Abstract
In the past few decades, fruits have been increasingly consumed, leading to an increase in global fruit production. However, fresh produce is susceptible to large losses during production and preservation. In the postharvest preservation stage, fruits undergo various technical treatments for maintaining their quality. A widely adopted technology is the application of edible coatings, which can be applied to a diverse range of fruits to regulate the exchange of moisture and gases between the fruit and its environment. In addition, edible coatings provide a significant benefit by allowing the integration of different active ingredients into the coating’s matrix, meaning that these substances will associate with and possibly be eaten together with the fruit. This would help improve the organoleptic and nutritional qualities of the fruit as well as the shelf life. This paper provides an overview of the available data on the typical components used in coating matrix, focusing on the effect of the material combinations and application techniques to fruit properties. The processors can use this knowledge in choosing a suitable coating material and concentration for various fresh and fresh-cut fruits. Additionally, this paper reviews recent developments and limitations in utilizing edible coatings for prolonging the shelf-life of fruits.
1. Introduction
In a human’s diet, fruits are considered as a crucial source that provides energy, dietary fibers and micronutrients such as vitamins, minerals, flavonoids, and other phytochemicals [1]. These health advantages highlight the obligation and profit of fruit consumption in human routine. Therefore, fruits are in rising demand, which requires more production as well as better quality control. Among horticultural products, fruits have a large amount of moisture (over 75%) and this is the key factor that is responsible for their short shelf life. Kader [2] calculated that only 30% of total produced fruits have been consumed by humans. Additionally, compared to rich countries, the losses that occur between manufacturing and retail outlets are even larger in underdeveloped nations. This highlights the need for major efforts to minimize postharvest losses [3].
Based on the maturity mechanism, fruits can be divided into climacteric and non-climacteric fruits. Non-climacteric fruits stop ripening after harvest, while climacteric fruits continue ripening after harvest, making the fruit more susceptible to microbial infection and spoilage [4]. Therefore, climacteric fruits mature naturally as a result of biochemical reactions and can be consumed only for a limited period of time. The only way to properly control this process is to postpone the postharvest ripening. It is possible to adapt low storage temperature to slow down both chemical and enzymatic reactions in fruits [5]. However, fruits from warm and humid regions are sensitive to low storage temperature. Fruits that are kept in this unsuitable condition will suffer from chilling or freezing injury [6].
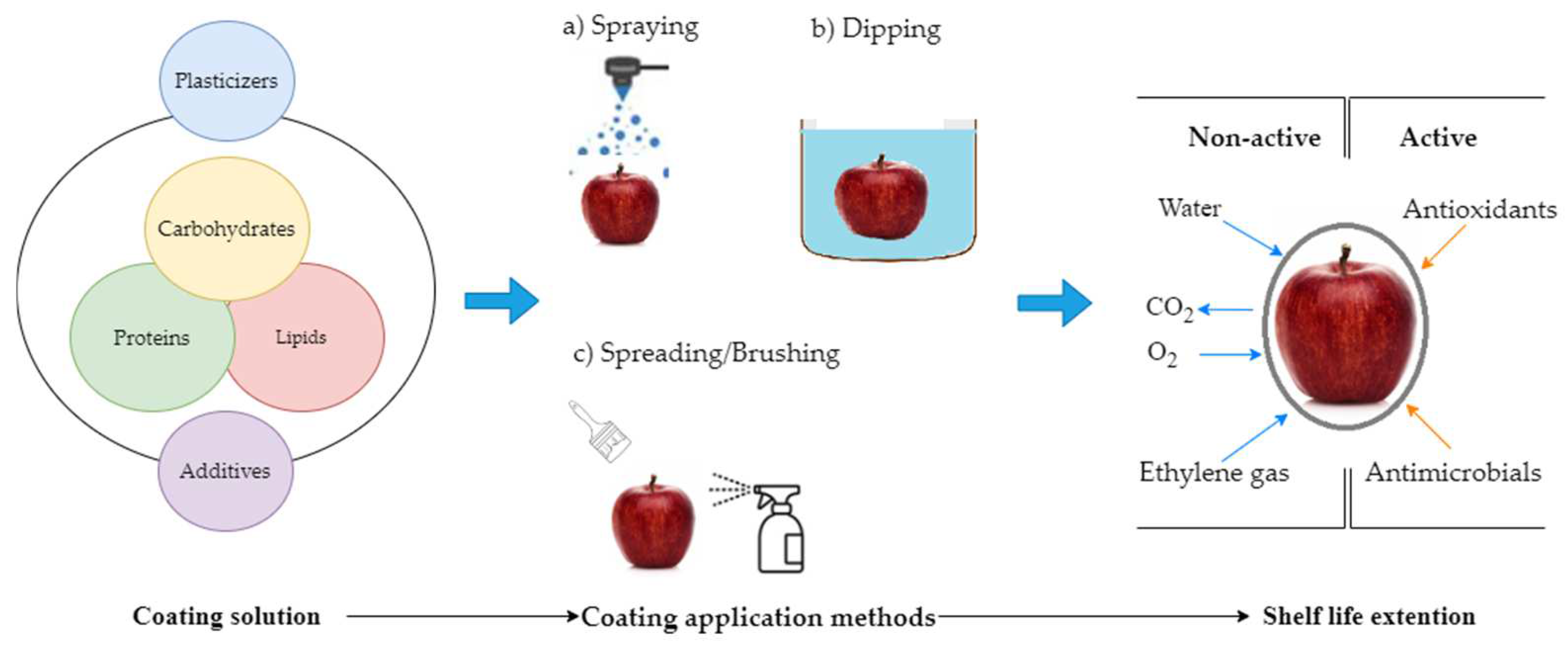
Edible coating offers another strategy as a kind of packaging. An edible coating, by definition, is the material used on the surface of food for wrapping and it is safe to be consumed together with the food [7]. Protection against mechanical damage, light exposure, and contamination can be achieved through the use of coatings. Numerous coating materials can be found in the literature for a diverse range of food items. Polysaccharides, proteins and lipids or their combination are the primary biopolymers employed to develop edible coating (Figure 1) [8,9]. In general, fat-based coatings reduce water transfer capacity, while polysaccharide-based coatings have lower gas permeability and protein-based coatings have better mechanical properties. Additionally, resins, solvents, and plasticizers are typically used to achieve the appropriate characteristics for edible coatings. Plasticizers contribute flexibility and permeability, solvents improve tensile strength, and resins limit water vapor permeability of edible coatings [10]. In addition, coating adhesion is a critical property that is determined by various parameters such as food surface properties, coating targets, and applied techniques [11,12]. Depending on the fruit variety, coating materials may have different levels of effectiveness. It should be noted that from the commercial point of view, coating is used to preserve the quality of commodities for market requirements and nutritional benefits, optimize production and packaging costs [13]. The purpose of edible coating is to play a key role of a barrier for regulating the migration of substances such as O2, CO2, flavorings, lipids, moisture and other dissolved compounds [14]. Thus, the application of coatings leads to a lower rate of respiration and a reduction in weight loss. Moreover, edible coatings hold immense potential in serving as vehicles for antimicrobial agents. According to Passafiume et al. [15] and Shafiei and Mostaghim [16], the diseases and microbial load in fruits are significantly reduced by adding antimicrobial compounds to the coating matrix. A recent study by Ranjith et al. [17] demonstrated that the use of peptide-based edible coatings is promising in controlling mango diseases. The use of an edible coating resulted in a reduction in the ripening process and delay in the synthesis of anthocyanin [18]. Interestingly, chitosan is a biopolymer with antimicrobial properties that can also act as an elicitor by stimulating enzyme production associated with the fruit’s defense mechanism [19]. Edible coatings offer significant benefits and they can be applied using various techniques as shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1.
Main components of edible coatings and application methods on fruits.
Herein, this review summarizes and highlights the current applications of edible coatings, the types of active additives that are incorporated, and their impact on the functional properties of the coating matrix. Recent developments and trends related to composition, formulation, and application are also discussed in this review.
2. Ripening in Climacteric Fruit
Fruit ripening is controlled by a combination of internal biochemical processes and external factors. Fruit ripening involves complex processes that cause significant changes in their properties such as color, texture, aroma, taste and others. These changing properties are directly associated with the final product quality [20]. There are two groups of fruits following their respiration patterns: climacteric fruits, and non-climacteric fruits. While the climacteric group shows parallel high respiration rate and ethylene production along ripening, the non-climacteric group does not show a noticeable burst neither in the respiration rate nor in the ethylene release [21]. Climacteric fruits use oxygen as a substrate for ethylene biosynthesis during ripening [22]. Therefore, the increased respiratory rate of fruit is essential to an inflation in ethylene generation, which promotes biochemical reactions in the fruit [23]. The increase in respiration occurs concurrently with or immediately after the increase in the rate of ethylene synthesis. Exogenous ethylene therapy can start and speed up the maturation procedure in climactic fruits. The ripening process leads to changes in fruit such as softening, color change, reduction in acidity and increase in total dissolved matters [24]. The primary factor affecting fruit storage, shelf life and quality is postharvest metabolism. It has been proved that changes in postharvest metabolism induce escalation of respiratory exertion and deficiency of water. Controlling ripening and associated physio-biochemical processes in fruits (transpiration, respiration, ethylene production, softening and compositional changes) was attained by using controlled atmosphere (CA), modified atmosphere (MA) or modified atmosphere packaging (MAP) [25]. These approaches, at the moment, are established methods to extend fruit postharvest life [26]. At ambient conditions, the atmosphere inside fruits is a composition of several gases and volatiles including water vapor, oxygen, carbon dioxide, ethylene, and vapors of alcohols, aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids, esters, aromatic hydrocarbons, terpenes, ammonia, etc. [27]. Corresponding studies have concluded that the ripening, senescence, and associated processes are regulated by the above-mentioned gases and volatiles. It has been reported that CA, MA and MAP essentially adjust the gaseous atmosphere inside the fruits and facilitate maintaining the low O2 to CO2 ratio and thereby regulating ethylene production [28].
3. Characterizations of Edible Coatings
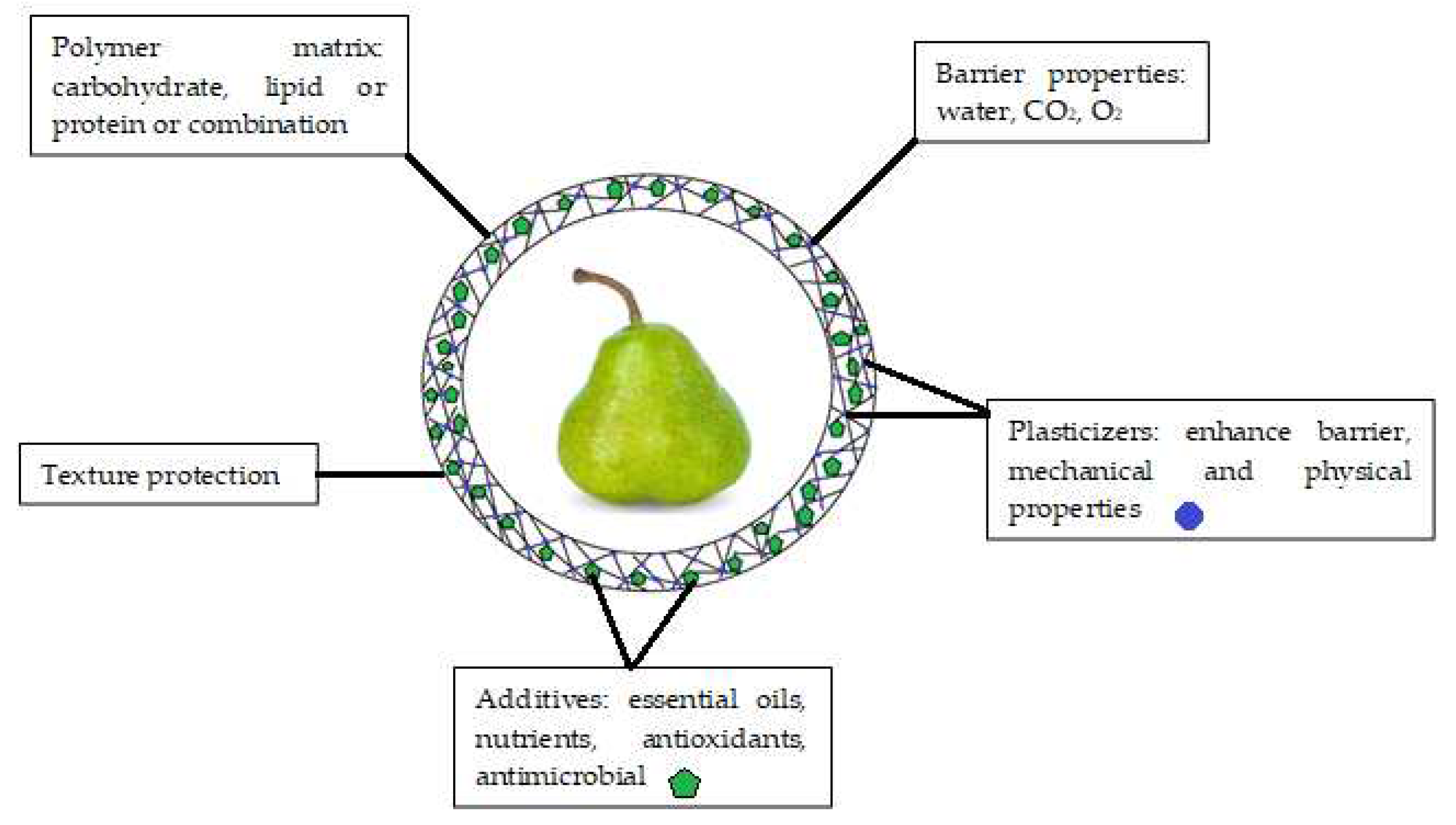
Initially, edible coatings were developed to replace and decrease the usage of other kinds of chemicals and synthetic compounds that may be harmful to customers’ health. An edible coating is a covering sheet composed of biological or chemical ingredients and utilized as a monolayer film or multilayer films on the surface of the product [29]. Edible coatings help maintaining the phytonutrients (antioxidants, phenolics, pigments) and controlling physicochemical qualities (inhalation and exhalation rate, weight loss, total dissolved matters, pH) of fruits for longer time [30]. As a result, fruit deterioration is delayed, fruit quality is improved, and fruit shelf life is extended [31]. To be effective, edible coatings must meet several functional requirements (Figure 2), including (i) being free of toxic materials and harmless for human beings; (ii) having superb boundary capabilities regarding water, humidity, O2, CO2, and C2H4; and (iii) improving the visual as well as textural properties of the coated products [32]. The coating should not alter the sensory properties of the fruit [33]. Therefore, edible coating formula needs to be carefully considered during development. Furthermore, the coating should control the gas exchange to avoid fruit fermentation and undesirable off-flavor [12]. In the case of fruit coating, when the oxygen level falls below 3%, anaerobic respiration takes over, which generates undesirable flavors and induces other issues such as colorant and structure alterations. Therefore, high concentration of O2 (>8%) and low concentration of CO2 (<5%) are recommended to prevent or delay deterioration, hence preserving food quality [34].
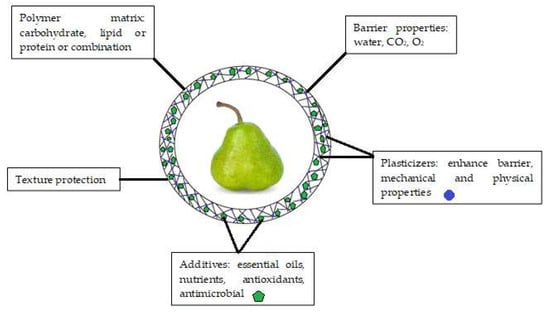
Figure 2.
Main components and functions of edible coatings.
The coating-forming solutions can comprise a single main component from proteins, polysaccharides, lipids, or a mixture of them to achieve desired properties [35]. New edible coating candidates should be inexpensive and available in large quantity. The coating should provide easy application, have good adhesive characteristics, and dry quickly with uniform thickness. Moreover, the coating performance and structural stability must be maintained during long-term storage. The coating must be flexible enough to adapt to specific morphological changes such as fruit shrinkage or mechanical damage [36].
The characteristics of coating polymers determine their use and function [37]. Proteins and polysaccharides establish strong molecular interactions in polymers. They have superb mechanical and gas isolation (oxygen and carbon dioxide) qualities that inhibit the common ripening process in many fruits [38,39]. The most universally used polysaccharides in food production can be attributed to cellulose and its derivatives, namely pectin, chitosan, and gums [40]. However, studies showed that the drawback of their application is the poor performance in preventing fruit moisture loss [41]. In addition, usage of proteins in edible coatings may be limited because they are potentially allergenic or refused due to religious belief [42]. Coatings made from lipids (fatty acids, acylglycerol or waxes) are great moisture barriers due to their hydrophobic property [36]. Unfortunately, coatings based on lipids were found to be poor in mechanical attributes and brittleness due to their lack of cohesiveness and structural integrity [43]. Lipid molecules are frequently added to matrices to reduce the water sensitivity of a hydrocolloid-based coating [43]. Therefore, mixtures of different components can be used for production of edible coatings that enhance the physicochemical characteristics and solve the drawbacks of the individual components [44].
Coatings that are based on polysaccharides and proteins achieved excellent barrier characteristics. However, they are also less flexible due to strong intermolecular forces along the polymer chain. As a result, blisters, flakes, or cracks may appear in the coating as the fruit shrinks during storage [33]. The primary role of plasticizers is to strengthen coating flexibility and decrease brittleness. Glycerol, mannitol and sorbitol are the food grade plasticizers typically used in edible coatings [45]. In addition, sugars with small molecules (such as fructose-glucose syrups and honey), other polyols (such as glycerol derivatives and propylene glycols), lipids and by-products (such as phospholipids, fatty acids, lecithin, oils, and waxes), and water are also popular examples of food grade plasticizers that can be added to coatings [46]. The plasticizer absorbs more water into the coating matrix and decreases the intermolecular interactions along the polymer chain, thereby preventing the coating from blistering, flaking and cracking [47,48]. Furthermore, the amount of plasticizer used in the coating formulation must be examined according to its influence on the permeability of the wrapping. Plasticizers increase the moisture and gas permeability through the coating by reducing polymer interactions and increasing intermolecular space [47]. Even though plasticizers are supposed to give the coatings elastic structure, overusing plasticizers results in decreased moisture resistance and weaker mechanical strength. Table 1 summarizes the advantages and challenges of plasticizers reported in edible coatings of fruits.

Table 1.
Effect of plasticizers on the characteristics of edible coatings.
When using hydrophilic polyols (such as glycerol or sorbitol) as plasticizers, the water solubility, elongation, and the moisture permeability of coatings were substantially improved following the plasticizer concentration. The observed total color difference and the puncture strength, on the other hand, decreased with higher plasticizer content. The mechanical properties of puncture strength and elongation of coatings are more affected by glycerol than sorbitol. In addition, sorbitol-plasticized coatings had decreased water vapor permeability, which can be increased with higher plasticizer concentration. However, this rise was less than that found with glycerol-plasticized coatings [52]. Additionally, Yang and Paulson [53] found that sorbitol did not show a plasticizing effect on gellan films, although it had been widely used in protein-based films. That study showed that polyethylene glycol and glycerol were effective in plasticizing gellan films at 60% concentration. It has been proved that at lower concentration, the films turned to be more fragile, and their manipulation became challenging, while glycerol concentration beyond 75% results in sticky behavior. Additionally, the presence of plasticizers promoted the homogenous coating structure, preventing phase separation. By limiting the development of pores or cracks, the integrity of the coating can be maintained [54]. The coatings with low protein content in the formulation showed smoother surfaces when treated with plasticizers [55].
4. Application Technology of Edible Coating
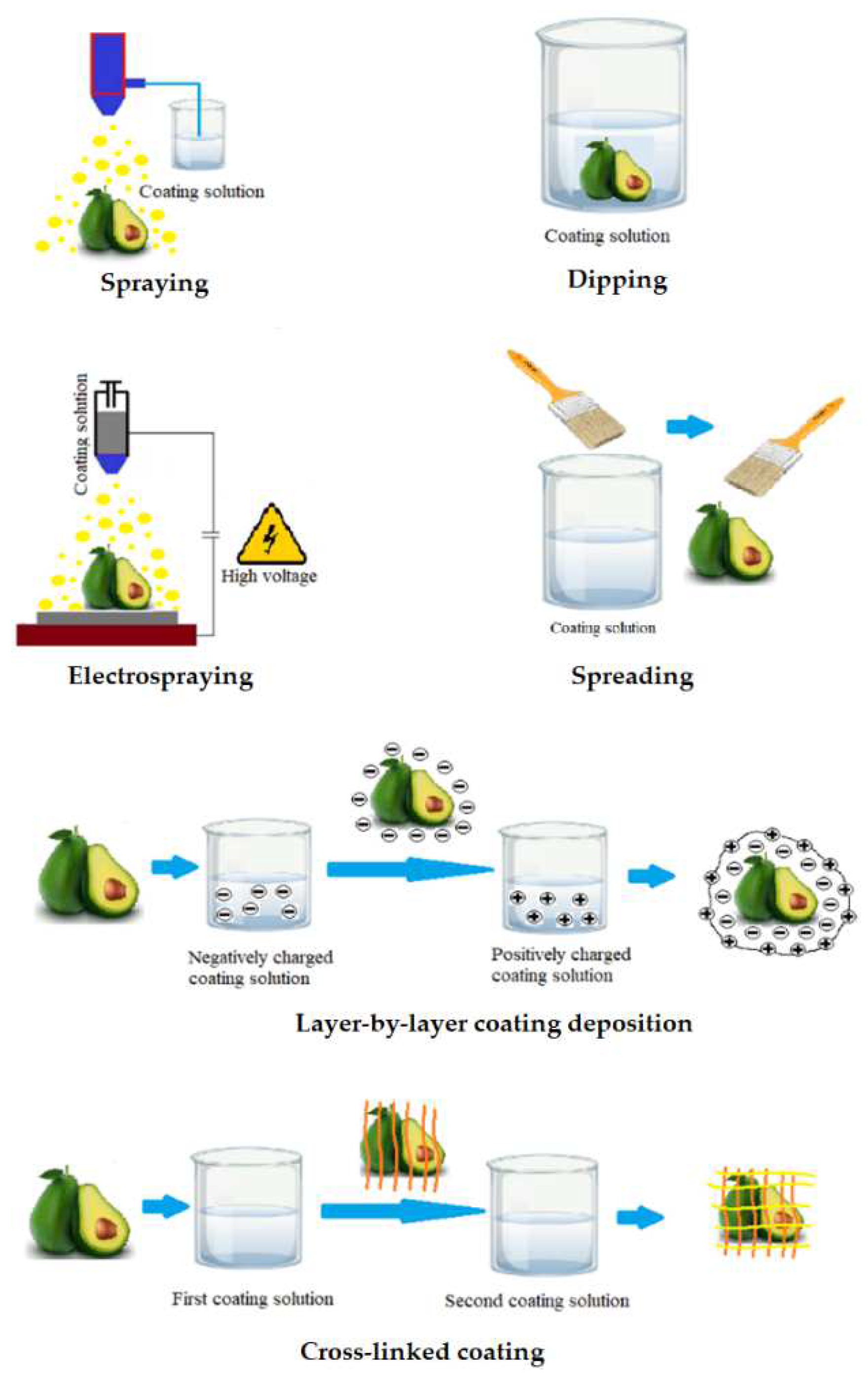
Following the selection of the wrapping composition, the application of the solution to the surface of the fruit is the next important step. There are different approaches about how to cover the food surface with edible coating (Figure 3). Dipping is the simplest method consisting of three steps: (i) immersion and dwelling, (ii) deposition and (iii) evaporation of solvents [56]. After the excess solution has been drained away, the food is typically dried at ambient condition or treated with a dryer [11]. Previous studies showed that the density and morphology of coatings precipitated by dipping are significantly affected by several factors including time for immersion, speed of withdrawal, number of cycles for dip-coating, coating solution parameters such as density, viscosity, surface tension, substrate surface characteristics, and drying conditions [57]. However, there are numerous disadvantages of the dipping method. Dipping commonly results in a layer with heavy thickness leading to substantially reduced fruit respiration, damage food surfaces and degraded function. In addition, microorganisms and dirt from the fruit surface may contaminate the coating solution, hence challenging the industrial up-scaling. Another drawback of the dipping approach is the large quantity of solution needed for coating per unit mass of product to guarantee optimum dipping conditions [33].
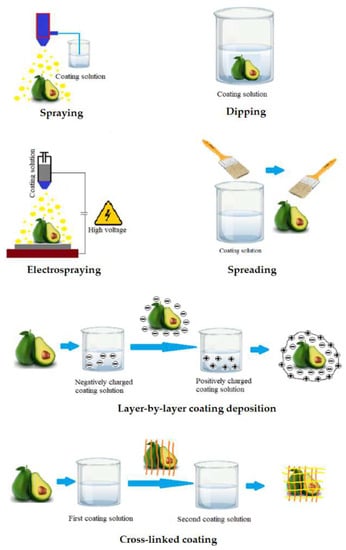
Figure 3.
Application methods of edible coating.
The spreading technique is effective for coating solutions with high viscosity. In general, the wetting level and spreading rate are the key factors used to describe how the coating solution is spread across the food surface. Several parameters influence the efficiency of coating deposition by spreading, including substrate quality, particularly drying conditions, liquid characteristics, and surface geometry [58]. Specialized operators and technicians typically perform brushing. Thus, the human factor has a significant impact on the quality of coating and thickness homogeneity.
Spraying is the process of using a set of nozzles to distribute small droplets on the fruit surface. Spraying methods are used in three different ways, including air spray atomization, pressure atomization and air assisted airless atomization [11]. The spraying technology allows multi-layer applications such as interlayer solutions, as well as consistent coating with homogeneous thickness [59]. Additionally, the coating thickness is greater than that of dipping method due to the low viscosity of the solution [11].
The electrospraying method uses a strong electric field to produce charged droplets, with a very narrow size distribution, that are micrometric and sub-micrometric in size [60]. The electrospraying process can adjust droplet specifications such as size, or produced layer thickness by controlling the flow rate as well as the viscosity of the solution [61].
The layer-by-layer deposition method is based on the electrostatic interactions of the food surface with charged polyelectrolytes. These electrostatic interactions improve adhesion of the coating to the food surface and may be used to create coatings with two or more thin layers that are chemically or physically linked to each other. Such linked multilayer coating improves the effectiveness compared to conventional edible coatings [62]. The use of the multilayer coating approach to increase the compactness of the coating layers during postharvest storage of fruits were documented for polysaccharides and charged polyelectrolytes capable of hydrogen and covalent bonding. Polysaccharides and charged polyelectrolyte demonstrated efficiency in fruit preservation when applying the multi-layer coating method to improve the tightness of the coatings [63].
The final technique in the list is cross-linking, which is defined as the process of combining polymer chains using covalent and non-covalent linkages. Cross-linked coatings are typically created by spraying, dipping, or spreading the coating solution onto the food surface. A cross-linking agent is then added to provide a more compact and stable coating. Cross-linked coatings have substantial benefits, including better mechanical properties, chemical and thermal stability as well as better molecular migration [64]. Cross-linking is particularly effective for biopolymer materials formed from proteins or polysaccharides. Proteins are used more frequently than polysaccharides with this technique due to the greater number of functional groups in proteins [37].
The results of different application techniques for edible coatings are listed in Table 2. The findings in the list confirm the idea that coating technology in postharvest preservation of fruits can be considered a sustainable solution.

Table 2.
Edible coatings applied to fruits.
5. Application of Edible Coatings on Fruits
Over the past few decades, there has been a sharp increase in consumer demand for products that are natural, safe and eco-friendly. Therefore, it is encouraged to develop fruit preservation technologies that are safe for consumers and the environment and enhance the quality and safety of a product without reducing its sensory or nutritional characteristics [85]. Thus, edible coatings offer an alternative method to replace conventional plastic containers, which do not biodegrade and are harmful to the environment. These low-cost edible coatings can also prevent moisture loss, act as effective oxygen barriers, and preserve food quality. Additionally, they form a shield that protects fruits from microbial growth [86].
Post-harvest diseases usually result from bacterial and fungal infections, which can arise through two common pathways: latent infection and wound injuries [86]. Thus, a new strategy of edible coatings has been developed recently against fruit diseases, that combines active additives such as natural extracts, biological inhibitors, antimicrobial compounds and safe chemicals [87]. The purpose of active coatings is to directly interact with the fruit’s environment and delay both the oxidation process and the development of phytopathogenic fungi [88]. For example, bioactive peptides have been effectively used against many strains of mold. Peptides interact with the cell membrane of microorganisms through electrostatic forces, which can lead to membrane permeabilization and iron chelation [89]. However, applying antimicrobial peptides directly to fruit surfaces is difficult due to their inherent instability and hydrophobic nature, so this could reduce their effectiveness [90]. Incorporation of antimicrobial peptides within edible coatings presents a solution to the challenge. Therefore, active ingredients incorporated in edible coatings can prolong the fruit shelf life by preventing it from deteriorating while stored. In addition, the effectiveness of active ingredients depends on both the targeted pathogen and the characteristics of the fruit host. These edible active coatings are investigated to evaluate their bioactivity, including their antibacterial and antioxidant properties. Furthermore, by developing chemical interactions with the reactive groups of polymer chains, they could also enhance the coating structure and physicochemical characteristics [91]. However, the impact of the active ingredient on coating matrix depends on the specific case. For instance, in the case of a chitosan-based bioactive film, Mohamed et al. [92] reported that the incorporation of lactoperoxidase systems did not change the mechanical properties but enhanced the resistance to microbial growth. By contrast, when bergamot and lemongrass oil were incorporated into a gelatin-based coating, the mechanical properties were modified including a decrease in tensile strength, elongation-at-break capacity [93]. The ingredients and the type of coating used in the polymer matrix of edible coatings are summarized in Table 3.

Table 3.
The influence of edible coating composition on fresh fruit quality parameters.
Chitosan coating using Schiff-base reaction and reductive amination to bind vanillin and trans-cinnamaldehyde showed beneficial effects on the adhesion of the coating and antibacterial effects on fresh-cut melon [94]. Studies on strawberry storage showed that the application of coatings with 1% w/v lemongrass essential oil had a positive effect on the ascorbic acid content and resulted in better antioxidant activity [104]. The authors also found that carrageenan gum coating gave better results than arabic gum and xanthan gum coating in terms of anthocyanin and phenolic compounds retention and overall quality during storage. Although incorporating essential oils enhanced the antimicrobial properties, it also led to poor water solubility, strong odors, and high volatility of edible coatings [105]. Muley and Singhal [106] developed a functional coating comprised of whey protein isolate with plasticizers to prolong the strawberries shelf life. According to their observations, it was concluded that the coated samples had less weight loss, pH alterations, and color changes. The shelf life of strawberry was extended up to 8 days for treated samples. In a recent study, Alali et al. [107] found that using a coating comprised of arabic gum and salicylic acid improved the quality and shelf life of bananas. Salicylic acid coating was less effective than the coating made of arabic gum [108]. In addition, the peel browning index was better in the case of arabic gum coating than salicylic acid coating [109,110]. However, the gum concentration should be considered carefully, as high concentrations of gum could have a detrimental effect on fruit sensory properties [111].
It has been shown that the application of edible gelatin-based coating containing an ethanol-based propolis extract on raspberries had significant antifungal activity against mold, with a strong inhibitory impact on Penicillium digitatum and Botrytis cinerea strains [75]. Priyadarshi et al. [98] studied the possibility to prolong the shelf life of peanuts by a bioactive binary coating made of pectin, pullulan with Vitis vinifera L. grape seed extract. The coated samples had longer shelf life because lipid oxidation was reduced, which delayed rancidity. Furthermore, the coating had antibacterial effect against Escherichia coli and Listeria monocytogenes. In contrast, the application of pectin-based coating on tomatoes resulted in a reduction in color, which had a negative impact on the sensory perception [112].
Edible chitosan coating with acetic acid or lactic acid was applied on blackberry samples to evaluate antifungal activity on Mucor racemosus for 14 days at 4 °C. In that experiment, edible coating samples were compared to those treated with the chemical fungicide imazalil (0.4 g L−1) and untreated control samples. The chitosan coating that contained lactic acid had the best antifungal activity against Mucor racemosus [113]. Khodaei and Hamidi-Esfahani [114] investigated the addition of Lactobacillus plantarum (6 log10 CFU/g) to the carboxymethyl cellulose coating to inhibit mold and yeast in fruit. Due to the competitive and antibacterial properties of Lactobacillus plantarum, the treated strawberries suffered less mold and yeast growth on the surface when compared to the control pieces.
Recently, Leena et al. [99] used a controlled release system to generate zein-based nanostructured coatings on apple slices. Resveratrol with different concentrations (2%, 5% and 10%) was encapsulated in zein nanofibers by electrospinning process. The results showed that coated apple slices maintained their color longer and reduced moisture loss. Carrageenan-based coating incorporated with zinc nanoparticles was found to be a successful method for mango preservation when compared with carrageenan alone [115]. Furthermore, chitosan nanoparticles-based coating exhibited significant effects compared with chitosan. The smaller size of the particles and their increased contact area led to improved function and properties of coating even at lower concentrations [116]. However, the use of high concentration of nanoparticles may result in physiological damage and promote fruit ripening [117]. Another packaging strategy is the combinations of edible coatings with MAP, which may represent a practical approach to enhance the quality of fruits. The combined approach overcomes the drawbacks of relying solely on either MAP or coatings. Sothornvit and Rodsamran [118] investigated the impact of a film made from mango combined with low oxygen atmosphere (LOA) packaging on preserving fresh-cut mango. Results showed that the use of MAP at low temperature, with or without the mango film wrap, increased the storage life of fresh-cut mango to 6 days. Interestingly, at room temperature, the use of both LOA packaging and the edible mango film markedly reduced off-flavor and prolonged the shelf life of fresh-cut mango to 4 days. Furthermore, the development of aerobic microorganisms on carrots was dramatically slowed down by the use of MAP and gamma radiation. The combination with an edible coating based on calcium caseinate and whey protein, although ineffective in inhibiting microorganisms, was necessary to protect carrots from dehydration and whiten [119]. By applying coatings on fruits, the ripening process and degradation is slowed down during storage, resulting in a significant improvement in the quality and preservation of the bioactive compounds. However, it seems there are still open questions regarding the effects of edible coatings on physicochemical properties and potential improvement of nutritional values.
6. Future Trends
The inhibition or elimination of microorganisms (both bacteria and mold) on fruits is important because it has a direct impact on the shelf life of fruits [120]. In recent years, numerous edible coating formulations were created for maintaining fruit quality and reducing foodborne bacteria. Jin et al. [121] developed multiple formulations of edible coating composed of N-acetyl-lcysteine, L-cysteine with chitosan. That coating proved to be effective in preventing browning, inhibiting mold and yeast growth, and prolonging the freshness of fresh-cut apples for 35 days by incorporating organic acids into the solution. According to Alvarez et al. [122], the pectin-beeswax coating incorporated eugenol might be a profitable commercial method to avoid deterioration and maintain the quality of citrus fruit. It provided a safe option for current waxes that use dangerous synthetic fungicides. Furthermore, melons coated with zein-based film incorporated with eugenol demonstrated effectiveness in inhibiting pathogens on the surface of melon. However, further investigations are required to suppress the unpleasant aromas of the essential oils in the films [123]. Studies clearly rely on plant extracts to keep ingredients natural and decrease the use of synthetic chemicals. Furthermore, there is a rising interest in using probiotics as an innovative bioprotective method for fruit preservation. Probiotics are bioactive compounds with specific health benefits. Thus, edible coatings can be supplemented with bioactive substances to improve consumers’ health. In the research of Wong et al. [124], fresh-cut apples were coated with double layer of probiotics and zein. The coated samples reduced the development of Listeria monocytogenes during one week of storage, while the number of probiotic Lactobacillus plantarum was steady (>6 log10 CFU/g). Davachi et al. [125] developed a coating supplemented with probiotic lactic acid to prolong the freshness of bananas, strawberries, cucumbers and tomatoes. The presence of probiotic lactic acid resulted in poorer hydrophilicity property, increased water solubility and surface roughness. The findings demonstrated that the addition of lactic acid improved potential health benefits and strengthened protective capacities by competing for resources with other bacteria and pathogens. Additionally, the quality of food products could be improved by using edible coatings to encapsulate for controlled release of bioactive compounds, wherein bioactive compounds are released in a certain amount at a specific location and time [126].
Nanoemulsion is an innovative edible coatings technique that is receiving much interest. In comparison to traditional emulsions, nanoemulsion has numerous advantages that make it more efficient at maintaining coating stability and enhancing product quality. Moreover, the oxidation of bioactive substances was slowed by nanoemulsion, and dispensing became simple and the sensory qualities of products were improved [127,128]. Nevertheless, there is a lack of research to understand the characteristics of nanoemulsions, including their beneficial effects on human health and their potential for application in the food industry. In addition, edible coatings are a potential method not only for fruits and vegetables but also for other products such as eggs or medicine encapsulation [14,129]. Studies on the characteristics and applications of edible coating on other products are still limited when compared to applications on fruits and vegetables. Finally, studies on edible coatings for fruits are still in their initial phases and investigations are running prior to large-scale industrial implementation. There is a requirement that compounds should maintain unique characteristics, flavor, and interactions between components that otherwise would cause change to the sensory profile. This limitation puts a barrier on the development of new coating materials. Therefore, the research of edible coating materials is expected to depend on a comprehensive knowledge of biochemistry and how it interacts with physicochemical, antibacterial, and possibly toxicological features, as well as risk assessment.
7. Conclusions
Edible coating technology provides a promising solution in maintaining the quality of fresh produce. The application of non-active coating alters the internal environment of fruits by inhibiting the exchange of gases and water. As a result, the respiration rate decreases, reducing the changes in color and loss of firmness. Active edible coatings that incorporate additional ingredients become more effective in extending the shelf life of fruits compared to non-active coatings. This is due to their ability to inhibit the development of pathogens on fruit, which is more effective than just a physical barrier. Therefore, fruit quality preservation is significantly influenced by the interactions of the coating formulation. A wide range of options are available due to the carrying capacity of biopolymers, including the incorporation of a variety of plasticizers and additives. Thus, a proper choice of biomaterial for specific fruits requires an understanding of the physicochemical properties of biopolymers and nature of fruits. Application techniques are also important in fruit quality control. In order to choose the appropriate method for applying coatings to fruits, it is crucial to have a clear understanding of both the coating matrix and the surface properties of the fruits. Furthermore, most studies focus on evaluating the effects of coatings on the nutritional aspects of fruits. There is limited literature on the health benefits of consuming coated fruits and how these coatings may enhance the positive effects associated with fruit consumption. It offers a new approach for further research that could increase the value and application of biopolymers in the food sector. Future research is required to produce biopolymers using low-cost technologies that are highly compatible with environmentally safe and valuable components. Additionally, it is important to conduct large-scale studies on edible coatings on an industrial scale to confirm their practical feasibility.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, T.T.P., L.L.P.N., M.S.D. and L.B.; methodology, T.T.P., L.L.P.N., M.S.D. and L.B.; software, T.T.P., L.L.P.N., M.S.D. and L.B.; formal analysis, T.T.P., L.L.P.N., M.S.D. and L.B.; investigation, T.T.P., L.L.P.N., M.S.D. and L.B.; resources, T.T.P., L.L.P.N., M.S.D. and L.B.; data curation, T.T.P., L.L.P.N., M.S.D. and L.B.; writing—original draft preparation, T.T.P., L.L.P.N., M.S.D. and L.B.; writing—review and editing, T.T.P., L.L.P.N., M.S.D. and L.B.; visualization, T.T.P., L.L.P.N., M.S.D. and L.B.; supervision, T.T.P., L.L.P.N., M.S.D. and L.B.; project admin-istration, T.T.P., L.L.P.N., M.S.D. and L.B.; funding acquisition, T.T.P., L.L.P.N., M.S.D. and L.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.All authors have equal contributions. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the Doctoral School of Food Science of the Hungarian University of Agriculture and Life Sciences for the support in this study. Special gratitude is given to HCMC University of Technology and Education for stimulating suggestions and encouragement that helped us to finish this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Mares-Perlman, J.A.; Millen, A.E.; Ficek, T.L.; Hankinson, S.E. The body of evidence to support a protective role for lutein and zeaxanthin in delaying chronic disease. Overview. J. Nutr. 2002, 132, 518S–524S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kader, A.A. Future research needs in post harvest biology and technology of fruits. Acta Hortic. 2005, 485, 209–213. [Google Scholar]
- Pulamte, L. Key issues in post harvest management of fruits and vegetables in India. India Sci. Technol. 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Jafarzadeh, S.; Nafchi, A.M.; Salehabadi, A.; Oladzad-Abbasabadi, N.; Jafari, S.M. Application of bio-nanocomposite films and edible coatings for extending the shelf life of fresh fruits and vegetables. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 291, 102405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mworia, E.G.; Yoshikawa, T.; Salikon, N.; Oda, C.; Asiche, W.O.; Yokotani, N.; Kubo, Y. Low-temperature-modulated fruit ripening is independent of ethylene in ‘Sanuki Gold’kiwifruit. J. Exp. Bot. 2012, 63, 963–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, B.; Tandel, Y.N.; Patel, A.H.; Patel, B.L. Chilling injury in tropical and subtropical fruits: A cold storage problem and its remedies: A review. Int. J. Sci. Environ. Technol. 2016, 5, 1882–1887. [Google Scholar]
- Summo, C.; De Angelis, D. The importance of edible films and coatings for sustainable food development. Foods 2022, 11, 3221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendy, T.K.; Misran, A.; Mahmud, T.M.M.; Ismail, S.I. Application of Aloe vera coating delays ripening and extend the shelf life of papaya fruit. Sci. Hortic. 2019, 246, 769–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, R.; Pristijono, P.; Golding, J.B.; Stathopoulos, C.E.; Scarlett, C.J.; Bowyer, M.; Vuong, Q.V. Development and application of rice starch based edible coating to improve the postharvest storage potential and quality of plum fruit (Prunus salicina). Sci. Hortic. 2018, 237, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyza, H.; Fatma, K.; Hecer, C. Edible films and coatings: A good idea from past to future technology. J. Food Technol. 2018, 5, 28–33. [Google Scholar]
- Andrade, R.D.; Skurtys, O.; Osorio, F.A. Atomizing spray systems for application of edible coatings. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2012, 11, 323–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, K.; Schmid, M. Alginate-based edible films and coatings for food packaging applications. Foods 2018, 7, 170. [Google Scholar]
- Bhardwaj, A.; Alam, T.; Talwar, N. Recent advances in active packaging of agri-food products: A review. J. Postharvest Technol. 2019, 7, 33–62. [Google Scholar]
- Quirós-Sauceda, A.E.; Ayala-Zavala, J.F.; Olivas, G.I.; González-Aguilar, G.A. Edible coatings as encapsulating matrices for bioactive compounds: A review. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 51, 1674–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passafiume, R.; Gaglio, R.; Sortino, G.; Farina, V. Effect of three different aloe vera gel-based edible coatings on the quality of fresh-cut “hayward” kiwifruits. Foods 2020, 9, 939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafiei, R.; Mostaghim, T. Improving shelf life of calf fillet in refrigerated storage using edible coating based on chitosan/natamycin containing Spirulina platensis and Chlorella vulgaris microalgae. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2022, 16, 145–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjith, F.H.; Adhikari, B.; Muhialdin, B.J.; Yusof, N.L.; Mohammed, N.K.; Ariffin, S.H.; Hussin, A.S.M. Peptide-based edible coatings to control postharvest fungal spoilage of mango (Mangifera indica L.) fruit. Food Control 2022, 135, 108789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emragi, E.; Kalita, D.; Jayanty, S.S. Effect of edible coating on physical and chemical properties of potato tubers under different storage conditions. LWT 2022, 153, 112580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Estrada, R.R.; Blancas-Benitez, F.J.; Moreno-Hernández, C.L.; Coronado-Partida, L.; Ledezma-Delgadillo, A.; Gutiérrez-Martínez, P. Nanotechnology: A promising alternative for the control of postharvest pathogens in fruits. In Nanotechnology for Agriculture: Crop Production & Protection; Deepak, G.P., Yogeshvari, K.J., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 323–337. ISBN 978-981-32-9373-1. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, T.; Qin, G.; Tian, S. Regulatory network of fruit ripening: Current understanding and future challenges. New Phytol. 2020, 228, 1219–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinozaki, Y.; Nicolas, P.; Fernandez-Pozo, N.; Ma, Q.; Evanich, D.J.; Shi, Y.; Rose, J.K. High-resolution spatiotemporal transcriptome mapping of tomato fruit development and ripening. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farcuh, M.; Rivero, R.M.; Sadka, A.; Blumwald, E. Ethylene regulation of sugar metabolism in climacteric and non-climacteric plums. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2018, 139, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillén, F.; Díaz-Mula, H.M.; Zapata, P.J.; Valero, D.; Serrano, M.; Castillo, S.; Martínez-Romero, D. Aloe arborescens and Aloe vera gels as coatings in delaying postharvest ripening in peach and plum fruit. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2013, 83, 54–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Sethi, S.; Sharma, R.R.; Srivastav, M.; Varghese, E. Effect of chitosan coating on postharvest life and quality of plum during storage at low temperature. Sci. Hortic. 2017, 226, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangaraj, S.; Goswami, T.K. Modified atmosphere packaging-an ideal food preservation technique. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2009, 46, 399–410. [Google Scholar]
- Ramayya, N.; Niranjan, K.; Duncan, E. Effects of modified atmosphere packaging on quality of ‘Alphonso’ mangoes. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 49, 721–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De León-Sánchez, F.D.; Pelayo-Zaldívar, C.; Rivera-Cabrera, F.; Ponce-Valadez, M.; Ávila-Alejandre, X.; Fernández, F.J.; Pérez-Flores, L.J. Effect of refrigerated storage on aroma and alcohol dehydrogenase activity in tomato fruit. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2009, 54, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanellis, A.; Tonutti, P.; Perata, P. Biochemical and molecular aspects of modified and controlled atmospheres. In Modified and Controlled Atmospheres for Storage; Transportation and Packaging of Horticultural Commodities; Yahia, E.M., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009; pp. 553–568. [Google Scholar]
- Paidari, S.; Zamindar, N.; Tahergorabi, R.; Kargar, M.; Ezzati, S.; Musavi, S.H. Edible coating and films as promising packaging: A mini review. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2021, 15, 4205–4214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Shehin, V.P.; Kaur, N.; Vyas, P. Application of edible coatings on fresh and minimally processed vegetables: A review. Int. J. Veg. Sci. 2019, 25, 295–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irimia, A.; Stoleru, E.; Vasile, C.; Bele, A.; Brebu, M. Application of vegetal oils in developing bioactive paper-based materials for food packaging. Coatings 2021, 11, 1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otoni, C.G.; Avena-Bustillos, R.J.; Azeredo, H.M.; Lorevice, M.V.; Moura, M.R.; Mattoso, L.H.; McHugh, T.H. Recent advances on edible films based on fruits and vegetables—A review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2017, 16, 1151–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Zhao, Y. Innovations in the development and application of edible coatings for fresh and minimally processed fruits and vegetables. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2007, 6, 60–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kader, A.A. Biochemical and physiological basis for effects of controlled and modified atmospheres on fruits and vegetables. Food Technol. 1986, 40, 99–104. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, B.; Chatha, S.A.S.; Hussain, A.I.; Zia, K.M.; Akhtar, N. Recent advances on polysaccharides; lipids and protein based edible films and coatings: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 109, 1095–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ncama, K.; Magwaza, L.S.; Mditshwa, A.; Tesfay, S.Z. Plant-based edible coatings for managing postharvest quality of fresh horticultural produce: A review. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2018, 16, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Zhang, J.; Cheng, F. Cross-linked starch-based edible coating reinforced by starch nanocrystals and its preservation effect on graded Huangguan pears. Food Chem. 2020, 311, 125891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azeredo, H.M.; Waldron, K.W. Crosslinking in polysaccharide and protein films and coatings for food contact–A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 52, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wihodo, M.; Moraru, C.I. Physical and chemical methods used to enhance the structure and mechanical properties of protein films: A review. J. Food Eng. 2013, 114, 292–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, P.; Feng, J.; Sun, P.; Xiang, N.; Lu, B.; Qiu, D. Recent advances in improving stability of food emulsion by plant polysaccharides. Food Res. Int. 2020, 137, 109376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mederos-Torres, Y.; Bernabe-Galloway, P.; Ramirez-Arrebato, M.A. Polysaccharide-based films as biodegradable coatings in fruits postharvest. Cultiv. Trop. 2020, 41. [Google Scholar]
- Arnon-Rips, H.; Poverenov, E. Improving food products' quality and storability by using Layer by Layer edible coatings. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 75, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Castro e Silva, P.; de Oliveira, A.C.; Pereira, L.A.; Valquíria, M.; Carvalho, G.R.; Miranda, K.W.; Oliveira, J.E. Development of bionanocomposites of pectin and nanoemulsions of carnauba wax and neem oil pectin/carnauba wax/neem oil composites. Polym. Compos. 2020, 41, 858–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shigematsu, E.; Dorta, C.; Rodrigues, F.J.; Cedran, M.F.; Giannoni, J.A.; Oshiiwa, M.; Mauro, M.A. Edible coating with probiotic as a quality factor for minimally processed carrots. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 55, 3712–3720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hershko, V.; Klein, E.; Nussinovitch, A. Relationships between edible coatings and garlic skin. J. Food Sci. 1996, 61, 769–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.H. Edible films and coatings: A review. In Innovations and Food Packaging; Han, J.H., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 213–255. ISBN 978-0-12-394601-0. [Google Scholar]
- Navarro-Tarazaga, M.L.; Sothornvit, R.; Pérez-Gago, M.B. Effect of plasticizer type and amount on hydroxypropyl methylcellulose− beeswax edible film properties and postharvest quality of coated plums (cv. Angeleno). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 9502–9509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falguera, V.; Quintero, J.P.; Jiménez, A.; Muñoz, J.A.; Ibarz, A. Edible films and coatings: Structures; active functions and trends in their use. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 22, 292–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McHugh, T.H.; Senesi, E. Apple wraps: A novel method to improve the quality and extend the shelf life of fresh-cut apples. J. Food Sci. 2000, 65, 480–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellá, M.C.; Silva, O.A.; Pellá, M.G.; Beneton, A.G.; Caetano, J.; Simões, M.R.; Dragunski, D.C. Effect of gelatin and casein additions on starch edible biodegradable films for fruit surface coating. Food Chem. 2020, 309, 125764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawab, A.; Alam, F.; Hasnain, A. Mango kernel starch as a novel edible coating for enhancing shelf-life of tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) fruit. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 103, 581–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballesteros-Mártinez, L.; Pérez-Cervera, C.; Andrade-Pizarro, R. Effect of glycerol and sorbitol concentrations on mechanical; optical; and barrier properties of sweet potato starch film. NFS J. 2020, 20, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Paulson, A.T. Mechanical and water vapour barrier properties of edible gellan films. Food Res. Int. 2000, 33, 563–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basiak, E.; Lenart, A.; Debeaufort, F. Effect of starch type on the physico-chemical properties of edible films. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 98, 348–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hassan, A.A.; Norziah, M.H. Starch–gelatin edible films: Water vapor permeability and mechanical properties as affected by plasticizers. Food Hydrocoll. 2012, 26, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavassoli-Kafrani, E.; Shekarchizadeh, H.; Masoudpour-Behabadi, M. Development of edible films and coatings from alginates and carrageenans. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 137, 360–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Yan, X. Dip-coating for fibrous materials: Mechanism; methods and applications. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2017, 81, 378–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, G.; Prabhu, K.N. Review of non-reactive and reactive wetting of liquids on surfaces. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2007, 133, 61–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Belloso, O.; Rojas-Graü, M.A.; Soliva-Fortuny, R. Edible Films and Coatings for Food Applications; Embuscado, M.E., Huber, K.C., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 295–313. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M.K.I.; Schutyser, M.; Schroën, K.; Boom, R. Barrier properties and storage stability of edible coatings prepared with electrospraying. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2014, 23, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaworek, A.T.S.A.; Sobczyk, A.T. Electrospraying route to nanotechnology: An overview. J. Electrost. 2008, 66, 197–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skurtys, O.; Acevedo, C.; Pedreschi, F.; Enrione, J.; Osorio, F.; Aguilera, J.M. Food hydrocolloid edible films and coatings. In Food Hydrocolloids: Characteristics; Properties and Structures; Hollingworth, C.S., Ed.; Nova Science: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 41–80. ISBN 9781608762224. [Google Scholar]
- Kocira, A.; Kozłowicz, K.; Panasiewicz, K.; Staniak, M.; Szpunar-Krok, E.; Hortyńska, P. Polysaccharides as edible films and coatings: Characteristics and influence on fruit and vegetable quality—A review. Agronomy 2021, 11, 813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Paliy, M.; Kobe, B.; Trebicky, T.; Suhan, N.; Arsenault, G.; Yang, J. Characterization of cross-linking depth for thin polymeric films using atomic force microscopy. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132, 41493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Yue, J.; Gong, X.; Qian, B.; Wang, H.; Deng, Y.; Zhao, Y. Blueberry leaf extracts incorporated chitosan coatings for preserving postharvest quality of fresh blueberries. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2014, 92, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorram, F.; Ramezanian, A.; Hosseini, S.M.H. Shellac; gelatin and Persian gum as alternative coating for orange fruit. Sci. Hortic. 2017, 225, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, A.; Baskaran, R.; Vadivel, V. Citral nanoemulsion incorporated edible coating to extend the shelf life of fresh cut pineapples. LWT 2020, 118, 108851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oregel-Zamudio, E.; Angoa-Pérez, M.V.; Oyoque-Salcedo, G.; Aguilar-González, C.N.; Mena-Violante, H.G. Effect of candelilla wax edible coatings combined with biocontrol bacteria on strawberry quality during the shelf-life. Sci. Hortic. 2017, 214, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arroyo, B.J.; Bezerra, A.C.; Oliveira, L.L.; Arroyo, S.J.; de Melo, E.A.; Santos, A.M.P. Antimicrobial active edible coating of alginate and chitosan add ZnO nanoparticles applied in guavas (Psidium guajava L.). Food Chem. 2020, 309, 125566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iñiguez-Moreno, M.; Ragazzo-Sánchez, J.A.; Barros-Castillo, J.C.; Sandoval-Contreras, T.; Calderón-Santoyo, M. Sodium alginate coatings added with Meyerozyma caribbica: Postharvest biocontrol of Colletotrichum gloeosporioides in avocado (Persea americana Mill. cv. Hass). Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2020, 163, 111123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.K.I.; Cakmak, H.; Tavman, Ş.; Schutyser, M.; Schroёn, K. Anti-browning and barrier properties of edible coatings prepared with electrospraying. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2014, 25, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saavedra, S.C.; Ventura-Aguilar, R.I.; Bautista-Baños, S.; Barrera-Necha, L.L. Biodegradable chitosan coating for improving quality and controlling Alternaria alternata growth in figs. World J. Adv. Res. Rev. 2020, 7, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, M.; Gozalbo, A.M.; Sun, X.; Plotto, A.; Bai, J.; de Assis, O.B.G.; Ferreira, M.D.; Baldwin, E. Effect of mono and bilayer of carnauba wax based nano-emulsion and HPMC coatings on post-harvest quality of 'redtainung' papaya. In Proceedings of the SIAGRO 2019 Simpósio Nacional de Instrumentação Agropecuária, São Carlos, Brazil, 3–5 December 2019; p. 5. [Google Scholar]
- Moreno, M.A.; Vallejo, A.M.; Ballester, A.R.; Zampini, C.; Isla, M.I.; López-Rubio, A.; Fabra, M.J. Antifungal edible coatings containing Argentinian propolis extract and their application in raspberries. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 107, 105973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasirifar, S.Z.; Maghsoudlou, Y.; Oliyaei, N. Effect of active lipid-based coating incorporated with nanoclay and orange peel essential oil on physicochemical properties of Citrus sinensis. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 6, 1508–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cakmak, H.; Kumcuoglu, S.; Tavman, S. Production of edible coatings with twin-nozzle electrospraying equipment and the effects on shelf-life stability of fresh-cut apple slices. J. Food Process Eng. 2018, 41, e12627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cakmak, H.; Kumcuoglu, S.; Tavman, S. Electrospray coating of minimally processed strawberries and evaluation of the shelf-life quality properties. J. Food Process Eng. 2019, 42, e13082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Rong, L.; Li, Y.; Cao, Y.; Kong, L.; Zhu, Z.; Huang, J. Fabrication of bio-based hierarchically structured ethylene scavenger films via electrospraying for fruit preservation. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 133, 107837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Han, W.; Zhu, Y.; Xuan, H.; Ren, J.; Zhang, J.; Ge, L. Anti-oxidative and antibacterial self-healing edible polyelectrolyte multilayer film in fresh-cut fruits. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2018, 18, 2592–2600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnon, H.; Zaitsev, Y.; Porat, R.; Poverenov, E. Effects of carboxymethyl cellulose and chitosan bilayer edible coating on postharvest quality of citrus fruit. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2014, 87, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kittitheeranun, P.; Dubas, S.T.; Dubas, L. Layer-by-layer surface modification of fruits with edible nano-coatings. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2012, 229, 2745–2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hira, N.; Mitalo, O.W.; Okada, R.; Sangawa, M.; Masuda, K.; Fujita, N.; Kubo, Y. The effect of layer-by-layer edible coating on the shelf life and transcriptome of ‘Kosui’Japanese pear fruit. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2022, 185, 111787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duong, N.T.C.; Uthairatanakij, A.; Laohakunjit, N.; Jitareerat, P.; Kaisangsri, N. An innovative single step of cross-linked alginate-based edible coating for maintaining postharvest quality and reducing chilling injury in rose apple cv.'Tabtimchan'(Syzygium samarangenese). Sci. Hortic. 2022, 292, 110648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez-Jara, C.; Bilbao-Sainz, C.; McHugh, T.; Chiou, B.S.; Williams, T.; Villalobos-Carvajal, R. Effect of cross-linked alginate/oil nanoemulsion coating on cracking and quality parameters of sweet cherries. Foods 2021, 10, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, J.; Xie, Y.; Guo, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Qian, H.; Yao, W. Application of edible coating with essential oil in food preservation. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 59, 2467–2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Montes, E.; Castro-Muñoz, R. Edible films and coatings as food-quality preservers: An overview. Foods 2021, 10, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palou, L.; Valencia-Chamorro, S.A.; Pérez-Gago, M.B. Antifungal edible coatings for fresh citrus fruit: A review. Coatings 2015, 5, 962–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nor, S.M.; Ding, P. Trends and advances in edible biopolymer coating for tropical fruit: A review. Food Res. Int. 2020, 134, 109208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, M.; Pandit, R.; Gaikwad, S.; Kövics, G. Antimicrobial peptides as natural bio-preservative to enhance the shelf-life of food. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 53, 3381–3394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treviño-Garza, M.Z.; García, S.; del Socorro Flores-González, M.; Arévalo-Niño, K. Edible active coatings based on pectin, pullulan, and chitosan increase quality and shelf life of strawberries (Fragaria ananassa). J. Food Sci. 2015, 80, M1823–M1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desobry, S.; Debeaufort, F. Encapsulation of flavors, nutraceuticals, and antibacterials. In Applications of Encapsulation and Controlled Release; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2019; pp. 343–373. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed, C.; Clementine, K.A.; Didier, M.; Gérard, L.; Noëlle, D.C.M. Antimicrobial and physical properties of edible chitosan films enhanced by lactoperoxidase system. Food Hydrocoll. 2013, 30, 576–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, R.; Kalbasi-Ashtari, A.; Oromiehie, A.; Yarmand, M.S.; Jahandideh, F. Development and characterization of a novel biodegradable edible film obtained from psyllium seed (Plantago ovata Forsk). J. Food Eng. 2012, 109, 745–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnon-Rips, H.; Cohen, Y.; Saidi, L.; Porat, R.; Poverenov, E. Covalent linkage of bioactive volatiles to a polysaccharide support as a potential approach for preparing active edible coatings and delivery systems for food products. Food Chem. 2021, 338, 127822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Wu, Q.; Picha, D.H.; Ferguson, M.H.; Ndukwe, I.E.; Azadi, P. Comparative performance of bio-based coatings formulated with cellulose; chitin; and chitosan nanomaterials suitable for fruit preservation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 259, 117764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.J.; Zhang, B.; Yan, H.; Feng, J.T.; Ma, Z.Q.; Zhang, X. Effect of lotus leaf extract incorporated composite coating on the postharvest quality of fresh goji (Lycium barbarum L.) fruit. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2019, 148, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poverenov, E.; Arnon-Rips, H.; Zaitsev, Y.; Bar, V.; Danay, O.; Horev, B.; Rodov, V. Potential of chitosan from mushroom waste to enhance quality and storability of fresh-cut melons. Food Chem. 2018, 268, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priyadarshi, R.; Riahi, Z.; Rhim, J.W. Antioxidant pectin/pullulan edible coating incorporated with Vitis vinifera grape seed extract for extending the shelf life of peanuts. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2022, 183, 111740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leena, M.M.; Yoha, K.S.; Moses, J.A.; Anandharamakrishnan, C. Edible coating with resveratrol loaded electrospun zein nanofibers with enhanced bioaccessibility. Food Biosci. 2020, 36, 100669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aitboulahsen, M.; Zantar, S.; Laglaoui, A.; Chairi, H.; Arakrak, A.; Bakkali, M.; Hassani Zerrouk, M. Gelatin-based edible coating combined with Mentha pulegium essential oil as bioactive packaging for strawberries. J. Food Qual. 2018, 2018, 8408915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dave, R.K.; Ramana Rao, T.V.; Nandane, A.S. Improvement of post-harvest quality of pear fruit with optimized composite edible coating formulations. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 54, 3917–3927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Betanzos, C.I.; Hernández-Sánchez, H.; Bernal-Couoh, T.F.; Quintanar-Guerrero, D.; de la Luz Zambrano-Zaragoza, M. Physicochemical; total phenols and pectin methylesterase changes on quality maintenance on guava fruit (Psidium guajava L.) coated with candeuba wax solid lipid nanoparticles-xanthan gum. Food Res. Int. 2017, 101, 218–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Sun, Z.; Yang, H. Effect of carnauba wax-based coating containing glycerol monolaurate on the quality maintenance and shelf-life of Indian jujube (Zizyphus mauritiana Lamk.) fruit during storage. Sci. Hortic. 2019, 244, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wani, S.M.; Gull, A.; Ahad, T.; Malik, A.R.; Ganaie, T.A.; Masoodi, F.A.; Gani, A. Effect of gum Arabic; xanthan and carrageenan coatings containing antimicrobial agent on postharvest quality of strawberry: Assessing the physicochemical; enzyme activity and bioactive properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 183, 2100–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousuf, B.; Wu, S.; Siddiqui, M.W. Incorporating essential oils or compounds derived thereof into edible coatings: Effect on quality and shelf life of fresh/fresh-cut produce. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 108, 245–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muley, A.B.; Singhal, R.S. Extension of postharvest shelf life of strawberries (Fragaria ananassa) using a coating of chitosan-whey protein isolate conjugate. Food Chem. 2020, 329, 127213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alali, A.A.; Awad, M.A.; Al-Qurashi, A.D.; Mohamed, S.A. Postharvest gum Arabic and salicylic acid dipping affect quality and biochemical changes of ‘Grand Nain’bananas during shelf life. Sci. Hortic. 2018, 237, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo’ay, A.A.; Rabie, M.M.; Alhaithloul, H.A.; Alghanem, S.M.; Ibrahim, A.M.; Abdein, M.A.; Abdelgawad, Z.A. On the biochemical and physiological responses of ‘Crimson seedless’ grapes coated with an edible composite of pectin, polyphenylene alcohol, and salicylic acid. Horticulturae 2021, 7, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Gioushy, S.F.; Abdelkader, M.F.; Mahmoud, M.H.; Abou El Ghit, H.M.; Fikry, M.; Bahloul, A.M.; Gawish, M.S. The effects of a gum arabic-based edible coating on guava fruit characteristics during storage. Coatings 2022, 12, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taher, M.A.; Lo’ay, A.A.; Gouda, M.; Limam, S.A.; Abdelkader, M.F.; Osman, S.O.; Hikal, D.M. Impacts of gum arabic and polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) with salicylic acid on peach fruit (Prunus persica) shelf life. Molecules 2022, 27, 2595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahir, H.E.; Xiaobo, Z.; Mahunu, G.K.; Arslan, M.; Abdalhai, M.; Zhihua, L. Recent developments in gum edible coating applications for fruits and vegetables preservation: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 224, 115141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaturvedi, K.; Sharma, N.; Yadav, S.K. Composite edible coatings from commercial pectin, corn flour and beetroot powder minimize post-harvest decay, reduces ripening and improves sensory liking of tomatoes. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 133, 284–293. [Google Scholar]
- Vilaplana, R.; Guerrero, K.; Guevara, J.; Valencia-Chamorro, S. Chitosan coatings to control soft mold on fresh blackberries (Rubus glaucus Benth.) during postharvest period. Sci. Hortic. 2020, 262, 109049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodaei, D.; Hamidi-Esfahani, Z. Influence of bioactive edible coatings loaded with Lactobacillus plantarum on physicochemical properties of fresh strawberries. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2019, 156, 110944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meindrawan, B.; Suyatma, N.E.; Wardana, A.A.; Pamela, V.Y. Nanocomposite coating based on carrageenan and ZnO nanoparticles to maintain the storage quality of mango. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2018, 18, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orellano, M.S.; Isaac, P.; Breser, M.L.; Bohl, L.P.; Conesa, A.; Falcone, R.D.; Porporatto, C. Chitosan nanoparticles enhance the antibacterial activity of the native polymer against bovine mastitis pathogens. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 213, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambrano-Zaragoza, M.L.; Mercado-Silva, E.; Ramirez-Zamorano, P.; Cornejo-Villegas, M.A.; Gutiérrez-Cortez, E.; Quintanar-Guerrero, D. Use of solid lipid nanoparticles (SLNs) in edible coatings to increase guava (Psidium guajava L.) shelf-life. Food Res. Int. 2013, 51, 946–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sothornvit, R.; Rodsamran, P. Mango film coated for fresh-cut mango in modified atmosphere packaging. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 45, 1689–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafortune, R.; Caillet, S.; Lacroix, M. Combined effects of coating, modified atmosphere packaging, and gamma irradiation on quality maintenance of ready-to-use carrots (Daucus carota). J. Food Prot. 2005, 68, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Food Spoilage Microorganisms; Woodhead Publishing in Food Science, Technology and Nutrition; Blackburn, C.D.W., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, T.Z.; Chen, W.; Gurtler, J.B.; Fan, X. Effectiveness of edible coatings to inhibit browning and inactivate foodborne pathogens on fresh-cut apples. J. Food Saf. 2020, 40, e12802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, M.V.; Palou, L.; Taberner, V.; Fernández-Catalán, A.; Argente-Sanchis, M.; Pitta, E.; Pérez-Gago, M.B. Natural pectin-based edible composite coatings with antifungal properties to control green mold and reduce losses of ‘valencia’oranges. Foods 2022, 11, 1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyacı, D.; Iorio, G.; Sozbilen, G.S.; Alkan, D.; Trabattoni, S.; Pucillo, F.; Yemenicioğlu, A. Development of flexible antimicrobial zein coatings with essential oils for the inhibition of critical pathogens on the surface of whole fruits: Test of coatings on inoculated melons. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2019, 20, 100316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.H.; Mak, I.E.K.; Li, D. Bilayer edible coating with stabilized Lactobacillus plantarum 299v improved the shelf life and safety quality of fresh-cut apple slices. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2021, 30, 100746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davachi, S.M.; Pottackal, N.; Torabi, H.; Abbaspourrad, A. Development and characterization of probiotic mucilage based edible films for the preservation of fruits and vegetables. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 16608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Polo, J.; Monasterio, A.; Cantero-López, P.; Osorio, F.A. Combining edible coatings technology and nanoencapsulation for food application: A brief review with an emphasis on nanoliposomes. Food Res. Int. 2021, 145, 110402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Tayyar, N.A.; Youssef, A.M.; Al-Hindi, R.R. Edible coatings and antimicrobial nanoemulsions for enhancing shelf life and reducing foodborne pathogens of fruits and vegetables: A review. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2020, 26, e00215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, S.K.; Ferrentino, G.; Scampicchio, M. Nanoemulsion as advanced edible coatings to preserve the quality of fresh-cut fruits and vegetables: A review. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 55, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eddin, A.S.; Ibrahim, S.A.; Tahergorabi, R. Egg quality and safety with an overview of edible coating application for egg preservation. Food Chem. 2019, 296, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).