Experimental Control of a Methanol Catalytic Membrane Reformer †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Setup
2.2. Control Variables
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Dynamic Behaviour of the System
3.2. Controller Design
3.2.1. Transfer Functions
3.2.2. PI Controller Design
3.3. Implementation and Experimental Validation of the Controller
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| PI | proportional integral controller |
| PID | proportional integral derivate controller |
| CMR | catalytic membrane reactor |
| MSR | methanol steam reforming |
| WGS | water–gas shift reaction |
| S/C | steam to carbon |
| proportional constant of PID controller | |
| integrative constant of PID controller | |
| proportional constant of transfer function | |
| integrative constant of transfer function | |
| time delay constant of transfer function | |
| SP | setpoint |
| P | pressure, Pa |
| T | temperature, K |
| methanol | |
| carbon monoxide | |
| carbon dioxide | |
| water | |
| Superscripts | |
| standard condition | |
| Subscripts | |
| liq | liquid |
References
- Algieri, C.; Coppola, G.; Mukherjee, D.; Shammas, M.I.; Calabro, V.; Curcio, S.; Chakraborty, S. Catalytic membrane reactors: The industrial applications perspective. Catalysts 2021, 11, 691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Pei, C.; Gong, J. Insights into interface engineering in steam reforming reactions for hydrogen production. Energy Environ. Sci. 2019, 12, 3473–3495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iulianelli, A.; Ribeirinha, P.; Mendes, A.; Basile, A. Methanol steam reforming for hydrogen generation via conventional and membrane reactors: A review. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 2014, 29, 355–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iulianelli, A.; Ghasemzadeh, K.; Basile, A. Progress in Methanol Steam Reforming Modelling via Membrane Reactors Technology. Membranes 2018, 8, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jazani, O.; Bennett, J.; Liguori, S. Carbon-low, renewable hydrogen production from methanol steam reforming in membrane reactors—A review. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2023, 189, 109382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lytkina, A.A.; Orekhova, N.V.; Yaroslavtsev, A.B. Methanol Steam Reforming in Membrane Reactors. Pet. Chem. 2018, 58, 911–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Song, Y.; Kim, T.; Kim, S. Recent trends in the development of reactor systems for hydrogen production via methanol steam reforming. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47, 3587–3610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, G.; Arriola, E.; Chen, W.-H.; De Luna, M.D. A comprehensive review of hydrogen production from methanol thermochemical conversion for sustainability. Energy 2021, 217, 119384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjekar, A.M.; Yadav, G.D. Steam Reforming of Methanol for Hydrogen Production: A Critical Analysis of Catalysis, Processes, and Scope. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2021, 60, 89–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Weng, J.; Liao, M.; Luo, Q.; Luo, X.; Tian, Z.; Shu, R.; Chen, Y.; Du, Y. Configuration of coupling methanol steam reforming over Cu-based catalyst in a synthetic palladium membrane for one-step high purity hydrogen production. J. Energy Inst. 2023, 108, 101245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedayati, A.; Le Corre, O.; Lacarrière, B.; Llorca, J. Dynamic simulation of pure hydrogen production via ethanol steam reforming in a catalytic membrane reactor. Energy 2016, 117, 316–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pravin, P.S.; Gudi, R.D.; Bhartiya, S. Dynamic Modeling and Control of an Integrated Reformer-Membrane-Fuel Cell System. Processes 2018, 6, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pravin, P.S.; Bhartiya, S.; Gudi, R.D. Modeling and Predictive Control of an Integrated Reformer–Membrane–Fuel Cell–Battery Hybrid Dynamic System. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 11392–11406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquez-Ruiz, A.; Wu, J.; Özkan, L.; Gallucci, F.; Annaland, M.V.S. Optimal Operation and Control of Fluidized Bed Membrane Reactors for Steam Methane Reforming. Comput. Aided Chem. Eng. 2019, 46, 1231–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.-C.; Tzeng, S.-Y.; Chen, P.-H. Optimization Design of PID Controllers for PEMFC with Reformer Using Genetic Algorithm. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning and Cybernetics, ICMLC 2010, Qingdao, China, 11–14 July 2010; pp. 2990–2995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyriakides, A.-S.; Voutetakis, S.; Papadopoulou, S.; Seferlis, P. Integrated Design and Control of Various Hydrogen Production Flowsheet Configurations via Membrane Based Methane Steam Reforming. Membranes 2019, 9, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyriakides, A.-S.; Seferlis, P.; Voutetakis, S.; Papadopoulou, S. Model Predictive Control for Hydrogen Production in a Membrane Methane Steam Reforming Reactor. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2016, 52, 991–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra, M.; Ocampo-Martinez, C.; Li, M.; Llorca, J. Model predictive control for ethanol steam reformers with membrane separation. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 1949–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, R.; López, E.; Divins, N.J.; Allué, M.; Jossen, A.; Riera, J.; Llorca, J. Ethanol catalytic membrane reformer for direct PEM FC feeding. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2013, 38, 5605–5615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamps, A.T.; Gatzke, E.P. Dynamic modeling of a methanol reformer—PEMFC stack system for analysis and design. J. Power Sources 2006, 161, 356–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sharkh, M.Y.; Rahman, A.; Alam, M.S.; Byrne, P.C.; Sakla, A.A.; Thomas, T. A dynamic model for a stand-alone PEM fuel cell power plant for residential applications. J. Power Sources 2004, 138, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Pai, C.-C. Control of a heat-integrated proton exchange membrane fuel cell system with methanol reforming. J. Power Sources 2009, 194, 920–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ipsakis, D.; Ouzounidou, M.; Papadopoulou, S.; Seferlis, P.; Voutetakis, S. Dynamic modeling and control analysis of a methanol autothermal reforming and PEM fuel cell power system. Appl. Energy 2017, 208, 703–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cifuentes, A.; Soler, L.; Torres, R.; Llorca, J. Methanol steam reforming over PdZn/ZnAl2O4/Al2O3 in a catalytic membrane reactor: An experimental and modelling study. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47, 11574–11588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cifuentes, A.; Serra, M.; Torres, R.; Llorca, J. Experimental control of a methanol catalytic membrane reformer. In Proceedings of the VIII Symposium on Hydrogen, Fuel Cells and Advanced Batteries (HYCELTEC), Buenos Aires, Argentina, 10–13 July 2022; pp. 52–54. [Google Scholar]
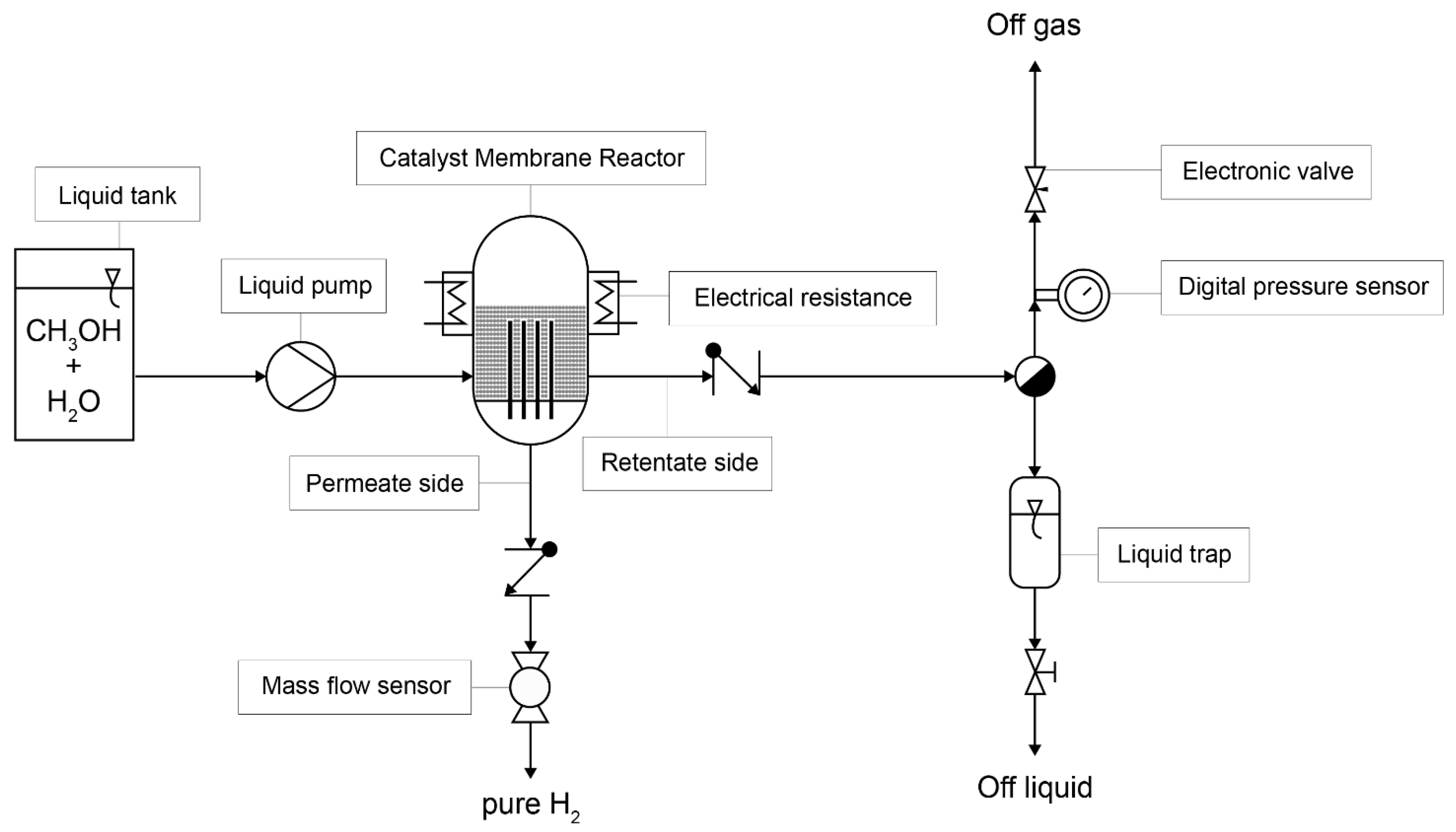
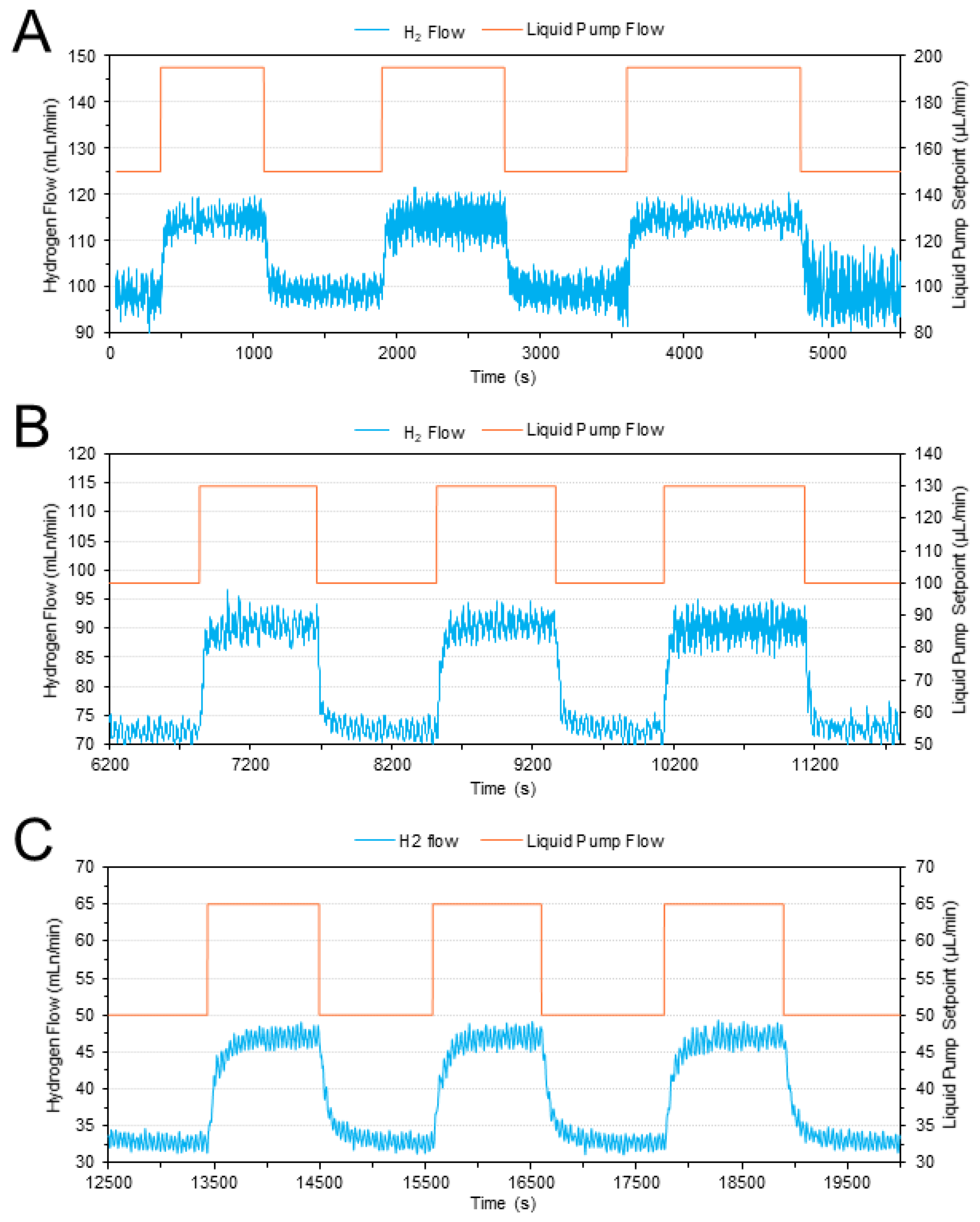


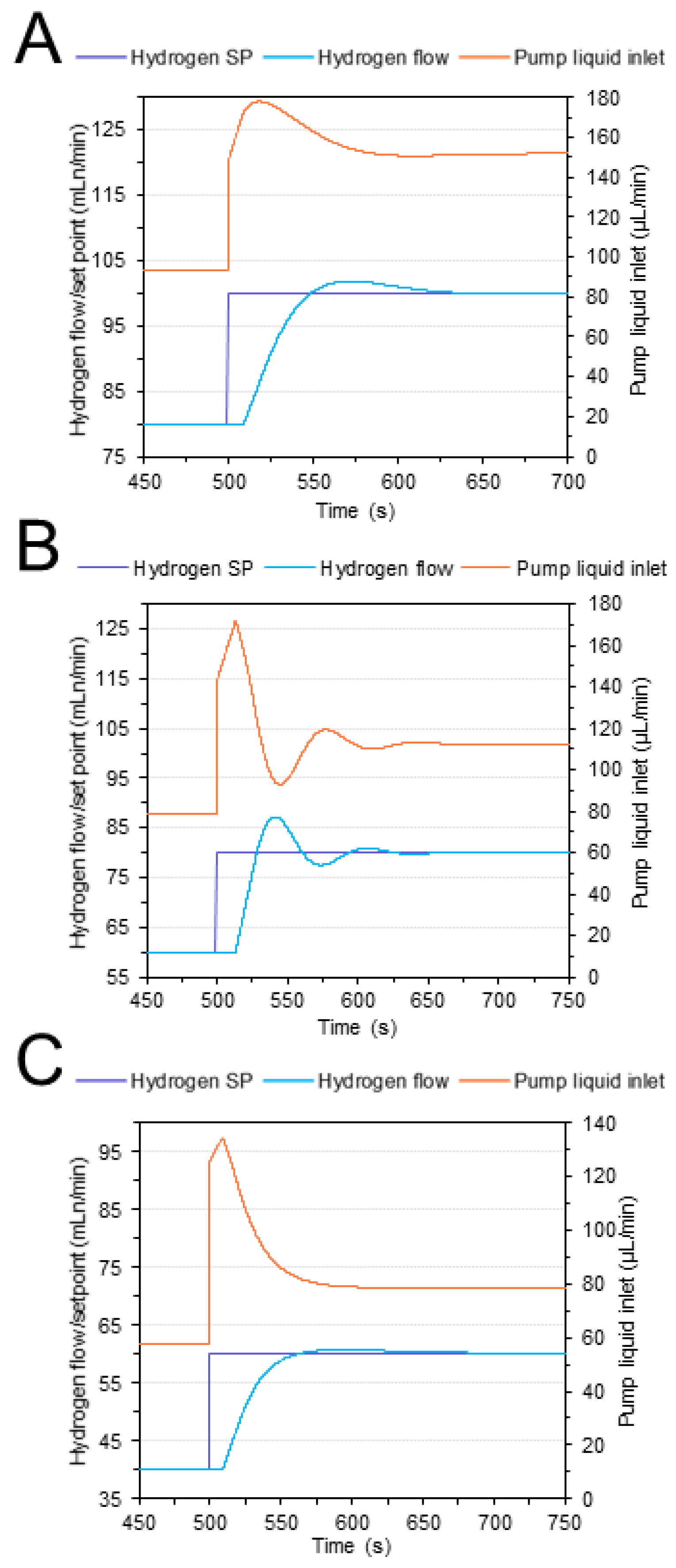
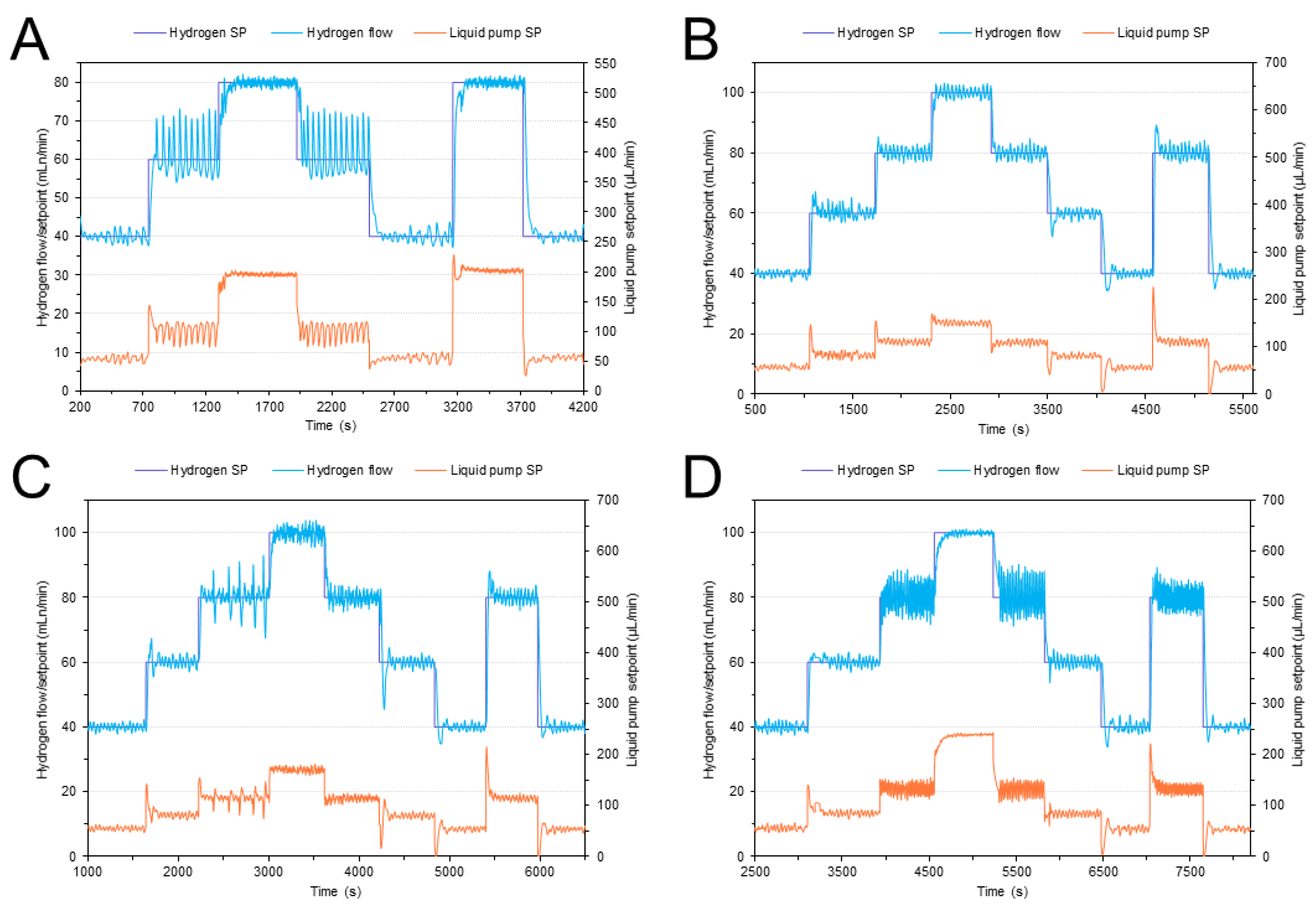
| Reactor temperature (°C) | 450 |
| Reactor relative pressure (bar) | 6, 8, 10, 12 |
| Inlet flow rate (µLliq/min) | 50–200 |
| Pressure (Bar) | Liquid Flow Inlet (µLliq/min) | Transfer Function Parameters | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12 | 150–195 | 0.34 | 30 | 9 |
| 100–130 | 0.60 | 29 | 13 | |
| 50–65 | 0.95 | 91 | 9 | |
| 10 | 150–195 | 0.29 | 26 | 7 |
| 100–130 | 0.52 | 29 | 10 | |
| 50–65 | 0.92 | 81 | 13 | |
| 8 | 150–195 | 0.23 | 24 | 6 |
| 100–130 | 0.45 | 28 | 8 | |
| 50–65 | 0.83 | 71 | 19 | |
| 6 | 150–195 | 0.15 | 18 | 7 |
| 100–130 | 0.32 | 21 | 10 | |
| 50–65 | 0.76 | 68 | 11 | |
| Pressure (Bar) | Kc Low Flow (50–60 µLliq/min) | Kc Medium Flow (100–130 µLliq/min) | Kc High Flow (150–195 µLliq/min) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 6 | 3.87 | 3.19 | 2.82 |
| 8 | 2.54 | 3.96 | 2.64 |
| 10 | 3.52 | 3.56 | 2.75 |
| 12 | 3.73 | 2.17 | 2.76 |
| Average values | 3.42 | 3.22 | 2.74 |
| Pressure (Bar) | τi Low Flow (50–60 µLliq/min) | τi Medium Flow (100–130 µLliq/min) | τi High Flow (150–195 µLliq/min) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 6 | 0.015 | 0.048 | 0.085 |
| 8 | 0.015 | 0.037 | 0.055 |
| 10 | 0.012 | 0.027 | 0.047 |
| 12 | 0.013 | 0.032 | 0.036 |
| Average values | 0.014 | 0.034 | 0.051 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cifuentes, A.; Serra, M.; Torres, R.; Llorca, J. Experimental Control of a Methanol Catalytic Membrane Reformer. Reactions 2023, 4, 702-712. https://doi.org/10.3390/reactions4040040
Cifuentes A, Serra M, Torres R, Llorca J. Experimental Control of a Methanol Catalytic Membrane Reformer. Reactions. 2023; 4(4):702-712. https://doi.org/10.3390/reactions4040040
Chicago/Turabian StyleCifuentes, Alejandro, Maria Serra, Ricardo Torres, and Jordi Llorca. 2023. "Experimental Control of a Methanol Catalytic Membrane Reformer" Reactions 4, no. 4: 702-712. https://doi.org/10.3390/reactions4040040
APA StyleCifuentes, A., Serra, M., Torres, R., & Llorca, J. (2023). Experimental Control of a Methanol Catalytic Membrane Reformer. Reactions, 4(4), 702-712. https://doi.org/10.3390/reactions4040040








