The Effect of Anti-COVID-19 Policies on the Evolution of the Disease: A Complex Network Analysis of the Successful Case of Greece
Abstract
:1. Introduction
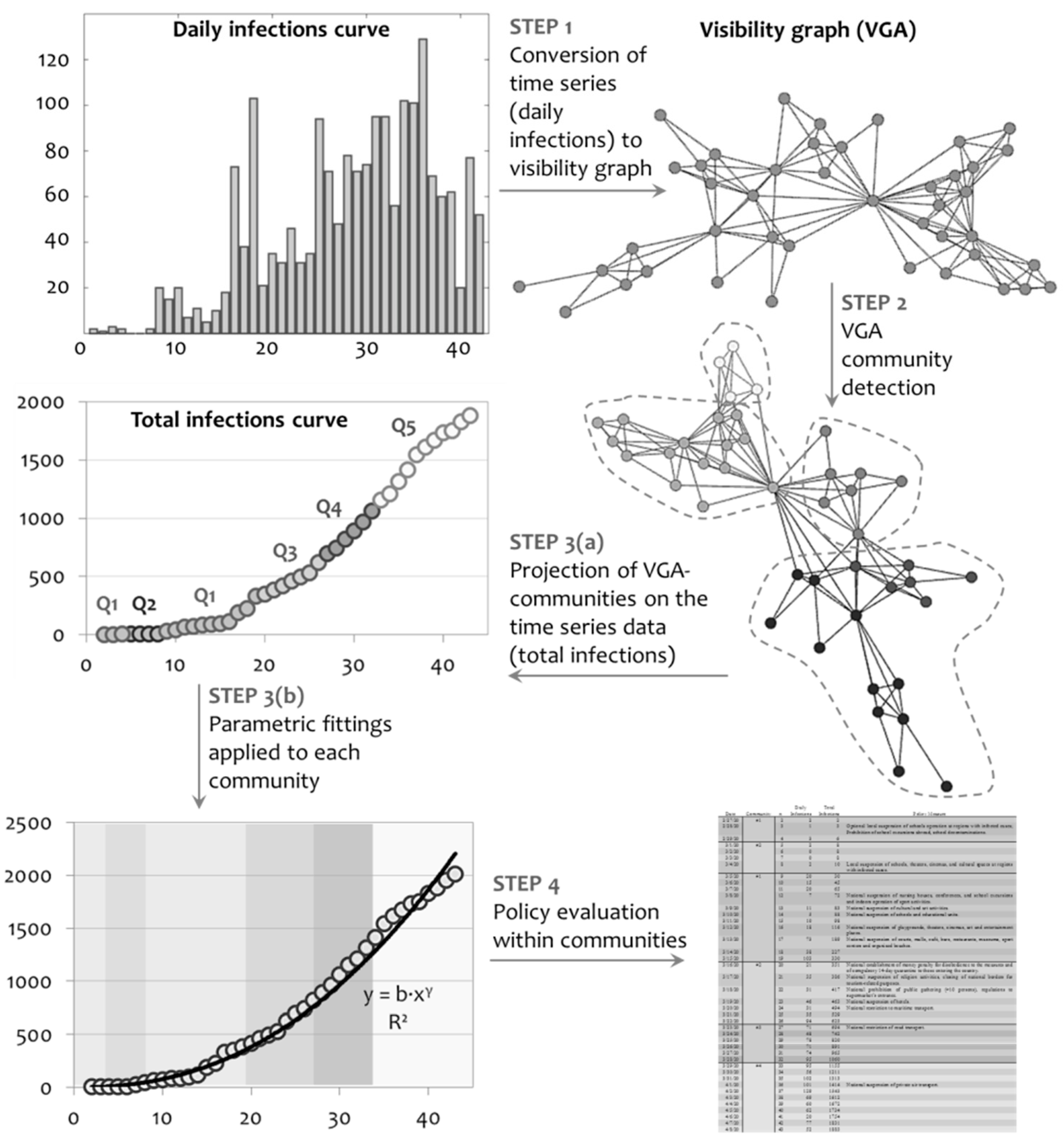
2. Methodology and Data
3. Results and Discussion
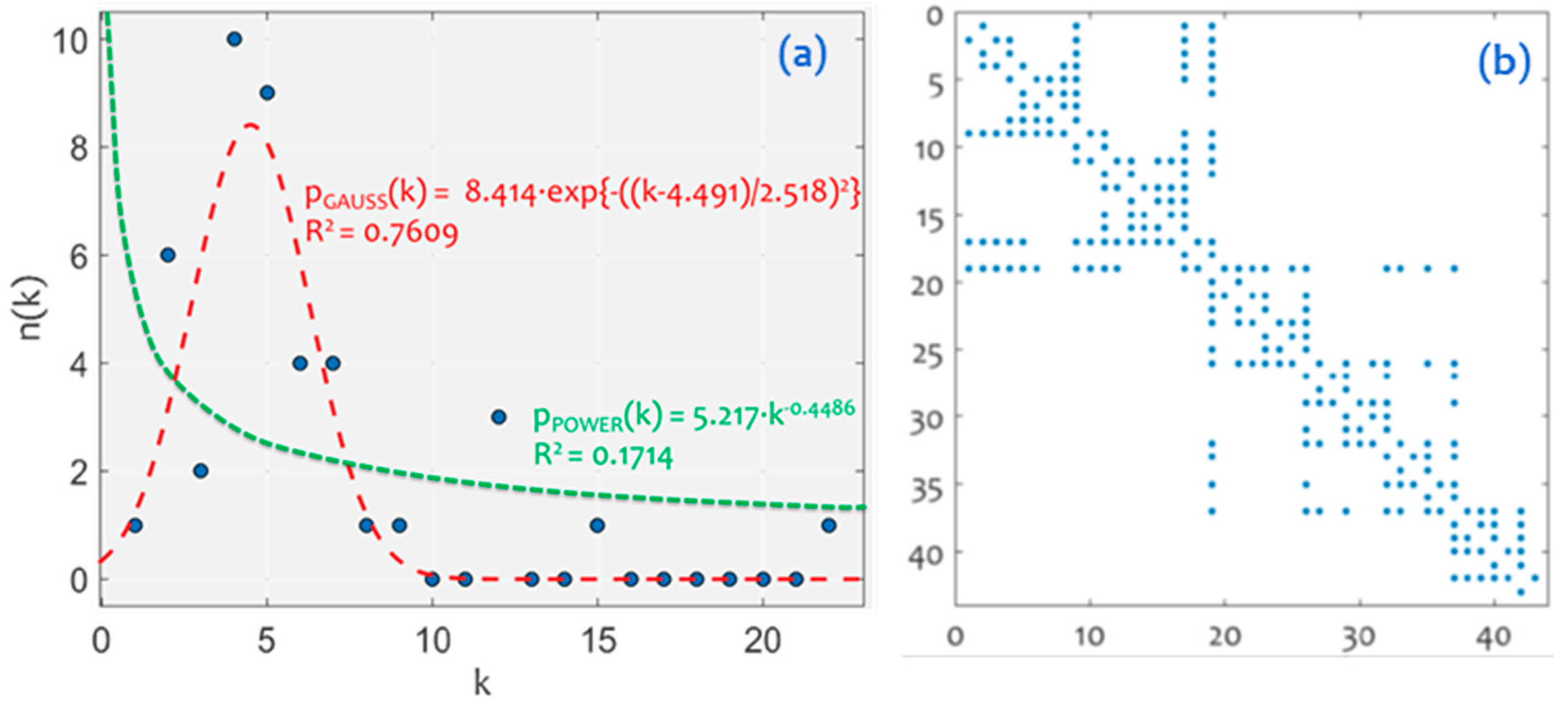
3.1. Network Analysis
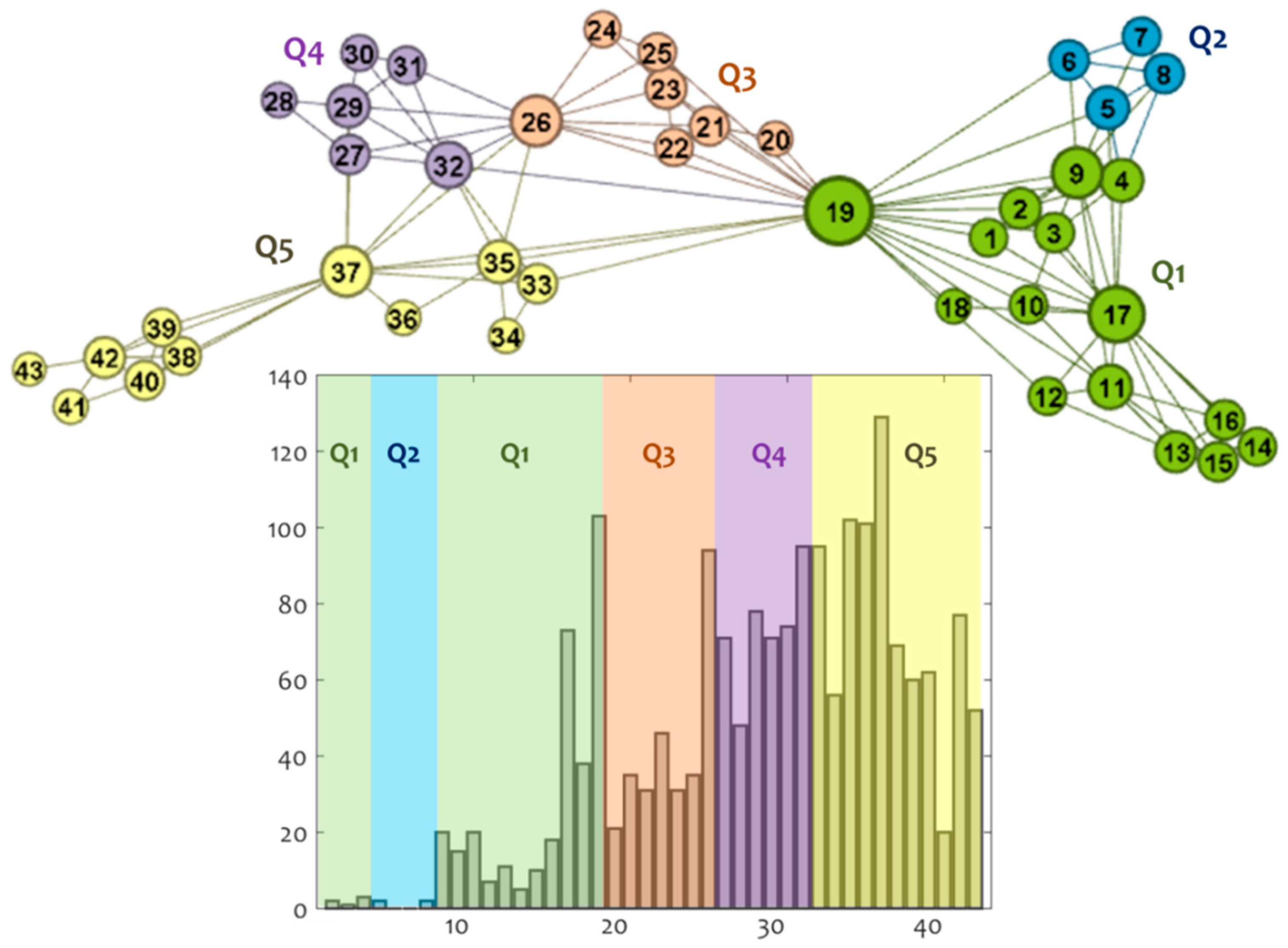
3.2. Community Detection
3.2.1. Structural Analysis
3.2.2. Forecasting
3.3. Policy Assessment
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Date | Community | n | Daily Infections | Total Infections | Policy Measure |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2/27/20 | Q1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | |
| 2/28/20 | 3 | 1 | 3 | Optional local suspension of schools operation at regions with infected cases; Prohibition of school excursions abroad, school decontaminations. | |
| 2/29/20 | 4 | 3 | 6 | ||
| 3/1/20 | Q2 | 5 | 2 | 8 | |
| 3/2/20 | 6 | 0 | 8 | ||
| 3/3/20 | 7 | 0 | 8 | ||
| 3/4/20 | 8 | 2 | 10 | Local suspension of schools, theaters, cinemas, and cultural spaces at regions with infected cases. | |
| 3/5/20 | Q1 | 9 | 20 | 30 | |
| 3/6/20 | 10 | 15 | 45 | ||
| 3/7/20 | 11 | 20 | 65 | ||
| 3/8/20 | 12 | 7 | 72 | National suspension of nursing houses, conferences, and school excursions and indoors operation of sport activities. | |
| 3/9/20 | 13 | 11 | 83 | National suspension of cultural and art activities. | |
| 3/10/20 | 14 | 5 | 88 | National suspension of schools and educational units. | |
| 3/11/20 | 15 | 10 | 98 | ||
| 3/12/20 | 16 | 18 | 116 | National suspension of playgrounds, theaters, cinemas, art and entertainment places. | |
| 3/13/20 | 17 | 73 | 189 | National suspension of courts, malls, café, bars, restaurants, museums, sport centers and organized beaches. | |
| 3/14/20 | 18 | 38 | 227 | ||
| 3/15/20 | 19 | 103 | 330 | ||
| 3/16/20 | Q3 | 20 | 21 | 351 | National establishment of money penalty for disobedience to the measures and of compulsory 14-day quarantine to those entering the country. |
| 3/17/20 | 21 | 35 | 386 | National suspension of religion activities, closing of national borders for tourism-related purposes. | |
| 3/18/20 | 22 | 31 | 417 | National prohibition of public gathering (>10 persons), regulations to supermarket’s entrance. | |
| 3/19/20 | 23 | 46 | 463 | National suspension of hotels. | |
| 3/20/20 | 24 | 31 | 494 | National restriction to maritime transport. | |
| 3/21/20 | 25 | 35 | 529 | ||
| 3/22/20 | 26 | 94 | 623 | ||
| 3/23/20 | Q4 | 27 | 71 | 694 | National restriction of road transport. |
| 3/24/20 | 28 | 48 | 742 | ||
| 3/25/20 | 29 | 78 | 820 | ||
| 3/26/20 | 30 | 71 | 891 | ||
| 3/27/20 | 31 | 74 | 965 | ||
| 3/28/20 | 32 | 95 | 1060 | ||
| 3/29/20 | Q5 | 33 | 95 | 1155 | |
| 3/30/20 | 34 | 56 | 1211 | ||
| 3/31/20 | 35 | 102 | 1313 | ||
| 4/1/20 | 36 | 101 | 1414 | National suspension of private air transport. | |
| 4/2/20 | 37 | 129 | 1543 | ||
| 4/3/20 | 38 | 69 | 1612 | ||
| 4/4/20 | 39 | 60 | 1672 | ||
| 4/5/20 | 40 | 62 | 1734 | ||
| 4/6/20 | 41 | 20 | 1754 | ||
| 4/7/20 | 42 | 77 | 1831 | ||
| 4/8/20 | 43 | 52 | 1883 |
References
- Anderson, R.M.; Heesterbeek, H.; Klinkenberg, D.; Hollingsworth, T.D. How will country-based mitigation measures influence the course of the COVID-19 epidemic? Lancet 2020, 395, 931–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKibbin, W.J.; Fernando, R. The Global Macroeconomic Impacts of COVID-19: Seven Scenarios. CAMA Working Paper No. 19/2020. 2020. Available online: https://ssrn.com/abstract=3547729 (accessed on 22 June 2020).
- World Health Organization. Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19); Situation Report 72; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.T.; Leung, K.; Bushman, M.; Kishore, N.; Niehus, R.; de Salazar, P.M.; Leung, G.M. Estimating clinical severity of COVID-19 from the transmission dynamics in Wuhan, China. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 506–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, M.; Chen, J.; Deng, Y. Scaling features in the spreading of COVID-19. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2002.09199. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Liang, M.; Yin, X.; Liu, X.; Hao, M.; Hu, Z.; Jin, L. COVID-19 epidemic outside China: 34 founders and exponential growth. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Gayle, A.A.; Wilder-Smith, A.; Rocklöv, J. The reproductive number of COVID-19 is higher compared to SARS coronavirus. J. Travel Med. 2020, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schlickeiser, R.; Schlickeiser, F. A Gaussian model for the time development of the sars-cov-2 corona pandemic disease. Predictions for Germany made on 30 March 2020. Physics 2020, 2, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuttler, J.; Schlickeiser, R.; Schlickeiser, F.; Kroger, M. Covid-19 predictions using a Gauss model, based on data from April 2. Physics 2020, 2, 197–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Tian, Z.; Yang, X. Breakthrough: Chloroquine phosphate has shown apparent efficacy in treatment of COVID-19 associated pneumonia in clinical studies. Biosci. Trends 2020, 14, 72–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gautret, P.; Lagier, J.C.; Parola, P.; Meddeb, L.; Mailhe, M.; Doudier, B.; Honoré, S. Hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin as a treatment of COVID-19: Results of an open-label non-randomized clinical trial. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remuzzi, A.; Remuzzi, G. COVID-19 and Italy: What next? Lancet 2020, 395, 1225–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roser, M.; Ritchie, H. Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19). Available online: https://ourworldindata.org/coronavirus-data (accessed on 10 April 2020).
- Livingston, E.; Bucher, K. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in Italy. JAMA 2020, 323, 1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Watts, D.; Strogatz, D. Collective dynamics of small-world networks. Nature 1998, 393, 440–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christakis, N.A.; Fowler, J.H. Connected: The Surprising Power of our Social Networks and How They Shape Our Lives; Little, Brown and Company: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Tsiotas, D. Detecting different topologies immanent in scalefree networks with the same degree distribution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 6701–6706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bedford, J.; Enria, D.; Giesecke, J.; Heymann, D.L.; Ihekweazu, C.; Kobinger, G.; Ungchusak, K. COVID-19: Towards controlling of a pandemic. Lancet 2020, 395, 1015–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohrabi, C.; Alsafi, Z.; O’Neill, N.; Khan, M.; Kerwan, A.; Al-Jabir, A.; Agha, R. World Health Organization declares global emergency: A review of the 2019 novel coronavirus (COVID-19). Int. J. Surg. 2020, 76, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J.; Kupferschmidt, K. Countries test tactics in ‘war’against COVID-19. Science 2020, 367, 1287–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, B.; Gutierrez, B.; Mekaru, S.; Sewalk, K.; Goodwin, L.; Loskill, A.; Zarebski, A.E. Epidemiological data from the COVID-19 outbreak, real-time case information. Sci. Data 2020, 7, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Box, G.; Jenkins, G.M.; Reinsel, G.C.; Ljung, G.M. Time Series Analysis: Forecasting and Control; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Lacasa, L.; Luque, B.; Ballesteros, F.; Luque, J.; Nuno, J.C. From time-series to complex networks: The visibility graph. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 4972–4975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsiotas, D.; Charakopoulos, A. VisExpA: Visibility expansion algorithm in the topology of complex networks. SoftwareX 2020, 11, 100379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blondel, V.; Guillaume, J.-L.; Lambiotte, R.; Lefebvre, E. Fast unfolding of communities in large networks. J. Stat. Mech. 2008, 10, 10008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- National Public Health Organization of Greece—NPHOG. New coronavirus Covid-19—Instructions. Available online: https://eody.gov.gr/neos-koronaios-covid-19 (accessed on 26 April 2020).
- Ministry of Health of Greece—MOHG. Press Releases. Available online: https://www.moh.gov.gr/articles/ministry/grafeio-typoy/press-releases (accessed on 30 April 2020).
- Gao, Z.-K.; Small, M.; Kurths, J. Complex network analysis of time-series. Europhys. Lett. 2017, 116, 50001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barabasi, A.L. Network Science; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Barthelemy, M. Spatial networks. Phys. Rep. 2011, 499, 1–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fortunato, S. Community detection in graphs. Phys. Rep. 2010, 486, 75–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Walpole, R.E.; Myers, R.H.; Myers, S.L.; Ye, K. Probability & Statistics for Engineers & Scientists; Prentice Hall Publications: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Demertzis, K.; Tsiotas, D.; Magafas, L. Modeling and forecasting the COVID-19 temporal spread in Greece: An exploratory approach based on complex network defined splines. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2005.01163. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Xie, J.; Lin, M.; Ying, L.; Pang, P.; Ji, W. Sensitivity of chest CT for COVID-19: Comparison to RT-PCR. Radiology 2020, 200432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heymann, D.L.; Shindo, N. COVID-19: What is next for public health? Lancet 2020, 395, 542–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chapra, S.C. Applied Numerical Methods with MATLAB for Engineers and Scientists; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Tsiotas, D.; Polyzos, S. The complexity in the study of spatial networks: An epistemological approach. Netw. Spat. Econ. 2018, 18, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
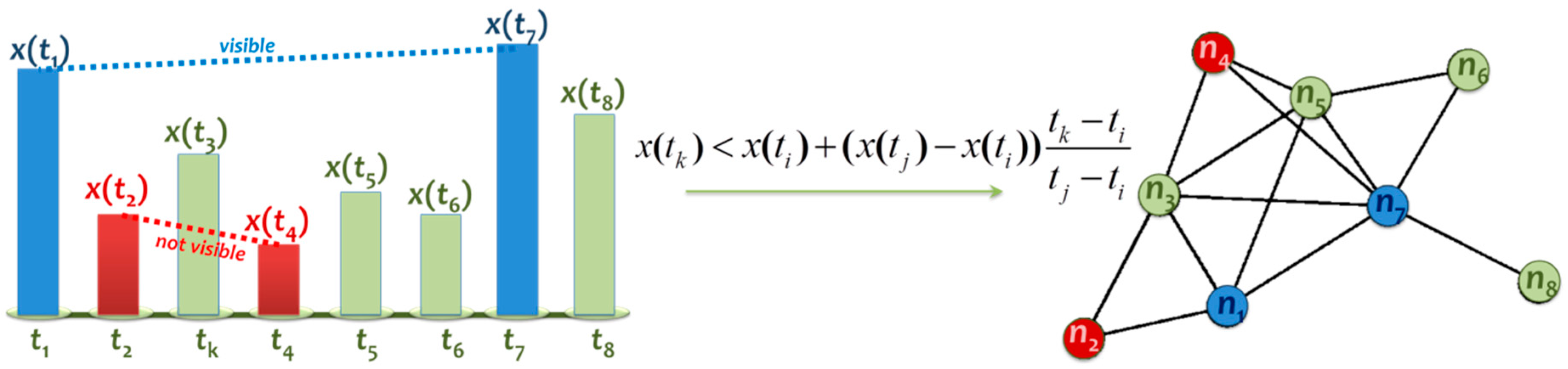
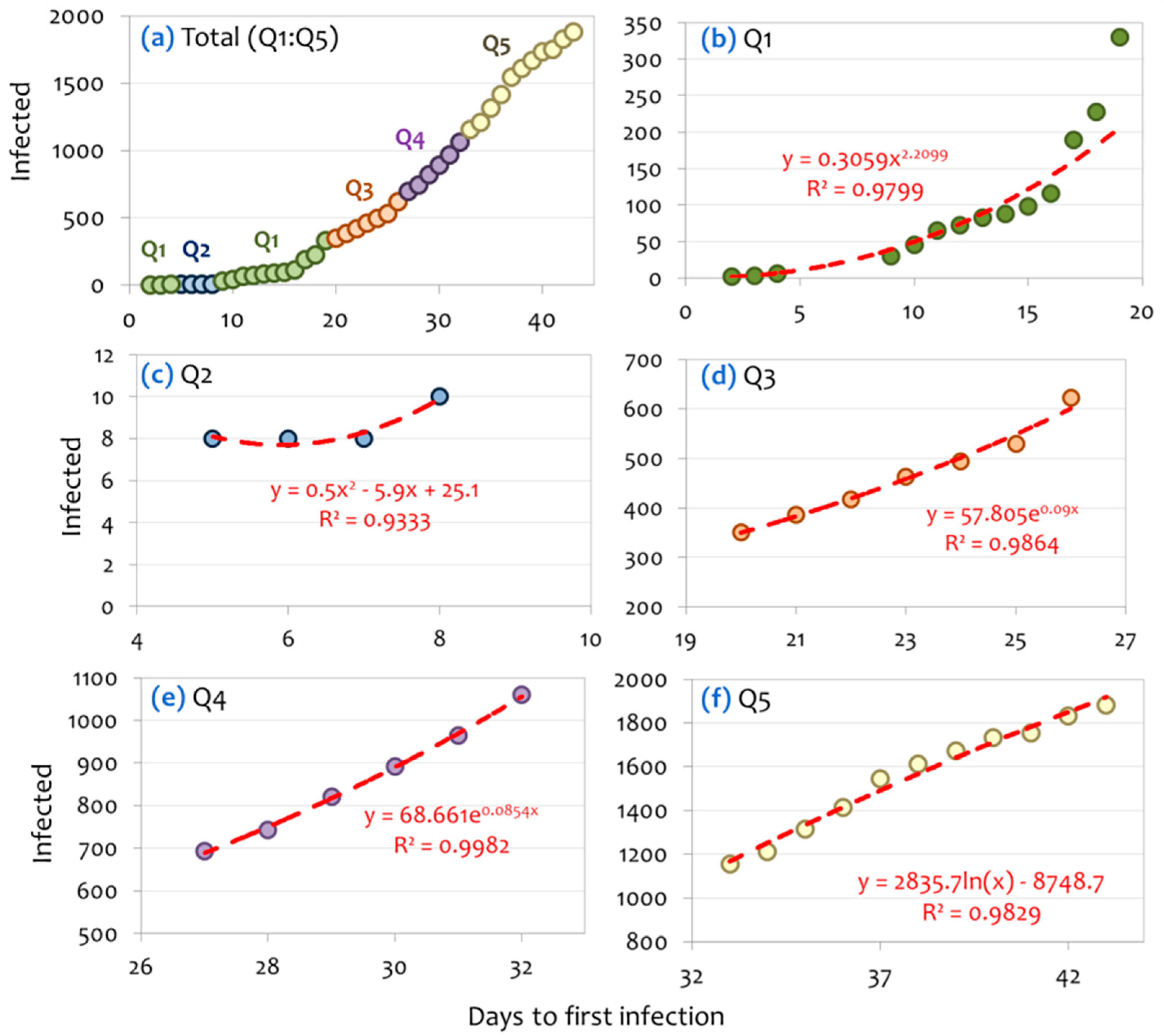
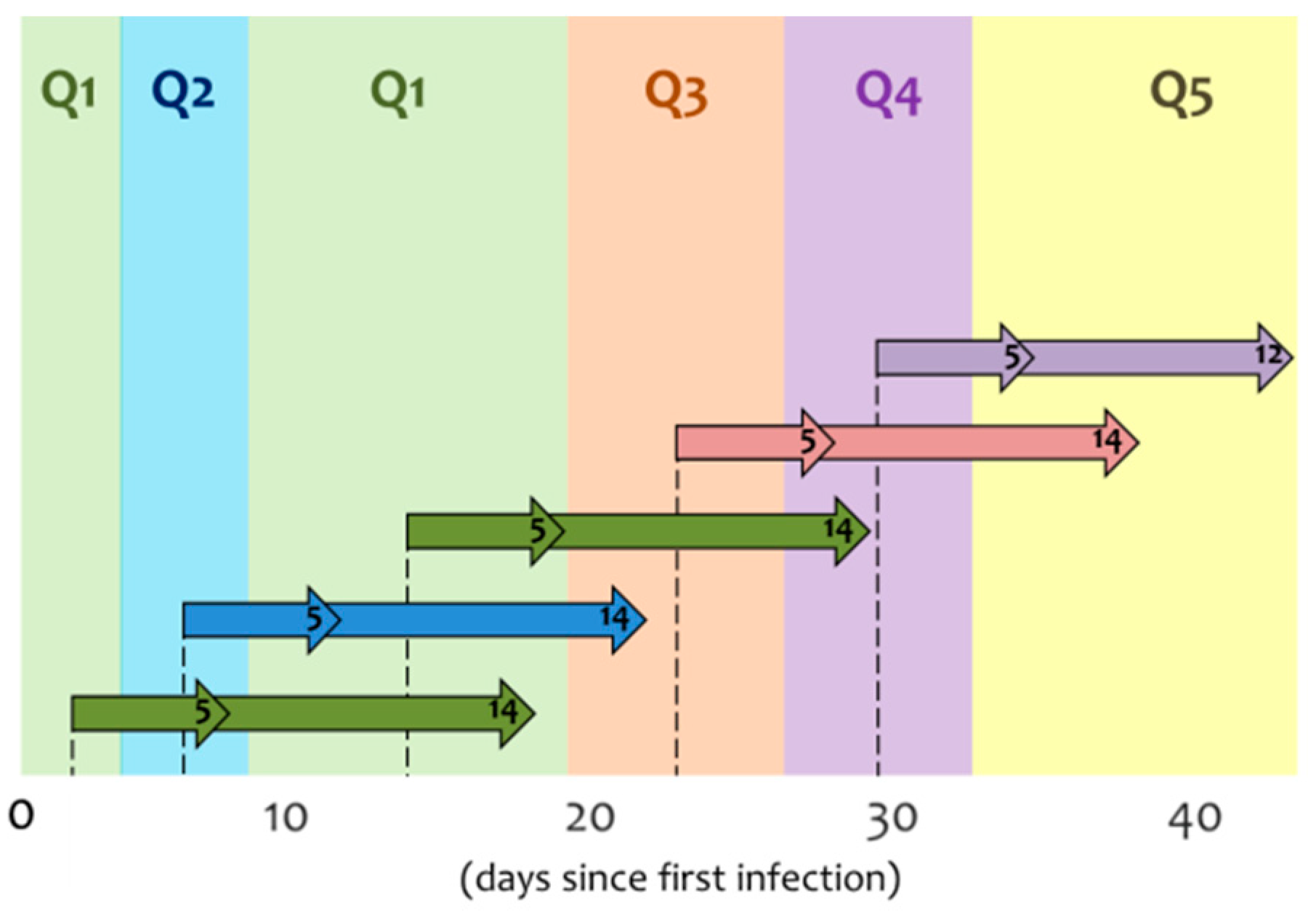
| Date | Observed | Estimations | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q1 | Diff | Q2 | Diff | Q3 | Diff | Q4 | Diff | Q5 | Diff | Q1:5 (a) | Diff | GM (b) | Diff | ||
| 4/9/20 | 1955 | 1311 | 644 | 734 | 1222 | 3032 | −1077 | 2942 | −987 | 1982 | −27 * | 2194 | −239 | 2047 | −92 |
| 4/10/20 | 2011 | 1377 | 634 | 772 | 1239 | 3318 | −1307 | 3204 | −1193 | 2046 | −35 | 2325 | −314 | 2101 | −90 |
| 4/11/20 | 2081 | 1446 | 635 | 812 | 1269 | 3630 | −1549 | 3490 | −1409 | 2108 | −27 | 2461 | −380 | 2149 | −68 |
| 4/12/20 | 2114 | 1516 | 598 | 852 | 1262 | 3972 | −1858 | 3801 | −1687 | 2169 | −55 | 2601 | −487 | 2189 | −75 |
| 4/13/20 | 2145 | 1588 | 557 | 894 | 1251 | 4346 | −2201 | 4140 | −1995 | 2229 | −84 | 2747 | −602 | 2221 | −76 |
| 4/14/20 | 2170 | 1662 | 508 | 937 | 1234 | 4756 | −2586 | 4509 | −2339 | 2287 | −117 | 2897 | −727 | 2245 | −75 |
| 4/15/20 | 2192 | 1738 | 454 | 980 | 1212 | 5203 | −3011 | 4911 | −2719 | 2345 | −153 | 3052 | −860 | 2261 | −69 |
| 4/16/20 | 2207 | 1816 | 391 | 1025 | 1182 | 5693 | −3486 | 5349 | −3142 | 2401 | −194 | 3212 | −1005 | 2268 | −61 |
| 4/17/20 | 2224 | 1896 | 328 | 1070 | 1154 | 6230 | −4006 | 5825 | −3601 | 2456 | −232 | 3377 | −1153 | 2266 | −42 |
| 4/18/20 | 2235 | 1977 | 258 | 1117 | 1118 | 6816 | −4581 | 6345 | −4110 | 2510 | −275 | 3547 | −1312 | 2255 | −20 |
| 4/19/20 | 2235 | 2061 | 174 | 1165 | 1071 | 7458 | −5223 | 6910 | −4675 | 2563 | −328 | 3722 | −1487 | 2236 | −1 |
| Q1 | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 | Q5 | Q1:5 | GM | |||||||||
| ME (c) | 471 | 1201.3 | −2807.7 | −2532.5 | −138.82 | −778.73 | −60.8182 | ||||||||
| MAE (d) | 471 | 1201.3 | 2807.7 | 2532.5 | 138.82 | 778.73 | 60.8182 | ||||||||
| MAPE (e) | 0.2229 | 0.5624 | 1.2894 | 1.1632 | 0.0632 | 0.3569 | 0.0289 | ||||||||
| MSE (f) | 2.4630 × 105 | 1.4467 × 106 | 9,616,653 | 7.7872 × 106 | 29,503 | 7.6725 × 105 | 4441.9 | ||||||||
| Model | R | R2 | RMSE (a) | RAE (b) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cubic | 0.998 | 0.996 | 2.229 | 4.182% |
| Regression Splines with 3 random knots | 0.999 | 0.998 | 1.805 | 3.798% |
| Regression Splines with 4 random knots | 0.999 | 0.998 | 1.621 | 3.277% |
| Regression Splines with 5 random knots | 0.999 | 0.998 | 1.420 | 2.986% |
| Complex-Network Regression Splines (c) | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.308 | 2.752% |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tsiotas, D.; Magafas, L. The Effect of Anti-COVID-19 Policies on the Evolution of the Disease: A Complex Network Analysis of the Successful Case of Greece. Physics 2020, 2, 325-339. https://doi.org/10.3390/physics2020017
Tsiotas D, Magafas L. The Effect of Anti-COVID-19 Policies on the Evolution of the Disease: A Complex Network Analysis of the Successful Case of Greece. Physics. 2020; 2(2):325-339. https://doi.org/10.3390/physics2020017
Chicago/Turabian StyleTsiotas, Dimitrios, and Lykourgos Magafas. 2020. "The Effect of Anti-COVID-19 Policies on the Evolution of the Disease: A Complex Network Analysis of the Successful Case of Greece" Physics 2, no. 2: 325-339. https://doi.org/10.3390/physics2020017
APA StyleTsiotas, D., & Magafas, L. (2020). The Effect of Anti-COVID-19 Policies on the Evolution of the Disease: A Complex Network Analysis of the Successful Case of Greece. Physics, 2(2), 325-339. https://doi.org/10.3390/physics2020017






