Artificial Reef Deployment Reduces Diving Pressure from Natural Reefs—The Case of Introductory Dives in Eilat, Red Sea
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
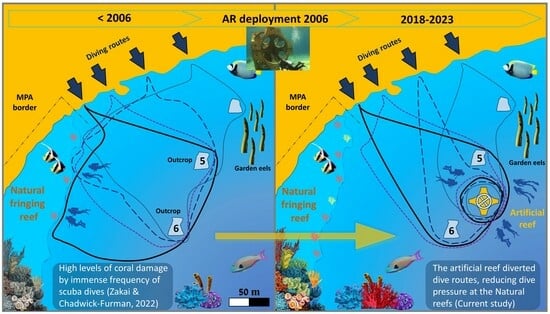
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Artificial Reef Design
2.3. Data Collection
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Future Directions and Open Questions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gladstone, W.; Curley, B.; Shokri, M.R. Environmental impacts of tourism in the Gulf and the Red Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 72, 375–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerutti-Pereyra, F.; López-Ercilla, I.; Sánchez-Rivera, G.; Francisco, V.; Arvizu-Torres, X.; Adame-Sánchez, T. Impact of SCUBA divers on the coral reefs of a national park in the Mexican Caribbean. J. Ecotour. 2022, 21, 71–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, K.; Nanajkar, M.; Mote, S.; Ingole, B. Coral damage by recreational diving activities in a Marine Protected Area of India: Unaccountability leading to ‘tragedy of the not so commons’. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 155, 111190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B. Close encounters of the worst kind: Reforms needed to curb coral reef damage by recreational divers. Coral Reefs 2021, 40, 1429–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumanapala, D.; Dimmock, K.; Wolf, I.D. A review of ecological impacts from recreational SCUBA diving: Current evidence and future practice. Tour. Hosp. Res. 2023, 23, 564–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakai, D.; Chadwick-Furman, N.E. Impacts of intensive recreational diving on reef corals at Eilat, northern Red Sea. Biol. Conserv. 2002, 105, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uyarra, M.C.; Côté, I.M. The quest for cryptic creatures: Impacts of species-focused recreational diving on corals. Biol. Conserv. 2007, 136, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasler, H.; Ott, J.A. Diving down the reefs? Intensive diving tourism threatens the reef of the northern Red Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2008, 26, 1788–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luna, B.; Pérez, C.V.; Sánchez-Lizaso, J.L. Benthic impacts of recreational divers in a Mediterranean Marine Protected Area. J. Mar. Sci. 2009, 66, 517–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giglio, V.J.; Luiz, O.J.; Ferreira, C.E. Ecological impacts and management strategies for recreational diving: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 256, 109949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouphael, A.B.; Inglis, G.J. Impacts of recreational SCUBA diving at sites with different reef topographies. Biol. Conserv. 1997, 82, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, G.P.; McCormick, M.I.; Srinivasan, M.; Eagle, J.V. Coral decline threatens fish biodiversity in marine reserves. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 8253–8257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, D.; Tisdell, C. Recreational scuba-diving and carrying capacity in marine protected areas. Ocean. Coast. Manag. 1995, 26, 19–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skulpichetrat, J. Thailand Closes Dive Sites to Halt Damage to Reefs. Reuters 2011. Available online: https://www.reuters.com/article/uk-thailand-reefs-idUSLNE70J02220110120 (accessed on 11 December 2023).
- Grace, J. Thailand Closes Dive Sites over Coral Bleaching Crisis. The Guardian 2016. Available online: https://www.theguardian.com/environment/2016/may/26/thailand-closes-dive-sites-over-coral-bleaching-crisis (accessed on 11 December 2023).
- Roche, R.C.; Harvey, C.V.; Harvey, J.J.; Kavanagh, A.P.; McDonald, M.; Stein-Rostaing, V.R.; Turner, J.R. Recreational diving impacts on coral reefs and the adoption of environmentally responsible practices within the SCUBA diving industry. Environ. Manag. 2016, 58, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trujillo, J.C.; Navas, E.J.; Vargas, D.M. Valuing coral reef preservation in a Caribbean marine protected area. Economic impact of scuba diving in corals of Rosario and San Bernardo national natural park, Colombia. Cuad. Desarro. Rural. 2017, 14, 38–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tynyakov, J.; Rousseau, M.; Chen, M.; Figus, O.; Belhassen, Y.; Shashar, N. Artificial reefs as a means of spreading diving pressure in a coral reef environment. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2017, 149, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, N.T.; Cong, L.; Wall, G. China’s scuba divers’ marine-based environmental behaviors. J. Sustain. Tour. 2020, 29, 616–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcos-Aguilar, R.; Favoretto, F.; Kumagai, J.A.; Jiménez-Esquivel, V.; Martínez-Cruz, A.L.; Aburto-Oropeza, O. Diving tourism in Mexico–Economic and conservation importance. Mar. Policy 2021, 126, 104410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calò, A.; Pereñiguez, J.M.; Hernandez-Andreu, R.; García-Charton, J.A. Quotas regulation is necessary but not sufficient to mitigate the impact of SCUBA diving in a highly visited marine protected area. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 302, 113997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bideci, C.; Cater, C. In Search of Underwater Atmosphere: A New Diving World on Artificial Reefs. In Atmospheric Turn in Culture and Tourism: Place, Design and Process Impacts on Customer Behaviour, Marketing and Branding; Volgger, M., Pfister, D., Eds.; Emerald Publishing Limited: Leeds, UK, 2019; pp. 245–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leeworthy, V.R.; Maher, T.; Stone, E.A. Can Artificial Reefs alter user pressure on adjacent natural reefs? Bull. Mar. Sci. 2006, 78, 29–37. [Google Scholar]
- Shani, A.; Polak, O.; Shashar, N. Artificial reefs and mass marine ecotourism. Tour. Geogr. 2012, 14, 361–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkbride-Smith, A.E.; Wheeler, P.M.; Johnson, M.L. The relationship between diver experience levels and perceptions of attractiveness of artificial reefs—Examination of a potential management tool. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e68899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belhassen, Y.; Rousseau, M.; Tynyakov, J.; Shashar, N. Evaluating the attractiveness and effectiveness of artificial coral reefs as a recreational ecosystem service. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 203, 448–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Özgül, A.; Lök, A. Artificial Reef Applications for Diving Tourism: Artificial Wreck Reefs in Turkey. In Impact of Artificial Reefs on the Environment and Communities; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2022; pp. 151–168. [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira, M.T.; Ramos, J.; Santos, M.N. An approach to the economic value of diving sites: Artificial versus natural reefs off Sal Island, Cape Verde. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2015, 31, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firth, L.B.; Farnworth, M.; Fraser, K.P.; McQuatters-Gollop, A. Make a difference: Choose artificial reefs over natural reefs to compensate for the environmental impacts of dive tourism. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 901, 165488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sensurat-Genc, T.; Shashar, N.; Ozsueer, M.; Ozguel, A. Shipwrecks are not the ultimate attracting features in a natural marine environment-the case of Karaburun, Turkey. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 315, 115159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, C.O.; Ditton, R.B.; Stoll, J.R. The Economic Value of Scuba-Diving Use of Natural and Artificial Reef Habitats. Soc. Nat. Resour. 2008, 21, 455–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polak, O.; Shashar, N. Can a Small Artificial Reef Reduce Diving Pressure from a Natural Coral Reef? Lessons learned from Eilat, Red Sea. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2012, 55, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huth, W.L.; Morgan, O.A.; Hindsley, P. Artificial Reef Attributes and The Relationship with Natural Reefs: Evidence From The Florida Keys. J. Ocean Coast. Econ. 2015, 2, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramm, L.A.; Florisson, J.H.; Watts, S.L.; Becker, A.; Tweedley, J.R. Artificial reefs in the Anthropocene: A review of geographical and historical trends in their design, purpose, and monitoring. Bull. Mar. Sci. 2021, 97, 699–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinchey, E.K.; Nicholson, M.C.; Zajac, R.N.; Irlandi, E. APreface: Marine and coastal applications in landscape ecology. Landsc. Ecol. 2018, 23, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivier, B.; Dauvin, J.C.; Navon, M.; Rusig, A.M.; Mussio, I.; Orvain, F.; Boutouil, M.; Claquin, P. Marine artificial reefs, a meta-analysis of their design, objectives and effectiveness. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2021, 27, e01538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Israel Diving Authority. Introductory Dives. 2014. Available online: https://www.gov.il/BlobFolder/policy/introductory_dive_procedure/he/%D7%A6%D7%9C%D7%99%D7%9C%D7%AA%20%D7%94%D7%9B%D7%A8%D7%95%D7%AA.pdf (accessed on 11 December 2023).
- Tickell, S.C.Y.; Sáenz-Arroyo, A.; Milner-Gulland, E.J. Sunken worlds: The past and future of human-made reefs in marine conservation. BioScience 2019, 69, 725–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koulouri, P.; Mogias, A.; Dounas, C. A Pilot Survey Investigating Naturoid Reefs as a Tool for Sustainable Marine Ecotourism. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ropicki, A.; Adams, C.; Lindberg, B.; Stevely, J. The Economic Benefits Associated with Florida’s Artificial Reefs; IFAS Publication Series; IFAS Publication: Milpitas, CA, USA, 2021; p. FE649. [Google Scholar]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shashar, N.; Oren, A.; Neri, R.; Waizman, O.; Chernihovsky, N.; Tynyakov, J. Artificial Reef Deployment Reduces Diving Pressure from Natural Reefs—The Case of Introductory Dives in Eilat, Red Sea. Oceans 2024, 5, 71-80. https://doi.org/10.3390/oceans5010005
Shashar N, Oren A, Neri R, Waizman O, Chernihovsky N, Tynyakov J. Artificial Reef Deployment Reduces Diving Pressure from Natural Reefs—The Case of Introductory Dives in Eilat, Red Sea. Oceans. 2024; 5(1):71-80. https://doi.org/10.3390/oceans5010005
Chicago/Turabian StyleShashar, Nadav, Asa Oren, Re’em Neri, Omer Waizman, Natalie Chernihovsky, and Jenny Tynyakov. 2024. "Artificial Reef Deployment Reduces Diving Pressure from Natural Reefs—The Case of Introductory Dives in Eilat, Red Sea" Oceans 5, no. 1: 71-80. https://doi.org/10.3390/oceans5010005
APA StyleShashar, N., Oren, A., Neri, R., Waizman, O., Chernihovsky, N., & Tynyakov, J. (2024). Artificial Reef Deployment Reduces Diving Pressure from Natural Reefs—The Case of Introductory Dives in Eilat, Red Sea. Oceans, 5(1), 71-80. https://doi.org/10.3390/oceans5010005