Abstract
The design and synthesis of artificial receptors based on molecular imprinting (MI) technology for the development of a new MIP-based biosensor for detection of the stress biomarker α-amylase in human saliva in point-of-care (PoC) applications is described in this work. The portable electrochemical devices for monitoring α-amylase consists of cost-effective and disposable gold screen-printed electrodes (AuSPEs). To build the electrochemical device, the template biomolecule was firstly immobilized directly over the working area of the gold chip previously activated with a self-assembled monolayer (SAM) of cysteamine (CA). Then, pyrrole (Py) monomer was selected as building block of a polymeric network prepared by CV electropolymerization. After the electropolymerization process, the enzyme was removed from the polymer film in order to build the specific recognition sites for the target enzyme. The MIP biosensor showed a very wide linear concentration range (between 3.0 × 10−4 to 0.60 mg mL−1 in buffer solution and between 3.0 × 10−4 to 3.0 × 10−2 mg mL−1 in human saliva) and low detection levels were achieved (LOD < 3.0 × 10−4 mg mL−1) using square wave voltammetry (SWV) as the electroanalytical technique.
1. Introduction
Nowadays, one of the main challenges of our society and health systems is the early detection of several diseases, which directly depends on the correct identification of specific disease biomarkers. Over the past decades, salivary biomarkers of oxidative stress attracted the attention of scientific community since they are able to reflect local and systemic pathologies and can provide valuable information on the diagnosis, prognosis and therapeutic responsiveness of numerous human diseases [1].
Recently, α-amylase, an enzyme of ~60 kDa that belongs to a distinctive group of isoenzymes produced in salivary glands for starch digestion, was identified as a promising sensitive biomarker for stress-related changes in the body that reflect the activity of the sympathetic nervous system [2,3]. Thus, increasing levels of both, physiological and psychological stress, leads to an increase of α-amylase concentration in saliva (above ~0.5 mg mL−1) [4,5].
Nowadays, methods for α-amylase quantification rely on electrophoresis [5,6], chromatography [7,8], Phadebas test [9] or immunological assays [10,11,12,13]. Although these detection methodologies can offer reliable and sensitive (and selective) detection, some issues have been identified, namely: (i) the biorecognition elements used (usually antibodies) makes the detection rather expensive, sometimes carrying problems related to bioreceptors instability; (ii) need of labelling and/or complex signal amplification strategies or coloration of the test solution and; (iii) laborious and time consuming procedures, very dependent on laboratory instrumentation.
Electrochemical biosensing can be a valuable alternative to conventional detection methodologies due to their high sensitivity and cost-effective detection, allowing portability for point-of-care (PoC) analysis [14,15,16,17]. Besides, the integrated recognition element can be either biological (enzymes, antibodies, etc.) or based on artificial antibodies, by using molecularly imprinted polymers (MIPs) [18,19,20,21,22]. This molecular molding technology provides an easy and simple way to build rigid 3D polymeric materials grown over target molecules (from small drugs to large proteins), having the ability of specific molecular recognition by the formation of specific interactions between the polymeric structures and the template [18,19,20,21,22].
Several approaches for surface protein imprinting have been accessible for electrochemical detection, where target biomolecules can be simply adsorbed [14,15] or covalently bonded (oriented immobilization) [23] to the sensing platforms. After effective template immobilization, the polymerization can be performed by chemical [23] or electrochemical processes [14,15,16]. Compared to bulk polymerization, electropolymerization is much simpler and less time-consuming, allowing the easy control of the film thickness [14,15,16]. In this process, the selection of adequate monomer is crucial for effective entrapment of template molecules and to achieve the desired physical features (including conductivity) of the thin polymer layers over the electrode surface [24].
Poly(pyrrole) is a conducting polymer extensively used for (bio)sensing applications [25,26,27,28,29,30], including the design of new electrochemical biosensors for detection of several important biomolecules, such as hemoglobin [27], quercetin [28], tryptamine [29] and paracetamol [30]. Thus, its good biocompatibility and easy electrochemical generation (and deposition) on electrodes surfaces [25,26,27,28,29,30] was deeply considered and pyrrole (Py) monomer was chosen in this work to build the MIP sensing surface for selective detection of α-amylase.
This work describes the assembly and test of a new MIP-based electrochemical biosensor for detection of α-amylase, which represents about 50–60% of human salivary protein, in PoC, using gold screen-printed electrodes (AuSPEs) as transducers. In the initial stage of the sensor assembly, the AuSPE surface was modified with a self-assembled monolayer (SAM) for α-amylase immobilization prior to electropolymerization. In contrast to carbon surfaces, in bare metal electrodes, such as gold, the unfolding of the protein during adsorption at the bare electrode surface can lead to its denaturation [31], resulting in poor imprinting process. Thus, SAM approach was used in this work for effective immobilization of template biomolecules at the gold surface, prior to electropolymerization, avoiding template denaturation [31], while promoting imprinting quality and recognition ability of the MIP surface [20,31,32]. After that, the electrosynthesis of the MIP layer at the electrode surface, was achieved by CV technique, followed by removal of template biomolecules physically entrapped within the polymeric matrix. Finally, after template removal from the polymeric matrix, the resulting MIP film was able to selectively recognize target molecule during the rebinding studies (quantification). The adopted procedure for the MIP preparation is schematically represented in Figure 1. To evaluate the performance of the electrochemical biosensor for α-amylase detection (in buffer solution and in saliva samples) a systematic study of several analytical parameters (such as sensitivity, dynamic linear range, limit of detection and selectivity) was implemented in this work.
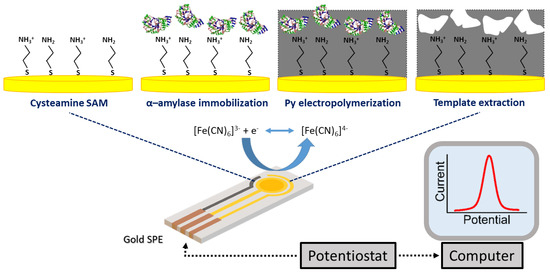
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the synthetic process for preparation of the MIP film at the AuSPE surface. The overall process incorporates the following steps: (i) adsorption of a cysteamine (CA) SAM on the electrode working area for (ii) immobilization of template biomolecules; (iii) imprinting process by electrosynthesis of a poly(pyrrole) thin film in the presence of template molecules; (iv) removal of target biomolecules from the polymeric matrix.
2. Results and Discussion
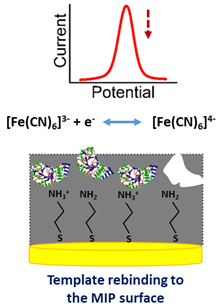
MIPs are synthetic materials used for molecular recognition (plastic antibodies), thus, presenting high affinity for specific targets. This strategy was used in this work for selective detection of stress biomarker α-amylase. First, a systematic investigation of the biosensor preparation procedures was performed. Then, the biosensor performance was evaluated by quantification of α-amylase in buffer solution and in saliva samples. Electrochemical measurements at the MIP electrode surface were performed in the presence of the biocompatible [Fe(CN)6]3-/4- redox couple since it can provide stable and reliable electrochemical response at SPE surface [33]. SWV was selected as electroanalytical technique for the quantification studies due to its high sensitivity along with fast time of analysis [15,34,35,36].
2.1. Step-by-Step Preparation of the Sensor Surfaces
The surface modification procedures started with the formation of an amine layer at the AuSPE surface after incubating the chip working area with a CA solution, allowing the spontaneous formation of a narrow packed SAM through the strong Au-S interaction [37]. Then, effective template protein immobilization over the pre-formed CA SAM was achieved mainly by hydrophilic interactions [38] between the thiolated surface and the enzyme but also through electrostatic interactions. At medium pH = 7.2, the amine groups at the CA SAM surface (pKa: 8.27 [39,40]) were expected to be slightly positively charged and attracted the negatively carboxylic acid groups of the enzyme (pKa: 6.0 to 6.9 [5]). The electropolymerization process was performed by incubating the chip surface with Py monomer solution followed by scanning the electrode potential between −0.2 V to 1.0 V, at 100 mV s−1. Preliminary studies were performed in order to evaluate the optimal film thickness to improve the biosensor performance (see Figure S2, SI) and one CV cycle for Py electropolymerization was selected to build the MIP film surface.
The typical CV voltammograms obtained for the electropolymerization of Py monomer at the CA SAM/AuSPE surface for both systems, MIP and NIP, are presented in Figure 2. The monomer oxidation to a radical, which occurs near the positive end of the potential window (at ~0.8 V), initiated the polymerization reaction that allowed the deposition of a very thin and homogeneous poly(Py) film on the working electrode surface [28,41,42]. As can be seen in the figure, a lower peak current intensity due to monomer oxidation was obtained at the MIP surface relatively to the NIP surface, which was due to the template biomolecules immobilized at the SAM surface that caused an additional barrier to diffusional monomer for its further oxidation at the electrode surface.
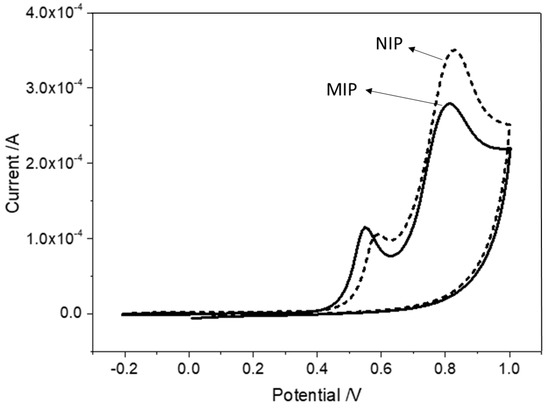
Figure 2.
Typical CV voltammograms obtained for of electropolymerization of Py monomer (C = 10 mmol L−1, in 0.1 mol L−1 PBS at pH 7.2) at the (―) MIP and (---) NIP surfaces. Number of cycles: 1. Scan rate: 100 mV·s−1.
Finally, after (iv) template extraction, the MIP film surface containing the empty binding sites was ready for rebinding (detection). Three different strategies were applied in this work for the effective removal of α-amylase from the imprinted surface, namely the use of acidic (H2SO4) and basic (NaOH) solutions and buffer solution containing the surfactant SDS [15]. From the extraction procedures tested, buffer solution containing the SDS surfactant proved to be the most effective for template removal while preserving the polymeric surface integrity (see SI Figure S5).
The EIS technique was used to follow the changes in the electron transfer properties of the [Fe(CN)6]3−/4− redox couple on the receptor surface after each modification step. Typical impedance diagrams obtained, displayed as Nyquist plots, are shown in Figure 3.
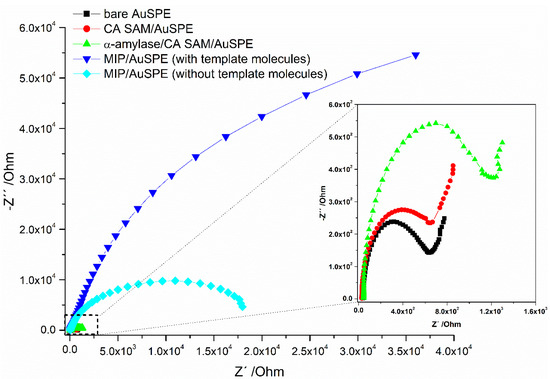
Figure 3.
EIS data, collected in the presence of 5 mmol L−1 [Fe(CN)6]3−/4− redox couple, during the step-by-step modification of the AuSPE surface to build the MIP sensing surface.
In order to quantify the redox probe diffusion variations that occured at the different stages of surface modification, the experimental data was analyzed using a Randles equivalent circuit (see SI Figure S1). The numerical values extracted from the fitting, with particular relevance for the charge transfer resistance (Rct) circuit element, are displayed in Table S1 (SI). The impedance data obtained revealed a sequential increase of the Rct (due to a decrease of electron transfer kinetics) after incubation of the bare AuSPE surface with CA and template enzyme solutions, revealing successful (i) SAM formation and (ii) α-amylase immobilization, prior to electropolymerization. Moreover, the (iii) formation of the specific cavities on the electrode surface by (one CV cycle) electropolymerization of Py in the presence of template protein involved the coverage of the chip surface by a huge amount of material, thus, inducing a large increase of Rct due to high surface blocking to the diffusional redox probe. After (iv) treating the chip surface with extraction solution, a decrease in the Rct was observed. This was consistent with the effective removal of α-amylase from the imprinted polymer layer, leaving empty the binding sites in the polymeric structure and providing pathways for redox probe diffusion to the electrode surface.
In this work, the NIP surface was used as reference system, where only non-specific interactions can occur. Thus, similar experiments were performed at the MIP and NIP surfaces, but for NIP, the electropolymerization of Py monomer took place after surface incubation with pure PBS (absence of α-amylase as template).
2.2. Surface Characterization by AFM
Surface characterization studies using AFM were performed at the AuSPE surface before (bare electrode) and after electrosynthesis of the MIP film, and after template removal from the deposited polymer layer. The collected images are represented in Figure 4.
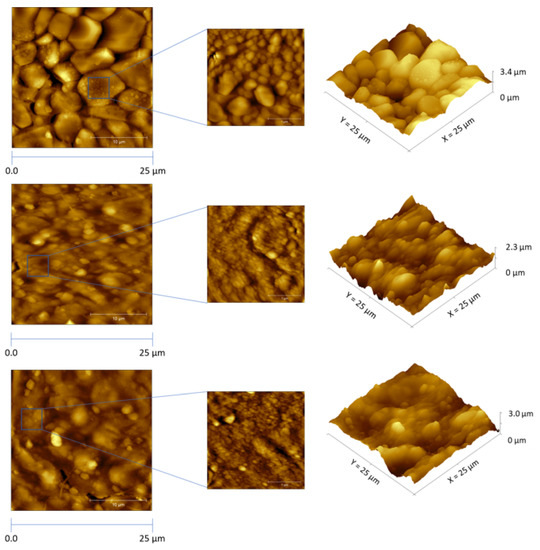
Figure 4.
AFM images in (left) 2D and (right) 3D collected at the AuSPE surface (top) before and (middle) after Py monomer electropolymerization in the presence of template protein, followed by (bottom) template extraction from the MIP film.
As can be seen in Figure 4 (top image), the bare gold surface had a grain-like morphology with a domain size of ~5–10 µm in diameter. The rough profile was associated to the gold ink composition used for fabrication of the gold screen-printed chips, which contains gold particles [43]. The root mean square (RMS) surface roughness value obtained was 108.0 nm. After Py electropolymerization over the SAM surface containing the immobilized template biomolecules (Figure 4, middle image), the RMS value decreased to 69.2 nm, meaning that a considerably more flattened and smoother surface was obtained after coating the electrode surface with the MIP film. Furthermore, from the 3D-images, the surface depth of the MIP film (2.3 µm) decreased relatively to the bare surface (3.4 µm). The AFM images showed that surface modification with poly(Py) was accomplished homogenously.
After removal of α-amylase from the polymer layer (Figure 4, bottom image), the RMS value increased to 100.0 nm (while the surface depth increased to 3.0 µm), indicating that empty cavities (binding sites) were formed at the polymeric matrix, leading to an increase of surface roughness.
2.3. Analytical Response of MIP Biosensor
After optimization of the experimental conditions, the prepared MIP-based biosensor was applied for the amperometric quantification of α-amylase (see detection scheme in Appendix A) in buffer solution. The rebinding studies were performed by incubating the MIP film surface for 10 min with several buffer solutions with increasing concentrations of analyte, ranging from 6.0 × 10−6 to 0.60 mg mL−1. After surface washing and drying, electrochemical measurements were recorded in the presence of the [Fe(CN)6]3−/4− redox couple. The collected SWVs and the corresponding calibration curve obtained are shown in Figure 5.

Figure 5.
(A) SWV measurements, obtained in the presence of 5 mmol L−1 [Fe(CN)6]3−/4− redox couple, at the MIP surface for the several α-amylase standard solutions tested (from 6.0 × 10−6 to 0.60 mg mL−1). (B) Graphical representation of the redox probe peak current vs. concentration logarithm, obtained at the MIP surface. Inset: Graphical representation of the redox probe peak current vs. α-amylase concentration obtained at the MIP and NIP surfaces. Error bars correspond to standard deviations of analytical signals collected from three independent assays.
As can be seen in Figure 5A, increasing α-amylase concentration in solution led to a decrease of redox probe anodic peak current due to the enzyme cumulative binding to the empty imprinted sites at the MIP film surface that blocked the diffusional redox probe pathway within the polymer layer. Moreover, the plot of the estimated redox probe peak current (Ipeak) as a function the α-amylase concentration, shown in the inset of Figure 5B, gave origin to a non-linear dependence. By opposition, a linear pattern against the concentration logarithm was obtained for analyte concentration ranges between (1) 6.0 × 10−6 to 3.0 × 10−4 mg mL−1 and from (2) 3.0 × 10−4 to 0.60 mg mL−1 (see Figure 5B). The limit of detection (LOD < 3.0 × 10−4 mg mL−1) was estimated according to IUPAC recommendation for ion-selective electrodes, where log(C) is used [44].
For comparison, the results obtained at the NIP surface are also shown in the inset of Figure 5B. As expected, there was no net response tendency over the concentration range tested. This might indicate that the interaction between the enzyme and the NIP surface was randomly and uncontrolled due to the absence of specific interactions. Thus, the significant difference in the interaction between MIP and NIP was a good indicator that MIP specific synthetic receptors can improve the affinity of the sensor device for the target α-amylase.
Furthermore, the prepared MIP-based biosensor can be reused at least for two times (decrease in sensitivity is only 2.9%) after surface regeneration with surfactant solution overnight, following by abundant washing with PBS and pure water (see Figure S3).
The analytical features of the developed MIP-based biosensor for detection of α-amylase were compared with the obtained by other detection methodologies reported in the literature (see SI Table S2). The detection levels achieved in this work (LOD < 3.0 × 10−4 mg mL−1) was of the same order of magnitude, or even inferior, to reported values which makes the developed electrochemical device suitable for amylase determination in other biological fluids, like serum and urine, where trace amount of this enzyme can be found (~1 × 10−3–2 × 10−2 mg mL−1) [5,11,45,46]. In addition, taking into account that α-amylase is the most abundant protein in saliva, with an average concentration in undiluted saliva of ~0.5 mg mL−1 [4,5], and depends on gender and age, beside stress [17], the linear concentration range of response also plays an important role for application of the biosensor in clinical context. Comparing with other detection approaches, the developed MIP biosensor has one of the widest working concentration range, allowing the easy detection of α-amylase in undiluted or diluted saliva samples (10 to 100 times, for example) to minimize matrix effects. Besides, the advantages of simple, rapid, sensitive and cost-effective detection procedures make our electrochemical approach a valid alternative to more complex, expensive and long analysis time methods, very dependent on laboratory instrumentation and well-trained operators, for regular quantification of α-amylase in clinical context.
2.4. Selectivity and Application of the MIP-Based Biosensor
In this work, quantification studies were also performed in human saliva, collected from five healthy donors. To do so, saliva samples were previously boiled (T = 100 °C for 10 min), for thermal denaturation of α-amylase [47] (see Figure S4, SI), and then, filtered and diluted 10 times in PBS.
In order to evaluate the selectivity of the sensor response, the analytical features resulting from the calibration curve obtained in saliva (linear concentration range, slope and LOD) were compared with the previously obtained in buffer solution. Data obtained are resumed in Table 1.

Table 1.
Comparison of the analytical features resulting from calibration curves obtained in buffer solution and human saliva samples.
After performing the experiments in diluted saliva, a saturation of the sensor response at higher concentrations was observed, leading to a decrease of the linear concentration range relatively to buffer solution. However, the sensitivity of the MIP-biosensor in saliva (−7.94 µA decade−1) was very similar to the obtained in buffer solution (−8.04 µA decade−1), indicating no significant interference of the saliva matrix in the working range used. Thus, the developed MIP-based biosensor can be used for amylase detection in saliva after simple sample dilution (to avoid signal saturation).
In order to access the applicability of the prepared MIP biosensor in clinical context, recovery studies were performed in treated blank human saliva samples spiked with known amounts of α-amylase (from 6.50 × 10−4 to 1.50 × 10−2 mg mL−1). The results obtained are summarized in Table S3 (SI). As can be seen, a good agreement between added and found amounts of α-amylase was achieved. The recoveries ranged from 87.3 to 108% with an average relative error of 9.1%, suggesting that the proposed biosensor can be successfully used in real applications in clinical context.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Reagents and Solutions
The chemicals used throughout this work were: α-amylase (extracted from porcine pancreas, Sigma-Aldrich (Darmstadt, Germany), sodium dihydrogen phosphate (Sigma-Aldrich, Darmstadt, Germany), sodium hydrogen phosphate (Sigma-Aldrich), cysteamine (CA, Fluka, Dorset, UK), pyrrole (Py, TCI, Eschborn, Germany), potassium ferricyanide (K3[Fe(CN)6], Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany), potassium ferrocyanide trihydrate (K4[Fe(CN)6].3H2O, Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany) and dodecyl sulfate sodium (SDS, Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany). All other chemicals were of analytical grade and were used without any further purification.
Stock solutions of α-amylase (C = 6 mg mL−1) were prepared in 0.1 mol L−1 PBS, pH 7.2, and less concentrated standards were prepared by suitable dilution in the buffer solution. All aqueous solutions were prepared using water purified with a Milli-RO3 Plus and Milli-Q purification systems (resistivity > 18 MΩ cm).
3.2. Apparatus
Electrochemical measurements were conducted in an Autolab PGSTAT302N potentiostat/galvanostat (Metrohm Autolab, Utrecht, The Netherlands), containing an impedance module, controlled by GPES software. Gold screen-printed electrodes (AuSPEs, DRP-220AT, DropSens, Merck, Oviedo, Spain) were used as sensor platforms in this work.
Atomic force microscopy (AFM) images of surface topography were recorded using a Molecular Imaging PicoLe atomic force microscope using a silicon cantilever/tip (model ACT, App Nano, Orsay, France) with a resonance frequency between 200 and 400 kHz.
3.3. Synthesis of MIP on the AuSPE Surface
Before surface modification, the gold chips were cleaned by sequential washing with pure water, acetone and ethanol. Then, an electrode surface electrochemical cleaning procedure, using CV technique, was employed by sweeping the electrode potential between 0 and 1.25 V, at a scan rate of 100 mV s−1, in a 0.5 mol L−1 sulfuric acid solution. Several cycles were performed until a reproducible voltammogram as obtained (~12 CV cycles). The chips were then carefully rinsed with pure water and dried under a N2 stream.
For preparation of the sensor surfaces the following procedure was adopted: the working area (4 mm diameter) of the freshly cleaned AuSPE was firstly incubated with a 25 mmol L−1 solution of CA for 2 h, at 25 °C, followed by washing with pure water and dried under a N2 stream. Then, the chip surface was incubated with a α-amylase solution (C = 12 µg mL−1, prepared in 0.1 mol L−1 PBS, pH 7.2) for 15 min, at 4 °C, for effective protein immobilization over the pre-formed CA SAM. After that, the specific binding sites were created by electropolymerization of Py monomer in the presence of the template protein. Briefly, one CV cycle was recorded between −0.2 V to 1.0 V, at 100 mV s−1, in a 10 mmol L−1 Py solution (prepared in 0.1 mol L−1 PBS, pH 7.2). Finally, extraction of template biomolecules physically entrapped within the polymeric network was achieved by incubating the MIP film overnight with a 25 mmol L−1 SDS solution, prepared in a mixture of PBS and methanol (10:1, v/v) [15]. After incubating the chip surface with the extraction solution, the AuSPE was abundantly washed with pure water to completely remove protein residues from the polymeric film and dried under a N2 stream.
Non-imprinted polymer (NIP) surfaces were used as reference system in this work and were prepared by following the same method used for MIP fabrication but in the absence of α-amylase during the electropolymerization process (non-specific adsorption).
3.4. Electrochemical Measurements
Electrochemical measurements were performed in the presence of 5 mmol L−1 [Fe(CN)6]3-/4- redox pair, prepared in 0.1 mol L−1 PBS (pH = 7.2). For SWV measurements, the potential was scanned from −0.2 to 0.6 V, at a frequency of 10 Hz, with an amplitude of 50 mV and a step potential of 2 mV. EIS measurements were performed at open circuit potential (0.12 V) using a sinusoidal potential perturbation with an amplitude of 0.01 V. The frequency range was from 0.1 to 100,000 Hz. Impedance data were represented as Nyquist plots and fitted to a Randles type equivalent circuit (see Figure S1, SI) using the adequate module in the FRA software.
4. Conclusions
In this work, an efficient strategy to develop an electrochemical device to collect valuable salivary proteomic information in a clinical context was reported. Molecular imprinting technology, combined with electrochemical techniques, were the basis for the design and electrosynthesis of artificial receptors at the sensor surface to selectively recognise the stress biomarker α-amylase, in order to evaluate patients’ physiological and psychological stress. In addition, detection was performed in a straightforward manner. The use of portable and compact potentiostats along with disposable chips, the AuSPEs, makes the detection simple, cost-effective and suitable for PoC application. Besides, minimal sample volumes were needed for the electrochemical readout.
The developed MIP-biosensor was successfully applied to the analysis of α-amylase in human saliva samples. Sample preparation was minimal and aby simple dilution a very wide working concentration range was obtained, between 3.0 × 10−4 to 3.0 × 10−2 mg mL−1, and low detection levels were achieved (LOD < 3.0 × 10−4 mg mL−1). The biosensor performance revealed no apparent effect of the sample matrix and good recoveries were obtained. Thus, the proposed MIP-based biosensor can be used for fast and accurate screening assays for α-amylase determination in a clinical diagnosis context.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/electrochem2030028/s1, Figure S1: Randle’s equivalent circuit, Table S1: Fitting parameters using the Randles circuit, Figure S2: optimization of the MIP film thickness, Table S2: methodologies reported in literature for α-amylase detection in saliva, Figure S3: reusability, Figure S4: selectivity and application of the biosensor, Table S3: determination of α-amylase in human saliva.
Author Contributions
T.S.C.R.R. contributed to the experimental work and writing—original draft and conceptualization. I.M.M. contributed to the experimental work. A.T.S.C.B. contributed to the experimental work. L.I.G.S. contributed to the experimental work. J.A.R. contributed to the experimental work and writing—review and editing and conceptualization. A.F.S. contributed to work supervision and financing. C.M.P. performed writing—review and editing, conceptualization, supervision and financing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research had the financial support of FCT (Fundação para a Ciência e Tecnologia) and co-financed by the European Union (FEDER funds) under the Partnership Agreement PT2020, Research Grants UIDB/00081/2020 (CIQUP) and project AlleRiskAssess-PTDC/BAA-AGR/31720/2017. Ana Brandão would like to thank SCANSCI—equipamentos de laboratório for the financial support given to the PhD program and IL4Energy project (02/SAICT/2017), funded by FCT and the European Funds for regional development (FEDER) through the operational program of competitiveness and internationalization with reference POCI-01-0145-FEDER-032294, for the research grant. J.A. Ribeiro (ref. SFRH/BPD/105395/2014) and I. Miranda (SFRH/BD/75026/2010) acknowledge FCT under the QREN—POPH—Advanced Training, subsidized by European Union and national MEC funds.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data sharing not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A. Table of Contents
References
- Wang, J.; Schipper, H.M.; Velly, A.M.; Mohit, S.; Gornitsky, M. Salivary biomarkers of oxidative stress: A critical review. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2015, 85 (Suppl. C), 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nater, U.M.; Rohleder, N. Salivary alpha-amylase as a non-invasive biomarker for the sympathetic nervous system: Current state of research. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2009, 34, 486–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohleder, N.; Nater, U.M. Determinants of salivary α-amylase in humans and methodological considerations. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2009, 34, 469–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deutsch, O.; Fleissig, Y.; Zaks, B.; Krief, G.; Aframian, D.J.; Palmon, A. An approach to remove alpha amylase for proteomic analysis of low abundance biomarkers in human saliva. Electrophoresis 2008, 29, 4150–4157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarabadi, A.S.; Huang, T.; Mielke, J.G. Capillary isoelectric focusing with whole column imaging detection (iCIEF): A new approach to the characterization and quantification of salivary α-amylase. J. Chromatogr. B 2017, 1053, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, E.; Kataoka, M.; Yatsushiro, S.; Kajimoto, K.; Hino, M.; Kaji, N.; Tokeshi, M.; Bando, M.; Kido, J.; Ishikawa, M.; et al. Accurate quantitation of salivary and pancreatic amylase activities in human plasma by microchip electrophoretic separation of the substrates and hydrolysates coupled with immunoinhibition. Electrophoresis 2008, 29, 1902–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, J.-F.; Lin, F.-P.; Chen, S.-C.; Chen, H.-C. Purification and properties of an extracellular amylase from Thermus sp. Bot. Bull. Acad. Sin. 1995, 36, 195–200. [Google Scholar]
- O’Donnell, M.D.; FitzGerald, O.; McGeeney, K.F. Differential serum amylase determination by use of an inhibitor, and design of a routine procedure. Clin. Chem. 1977, 23, 560–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valls, C.; Rojas, C.; Pujadas, G.; Garcia-Vallve, S.; Mulero, M. Characterization of the activity and stability of amylase from saliva and detergent: Laboratory practicals for studying the activity and stability of amylase from saliva and various commercial detergents. Biochem. Mol. Biol. Educ. 2012, 40, 254–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandel, A.L.; Peyrot des Gachons, C.; Plank, K.L.; Alarcon, S.; Breslin, P.A.S. Individual Differences in AMY1 Gene Copy Number, Salivary α-Amylase Levels, and the Perception of Oral Starch. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e13352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della Ventura, B.; Sakač, N.; Funari, R.; Velotta, R. Flexible immunosensor for the detection of salivary α-amylase in body fluids. Talanta 2017, 174 (Suppl. C), 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguirre, A.; Levine, M.J.; Cohen, R.E.; Tabak, L.A. Immunochemical quantitation of Amylase and secretory IgA in parotid saliva from people of various ages. Arch. Oral Biol. 1987, 32, 297–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentes-Rubio, M.; Fuentes, F.; Otal, J.; Quiles, A.; Hevia, M.L. Validation of an assay for quantification of alpha-amylase in saliva of sheep. Can. J. Vet. Res. 2016, 80, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Moreira, F.T.C.; Sharma, S.; Dutra, R.A.F.; Noronha, J.P.C.; Cass, A.E.G.; Sales, M.G.F. Protein-responsive polymers for point-of-care detection of cardiac biomarker. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 196, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ribeiro, J.A.; Pereira, C.M.; Silva, A.F.; Sales, M.G.F. Electrochemical detection of cardiac biomarker myoglobin using polyphenol as imprinted polymer receptor. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 981, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, J.A.; Pereira, C.M.; Silva, A.F.; Sales, M.G.F. Disposable electrochemical detection of breast cancer tumour marker CA 15-3 using poly(Toluidine Blue) as imprinted polymer receptor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 109, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, P.T.; Guimarães, L.N.; Dias, A.A.; Ulhoa, C.J.; Coltro, W.K.T. Amperometric detection of salivary α-amylase on screen-printed carbon electrodes as a simple and inexpensive alternative for point-of-care testing. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 258, 342–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BelBruno, J.J. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 94–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzun, L.; Turner, A.P.F. Molecularly-imprinted polymer sensors: Realising their potential. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 76, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheller, F.W.; Zhang, X.; Yarman, A.; Wollenberger, U.; Gyurcsányi, R.E. Molecularly imprinted polymer-based electrochemical sensors for biopolymers. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2019, 14, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Turner, A.P.F. Biosensors: Sense and sensibility. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 3184–3196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vasapollo, G.; Del Sole, R.; Mergola, L.; Lazzoi, M.R.; Scardino, A.; Scorrano, S.; Mele, G. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers: Present and Future Prospective. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011, 12, 5908–5945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rebelo, T.S.C.R.; Santos, C.; Costa-Rodrigues, J.; Fernandes, M.H.; Noronha, J.P.; Sales, M.G.F. Novel Prostate Specific Antigen plastic antibody designed with charged binding sites for an improved protein binding and its application in a biosensor of potentiometric transduction. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 132, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, Q.; Hu, X.-Y.; Hao, S.-R. Electrochemical Sensors Based on Electropolymerized Films. 2011. Available online: http://www.intechopen.com/books/electropolymerization/electrochemical-sensors-based-onelectropolymerized-films (accessed on 23 June 2021).
- Ramanavičius, A.; Ramanavičienė, A.; Malinauskas, A. Electrochemical sensors based on conducting polymer—Polypyrrole. Electrochim. Acta 2006, 51, 6025–6037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, U.; Roznyatovskaya, N.V.; Mirsky, V.M. Conducting polymers in chemical sensors and arrays. Anal. Chim. Acta 2008, 614, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, X.; Xing, Z.; Zhu, A.; Zhao, Z.; Xu, G.; Li, C.; Zhou, H. Molecularly imprinted polymers based electrochemical sensor for bovine hemoglobin recognition. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 168, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.; Xia, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, F.; Yang, M.; Li, Y.; Xia, Y. Molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensor based on an electrode modified with an imprinted pyrrole film immobilized on a [small beta]-cyclodextrin/gold nanoparticles/graphene layer. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 82930–82935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, X.; Liu, S.; Yu, J.; Lian, W.; Huang, J. Electrochemical sensor based on molecularly imprinted film at polypyrrole-sulfonated graphene/hyaluronic acid-multiwalled carbon nanotubes modified electrode for determination of tryptamine. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2012, 31, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özcan, L.; Şahin, Y. Determination of paracetamol based on electropolymerized-molecularly imprinted polypyrrole modified pencil graphite electrode. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2007, 127, 362–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras-Naranjo, J.E.; Aguilar, O. Suppressing Non-Specific Binding of Proteins onto Electrode Surfaces in the Development of Electrochemical Immunosensors. Biosensors 2019, 9, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Crapnell, R.D.; Hudson, A.; Foster, C.W.; Eersels, K.; Grinsven, B.V.; Cleij, T.J.; Banks, C.E.; Peeters, M. Recent Advances in Electrosynthesized Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Sensing Platforms for Bioanalyte Detection. Sensors 2019, 19, 1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ribeiro, J.A.; Silva, E.; Moreira, P.S.; Pereira, C.M. Electrochemical Characterization of Redox Probes at Gold Screen-Printed Electrodes: Efforts towards Signal Stability. ChemistrySelect 2020, 5, 5041–5048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Han, M.; Ye, X.; Wu, K.; Wu, T.; Li, C. Voltammetric myoglobin sensor based on a glassy carbon electrode modified with a composite film consisting of carbon nanotubes and a molecularly imprinted polymerized ionic liquid. Microchim. Acta 2017, 184, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhao, H.; Chen, Z.; Mu, X.; Guo, L. Aptamer biosensor for label-free square-wave voltammetry detection of angiogenin. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 30, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snir, E.; Amit, E.; Friedler, A.; Yitzchaik, S. A highly sensitive square wave voltammetry based biosensor for kinase activity measurements. Pept. Sci. 2015, 104, 515–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreira, F.T.C.; Dutra, R.A.F.; Noronha, J.P.; Sales, M.G.F. Novel sensory surface for creatine kinase electrochemical detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 56, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anzai, J.-I.; Guo, B.; Osa, T. Quartz-crystal microbalance and cyclic voltammetric studies of the adsorption behaviour of serum albumin on self-assembled thiol monolayers possessing different hydrophobicity and polarity. Bioelectrochem. Bioenerg. 1996, 40, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerekovic, I.; Milardovic, S.; Palcic, M.; Grabaric, Z. Characterization of cysteamine self assembled on gold functionalized with nitrilotriacetic acid and evaluation of copper(II) binding capacity with adsorption transfer stripping voltammetry. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2014, 724, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garyfallou, G.-Z.; Ketebu, O.; Şahin, S.; Mukaetova-Ladinska, E.B.; Catt, M.; Yu, E.H. Electrochemical Detection of Plasma Immunoglobulin as a Biomarker for Alzheimer’s Disease. Sensors 2017, 17, 2464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Martins, J.I.; Bazzaoui, M.; Reis, T.C.; Bazzaoui, E.A.; Martins, L. Electrosynthesis of homogeneous and adherent polypyrrole coatings on iron and steel electrodes by using a new electrochemical procedure. Synth. Met. 2002, 129, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, R. Polypyrrole Conducting Electroactive Polymers: Synthesis and Stability Studies. J. Chem. 2006, 3, 186–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Butterworth, A.; Blues, E.; Williamson, P.; Cardona, M.; Gray, L.; Corrigan, D.K. SAM Composition and Electrode Roughness Affect Performance of a DNA Biosensor for Antibiotic Resistance. Biosensors 2019, 9, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Buck, R.P.; Lindner, E. Recommendations for nomenclature of ion-selective electrodes (IUPAC Recommendations 1994). Pure Appl. Chem. 1994, 66, 2527–2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, S.; Mandal, N.; Bandyopadhyay, D. Paper-based α-amylase detector for point-of-care diagnostics. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 78, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Zhou, X.; Ji, X.; Lin, R.; Lin, W. Simultaneous determination of ascorbic acid, dopamine and uric acid using poly(4-aminobutyric acid) modified glassy carbon electrode. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 178, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.; Shandilya, M.; Kundu, S.; Kayastha, A.M. Heat, Acid and Chemically Induced Unfolding Pathways, Conformational Stability and Structure-Function Relationship in Wheat α-Amylase. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0129203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).