Study on the Synergistic Effect and Mechanism of Octenyl Succinic Anhydride-Modified Starch on the Stability of Myofibrillar Protein Emulsion
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Hydrophobic Starch Particles
2.3. Determination of Degree of Substitution (DS) of Hydrophobically Modified Starch
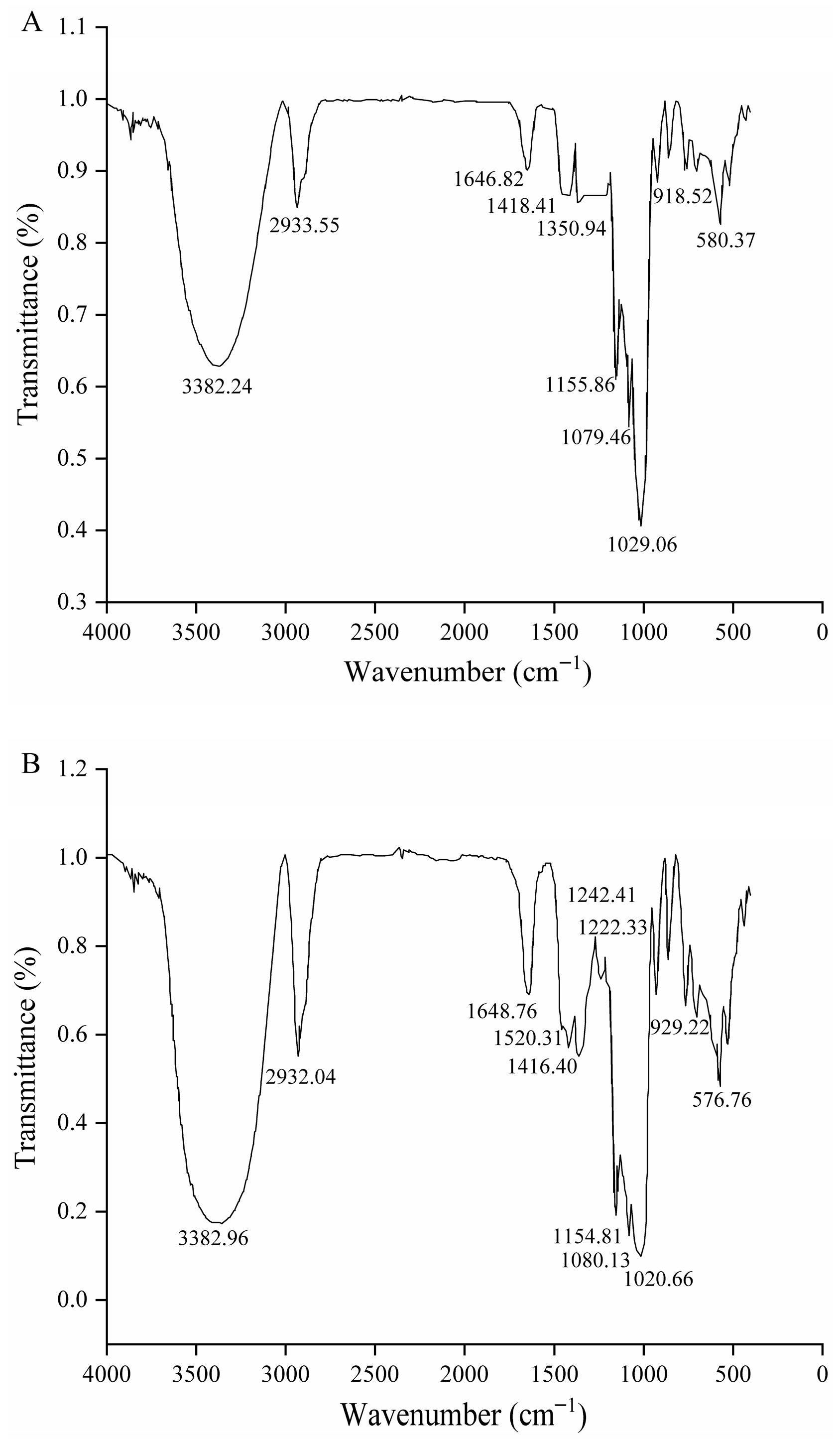
2.4. Determination of Hydrophobic Modified Starch by Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
2.5. Preparation of MP
2.6. Preparation of Emulsions
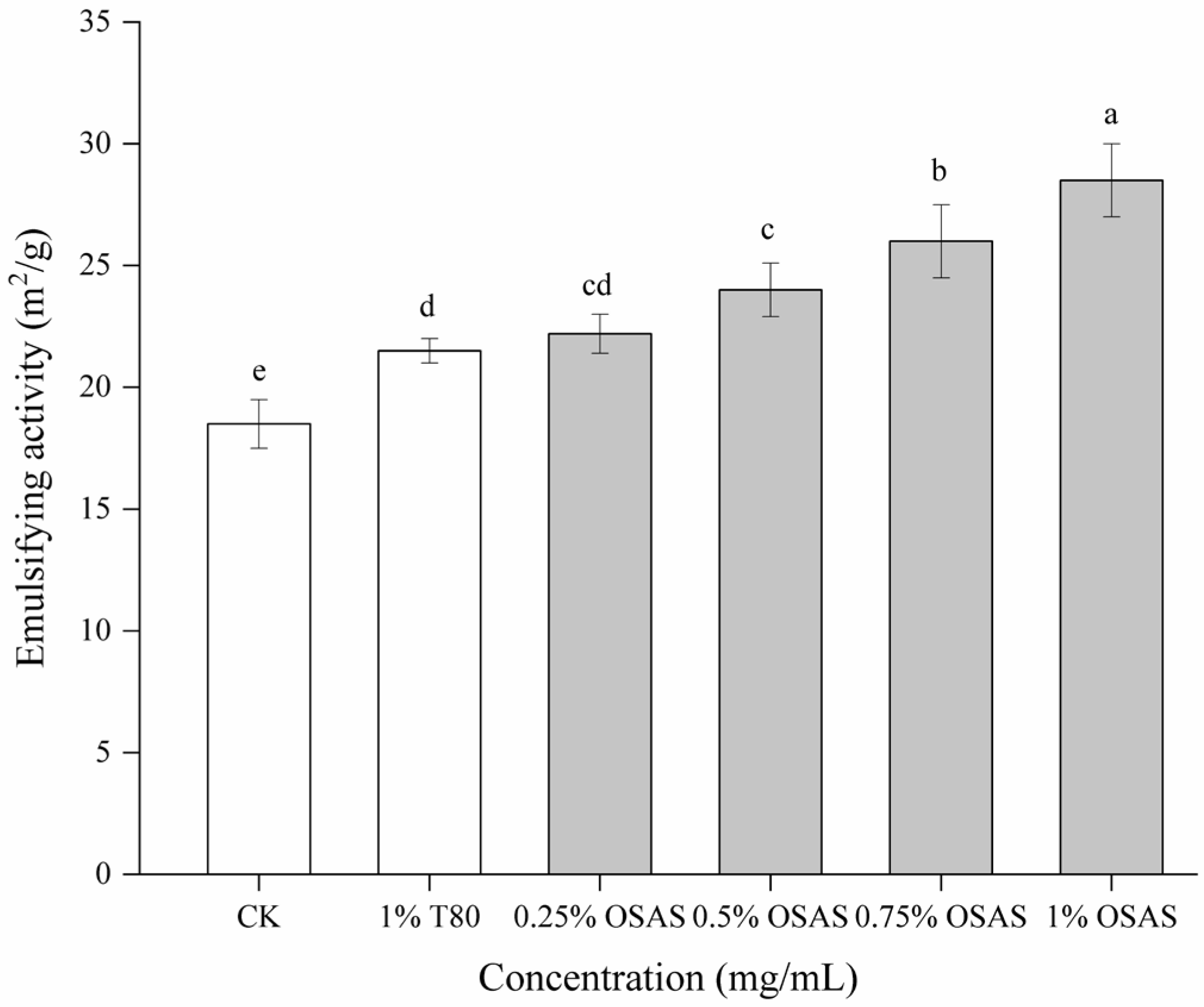
2.7. Emulsifying Properties
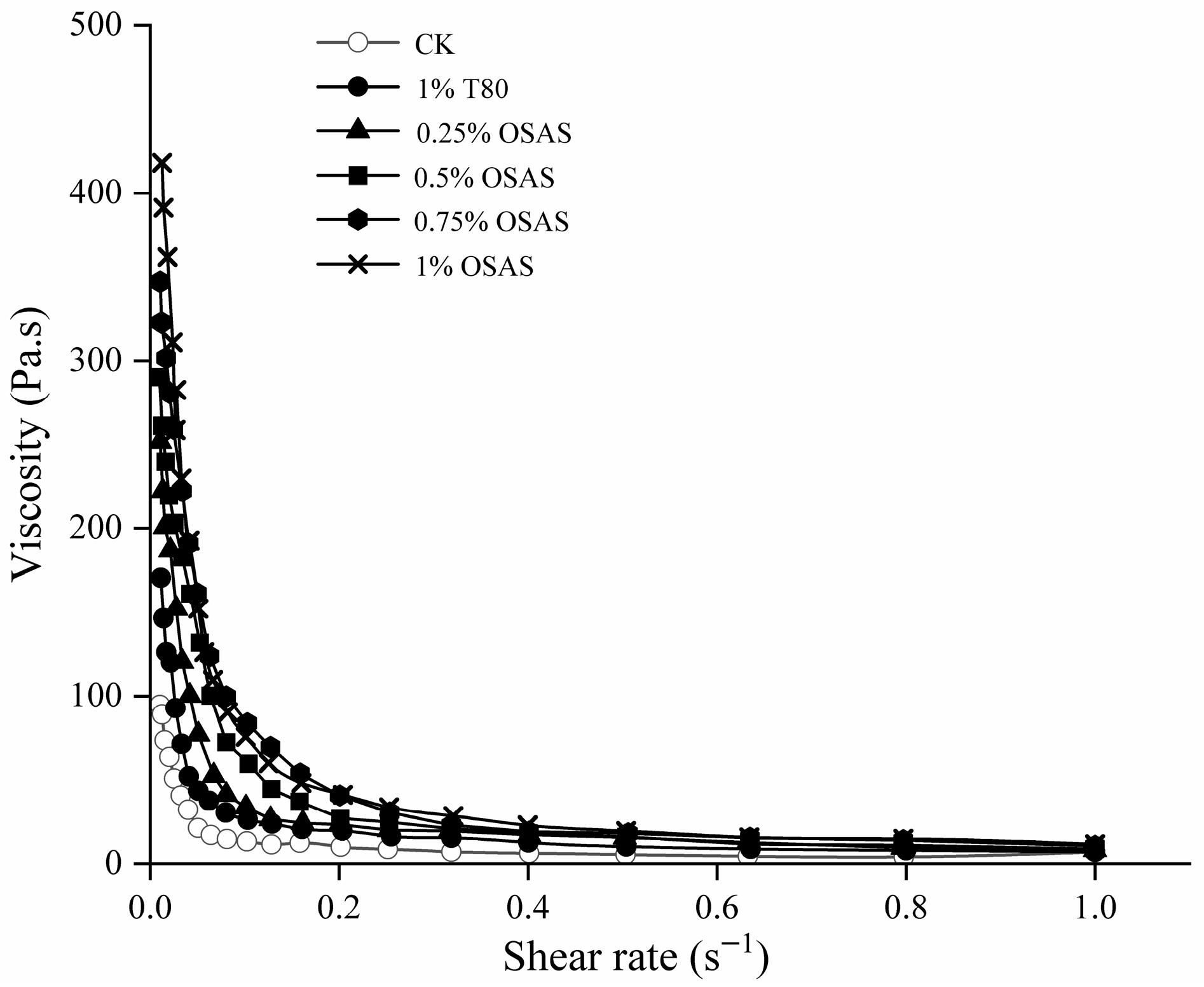
2.8. Viscosity of Emulsions
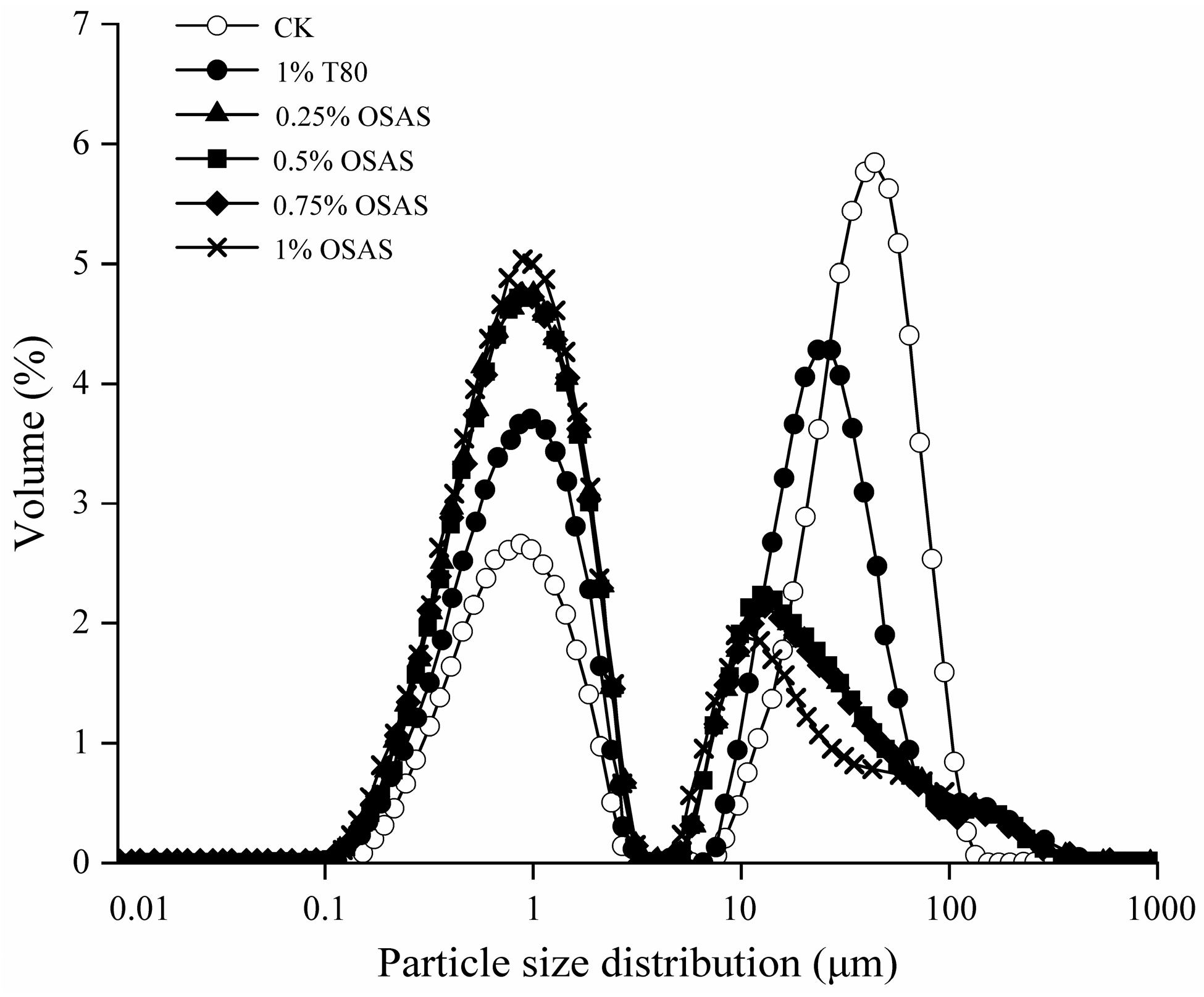
2.9. Determination of the Particle Size and Particle Size Distribution
2.10. Zeta Potential Measurements
2.11. Determination of Thiol Content in Emulsion
2.12. Determination of Interfacial Protein Content
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Hydrophobic Modified Starch Substitution Degree
3.2. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
3.3. Emulsifying Properties
3.4. Emulsion Apparent Viscosity
3.5. Emulsion Particle Size Distribution
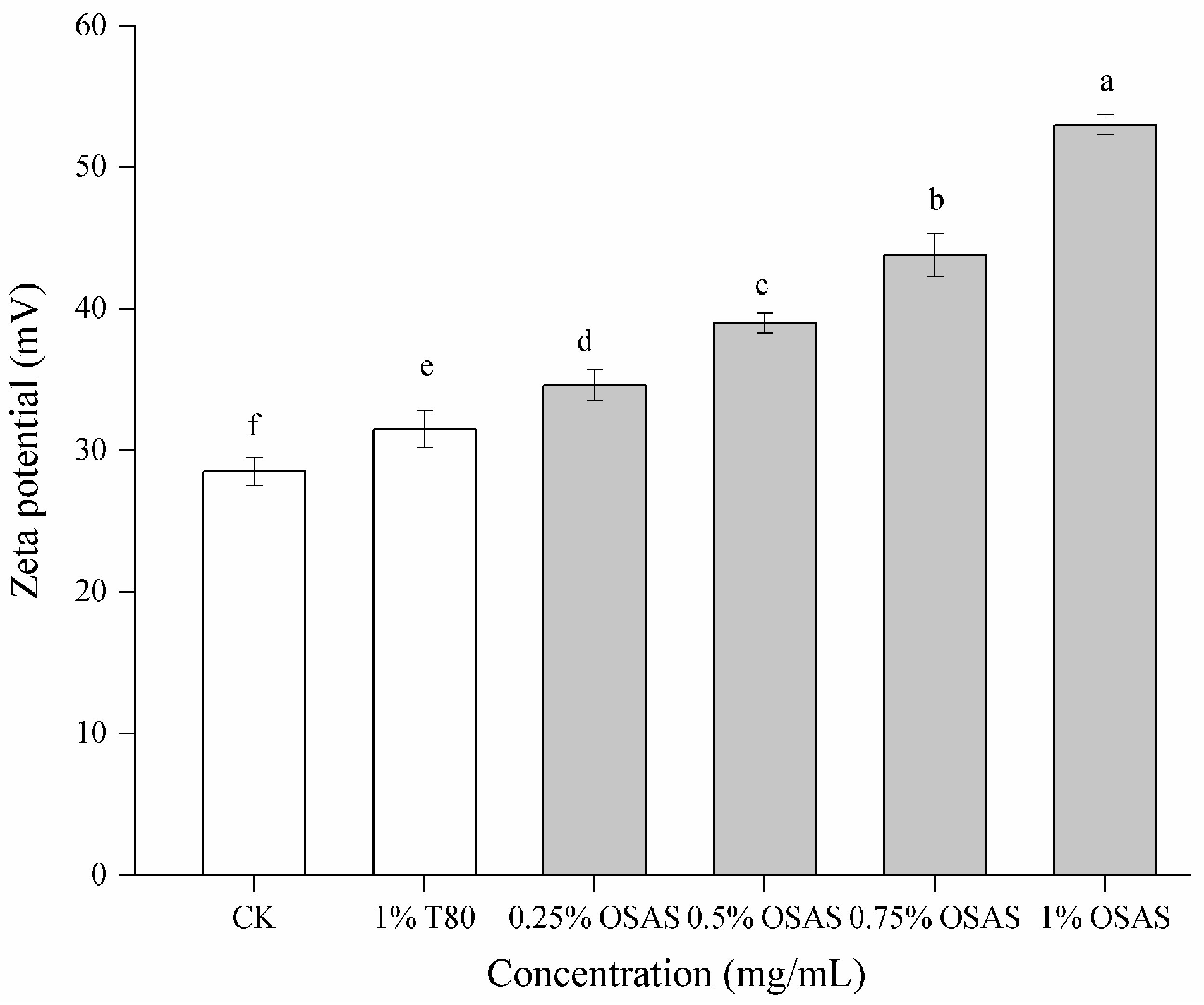
3.6. Emulsion Potential
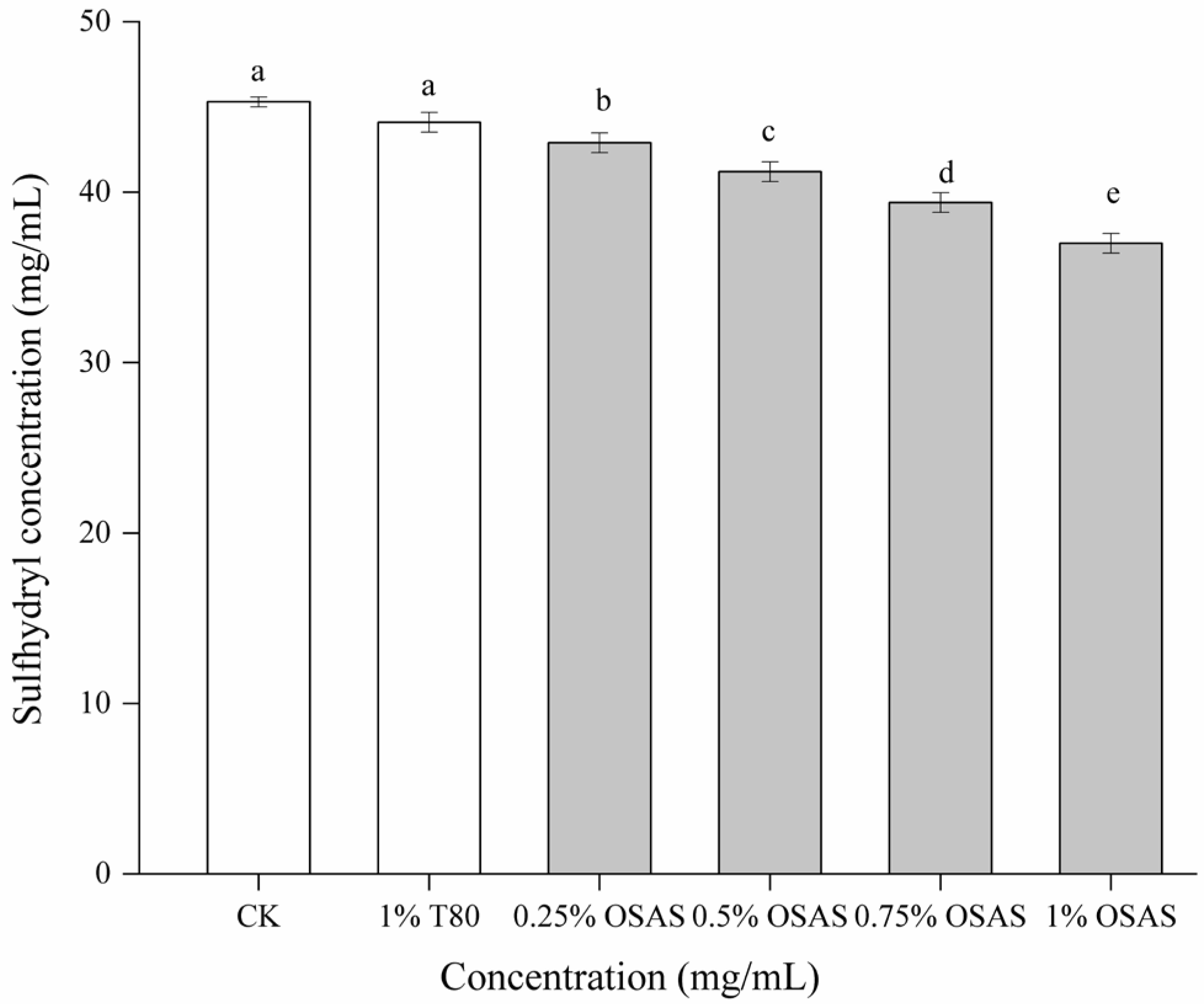
3.7. Emulsion Thiol Content
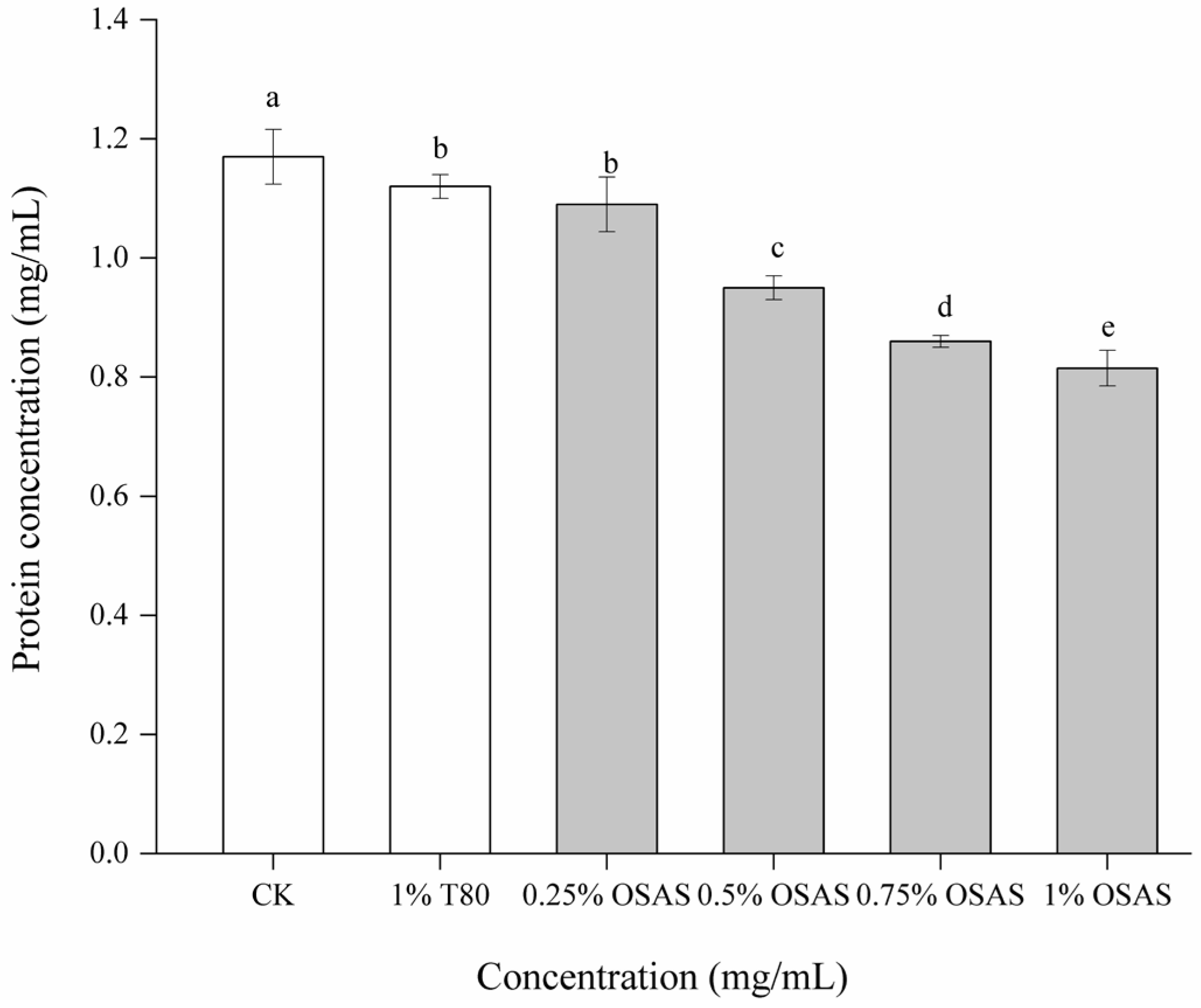
3.8. Content of Interfacial Protein in Composite Protein Emulsion
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhu, X.F.; Zhang, N.; Lin, W.F.; Tang, C.H. Freeze-thaw stability of Pickering emulsions stabilized by soy and whey protein particles. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 69, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickinson, E. Milk protein interfacial layers and the relationship to emulsion stability and rheology. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2001, 20, 197–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damodaran, S. Protein Stabilization of Emulsions and Foams. J. Food Sci. 2005, 70, 54–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tornberg, E.V.A. Effects of heat on meat proteins-Implications on structure and quality of meat products. Meat Sci. 2005, 70, 493–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schilling, M.W. Emulsifier applications in meat products. In Food Emulsifiers and Their Applications; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 347–377. [Google Scholar]
- Jimenez-Castano, L.; Lopez-Fandino, R.; Olano, A.; Villamiel, M. Study on β-lactoglobulin glycosylation with dextran: Effect on solubility and heat stability. Food Chem. 2005, 93, 689–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reger, M.; Sekine, T.; Okamoto, T.; Watanabe, K.; Hoffmann, H. Pickering emulsions stabilized by novel clay-hydrophobin synergism. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 11021–11030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binks, B.P.; Rocher, A. Effects of temperature on water in oil emulsions stabilized, solely by wax microparticles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 335, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Vogel, R.; Werner, S.; Heinrich, G.; Clausse, D.; Dutschk, V. Influence of the particle type on the rheological behavior of Pickering emulsions. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2011, 382, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Wang, C.; Liu, H.; Wang, C.; Liu, X.; Tong, Z. Suspension polymerization based on inverse Pickering emulsion droplets for thermos-sensitive hybrid microcapsules with tunable supracolloidal structures. Carbohydr. Polym. 2009, 50, 2587–2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevalier, Y.; Bolzinger, M.A. Emulsions stabilized with solid nanoparticles: Pickering emulsions. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2013, 439, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capron, I.; Cathala, B. Surfactant-free high internal phase emulsions stabilized by cellulose nanocrystals. Macromolecules. 2013, 14, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousseau, D. Trends in structuring edible emulsions with Pickering fat crystals. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 18, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.J.; Murray, B.S.; Ross, A.L.; Povey, M.J.W.; Morgan, M.R.A.; Day, A.J. Effects of pH on the ability of flavonoids to act as Pickering emulsion stabilizers. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2012, 92, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayner, M.; Marku, D.; Eriksson, M.; Sjöö, M.; Wahlgrena, M. Biomass-based particles for the formulation of Pickering type emulsions in food and topical applications. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2014, 458, 48–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prochaska, K.; Kedziora, P.; Le Thanh, J.; Lewandowicz, G. Surface activity of commercial food grade modified starches. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2007, 60, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanamai, R.; McClements, D.J. Depletion flocculation of beverage emulsions by gum arabic and modified starch. J. Food Sci. 2001, 66, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.H.; Liu, L.; Han, S.Y. Preparation of octyl-grafted alginate-amide gel particle and its application in Pickering emulsion. Colloids Surf. A 2017, 529, 320–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Luan, Y.; Tang, Z.; Li, Z.; Gu, C.; Liu, R.; Ge, Q.; Yu, H.; Wu, M. Consolidating the gelling performance of myofibrillar protein using a novel OSA-modified-starch-stabilized Pickering emulsion filler: Effect of starches with distinct crystalline types. Food Res. Int. 2023, 164, 112443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mi, H.; Wang, C.; Su, Q.; Li, X.; Yi, S.; Li, J. The effect of modified starches on the gel properties and protein conformation of Nemipterus virgatus surimi. J. Texture Stud. 2019, 50, 571–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dokic, L.; Krstonosic, V.; Nikolic, I. Physicochemical characteristics and stability of oil-in-water emulsions stabilized by OSA starch. Food Hydrocoll. 2012, 29, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remya, R.; Jyothi, A.N.; Sreekumar, J. Morphological, structural and digestibility properties of RS4 enriched octenyl succinylated sweet potato, banana and lentil starches. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 82, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Li, Y.; Goff, H.D.; Nsor-Atindana, J.; Zhong, F. Distribution of octenylsuccinic groups in modified waxy maize starch: An analysis at granular level. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 84, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.; Xiong, Y.L.; Alderton, A.L. Concentration effects of hydroxyl radical oxidizing systems on biochemical properties of porcine muscle myofibrillar protein. Food Chem. 2007, 101, 1239–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Xu, Y.; Gu, C.; Wang, J.; Wang, Q.; Yin, P.; Yu, H. Characteristics of OSA modified starch-based Pickering emulsion and its application to myofibrillar protein gel. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2025, 105, 3397–3405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Q.; Dai, H.; Wen, L.; Zheng, W.; Li, B.; Dai, J.; Li, B.; Chen, Y. Effects of pH-shifting treatments on the emulsifying properties of rice protein isolates: Quantitative analysis of interfacial protein layer. Food Res. Int. 2023, 164, 112306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Mu, T.H. Emulsifying properties of sweet potato protein: Effect of protein concentration and oil volume fraction. Food Hydrocoll. 2011, 25, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keerati-U-Rai, M.; Corredig, M. Heat-induced changes in oil-in-water emulsions stabilized with soy protein isolate. Food Hydrocoll. 2009, 23, 2141–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crudden, A.; Afoufa-Bastien, D.; Fox, P.F.; Brisson, G.; Kelly, A.L. Effect of hydrolysis of casein by plasmin on the heat stability of milk. Int. Dairy J. 2005, 15, 1017–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Ye, A.; Singh, H. Characterizations of emulsion gel formed with the mixture of whey and soy protein and its protein digestion under in vitro gastric conditions. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2024, 8, 100674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Ai, M.; Cao, Y.; Long, J.; Li, S.; Jiang, A. Understanding the hydration of alkali-induced duck egg white gel at high temperature. LWT 2021, 142, 110976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altuna, L.; Herrera, M.L.; Foresti, M.L. Synthesis and characterization of octenyl succinic anhydride modified starches for food applications. A review of recent literature. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 80, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.M.; Fowler, P.A.; Sayers, C.; Williams, P.A. The chemical modification of a range of starches under aqueous reaction conditions. Carbohydr. Polym. 2004, 55, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omana, D.A.; Xu, Y.; Moayedi, V.; Betti, M. Alkali-aided protein extraction from chicken dark meat: Chemical and functional properties of recovered proteins. Process Biochem. 2010, 45, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Ma, Y.; Li, X.; Yan, T.; Cui, J. Effects of milk protein-polysaccharide interactions on the stability of ice cream mix model systems. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 45, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickinson, E. Hydrocolloids at interfaces and the influence on the properties of dispersed systems. Food Hydrocoll. 2003, 17, 25–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Yang, J.; Shao, G.; Liu, J.; Wang, J.; Yang, L.; Li, J.; Liu, H.; Zhu, D.; Li, Y.; et al. pH-induced conformational changes and interfacial dilatational rheology of soy protein isolated/soy hull polysaccharide complex and its effects on emulsion stabilization. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 109, 106075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, A.; Hemar, Y.; Singh, H. Enhancement of coalescence by xanthan addition to oil-in-water emulsions formed with extensively hydrolysed whey proteins. Food Hydrocoll. 2004, 18, 737–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Sanchez, P.; Fredriksson, N.; Larsson, A.; Altskar, A.; Strom, A. High sugar content impacts microstructure, mechanics and release of calcium-alginate gels. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 84, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutin, C.; Giroux, H.J.; Paquin, P.; Britten, M. Characterization and acid-induced gelation of butter oil emulsions produced from heated whey protein dispersions. Int. Dairy J. 2007, 17, 693–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Tang, C.H. Cold, gel-like whey protein emulsions by microfluidisation emulsification: Rheological properties and microstructures. Food Chem. 2011, 127, 1641–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, G.P.; Min, S.G.; Chin, K.B. Emulsion properties of pork myofibrillar protein in combination with microbial transglutaminase and calcium alginate under various pH conditions. Meat Sci. 2012, 90, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golovkova, I.; Montel, L.; Wandersman, E.; Bertrand, T.; Prevost, A.M.; Pontani, L.L. Depletion attraction impairs the plasticity of emulsions flowing in a constriction. Soft Matter 2020, 16, 3294–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Belwal, T.; Li, L.; Lin, X.; Xu, Y.; Luo, Z. Recent advances in polysaccharides stabilized emulsions for encapsulation and delivery of bioactive food ingredients: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 242, 116388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumann, H.; Khatib, M.; Tutkun, M.H.; Pettersen, B.; Yang, Z.; Nydal, O.J. Droplet size measurements in oil-water dispersions: A comparison study using FBRM and PVM. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2015, 36, 1432–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, X.; Guan, H.; Zhao, X.; Chen, Q.; Kong, B. Properties and oxidative stability of emulsions prepared with myofibrillar protein and lard diacylglycerols. Meat Sci. 2016, 115, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perissutti, G.E.; Bresolin, T.M.B.; Ganter, J.L.M.S. Interaction between the galactomannan from Mimosa scabrella and milk proteins. Food Hydrocoll. 2002, 16, 403–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Liu, H.; Li, Y.; Tian, J.; Liu, X. Characterization of Pickering emulsions stabilized by OSA-modified sweet potato residue cellulose: Effect of degree of substitute and concentration. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 108, 105915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcclements, D.J. Critical review of techniques and methodologies for characterization of emulsion stability. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2007, 47, 611–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krstonosic, V.; Dokic, L.; Dokic, P.; Dapcevic, T. Effects of xanthan gum on physicochemical properties and stability of corn oil-in-water emulsions stabilized by polyoxyethylene (20) sorbitan monooleate. Food Hydrocoll. 2009, 23, 2212–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzey, D.; Kim, H.J.; McClements, D.J. Factors influencing the production of o/w emulsions stabilized by β-lactoglobulin-pectin membranes. Food Hydrocoll. 2004, 18, 967–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, M.; Karthik, P.; Chen, J.; Holmes, M.; Ettelaie, R. Effect of amylose and amylopectin content on the colloidal behaviour of emulsions stabilised by OSA-Modified starch. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 111, 106363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazith, J.; Himmelfarb, S.; Harrington, W.F. Studies on the subunit structure of myosin. J. Biol. Chem. 1970, 245, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, H.; He, Y.; Fu, L.; Xiong, H.; Lu, M.; Zhang, C.; Chen, L. Effects of blackberry (Rubus spp.) polysaccharide on the structure and thermal behavior of the myofibrillar protein of chicken breast meat. Food Chem. X 2023, 20, 100914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, B.; Deng, W.; Xu, K.; Huang, L.; Yao, P. Stable nano-sized emulsions produced from soy protein and soy polysaccharide complexes. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 380, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tcholakova, S.; Denkov, N.D.; Danner, T. Role of surfactant type and concentration for the mean drop size during emulsification in turbulent flow. Langmuir 2004, 20, 7444–7458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeboah, G.B.; Wang, S.; Wu, W.; Zhang, H.; Donkor, P.O.; Wu, J.; Cheng, Y. Interfacial composition on the mechanical properties, microstructure and digestion of emulsion-filled whey protein gels: Effect of soy and whey protein ratios. Food Biosci. 2025, 64, 105886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Treatment | Time | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 min | 30 min | 60 min | 120 min | |
| CK (1% MP) | 0.292 ± 0.033 fA | 0.251 ± 0.010 fB | 0.232 ± 0.031 fC | 0.212 ± 0.041 fD |
| MP + 1% T80 | 0.313 ± 0.020 eA | 0.294 ± 0.023 eB | 0.262 ± 0.040 eC | 0.242 ± 0.053 eD |
| MP + 0.25% OSAS | 0.402 ± 0.031 dA | 0.358 ± 0.054 dB | 0.287 ± 0.070 dC | 0.253 ± 0.034 dD |
| MP + 0.5% OSAS | 0.511 ± 0.022 cA | 0.425 ± 0.043 cB | 0.398 ± 0.032 cC | 0.303 ± 0.050 cD |
| MP + 0.75% OSAS | 0.589 ± 0.063 bA | 0.503 ± 0.070 bB | 0.455 ± 0.040 bC | 0.351 ± 0.053 bD |
| MP + 1% OSAS | 0.612 ± 0.030 aA | 0.568 ± 0.030 aB | 0.503 ± 0.063 aC | 0.468 ± 0.070 aD |
| Treatment | D(x) 10 | D(x) 50 | D(x) 90 |
|---|---|---|---|
| CK (1% MP) | 0.575 ± 0.025 a | 26.354 ± 0.722 a | 77.453 ± 0.802 a |
| MP + 1% T 80 | 0.522 ± 0.009 b | 18.264 ± 0.912 b | 52.049 ± 0.800 b |
| MP + 0.25% OSAS | 0.486 ± 0.006 c | 12.657 ± 1.129 c | 36.214 ± 0.954 c |
| MP + 0.5% OSAS | 0.426 ± 0.007 d | 6.824 ± 0.125 d | 34.269 ± 0.764 c |
| MP + 0.75% OSAS | 0.398 ± 0.012 de | 1.569 ± 0.006 e | 31.069 ± 1.356 d |
| MP + 1% OSAS | 0.375 ± 0.004 e | 1.262 ± 0.004 e | 28.654 ± 0.695 e |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yin, P.; Bi, X.; Xu, Y.; Zhu, T.; Yin, Q.; Wang, Q.; Wu, M. Study on the Synergistic Effect and Mechanism of Octenyl Succinic Anhydride-Modified Starch on the Stability of Myofibrillar Protein Emulsion. Chemistry 2025, 7, 113. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry7040113
Yin P, Bi X, Xu Y, Zhu T, Yin Q, Wang Q, Wu M. Study on the Synergistic Effect and Mechanism of Octenyl Succinic Anhydride-Modified Starch on the Stability of Myofibrillar Protein Emulsion. Chemistry. 2025; 7(4):113. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry7040113
Chicago/Turabian StyleYin, Peipei, Xiaozhong Bi, Yuyu Xu, Tianhao Zhu, Qing Yin, Qingling Wang, and Mangang Wu. 2025. "Study on the Synergistic Effect and Mechanism of Octenyl Succinic Anhydride-Modified Starch on the Stability of Myofibrillar Protein Emulsion" Chemistry 7, no. 4: 113. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry7040113
APA StyleYin, P., Bi, X., Xu, Y., Zhu, T., Yin, Q., Wang, Q., & Wu, M. (2025). Study on the Synergistic Effect and Mechanism of Octenyl Succinic Anhydride-Modified Starch on the Stability of Myofibrillar Protein Emulsion. Chemistry, 7(4), 113. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry7040113







