Glow on Sharks: State of the Art on Bioluminescence Research
Abstract
1. Introduction
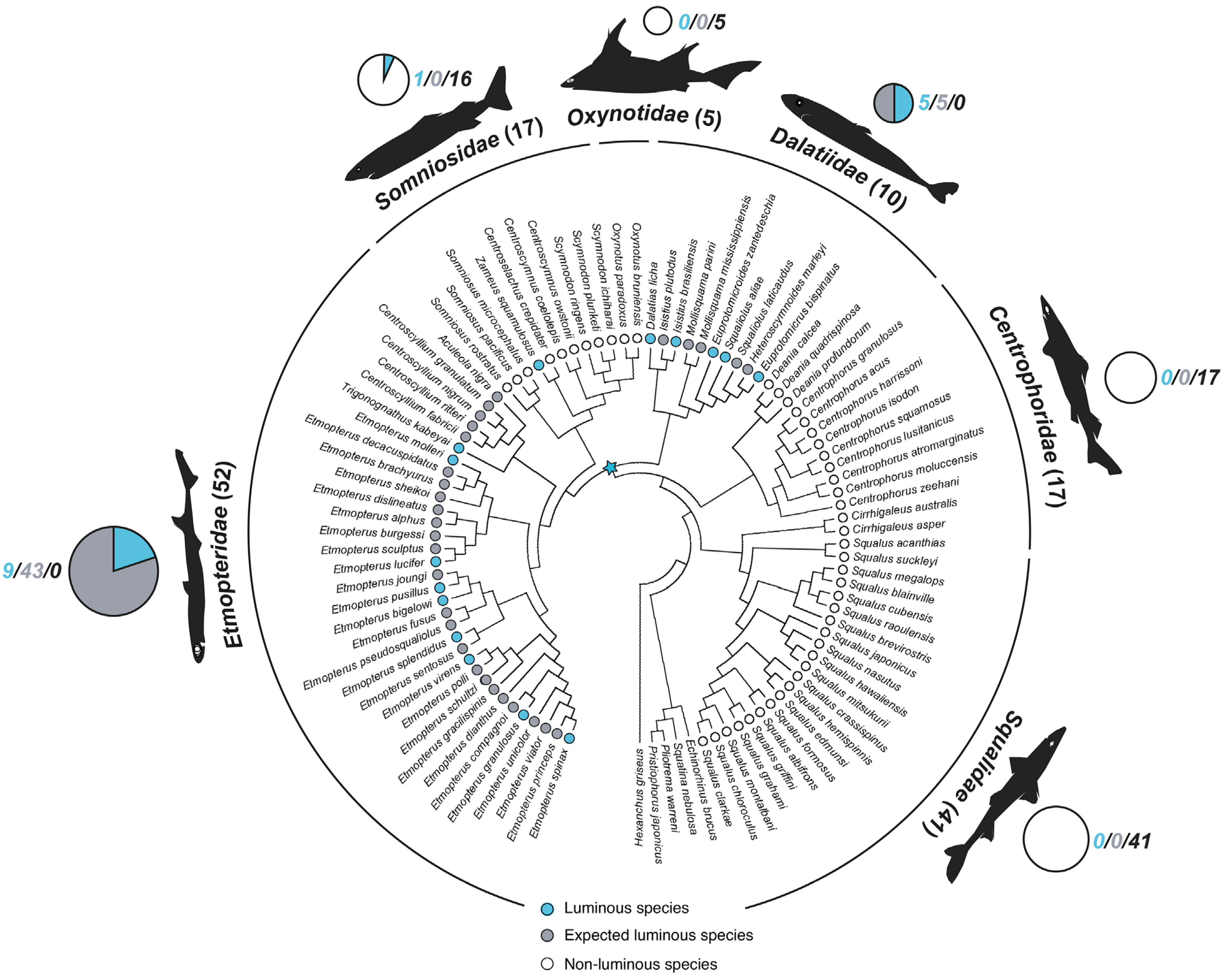
2. Luminous Shark Diversity
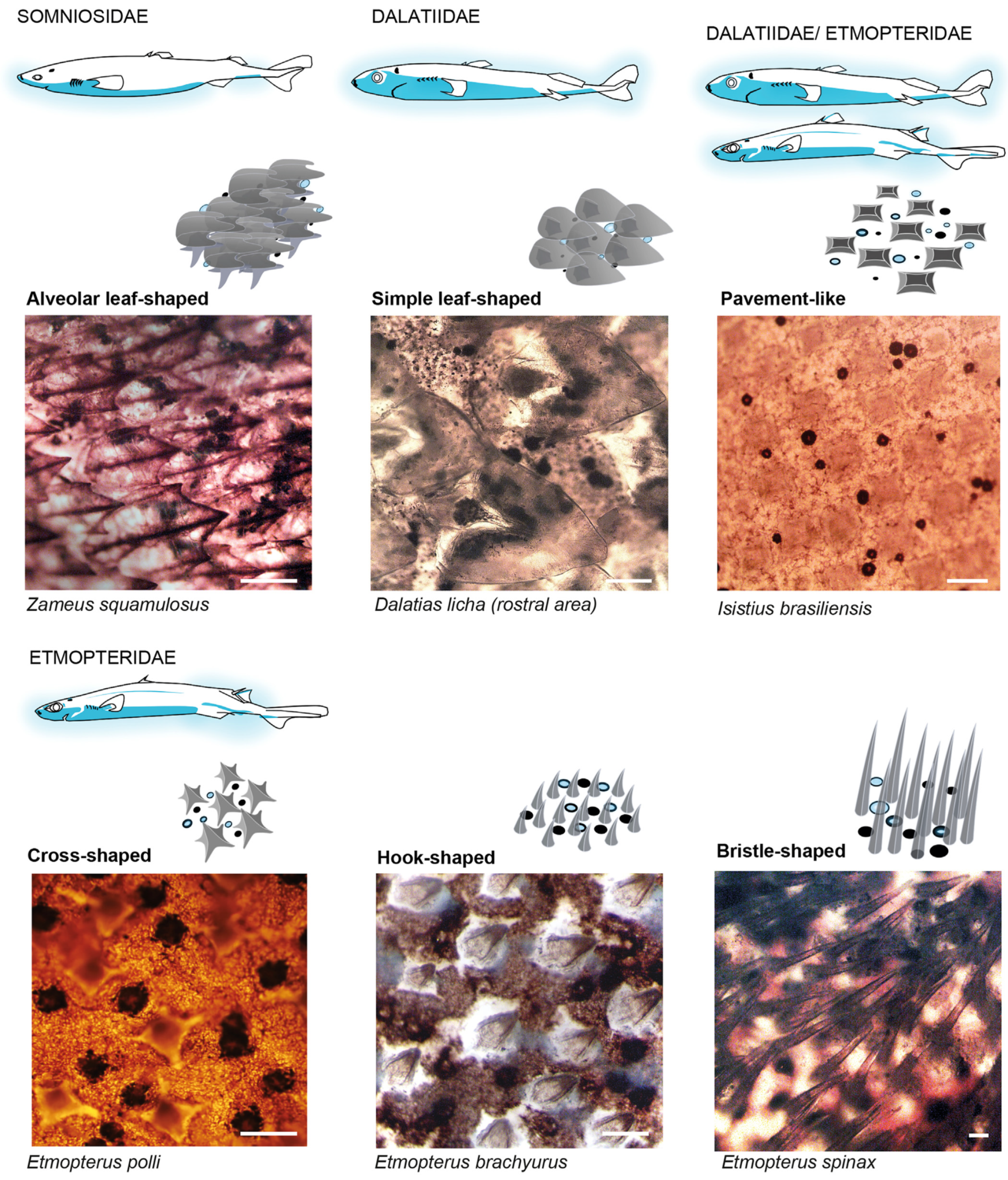
3. Ecology of Shark Luminescence
| Species | Photogenic Structure | Luminescence Color (Wavelength Peak) | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Isistius brasiliensis | Photophores | Dark blue (455 nm) | [16] |
| Squaliolus aliae | Photophores | Dark blue (457 nm) | [65] |
| Euprotomicroides zantedeschia | Pelvic pouch (fluid) | Dark blue | [49] |
| Dalatias licha | Photophores | Blue | [41] |
| Euprotomicrus bispinatus | Photophores | Blue | This study |
| Etmopterus splendidus | Photophores | Blue (476 nm) | [65] |
| Etmopterus molleri | Photophores | Blue (477 nm) | [65] |
| Etmopterus bigelowi | Photophores | Blue | [40] |
| Etmopterus granulosus | Photophores | Blue | [41] |
| Etmopterus lucifer | Photophores | Blue | [41] |
| Trigonognathus kabeyai | Photophores | Blue | This study |
| Etmopterus spinax | Photophores | Blue-green (488 nm) | [65] |
| Zameus squamulosus | Photophores | Blue-green | [36] |
| Etmopterus virens | Photophores | Green | [40] |
| Etmopterus pusillus | Photophores | “Whitish” | [44] |
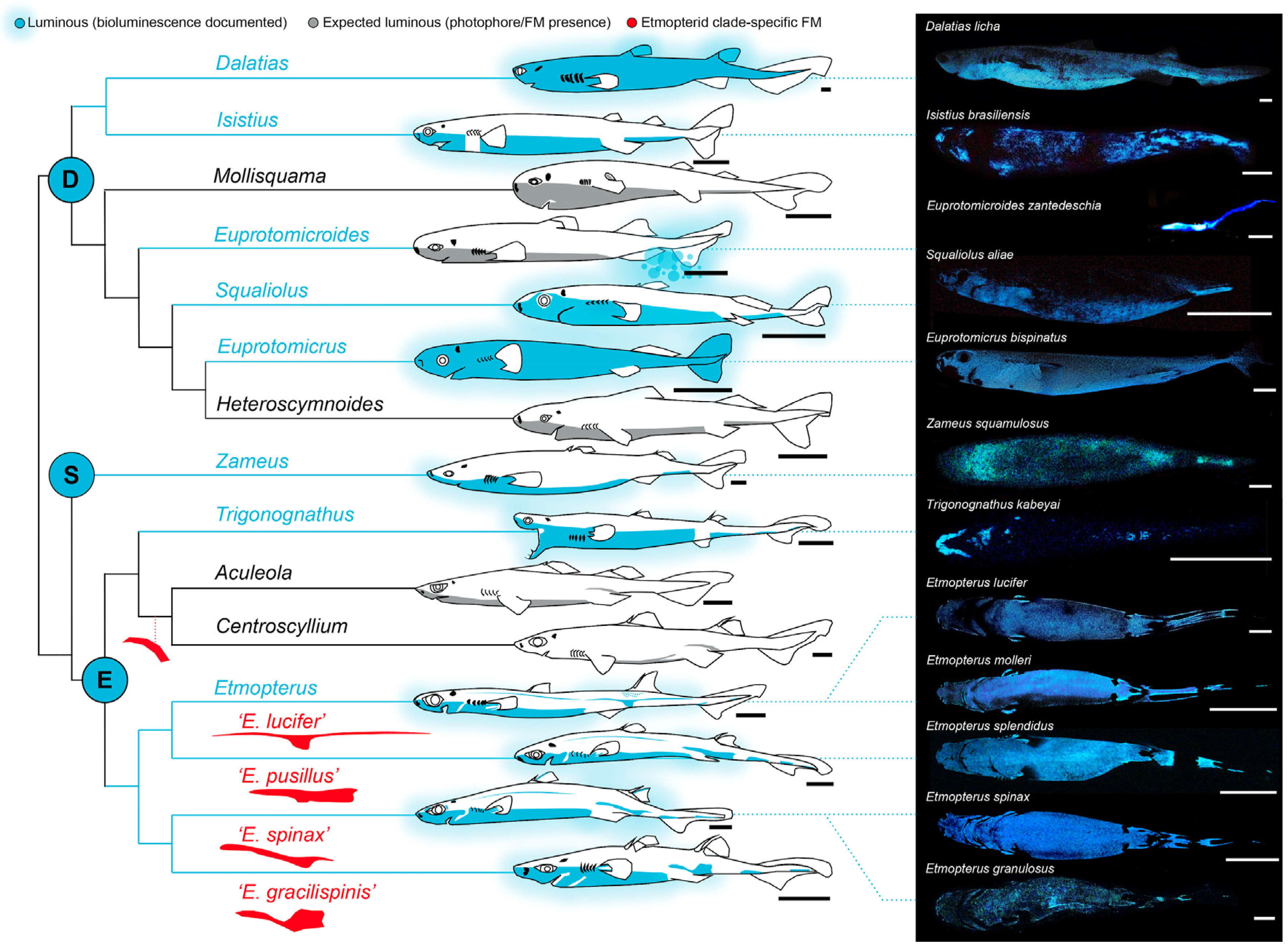
4. Photogenic Structures and Specialized Squamation of Bioluminescent Sharks
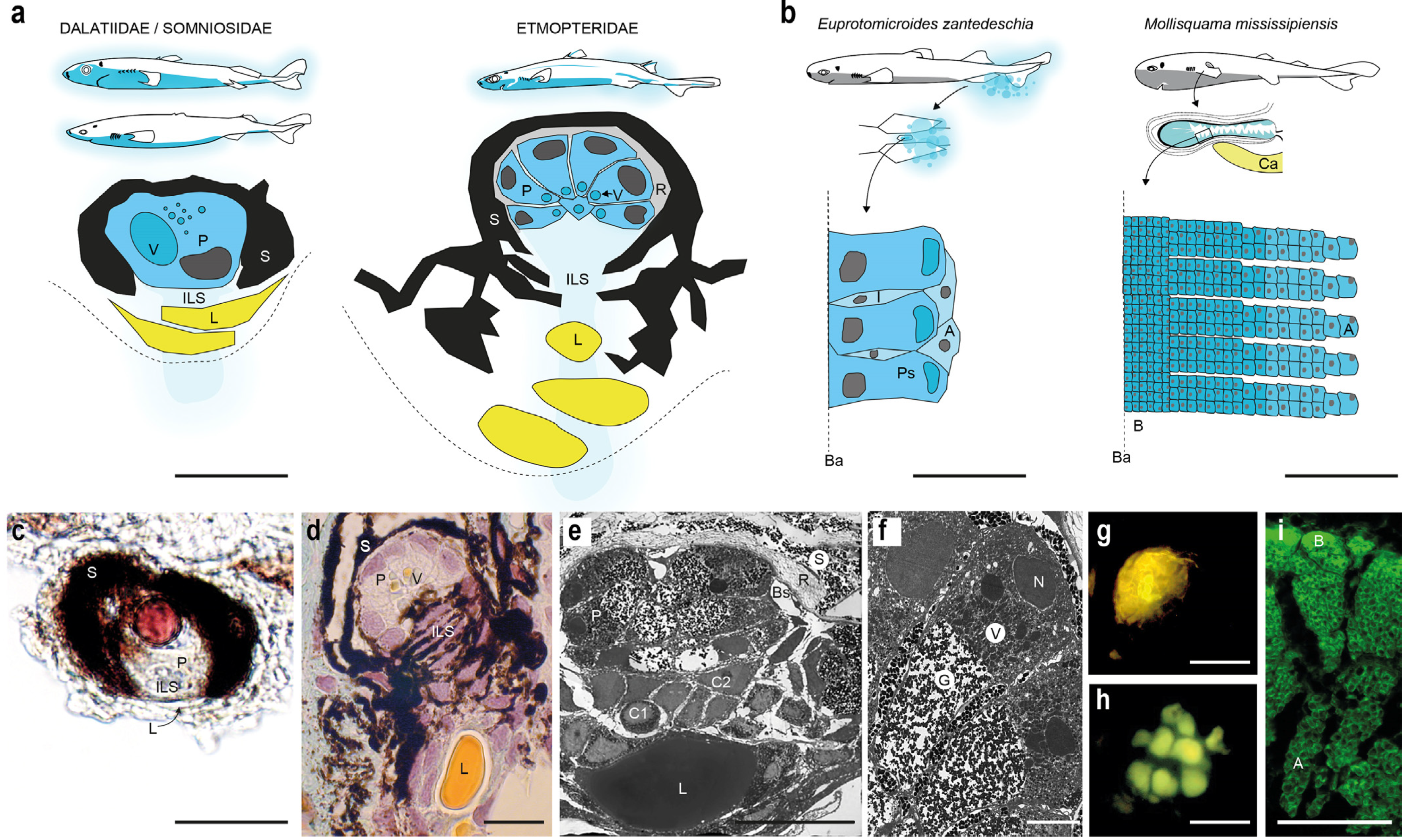
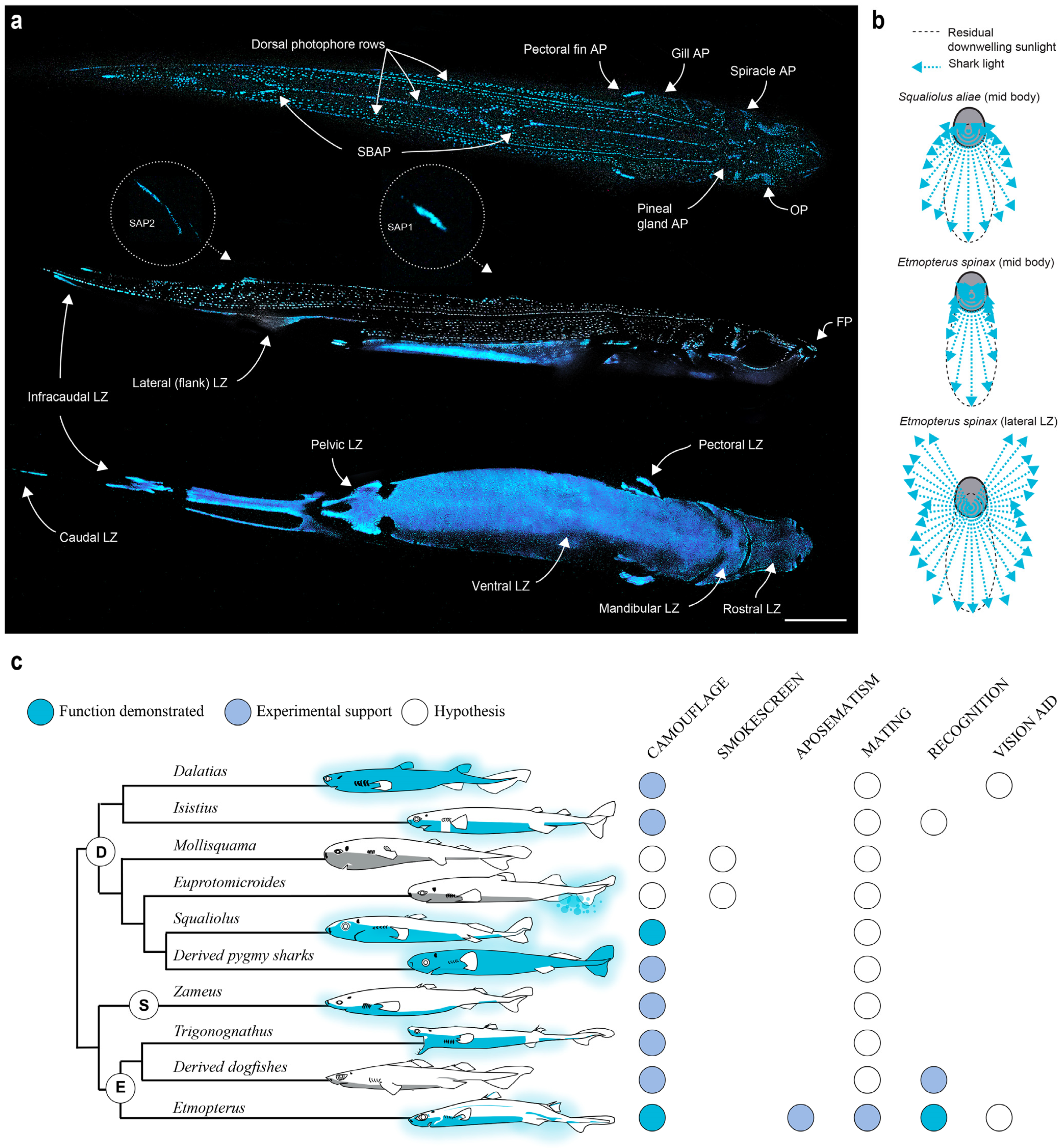
5. Control of Bioluminescence from Shark Photophores
5.1. Hormonal Control
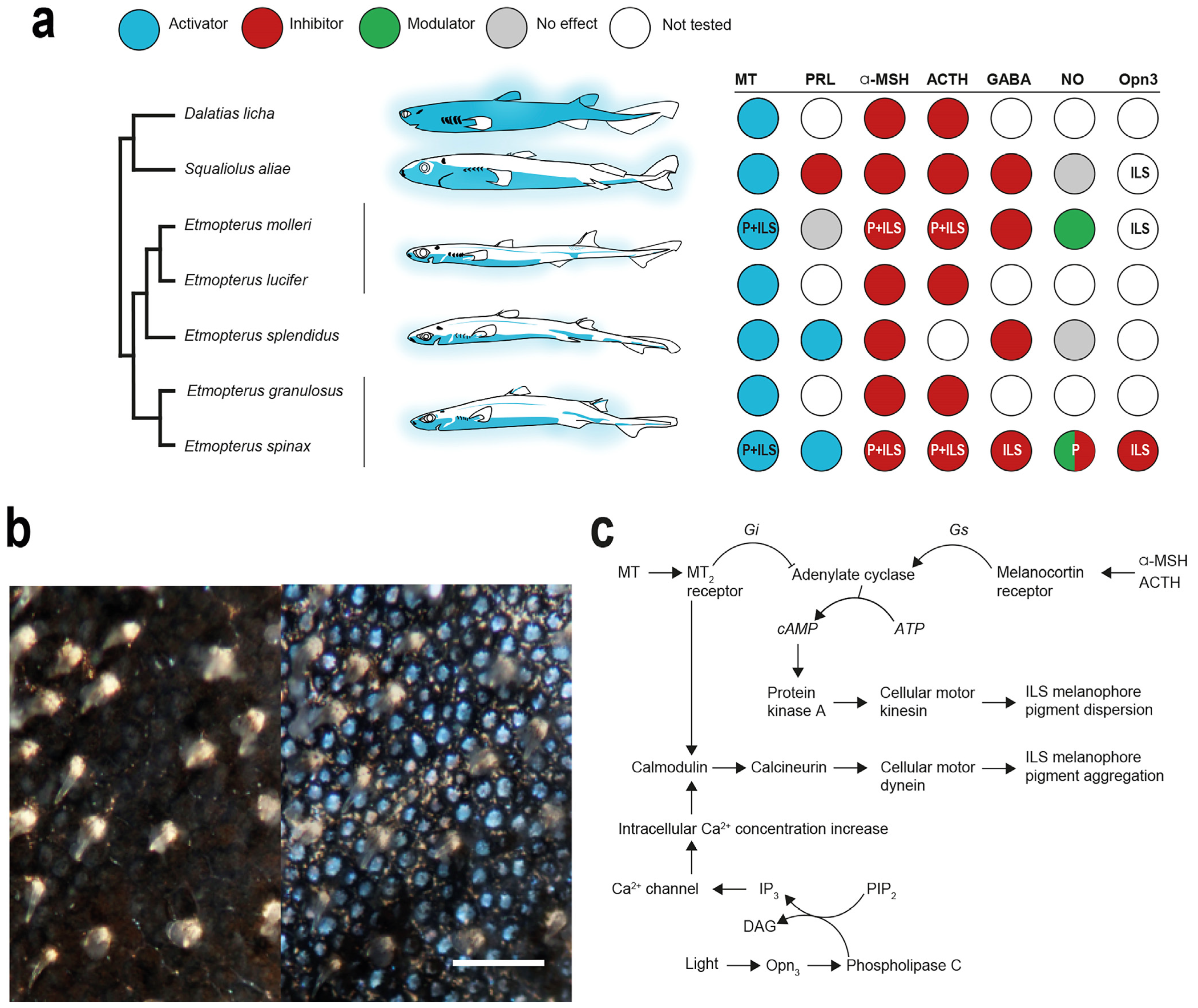
5.2. Extraocular Photoreception and Pigment Motion Regulation
6. Biochemistry of Shark Luminescence
7. Conclusions and Perspectives
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Haddock, S.H.D.; Moline, M.A.; Case, J.F. Bioluminescence in the sea. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2010, 2, 443–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hastings, J.W.; Morin, J.G. Bioluminescence. In Comparative Animal Physiology. Neural and Integrative Animal Physiology; Prosser, C.L., Ed.; John Wiley and Sons: Chichester, NY, USA, 1991; Chapter 3; pp. 131–170. [Google Scholar]
- Hastings, J.W. Biological diversity, chemical mechanisms, and the evolutionary origins of bioluminescent systems. J. Mol. Evol. 1983, 19, 309–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, T.; Hastings, J.W. Bioluminescence. Ann. Rev. Cell. Dev. Biol. 1998, 14, 197–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimomura, O. Bioluminescence: Chemical Principles and Methods; World Scientific Publishing Co. Pte. Ltd.: Singapore, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Widder, E.A. Bioluminescence in the ocean: Origins of biological, chemical, and ecological diversity. Science 2010, 328, 704–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimenez, G.; Metcalf, P.; Paterson, N.G.; Sharpe, M.L. Mass spectrometry analysis and transcriptome sequencing reveal glowing squid crystal proteins are in the same superfamily as firefly luciferase. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delroisse, J.; Ullrich-Lüter, E.; Blaue, S.; Ortega-Martinez, O.; Eeckhaut, I.; Flammang, P.; Mallefet, J. A puzzling homology: A brittle star using a putative cnidarian-type luciferase for bioluminescence. Open Biol. 2017, 7, 160300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delroisse, J.; Duchatelet, L.; Flammang, P.; Mallefet, J. Leaving the dark side? Insights into evolution of luciferases. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 673620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastings, J.W. Bioluminescence. In Cell Physiology Source Book; Sperelakis, N., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1995; pp. 665–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oba, Y.; Schultz, D.T. Eco-Evo bioluminescence on land and in the sea. In Bioluminescence: Fundamentals and Applications in Biotechnology—Volume 1. Advances in Biochemical Engineering/Biotechnology; Thouand, G., Marks, R., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; Volume 144, pp. 3–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, M.P.; Sparks, J.S.; Smith, W.L. Repeated and widespread evolution of bioluminescence in marine fishes. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0155154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, E.S.; Oakley, T.H. Multi-level convergence of complex traits and the evolution of bioluminescence. Biol. Rev. 2020, 96, 673–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morin, J.G. Coastal bioluminescence: Patterns and functions. Bull. Mar. Sci. 1983, 33, 787–817. [Google Scholar]
- Martini, S.; Kuhnz, L.; Mallefet, J.; Haddock, S.H.D. Distribution and quantification of bioluminescence as an ecological trait in the deep sea benthos. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 14654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herring, P.J.; Morin, J.G. Bioluminescence in fishes. In Bioluminescence in Action; Herring, P.J., Ed.; New York Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1978; pp. 273–329. [Google Scholar]
- Haneda, Y. Further studies on a luminous land snail, Quantula striata, in Malaya. Sci. Rep. Yokosuka City Mus. 1963, 8, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Rudie, N.G.; Mulkerrin, M.G.; Wampler, J.E. Earthworm bioluminescence: Characterization of high specific activity Diplocardia longa luciferase and the reaction it catalyzes. Biochemistry 1981, 20, 344–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, K.V. The chemical mechanism and evolutionary development of beetle bioluminescence. Photochem. Photobiol. 1995, 62, 662–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broadley, R.A.; Stringer, I.A.N. Prey attraction by larvae of the New Zealand glowworm, Arachnocampa luminosa (Diptera: Mycetophilidae). Invertebr. Biol. 2001, 120, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer-Rochow, V.B.; Moore, S. Hitherto unreported aspects of the ecology and anatomy of a unique gastropod: The bioluminescent freshwater pulmonated Latia neritoides. In Bioluminescence in Focus—A Collection of Illuminating Essays; Meyer-Rochow, V.B., Ed.; Research Signpost: Kerala, India, 2009; pp. 85–104. [Google Scholar]
- Oba, Y.; Branham, M.A.; Fukatsu, T. The terrestrial bioluminescent animals of Japan. Zool. Sci. 2011, 28, 771–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, G.J.; Branham, M.A.; Whiting, M.F.; Bybee, S.M. Total evidence phylogeny and the evolution of adult bioluminescence in fireflies (Coleoptera: Lampyridae). Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 2017, 107, 564–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennett, F.D. Narrative of a Whaling Voyage Round the Globe, from the Year 1833 to 1836; Рипoл Классик: Moscow, Russia, 1840; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Claes, J.M. Function and Control of Luminescence from Lantern Shark (Etmopterus spinax) Photophores. Ph.D. Thesis, Université catholique de Louvain—UCLouvain, Ottignies-Louvain-la-Neuve, Belgium, 4 May 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Renwart, M. Ultrastructure and Biochemistry of the Light-Emitting System of Lantern Shark (Etmopterus spinax) Photophores. Ph.D. Thesis, Université catholique de Louvain—UCLouvain, Ottignies-Louvain-la-Neuve, Belgium, 18 December 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Duchatelet, L. Extraocular Photoreception and Bioluminescence of Representatives of Two Luminous Shark Families, Etmopteridae and Dalatiidae. Ph.D. Thesis, Université Catholique de Louvain—UCLouvain, Ottignies-Louvain-la-Neuve, Belgium, 3 October 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Harvey, E.N. Bioluminescence. Chapter XVI Pisces; Academic Press Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1952; pp. 494–553. [Google Scholar]
- Alcock, A. A Naturalist in Indian Seas: Or, Four Years with the Royal Indian Marine Survey Ship “Investigator”; Dutton: New York, NY, USA, 1902. [Google Scholar]
- de Carvalho, M.R. A synopsis of the deep-sea genus Benthobatis Alcock, with a redescription of the type species Benthobatis moresbyi Alcock, 1898 (Chondrichthyes, Torpediniformes, Narcinidae). In Proceedings of the 5th Indo-Pacific Fish Conference, Nouméa, New Caledonia, 3–8 November 1997; Séret, B., Sire, J.-Y., Eds.; Societe Francaise d’ Ichtyologie: Paris, France, 1999; pp. 231–255. [Google Scholar]
- de Carvalho, M.R.; Compagno, L.J.V.; Ebert, D.A. Benthobatis yangi, a new species of blind electric ray from Taiwan (Chondrichthyes: Torpediniformes: Narcinidae). Bull. Mar. Sci. 2003, 72, 923–939. [Google Scholar]
- Duchatelet, L.; Moris, V.; Tomita, T.; Mahillon, J.; Sato, K.; Behets, C.; Mallefet, J. The megamouth shark, Megachasma pelagios, is not a luminous species. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0242196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubbs, C.L.; Iwai, T.; Matsubara, K. External and internal characters, horizontal and vertical distribution, luminescence, and food of the dwarf pelagic shark, Euprotomicrus bispinatus. Bull. Scripps Inst. Oceanogr. 1967, 10, 1–64. [Google Scholar]
- Claes, J.M.; Mallefet, J. Bioluminescence of sharks: First synthesis. In Bioluminescence in Focus—A Collection of Illuminating Essays; Meyer-Rochow, V.B., Ed.; Research Signpost: Kerala, India, 2009; pp. 51–65. [Google Scholar]
- Straube, N.; Li, C.; Claes, J.M.; Corrigan, S.; Naylor, G.J.P. Molecular phylogeny of Squaliformes and first occurrence of bioluminescence in sharks. BMC Evol. Biol. 2015, 15, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duchatelet, L.; Marion, R.; Mallefet, J. A third luminous shark family: Confirmation of luminescence ability for Zameus squamulosus (Squaliformes; Somniosidae). Photochem. Photobiol. 2021, 97, 739–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adnet, S.; Capetta, H. A paleontological and phylogenetical analysis of Squaliform sharks (Chondrichthyes: Squaliformes) based on dental characters. Lethaia 2001, 34, 234–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straube, N.; Iglésias, S.P.; Sellos, D.Y.; Kriwet, J.; Schliewen, U.K. Molecular phylogeny and node time estimation of bioluminescent lantern sharks (Elasmobranchii: Etmopteridae). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2010, 56, 905–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Compagno, L.J.V.; Dando, M.; Fowler, S. Sharks of the World; Harper Collins: London, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Castro, J.I. The Sharks of North America; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Mallefet, J.; Stevens, D.W.; Duchatelet, L. Bioluminescence of the largest luminous vertebrate, the kitefin shark, Dalatias licha: First insights and comparative aspects. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 633582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claes, J.M.; Mallefet, J. Comparative control of luminescence in sharks: New insights from the slendertail lanternshark (Etmopterus molleri). J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2015, 467, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duchatelet, L.; Delroisse, J.; Pinte, N.; Sato, K.; Ho, H.-C.; Mallefet, J. Adrenocorticotropic hormone and cyclic adenosine monophosphate are involved in the control of shark bioluminescence. Photochem. Photobiol. 2020, 96, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohshima, H. Some observations on the luminous organs of fishes. J. Coll. Sci. Imp. Univ. Tokyo 1911, 27, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claes, J.M.; Mallefet, J. Early development of bioluminescence suggests camouflage by counter-illumination in the velvet belly lantern shark Etmopterus spinax (Squaloidea: Etmopteridae). J. Fish Biol. 2008, 73, 1337–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johann, L.; der Organe, I.V. Über eigentümliche epitheliale Gebilde (Leuchtorgane) bei Spinax niger Aus dem zoologischen Institut der Universität Rostock. Von. Z. Wiss. Zool. 1899, 66, 136. [Google Scholar]
- Claes, J.M.; Sato, K.; Mallefet, J. Morphology and control of photogenic structures in a rare dwarf pelagic lantern shark (Etmopterus splendidus). J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2011, 406, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claes, J.M.; Ho, H.-C.; Mallefet, J. Control of luminescence from pygmy shark (Squaliolus aliae) photophores. J. Exp. Biol. 2012, 215, 1691–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Stehmann, M.F.W.; Van Oijen, M.; Kamminga, P. Re-description of the rare taillight shark Euprotomicroides zantedeschia (Squaliformes, Dalatiidae), based on third and fourth record from off Chile. Cybium 2016, 40, 187–197. [Google Scholar]
- Dickens, D.A.G.; Marshall, N.J. Observations on Euprotomicrus. Mar. Obs. 1956, 26, 73–74. [Google Scholar]
- Widder, E.A. A predatory use of counterillumination by the squaloid shark, Isistius brasiliensis. Environ. Biol. Fishes 1998, 53, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delroisse, J.; Duchatelet, L.; Flammang, P.; Mallefet, J. Photophore distribution and enzymatic diversity within the photogenic integument of the cookie cutter shark Isistius brasiliensis (Chondrichthyes: Dalatiidae). Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 627045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebert, D.A.; Straube, N.; Leslie, R.W.; Weigmann, S. Etmopterus alphus n. sp.: A new lanternshark (Squaliformes: Etmopteridae) from the south-western Indian Ocean. Afr. J. Mar. Sci. 2016, 38, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebert, D.A.; Leslie, R.W.; Weigmann, S. Etmopterus brosei sp. nov.: A new lanternshark (Squaliformes: Etmopteridae) from the southeastern Atlantic and southwestern Indian oceans, with a revised key to the Etmopterus lucifer clade. Mar. Biodiv. 2021, 51, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grace, M.A.; Doosey, M.H.; Denton, J.S.S.; Naylor, G.J.P.; Bart, H.L.; Maisey, J.G. A new Western North Atlantic Ocean kitefin shark (Squaliformes: Dalatiidae) from the Gulf of Mexico. Zootaxa 2019, 4619, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burckhardt, R. On the luminous organs of selachian fishes. Ann. Mag. Nat. Hist. 1900, 7, 558–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigelow, H.B.; Schoeder, W.C.; Springer, S. New and little known sharks from the Atlantic and from the Gulf of Mexico. Bull. Mus. Comp. Zool. Harv. Coll. 1953, 109, 213–276. [Google Scholar]
- Abe, T. Description of a new squaloid shark, Centroscyllium kamoharai, from Japan. Jpn. J. Ichthyol. 1966, 13, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, W.L. New sharks from the South China Sea. J. Zool. 1966, 148, 218–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolganov, V.N. A new shark from the family Squalidae caught on the Naska submarine ridge. Zool. Z. 1984, 63, 1589–1591. [Google Scholar]
- Munk, O.; Jørgensen, J.M. Putatively luminous tissue in the abdominal pouch of a male dalatiine shark, Euprotomicroides zantedeschia Hulley & Penrith, 1966. Acta Zool. 1988, 69, 247–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirai, S.; Nakaya, K. A new squalid species of the genus Centroscyllium from the Emperor seamont chain. Jpn. J. Ichtyol. 1990, 36, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Last, P.R.; Burgess, G.H.; Séret, B. Description of six new species of lantern-sharks of the genus Etmopterus (Squaloidea: Etmopteridae) from the Australasian region. Cybium 2002, 26, 203–223. [Google Scholar]
- Knuckey, J.D.S.; Ebert, D.A.; Burgess, G.H. Etmopterus joungi n. sp., a new species of lanternshark (Squaliformes: Etmopteridae) from Taiwan. Aqua Int. J. Ichthyol. 2010, 17, 61–72. [Google Scholar]
- Claes, J.M.; Nilsson, D.-E.; Straube, N.; Collin, S.P.; Mallefet, J. Iso-luminance counterillumination drove bioluminescent shark radiation. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 4328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grace, M.A.; Doosey, M.H.; Bart, H.L.; Naylor, G.J.P. First record of Mollisquama sp. (Chondrichthyes: Squaliformes: Dalatiidae) from the Gulf of Mexico, with a morphological comparison to the holotype description of Mollisquama parini Dolganov. Zootaxa 2015, 3948, 587–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vásquez, V.E.; Ebert, D.A.; Long, D.J. Etmopterus benchleyi n. sp., a new lanternshark (Squaliformes: Etmopteridae) from the central eastern Pacific Ocean. J. Ocean. Sci. Found 2015, 17, 43–55. [Google Scholar]
- Ebert, D.A.; Papastamatiou, Y.P.; Kajiura, S.M.; Wetherbee, B.M. Etmopterus lailae sp. nov., a new lanternshark (Squaliformes: Etmopteridae) from the Northwestern Hawaiian Islands. Zootaxa 2017, 4237, 371–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, W.T.; Ebert, D.A.; Mana, R.R.; Corrigan, S. Etmopterus samadiae n. sp., a new lanternshark (Squaliformes: Etmopteridae) from Papua New Guinea. Zootaxa 2017, 4244, 339–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Figueiredo Petean, F.; de Carvalho, M.R. Comparative morphology and systematics of the cookiecutter sharks, genus Isistius Gill (1864) (Chondrichthyes: Squaliformes: Dalatiidae). PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0201913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolganov, V.N.; Balanov, A.A. Etmopterus parini sp. n. (Squaliformes: Etmopteridae), a new shark species from the northwestern Pacific Ocean. Biol. Morya 2018, 44, 427–430. [Google Scholar]
- Ebert, D.A.; Van Hees, K.E. Etmopterus marshae sp. Nov, a new lanternshark (Squaliformes: Etmopteridae) from the Philippine Islands, with a revised key to the Etmopterus lucifer clade. Zootaxa 2018, 4508, 197–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolganov, V.N. On the little-known sharks Etmopterus villosus (Etmopteridae) and Scymnodalatias sherwoodi (Somniosidae) from the Pacific Ocean. J. Ichthyol. 2019, 59, 275–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claes, J.M.; Delroisse, J.; Grace, M.A.; Doosey, M.H.; Duchatelet, L.; Mallefet, J. Histological evidence for secretory bioluminescence from pectoral pockets of the American pocket shark (Mollisquama mississippiensis). Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 18762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claes, J.M.; Nilsson, D.-E.; Mallefet, J.; Straube, N. The presence of lateral photophores correlates with increased speciation in deep-sea bioluminescent sharks. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2015, 2, 150219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renwart, M.; Delroisse, J.; Claes, J.M.; Mallefet, J. Ultrastructural organization of lantern shark (Etmopterus spinax Linnaeus, 1758) photophores. Zoomorphology 2014, 133, 405–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duchatelet, L.; Claes, J.M.; Mallefet, J. Embryonic expression of encephalopsin supports bioluminescence perception in lanternshark photophores. Mar. Biol. 2019, 166, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duchatelet, L.; Delroisse, J.; Flammang, P.; Mahillon, J.; Mallefet, J. Etmopterus spinax, the velvet belly lanternshark, does not use bacterial luminescence. Acta Histochem. 2019, 121, 516–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schofield, P.J.; Burgess, G.H. Etmopterus robinsi (Elasmobranchii, Etmopteridae), a new species of deepwater lantern shark from the Caribbean Sea and Western North Atlantic, with a redescription of Etmopterus hillianus. Bull. Mar. Sci. 1997, 60, 1060–1073. [Google Scholar]
- Straube, N.; Duhamel, G.; Gasco, N.; Kriwet, J.; Schliewen, U.K. Description of a new deep-sea lantern shark Etmopterus viator sp. nov. (Squaliformes: Etmopteridae) from the Southern Hemisphere. In The Kerguelen Plateau, Marine Ecosystem and Fisheries; Société Française d’Ichtyologie: Paris, France, 2011; pp. 135–148. [Google Scholar]
- Fricke, R.; Koch, I. A New Species of the Lantern Shark Genus Etmopterus from Southern Africa (Elasmobranchii: Squalidae)/With 4 Figures and 1 Table; Stuttgarter Beiträge zur Naturkunde: Stuttgart, Germany, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Iwai, T. Luminous organs of the deep-sea squaloid shark, Centroscyllium ritteri Jordan and Fowler. Pac. Sci. 1960, 14, 51–54. [Google Scholar]
- Schaaf-DaSilva, J.A.; Ebert, D.A. Etmopterus burgessi sp. nov., a new species of lanternshark (Squaliformes: Etmopteridae) from Taiwan. Zootaxa 2006, 1373, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Springer, S.; Burgess, G.H. Two new dwarf dogsharks (Etmopterus, Squalidae), found off the Caribbean coast of Colombia. Copeia 1985, 1985, 584–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirai, S.; Tachikawa, H. Taxonomic resolution of the Etmopterus pusillus species group (Elasmobranchii, Etmopteridae), with description of E. bigelowi, n. sp. Copeia 1993, 1993, 483–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolganov, V.N. Description of new species of sharks of the family Squalidae (Squaliformes) from the north-western part of the Pacific Ocean with remarks of validity of Etmopterus. Zool. Zhurnal 1986, 65, 149–153. [Google Scholar]
- Gubanov, E.P.; Kondyurin, V.V.; Myagkov, N.A. Sharks of the World Ocean: Identification Handbook. [=Akuly Mirovogo Okeana: Sparvochnik-Opredelitel’]; Agropromizdat: Moscow, Russia, 1986; pp. 1–272. [Google Scholar]
- Mochizuki, K.; Ohe, F. Trigonognathus kabeyai, a new genus and species of the Squalid sharks from Japan. Jpn. J. Ichthyol. 1990, 36, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seigel, J.A. Revision of the Dalatiid shark genus Squaliolus: Anatomy, systematics, ecology. Copeia 1978, 1978, 602–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrick, J.A.F.; Springer, S. Isistius plutodus, a new Squaloid shark from the Gulf of Mexico. Copeia 1964, 1964, 678–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollerspöck, J.; Straube, N. Bibliography Database of Living/Fossil Sharks, Rays and Chimaeras (Chondrichtyes: Elasmobranchii, Holocephali)—List of Valid Extant Species; List of Described Extant Species; Statistic, World Wide Web Electronic Publication, Version 10/2021; ISSN: 2195-6499. Available online: www.shark-references.com (accessed on 23 November 2021).
- Denton, J.S.S.; Maisey, J.G.; Grace, M.; Pradel, A.; Doosey, M.H.; Bart, H.L., Jr.; Naylor, G.J.P. Cranial morphology in Mollisquama sp. (Squaliformes; Dalatiidae) and patterns of cranial evolution in dalatiid sharks. J. Anat. 2018, 233, 15–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daley, R.; Appleyard, S.A.; Koopman, M. Genetic catch verification to support recovery plans for deepsea gulper sharks (genus Centrophorus, family Centrophoridae)- an Australian example using the 16S gene. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2012, 63, 708–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanni, S.; Catarino, D.; Ribeiro, P.A.; Freitas, M.; Menezes, G.M.; Neat, F.; Stankovic, D. Molecular systematics of the long-snouted deep water dogfish (Centrophoridae, Deania) with implications for identification, taxonomy, and conservation. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 7, 588192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziadi-Künzli, F.; Soliman, T.; Imai, H.; Sakurai, M.; Maeda, K.; Tachihara, K. Re-evaluation of deep-sea dogfishes (genus Squalus) in Japan using phylogenetic inference. Deep Sea Res. I 2020, 160, 103261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, W.T.; Vaz, D.F.B.; Ho, H.-C.; Ebert, D.A.; de Carvalho, M.R.; Corrigan, S.; Rochel, E.; de Carvalho, M.; Tanaka, S.; Naylor, G.J.P. Redescription of Scymnodon ichiharai Yano and Tanaka 1984 (Squaliformes: Somniosidae) from the western North Pacific, with comments on the definition of somniosid genera. Ichthyol. Res. 2015, 62, 213–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebert, D.A.; Dando, M.; Fowler, S. Sharks of the World, a Complete Guide; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 1–624. [Google Scholar]
- Ebert, D.A.; Compagno, L.J.V.; De Vries, M.J. A new lanternshark (Squaliformes: Etmopteridae: Etmopterus) from Southern Africa. Copeia 2011, 2011, 379–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, W.D. Function of bioluminescence in mesopelagic organisms. Nature 1963, 198, 1244–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denton, E.J.; Gilpin-Brown, J.B.; Wright, P.J. The angular distribution of the light produced by some mesopelagic fish in relation to their camouflage. Proc. R. Soc. B 1972, 182, 145–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, R.E.; Kampa, E.M.; Maynard, S.D.; Mencher, F.M.; Roper, C.F.E. Counterillumination and the upper depth limits of midwater animals. Deep Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 1980, 27, 671–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFall-Ngai, M.; Morin, J.G. Camouflage by disruptive illumination in Leiognathids, a family of shallow-water, bioluminescent fishes. J. Exp. Biol. 1991, 156, 119–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claes, J.M.; Aksnes, D.L.; Mallefet, J. Phantom hunter of the fjords: Camouflage by counterillumination in a shark (Etmopterus spinax). J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2010, 388, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claes, J.M.; Dean, M.N.; Nilsson, D.-E.; Hart, N.S.; Mallefet, J. A deepwater fish with ‘lightsabers’—Dorsal spine-associated luminescence in a counterilluminating lanternshark. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duchatelet, L.; Pinte, N.; Tomita, T.; Sato, K.; Mallefet, J. Etmopteridae bioluminescence: Dorsal pattern specificity and aposematic use. Zool. Lett. 2019, 5, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claes, J.M.; Mallefet, J. Ecological Functions of shark luminescence. Luminescence 2014, 29, 13. [Google Scholar]
- Claes, J.M.; Mallefet, J. Functional physiology of lantern shark (Etmopterus spinax) luminescent pattern: Differential hormonal regulation of luminous zones. J. Exp. Biol. 2010, 213, 1852–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claes, J.M.; Mallefet, J. Hormonal control of luminescence from lantern shark (Etmopterus spinax) photophores. J. Exp. Biol. 2009, 212, 3684–3692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinte, N.; Parisot, P.; Martin, U.; Zintzen, V.; De Vleeschouwer, C.; Roberts, C.D.; Mallefet, J. Ecological features and swimming capabilities of deep-sea sharks from New Zealand. Deep-Sea Res. I 2020, 156, 103187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinte, N.; Coubris, C.; Jones, E.; Mallefet, J. Red and white muscle proportions and enzyme activities in mesopelagic sharks. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B 2021, 256, 110649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claes, J.M.; Partridge, J.C.; Hart, N.S.; Garza-Gisholt, E.; Ho, H.-C.; Mallefet, J.; Collin, S.P. Photon hunting in the twilight zone: Visual features of mesopelagic bioluminescent sharks. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e104213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claes, J.M.; Mallefet, J. Ontogeny of photophore pattern in the velvet belly lanternshark, Etmopterus spinax. Zoology 2009, 112, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.C.; Coloma, L.A.; Cannatella, D.C. Multiple, recurring origins of aposematism and diet specialization in poison frogs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 12792–12797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marek, P.; Papaj, D.; Yeager, J.; Molina, S.; Moore, W. Bioluminescent aposematism in millipedes. Curr. Biol. 2011, 21, R680–R681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolin, R.L. The function of the luminous organs of deep-sea fishes. In Proceedings of the 9th Pacific Science Congress, Bangkok, Thailand, 18 November–9 December 1957; Volume 10, pp. 37–39. [Google Scholar]
- Matsui, T.; Rosenblatt, R.H. Review of the deep-sea fish family Platytroctidae (Pisces: Salmoniformes). Bull. Scripps Inst. Oceanogr. Univ. Calif. 1987, 26, 1–159. [Google Scholar]
- Poulsen, J.Y. New observations and ontogenetic transformation of photogenic tissues in the tubeshoulder Sagamichthys schnakenbecki (Platytroctidae, Alepocephaliformes). J. Fish Biol. 2019, 94, 62–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, A.L.; Sutton, T.T.; Kier, W.M.; Johnsen, S. Evidence that eye-facing photophores serve as a reference for counterillumination in an order of deep-sea fishes. Proc. R. Soc. B 2020, 287, 20192918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herring, P.J.; Cope, C. Red bioluminescence in fishes: On the suborbital photophores of Malacosteus, Pachystomias and Aristostomias. Mar. Biol. 2005, 148, 383–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renwart, M.; Delroisse, J.; Flammang, P.; Claes, J.M.; Mallefet, J. Cytological changes during luminescence production in lanternshark (Etmopterus spinax Linnaeus, 1758) photophores. Zoomorphology 2015, 134, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claes, J.M.; Mallefet, J. The lantern shark’s light switch: Turning shallow water crypsis into midwater camouflage. Biol. Lett. 2010, 6, 685–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duchatelet, L.; Sugihara, T.; Delroisse, J.; Koyanagi, M.; Rezsohazy, R.; Terakita, A.; Mallefet, J. From extraocular photoreception to pigment movement regulation: A new control mechanism of the lanternshark luminescence. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 10195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claes, J.M.; Krönström, J.; Holmgren, S.; Mallefet, J. Nitric oxide in the control of luminescence from lantern shark (Etmopterus spinax) photophores. J. Exp. Biol. 2010, 213, 3005–3011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reif, W.E. Functions of scales and photophores in mesopelagic luminescent sharks. Acta Zool. 1985, 66, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrón, H.G.; Paredes-Aliaga, M.V.; Martínez-Pérez, C.; Botella, H. Bioluminescent-like squamation in the galeomorph shark Apristurus ampliceps (Chondrichthyes: Elasmobranchii). Contrib. Zool. 2018, 87, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christophe, B.; Baguet, F. The adrenergic control of the photocytes luminescence of the Porichthys photophores. Comp. Bioch. Physiol. C Comp. Pharmacol. 1985, 81, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallefet, J.; Anctil, M. Immunohistochemical detection of biogenic amines in the photophores of the midshipman fish Porichthys notatus. Can. J. Zool. 1992, 70, 1968–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaccone, G.; Abelli, L.; Salpietro, L.; Zaccone, D.; Macrì, B.; Marino, F. Nervous control of photophores in luminescent fishes. Acta Hictochem. 2011, 113, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallefet, J.; Duchatelet, L.; Hermans, C.; Baguet, F. Luminescence control of Stomiidae photophores. Acta Histochem. 2019, 121, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visconti, M.A.; Ramanzini, G.C.; Camargo, C.R.; Castrucci, A.M.L. Elasmobranch color change: A short review and novel data on hormone regulation. J. Exp. Zool. 1999, 284, 485–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelsleichter, J.; Evans, A.N. Hormonal regulation of elasmobranch physiology. In Biology of Sharks and Their Relatives; Carrier, J.C., Musick, J.A., Heithaus, M.R., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2004; Chapter 11; pp. 314–338. [Google Scholar]
- Nagai, M.; Oshima, N.; Fujii, R. A comparative study of melanin concentrating hormone (MCH) action on teleost melanophores. Biol. Bull. 1986, 171, 360–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshima, N.; Kasukawa, H.; Fujii, R.; Wilkes, B.C.; Hruby, V.J.; Hadley, M.E. Action of melanin-concentrating hormone (MCH) on teleost chromatophores. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 1986, 64, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizusawa, K.; Kobayashi, Y.; Sunuma, T.; Asahida, T.; Saito, Y.; Takahashi, A. Inhibiting roles of melanin-concentrating hormone for skin pigment dispersion in barfin flounder, Verasper moseri. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2011, 171, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizusawa, K.; Amiya, N.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Takabe, S.; Amano, M.; Breves, J.P.; Fox, B.K.; Grau, E.G.; Hyodo, S.; Takahashi, A. Identification of mRNAs coding for mammalian-type melanin-concentrating hormone and its receptors in the scalloped hammerhead shark Sphyrna lewini. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2012, 179, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duchatelet, L.; Delroisse, J.; Mallefet, J. Melanin-concentrating hormone is not involved in luminescence emission in the velvet belly lanternshark, Etmopterus spinax. Mar. Biol. 2019, 166, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duchatelet, L.; Delroisse, J.; Mallefet, J. Bioluminescence in lanternsharks: Insight from hormone receptor localization. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2020, 294, 113488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claes, J.M.; Mallefet, J. Control of luminescence from lantern shark (Etmopterus spinax) photophores. Commun. Integr. Biol. 2011, 4, 251–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claes, J.M.; Krönström, J.; Holmgren, S.; Mallefet, J. GABA inhibition of luminescence from lantern shark (Etmopterus spinax) photophores. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2011, 153, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocampo Daza, D.; Larhammar, D. Evolution of the receptors for growth hormone, prolactin, erythropoietin and thrombopoietin in relation to the vertebrate tetraploidizations. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2018, 257, 143–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanacek, J. Cellular mechanisms of melatonin action. Physiol. Rev. 1998, 78, 687–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busca, R.; Ballotti, R. Cyclic AMP a key messenger in the regulation of skin pigmentation. Pigment Cell Res. 2000, 13, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugden, D.; Davidson, K.; Hough, K.A.; The, M.-T. Melatonin, melatonin receptors and melanophores: A moving story. Pigment Cell Res. 2004, 17, 454–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visconti, M.A.; Castrucci, A.M.L. Melanotropin receptors in the cartilaginous fish, Potamotrygon reticulatus and in the lungfish, Lepidosiren paradoxa. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Pharmacol. Toxicol. Endocrinol. 1993, 106, 523–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nery, L.E.M.; Castrucci, A.M.L. Pigment cell signalling for physiological color change. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Interg. Physiol. 1997, 118, 1135–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, D.; Rozas, N.S.; Oakley, T.H.; Mitchell, J.; Colley, N.J.; McFall-Ngai. Evidence for light perception in a bioluminescent organ. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 9836–9841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFall-Ngai, M.; Heath-Heckman, E.A.C.; Gillette, A.A.; Peyer, S.M.; Harvie, E.A. The secret languages of coevolved symbioses: Insights from the Euprymna scolopes-Vibrio fischeri symbiosis. Semin. Immunol. 2012, 24, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnitzler, C.E.; Pang, K.; Powers, M.L.; Reitzel, A.M.; Ryan, J.F.; Simmons, D.; Tada, T.; Park, M.; Gupta, J.; Brooks, S.Y.; et al. Genomic organization, evolution, and expression of photoprotein and opsin genes in Mnemiopsis leidyi: A new view of ctenophore photocytes. BMC Biol. 2012, 10, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delroisse, J.; Ullrich-Luter, E.; Ortega-Martinez, O.; Dupont, S.; Arnone, M.I.; Mallefet, J.; Flammang, P. High opsin diversity in a non-visual infaunal brittle star. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delroisse, J.; Ullrich-Lüter, E.; Blaue, S.; Ortega-Martinez, O.; Eeckhaut, I.; Flammang, P.; Mallefet, J. Fine structure of the luminous spines and luciferase detection in the brittle star Amphiura filiformis. Zool. Anz. 2017, 269, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bracken-Grissom, H.D.; DeLeo, D.M.; Porter, M.L.; Iwanicki, T.; Sickles, J.; Frank, T.M. Light organ photosensitivity in deep-sea shrimp may suggest a novel role in counterillumination. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delroisse, J.; Duchatelet, L.; Flammang, P.; Mallefet, J. De novo transcriptome analyses provide insights into opsin-based photoreception in the lanternshark Etmopterus spinax. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0209767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCapra, F. Chemical mechanisms in bioluminescence. Acc. Chem. Res. 1976, 9, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaskova, Z.M.; Tsarkova, A.S.; Yampolsky, I.V. 1001 lights: Luciferins, luciferases, their mechanisms of action and applications in chemical analysis, biology and medicine. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 6048–6077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warner, J.A.; Case, J.F. The zoogeography and dietary induction of bioluminescence in the midshipman fish, Porichthys notatus. Biol. Bull. 1980, 159, 231–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, T.M.; Widder, E.A.; Latz, M.I.; Case, J.F. Dietary maintenance of bioluminescence in a deep-sea mysid. J. Exp. Biol. 1984, 109, 385–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, E.M.; Nafpaktitis, B.G.; Tsuji, F.I. Dietary uptake and blood transport of Vargula (crustacean) luciferin in the bioluminescent fish, Porichthys notatus. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 1988, 89, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddock, S.H.D.; Rivers, T.J.; Robison, B.H. Can coelenterates make coelenterazine? Dietary requirement for luciferin in cnidarian bioluminescence. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 11151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mallefet, J.; Duchatelet, L.; Coubris, C. Bioluminescence induction in the ophiuroid Amphiura filiformis (Echinodermata). J. Exp. Biol. 2020, 223, jeb218719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bessho-Uehara, M.; Yamamoto, N.; Shigenobu, S.; Mori, H.; Kuwata, K.; Oba, Y. Kleptoprotein bioluminescence: Parapriacanthus fish obtain luciferase from ostracod prey. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaax4942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, C.M.; Herring, P.J.; Campbell, A.K. Evidence for de novo biosynthesis of coelenterazine in the bioluminescent midwater shrimp, Systellaspis debilis. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 1995, 75, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oba, Y.; Kato, S.-I.; Ojika, M.; Inouye, S. Biosynthesis of coelenterazine in the deep-sea copepod, Metridia pacifica. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 390, 684–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bessho-Uehara, M.; Huang, W.; Patry, W.L.; Browne, W.E.; Weng, J.-K.; Haddock, S.H.D. Evidence for de novo biosynthesis of the luminous substrate coelenterazine in ctenophores. iScience 2020, 23, 101859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimomura, O. Presence of coelenterazine in non-bioluminescent marine organisms. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 1987, 86B, 361–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallefet, J.; Shimomura, O. Presence of coelenterazine in mesopelagic fishes from the Strait of Messina. Mar. Biol. 1995, 124, 381–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, C.M.; Herring, P.J.; Campbell, A.K. The widespread occurrence and tissue distribution of the imidazolopyrazine luciferins. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 2, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duchatelet, L.; Hermans, C.; Duhamel, G.; Cherel, Y.; Guinet, C.; Mallefet, J. Coelenterazine detection in five myctophid species from the Kerguelen Plateau. In The Kerguelen Plateau: Marine Ecosystem and Fisheries. Proceedings of the Second Symposium; Welsford, D., Dell, J., Duhamel, G., Eds.; Australian Antartic Division: Kingston, TAS, Australia; pp. 31–41.
- Renwart, M.; Mallefet, J. First study of the chemistry of the luminous system in a deep-sea shark, Etmopterus spinax Linnaeus, 1758 (Chondrichthyes: Etmopteridae). J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2013, 448, 214–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stingo, V.; Du Buit, M.-H.; Odierna, G. Genome size of some selachian fishes. Boll. Zool. 1980, 47, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojima, Y.; Yamamoto, K. Cellular DNA contents of fishes determined by flow cytometry. La Kromosomo II 1990, 57, 1871–1888. [Google Scholar]
- Hardie, D.C.; Hebert, P.D.N. The nucleotypic effects of cellular DNA content in cartilaginous and ray-finned fishes. Genome 2003, 46, 683–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marra, N.J.; Stanhope, M.J.; Jue, N.K.; Wang, M.; Sun, Q.; Bitar, P.P.; Richards, V.P.; Komissarov, A.; Rayko, M.; Kliver, S.; et al. White shark genome reveals ancient elasmobranch adaptations associated with wound healing and the maintenance of genome stability. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 4446–4455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, J.A.; Park, S.G.; Luria, V.; Jeon, S.; Kim, H.-M.; Jeon, Y.; Bhak, Y.; Jun, J.H.; Kim, S.W.; Hong, W.H.; et al. The whale shark genome reveals how genomic and physiological properties scale with body size. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 20662–20671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufresne, F.; Jeffery, N. A guided tour of large genome size in animals: What we know and where we are heading. Chromosome Res. 2011, 19, 925–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Duchatelet, L.; Claes, J.M.; Delroisse, J.; Flammang, P.; Mallefet, J. Glow on Sharks: State of the Art on Bioluminescence Research. Oceans 2021, 2, 822-842. https://doi.org/10.3390/oceans2040047
Duchatelet L, Claes JM, Delroisse J, Flammang P, Mallefet J. Glow on Sharks: State of the Art on Bioluminescence Research. Oceans. 2021; 2(4):822-842. https://doi.org/10.3390/oceans2040047
Chicago/Turabian StyleDuchatelet, Laurent, Julien M. Claes, Jérôme Delroisse, Patrick Flammang, and Jérôme Mallefet. 2021. "Glow on Sharks: State of the Art on Bioluminescence Research" Oceans 2, no. 4: 822-842. https://doi.org/10.3390/oceans2040047
APA StyleDuchatelet, L., Claes, J. M., Delroisse, J., Flammang, P., & Mallefet, J. (2021). Glow on Sharks: State of the Art on Bioluminescence Research. Oceans, 2(4), 822-842. https://doi.org/10.3390/oceans2040047