A New Nonaqueous Flow Battery with Extended Cycling
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
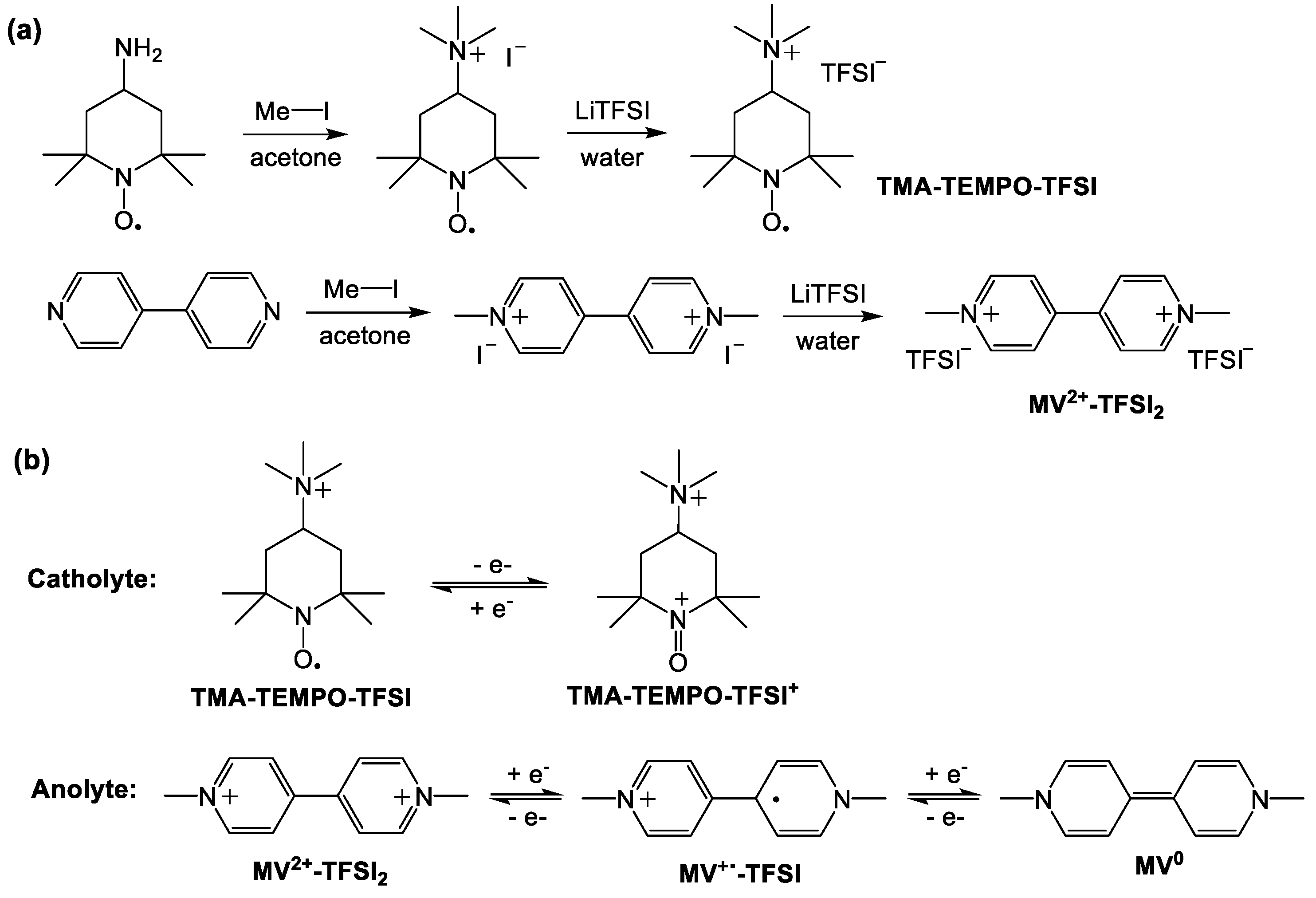
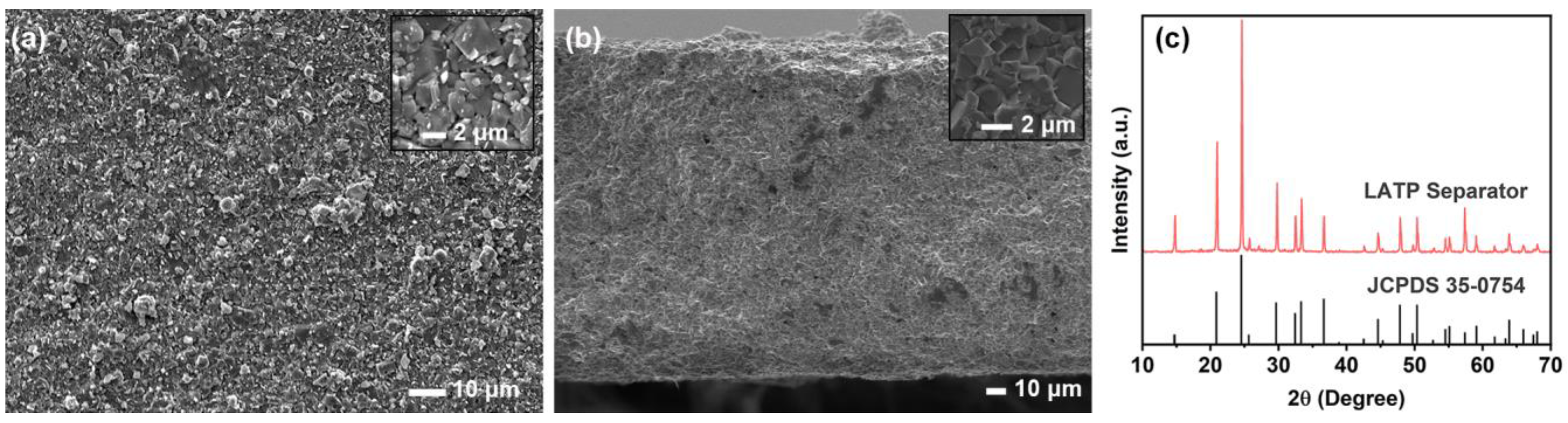
2.1. Materials and Methods
2.2. Cyclic Voltammetry (CV)
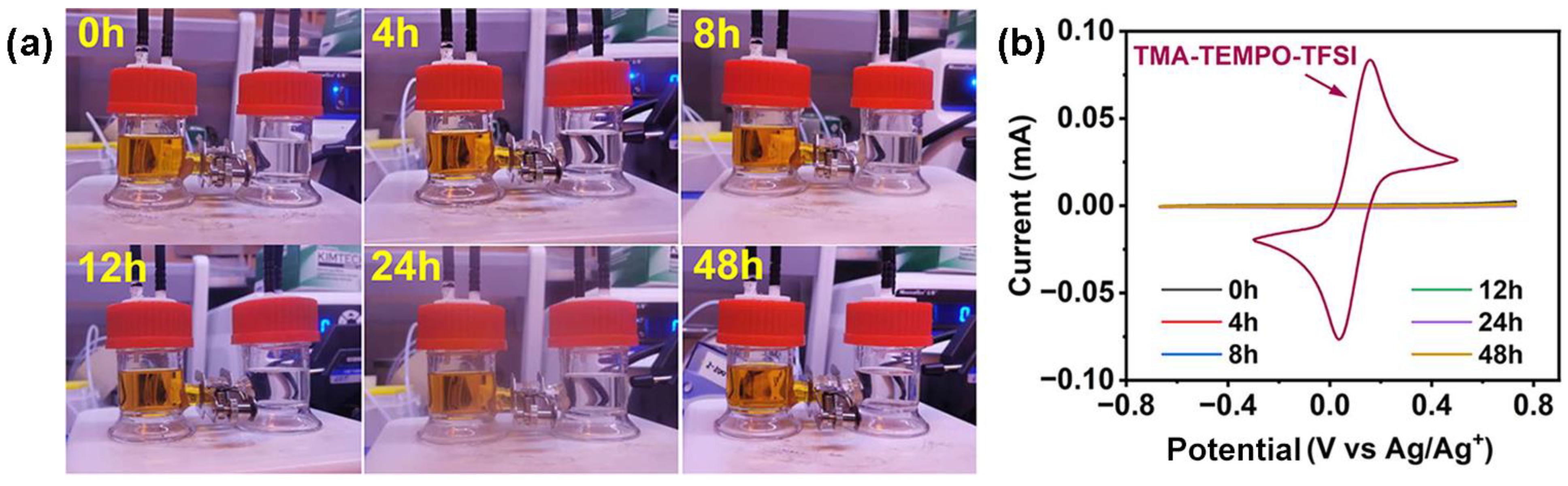
2.3. Crossover Test
2.4. Flow Cell Tests
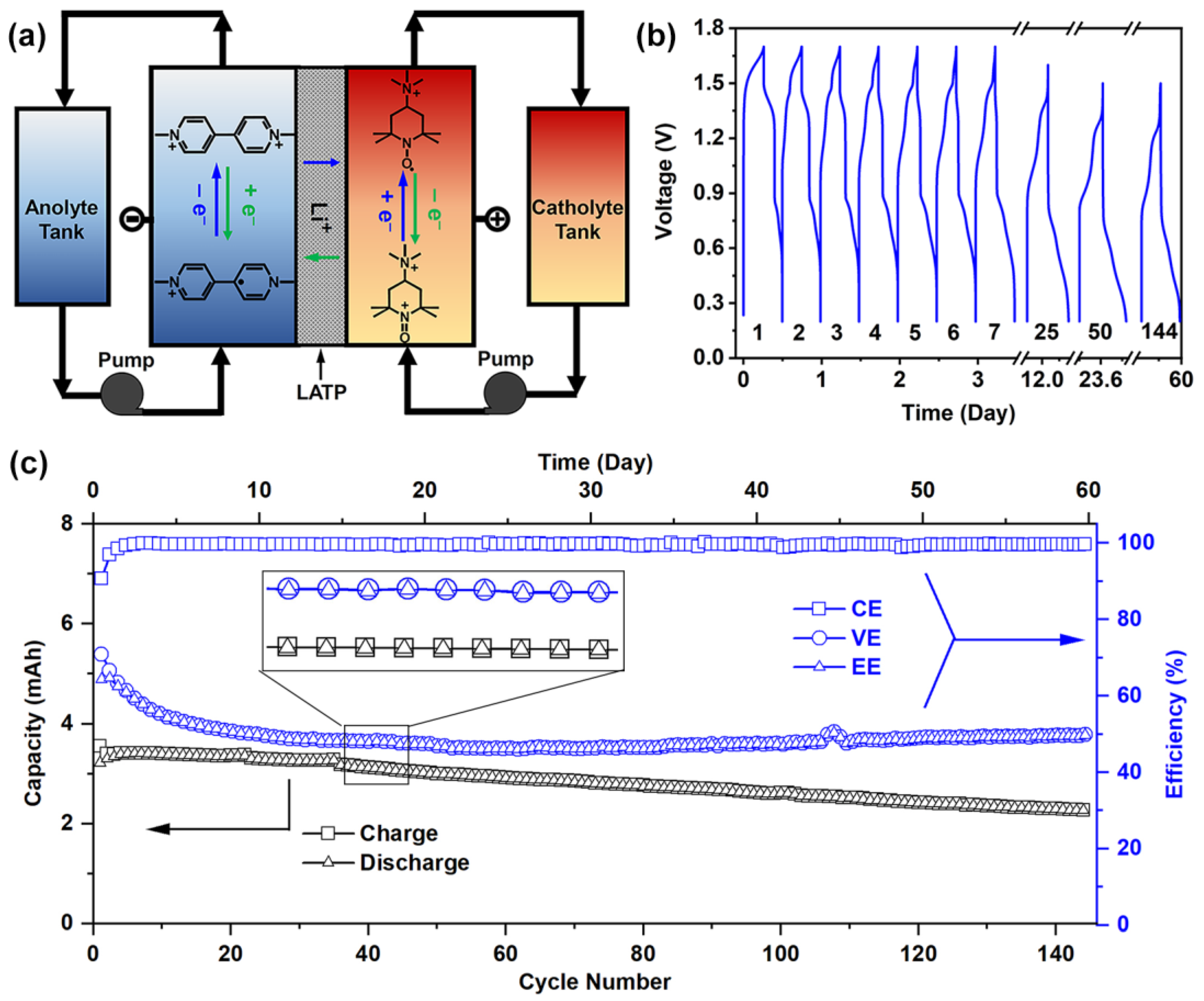
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dunn, B.; Kamath, H.; Tarascon, J.M. Electrical Energy Storage for the Grid: A Battery of Choices. Science 2011, 334, 928–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.G.; Zhang, J.L.; Kintner-Meyer, M.C.W.; Lu, X.C.; Choi, D.W.; Lemmon, J.P.; Liu, J. Electrochemical Energy Storage for Green Grid. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 3577–3613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, K.; Fang, Q.R.; Gu, S.; Li, S.F.Y.; Yan, Y.S. Nonaqueous redox-flow batteries: Organic solvents, supporting electrolytes, and redox pairs. Energ. Environ. Sci. 2015, 8, 3515–3530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winsberg, J.; Hagemann, T.; Janoschka, T.; Hager, M.D.; Schubert, U.S. Redox-Flow Batteries: From Metals to Organic Redox-Active Materials. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 686–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.A.; Hu, B.; Hu, M.W.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, T.L. Status and Prospects of Organic Redox Flow Batteries toward Sustainable Energy Storage. Acs Energy Lett. 2019, 4, 2220–2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.Y.; Tian, J.Y.; Xu, J.; Wang, Y.G. Organic Flow Batteries: Recent Progress and Perspectives. Energ. Fuel 2020, 34, 13384–13411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Rhodes, Z.; Cabrera-Pardo, J.R.; Minteer, S.D. Recent advancements in rational design of non-aqueous organic redox flow batteries. Sustain. Energ. Fuels 2020, 4, 4370–4389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.L.; Cosimbescu, L.; Xu, W.; Hu, J.Z.; Vijayakumar, M.; Feng, J.; Hu, M.Y.; Deng, X.C.; Xiao, J.; Liu, J.; et al. Towards High-Performance Nonaqueous Redox Flow Electrolyte Via Ionic Modification of Active Species. Adv. Energy Mater. 2015, 5, 1400678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Xu, W.; Vijayakumar, M.; Cosimbescu, L.; Liu, T.; Sprenkle, V.; Wang, W. TEMPO-Based Catholyte for High-Energy Density Nonaqueous Redox Flow Batteries. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 7649–7653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.H.; Cheng, L.; Assary, R.S.; Wang, P.Q.; Xue, Z.; Burrell, A.K.; Curtiss, L.A.; Zhang, L. Liquid Catholyte Molecules for Nonaqueous Redox Flow Batteries. Adv. Energy Mater. 2015, 5, 1401782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milshtein, J.D.; Kaur, A.P.; Casselman, M.D.; Kowalski, J.A.; Modekrutti, S.; Zhang, P.L.; Attanayake, N.H.; Elliott, C.F.; Parkin, S.R.; Risko, C.; et al. High current density, long duration cycling of soluble organic active species for non-aqueous redox flow batteries. Energ. Environ. Sci. 2016, 9, 3531–3543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevov, C.S.; Hickey, D.P.; Cook, M.E.; Robinson, S.G.; Barnett, S.; Minteer, S.D.; Sigman, M.S.; Sanford, M.S. Physical Organic Approach to Persistent, Cyclable, Low-Potential Electrolytes for Flow Battery Applications. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 138, 2924–2927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sevov, C.S.; Samaroo, S.K.; Sanford, M.S. Cyclopropenium Salts as Cyclable, High-Potential Catholytes in Nonaqueous Media. Adv. Energy Mater. 2017, 7, 1602027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.J.; Slikrob, I.A.; Assary, R.S.; Tung, S.O.; Silcox, B.; Curtiss, L.A.; Thompson, L.; Zhang, L. Toward Improved Catholyte Materials for Redox Flow Batteries: What Controls Chemical Stability of Persistent Radical Cations? J. Phys. Chem. C 2017, 121, 23347–23358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.J.; Huang, J.H.; Robertson, L.A.; Assary, R.S.; Shkrob, I.A.; Zhang, L. Elucidating Factors Controlling Long-Term Stability of Radical Anions for Negative Charge Storage in Nonaqueous Redox Flow Batteries. J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 122, 8116–8127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.L.; Xu, W.; Huang, J.H.; Zhang, L.; Walter, E.; Lawrence, C.; Vijayakumar, M.; Henderson, W.A.; Liu, T.B.; Cosimbescu, L.; et al. Radical Compatibility with Nonaqueous Electrolytes and Its Impact on an All-Organic Redox Flow Battery. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 8684–8687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.Y.; Qian, Y.M.; Feng, R.Z.; Ding, Y.; Zu, X.H.; Zhang, C.K.; Guo, X.L.; Wang, W.; Yu, G.H. Reversible redox chemistry in azobenzene-based organic molecules for high-capacity and long-life nonaqueous redox flow batteries. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowalski, J.A.; Casselman, M.D.; Kaur, A.P.; Milshtein, J.D.; Elliott, C.F.; Modekrutti, S.; Attanayake, N.H.; Zhang, N.J.; Parkin, S.R.; Risko, C.; et al. A stable two-electron-donating phenothiazine for application in nonaqueous redox flow batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 24371–24379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walser-Kuntz, R.; Yan, Y.C.; Sigman, M.; Sanford, M.S. A Physical Organic Chemistry Approach to Developing Cyclopropenium-Based Energy Storage Materials for Redox Flow Batteries. Accounts Chem. Res. 2023, 56, 1239–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, W.T.; Vemuri, R.S.; Milshtein, J.D.; Laramie, S.; Dmello, R.D.; Huang, J.H.; Zhang, L.; Hu, D.H.; Vijayakumar, M.; Wang, W.; et al. A symmetric organic-based nonaqueous redox flow battery and its state of charge diagnostics by FTIR. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 5448–5456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.S.; Pan, Z.Z.; Jin, Y.; Qiu, Q.Y.; Zhang, C.J.; Zhao, Y.C.; Li, Y.D. Membranes in non-aqueous redox flow battery: A review. J. Power Sources 2021, 500, 229983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, M.L.; Tyler, L.; Self, E.C.; Yang, G.; Nanda, J.; Saito, T. Membrane design for non-aqueous redox flow batteries: Current status and path forward. Chem 2022, 8, 1611–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.L.; Duan, W.T.; Huang, J.H.; Zhang, L.; Li, B.; Reed, D.; Xu, W.; Sprenkle, V.; Wang, W. A High-Current, Stable Nonaqueous Organic Redox Flow Battery. Acs Energy Lett. 2016, 1, 705–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, X.F.; Zhao, H.; Ren, X.R.; Zhang, D.H.; Wei, H.; Liu, J.G.; Zhang, X.; Yang, J.S. Porous polybenzimidazole membranes with high ion selectivity for the vanadium redox flow battery. J. Membrane Sci. 2020, 611, 118359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, X.F.; Tang, W.Q.; Dong, J.H.; Aili, D.; Yang, J.S. Anion exchange membranes based on long side-chain quaternary ammonium-functionalized poly(arylene piperidinium)s for vanadium redox flow batteries. Sci. China Mater. 2022, 65, 683–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahari, S.K.; Gokoglan, T.C.; Chaurasia, S.; Bolibok, J.N.; Golen, J.A.; Agar, E.; Cappillino, P.J. Toward High-Performance Nonaqueous Redox Flow Batteries through Electrolyte Design. ACS Appl. Energ. Mater. 2023, 6, 7521–7534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, Y.H.; Zhang, C.J.; Yuan, J.S.; Zhao, Y.C.; Li, Y.D. A high-performance all-iron non-aqueous redox flow battery. J. Power Sources 2020, 445, 227331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paddison, S.J.; Paul, R. The nature of proton transport in fully hydrated Nafion®. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2002, 4, 1158–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.B.; Wei, X.L.; Nie, Z.M.; Sprenkle, V.; Wang, W. A Total Organic Aqueous Redox Flow Battery Employing a Low Cost and Sustainable Methyl Viologen Anolyte and 4-HO-TEMPO Catholyte. Adv. Energy Mater. 2016, 6, 1501449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeBruler, C.; Hu, B.; Moss, J.; Liu, X.A.; Luo, J.A.; Sun, Y.J.; Liu, T.L. Designer Two-Electron Storage Viologen Anolyte Materials for Neutral Aqueous Organic Redox Flow Batteries. Chem 2017, 3, 961–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.H.; Goulet, M.A.; Tong, L.C.; Liu, Y.Z.; Ji, Y.L.; Wu, L.; Gordon, R.G.; Aziz, M.J.; Yang, Z.J.; Xu, T.W. A Long-Lifetime All-Organic Aqueous Flow Battery Utilizing TMAP-TEMPO Radical. Chem 2019, 5, 1861–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Liu, T.L. Two electron utilization of methyl viologen anolyte in nonaqueous organic redox flow battery. J. Energy Chem. 2018, 27, 1326–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attanayake, N.H.; Liang, Z.M.; Wang, Y.L.; Kaur, A.P.; Parkin, S.R.; Mobley, J.K.; Ewoldt, R.H.; Landon, J.; Odom, S.A. Dual function organic active materials for nonaqueous redox flow batteries. Mater. Adv. 2021, 2, 1390–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.W.; Kim, D.S. Paraquat: Toxicology and impacts of its ban on human health and agriculture. Weed Sci. 2020, 68, 208–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xing, X.Q.; Huo, Y.J.; Zhao, Y.C.; Li, Y.D. A systematic study of the co-solvent effect for an all-organic redox flow battery. Rsc Adv. 2018, 8, 24422–24427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Sayed, S.Y.; Luber, E.J.; Olsen, B.C.; Shirurkar, S.M.; Venkatakrishnan, S.; Tefashe, U.M.; Farquhar, A.K.; Smotkin, E.S.; McCreery, R.L.; et al. Redox Flow Batteries: How to Determine Electrochemical Kinetic Parameters. Acs Nano 2020, 14, 2575–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, X.L.; Pan, W.X.; Duan, W.T.; Hollas, A.; Yang, Z.; Li, B.; Nie, Z.M.; Liu, J.; Reed, D.; Wang, W.; et al. Materials and Systems for Organic Redox Flow Batteries: Status and Challenges. ACS Energy Lett. 2017, 2, 2187–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Y.; Goodenough, J.B.; Yu, G. A high-performance all-metallocene-based, non-aqueous redox flow battery. Energ. Environ. Sci. 2017, 10, 491–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Byon, H.R. High-Performance Lithium-Iodine Flow Battery. Adv. Energy Mater. 2013, 3, 1630–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Chen, H. High-capacity polysulfide–polyiodide nonaqueous redox flow batteries with a ceramic membrane. Nanoscale Adv. 2023, 5, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forner-Cuenca, A.; Penn, E.E.; Oliveira, A.M.; Brushett, F.R. Exploring the role of electrode microstructure on the performance of non-aqueous redox flow batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2019, 166, A2230–A2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compton, R.G.; Banks, C.E. Understanding Voltammetry; World Scientific: Singapore, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- ASTMC1499-09; Standard Test Method for Monotonic Equibiaxial Flexure Strength of Advanced Ceramics at Ambient Temperature. ASTM: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2009.
- Weibull, W. A statistical distribution function of wide applicability. J. Appl. Mech. 1951, 18, 293–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
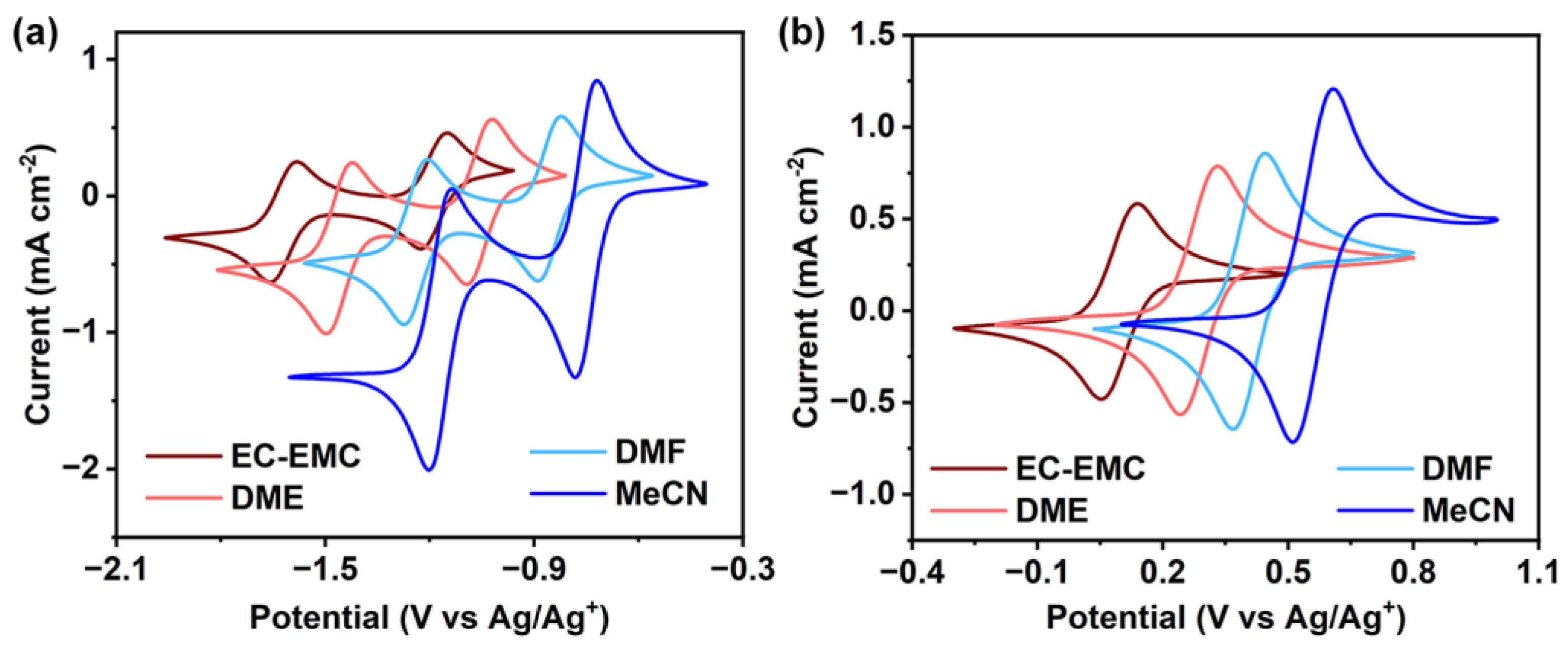
| Solvent | MV2+-TFSI2 | TMA-TEMPO-TFSI | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solubility | E1 a | D1 a | k0,1 a | E2 b | D2 b | k0,2 b | Solubility | E | D | k0 | |
| EC-EMC (3:7) | 1.13 M | −1.62 | 1.18 × 10−6 | 2.42 × 10−3 | −1.19 | 1.24 × 10−6 | 2.00 × 10−3 | 0.21 M | 0.10 | 0.97 × 10−6 | 1.46 × 10−3 |
| DME | 0.90 M | −1.46 | 1.64 × 10−6 | 1.64 × 10−3 | −1.06 | 2.16 × 10−6 | 1.83 × 10−3 | <0.1 M | 0.28 | 3.43 × 10−6 | 2.92 × 10−3 |
| DMF | 1.30 M | −1.24 | 2.71 × 10−6 | 5.90 × 10−3 | −0.86 | 2.62 × 10−6 | 5.04 × 10−3 | 1.00 M | 0.41 | 3.69 × 10−6 | 5.14 × 10−3 |
| MeCN | 1.36 M | −1.17 | 5.49 × 10−6 | 6.58 × 10−3 | −0.75 | 5.50 × 10−6 | 3.85 × 10−3 | 0.55 M | 0.56 | 5.89 × 10−6 | 2.56 × 10−3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yue, D.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, I.; Fang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Li, J.; Zhao, F.; Wei, X. A New Nonaqueous Flow Battery with Extended Cycling. Reactions 2024, 5, 452-461. https://doi.org/10.3390/reactions5030023
Yue D, Zhang W, Zhao I, Fang X, Zhao Y, Li J, Zhao F, Wei X. A New Nonaqueous Flow Battery with Extended Cycling. Reactions. 2024; 5(3):452-461. https://doi.org/10.3390/reactions5030023
Chicago/Turabian StyleYue, Diqing, Weilin Zhang, Ivy Zhao, Xiaoting Fang, Yuyue Zhao, Jenny Li, Feng Zhao, and Xiaoliang Wei. 2024. "A New Nonaqueous Flow Battery with Extended Cycling" Reactions 5, no. 3: 452-461. https://doi.org/10.3390/reactions5030023
APA StyleYue, D., Zhang, W., Zhao, I., Fang, X., Zhao, Y., Li, J., Zhao, F., & Wei, X. (2024). A New Nonaqueous Flow Battery with Extended Cycling. Reactions, 5(3), 452-461. https://doi.org/10.3390/reactions5030023






