Controlled Traffic Farm: Fuel Demand and Carbon Emissions in Soybean Sowing
Abstract
1. Introduction
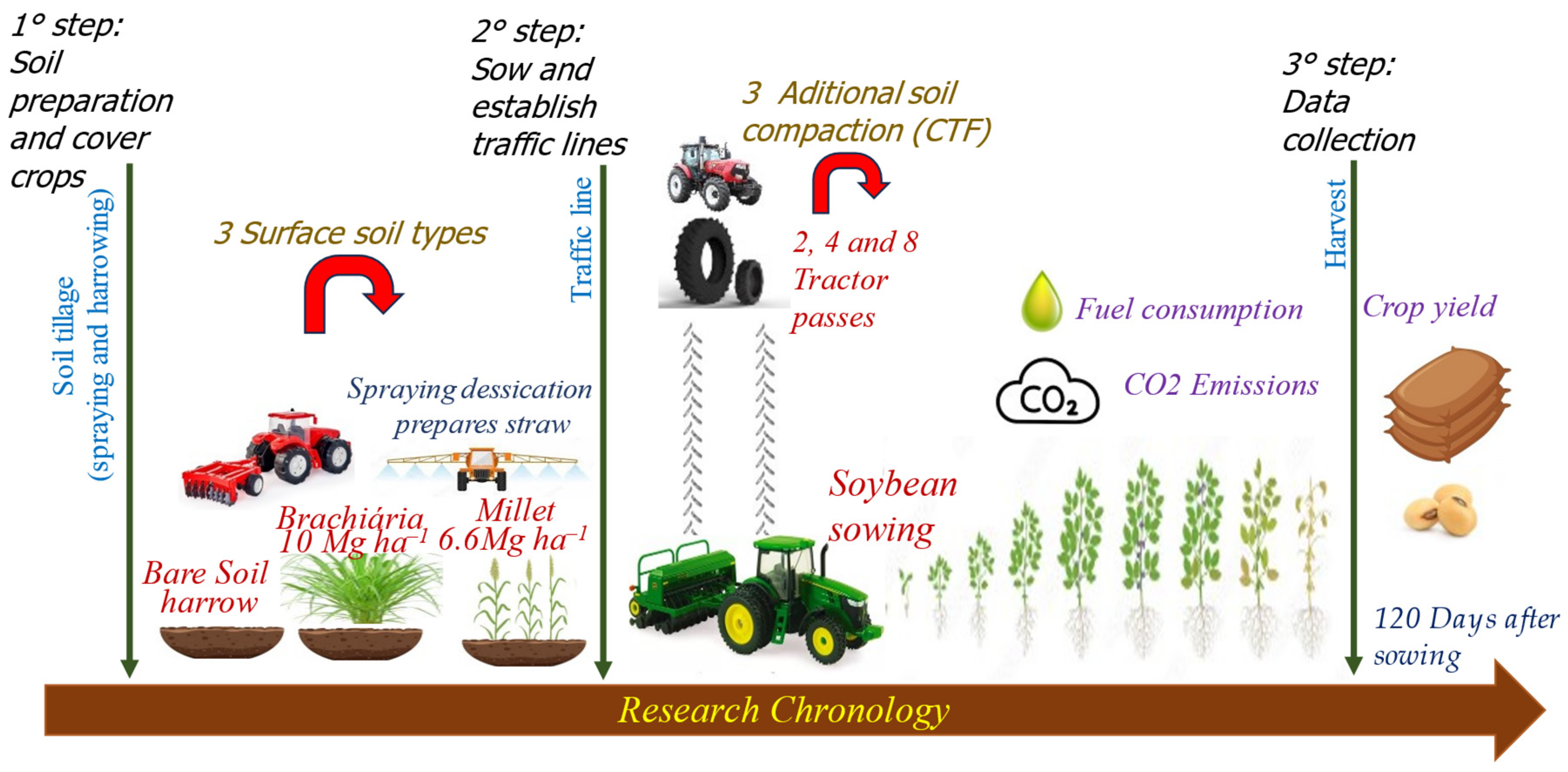
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site and Experimental Design
2.2. Data Collection and Statistical Analysis
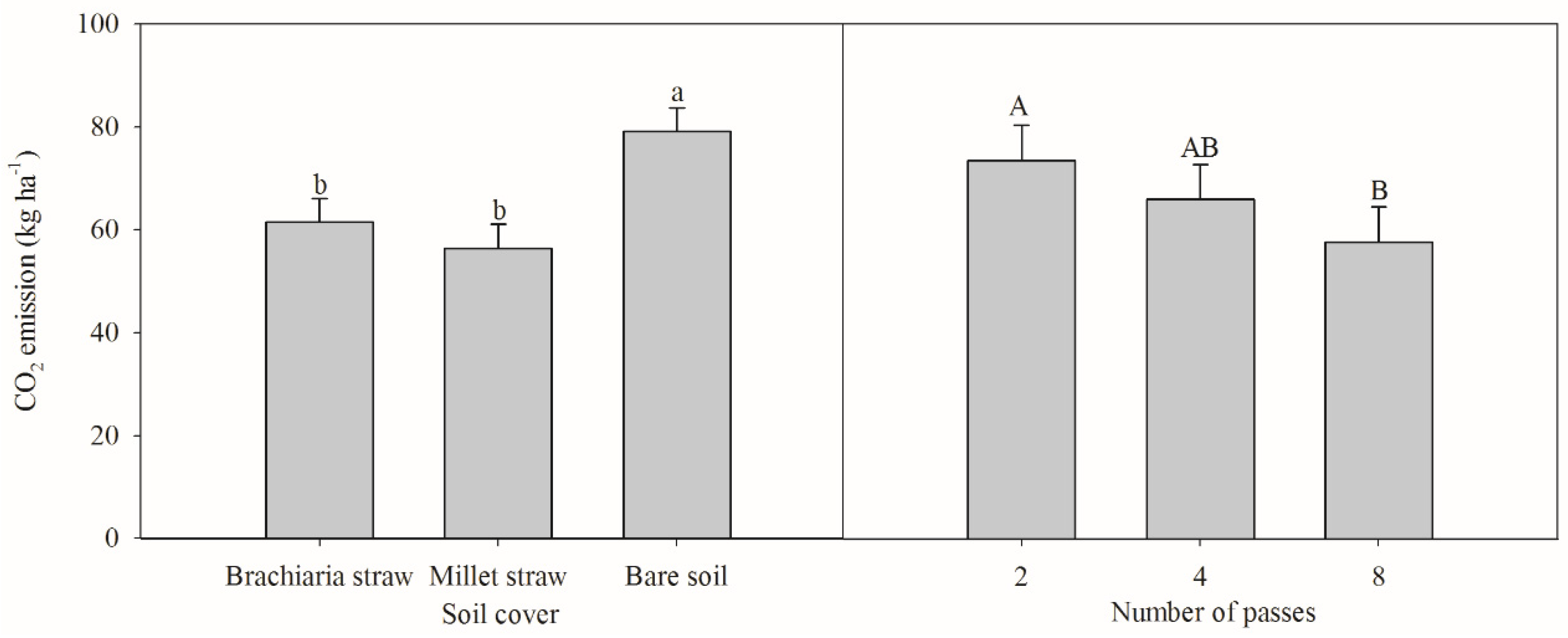
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, X.; Ma, L.; Yan, S.; Chen, X.; Growe, A. Trade for Food Security: The Stability of Global Agricultural Trade Networks. Foods 2023, 12, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartman, G.L.; West, E.D.; Herman, T.K. Crops that feed the World 2. Soybean—Worldwide production, use, and constraints caused by pathogens and pests. Food Secur. 2011, 3, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, H.S.; Luna, F.V. Soybeans. In Brazilian Crops in the Global Market: The Emergence of Brazil as a World Agribusiness Exporter Since 1950; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 79–106. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Wang, T.; Yao, S.; Sun, H.; Zhang, B. Soil compaction development facilitated the decadal improvement of the root system architecture and rhizosheath soil traits of soybean in the North China Plain. Soil Tillage Res. 2024, 237, 105983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schjønning, P.; Lamandé, M.; De Pue, J.; Cornelis, W.M.; Labouriau, R.; Keller, T. The challenge in estimating soil compressive strength for use in risk assessment of soil compaction in field traffic. Adv. Agron. 2023, 178, 61–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.N.; Tanveer, M.; Shahzad, B.; Shah, A.N.; Tanveer, M.; Shahzad, B.; Yang, G.; Fahad, S.; Ali, S.; Bukhari, M.A.; et al. Soil compaction efects on soil health and cropproductivity: An overview. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 10056–10067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, C.; Mawodza, T.; Atkinson, B.S.; Atkinson, J.A.; Sturrock, C.J.; Whalley, R.; Hawkesford, M.J.; Cooper, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, H.; et al. The effects of soil compaction on wheat seedling root growth are specific to soil texture and soil moisture status. Rhizosphere 2024, 29, 100838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, S.; Chakraborty, D. Root growth and physiological responses in wheat to topsoil and subsoil compaction with or without artificial vertical macropores. Heliyon 2023, 9, e18834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colombi, T.; Keller, T. Developing Strategies to Recover Crop Productivity after Soil Compaction—A Plant Eco-Physiological Perspective. Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 191, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, T.; Sandim, M.; Colombi, T.; Horn, R.; Or, D. Historical increase in agricultural machinery weights enhanced soil stress levels and adversely affected soil functioning. Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 194, 104293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, S.A.; Hussein, M.A.; Al-Rijabo, S.A. Mechanization Assessment of Soil Compaction Induced by Traffic of Farm Machinery. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2023, 1214, 012051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivarajan, S.; Maharlooei, M.; Bajwa, S.G.; Nowatzki, J. Impact of soil compaction due to wheel traffic on corn and soybean growth, development and yield. Soil Tillage Res. 2018, 175, 234–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trentin, R.G.; Modolo, A.J.; de Oliveira Vargas, T.; Campos, J.R.R.; Baesso, M.M.; Trogello, E.; Madaloz, J.C.C. Traction force demand of soybean planting in compacted Oxisol. Aust. J. Crop Sci. 2018, 12, 374–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, C.J.B.; da Silva, A.G.; de Oliveira Preto, V.R.; Tormena, C.A.; Braz, G.B.P.; de Freitas Souza, M.; da Silva, A.L.B.R. Effects of Second-Season Crops on Soybean Cultivation in Compacted Soil in Brazilian Cerrado. Agronomy 2023, 13, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa-Henriksen, A.; Skou-Nielsen, N.; Munkholm, L.J.; Sørensen, C.A.; Green, O.; Edwards, G.T. Infield optimized route planning in harvesting operations for risk of soil compaction reduction. Soil Use Manag. 2021, 37, 810–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godwin, R.J.; White, D.R.; Dickin, E.T.; Kaczorowska-Dolowy, M.; Millington, W.A.; Pope, E.K.; Misiewicz, P.A. The effects of traffic management systems on the yield and economics of crops grown in deep, shallow and zero tilled sandy loam soil over eight years. Soil Tillage Res. 2022, 223, 105465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minhas, W.A.; Mumtaz, N.; Ur-Rehman, H.; Farooq, S.; Farooq, M.; Ali, H.M.; Hussain, M. Weed infestation and productivity of wheat crop sown in various cropping systems under conventional and conservation tillage. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1176738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marques Filho, A.C.; de Medeiros, S.D.S.; Martins, M.B.; Moura, M.S.; Lanças, K.P. Can the straw remaining on the ground reduce the wheelsets impact on sugarcane crop? Sugar Tech 2022, 24, 1814–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulgakov, V.; Pascuzzi, S.; Nadykto, V.; Adamchuk, V.; Kaminskiy, V.; Kyurchev, V.; Santoro, F. Effects of Tractor and Soil Parameters on the Depth of the Permanent Traffic Lanes in Controlled Traffic Farming Systems. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 6620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šimanský, V.; Wójcik-Gront, E.; Rustowska, B.; Juriga, M.; Chlpík, J.; Macák, M. Reducing machine movement intensity in the field improves soil structure. Acta Fytotech. Zootech. 2023, 26, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botta, G.F.; Antille, D.L.; Ghelfi, D.G.; Rivero, D.; Ezquerra-Canalejo, A. Quantifying the wheeled area of a random traffic, no-tillage soybean production system. In Proceedings of the 2023 ASABE Annual International Meeting, Omaha, NE, USA, 9–12 July 2023; American Society of Agricultural and Biological Engineers: St. Joseph, MI, USA, 2023; p. 2300771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medel-Jiménez, F.; Krexner, T.; Gronauer, A.; Kral, I. Life cycle assessment of four different precision agriculture technologies and comparison with a conventional scheme. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 434, 140198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, M.A.; Antille, D.L.; Kodur, S.; Chen, G.; Tullberg, J.N. Controlled traffic farming effects on productivity of grain sorghum, rainfall and fertiliser nitrogen use efficiency. J. Agric. Food Res. 2021, 3, 100111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamirat, T.W.; Pedersen, S.M.; Farquharson, R.J.; de Bruin, S.; Forristal, P.D.; Sørensen, C.G.; Nuyttens, D.; Pedersen, H.H.; Thomsen, M.N. Controlled traffic farming and field traffic management: Perceptions of farmers groups from Northern and Western European countries. Soil Tillage Res. 2022, 217, 105288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hefner, M.; Labouriau, R.; Nørremark, M.; Kristensen, H.L. Controlled traffic farming increased crop yield, root growth, and nitrogen supply at two organic vegetable farms. Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 191, 117–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antille, D.L.; Peets, S.; Galambošová, J.; Botta, G.F.; Rataj, V.; Macak, M.; Tullberg, J.N.; Chamen, W.C.T.; White, D.R.; Misiewicz, P.A.; et al. Review: Soil compaction and controlled traffic farming in arable and grass cropping systems. Agron. Res. 2019, 17, 653–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botta, G.F.; Antille, D.L.; Nardon, G.F.; Rivero, D.; Bienvenido, F.; Contessotto, E.E.; Ressia, J.M. Zero and controlled traffic improved soil physical conditions and soybean yield under no-tillage. Soil Tillage Res. 2022, 215, 105235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Luz, F.B.; Gonzaga, L.C.; Castioni, G.A.F.; de Lima, R.P.; Carvalho, J.L.N.; Cherubin, M.R. Controlled traffic farming maintains soil physical functionality in sugarcane fields. Geoderma 2023, 432, 116427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antille, D.L.; Chamen, W.C.T.; Tullberg, J.N.; Lal, R. The potential of controlled traffic farming to mitigate greenhouse gas emissions and enhance carbon sequestration in arable land: A critical review. Trans. ASABE 2015, 58, 707–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertollo, G.M.; Schlosser, J.F.; Bertinatto, R.; Martini, A.T.; Farias, M.S.D. Pollutant emissions from a tractor towing a seeder-fertilizer in an area with controlled machinery traffic. Ciência Rural 2024, 54, e20230173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, D.M.S.; Santos, R.S.; Chizzotti, F.H.M.; Bretas, I.L.; Franco, A.L.C.; Lima, R.P.; Freitas, D.A.F.; Cherubin, M.R.; Cerri, C.E.P. Crop, livestock, and forestry integration to reconcile soil health, food production, and climate change mitigation in the Brazilian Cerrado: A review. Geoderma Reg. 2024, 37, e00796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagoudis, I.N.; Shakri, A.R. A framework for measuring carbon emissions for inbound transportation and distribution networks. Res. Transp. Bus. Manag. 2015, 17, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvares, C.A.; Stape, J.L.; Sentelhas, P.C.; Gonçalves, J.D.M.; Sparovek, G. Köppen’s climate classification map for Brazil. Meteorol. Z. 2013, 22, 711–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, H.G.; Jacomine, P.K.T.; Anjos, L.H.C.; Oliveira, V.Á.; Lumbreras, J.F.; Coelho, M.R.; Almeida, J.A.; de Filho, J.C.A.; Oliveira, J.B.; Cunha, T.J.F. Sistema Brasileiro de Classificação de Solos; Centro Nacional de Pesquisa de Solos: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2018; ISBN 978-85-7035-198-2. [Google Scholar]
- IUSS Working Group. World Reference Base for Soil Resources 2014: International Soil Classification System for Naming Soils and Creating Legends for Soil Maps; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Manzone, M.; Calvo, A. Energy and CO2 analysis of poplar and maize crops for biomass production in north Italy. Renew. Energy 2016, 86, 675–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šarauskis, E.; Vaitauskienė, K.; Romaneckas, K.; Jasinskas, A.; Butkus, V.; Kriaučiūnienė, Z. Fuel consumption and CO2 emission analysis in different strip tillage scenarios. Energy 2017, 118, 957–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, R. Effect of Controlled Traffic on Energy Use Efficiency in Wheat-Maize Production in North China Plain. J. Comput. Theor. Nanosci. 2016, 4, 2634–2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laufer, D.; Koch, H.J. Growth and yield formation of sugar beet (Beta vulgaris L.) under strip tillage compared to full width tillage on silt loam soil in Central Europe. Eur. J. Agron. 2017, 82, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lekavičienė, K.; Šarauskis, E.; Naujokienė, V.; Buragienė, S.; Kriaučiūnienė, Z. The effect of the strip tillage machine parameters on the traction force, diesel consumption and CO2 emissions. Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 192, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gozubuyuk, Z.; Sahin, U.; Celik, A. Operational and yield performances and fuel-related CO2 emissions under different tillage-sowing practices in a rainfed crop rotation. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 17, 4563–4576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altikat, S.; Kus, E.; Kucukerdem, H.K.; Gozubuyuk, Z. The applications of no-tillage in Turkey. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Science, Ecology and Technology, Rome, Italy, 14–16 August 2017; pp. 14–16. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, A.; Prakash, A.; Bhambota, S.; Kumar, S. Investigations of precision agriculture technologies with application to developing countries. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, M.B.; Bortolheiro, F.P.A.P.; Testa, J.V.P.; Sartori, M.M.P.; Crusciol, C.A.C.; Lanças, K.P. Fuel Consumption Between Two Soil Tillage Systems for Planting Sugarcane. Sugar Tech 2021, 23, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, M.B.; Sandi, J.; de Souza, F.L.; Santos, R.; Lanças, K.P. Otimização energética de um trator agrícola utilizando normas técnicas em operações de gradagem. Rev. Eng. Agric. 2018, 26, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, A.G.; Marques Filho, A.C.; Correia, T.P.d.S.; Firmino, P.C.; Arbex Silva, P.R. Agricultural tractor: Influence to gear selection on energy demand and costs in sugarcane transshipment. Eng. Agrícola 2023, 43, e20230037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartholomeu, D.B.; Lopes, C.J.R.; Yoshizaki, H.T.Y. CO2 Emissions from Fuel Consumption in the Logistic Stages of the Brazilian Bioethanol Supply Chain. Sustainability 2020, 12, 9979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balafoutis, A.; Beck, B.; Fountas, S.; Vangeyte, J.; Wal, T.V.d.; Soto, I.; Gómez-Barbero, M.; Barnes, A.; Eory, V. Precision Agriculture Technologies Positively Contributing to GHG Emissions Mitigation, Farm Productivity and Economics. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damanauskas, V.; Janulevičius, A. Validation of Criteria for Predicting Tractor Fuel Consumption and CO2 Emissions When Ploughing Fields of Different Shapes and Dimensions. AgriEngineering 2023, 5, 2408–2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangalassery, S.; Sjögersten, S.; Sparkes, D.L.; Sturrock, C.J.; Craigon, J.; Mooney, S.J. To what extent can zero tillage lead to a reduction in greenhouse gas emissions from temperate soils? Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 4586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steponavičienė, V.; Žiūraitis, G.; Rudinskienė, A.; Jackevičienė, K.; Bogužas, V. Long-Term Effects of Different Tillage Systems and Their Impact on Soil Properties and Crop Yields. Agronomy 2024, 14, 870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crystal-Ornelas, R.; Thapa, R.; Tully, K.L. Soil Organic Carbon is Affected by Organic Amendments, Conservation Tillage, and Cover Cropping in Organic Farming Systems: A Meta-Analysis. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2021, 312, 107356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, H.; Colombi, T.; Keller, T. The Influence of Soil Management on Soil Health: An On-Farm Study in Southern Sweden. Geoderma 2020, 360, 114010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, C.J.B.; Tormena, C.A.; Severiano, E.C.; Zotarelli, L.; Júnior, E.B. Soil compaction influences soil physical quality and soybean yield under long-term no-tillage. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2021, 3, 383–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azevedo, C.V.G.; Val, B.H.P.; Araújo, L.C.A.; Juhász, A.C.P.; Di Mauro, A.O.; Trevisoli, S.H.U. Genetic Parameters of Soybean Populations Obtained from Crosses between Grain and Food Genotypes. Acta Sci. Agron. 2021, 43, e46968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Assis, R.L.; De Freitas, R.S.; Mason, S.C. Pearl Millet Production Practices in Brazil: A Review. Exp. Agric. 2017, 54, 699–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boussinesq, J. Application des Potentiels à L’étude de L’équilibre et du Mouvement des Solides Élastiques; Gauthier-Villars: Lille, France, 1885. [Google Scholar]
- Soane, B.D.; Blackwell, P.S.; Dickson, J.W.; Painter, D.J. Compaction by agricultural vehicles: A review ii. compaction under tyres and other running gear. Soil Tillage Res. 1980, 1, 373–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalise, K.S.; Singh, S.; Wegner, B.R.; Kumar, S.; Pérez-Gutiérrez, J.D.; Osborne, S.L.; Nleya, T.; Guzman, J.; Rohila, J.S. Cover crops and returning residue impact on soil organic carbon, bulk density, penetration resistance, water retention, infiltration, and soybean yield. Agron. J. 2019, 1, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, G.F.; Calonego, J.C.; Luperini, B.C.O.; Chamma, L.; Alves, E.R.; Rodrigues, S.A.; Putti, F.F.; da Silva, V.M.; de Almeida Silva, M. Soil—Plant Relationships in Soybean Cultivated under Conventional Tillage and Long-Term No-Tillage. Agronomy 2022, 12, 697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alakukku, L. Subsoil compaction due to wheel traffic. Agric. Food Sci. 1999, 8, 333–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girardello, V.C.; Amado, T.J.C.; Santi, A.L.; Lanzabova, M.E.; Tasca, A. Resistência do solo a penetração e desenvolvimento radicular da soja sob sistema plantio direto com tráfego controlado de máquinas agrícolas. Sci. Agrar. 2017, 2, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masola, M.J.; Alesso, C.A.; Carrizo, M.E.; Berhongaray, G.; Botta, G.F.; Horn, R.; Imhoff, S. Advantages of the one-wheeled tramline for multiple machinery widths method on sunflower (Helianthus annus L.) and maize (Zea mays L.) responses in the Argentinean Flat Pampas. Soil Tillage Res. 2020, 196, 104462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martins, M.B.; Marques Filho, A.C.; Seron, C.d.C.; Guimarães Júnnyor, W.d.S.; Vendruscolo, E.P.; Bortolheiro, F.P.d.A.P.; Blanco Bertolo, D.M.; Lopes, A.G.C.; Santana, L.S. Controlled Traffic Farm: Fuel Demand and Carbon Emissions in Soybean Sowing. AgriEngineering 2024, 6, 1794-1806. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriengineering6020104
Martins MB, Marques Filho AC, Seron CdC, Guimarães Júnnyor WdS, Vendruscolo EP, Bortolheiro FPdAP, Blanco Bertolo DM, Lopes AGC, Santana LS. Controlled Traffic Farm: Fuel Demand and Carbon Emissions in Soybean Sowing. AgriEngineering. 2024; 6(2):1794-1806. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriengineering6020104
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartins, Murilo Battistuzzi, Aldir Carpes Marques Filho, Cássio de Castro Seron, Wellingthon da Silva Guimarães Júnnyor, Eduardo Pradi Vendruscolo, Fernanda Pacheco de Almeida Prado Bortolheiro, Diego Miguel Blanco Bertolo, Arthur Gabriel Caldas Lopes, and Lucas Santos Santana. 2024. "Controlled Traffic Farm: Fuel Demand and Carbon Emissions in Soybean Sowing" AgriEngineering 6, no. 2: 1794-1806. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriengineering6020104
APA StyleMartins, M. B., Marques Filho, A. C., Seron, C. d. C., Guimarães Júnnyor, W. d. S., Vendruscolo, E. P., Bortolheiro, F. P. d. A. P., Blanco Bertolo, D. M., Lopes, A. G. C., & Santana, L. S. (2024). Controlled Traffic Farm: Fuel Demand and Carbon Emissions in Soybean Sowing. AgriEngineering, 6(2), 1794-1806. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriengineering6020104







