Abstract
Using the formulation of the electromagnetic Green’s function of a perfectly conducting cone in terms of analytically continued angular momentum, we compute the Casimir–Polder interaction energy of a cone with a polarizable particle. We introduce this formalism by first reviewing the analogous approach for a perfectly conducting wedge, and then demonstrate the calculation through numerical evaluation of the resulting integrals.
1. Introduction
The Casimir–Polder interaction between an uncharged conducting object on a polarizable particle [1,2,3] provides one of the simplest examples of a mesoscopic fluctuation-based force. Since the particle can be treated as a delta-function potential, its effects can be evaluated in any basis. As a result, in the scattering formalism, the interaction energy between the particle and conducting object can be determined directly from the full electromagnetic Green’s function in the presence of the object. In contrast, for the Casimir force between two objects, one needs the scattering T-matrices for each object connected by the free Green’s function expressed in each object’s scattering basis to propagate fluctuations between objects [4,5,6,7,8,9].
Along with the standard plane, cylinder, and sphere geometries, for which there exist analytic expressions in terms of scattering modes for the Green’s function in the presence of a perfect conductor, the conducting wedge [10,11], which also models a cosmic string [12], is a case where the Green’s function can be obtained analytically as a mode sum, by imposing the wedge boundary conditions through a discrete, fractional, angular momentum index. However, one can also use analytic continuation to a continuous, complex angular momentum to express this Green’s function in terms of the T-matrix for scattering in the angular (rather than radial) variable [13,14,15,16], an approach that then extends to the case of the cone [16] and puts the Green’s function into a form that is more directly analogous to the sphere, cylinder, and plane results. Mathematically, this approach is based on the Mehler–Fock and Kontorovich–Lebedev transforms [17]. The complex angular momentum approach requires that one consider only imaginary frequencies, however, so though it is well-suited to equilibrium problems at both zero and nonzero temperature, it cannot be applied to heat transfer [18], which must be computed on the real axis.
All of these calculations allow for investigation of the Casimir–Polder interaction near a sharp edge or tip, where the derivative expansion approach [19,20,21,22,23] is not applicable, yielding semi-analytic results in terms of a small number of integrals and sums. However, this approach is limited to perfect conductors and, as a result, complements calculations based on surface current methods [24,25,26,27], which are more complex numerically, but applicable to more general geometries and materials. Recent work using the multiple scattering surface method, in which one combines expansions in scattering between and within objects [28], provides a particularly relevant comparison by demonstrating the Casimir force between a dielectric wedge and plane.
Here we use the analytically continued scattering formalism to calculate the Casimir–Polder force of a conducting cone on a polarizable atom, as might arise, for example, in the case of a particle beam passing by an atomic force microscope. We begin by reviewing the wedge calculation in the discrete angular momentum approach, and show how to obtain the same result using the analytic continuation approach. We then extend this calculation to the case of the cone, obtaining a result in terms of a sum and integral over angular momentum variables. For a special case where the particle lies on the cone axis, the calculation simplifies to a single integral. This calculation can be straightforwardly extended to frequency-dependent polarizability and nonzero temperature, although, in those cases, an additional sum or integral over frequency must be done numerically.
2. Review of Casimir–Polder Wedge
Let us begin by reviewing the Casimir–Polder interaction energy for a conducting wedge, which was computed in Refs. [10,29] and considered in the context of repulsive forces in Refs. [30,31]. Let the wedge run parallel to the z-axis and have a half-opening angle around with the wedge vertex located at , and consider imaginary wavenumber with . Note that by allowing , one is able to consider a case where the particle is inside the wedge. For a particle located at angle obeying , one can write the full Green’s function for the wedge in terms of ordinary cylindrical wavefunctions of fractional order [10,11],
in terms of the magnetic (transverse electric) and electric (transverse magnetic) modes, respectively,
with ℓ the quantum number, the hat denoting unit vector, and , where the regular (outgoing) function is evaluated at the point or with the smaller (larger) value of the cylindrical radius r and the radial functions given in terms of Bessel functions for regular and outgoing modes as:
This Green’s function then obeys:
in the presence of the conducting wedge, whereas the free Green’s function , given by setting and replacing the trigonometric functions and in Equation (2) with , obeys the same equation in empty space.
One can then use the “TGTG” (T-matrix/free Green’s function) [4,5,6,7,8,9] formulation of the Casimir energy, considering only the lowest-order interaction with the potential for a particle with polarizability at position ,
which can be expressed in any basis since it is a delta function, .
The result for the interaction energy of a particle with isotropic polarizability becomes [10,29]:
where ℏ is the reduced Planck’s constant, c denotes the speed of light, ‘’ denotes the trace, which includes the trace over the spatial coordinate, and ‘’ denotes the trace only over polarizations. In this approach, there is not a straightforward way to subtract the free contribution mode-by-mode, so one instead uses a point-splitting argument to subtract the entire contribution from the free Green’s function at once.
For the case of the cone, there does not exist an analog of this full Green’s function written in terms of a rescaled order. As a result, we next recompute the result for the wedge using a different form of the Green’s function, which generalizes more readily to the case of the cone. In this approach, the angular momentum sum is replaced via analytic continuation by an integral, yielding for the free Green’s function [13,16]:
where the transverse modes are:
and . One has both even and odd modes, with regular modes given by:
and outgoing modes given by
where denotes the analytically continued angular quantum number, and the regular (outgoing) functions are evaluated at the point or with the smaller (larger) value of . Note that the star indicates the conjugation of the complex exponential part of the function only.
Although not needed for the computation, the corresponding longitudinal mode is:
If its contribution is added to the free Green’s function, the result is equal to the scalar Green’s function, , times the identity matrix; without this contribution, one obtains the same scalar times the projection matrix on to the transverse components. Here, () is the z coordinate associated with the point with the larger (smaller) value of .
In this approach, we take the wedge to be located at and the particle’s location will always have . One then obtains the full Green’s function by replacing the regular solution with a combination of regular and outgoing solutions given in terms of the T-matrix:
so that it now obeys the conducting boundary conditions on the wedge, yielding:
In this form, one can subtract the free Green’s function mode-by-mode, leaving only the terms with outgoing waves multiplied by the T-matrix. One obtains for the energy:
where the integrals over and are done using polar coordinates. After carrying out the integral, one obtains agreement with Equation (6).
3. Electromagnetic Cone Green’s Function
Let us now construct the Green’s function for the perfectly conducting cone with half-opening angle , centered on the z-axis with the cone vertex at , as shown in Figure 1. We again consider imaginary wavenumber with . Note that by allowing , one can consider a case where the particle is inside the cone. From Ref. [16], one has magnetic (transverse electric) and electric (transverse magnetic) transverse modes:
with
where is the Legendre function of the first kind and is the modified spherical Bessel function of the third kind, both with complex degree/order . The “ghost” mode [16] is:
where the ± sign is for regular (‘+’) and outgoing (‘−’) modes. Its contribution arises from the contour integral used to turn the sum over the angular momentum quantum number ℓ into the integral over its analytic continuation , in which it cancels the contribution from the mode, since that mode does not exist in electromagnetism. As a result, it is only ever evaluated at , corresponding to .
Figure 1.
Geometry of cone with half-opening angle and particle at radius r and angle .
In this basis, the free Green’s function is [16]:
where the regular (outgoing) function is evaluated at the point or with the smaller (larger) value of , and is the gamma function. Note that, as above, the star indicates the conjugation of the complex exponential part of the function only. Here, the integral over represents the analytic continuation of the sum over ℓ.
For completeness, we also give the longitudinal mode:
for this geometry. If its contribution is added to the free Green’s function, the result is equal to the scalar Green’s function times the identity matrix; without this contribution, one obtains the same scalar times the projection matrix on to the transverse components.
The full Green’s function in the presence of the conducting boundary is then given by the same expression with the replacement, , where ; again, the star indicates the conjugation of the complex exponential part of the function only, and is the corresponding T-matrix element [16],
in terms of , the half-opening angle of the cone. Subtracting the contribution from the free Green’s function then cancels the term with the regular solution, leaving only the product of outgoing solutions in the interaction energy.
4. Electromagnetic Cone Casimir–Polder Energy
After some algebra and simplification, one obtains the Casimir–Polder interaction energy for an atom with isotropic and frequency-independent polarizability at distance r from the cone vertex and angle from the cone axis, with , as:
where the last term arises from the “ghost” mode contribution. Here,
is used [32] to carry out the integral over , with integrals involving derivatives with respect to r obtained by differentiating under the integral sign. The ghost term can be computed using the derivative of a geometric series,
along with an elementary integral.
One can check the result (21) numerically in the case of , when this result becomes the Casimir–Polder energy of a particle at a distance from a conducting plane, . Let us also note that the difference of T-matrices simplifies to
by using the Wronskian relation between and .
Carefully taking the limit , one obtains a special case where the particle lies on the cone axis. Here, the only contributions arise from , leading to a result that simplifies to:
for the cone–particle interaction energy when . Here, it is helpful to obtain the result in the first line, before integration over , because that result can straightforwardly be extended to nonzero temperature and frequency-dependent polarization, as will be described in more detail below.
Within this special case, it is illustrative to consider , where the cone becomes a plane, for which and . One then uses the integrals above along with the integrals [32,33] (the second integral does not appear to have been obtained previously):
where, again, the integrals involving derivatives with respect to r are obtained by differentiating under the integral sign, to do both the and integrals explicitly and in either order and obtain the standard results for the plane,
where, in the second line, we have done the integral first and, in the third line, we have done the integral first. The former expression shows that if the ghost contribution is grouped with the electric modes, the contributions from the electric and magnetic modes match the planar calculation individually as functions of , and, as a result, reproduce the 5:1 ratio of the total contributions of the electric and magnetic modes [34].
5. Anisotropic Polarizability
By repeating the above calculation in the case where is a matrix, one can extend these results to the case of an anisotropic particle. We write the polarizability in the general form:
which includes both the symmetric and antisymmetric (nonreciprocal) off-diagonal components. Without loss of generality, we take the particle to be at , so that it lies in the -plane. In terms of these parameters, one obtains for the energy:
which, on the axis , simplifies to
Of particular interest is the term, which generates a nonreciprocal torque around the z-axis. Comparing the and contributions also enables us to compare whether a particle with a single polarization axis prefers to be aligned with or perpendicular to the axis of the cone.
6. Results and Discussion
To visualize these results numerically, in Figure 2, the Casimir–Polder interaction energy of an isotropic particle is plotted scaled by the fourth power of , which gives the perpendicular distance from the particle to the plane in the case where . For , the result in units of is , and past this inflection point, as the the cone envelops the particle, its interaction becomes much stronger.
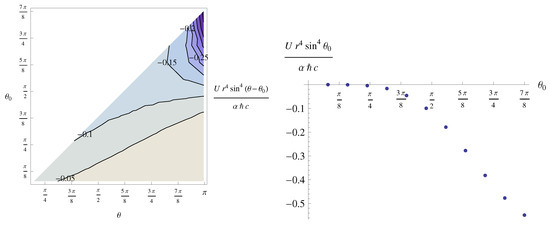
Figure 2.
Scaled Casimir–Polder interaction energy, , for an isotropic particle as a function of and (left) and as a function of for (right). See text for details.
All of the above calculations can be extended to nonzero equilibrium temperature T, in which case the integral over from 0 to ∞ is replaced by times the sum over Matsubara frequencies, , for all , where the contribution is counted with a weight of . This term must be considered carefully, since the Bessel function has a logarithmic singularity as for fixed . For the special case of , one can see explicitly from the above that this singularity disappears when the integral over is done first, which should remain the case in general. In all of these calculations, one can also straightforwardly move inside the integral or sum to model a frequency-dependent polarizability. However, introducing either or both nonzero temperature and frequency-dependent polarizability then requires the sum or integral to be carried out numerically.
Funding
N.G. is supported in part by the National Science Foundation (NSF) through grant PHY-2205708.
Data Availability Statement
All supporting data are available on request.
Acknowledgments
It is a pleasure to thank M. Kardar for suggesting this problem and, along with K. Asheichyk, T. Emig, D. Gelbwaser, and M. Krüger, for helpful conversations and feedback.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflict of interest.
References
- Casimir, H.B.G.; Polder, D. The influence of retardation on the London-van der Waals forces. Phys. Rev. 1948, 73, 360–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukenik, C.I.; Boshier, M.G.; Cho, D.; Sandoghdar, V.; Hinds, E.A. Measurement of the Casimir–Polder force. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1993, 70, 560–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harber, D.M.; Obrecht, J.M.; McGuirk, J.M.; Cornell, E.A. Measurement of the Casimir–Polder force through center-of-mass oscillations of a Bose-Einstein condensate. Phys. Rev. A 2005, 72, 033610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langbein, D. Theory of Van der Waals Attraction; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambrecht, A.; Maia Neto, P.A.; Reynaud, S. The Casimir effect within scattering theory. New J. Phys. 2006, 8, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emig, T.; Jaffe, R.L.; Kardar, M.; Scardicchio, A. Casimir interaction between a plate and a cylinder. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2006, 96, 080403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kenneth, O.; Klich, I. Opposites attract: A theorem about the Casimir force. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2006, 97, 160401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emig, T.; Graham, N.; Jaffe, R.; Kardar, M. Casimir forces between arbitrary compact objects. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2007, 99, 170403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahi, S.J.; Emig, T.; Graham, N.; Jaffe, R.L.; Kardar, M. Scattering theory approach to electrodynamic Casimir forces. Phys. Rev. D 2009, 80, 085021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deutsch, D.; Candelas, P. Boundary effects in quantum field theory. Phys. Rev. D 1979, 20, 3063–3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brevik, I.; Lygren, M. Casimir effect for a perfectly conducting wedge. Ann. Phys. 1996, 251, 157–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helliwell, T.M.; Konkowski, D.A. Vacuum fluctuations outside cosmic strings. Phys. Rev. D 1986, 34, 1918–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oberhettinger, F. Diffraction of waves by a wedge. Commun. Pure Appl. Math. 1954, 7, 551–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carslaw, H.S. The scattering of sound waves by a cone. Math. Ann. 1914, 75, 133–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felsen, L. Plane-wave scattering by small-angle cones. IEEE Trans. Anten. Propag. 1957, 5, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maghrebi, M.F.; Rahi, S.J.; Emig, T.; Graham, N.; Jaffe, R.L.; Kardar, M. Analytical results on Casimir forces for conductors with edges and tips. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 6867–6871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakubovich, S.B. Index Transforms; World Scientific: Singapore, 1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krüger, M.; Bimonte, G.; Emig, T.; Kardar, M. Trace formulas for nonequilibrium Casimir interactions, heat radiation, and heat transfer for arbitrary objects. Phys. Rev. B 2012, 86, 115423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fosco, C.D.; Lombardo, F.C.; Mazzitelli, F.D. Proximity force approximation for the Casimir energy as a derivative expansion. Phys. Rev. D 2011, 84, 105031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bimonte, G.; Emig, T.; Kardar, M. Casimir–Polder interaction for gently curved surfaces. Phys. Rev. D 2014, 90, 081702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bimonte, G.; Emig, T.; Jaffe, R.L.; Kardar, M. Casimir forces beyond the proximity approximation. Europhys. Lett. (EPL) 2012, 97, 50001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bimonte, G.; Emig, T.; Jaffe, R.L.; Kardar, M. Spectroscopic probe of the van der Waals interaction between polar molecules and a curved surface. Phys. Rev. A 2016, 94, 022509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bimonte, G.; Emig, T.; Kardar, M. Material dependence of Casimir forces: Gradient expansion beyond proximity. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 100, 074110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, A.; Ibanescu, M.; Iannuzzi, D.; Joannopoulos, J.D.; Johnson, S.G. Virtual photons in imaginary time: Computing exact Casimir forces via standard numerical electromagnetism techniques. Phys. Rev. A 2007, 76, 032106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homer Reid, M.T. Efficient computation of Casimir interactions between arbitrary 3D objects. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2009, 103, 040401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Homer Reid, M.T.; White, J.; Johnson, S.G. Fluctuating surface currents: An algorithm for efficient prediction of Casimir interactions among arbitrary materials in arbitrary geometries. Phys. Rev. A 2013, 88, 022514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bimonte, G.; Emig, T. Unifying theory for Casimir forces: Bulk and surface formulations. Universe 2021, 7, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emig, T.; Bimonte, G. Multiple scattering expansion for dielectric media: Casimir effect. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2023, 130, 200401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brevik, I.; Lygren, M.; Marachevsky, V. Casimir–Polder effect for a perfectly conducting wedge. Ann. Phys. 1998, 267, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milton, K.A.; Abalo, E.K.; Parashar, P.; Pourtolami, N.; Brevik, I.; Ellingsen, S.Å. Casimir–Polder repulsion near edges: Wedge apex and a screen with an aperture. Phys. Rev. A 2011, 83, 062507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milton, K.A.; Abalo, E.K.; Parashar, P.; Pourtolami, N.; Brevik, I.; Ellingsen, S.Å. Repulsive Casimir and Casimir–Polder forces. J. Phys. Math. Theor. 2012, 45, 374006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gradshteyn, I.S.; Ryzhik, I.M. Table of Integrals, Series, and Products; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2007; Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/book/9780123736376/table-of-integrals-series-and-products (accessed on 15 September 2023).
- Oberhettinger, F.; Higgins, T.P. Tables of Lebedev, Mehler and Generalized Mehler Transforms; Boeing Scientific Research Laboratories: Washington, DC, USA, 1961; Available online: https://apps.dtic.mil/sti/tr/pdf/AD0267210.pdf (accessed on 15 September 2023).
- Milton, K.A. Casimir–Polder forces in inhomogeneous backgrounds. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 2019, 36, C41–C45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).