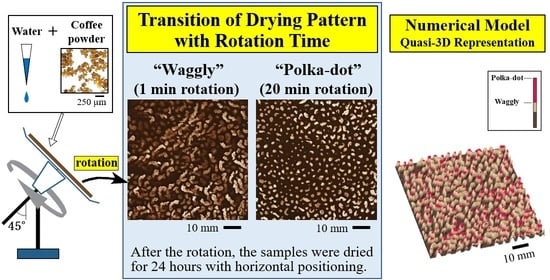
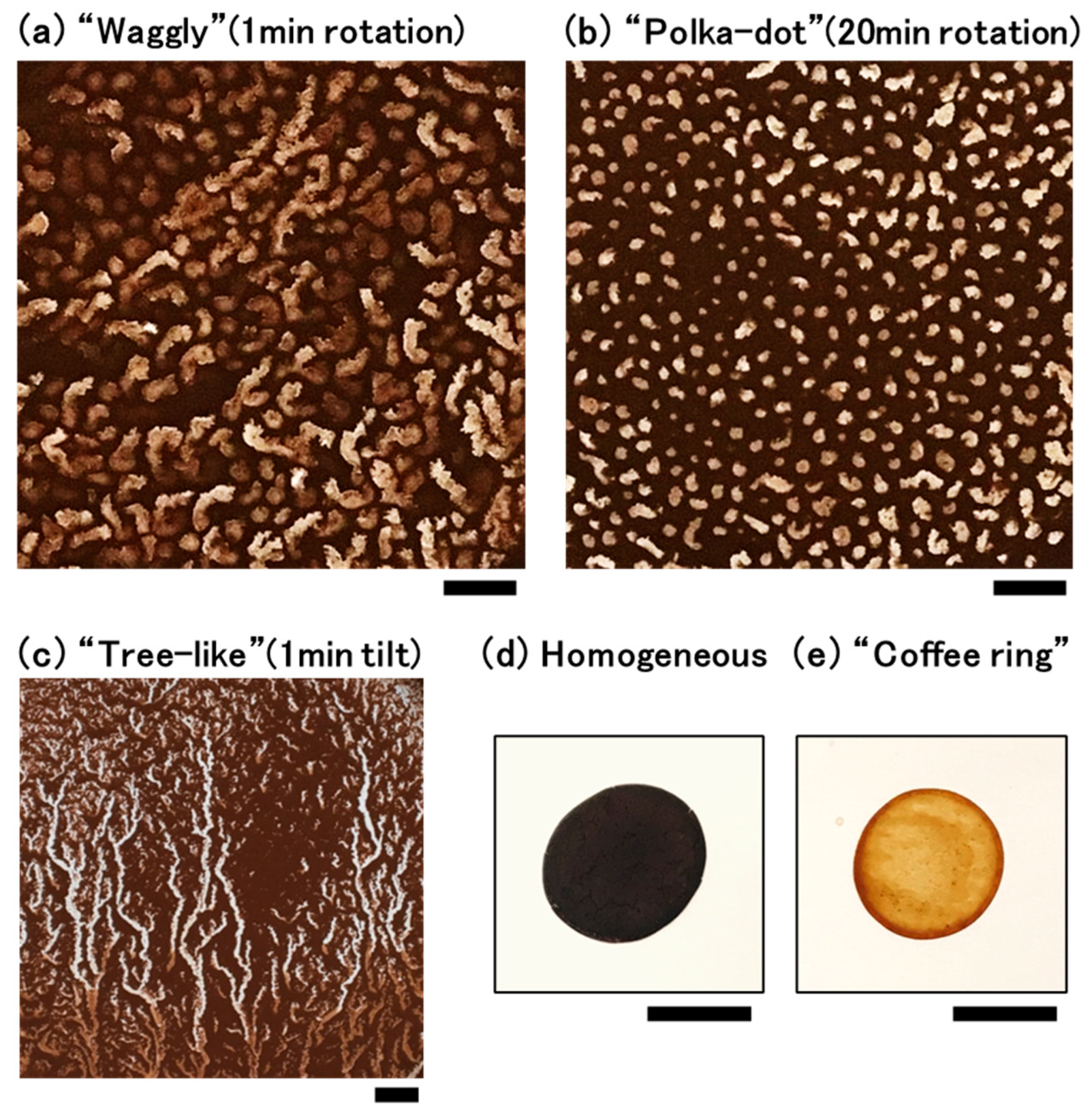
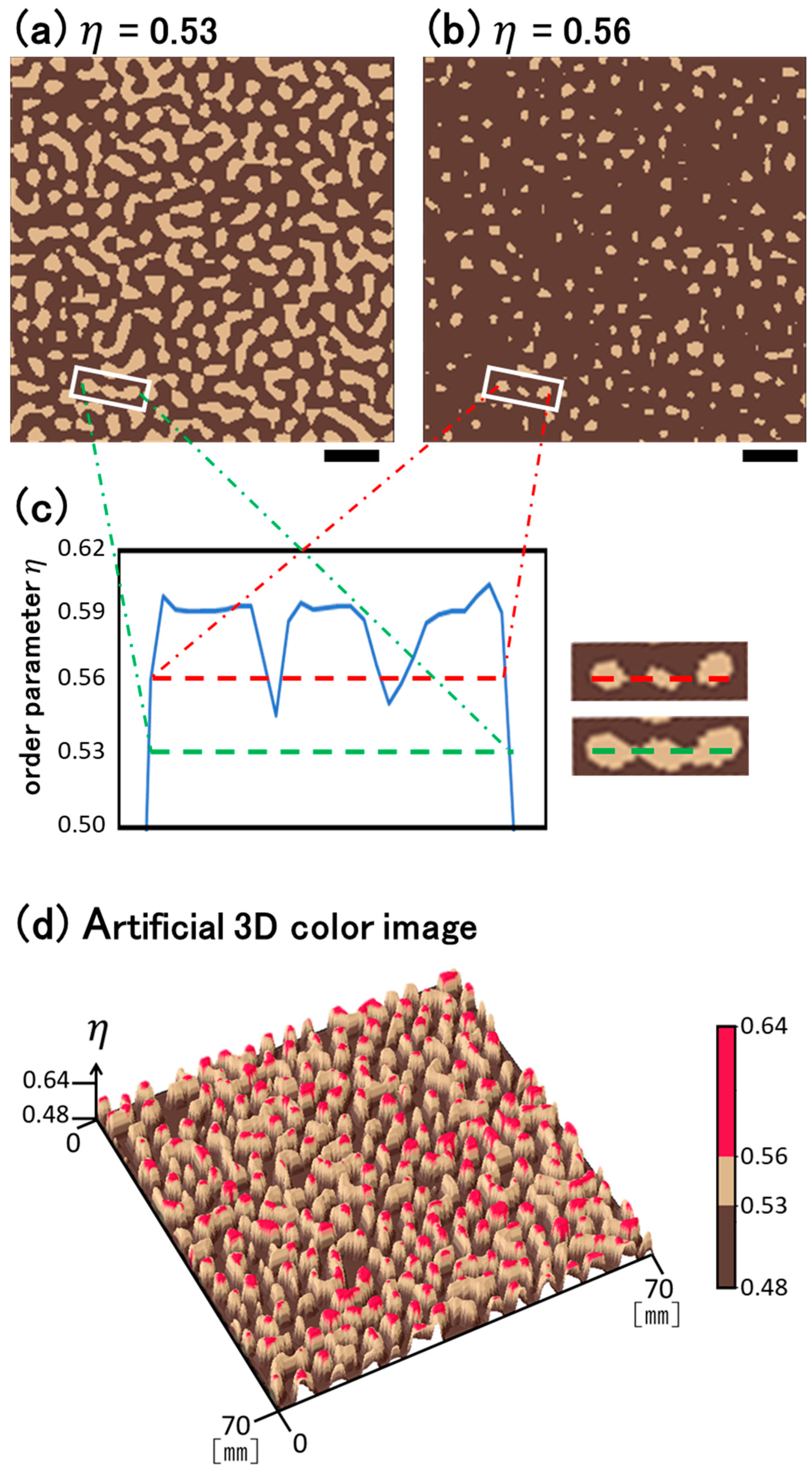
Emergence of Many Mini-Circles from a Coffee Suspension with Mechanical Rotation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Deegan, R.D.; Bakajin, O.; Dupont, T.F.; Huber, G.; Nagel, S.R. Capillary Flow as the Cause of Ring Stains from Dried Liquid Drops. Nature 1997, 5, 736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrithers, A.D.; Brown, M.J.; Rashed, M.Z.; Islam, S.; Velev, O.D.; Williams, S.J. Multiscale Self-Assembly of Distinctive Weblike Structures from Evaporated Drops of Dilute American Whiskeys. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 5417–5425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiele, U.; Todorova, D.V.; Lopez, H. Gradient Dynamics Description for Films of Mixtures and Suspensions: Dewetting Triggered by Coupled Film Height and Concentration Fluctuations. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2013, 111, 117801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Park, J.; Moon, J. Control of Colloidal Particle Deposit Patterns within Picoliter Droplets Ejected by Ink-Jet Printing. Langmuir 2006, 22, 3506–3513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, M.; Wang, L.; Song, Y. Controllable Printing Droplets for High-Resolution Patterns. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 6950–6958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deegan, R.D.; Bakajin, O.; Dupont, T.F.; Huber, G.; Nagel, S.R.; Witten, T.A. Contact Line Deposits in an Evaporating Drop. Phys. Rev. E 2000, 62, 756–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hampton, M.A.; Nguyen, T.A.H.; Nguyen, A.V.; Xu, Z.P.; Huang, L.; Rudolph, V. Influence of Surface Orientation on the Organization of Nanoparticles in Drying Nanofluid Droplets. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 377, 456–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weon, B.M.; Je, J.H. Fingering inside the Coffee Ring. Phys. Rev. E 2013, 87, 013003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Diddens, C.; Segers, T.; Wijshoff, H.; Versluis, M.; Lohse, D. Evaporating Droplets on Oil-Wetted Surfaces: Suppression of the Coffee-Stain Effect. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 16756–16763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsa, M.; Harmand, S.; Sefiane, K. Mechanisms of Pattern Formation from Dried Sessile Drops. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 254, 22–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Still, T.; Yunker, P.J.; Yodh, A.G. Surfactant-Induced Marangoni Eddies Alter the Coffee-Rings of Evaporating Colloidal Drops. Langmuir 2012, 28, 4984–4988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, G.; Yang, L.; Yang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Jin, X.; Dai, J.; Wu, Q.; Liu, S.; Zhu, X.; Wang, X.; et al. A General Ink Formulation of 2D Crystals for Wafer-Scale Inkjet Printing. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaba5029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parisse, F.; Allain, C. Drying of Colloidal Suspension Droplets: Experimental Study and Profile Renormalization. Langmuir 1997, 13, 3598–3602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiyama, Y.; Larsen, R.J.; Kim, J.-W.; Weitz, D.A. Buckling and Crumpling of Drying Droplets of Colloid−Polymer Suspensions. Langmuir 2006, 22, 6024–6030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sen, D.; Melo, J.S.; Bahadur, J.; Mazumder, S.; Bhattacharya, S.; Ghosh, G.; Dutta, D.; D’Souza, S.F. Buckling-Driven Morphological Transformation of Droplets of a Mixed Colloidal Suspension during Evaporation-Induced Self-Assembly by Spray Drying. Euro. Phys. J. E 2010, 31, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bück, A.; Peglow, M.; Naumann, M.; Tsotsas, E. Population Balance Model for Drying of Droplets Containing Aggregating Nanoparticles. AIChE J. 2012, 58, 3318–3328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goehring, L.; Clegg, W.J.; Routh, A.F. Plasticity and Fracture in Drying Colloidal Films. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2013, 110, 024301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, W.; Lan, D.; Wang, Y. Dewetting-Mediated Pattern Formation inside the Coffee Ring. Phys. Rev. E 2017, 95, 042607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler, A.; Virnau, P.; Binder, K.; Winkler, R.G.; Gompper, G. Hydrodynamic Mechanisms of Spinodal Decomposition in Confined Colloid-Polymer Mixtures: A Multiparticle Collision Dynamics Study. J. Chem. Phys. 2013, 138, 054901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Varanakkottu, S.N.; Anyfantakis, M.; Morel, M.; Rudiuk, S.; Baigl, D. Light-Directed Particle Patterning by Evaporative Optical Marangoni Assembly. Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 644–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joksimovic, R.; Watanabe, S.; Riemer, S.; Gradzielski, M.; Yoshikawa, K. Self-Organized Patterning through the Dynamic Segregation of DNA and Silica Nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 3660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mae, K.; Toyama, H.; Nawa-Okita, E.; Yamamoto, D.; Chen, Y.-J.; Yoshikawa, K.; Toshimitsu, F.; Nakashima, N.; Matsuda, K.; Shioi, A. Self-Organized Micro-Spiral of Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Anyfantakis, M.; Varanakkottu, S.N.; Rudiuk, S.; Morel, M.; Baigl, D. Evaporative Optical Marangoni Assembly: Tailoring the Three-Dimensional Morphology of Individual Deposits of Nanoparticles from Sessile Drops. ACS Appl. Matter Interfaces 2017, 9, 37435–37445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yen, T.M.; Fu, X.; Wei, T.; Nayak, R.U.; Shi, Y.; Lo, Y.-H. Reversing Coffee-Ring Effect by Laser-Induced Differential Evaporation. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mouhamad, Y. Dynamics and Phase Separation during Spin Casting of Polymer Films. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Sheffield, Sheffield, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, H.; Larson, R.G. Marangoni Effect Reverses Coffee-Ring Depositions. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 7090–7094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mampallil, D.; Reboud, J.; Wilson, R.; Wylie, D.; Klug, D.R.; Cooper, J.M. Acoustic Suppression of the Coffee-Ring Effect. Soft Matter 2015, 11, 7207–7213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.J.; Kang, K.H.; Lee, J.-G.; Kang, I.S.; Yoon, B.J. Control of Particle-Deposition Pattern in a Sessile Droplet by Using Radial Electroosmotic Flow. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 5192–5197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wray, A.W.; Papageorgiou, D.T.; Craster, R.V.; Sefiane, K.; Matar, O.K. Electrostatic Suppression of the “Coffee Stain Effect”. Langmuir 2014, 30, 5849–5858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Lv, C.; Li, Z.; Quéré, D.; Zheng, Q. From Coffee Rings to Coffee Eyes. Soft Matter 2015, 11, 4669–4673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anyfantakis, M.; Geng, Z.; Morel, M.; Rudiuk, S.; Baigl, D. Modulation of the Coffee-Ring Effect in Particle/Surfactant Mixtures: The Importance of Particle–Interface Interactions. Langmuir 2015, 31, 4113–4120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, Y.; Hung, L.T.; Feng, J.; Yuan, H.; Pan, Y.; Guo, W.; Zhang, Y.; Shum, H.C. Flower-like Droplets Obtained by Self-Emulsification of a Phase-Separating (SEPS) Aqueous Film. Soft Matter 2020, 16, 6050–6055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cahn, J.W.; Hilliard, J.E. Free Energy of a Nonuniform System. I. Interfacial Free Energy. J. Chem. Phys. 1958, 28, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamanaka, A.; Aoki, T.; Ogawa, S.; Takaki, T. GPU-Accelerated Phase-Field Simulation of Dendritic Solidification in a Binary Alloy. J. Cryst. Growth 2011, 318, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Huh, J.-Y.; Jeong, D.; Shin, J.; Yun, A.; Kim, J. Physical, Mathematical, and Numerical Derivations of the Cahn–Hilliard Equation. Comput. Mat. Sci. 2014, 81, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Dedè, L.; Evans, J.A.; Borden, M.J.; Hughes, T.J.R. Isogeometric Analysis of the Advective Cahn–Hilliard Equation: Spinodal Decomposition under Shear Flow. J. Comp. Phys. 2013, 242, 321–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh Pahlavan, A.; Cueto-Felgueroso, L.; Hosoi, A.E.; McKinley, G.H.; Juanes, R. Thin Films in Partial Wetting: Stability, Dewetting and Coarsening. J. Fluid Mech. 2018, 845, 642–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Pang, Y.; Liu, W.; Wu, X.; Hou, Z. Effect of Diffusivity on the Pseudospinodal Decomposition of the Γ′ Phase in a Ni-Al Alloy. J. Phase Equilib. Diffus. 2016, 37, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran Duc, V.-N.; Chan, P.K. Using the Cahn–Hilliard Theory in Metastable Binary Solutions. ChemEngineering 2019, 3, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holz, M.; Heil, S.R.; Sacco, A. Temperature-Dependent Self-Diffusion Coefficients of Water and Six Selected Molecular Liquids for Calibration in Accurate 1H NMR PFG Measurements. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2000, 2, 4740–4742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Two-Dimensional Phase-Field Model for Conserved Order Parameter (Cahn-Hilliard Equation). Available online: http://web.tuat.ac.jp/~yamanaka/pcoms2019/Cahn-Hilliard-2d.html (accessed on 31 October 2020).
- Elder, K.; Rogers, T.; Desai, R. Early Stages of Spinodal Decomposition for the Cahn-Hilliard-Cook Model of Phase Separation. Phy. Rev. B 1988, 38, 4725–4739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolaou, L. The Art of Coffee Cup Reading; Zeus Publications: Mermaid Waters, Australia, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Tjhung, E.; Nardini, C.; Cates, M.E. Cluster Phases and Bubbly Phase Separation in Active Fluids: Reversal of the Ostwald Process. Phys. Rev. X 2018, 8, 031080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamanaka, K.; Takagi, Y.; Inoue, T. Reaction-Induced Phase Separation in Rubber-Modified Epoxy Resins. Polymer 1989, 30, 1839–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Liu, Q.-X.; Jin, Z. Spatiotemporal Complexity of a Ratio-Dependent Predator-Prey System. Phys. Rev. E 2007, 75, 051913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Das, P.; Jaiswal, P.K.; Puri, S. Surface-Directed Spinodal Decomposition on Chemically Patterned Substrates. Phys. Rev. E 2020, 102, 012803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Posada, E.; López-Salas, N.; Carriazo, D.; Muñoz-Márquez, M.A.; Ania, C.O.; Jiménez-Riobóo, R.J.; Gutiérrez, M.C.; Ferrer, M.L.; del Monte, F. Predicting the Suitability of Aqueous Solutions of Deep Eutectic Solvents for Preparation of Co-Continuous Porous Carbons via Spinodal Decomposition Processes. Carbon 2017, 123, 536–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stenhammar, J.; Tiribocchi, A.; Allen, R.J.; Marenduzzo, D.; Cates, M.E. Continuum Theory of Phase Separation Kinetics for Active Brownian Particles. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2013, 111, 145702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stenhammar, J.; Marenduzzo, D.; Allen, R.J.; Cates, M.E. Phase Behaviour of Active Brownian Particles: The Role of Dimensionality. Soft Matter 2014, 10, 1489–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cates, M.E.; Tailleur, J. Motility-Induced Phase Separation. Annu. Rev. Cond. Matter Phys. 2015, 6, 219–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ueno, H.; Shono, M.; Ogawa, M.; Sadakane, K.; Yoshikawa, K. Emergence of Many Mini-Circles from a Coffee Suspension with Mechanical Rotation. Physics 2021, 3, 8-16. https://doi.org/10.3390/physics3010003
Ueno H, Shono M, Ogawa M, Sadakane K, Yoshikawa K. Emergence of Many Mini-Circles from a Coffee Suspension with Mechanical Rotation. Physics. 2021; 3(1):8-16. https://doi.org/10.3390/physics3010003
Chicago/Turabian StyleUeno, Hiroshi, Mayu Shono, Momoko Ogawa, Koichiro Sadakane, and Kenichi Yoshikawa. 2021. "Emergence of Many Mini-Circles from a Coffee Suspension with Mechanical Rotation" Physics 3, no. 1: 8-16. https://doi.org/10.3390/physics3010003
APA StyleUeno, H., Shono, M., Ogawa, M., Sadakane, K., & Yoshikawa, K. (2021). Emergence of Many Mini-Circles from a Coffee Suspension with Mechanical Rotation. Physics, 3(1), 8-16. https://doi.org/10.3390/physics3010003