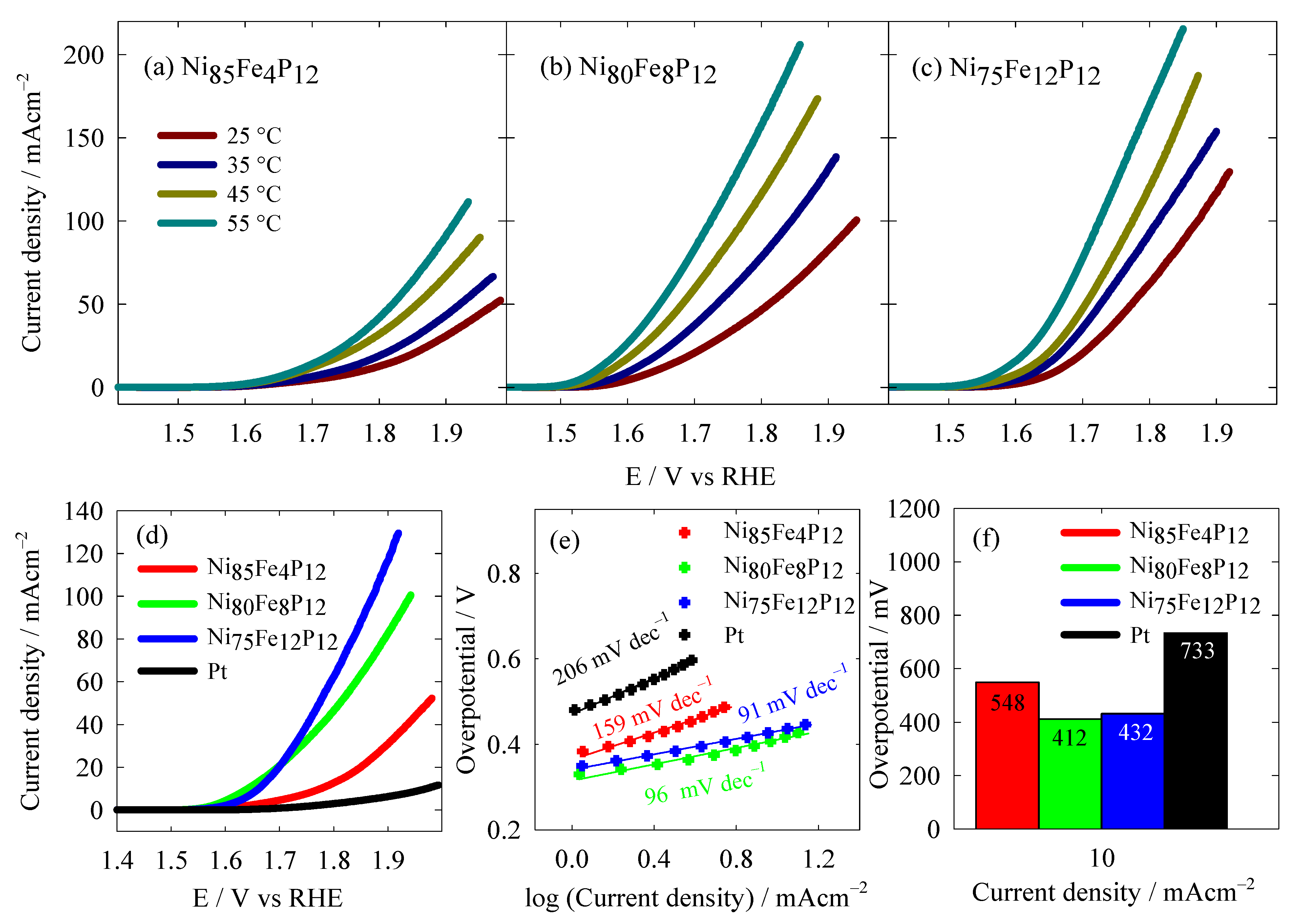
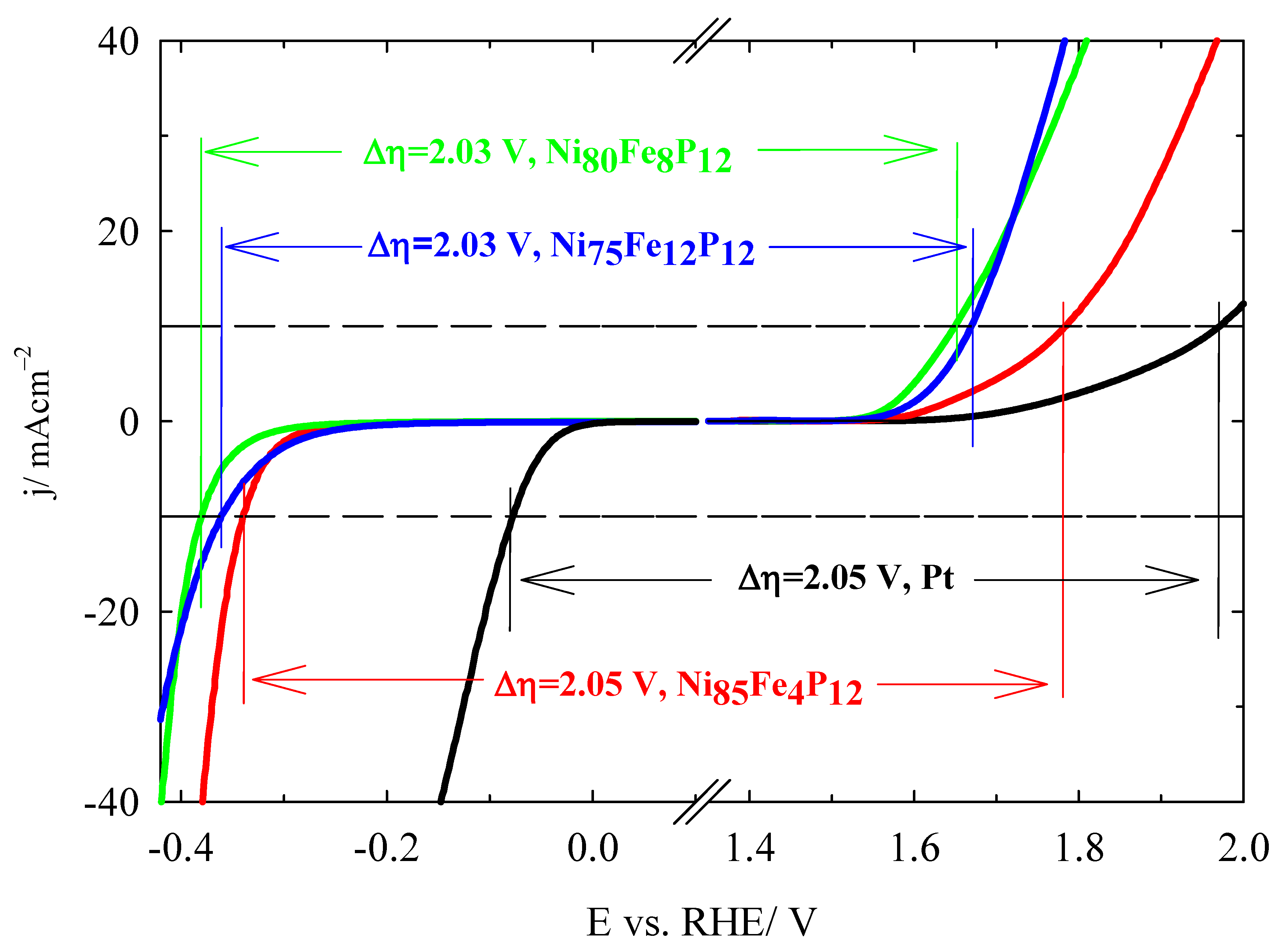
3.3. Oxygen Evolution Reaction Study
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
References
- World Population Prospects 2024. Available online: https://population.un.org/ (accessed on 7 July 2025).
- European Union. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=celex:52020DC0301 (accessed on 7 July 2025).
- Moore, J.; Durham, J.; Eijk, A.; Karakas, E.; Kurz, R.; Lesak, J.; Williams, B. Compressors and expanders. In Machinery and Energy Systems for the Hydrogen Economy; Brun, K., Allison, T., Eds.; Esevier: Machinery Separtment, Southwest Research Institute: San Antonio, TX, USA, 2022; pp. 333–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Energy Agency. Available online: https://www.iea.org/reports/global-hydrogen-review-2024/hydrogen-demand (accessed on 30 July 2025).
- Mu, Y.; Ma, R.; Xue, S.; Shang, H.; Lu, W.; Jiao, L. Recent advances and perspective on transition metal heterogeneous catalysts for efficient electrochemical water splitting. Carbon Neutr. 2024, 3, 4–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvò, D.; Mosconi, D.; Neyman, A.; Bar-Sadan, M.; Calvillo, L.; Granozzi, G.; Cattelan, M.; Agnoli, S. Nanoneedles of Mixed Transition Metal Phosphides as Bifunctional Catalysts for Electrocatalytic Water Splitting in Alkaline Media. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, B.; Sun, Y. Innovative strategies for electrocatalytic water splitting. Acc. Chem. Res. 2018, 51, 1571–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Zhang, L.; Gong, J. Recent progress made in the mechanism comprehension and design of electrocatalysts for alkaline water splitting. Energy Environ. Sci. 2019, 12, 2620–2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miles, M.H.; Thomason, M.A. Periodic variations of overvoltages for water electrolysis in acid solutions from cyclic voltammetric studies. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1976, 123, 1459–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miles, M.H. Evaluationofelectrocatalystsforwaterelectrolysisinalkalinesolutions. J. Electroanal. Chem. Interf. Electrochem. 1975, 60, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Baek, J.B. Recent advances in noble metal (Pt, Ru, and Ir)-based electrocatalysts for efficient hydrogen evolution reaction. ACS Omega 2019, 5, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherevko, S.; Geiger, S.; Kasian, O.; Kulyk, N.; Grote, J.P.; Savan, A.; Mayrhofer, K.J. Oxygen and hydrogen evolution reactions on Ru, RuO2, Ir, and IrO2 thin film electrodes in acidic and alkaline electrolytes: A comparative study on activity and stability. Catal. Today 2016, 262, 170–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, H.; Wang, Q.; Huang, C.; Zhang, M.; Yan, Y.; Liu, T.; Zhou, W. Noble metal-based heterogeneous catalysts for electrochemical hydrogen evolution reaction. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Hao, X.; Abudula, A.; Guan, G. Nanostructured catalysts for electrochemical water splitting: Current state and prospects. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 11973–12000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamzah, B.K.; Zhang, J.; Liang, Y.; Wei, Y.; Huang, Y.Z. A review of noble metal-free high entropy alloys for water splitting applications. J. Mater. Chem. A 2024, 12, 9933–9961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, D.; Xiong, H.; Zhang, T.; Fan, X.; Wang, J.; Xu, F. Recent progress in noble-metal-free electrocatalysts for alkaline oxygen evolution reaction. Front. Chem. 2022, 10, 1071274–1071294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Read, C.G.; Callejas, J.F.; Holder, C.F.; Schaak, R.E. General strategy for the synthesis of transition metal phosphide films for electrocatalytic hydrogen and oxygen evolution. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 12798–12803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, J.; Li, H.; Cheng, M.M.C.; Geyer, S.M.; Ng, K.S. Electro-synthesis of 3D porous hierarchical Ni–Fe phosphate film/Ni foam as a high-efficiency bifunctional electrocatalyst for overall water splitting. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 13866–13873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Fu, X.Z.; Wang, S. Etching oxide overlayers of NiFe phosphide to facilitate surface reconstruction for oxygen evolution reaction. Green Energy Environ. 2022, 7, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Gao, M.; Lei, T.; Ren, Z.; Luo, J.; Huang, Z.; Wu, A. Hollow urchin-like FeP as highly efficient hydrogen evolution catalyst. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2023, 156, 111143–111152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-P.; Huang, C.; Han, W.-K.; Ouyang, T.; Liu, Z.-Q. Transition metal-based electrocatalysts for overall water splitting. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2021, 32, 2597–2616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, X.; Yuan, X.; Dong, W.; Huang, F. Rational composition and structural design of in situ grown nickel-based electrocatalysts for efficient water electrolysis. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Zhai, H.; Chen, L.; Mei, L.; Tan, P.; Yang, K.; Pan, J. Unraveling the synergistic mechanism of bi-functional nickel–iron phosphides catalysts for overall waters plitting. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2302621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Barforoush, J.M.; Leonard, K.C. Sulfur incorporation into NiFe oxygen evolution electrocatalysts for improved high current density operation. Mater. Adv. 2023, 4, 122–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, C.; Wang, J.; Xia, W.; Zhu, J.; Peng, Z.; Xia, K.; Wang, D. Heteroatom (P, B, or S) incorporated NiFe-based nanocubes as efficient electrocatalysts for the oxygen evolution reaction. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 7062–7069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Q.; Lai, D.; Tang, W.; Lu, Q.; Gao, F. Intrinsic activity modulation and structural design of NiFe alloy catalysts for an efficient oxygen evolution reaction. Chem. Sci. 2021, 12, 3818–3835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oudejans, D.; Offidani, M.; Constantinou, A.; Albonetti, S.; Dimitratos, N.; Bansode, A.A. Comprehensive review on two-step thermochemical water splitting for hydrogen production in a redox cycle. Energies 2022, 15, 3044–3068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oruc, O.; Dincer, I. Assessing the potential of thermo-chemical water splitting cycles: A bridge towards clean and sustainable hydrogen generation. Fuel 2021, 286, 119325–119338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, T.; Ashida, S.; Inubuse, N.; Shimizu, S.; Miura, Y.; Mizutani, T.; Saitow, K. Room-temperature thermochemical water splitting: Efficient mechanocatalytic hydrogen production. J. Mater. Chem. A. 2024, 12, 30906–30918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Chen, C.; Liu, S.; Chen, Z.; Pu, Z.; Huang, Q.; Zhang, L.; M. Al-Enizi, A.; Nafady, A.; Sun, S.; et al. Transition metal phosphides as noble-metal-alternative co-catalysts for solar hydrogen production. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2024, 521, 216145–216162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, M.U.; Najam, T.; Helal, M.H.; Hossain, I.; El-Bahy, S.M.; El-Bahy, Z.M.; Rehman, A.; Shah, S.S.A.; Nazir, A.M. Transition metal chalcogenides and phosphides for photocatalytic H2 generation via water splitting: A critical review. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 62, 1113–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Li, W.; Ren, C.; Dong, M.; Geng, L.; Wang, T. Study of iron group transition metal phosphides (M2P,M = Ni, Co, Fe) for boosting photocatalytic H2 production. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 316, 123805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nozari-Asbemarz, M.; Imanzadeh, H.; Hazraty, L.; Babaei, B.; Abbasi, A.; Mehrabi-Kalajahi, S.S.; Vafolomeev, M.A.; Leahy, J.J.; Amiri, M. Construction of iron-nickel metal-organic framework anchored on reduced graphene oxide for enhanced oxygen evolution reaction electrocatalysis. J. Power Sources 2025, 652, 237555–237563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tumiwa, J.R.; Mizik, T. Advancing nickel-based catalysts for enhanced hydrogen production: Innovations in electrolysis and catalyst design. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2025, 109, 961–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Hui, B. Flexible NiFeP@filter paper electrode for alkaline overall water electro splitting. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 51, 615–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, G.; Chen, T.; Xie, F.; Xue, D.; Liu, T.; Chen, L.; Xia, J.; Du, S.; Wang, F.; Xie, F.; et al. NiFeP composites supported on Ni foam as an efficient and robust bifunctional electrocatalyst for overall water splitting in alkaline solution. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 968, 171746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Li, M.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, B. Recent advances in nanostructured transition metal phosphides: Synthesis and energy-related applications. Energy Environ. Sci. 2020, 13, 4564–4582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, C.C.; Ren, J.T.; Yuan, Z.Y. Transition metal phosphide-based materials for efficient electrochemical hydrogen evolution: A critical review. ChemSusChem 2020, 13, 3357–3375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Li, J.; Xiong, D.; Zhang, B.; Liu, Y.; Wu, K.H.; Liu, L. Trends in activity for the oxygen evolution reaction on transition metal (M= Fe, Co, Ni) phosphide pre-catalysts. Chem. Sci. 2018, 9, 3470–3476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, P.; Liu, Q.; Liang, Y.; Tian, J.; Asiri, A.M.; Sun, X. A cost-effective 3D hydrogen evolution cathode with high catalytic activity: FeP nanowire array as the active phase. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 126, 13069–13073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Vrubel, H.; Bensimon, M.; Hu, X. Easily-prepared dinickel phosphide (Ni2P) nanoparticles as an efficient and robust electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 5917–5921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.V.; Sarakonsri, T. Introduction to electrochemical cells. In Recheargable Ions Batteries: Materials, Design and Applications of Li-Ion Cells and Beyond; Kumar, R., Aifantis, K., Hu, P., Eds.; Wiley-WCH: Berlin, Germany, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS) Reference Pages. Available online: http://www.xpsfitting.com/search/label/Nickel (accessed on 23 June 2025).
- Biesinger, M.C.; Payne, B.P.; Grosvenor, A.P.; Lau, L.W.M.; Gerson, A.R.; Smart, R.S.C. Resolving surface chemical states in XPS analysis of first row transition metals, oxides and hydroxides: Cr, Mn, Fe, Co and Ni. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 257, 2717–2730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsener, B.; Atzei, D.; Krolikowski, A.; Rossi, A. Effect of phosphorus concentration on the electronic structure of nanocrystalline electrodeposited Ni–P alloys: An XPS and XAES investigation. Surf. Interface Anal. 2008, 40, 919–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS) Reference Pages. Available online: https://www.xpsfitting.com/search/label/Phosphorus (accessed on 23 June 2025).
- Bagus, P.S.; Nelin, C.J.; Brundle, C.R.; Crist, B.V.; Ilton, E.S.; Lahiri, N.; Rosso, K.M. Main and Satellite Features in the Ni 2p XPS of NiO. Inorg. Chem. 2022, 61, 18077–18094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.; Shah, J.; Negi, N.S.; Sharma, C.; Kotnala, R.K. Significance of interface barrier at electrode of hematite hydroelectric cell for generating ecopower by watersplitting. Int. J. Energy Res. 2019, 43, 4743–4755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iron X-ray Photoelectron Spectra, Iron Electron Configuration, and Other Elemental Information. Available online: https://www.thermofisher.com/lt/en/home/materials-science/learning-center/periodic-table/transition-metal/iron.html (accessed on 23 June 2025).
- Einert, M.; Waheed, A.; Lauterbach, S.; Mellin, M.; Rohnke, M.; Wagner, L.Q.; Gallenberger, J.; Tian, C.; Smarsly, B.M.; Jaegermann, W.; et al. Sol-gel-derived ordered mesoporous high entropy spinel ferrites and assessment of their photoelectrochemical and electrocatalytic water splitting performance. Small 2023, 19, 2205412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhu, H.; Guo, C.; Cao, S.; Wu, C.M.L.; Wang, Z.; Lu, X. Theoretical investigation on the hydrogen evolution reaction mechanism at MoS2 heterostructures: The essential role of the 1T/2H phase interface. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2020, 10, 458–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Yao, J.; Wang, P.; Li, Z.; Zhou, H.; Xu, C. Perspective of hydrogen energy and recent progress in electrocatalytic water splitting. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2022, 43, 282–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, H.F.; Gómez, J.A.; Santos, D.M.F. Proton-exchange membrane electrolysis for green hydrogen production: Fundamentals, cost breakdown, and strategies to minimize platinum-group metal content in hydrogen evolution reaction electrocatalysts. Catalysts 2024, 14, 845–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, I.H.; Im, H.S.; Jang, D.M.; Kim, Y.W.; Park, K.; Lim, Y.R.; Park, J. CoSe2 and NiSe2 nanocrystals as superior bifunctional catalysts for electrochemical and photoelectrochemical water splitting. ACS Appl. Matter. Interfaces 2016, 8, 5327–5334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashwani, K.; Sayan, B. PorousNiFe-oxidenanocubesasbifunctionalelectrocatalystsforefficientwater-splitting. ACS Appl. Mater. Interface 2017, 9, 41906–41915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shyshkin, D.; Tamašauskaitė-Tamašiūnaitė, L.; Šimkūnaitė, D.; Balčiūnaitė, A.; Sukackienė, Z.; Vaičiūnienė, J.; Norkus, E. Hydrogen and oxygen evolution on flexible catalysts based on nickel–iron coatings. Catalysts 2024, 14, 843–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, G.; Hao, Q.; Mao, J.; Liang, L.; Liu, H.; Liu, C.; Zhang, J. Ultrafast fabrication of nickel sulfide film on Ni foam for efficient overall water splitting. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 17347–17353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Y.; Xu, W.; Zhu, S.; Cui, Z.; Liang, Y.; Li, Z.; Luo, S. Self-supporting amorphous nanoporous NiFeCoP electrocatalyst for efficient overall water splitting. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2021, 82, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
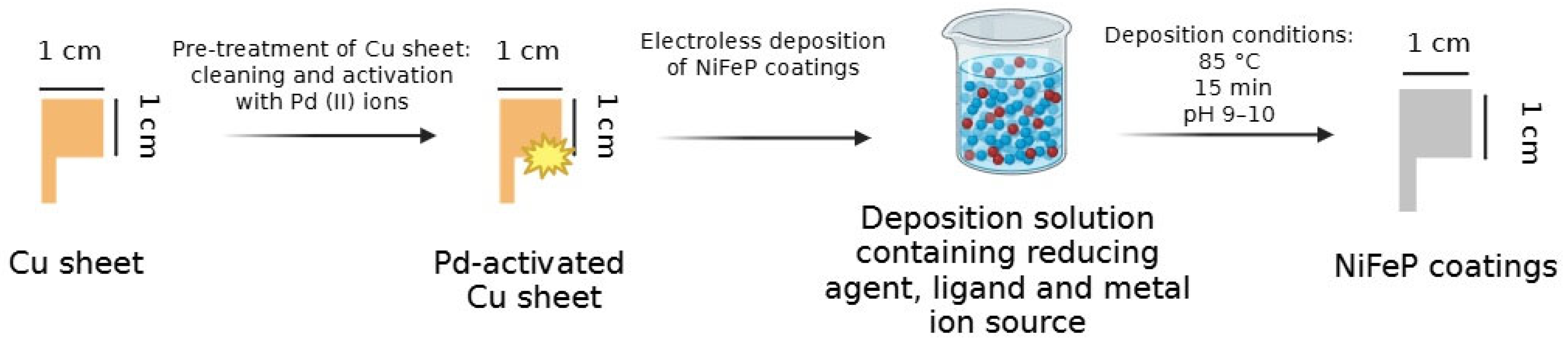


| Coatings | Glycine, M | Disodium Malonate, M | Sodium Hypophosphite, M | EDTA, M | Sodium Citrate, M | Ni2+, M | Fe2+, mM | pH | T, °C | t, min |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ni85Fe4P12 | 0.4 | 0.098 | 0.301 | 0.07 | 0.15 | 0.107 | 54 | 9 | 85 | 15 |
| Ni80Fe8P12 | 0.4 | 0.098 | 0.301 | 0.07 | 0.15 | 0.107 | 22 | 10 | 85 | 15 |
| Ni75Fe12P12 | 0.4 | 0.098 | 0.301 | 0.07 | 0.15 | 0.107 | 54 | 10 | 85 | 15 |
| Coating | Elemental Composition, at.% | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ni | Fe | P | |
| Ni85Fe4P12 | 84.56 ± 0.66 | 3.85 ± 0.14 | 11.59 ± 0.17 |
| Ni80Fe8P12 | 80.26 ± 0.41 | 7.85 ± 0.24 | 11.89 ± 0.25 |
| Ni75Fe12P12 | 75.48 ± 0.70 | 12.42 ± 0.14 | 12.10 ± 0.22 |
| Catalysts | Tafel Slope (mV dec−1) | η10 (mV) | Electrolyte | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ni85Fe4P12 | 61 | 340 | 1 M KOH | This work |
| Ni80Fe8P12 | 71 | 381 | 1 M KOH | This work |
| Ni75Fe12P12 | 106 | 361 | 1 M KOH | This work |
| Pt | 60 | 78 | 1 M KOH | This work |
| NiSe2 | 139 | 540 | 1 M KOH | [55] |
| Ni foam | 151 | 273 | 1 M KOH | [57] |
| NiFeP | 83 | 277 | 1 M KOH | [17] |
| Ni2P | 103 | 200 | 1 M KOH | [17] |
| Pt | 125 | 60 | 1 M KOH | [17] |
| Ni90Fe10 | 117.3 | 211.9 | 1 M KOH | [56] |
| Ni80Fe20 | 76.9 | 202.7 | 1 M KOH | [56] |
| NiO NP | 158 | 576 | 1 M KOH | [55] |
| Fe2O3 NP | 236 | 424 | 1 M KOH | [55] |
| np-NiP | 71.3 | 250 | 1 M KOH | [58] |
| Catalysts | Tafel Slope (mV dec−1) | η10 (mV) | Electrolyte | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ni85Fe4P12 | 159 | 548 | 1 M KOH | This work |
| Ni80Fe8P12 | 96 | 412 | 1 M KOH | This work |
| Ni75Fe12P12 | 91 | 432 | 1 M KOH | This work |
| Pt | 206 | 733 | 1 M KOH | This work |
| NiSe2 | 38 | 250 | 1 M KOH | [55] |
| Ni foam | 149 | 590 | 1 M KOH | [57] |
| NiFeP | - | 280 | 1 M KOH | [17] |
| Ni2P | - | 339 | 1 M KOH | [17] |
| Ni90Fe10 | 69.6 | 454.2 | 1 M KOH | [56] |
| Ni80Fe20 | 67.2 | 450.2 | 1 M KOH | [56] |
| NiO NP | 238 | 481 | 1 M KOH | [55] |
| Fe2O3 NP | 255 | 691 | 1 M KOH | [55] |
| np-NiP | 185.8 | 415 | 1 M KOH | [58] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Šakickaitė, R.; Sukackienė, Z.; Kepenienė, V.; Balčiūnaitė, A.; Stagniūnaitė, R.; Valeckytė, G.; Tamašauskaitė-Tamašiūnaitė, L. Ternary Nickel-Iron-Phosphorus (NiFeP) Electrocatalysts for Alkaline Water Splitting. Electrochem 2025, 6, 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/electrochem6030030
Šakickaitė R, Sukackienė Z, Kepenienė V, Balčiūnaitė A, Stagniūnaitė R, Valeckytė G, Tamašauskaitė-Tamašiūnaitė L. Ternary Nickel-Iron-Phosphorus (NiFeP) Electrocatalysts for Alkaline Water Splitting. Electrochem. 2025; 6(3):30. https://doi.org/10.3390/electrochem6030030
Chicago/Turabian StyleŠakickaitė, Raminta, Zita Sukackienė, Virginija Kepenienė, Aldona Balčiūnaitė, Raminta Stagniūnaitė, Gitana Valeckytė, and Loreta Tamašauskaitė-Tamašiūnaitė. 2025. "Ternary Nickel-Iron-Phosphorus (NiFeP) Electrocatalysts for Alkaline Water Splitting" Electrochem 6, no. 3: 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/electrochem6030030
APA StyleŠakickaitė, R., Sukackienė, Z., Kepenienė, V., Balčiūnaitė, A., Stagniūnaitė, R., Valeckytė, G., & Tamašauskaitė-Tamašiūnaitė, L. (2025). Ternary Nickel-Iron-Phosphorus (NiFeP) Electrocatalysts for Alkaline Water Splitting. Electrochem, 6(3), 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/electrochem6030030










