Abstract
The aim of this paper is to present the results of an experimental and numerical investigation into the degradation of reinforced concrete (RC) specimens subjected to an accelerated corrosion process using impressed current in the presence of chloride ions. The corrosion of the rebars was carried out using three current densities (50, 100, and 200 µA/cm2) and various exposure times. The experimental results characterised the internal degradation of the RC specimens through measurement of the corrosion product thicknesses at the steel–concrete interface; the widths, lengths and orientations of internal concrete cracks; and the external concrete crack widths. In addition, numerical modelling of the corroded RC specimens was conducted to describe the crack patterns. The comparison between the experimental and numerical results demonstrated a high degree of correlation, providing insights into the degradation process of RC specimens due to corrosion.
1. Introduction
Corrosion of steel reinforcing rebars is the primary cause of deterioration in existing reinforced concrete (RC) structures [1,2,3,4]. The corrosion process leads to a reduction in the cross-section of the rebar [5,6,7,8,9], the cracking of the concrete cover [10,11], and decreased bond strength between the steel and the concrete [12,13,14,15,16,17,18]. Once the protective passivation layer surrounding the rebar has been compromised, corrosion can initiate under favourable environmental conditions (oxygen, water, and temperature) [19,20,21]. The resulting corrosion products occupy a volume two to seven times greater than the original iron metal [21,22], creating pressure at the steel–concrete interface. This induces tensile stresses in the concrete, leading to cracking when the concrete’s tensile strength is exceeded [19,20,23,24,25]. These cracks propagate to the surface, potentially causing spalling and delamination of the concrete cover, thereby severely damaging the cross-section [19,20,26,27]. These cracks subsequently provide pathways for accelerated ingress of aggressive agents, further intensifying the corrosion process [19,20].
The impact of chloride ions on the performance of existing structures is of particular concern in coastal regions, where corrosion can significantly reduce their structural integrity, potentially resulting in loss of serviceability [28,29]. This represents a significant safety risk to users. And, in the absence of adequate maintenance, a possibility of compromised structural safety can be observed.
Concrete surface cracks are the most visible sign of corrosion and their width is a reliable indicator of the level of corrosion [11]. Thus, corrosion-induced cracking is a key parameter in predicting the service life of RC structures and in planning maintenance [11]. A well-defined relationship between corrosion level, crack width, and crack patterns would greatly improve the efficacy of condition assessment through visual inspection.
Some model studies have investigated corrosion-induced crack initiation and propagation [30,31], using uniform corrosion models [32]. It is evident that the expansive nature of corrosion products (CPs) is responsible for the cracking of concrete. Consequently, there have been several research efforts focused on modelling the expansive layer of CPs. In order to model the expansion of corrosion products, a thermal analogy was adopted. This approach proposes that the properties of a part of the steel vary linearly up to those of the corrosion products and thus allows a representation of both the reduction in the steel section and the expansion of the corrosion product layers [30,31]. Alternative approaches have been adopted by others, whereby steel and corrosion products are distinguished and treated separately. The corrosion product (CP) layers are thus considered as a third distinct material with linearly elastic behaviour [33]. Some researchers simulated CP expansion without explicitly accounting for the CP layers themselves. Instead, they used a zero-thickness interface between the steel and concrete [34,35,36,37]. It turned out that considering the expansion of CPs in a uniform way did not adequately reflect the complexity of the reality. Taking into account the non-uniformity of CP expansion around the reinforcement made it possible to reproduce more realistic cracking patterns by calculation [38]. Certain authors have focused on modelling the expansion of CPs in a non-uniform manner, with the objective of aligning closer to the distributions that have been observed in reality. This has been performed in order to determine its influence on cracking and consequently on the service life of corroded RC structures [39,40,41,42,43,44,45].
In order to model the non-uniformity of CP expansion, researchers opted to rely on an expansion of the CPs by a semi-uniform shape [46]. Some studies were conducted in which the expansion of the CP layer was modelled in elliptical form [39,47,48,49,50]. Others have used a Gaussian-type law [49,51,52] to describe the distribution due to CP expansion. Researchers such as Xi Yang [48] adopted von Mises distribution to express the shape of CP expansion.
Analysing the distribution of CPs is therefore crucial for understanding cracking mechanisms. It is therefore vital to analyse the distribution of CPs if one is to gain a full understanding of the mechanisms involved in cracking. It has been demonstrated that this distribution exerts a direct influence on the crack patterns that manifest in RC structures. Despite the existence of studies that have demonstrated a correlation between the loss of rebar sections and the widths of crack patterns [29,30,32], a more precise understanding and consideration of the degradation process are afforded by direct analysis of the distribution of the CPs at the steel/concrete interface [53,54]. The distribution of CPs, which is non-uniform, exerts a significant influence on the crack patterns that emerge [38,39,40,41,42,55]. Consequently, it is insufficient to consider only the total amount of CPs by the means of a rebar section loss [56,57]. Furthermore, the distribution of CPs is vital for improving condition assessment through visual inspection, as it enables the establishment of a highly accurate relationship between corrosion level, crack width, and crack patterns.
It is important to note that the most commonly used expansion types are elliptical, semi-uniform, or Gaussian or have von Mises distribution. However, given the experimental data obtained at the steel–concrete interface and their pertinence, it is necessary to employ expansion types based on the location and thickness of CPs observed in SEM images. For this reason, two types of expansion were selected and one was defined in order to more accurately represent corrosion product expansion: semi-uniform, elliptical, and homothetic expansions. The use of numerical modelling as a cost-effective analytical approach is predicated on the use of collected experimental data, given the expense associated with experimental testing. The idea is to develop a model to that can reproduce experimental results, thereby facilitating a more profound comprehension of the phenomena involved in the RC corrosion process. Additionally, the model is employed to expose the link between external and internal degradations.
This paper aims to analyse the relationship between the distribution of CPs, the evolution of internal cracking, and the development of surface crack patterns in RC specimens. These specimens were designed with a corner ribbed rebar and concrete strength representative of older structures. The analysis is based on the various expansion types observed in the literature and the experimental observations of the present study, particularly with a current density of 100 µA/cm2 [58,59].
The model should be able to provide a better understanding of experimental observations given their dispersion. In terms of the intended practical use, the ambition of the present study is to devise a numerical tool that is both simplified and capable of improving condition assessment through the use of both visual inspections and the correlation between internal and external degradations. Indeed, as a consequence of the visual inspections, which revealed a crack pattern, and given the established correlation between external and internal degradation, it will be possible to predict the internal degradation state from that which is observed externally. This will enable optimal decision-making with regard to the identification of suitable repairs and/or maintenance procedures.
2. Methodology
2.1. Experimental Programme
The specimens of the experimental programme labelled Pn were RC prisms with the dimensions 500 × 125 × 100 mm3 (Figure 1).
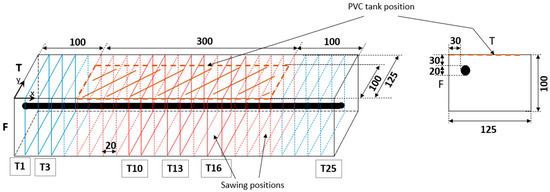
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the RC specimen and slice preparation. The letters T and F represent the top and front faces of the prisms, respectively (dimensions in mm).
In order to obtain cracks starting at the steel–concrete interface and propagating to the concrete surface, within a reasonable time frame, accelerated corrosion was necessary. To this end, chloride ions (NaOH = 1 g/L; KOH = 4.65 g/L; and NaCl = 30 g/L) and impressed current were used.
Three current densities (Y) expressed in µA/cm2 of steel surface were considered. Different durations (Xd) consistent with previous studies [45,57] were considered from 5 to 78 days for 50 µA/cm2, from 7 to 35 days for 100 µA/cm2, and from 3.5 to 19.5 days for 200 µA/cm2.
The selection of these current densities was not arbitrary but rather was guided by the existing literature [60,61]. Specifically, a current density of 100 µA/cm2 is frequently employed by numerous researchers [45,60,61]. Some authors suggested that this value corresponded to the highest corrosion current density observed in existing RC structures [30,54,62]. Others indicated that 100 µA/cm2 is a suitable value for accelerating corrosion, as it yields a corrosion pattern comparable to that of natural corrosion, prevents excessive internal pressure within the concrete sample, and avoids altering the concrete or compromising the integrity of the corrosion products formed [11,63,64]. The additional current densities of 50 and 200 µA/cm2 were chosen to investigate how variations in current density and exposure time influence corrosion-induced damage, including the thickness and distribution of corrosion products and cracks, while maintaining a constant total charge.
In order to characterise the corrosion-induced damage, a methodology was developed in [20,58,59]. This involved the analysis of different scales of observation, namely prism (Pn), slice (Ti), and square (Ei) samples.
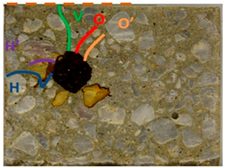
From a prism (Pn), 25 slices (Ti) were meticulously cut (Figure 1) with the dimensions 125 × 100 × 20 mm3 and labelled from T1 to T25. From a slice (Ti), smaller square samples (Ei) with the dimensions 45 × 45 × 20 mm3, including the steel rebar, were sawed. At the scale of the prism (Pn), two faces (T and F, see Figure 1) with a 30 mm concrete cover were analysed by noting the corrosion degradations (rust stains, cracks, etc.) and measuring the maximum crack width on the T (face with the salted pond) and F (front face) faces of the prisms. In order to characterise the degradation of the slices (Ti), both faces of each slice were photographed. And the crack patterns were analysed by determining the angular position of the cracks, the crack lengths, and the crack widths. To complete the analysis, the steel–concrete interface was examined. To perform this, the square sample (Ei) was divided into eight observable areas (Cj) (Figure 2). The implementation of this division was driven by the necessity to facilitate the assessment of the CP thickness and distribution around the rebar. Further details on these tests can be found in [58,59,65].
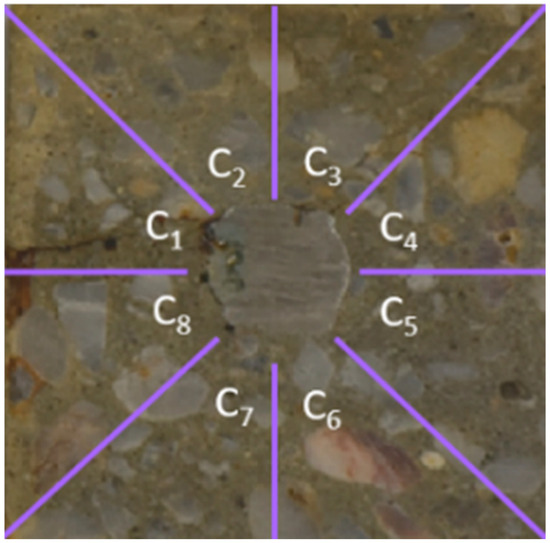
Figure 2.
Division of the steel–concrete sample (Ei) into eight observable areas (Cj) (j = 1 to 8).
2.2. Numerical Model
The numerical model developed in the present study exclusively considered concrete. Reinforcement and CPs were not explicitly modelled. However, the expansion of the CPs was simulated by a displacement imposed on the concrete surface at the location of the steel–concrete interface based on the experimental results. The calibration of the model’s parameters was based on experimentally observed CP thicknesses.
In order to model the mechanical behaviour of concrete, damage mechanics was adopted, specifically the model proposed by Mazars [66]. Tensile damage evolution is described by a decreasing exponential law, thereby facilitating energy regularisation [67]. Model parameters were calibrated on the basis of experimental data. The numerical quantification of crack widths was achieved using Matallah’s post-processing method of deformation fields [68]. In order to account for the concrete heterogeneity, the rotating band method was used to introduce random properties of concrete tensile strength.
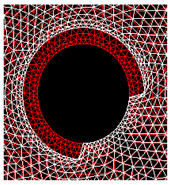
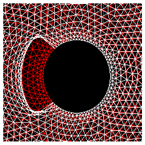
Figure 3a shows the mesh used in the model. The distribution of the eight areas (C1 to C8), as defined in the experimental study (Figure 2), was reproduced in the mesh generation (Figure 3b).
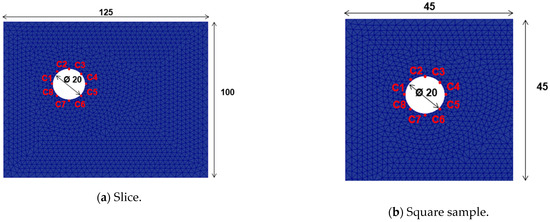
Figure 3.
Meshes of the right face of a prism slice. (a) Illustration of the geometry considered for the modelling of the prism cross-section. (b) Illustration of the eight areas (Cj) on the inner concrete contour (dimensions in mm).
The experimental observations of the location and thickness of the CPs indicated that a non-uniform expansion model would provide a more accurate representation of the expansion of the CPs.
All points in an area where corrosion was experimentally observed underwent an identical displacement. This displacement was equal to the average thickness of the CPs measured within this area. The selection of this methodology was predicated on the complex nature of the kinetics of the expansion and distribution of the CPs.
The use of energy regularisation technique in the numerical modelling enabled the use of OUVFISS procedure, which was developed by Matallah within the Cast3M framework [68,69]. The approach is constructed for a model describing nonlinear material behaviour based on a Hillerborg-type energy regularisation. The OUVFISS procedure is a method of calculating the crack width from the stress state and elastic properties.
3. Results
3.1. Experimental Results
3.1.1. Thickness and Distribution of CPs Around the Steel Rebar
The formation of CPs is a complex process influenced by environmental factors such as oxygen and water and chloride diffusion, which can affect the composition and properties of the CPs [70]. The volume of CPs is dynamic, influenced by factors such as chloride ion concentration, which can increase the solubility of CPs and lead to their migration through the concrete [18,71]. In addition, the geometry of the specimen and concrete properties can affect the distribution and thickness of CPs [54,72,73].
Table 1 shows the results of the thickness and distribution of CPs around the steel rebar for the same total charge.

Table 1.
Minimum and maximum thicknesses and locations of CPs at the steel–concrete interface (the labels used are Pn-Y-Xd, where Pn refers to the RC prism name, Y to the impressed current (in µA/cm2), and Xd to the time of exposure (in days)) using different impressed current densities and durations leading to a constant total charge.
At the lowest current density examined (50 µA/cm2), the CP formation was minimal. A significant increase in CP thickness, to approximately 1584 µm (Table 1), was observed for the current density of 100 µA/cm2. Notably, the relationship between current density and CP thickness was not linear, as a further increase to 200 µA/cm2 resulted in a reduction in the maximum localised CP thickness to 1228 µm.
This stabilisation may be due to the diffusion of CPs through cracks. The distribution of CPs around the rebar was observed to be non-uniform, with the thickest layers located in areas C2, C8, and C3 (Figure 2). This may have been due to the proximity of CPs to the thinnest concrete covers (30 mm) and the position of the counter-electrode (i.e., the T face of the prism where the salted tank was located (Figure 1)).
3.1.2. Evolution of Internal Cracks
In order to accurately assess the degradation state of the corroded RC prisms, it is important to analyse the internal crack patterns. Despite their frequent concealment beneath the concrete surface, these cracks were shown to have a significant impact on the service life of the structure.
Slices T10 to T17 (extracted from all prisms) exhibited various internal crack patterns, primarily oriented vertically (labelled V and ranging around 90°), horizontally (labelled H and H’ if a second horizontal crack was observed and ranging in the left part around 0°), and diagonally (O and O’ if a second diagonal crack was observed and ranging into the superior right part between 100 and 160°). Table 2 shows a selection of these patterns for prism corroded with current densities of 50, 100, and 200 µA/cm2.

Table 2.
Internal crack patterns of different slices (where Pn-TiR-Y-Xd represents the right face of the slice Pn-Ti-Y-Xd).
The main observations can be described as follows:
- i.
- At a current density of 50 µA/cm2, the slice had three cracks: H, H’, and V.
- ii.
- At 100 µA/cm2, the slice showed three differently oriented cracks: H, V, and O.
- iii.
- Although the number of cracks was comparable for current densities of 50 and 100 µA/cm2, the crack patterns were distinct.
- iv.
- At a current density of 200 µA/cm2, the slice developed five cracks: H, H’, V, O, and O’.
- v.
- For this current density, a higher number of cracks were observed, leading to a more severe degradation state.
3.1.3. Evolution of External Cracks
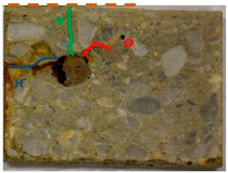
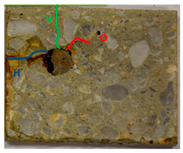
The photographs in Table 3 depict the T and F surfaces of RC prisms subjected to accelerated corrosion testing at current densities of 50, 100, and 200 μA/cm2. The duration of the test was subject to variation. Prisms marked with an asterisk were subjected to further examination through destructive testing. The blue and green lines correspond to the cracks on the front (F) and top (T) faces, respectively.

Table 3.
Photographs of prisms Pn with external visual disorders of the T and F faces as a function of accelerated corrosion duration for current densities of 50 µA/cm2, 100 µA/cm2, and 200 µA/cm2. Prisms marked with an asterisk were subjected to further examination through destructive testing.
The accelerated corrosion test resulted in observable concrete deterioration localised to the T and F faces of the RC prisms, those in immediate proximity to the steel rebar. No visual evidence of deterioration was identified on the remaining prism faces.
For prisms corroded with a current density of 50 µA/cm2, the colour of the CPs observed on the F face was orange and brown. For current densities of 100 and 200 µA/cm2, three CP colours were observed: orange, brown, and green. According to [74], the orange colour could correspond to lepidocrocite, akaganeite, or goethite. The brown colour may be indicative of the presence of maghemite, ferrihydrite, or feroxyhyte. The green colour of CPs could correspond to green rust [74].
Figure 4 shows the maximum values of external crack widths observed in the T and F faces of RC prisms. As demonstrated in this figure, it can be observed that for a current density of 50 µA/cm2, when the prism was cracked on faces T and F, the crack widths on face T were smaller than those on face F. Conversely, for current densities of 100 and 200 µA/cm2, when both cracks propagated, the crack widths on face T were larger than those on face F. For current densities of 100 and 200 µA/cm2, when face T cracked, chloride ions penetrated the newly formed crack more rapidly, leading to accelerated CP accumulation and consequently larger crack width on face T compared to face F.
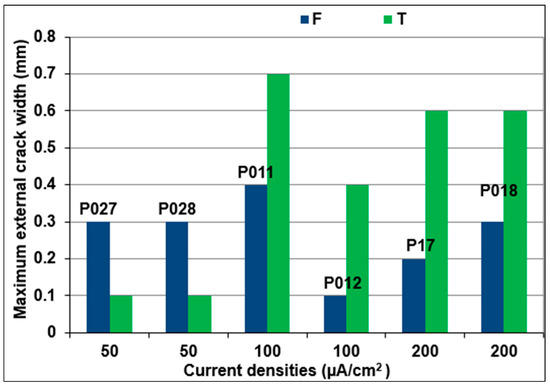
Figure 4.
Maximum width of external cracks on RC prisms using different impressed current densities: 50 µA/cm2, 100 µA/cm2, and 200 µA/cm2.
3.2. Numerical Results
3.2.1. Influence of Numerical Expansion Type on Induced-Crack Pattern
In this section, we detail how we aimed is to select the most pertinent numerical expansion type for the modelling of the present experiments. To this end, the numerical analysis was based on the various expansion types used in the literature and on our experimental observations, particularly those obtained with a current density of 100 µA/cm2. If a suitable numerical expansion type was to be considered in this numerical modelling, it would be imperative that the calculation would allow for a corrosion-induced cracking pattern that is consistent with experimental results.
The literature review first showed that the most common expansion types used in simulations are elliptical [38,46,47,48], semi-uniform, or Gaussian [51,52]. Moreover, the expansion types considered in numerical simulations had to be consistent with the location and thickness of CPs observed in SEM images at the steel–concrete interface. Consequently, two types of expansion were selected and one was defined in order to better represent CP expansion:
- Semi-uniform expansion: All points in the areas (Cj) where corrosion was observed experimentally underwent an identical displacement. This displacement was equal to the average thickness of CPs measured in these areas.
- Elliptical expansion: This expansion was based on the assumption that CPs expand in an elliptical way. The thickness of CPs was measured in four directions and applied to the model accordingly.
- Homothetic expansion: This was similar to semi-uniform expansion, yet a distinct expansion value was assigned to each corroded area (Cj). This value was the average thickness as determined by experimental measurements in the designated area.
In order to facilitate the understanding of the diverse expansion types (semi-uniform, elliptical, and homothetic) used in the modelling process, an example is presented in Table 4, based on the experimental CP distribution for a current density of 100 µA/cm2.

Table 4.
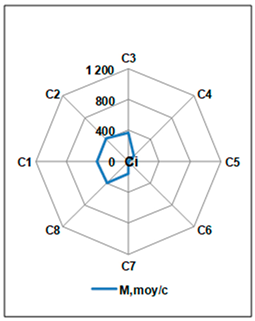
Correlation between experimental and modelled thickness and location of CPs. a/ Thickness (µm) and location of CPs (experimental results obtained with a current density of 100 µA/cm2 after 35 days of corrosion). b/ Example of SEM images of the steel/concrete interface showing the thickness of the corrosion product layer for a total charge equal to 168 A·h/m2, 100 µA/cm2 (P31-7d). The symbol M,moy/C represents the average of moy/C per area, calculated by considering the three samples E10, E13, and E16 presented in the graph. The symbol moy/C denotes the average of CP thickness per area for each sample.
In accordance with the expansion configurations outlined in Table 4, the associated numerical simulations were carried out. The numerical crack patterns obtained by calculation partially match the experimental crack pattern, regardless of the expansion type used in the simulation (see Table 5).

Table 5.
Experimental and simulated cracking induced by the expansion of CPs for a current density of 100 µA/cm2.
A potential explanation lies in the fact that the location of the CPs and the shape of the expansion of the CPs are not the two only parameters to be considered when calculating the crack pattern.
It is reasonable to hypothesise that the kinetics, the appearance, and the evolution of CPs play an important role in the results of simulations.
This discrepancy may be attributed to that the fact that the location of the corrosion product thickness does not systematically coincide with the location of the stresses that initiate cracking.
Although corrosion products were observed experimentally in multiple areas (covering C8, C1, C2, and C3 in Table 4), these corrosion products did not appear simultaneously on the large surface. As the kinetics of CP appearance is likely to play a role in the results of crack pattern calculations, the influence of CP distribution on crack patterns is studied numerically in the next section.
3.2.2. Influence of the Location of CP Expansion on the Crack Pattern
As previously highlighted, experimental observations revealed the presence of a layer of CPs at the steel–concrete interface over an area covering a substantial part of the rebar contour (Table 4). However, it is probable that each corrosion zone played a specific role in the concrete cracking mechanism.
To study this specific role, numerous numerical simulations were conducted assuming that corrosion had only developed in specific areas and not over the entire area covering C8 and C1–C4 (Table 4).
The numerical approach consisted of simulating semi-uniform expansions in areas C8, C1, C2, C3, and C4 in the following manner:
- Considering CP expansion in a single area (around only C3, for example).
- Considering CP expansion in two adjacent areas (around C2 and C3, for example).
- Considering CP expansion in three adjacent areas (around C1, C2, and C3, for example)
- Considering CP expansion in four adjacent areas (around C1, C2, C3, and C4, for example).
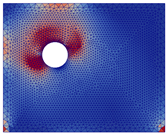
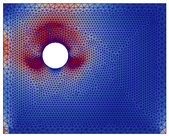
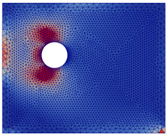
The semi-uniform expansion was selected for these simulations because it represented an unfavourable case in terms of degradation state (see Table 6 for details of the earliest cracking).

Table 6.
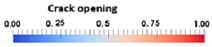
Evolution of crack patterns according to expansion type (crack opening corresponding to the trace of the crack opening displacement tensor).
As a preliminary approach, the proposed numerical analysis was carried out considering exclusively the experimental results obtained using a current density of 100 µA/cm2. For this current density, the areas C8, C1, C2, C3, and C4 exhibited the highest CP thicknesses and were thus selected for the analysis.
Certain scenarios considered in the calculation are presented in Table 7. The displacements were, respectively, imposed in areas C3, (C2; C3), (C1; C2; C3), (C1; C2; C3; C4), and (C8; C1) for the scenarios 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5, respectively.

Table 7.
Effect of the location of semi-uniform expansion on the crack pattern.
Based on the CP thicknesses experimentally observed, a displacement of 400 µm (value from Table 4) was applied, with the exception of scenario 4 where a displacement of 350 µm was employed due to the lower CP thickness exhibited in C4.
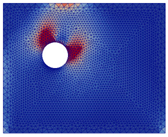
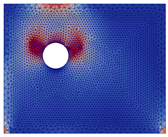
As illustrated in Table 7, which details pre-crack stress fields for each scenario, it can be concluded that locations of initial stress concentrations were highly dependent on the location zones of CPs (before cracking) and did not systematically appear in front of the corrosion expansion zones.
The crack patterns presented in Table 7 reveal the following:
- ■
- Crack patterns varied depending on the location of CP expansion. However, they did not systematically develop in front of the initial stress concentration zones or in front of CP expansion zones when there was expansion in a single area. The expansion of two or more areas led to the formation of cracks across both dials and at the shear points due to the expansion.
- ■
- A vertical or oblique crack was observed in the thickest concrete covers (50 or 75 mm) when expansion was applied to area C8 or C4.
3.2.3. Determination of the Crack-Driving Expansion: An Inverse Approach
As demonstrated in the preceding section, the cracking pattern depends on the location of the expansion of CPs. Numerous simulations were thus performed, exploring various expansion locations, with the objective of identifying the expansion scenario that reproduced a numerical crack pattern that was as close as possible to the experimental one.
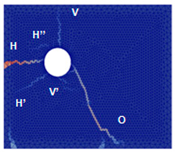
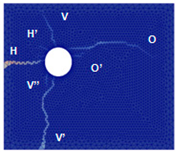
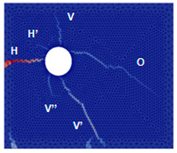
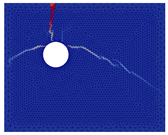
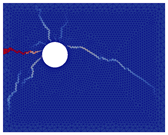
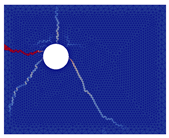
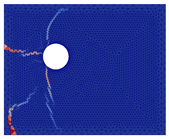
The numerical approach was applied to reproduce experimental results obtained for current densities of 50, 100, and 200 µA/cm2. Examples of the best results of simulations (in terms of cracking patterns) are presented in Figure 5, Figure 6 and Figure 7 where they are also compared with the experimental results.
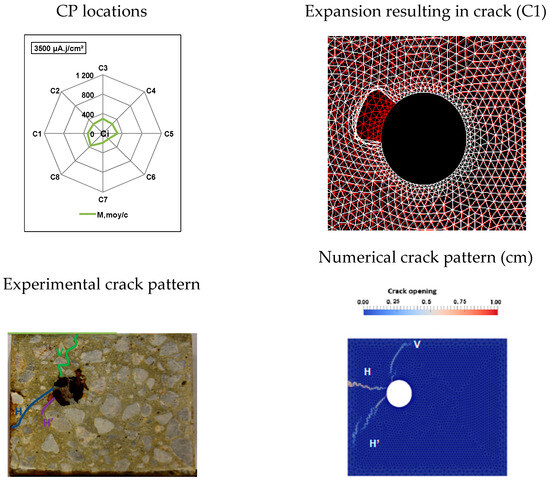
Figure 5.
Comparison of numerical and experimental cracking for a current density of 50 µA/cm2 with a duration of 70 days.
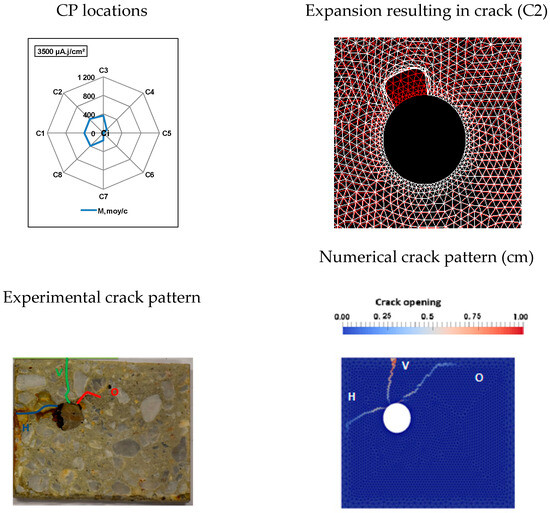
Figure 6.
Comparison of numerical and experimental cracking for a current density of 100 µA/cm2 with a duration of 35 days.
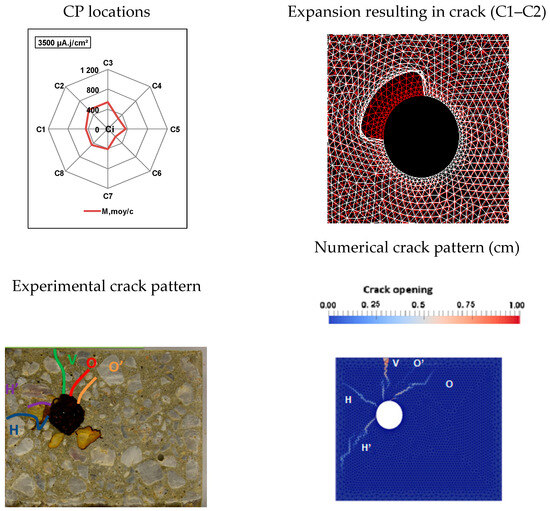
Figure 7.
Comparison of numerical and experimental cracking for a current density of 200 µA/cm2 with a duration of 17.5 days.
These results show that it is possible to obtain satisfactory agreement between the numerical and experimental results, particularly in specific locations of CP expansion. Furthermore, the results presented in Figure 5, Figure 6 and Figure 7 reveal that within our experimental framework (i.e., for corner RC specimens subjected to accelerated corrosion), the presence of CPs in areas C1 and/or C2 was the only scenario leading to crack patterns that corresponded to the experimental observations.
The experimental and numerical results of the present study show comparable levels of cracking to those in the numerical results obtained by Du [47] and Ozbolt [75] and are also in agreement with the experimental results of Fischer [76]. In Fischer’s study, there is an absence of SEM observations that could determine the thicknesses of CPs for comparison with the expansions applied by Du [47] and Ozbolt [75]. Therefore, it is not possible to provide an answer to the question of which the location of CPs lead to cracking based on their work.
The technique used in our work is similar to that of Zhao, as the numerically generated expansion is also based on the thicknesses of CPs observed experimentally. In the study of Zhao [46], cycles of humidification (with a NaCl solution) and drying were applied for 12 months on a RC specimen. The shape of the CP layer observed by SEM was elliptical. Crack widths varied between 0.05 and 0.9 mm. In her modelling [46], Zhao applied an elliptical expansion of the CPs based on her experimental data. The numerical crack pattern was found to overestimate the number of cracks when compared to the experimentally obtained crack pattern. The numerical crack pattern consisted of two horizontal cracks, one upward vertical crack, two downward vertical cracks, and two oblique cracks. It is noted that the numerical simulations carried out by Zhao showed two downward vertical cracks. The presence of these cracks is probably attributable to areas C5, C6, C7, and C8 which were exposed to CP expansion. With regard to the manifestation of crack patterns, the experimental and numerical results obtained in the present study in light of those obtained by Zhao [46] clearly show the necessity of consideration of the CP layers inducing cracking. This illustrates the reliability and rationality of the numerical approach that was implemented in the present study.
It is important to note that the prevailing discussion focuses mainly on qualitative aspects such as the similarity of crack patterns and the location of CPs. However, it may also be relevant to consider quantitative aspects. The subsequent section will address this issue.
3.2.4. Quantitative Study of Internal Cracks
In this section, the objective is to quantitively assess the correlation between experimental and numerical results. As illustrated in Figure 8, the internal crack orientations (O), widths (Wi), and lengths (L) and the external crack widths (We) were obtained experimentally and numerically for the three current densities of 50, 100, and 200 µA/cm2 for the same total charge. The experimental and numerical results show a good agreement with regard to crack orientation and width. However, the numerically predicted crack lengths are longer than those observed experimentally. The quantitative results presented herein corroborate the qualitative observations documented in the preceding sections.
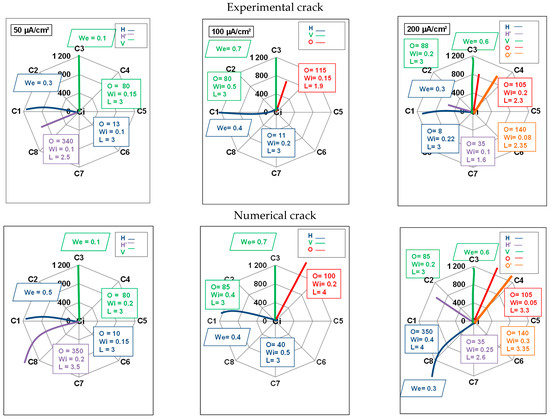
Figure 8.
Comparative analysis of experimental and numerical results regarding internal crack orientations (“O”) (degrees), widths (“Wi”) (cm), and lengths (“L”) (cm) and external crack widths (“We”) (cm) for the three current densities of 50, 100, and 200 µA/cm2.
3.2.5. Limitations of the Numerical Modelling
The experimental results provided data on the thickness of corrosion products at the steel/concrete interface; the orientation, the width, and the length of internal cracks; and the maximum width of external cracks. Due to the dispersion of the experimental results obtained, it proved difficult to interpret them in a comprehensive manner and to identify clear trends. Furthermore, during the process of corrosion-induced cracking of reinforced concrete, many phenomena occur and it is sometimes difficult to attribute them to one parameter rather than another.
Nevertheless, numerical modelling is a tool that can facilitate a detailed understanding of phenomena that are difficult to interpret experimentally. The modelling implemented had two primary objectives. The first one was to reproduce the experimental results of the experimental campaign with the primary goal of better understanding the effects of corrosion on reinforced concrete and the phenomena observed. The second one was to attempt to highlight the link that may have existed between internal (at the interface and in the surrounding concrete) and external degradations of the test specimen due to corrosion.
In order to determine the service life of a structure, it is necessary to establish a model capable of accounting for the initiation and propagation of corrosion. In our case, the mechanical approach adopted consisted of simplifying the model by not explicitly taking into account steel and corrosion products.
The authors elected to adopt a mechanical approach to attempt to highlight the mechanical degradations such as the crack patterns. It is evident that certain assumptions influenced the results such as the concrete heterogeneity and other pertinent parameters. However, this modelling approach appeared to be sufficient in view of the experimental tests (no external loading and therefore no need to explicitly take into account steel and corrosion products). This approach does not constitute an exhaustive modelling of the penetration of the chloride ions into the cracking process. This modelling is currently being improved by explicitly integrating steel and corrosion products, corrosion kinetics, and heterogeneity that are closer to reality.
4. Conclusions and Outlooks
This study successfully combined experimental and numerical approaches to investigate corrosion-induced cracking in RC specimens subjected to accelerated corrosion. Through meticulous experimental work, the internal degradation of RC specimens was characterised by measuring CP thicknesses at the steel–concrete interface, as well as the widths, lengths, and orientations of internal concrete cracks, alongside external concrete crack widths. The present study revealed that the formation of CPs is influenced by current density, with a significant increase observed from 50 µA/cm2 to 100 µA/cm2 and stabilisation at 200 µA/cm2, potentially due to CP diffusion through voids and cracks. Crucially, the distribution of CPs around the rebar was found to be non-uniform, with thicker layers in areas corresponding to thinner concrete covers and proximity to the counter-electrode. The internal crack patterns varied with current density, manifesting an increasing complexity and a number of cracks at higher current densities. Furthermore, external crack widths also exhibited a dependency on current density and face orientation, with larger crack widths observed on the T face at higher current densities. This phenomenon can be attributed to accelerated chloride ion penetration, its derived phenomena, and CP accumulation.
The numerical modelling employed Mazars’ damage model and utilised the rotating band method to account for concrete heterogeneity. This effectively simulated the expansion of CPs by imposing displacement at the steel–concrete interface based on experimental data. A key finding from our numerical simulations is the demonstration that the crack pattern is highly dependent on the location and thickness of the CPs. The inverse approach employed revealed that for the RC specimens studied, CP expansion specifically in areas C1 and/or C2 consistently led to numerical crack patterns that closely matched experimental observations across various current densities (50, 100, and 200 µA/cm2). However, numerical crack lengths exhibited a tendency to overestimate experimental values. The correlation between the experimental and numerical values of orientation and width of cracks was robust, providing quantitative validation of the qualitative observations.
The findings of this study hold significant practical implications for the assessment and maintenance of existing RC structures. Through the identification of the critical zones (C1 and C2 in the specimen geometry) where initial CP development primarily drives concrete cracking, this research provides a crucial basis for more targeted and efficient inspection strategies. Engineers are able to utilise this knowledge to focus their examination on particular areas of concrete structures, leading to the earlier detection of damage caused by corrosion and enabling timely interventions. Furthermore, the established correlation between CP distribution, internal cracking, and surface crack patterns offers a more robust framework for interpreting visual inspection results, potentially leading to improved durability prediction and maintenance planning for aged infrastructure. This combined experimental and numerical approach provides a cost-effective method for understanding complex corrosion processes, reducing the reliance on extensive and expensive experimental testing.
In order to further advance this field, several avenues for future research are recommended. Firstly, future modelling efforts should aim to explicitly incorporate CPs as a distinct third material with assigned mechanical properties, moving beyond merely accounting for their expansive effects. Secondly, it is crucial to consider the time-dependent phenomena of dissolution, diffusion, and precipitation of iron within the concrete and macrocracks. This will facilitate the more accurate study of their influence on crack initiation time and the evolution of cracking patterns over the service life of the structure.
A future direction that would be worthy of investigation would be to couple the proposed mechanical modelling with modelling of the transport mechanisms of aggressive agents, the depassivation of reinforcement (i.e., the transition from passive to active corrosion), and the underlying electrochemical reactions. This integrated approach would provide a holistic understanding of the corrosion process and its long-term impact on structural integrity.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, O.L. and L.A.; methodology, O.L., L.A., V.B. and M.Q.; software, O.L. and L.A.; validation, O.L., L.A., V.B. and M.Q.; formal analysis, O.L., L.A., V.B. and M.Q.; investigation, O.L., L.A., V.B. and M.Q.; data curation, O.L., L.A., V.B. and M.Q.; writing—original draft preparation, O.L.; writing—review and editing, L.A., V.B. and M.Q.; visualization, O.L., L.A.,. V.B. and M.Q.; supervision, L.A., V.B. and M.Q.; project administration, L.A. and V.B.; funding acquisition, L.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the Université Gustave Eiffel and Andra, the Frech National Agency for radioactive Waste Management (Xavier Bourbon and Laurent Trenty).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Some or all data, models, or code that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to express their gratitude to Thierry Chaussadent (Gustave Eiffel University), Frédéric Ragueneau (ENS Paris-Cachan), and Xavier Bourbon and Laurent Trenty (ANDRA) for their scientific discussions.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Zhang, H.; Liu, H.; Deng, Y.; Cao, Y.; He, Y.; Liu, Y.; Deng, Y. Fatigue behavior of high-strength steel wires considering coupled effect of multiple corrosion-pitting. Corros. Sci. 2025, 244, 112633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Liu, X.; Zhang, H.; Luo, Y.; Lu, N.; Liu, Y.; Xiao, X. Assessment of fatigue crack propagation and lifetime of double-sided U-rib welds considering welding residual stress relaxation. Ocean Eng. 2025, 332, 121400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, B.; Yu, Y.; Feng, Y.; Wu, D.; Zhao, G.; Liu, A.; Gao, W. Robust numerical solution for assessing corrosion of reinforced concrete structures under external power supply. Eng. Struct. 2023, 294, 116724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lliso-Ferrando, J.R.; Gasch, I.; Martínez-Ibernón, A.; Valcuende, M. Effect of macrocell currents on rebar corrosion in reinforced concrete structures exposed to a marine environment. Ocean Eng. 2022, 257, 111680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasser, H.; Vandewalle, L.; Verstrynge, E. Effect of pre-existing longitudinal and transverse corrosion cracks on the flexural behaviour of corroded RC beams. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 319, 126141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haefliger, S.; Kaufmann, W. Influence of cross section loss on the stress-strain characteristics of corroded quenched and self-tempered reinforcing bars. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 282, 122598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosso, M.M.; Asso, R.; Aloisio, A.; Di Benedetto, M.; Cucuzza, R.; Greco, R. Corrosion effects on the capacity and ductility of concrete half-joint bridges. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 360, 129555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daneshvar, K.; Moradi, M.J.; Ahmadi, K.; Hajiloo, H. Strengthening of corroded reinforced concrete slabs under multi-impact loading: Experimental results and numerical analysis. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 284, 122650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dackman, D.; Berrocal, C.G.; Rempling, R.; Fernandez, I. A framework for evaluating steel loss from the evolution of corrosion-induced deflections in reinforced concrete beams with non-uniform reinforcement corrosion. Eng. Struct. 2024, 317, 118593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, J.; Ortega, L.M.; Garcfa, A.M. Assessment of structural elements with corroded reinforcement. In Proceedings of the International Conference of Corrosion and Protection of Steel in Concrete, Sheffield, UK, 24–28 July 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Imam, A.; Mishra, S.; Bind, Y.K. Review study towards corrosion mechanism and its impact on the durability of concrete structures. AIMS Mater. Sci. 2018, 5, 276–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koulouris, K.; Charalampopoulos, A.; Apostolopoulos, C.A. Simulation of the degraded (steel—Concrete) bond strength due to corrosion via modeling pull out tests. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2024, 2692, 012002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Liu, B.; Tan, G.; Liu, H.; Jiao, Y.; Lv, D.; Wang, H.; Shi, D.; Zhang, S. Bond damage evolution and spatial micro-mechanism analysis of corroded reinforced concrete and failure mode assessment by acoustic emission. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2025, 37, 1086–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasser, H.; Van Steen, C.; Vandewalle, L.; Verstrynge, E. An experimental assessment of corrosion damage and bending capacity reduction of singly reinforced concrete beams subjected to accelerated corrosion. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 286, 122773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, M.; Guo, R.; Lin, Q.; Yu, Z. Prediction model for the bond behaviour of low-corrosion reinforced concrete considering corrosion time variability. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 444, 137891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zheng, J.; Ning, N.; Yan, L.; Zheng, C. Experimental study of bond performance of corroded reinforcement in concrete under various cooling methods. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 84, 108569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-B.; Zheng, S.-S.; Ji, J.-M.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, B. Bond performance of coupling corrosion of main reinforcement and stirrups in concrete under reversed cyclic loading. Structures 2025, 71, 107978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robuschi, S. Natural Corrosion in Reinforced Concrete Structures. Ph.D Thesis, Chalmers University of Technology, Göteborg, Sweden, 1930. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, B.; Wang, Y.; Gong, F.; Maekawa, K. Corrosion-Induced cracking pattern analysis of RC beam under sustained load considering the poromechanical characteristics of corrosion products. Buildings 2022, 12, 2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz Merino, B. Experimental and Numerical Study of Cracking of Concrete due to Reinforcement Corrosion. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidad Politécnica de Madrid, Madrid, Spain, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Bhargava, K.; Ghosh, A.K.; Mori, Y.; Ramanujam, S. Analytical model for time to cover cracking in RC structures due to rebar corrosion. Nucl. Eng. Des. 2006, 236, 1123–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- German, M.; Pamin, J. Numerical Simulation of Non-Uniformly Distributed Corrosion in Reinforced Concrete Cross-Section. Materials 2021, 14, 3975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.C.; Bui, Q.H.; Lambert, P. Experimental and numerical evaluation of the structural performance of corroded reinforced concrete beams under different corrosion schemes. Structures 2022, 45, 2318–2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuhaid, A.F.A.; Niaz, A. Carbonation and Corrosion Problems in Reinforced Concrete Structures. Buildings 2022, 12, 586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Haghani, R.; Blanksvärd, T.; Lundgren, K. Experimental study of FRP-strengthened concrete beams with corroded reinforcement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 301, 124076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Xu, J.; Sun, B.; Lin, L.; Wang, Y. Investigating non-uniform corrosion induced concrete cover cracking with a fracture-contact coupled computational method. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 415, 135105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Alami, E.; Fekak, F.-E.; Garibaldi, L.; Elkhalfi, A. A numerical study of pitting corrosion in reinforced concrete structures. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 43, 102789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, T.; Xiao, J.; Li, C.; Gan, Y.; Jiang, X. Experimental and numerical study on the chloride ions penetration in recycled aggregate concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 451, 138702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, F.J.; Alonso, C.; Andrade, C. Cover cracking as a function of rebar corrosion: Part 2 Numerical model. Mater. Struct. 1993, 26, 532–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, C.; Alonso, C.; Molina, F.J. Cover cracking as a function of bar corrosion: Part I-Experimental test. Mater. Struct. 1993, 26, 453–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, B.-T.; Nguyen, D.-D.; Tran, T.-T.; Tran, D.-N.; Nguyen, N.-L.; Bui, T.-T.; Nguyen, X.-L. Phase-field modeling for investigating the effect of rebar positioning and uniform versus non-uniform corrosion on concrete fracture. Fract. Struct. Integr. 2025, 19, 166–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikael, D. Etude du Comportement Mécanique des Structures en Béton Armé Dégradé par la Corrosion. Ph.D. Thesis, Univeristé de Lille 1, Villeneuve-d’Ascq, France, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Millard, A.; L’Hostis, V.; Beddiar, K.; Berthaud, Y.; Care, S. Modelling the Cracking of a Reinforced Concrete Structure Submitted to Corrosion; Rilem—DOCE: Barcelona, Spain, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- L’Hostis, V.; Foct, F.; Dillmann, P. Corrosion behaviour of reinforced concrete: Laboratory experiments and archaeological analogues for long-term predictive modelling. J. Nucl. Mater. 2008, 379, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, B.; Quiertant, M.; Bouteiller, V.; Adelaide, L.; Tailhan, J.L.; Cremona, C. Influence of accelerated corrosion on the reinforced cover concrete cracking behavior: Experimental and numerical study. Eur. J. Environ. Civ. Eng. 2012, 16, 450–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundgren, K. Initial Cross-Section Bond Between Corroded Reinforcement and Concrete; Chalmers: University of Technology: Göteborg, Sweden, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- François, R. A discussion on the order of magnitude of corrosion current density in reinforcements of concrete structures and its link with cross-section loss of reinforcement. Rilem Tech. Lett. 2021, 6, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, W.; Tang, Z.; Huang, Q. Experimental and numerical investigation of chloride-induced reinforcement corrosion and mortar cover cracking. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2020, 111, 103620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Zhang, C.; Li, Y. Simulation and analysis of rust expansion cracking of reinforced concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 426, 136199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Chen, Z.; Mehrmashhadi, J.; Bobaru, F. A stochastic multiscale peridynamic model for corrosion-induced fracture in reinforced concrete. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2020, 229, 106969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Meng, Z.; Liu, L.; Xu, L. An equivalent smeared layer method for simulating the non-uniform corrosion-induced damage of concrete. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2020, 224, 106791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Liu, M.; Zhang, R.; Du, X. Cracking of cover concrete due to non-uniform corrosion of corner rebar: A 3D meso-scale study. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 245, 118449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, C.; Zheng, Z.; Zhang, H.; Huang, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, G. 3D mesoscale investigation of non-uniform steel corrosion in reinforced concrete under chloride environments. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 411, 134273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Ren, Y.; Yu, Z.; Tang, F.; Xu, Y.; Xu, Y. Characteristics of the non-uniform corrosion of the steel bars extracted from the marine transportation infrastructures. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 87, 109108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, D.; Nakamura, H.; Yamamoto, Y.; Miura, T. Crack patterns of concrete with a single rebar subjected to non-uniform and localized corrosion. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 116, 366–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Karimi, A.R.; Wong, H.S.; Hu, B.; Buenfeld, N.R.; Jin, W. Comparison of uniform and non-uniform corrosion induced damage in reinforced concrete based on a Gaussian description of the corrosion layer. Corros. Sci. 2011, 53, 2803–2814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Jin, L.; Zhang, R. Modeling the cracking of cover concrete due to non-uniform corrosion of reinforcement. Corros. Sci. 2014, 89, 189–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, X.; Yang, S.; Li, C.Q. A non-uniform corrosion model and meso-scale fracture modelling of concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 2018, 108, 87–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Xu, K.; Yang, M.; Dong, Z.; Shao, J.; Fu, C.; Ni, W. Analysis of Circumferential and Longitudinal Non-Uniformity of Steel Corrosion in Concrete Subjected to Mechanical Load. Buildings 2024, 14, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Zou, W.; Bao, S.; Du, Q.; Song, R. Modeling concrete cracking induced by non-uniform rebar corrosion using experiments and mesoscale peridynamics. Comput. Part. Mech. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutrisno, W.; Suprobo, P.; Wahyuni, E.; Iranata, D. Investigation of Non-Uniform Rust Distribution and Its Effects on Corrosion Induced Cracking in Reinforced Concrete. In MATEC Web of Conferences; EDP Sciences: Les Ulis, France, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Ding, H.; Jin, W. Non-uniform distribution of a corrosion layer at a steel/concrete interface described by a Gaussian model. Corros. Sci. 2016, 112, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Ren, H.; Dai, H.; Jin, W. Composition and expansion coefficient of rust based on X-ray diffraction and thermal analysis. Corros. Sci. 2011, 53, 1646–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taheri-Shakib, J.; Al-Mayah, A. 4D evolutions of cracks, voids, and corrosion products in reinforced concrete materials. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 22455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Yang, J.; Su, X.; Peng, A.; Wang, L.; Huang, K. Crack propagation characterization of concrete under non-uniform corrosion of steel strand using digital image correlation. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 455, 139166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantazopoulou, B.S.J.; Papoulia, K.D. Modeling cover-cracking due to reinforcement corrosion in RC structures. J. Eng. Mech. 2001, 127, 342–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malumbela, G.; Alexander, M.; Moyo, P. Model for cover cracking of RC beams due to partial surface steel corrosion. Constr. Build. Mater. 2011, 25, 987–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loukil, O. Etude Expérimentale et Numérique de la Dégradation D’éléments Structurels en Béton Armé par Corrosion sous Courant Imposé’. Ph.D. Thesis, Science, Ingénierie et Environnement, Université Paris-Est, Créteil, France, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Loukil, O.; Adelaide, L.; Bouteiller, V.; Quiertant, M.; Ragueneau, F.; Chaussadent, T. Investigation of Corrosion Product Distribution and Induced Cracking Patterns in Reinforced Concrete Using Accelerated Corrosion Testing. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 11453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedrosa, F.; Andrade, C. Corrosion induced cracking: Effect of different corrosion rates on crack width evolution. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 133, 525–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malumbela, G.; Alexander, M.; Moyo, P. Interaction between corrosion crack width and steel loss in RC beams corroded under load. Cem. Concr. 2010, 40, 1419–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Steen, C.; Pahlavan, L.; Wevers, M.; Verstrynge, E. Localisation and characterisation of corrosion damage in reinforced concrete by means of acoustic emission and X-ray com-puted tomography. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 197, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caré, S.; Nguyen, Q.T.; Beddiar, K.; Berthaud, Y. Times to cracking in reinforced mortar beams subjected to accelerated corrosion tests. Mater. Struct./Mater. Constr. 2010, 43, 107–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Chen, J.; Luo, X. Effects of impressed current density on corrosion induced cracking of concrete cover. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 204, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loukil, O. Corrosion-Induced Degradation of Reinforced Concrete Elements: Preliminary Results. In 8th International Rilem Phd Workshop; Rilem, Ed.; Springer: Marne la vallée, France, 2019; pp. 129–140. [Google Scholar]
- Mazars, J. A description of micro and acroscale damage of concrete structures. Eng. Fract. Mech. 1986, 25, 729–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillerborg, A.; Modéer, M.; Petersson, P.-E. Analysis of crack formation and crack growth in concrete by means of fracture mechanics and finite elements. Cem. Concr. Res. 1976, 6, 773–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matallah, M.; La Borderie, C.; Maurel, O. A practical method to estimate crack openings in concrete structures. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Methods Geomech. 2010, 34, 1615–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laborderie, C.; Maurel, O.; Matalllah, M. Couplage endommagement fissuration: Applications aux calculs de structures en béton armé. In Proceedings of the 19 ème Congrès Français de Mécanique, Marseille, France, 24–28 August 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, G.; Ding, W.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Xing, F.; Dong, B. Identification of corrosion products and 3D distribution in reinforced concrete using X-ray micro computed tomography. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 207, 304–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanti, R. Effect of Impressed Current on the Microstructure of Corroded Steel-Concrete Interface; Imperial College London: London, UK, 2012; p. 13. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; Zhao, Y. Corrosion-induced cracking propagation of RC beams subjected to different corrosion methods and load levels. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 286, 122913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Yu, J.; Wu, Y.; Jin, W. Critical thickness of rust layer at inner and out surface cracking of concrete cover in reinforced concrete structures. Corros. Sci. 2012, 59, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornell, R.M.; Schwertmann, U. The Iron Oxides Structure, Properties, Reactions, Occurrence and Uses; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Ožbolt, J.; Oršanić, F.; Balabanić, G. Modeling pull-out resistance of corroded reinforcement in concrete: Coupled three-dimensional finite element model. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2014, 46, 41–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, C.; Leipzig, A. Auswirkungen der Bewehrungskorrosion auf den Verbund Zwischen Stahl und Beton. Ph.D. Thesis, Institut für Werkstoffe im Bauwesen der Universität Stuttgart, Stuttgart, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).