Abstract
Applying a constant electric field on a suspended film of liquid that carries an electric current, either by the transport of ions or surface charges, induces a rotation in the film. This system is known as “liquid film motor”. So far, the effect of permittivity of the liquid on its rotation has been ignored. We showed that the permittivity of the liquid can significantly affect the dynamics of rotation. Using an experimental approach, we studied the liquid film rotation for a broad range of pure liquids with diverse permittivities and surface tensions. We observed two different regimes of rotation depending on the permittivity of the liquids. We also found that there is no correlation between the surface tension of the liquid and the angular velocity of the rotation. We considered a theoretical framework and suggested scenarios to explain our experimental observations. These results help in better understanding the physics of liquid film motors and suggest opportunities for new flow manipulation techniques at small scales.
1. Introduction
Manipulation of flow at small scales has tremendous applications in microfluidics and two-dimensional-a-chip, chemical engineering, biology, and drug delivery [1,2,3,4,5]. A powerful method to control the flow at small scales can be achieved by applying electromagnetic fields. Therefore, fluid dynamics under applied electric/magnetic fields has been studied extensively [1,2,3,6,7,8,9,10,11]. In the seventeenth century, William Gilbert studied the first example of an electrohydrodynamic system by describing the formation of a conical shape on a sessile drop under a charged rod [12]. In the nineteenth century, Lord Rayleigh continued by studying drop dynamics under interfacial charge [13]. Fluid flow under applied electric fields was also studied by Melcher et al. [14,15]. Later, Taylor [16] and Saville [7] investigated electro-hydrodynamical instabilities. Electric fields have also been used to move, manipulate, and separate charged particles in a fluid, e.g., electro-phoresis [1,17]. They have been utilized for electro-wetting and dielectro-phoretic trapping [2,3,18]. Ramos et al. [19] have extensively studied electric field interactions with nano/micro particles immersed in a fluid. Interactions of electric fields and fluids have many applications in the field of biotechnology, e.g., investigating and controlling the fluid flow around a cell or delivery of molecules close to living cells.
A suspended liquid film under applied electric fields has also been studied by many scientists. Shirsavar et al. showed that a soap film under a non-uniform alternating electric field experiences rotation [20]. Faetti et al. [21,22,23] reported the formation of vortices by electric currents in a film of suspended liquid crystal. Morris et al. [24,25] suggested that the charges accumulated on the surface of the films can result in the formation of vertices in liquid crystal suspended films. Amjadi et al. [26,27,28] showed that applying an electric field perpendicular to a soap film and an electric current through the film produces rotation. They provided a method for controlling the direction and magnitude of the fluid rotation in the film. Such a phenomenon has been studied theoretically [29,30,31], and recently, Feiz et al. explained the rotation mechanism in a soap film based on a thin film electro-convection model [32]. The controllable rotation of liquids under electric fields has also been reported for polar liquid films [26,27], MBBA liquid crystal films [28], and even fluid bulks with free surfaces [10].
Previous research on liquid film motors was mostly limited to water and water solutions with very high permittivity [26,27,31]. Permittivity represents the tendency of the molecular charges to distort in the presence of an electric field. It is a constant of proportionality that connects the electric field to the electric displacement in a material. Therefore, it is expected that permittivity should affect the dynamics of induced movement by external electric fields in a liquid. Surprisingly, so far it is assumed that the fluid rotation in a liquid film motor is only controlled by the conductivity of the liquid and the strength of external electric fields and currents. Therefore, the effect of the permittivity of the liquid on the rotation profile has been completely neglected in all previous studies.
In this paper, we investigate the electrically driven rotation in thin suspended films of different pure liquids with a wide range of permittivities and surface tensions. Our experimental results for the first time indicate that permittivity has a strong effect on the distribution of rotational speeds in the liquid film. We observe a significant difference between the rotation profile of liquids with relative permittivities less than 5 as compared to liquids with permittivities higher than 5. Our results could be beneficial for developing new flow manipulation techniques at a small scale with possible applications in lab-on-a-chip devices and bio-fluidics.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
We have used a wide range of pure liquid purchased from Merck Inc. (Kenilworth, NJ, USA). These liquids are listed in Table 1 and Table 2 based on their permittivity. The permittivity is often shown by a non-dimensional parameter known as relative permittivity, which is the ratio of the absolute permittivity of the material by the permittivity of the vacuum. The liquids with permittivities lower than 5 times of the permittivity of vacuum are listed in Table 1 while the liquids with the relative permittivities between 5 to 81 are listed in Table 2. In this work we use relative permittivity as a parameter we change in our experiments. Surface tension and viscosity of most of the used liquids are also listed in the above mentioned tables [27,33,34,35,36,37,38]. All liquids had a purity above and were used without any additive or solvents.

Table 1.
Relative permittivity (), surface tension (), viscosity (), and density () of liquids used in our experiments with low relative permittivity. The relative permittivity is the ratio of liquid permittivity and permittivity of vacuum and is a dimensionless number. These properties are valid at temperatures of about 25 degrees Celsius. The data are gathered from different material handbooks and scientific papers [27,33,34,35,36,37,38].

Table 2.
Relative permittivity (), surface tension (), viscosity (), and density () of liquids used in our experiments with relative permittivity between 5 to 81. These properties are valid at temperatures of about 25 degrees Celsius. The data are gathered from different material handbooks and scientific papers [27,33,34,35,36,37,38].
2.2. Experimental Setup
We used the same experimental setup as suggested by Amjadi et al. for producing controllable rotation in a freely suspended liquid film [26,27]. A schematic of the experimental setup is shown in Figure 1a. The liquid film rotates when an electric current passes through the liquid film and, simultaneously, an external electric field is applied in the direction perpendicular to the current. For producing the liquid film, an electrically insulating frame is used (Figure 1). We used an insulating frame made of phenolic resin with a relative permittivity of 8. By drawing a wet pad containing the liquid over the frame, a freely suspended liquid film is produced on the frame aperture. Two thin electrodes are coated on the frame on opposite sides of the aperture to conduct the current, and the fluid film is in direct contact with the electrodes. By applying an electric voltage between the electrodes, a very small electric current of about 1 A is established in the film [27]. The frame is located between the two plates of a large capacitor in order to apply an external electric field (), initially parallel to the plane of the film and perpendicular to the electric current passing through the liquid film. When the external electric field is applied to the liquid film carrying the electric current, the film will rotate in the direction of . The experiments are performed at room temperature of 25 degrees Celsius.
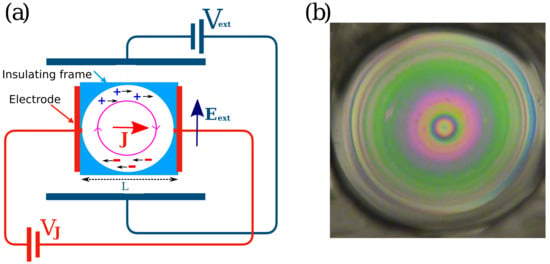
Figure 1.
(a) Schematic of experimental setup. Induced charges, body force exerted on the fluid, and direction of rotation are shown schematically. (b) Typical example of a rotating liquid film under applied electric field and potential difference . The film rotates in a direction given by the cross-product , where J is the overall direction of electronic current in the film. The liquid film is horizontal.
Figure 1b shows an example of a rotating liquid film. The rotation direction was observed to be independent of the aperture shape. The experiments showed that by inverting the direction of either or J, the rotation direction was reversed, and alternating the external electric field caused film vibration instead of rotation. In our experiment, we apply an electric voltage to induce current J in the liquid film. We control and measure and in our experiments.
2.3. Data Acquisition
Color images of rotating films under study were captured using a high-speed CCD camera. For each measurement, a set of consecutive images with the exposure time of 30 ms was generated, where the time separation between each frame was 40 ms. Due to the spatial gradient of film thickness, the recorded images of rotating films involved a strong color pattern reflecting the film thickness variation. This pattern eliminated the need for using tracer particles as visualizers for extracting the velocity field.
2.4. Particle-Image Velocimetry
Particle-Image Velocimetry (PIV) is a well-established analysis technique in fluid mechanics that can extract the fluid flow velocity field at many points simultaneously. The input analysis usually includes two successive images of visualized fluid flow, with a short enough time separation. This double frame is then divided into local small regions, and the pixel values of each corresponding region in the double frame, are correlated to each other, resulting in a displacement vector representing those regions. Repeating this on all of the local regions yields the displacement field. When the flow of interest is in a (quasi-)steady state, as in the case of this work, one can take advantage of the contribution of many double frames in order to effectively increase the velocity field estimation accuracy. In correlation-based PIV analysis, this method is better and known as ensemble correlation [39]. We have used this technique to determine the velocity field in our rotating films. Two examples of such PIV analysis for high and low relative permittivity liquids are shown in Figure 2.
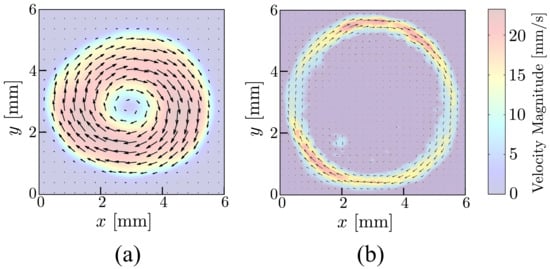
Figure 2.
(a) Results of PIV analysis for a water film with relative permittivity of 81, rotating under kV/cm and V. The rotational flow has its maximum somewhere in between the center and the edges. (b) PIV analysis of a liquid film with low relative permittivity. A film of nonyl chloride with relative permittivity 4.1 is rotating under kV/cm and V. The rotation is localized near the edges.
3. Experimental Results
Our experiments on liquids with a very broad range of permittivities from about 2 times the permittivity of vacuum to about 81 times the permittivity of vacuum (for pure water) show that the direction of rotation in the film for all fluids films independent of their permittivity will be determined by . However, liquids with very low relative permittivity (approximately between 2 and 4) show a very different flow profile with respect to the rest of the fluids and previously investigated liquid film motors. Liquids with relative permittivity of more than 5 (Table 2), produce the well known liquid film motor rotation profile (Figure 2a). Here, the angular velocity increases from about zero in the center to a maximum in the middle and then it decreases and goes to zero at the solid boundary due to no-slip flow condition. In this range of permittivities, the rotation velocity increases by increasing the electric current and field, as also observed previously in the case of water film motor [26,27].
Figure 3a shows the maximum values of angular velocity of the rotating 1-Nonanol film versus in constant external electric field of kV/cm for different values of . According to this graph, the angular velocity increases linearly by increasing . Another linear increment is also observed in the graph of angular velocity versus . Figure 3b shows the maximum value of the angular velocity of n-Butanol film rotation versus , while a constant of 20 V drives the current passing through the film. Interestingly, for liquids with electrical permittivity less than 5 (Table 1), the flow profile is completely different (Figure 2b). For these systems, the velocity field is almost zero everywhere except for a thin liquid layer close to the boundary where the rotation is localized. Another interesting observation for this range of permittivities is that the order of magnitude of rotations is smaller compared to other liquids at the same external field and current. However, we should consider that the order of magnitude of the angular velocity depends also on the viscosity of the liquids besides external fields. We believe that viscosity and permittivity of the liquid affect the angular velocity of the rotating film and hence, in Figure 4a, the angular velocity is plotted for different fluids, having different values of permittivity per viscosity, in a constant electric field of kV/cm and applied voltage of V. As shown in the figure, an increasing power-law behavior is observed for angular velocity versus permittivity over viscosity with an exponent around . In Figure 4b, the maximum angular velocity is plotted as a function of surface tension for different liquids. The experiments are performed at V and an external electric field of kV/cm. The data do not show a systematic correlation between the angular velocity and surface tension of the liquids.
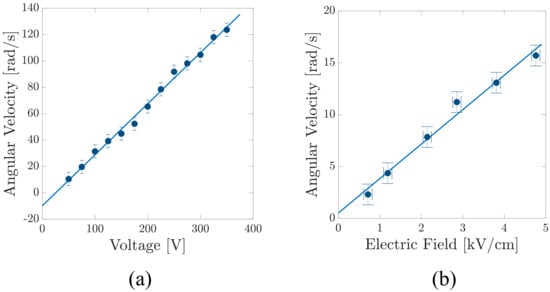
Figure 3.
(a) The maximum value of the angular velocity of 1-Nonanol isomer film versus in constant external electric field . (b) The maximum value of the angular velocity of n-Butanol film rotation versus in constant . By changing , the angular velocity changes linearly. The Reynolds number of these experiments varies between 0.2 and 0.01 considering the average thickness of the film (about 10 micrometers) as the relevant length scale of the system.
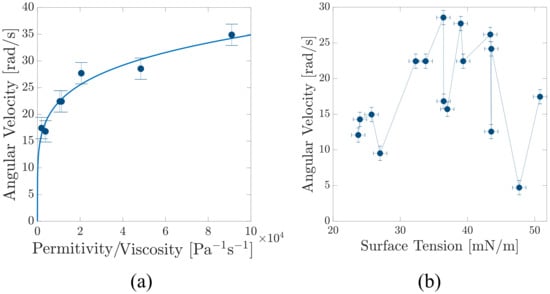
Figure 4.
(a) Angular velocity versus relative permittivity per viscosity of different liquid films rotation under constant and . Angular velocity changes with the relative permittivity per viscosity in a power-law manner with an exponent of . (b) Angular velocity as a function of surface tension for different liquids. The experiments are performed at V in a constant external electric field of kV/cm.
4. Theoretical Discussion
To get insight into the physical mechanism responsible for liquid film rotation, one needs to consider the coupled electro-hydrodynamic equations [25,40]. An effective two-dimensional picture of the liquid film immersed in ambient air can help us to model the system [31,32]. Denoting by , P, and , the velocity, pressure, and electric potential, the equations read as:
where density and viscosity of the liquid are denoted by and , respectively. Here, shows the in-plane component of gradient operator, and is the electric potential on the liquid film. In this effective two-dimensional description, stands for the thickness of the film. Surface charge density is related to the discontinuity of normal derivative of potential through relation . In this approximate two-dimensional model, the electric permittivity of liquid does not appear in the equations, and it is the air permittivity (roughly proportional to ) that enters into the equations. Furthermore, contribution to the force from electronic current J is neglected. The flow is subjected to a no-slip boundary condition where the velocity vanishes on the frame. Furthermore, electric potential is limited to the applied voltages on the electrodes (), and at large distances it asymptotically reaches to . Surface tension of the film is assumed to compensate the effects of gravity for a horizontal film. This is consistent with our experimental result (Figure 4b), where no systematic dependence to the surface tension is observed in the present geometry, i.e., the rotational flow.
As reflected from the above dynamical equations, the velocity profile is related to electric potential in a nonlinear way, and the potential is also maintained by and . As a result of this qualitative observation, we expect to see a steady state flow profile that depends on both applied fields.
The charge induction mechanism is a physical scenario that can capture the underlying physics behind the rotation in liquid-film motor [41]. It is shown that both external and internal electric fields, denoted by and , can approximately superimpose to result in the overall rotation of the liquid film (L is the lateral size of the film). Based on such a linearized description, the main effect of the external field is to separate the electric charges on the film. Referring to the geometry shown in Figure 1a and for , positive (negative) surface charges are mainly accumulated near the upper (lower) boundaries of the frame.
Furthermore, the in-plane component of the electric field near the liquid is mainly resulted from the voltage difference applied to the electrodes. As a naive approximation, we can set the strength of this field by , and its direction for is pointed from left to right in the figure. Electric force due to this in-plane field exerted on the surface charges will cause the fluid to move. This body force (force per unit volume of the fluid) scales as . Such electric effects enforce the fluid particles that are located near the upper (lower) boundary of the film to move toward right (left) direction. The position of induced charges and the body force they exert on the liquid are shown schematically in Figure 1a. Flow induced by this electric force when scattered from no-slip boundaries of the frame will result in a steady state rotational pattern.
Based on this scenario, the emerged rotational flow has its maximum value somewhere in between center and boundary of the frame. Electric force tends to push the fluid, but viscose forces near the boundaries, enforcing the flow to satisfy the no-slip boundary condition. Competition between the electric body force from one hand and the damping viscous force near the boundary from the other hand will eventually determine the location of maximum velocity.
In the above two-dimensional picture, physical properties of the liquid, such as its permittivity and thickness, do not contribute to the flow profile. A simple qualitative argument can help us to understand the role of permittivity. We note that a finite size dielectric body that is immersed in vacuum, depending on its relative permittivity, can either enhance or diminish the ambient electric field. For a simple spherical dielectric body with permittivity immersed in vacuum, the electric influence is proportional to . In the liquid-film experiment, the liquid with permittivity is immersed in air, and it is bounded by a dielectric frame. It is completely reasonable to imagine that in addition to , permittivities of liquid and frame play a role in the established rotational flow. Very near to the boundary, the electric influence of the frame on the electric field inside the liquid is roughly proportional to . This means that for , a high permittivity regime, electric effects inside the fluid and correspondingly induced charges near the boundary will be diminished. This will result in a shift in the place of maximum velocity toward the center of film. At low permittivity regimes where , the situation is different. Polarizibility of the frame will enhance the electric induced charges near the frame and eventually shift the liquid flow toward the boundaries. This transition from low to high permittivity behavior in the flow profile is observed in our experimental results.
It should be noted that as the real system is nonlinear in both electric and fluid parts, the above-mentioned scenario can be considered as an initial physical clue. In a more realistic description, it is completely reasonable to think that both the permittivities of frame and air contribute to the critical permittivity that separate low and high permittivity behaviors. Full understanding of the phenomenon requires a complete three-dimensional theoretical description that takes into account all characteristics of the liquid.
5. Conclusions
We found that despite the fact that the effect of permittivity was ignored in previous research on liquid film motors, it can play an important role in the rotation profile. In our study, we systematically changed the permittivity of the liquids in a very broad range, and we observe for the first time that the permittivity can dramatically influence the dynamics when it is below a threshold. Although the liquid permittivity does not affect the direction of rotation, a small change in the relative permittivity of the liquid film from about 4 to 5 will significantly change the rotation profile of the liquid film. For relative permittivities between 5 to 81, as observed in previous studies, the maximum speed in the profile occurs in the middle, between the center of the film and the solid boundary. However, when the relative permittivity of the liquid is below 5, the velocity profile changes dramatically and the velocities are localized in a thin liquid layer very close to the solid boundary, while in the middle of the film the liquid is at rest. In addition, we suggested a theoretical model that may explain this important experimental observation. This hypothesis raises new questions and needs further theoretical and experimental investigations to be able to fully address this phenomenon. We believe our results and observation have a strong potential for developing novel electro-capillary flow manipulation strategies at small scales.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.S., A.N. and M.H.; data acquisition and data analysis, R.S., M.M.R., S.M. and A.A.; methodology, R.S. and A.A.; visualization, A.-R.M.; theoretical discussion, A.N.; writing—original draft, M.H.; writing—review and editing, A.-R.M., A.N. and M.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The dataset is available upon request.
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge H. Stone for his generous support, fruitful discussions, and constructive comments. R.S. thanks A. Nejati, R. Rasuli, and M. Vahedi for their help.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Squires, T.M.; Quake, S.R. Microfluidics: Fluid physics at the nanoliter scale. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2005, 77, 977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pamme, N. Magnetism and microfluidics. Lab Chip 2006, 6, 24–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javadi, A.; Habibi, M.; Taheri, F.S.; Moulinet, S.; Bonn, D. Effect of wetting on capillary pumping in microchannels. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibi, M.; Hosseini, S.; Khatami, M.; Ribe, N. Liquid supercoiling. Phys. Fluids 2014, 26, 024101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, B.; Habibi, M.; Ognier, S.; Schelcher, G.; Mostafavi-Amjad, J.; Khalesifard, H.; Tatoulian, M.; Bonn, D. Silver nanocluster catalytic microreactors for water purification. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 2016, 225, 707–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atten, P. Electrohydrodynamic instability and motion induced by injected space charge in insulating liquids. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 1996, 3, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saville, D. Electrohydrodynamics: The Taylor-Melcher leaky dielectric model. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 1997, 29, 27–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Kang, I. Three-dimensional analysis of the steady-state shape and small-amplitude oscillation of a bubble in uniform and non-uniform electric fields. J. Fluid Mech. 1999, 384, 59–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirsavar, R.; Nasiri, M.; Amjadi, A.; Nejati, A.; Sobhani, S.; Habibi, M. Rotation induced by uniform and non-uniform magnetic fields in a conducting fluid carrying an electric current. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 112641–112645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saghaei, T.; Moradi, A.R.; Shirsavar, R.; Habibi, M. Liquid bulk rotation induced by electric field at free surface. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2015, 106, 053506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinzadeh, M.; Hajizadeh, F.; Habibi, M.; Milani Moghaddam, H.; Reihani, S.S.N. Optimized rotation of an optically trapped particle for micro mixing. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2018, 113, 223701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, G.I. Electrically driven jets. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Math. Phys. Sci. 1969, 313, 453–475. [Google Scholar]
- Frs, L. On the equilibrium of liquid conducting masses charged with electricity, Lond. Edinb. Dublin Philos. Mag. J. Sci. 1882, 14, 87. [Google Scholar]
- Melcher, J.R. Electrohydrodynamic and magnetohydrodynamic surface waves and instabilities. Phys. Fluids 1961, 4, 1348–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melcher, J.R.; Smith, C.V. Electrohydrodynamic charge relaxation and interfacial perpendicular-field instability. Phys. Fluids 1969, 12, 778–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, G.I. Studies in electrohydrodynamics. I. The circulation produced in a drop by an electric field. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Math. Phys. Sci. 1966, 291, 159–166. [Google Scholar]
- Schoch, R.B.; Han, J.; Renaud, P. Transport phenomena in nanofluidics. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2008, 80, 839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilkner, T.; Janasek, D.; Manz, A. Micro total analysis systems. Recent developments. Anal. Chem. 2004, 76, 3373–3386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos, A.; Morgan, H.; Green, N.G.; Castellanos, A. Ac electrokinetics: A review of forces in microelectrode structures. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 1998, 31, 2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirsavar, R.; Ramos, A.; Amjadi, A.; Taherinia, J.; Mashhadi, M.; Nejati, A. Induced soap-film flow by non-uniform alternating electric field. J. Electrost. 2015, 73, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faetti, S.; Fronzoni, L.; Rolla, P. Static and dynamic behavior of the vortex–electrohydrodynamic instability in freely suspended layers of nematic liquid crystals. J. Chem. Phys. 1983, 79, 5054–5062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faetti, S.; Fronzoni, L.; Rolla, P. Electrohydrodynamic domain patterns in freely suspended layers of nematic liquid crystals with negative dielectric anisotropy. J. Chem. Phys. 1983, 79, 1427–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faetti, S.; Fronzoni, L.; Rolla, P. Electrohydrodynamic flow in nematic thin films with two free surfaces. J. Phys. Colloq. 1979, 40, C3-497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, S.W.; de Bruyn, J.R.; May, A. Electroconvection and pattern formation in a suspended smectic film. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1990, 65, 2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daya, Z.A.; Morris, S.W.; De Bruyn, J.R. Electroconvection in a suspended fluid film: A linear stability analysis. Phys. Rev. E 1997, 55, 2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amjadi, A.; Shirsavar, R.; Radja, N.H.; Ejtehadi, M. A liquid film motor. Microfluid. Nanofluidics 2009, 6, 711–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirsavar, R.; Amjadi, A.; Tonddast-Navaei, A.; Ejtehadi, M. Electrically rotating suspended films of polar liquids. Exp. Fluids 2011, 50, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirsavar, R.; Amjadi, A.; Ejtehadi, M.; Mozaffari, M.; Feiz, M. Rotational regimes of freely suspended liquid crystal films under electric current in presence of an external electric field. Microfluid. Nanofluidics 2012, 13, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.Q.; Zhang, G.C.; Li, Y.J.; Jiang, S.R. Water film motor driven by alternating electric fields: Its dynamical characteristics. Phys. Rev. E 2012, 85, 036314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.Q.; Li, Y.J.; Gan, K.Y.; Jiang, S.R.; Zhang, G.C. Water film washers and mixers: Their rotational modes and electro-hydrodynamical flows induced by square-wave electric fields. Microfluid. Nanofluidics 2013, 14, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasiri, M.; Shirsavar, R.; Saghaei, T.; Ramos, A. Simulation of liquid film motor: A charge induction mechanism. Microfluid. Nanofluidics 2015, 19, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feiz, M.; Namin, R.; Amjadi, A. Theory of the liquid film motor. Phys. Rev. E 2015, 92, 033002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smallwood, I. Handbook of Organic Solvent Properties; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Wohlfarth, C.; Wohlfarth, B. Pure Liquids: Data: Datasheet from Landolt-Börnstein—Group IV Physical Chemistry: Volume 16: “Surface Tension of Pure Liquids and Binary Liquid Mixtures” in SpringerMaterials; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziadan, K.M.; Hussein, H.F.; Ajeel, K. Study of the electrical characteristics of poly (o-toluidine) and application in solar cell. Energy Procedia 2012, 18, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolotnikov, M.F.; Bolotnikova, S.S. Kinematic viscosity of 1-iodohexane, 1-iodoheptane, and 1-chlorononane at temperatures from (293.15 to 423.15) K. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2006, 51, 1740–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wohlfarth, C. Static Dielectric Constants of Pure Liquids and Binary Liquid Mixtures: Supplement to IV/6; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; Volume 17. [Google Scholar]
- Robert, C.W.; Astle, M.J.; William, H.B.; Lide, D.R. Crc Handbook of Chemistry and Physics a Ready Reference Book of Chemical and Physical Data; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Gui, L.; Merzkirch, W. A comparative study of the MQD method and several correlation-based PIV evaluation algorithms. Exp. Fluids 2000, 28, 36–44. [Google Scholar]
- Daya, Z.A.; Deyirmenjian, V.; Morris, S.W. Electrically driven convection in a thin annular film undergoing circular Couette flow. Phys. Fluids 1999, 11, 3613–3628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Najafi, A.; Shirsavar, R. Liquid-film Motor: Physical Mechanism. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).