Socioeconomic and Environmental Impact Assessment of Different Power-Sourced Drip Irrigation Systems in Punjab, Pakistan
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Description of Study Area
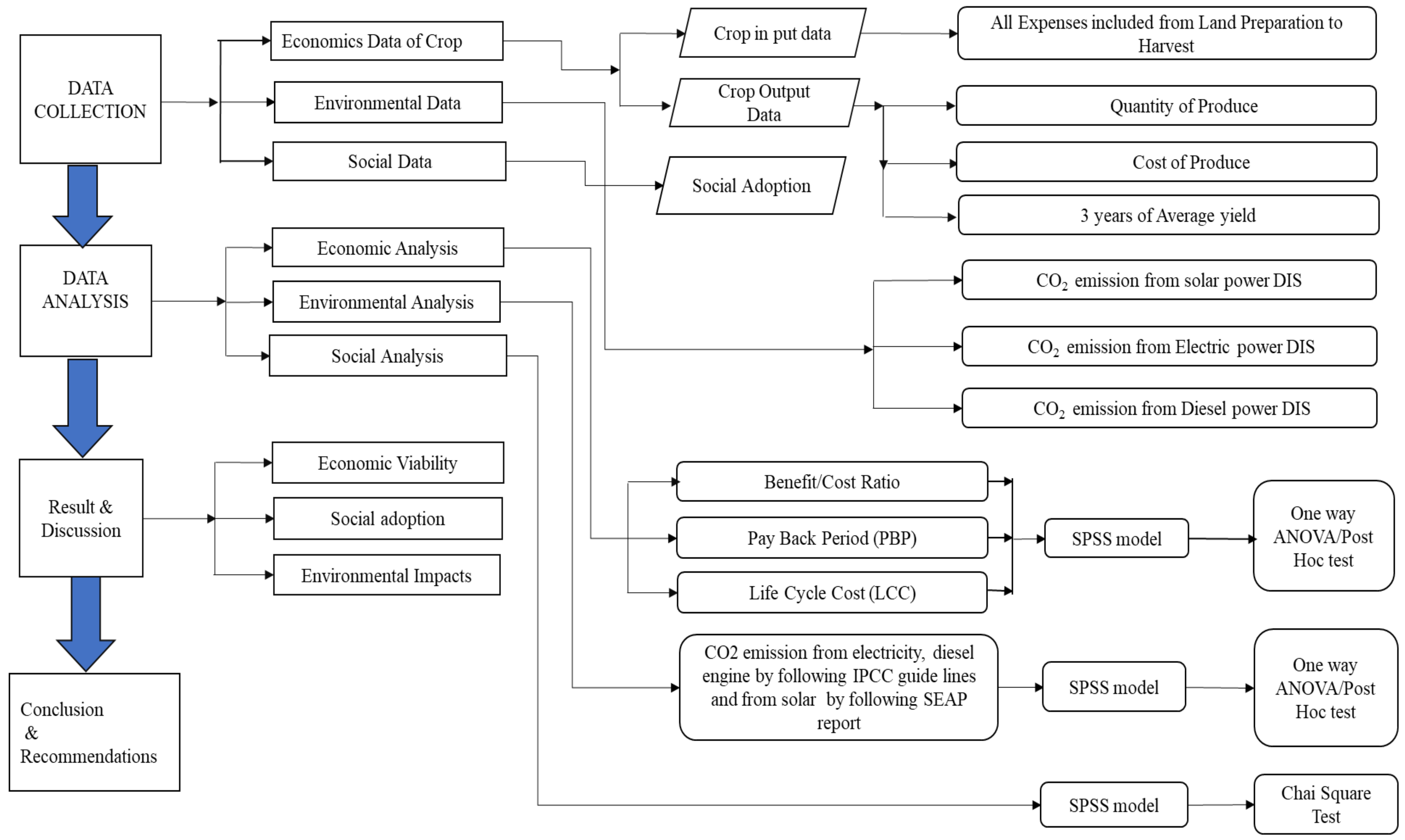
2.2. Data Collection
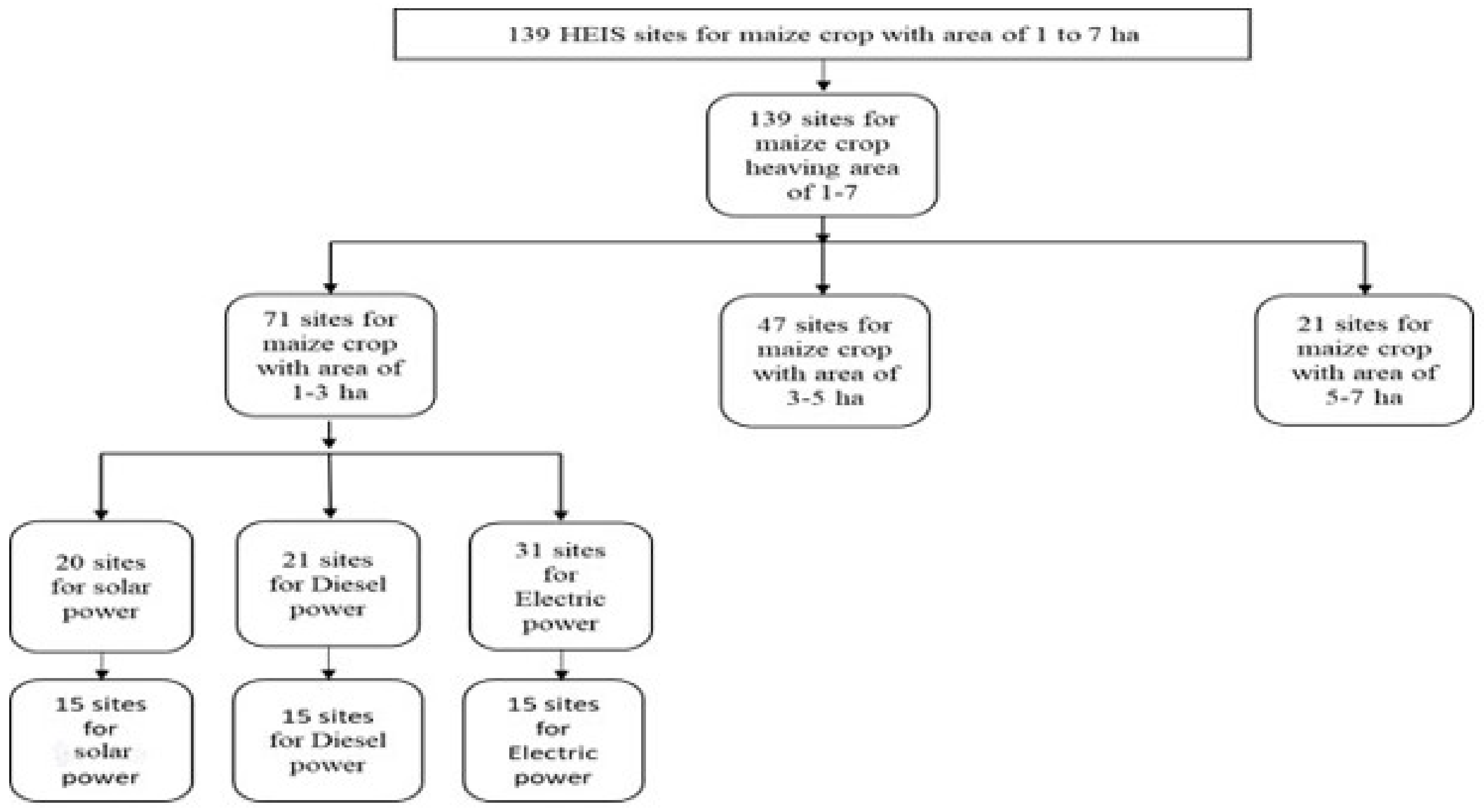
Sampling of Drip Irrigation System (DIS) Sites
- Data collection.
- Data analysis.
2.3. Economic Data
2.3.1. Crop Input and Output Data
2.3.2. Environmental Data
CO2 Emission
Social Adoption Data
2.4. Data Analysis
2.4.1. Economic Analysis
2.4.2. Benefit–Cost Analysis (BCA)
2.4.3. Present Value (PV)
2.4.4. Net Present Value (NPV)
2.4.5. Payback Period (PBP)
2.4.6. Life Cycle Cost (LCC)
2.4.7. Capital Cost
2.4.8. Maintenance Cost
2.4.9. Fuel Charges
2.4.10. Replacement Cost
2.4.11. Salvage Value
2.4.12. SPSS Model
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.5.1. One Way ANOVA
2.5.2. Post Hoc Test
2.5.3. Environmental Analysis
2.5.4. Social Analysis
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Economic Viability of Different Power Sources for Drip Irrigation System
3.2. Benefit–Cost Analysis of Different Power Sources for Drip Irrigation System
3.2.1. One-Way ANOVA
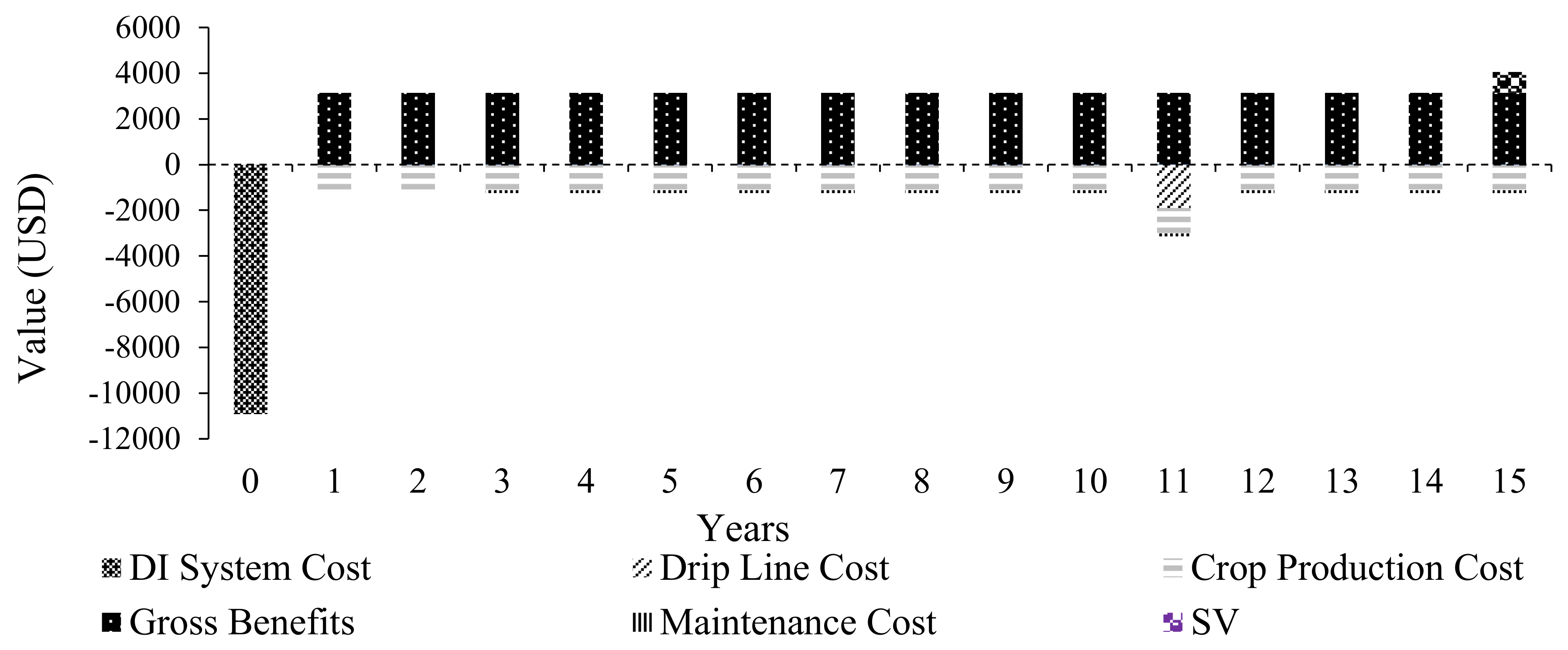
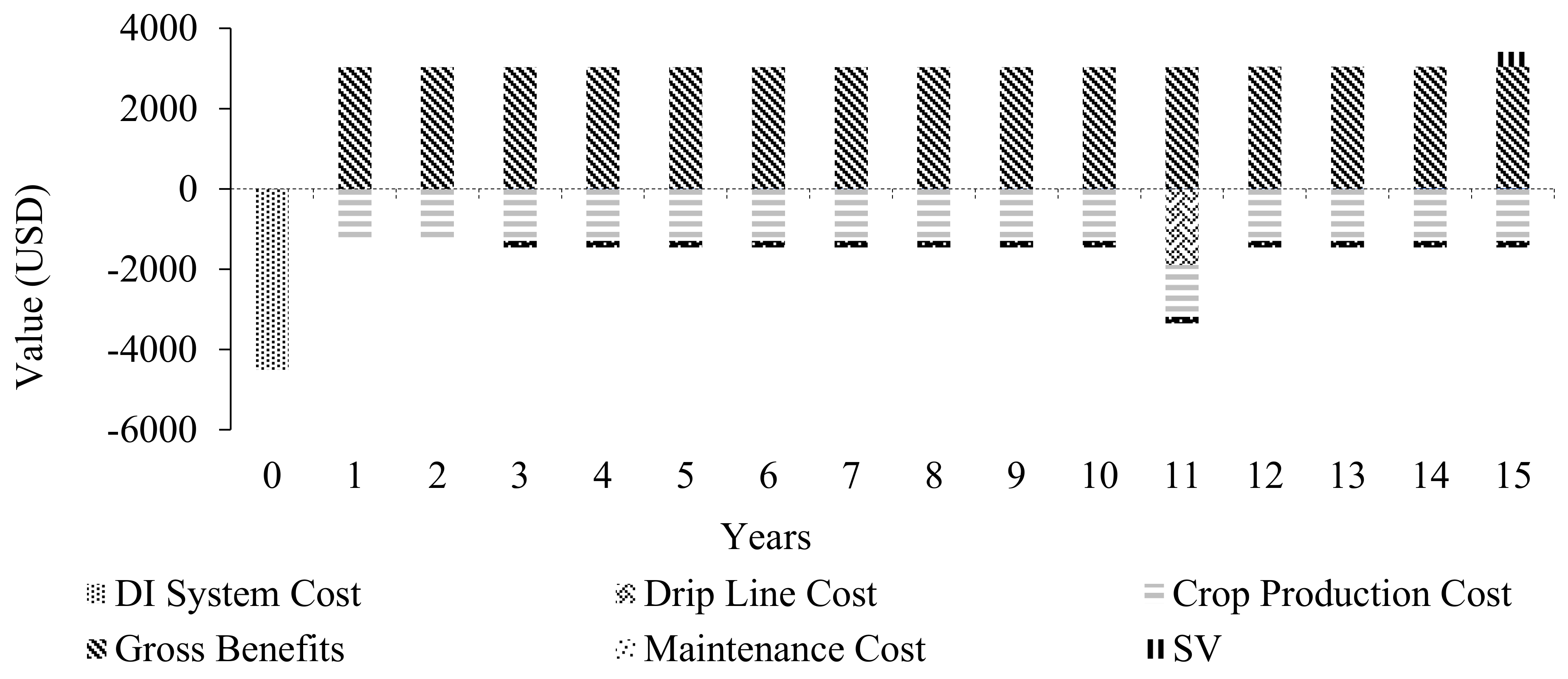
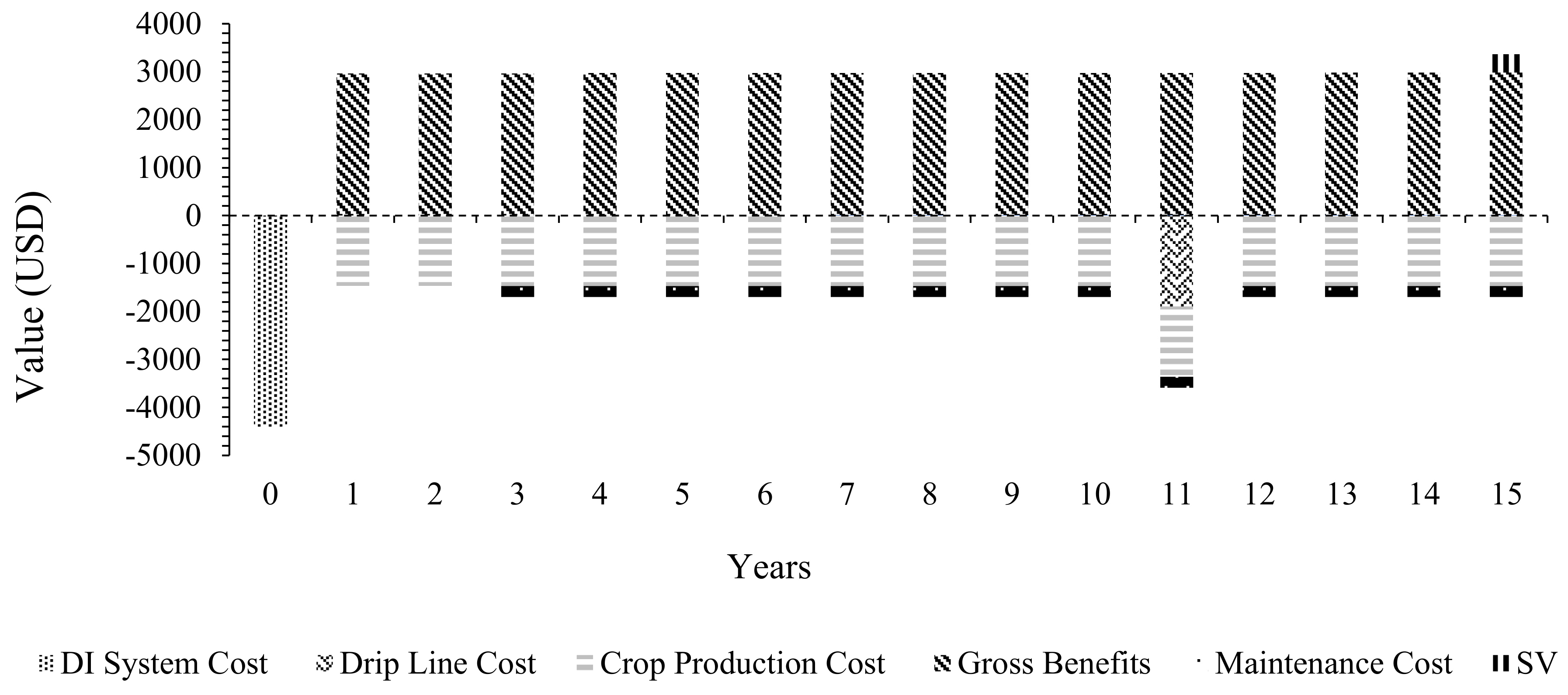
3.2.2. Cashflow Diagrams for All Power Sources Used for DIS
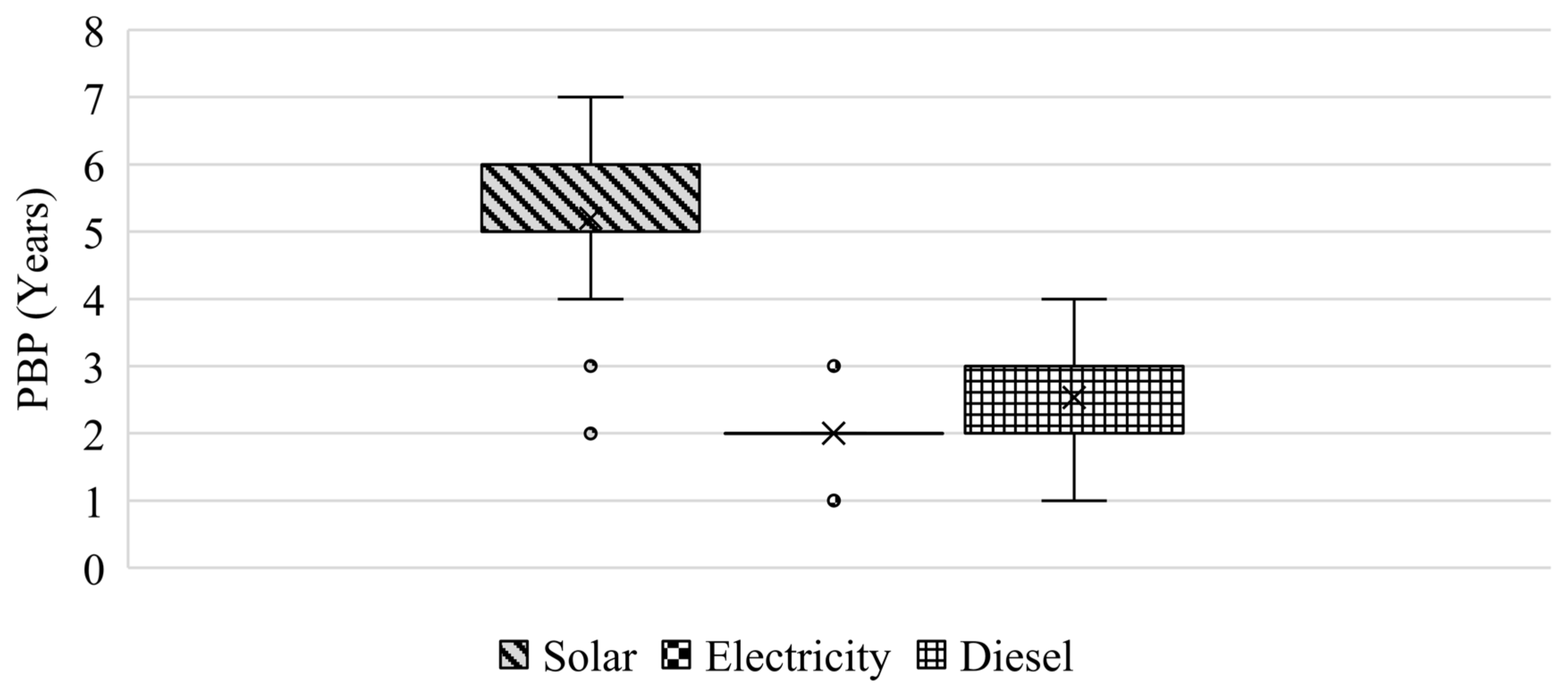
3.3. Payback Period of Different Power Sources for DIS
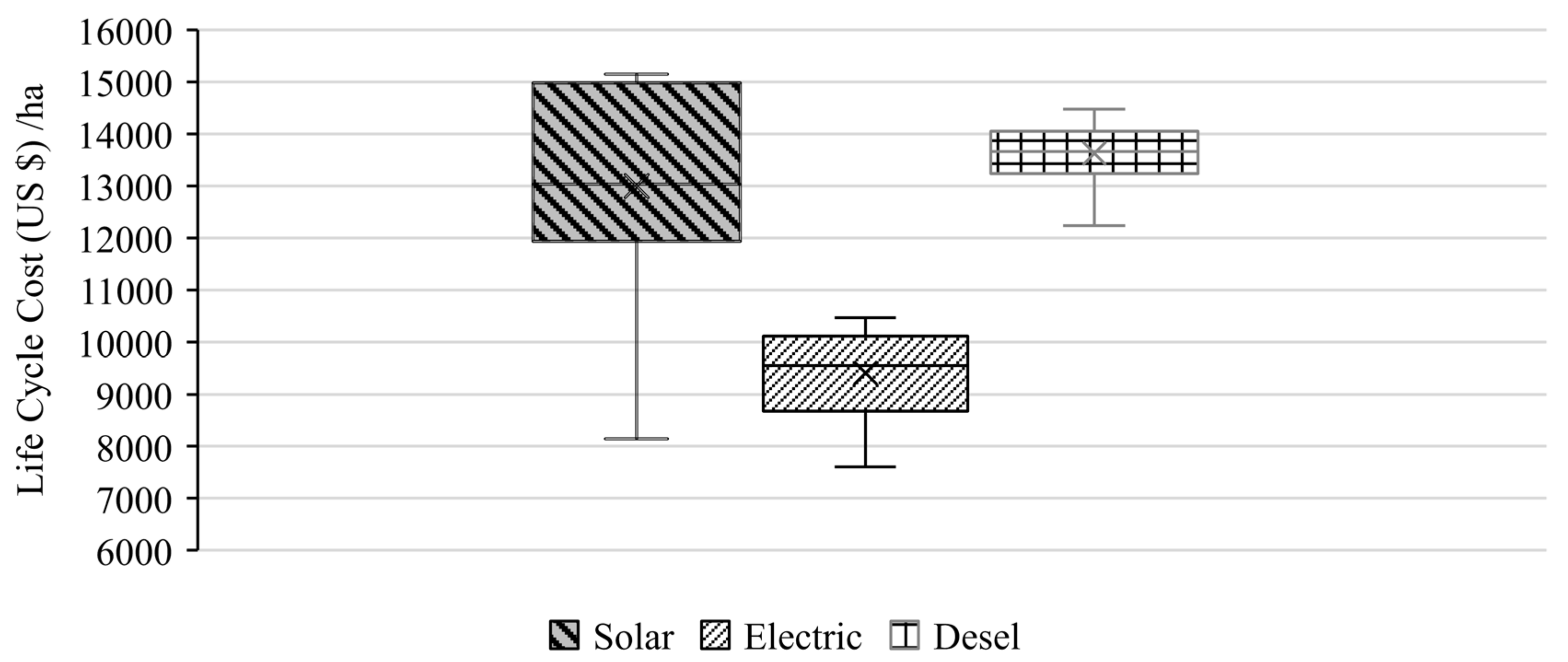
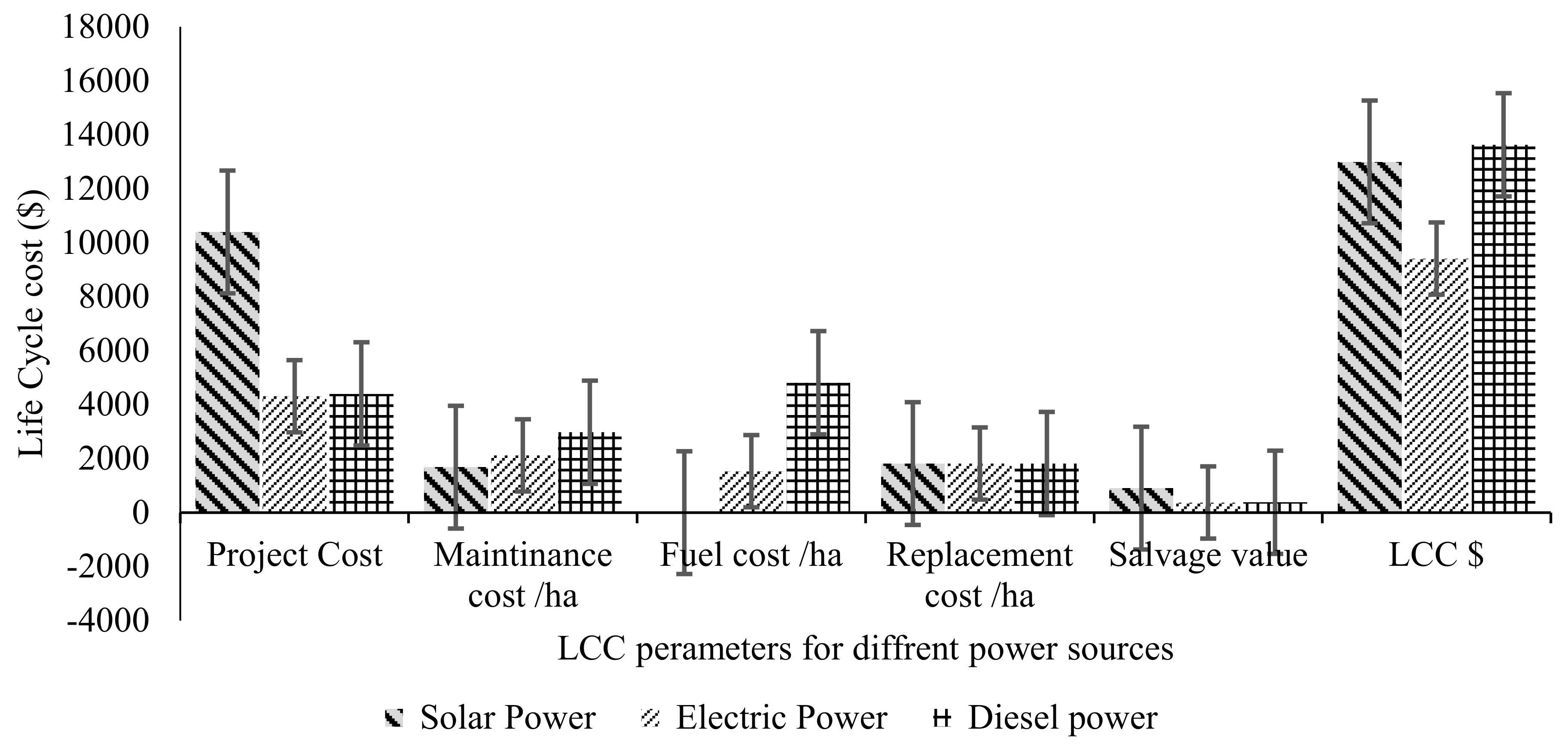
3.4. Life Cycle Cost Analysis of Different Power Sources for Drip Irrigation System
Production Cost for DIS
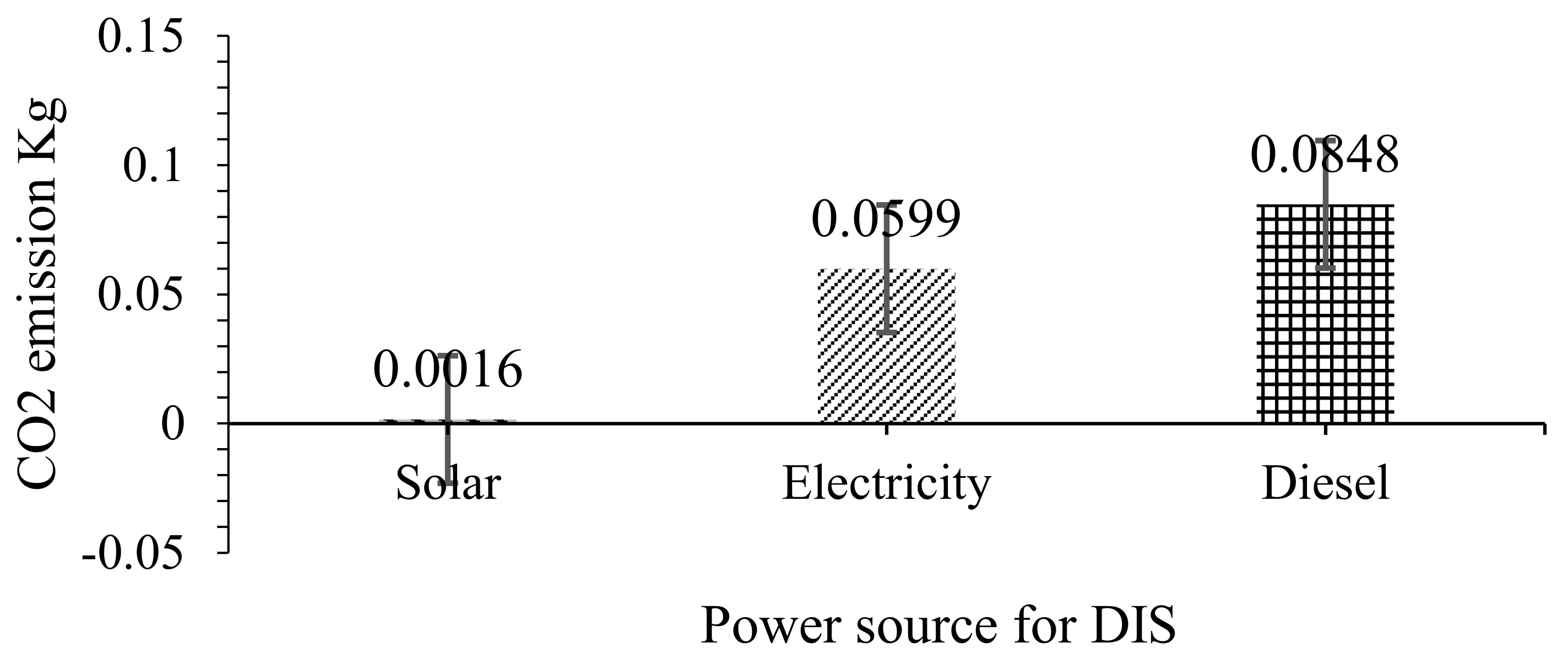
3.5. Environmental Impact of Different Power Sources for DIS
CO2 Emission Form Each Source for 1 kg Production of Maize
3.6. Social Adoption of Different Power Sources for Drip Irrigation System
3.6.1. Head of Family Education
3.6.2. Total Land under Control
3.6.3. Occupation of DIS Owner
3.6.4. Education of Farm Operators
4. Conclusions
5. Recommendations
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ashraf, M. Water Scarcity in Pakistan Issues and Options; PCRWR: Islamabad, Pakistan, 2018; pp. 34–38. [Google Scholar]
- Afzal, N.; Ahmad, S. Agricultural Input Use Efficiency in Pakistan: Key Issues and Reform Areas. Manag. Nat. Resour. Sustain. Future Agric. Res. Brief. 2009, 1, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- The Ministry of Finance and Revenue. Pakistan Economic Survey 2017–18; The Ministry of Finance and Revenue: Islamabad, Pakistan, 2018; pp. 13–32. [Google Scholar]
- Falkenmark, M.; Lundqvist, J.; Widstrand, C. Macro-scale water scarcity requires micro-scale approaches. Nat. Resour. Forum 1989, 13, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raskin, P.; Gleick, P.; Kirshen, P.; Pontius, G.; Strzepek, K. Water Futures: Assessment of Long-Range Patterns and Problems. Comprehensive Assessment of the Freshwater Resources of the World; SEI: Oaks, PA, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Planning Commission. Ten Year Perspective Development Plan 2001–11 and Three Year Development Program 2001–04/Government of Pakistan, Planning Commission; Planning Commission: Islamabad, Pakistan, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Adb. Water Resources Strategy Study; Adb: Mandaluyong, Philippines, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Ashraf, M.; Khan, M.A. Sustainable environment management: Impact of agriculture. Sci. Technol. Dev. 2000, 19, 51–57. [Google Scholar]
- Qureshi, A.S. Water Management in the Indus Basin in Pakistan: Challenges and Opportunities. Mt. Res. Dev. 2011, 31, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baksh, A.; Awan, Q.A. Water Issues and remedies in Pakistan. In Proceedings of the National Symposium on Drought and Water Resources in Pakistan, Lahore, Pakistan, 18 March 2002; pp. 145–150. [Google Scholar]
- Carruthers, I.; Rosegrant, M.W.; Seckler, D. Irrigation and Food Security in the 21st Century; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1997; pp. 83–101. [Google Scholar]
- Usman, M.; Tayyab, M.; Majid, M.; Ali, S.M.; Shilan, R.; Alireza, M.; Sergey, P. Drip Irrigation in Pakistan: Status, Challenges and Future Prospects. Russ. J. Agric. Socio Econ. Sci. 2016, 8, 114–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.; Kashyap, D.; Shah, T.; Crettaz, M.; Sikka, A. Solar: Solar Irrigation for Agriculture Resilience—A New SDC-IWMI Regional Partnership; IWMI: Colombo, Sri Lanka, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- World Bank. World Bank Project: PK Punjab Irrig Agri Productivity Improvement Program Project—P125999; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, M.A.; Zain-Bin-Akbar, M. Solar Irrigation in Pakistan: A Situation Analysis Report; IWMI: Colombo, Sri Lanka, 2021; p. 35. ISBN 978-92-9090-925-5. [Google Scholar]
- INCID. Drip Irrigation in India; INCID: New Delhi, India, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Alam, M.; Bhutta, N.; Azhar, A. Use and Limitations of Sprinkler and Drip Irrigation systems in Pakistan. In Proceedings of the Pakistan Engineering Congress, Lahore, Pakistan, 1 December 2006; pp. 78–97. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. Irrigation in Southern and Eastern Asia in Figures. AQUASTAT Survey—2011; Food and Agriculture Organization: Rome, Italy, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Government of Pakistan. Number of Tube Wells (Electric & Diesel) in the Punjab by Divisions and Districts during the Year 2013–14. Crop Reporting Service; Government of Pakistan: Islamabad, Pakistan, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- National Electric Power Regulatory Authority Government of Pakistan. State of Industry Report; National Electric Power Regulatory Authority Government of Pakistan: Islamabad, Pakistan, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Yousuf, I.; Ghumman, A.R.; Hashmi, H.N.; Kamal, M.A. Carbon emissions from power sector in Pakistan and opportunities to mitigate those. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 34, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, A. Power Crisis in Pakistan: A Crisis in Governance? Pakistan Institute of Development Economics Monograph Series; Pakistan Institute of Development Economics: Islamabad, Pakistan, 2012; p. 43. [Google Scholar]
- Faheem, S.A.; Mir, A.T. Energize Pakistan, Report for ‘Explore-a-Vision’ Competition, GIKI-IEEE Olympiad 2009; FAST National University of Computer & Emerging Sciences: Karachi, Pakistan, 2009; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Mongat, A.S.; Arshad, M.; Bakhsh, A.; Shakoor, A.; Anjum, L.; Hameed, A.; Shamim, F. Design, installation and evaluation of solar drip irrigation system at mini dam command area. Pak. J. Agric. Sci. 2015, 52, 483–490. [Google Scholar]
- Raza, M.Y.; Lin, B. Analysis of Pakistan’s electricity generation and CO2 emissions: Based on decomposition and decoupling approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 359, 132074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, A. Gas and Petroleum Market Structure and Pricing; Pakistan Institute of Development Economics: Islamabad, Pakistan, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Hansona, B.R.; Schwankl, L.J.; Schulbach, K.F.; Pettygrove, G.S. A comparison of furrow, surface drip, and subsurface drip irrigation onlettuce yield and applied water. Agric. Water Manage. 1997, 33, 139–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haq, N. Evaluation of Modern Irrigation Techniques for Sandy Loam Soil Having Low Slope. Master’s Thesis, Department of Irrigation and Drainage, University of Agriculture, Faisalabad, Pakistan, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Humphreys, L.; Fawcett, B.R.A.D.; O’Neill, C.; Muirhead, W. Maize under sprinkler, dripand furrow irrigation. IREC Farmers’ Newsl. 2005, 170, 35–38. [Google Scholar]
- Qureshi, A.S.; McCornick, P.G.; Qadir, M.; Aslam, Z. Managing salinity and waterlogging in the Indus Basin of Pakistan. Agric. Water Manag. 2008, 95, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, M.A. Energy and renewable energy scenario of Pakistan. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2010, 14, 354–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.; Tariq, S.; Mahmood, K.; Daud, A.; Batool, A.; Zia Ul, H. A study of aerosol properties over Lahore (Pakistan) by using AERONET data. Asia-Pac. J. Atmos. Sci. 2014, 50, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zare, E.; Akhash, S.; Hasanshahi, M.; Rahimi, M. Study the Effective Economic Factors on Diffusion of Environmental Pollutions, Case Study: Carbon De-Oxide. J. Basic Appl. Sci. Res. 2012, 2, 8150–8154. [Google Scholar]
- Nawaz, A.; Ghauri, B.M.; Jilani, R.; Rahman, S. Climate Change: Emissions and Sinks of Greenhouse Gases in Pakistan. In Proceedings of the Symposium on Changing Environmental Pattern and its impact with Special Focus on Pakistan, Lahore, Pakistan, 4 July 2011; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Amiraslany, A. The Impact of Climate Change on Canadian Agriculture: A Ricardian Approach. Doctoral Dissertation, University of Saskatchewan, Saskatoon, SK, Canada, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- The Investopedia Team. Feasibility Study; Investopedia: New York, NY, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Srivastav, A.K. Cost-Benefit Analysis Formula; Wall Street Mojo: New York, NY, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Fernando, J. What Is Present Value in Finance, and How Is It Calculated? Investopedia: New York, NY, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Jagerson, J. How to Calculate Net Present Value (NPV); Investopedia: New York, NY, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Kagan, J. Payback Period Explained, with the Formula and How to Calculate It; Investopedia: New York, NY, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.; Ma, K.; Liu, Z.; Ren, J.; Man, Y. Development and applicability of life cycle impact assessment methodologies. In Life Cycle Sustainability Assessment for Decision-Making: Methodologies and Case Studies; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 95–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wall Street, P. Salvage Value; Wall Street Prep: New York, NY, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharya, J.; Saha, N.K.; Mondal, M.K.; Bhandari, H.; Humphreys, E. The feasibility of high yielding aus-aman-rabi cropping systems in the polders of the low salinity coastal zone of Bangladesh. Field Crops Res. 2019, 234, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Kumar, S.; Nangare, D.D.; Meena, M.S. Drip irrigation and black polyethylene mulch influence on growth, yield and water-use efficiency of tomato. Afr. J. Agric. Res. 2009, 4, 1427–1430. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.; Liu, J.; Qin, D.; Gao, X.; Yan, J. Feasibility analysis of solar irrigation system for pastures conservation in a demonstration area in Inner Mongolia. Appl. Energy 2013, 112, 697–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Li, Y.; Li, M.; Pan, Y.; Shi, P. Agricultural irrigation in China. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2013, 68, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Site Code | Electricity Power | Diesel Power | Solar Power |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.64 | 1.55 | 1.73 |
| 2 | 1.78 | 1.59 | 1.86 |
| 3 | 1.76 | 1.41 | 1.65 |
| 4 | 1.58 | 1.60 | 1.57 |
| 5 | 1.55 | 1.39 | 1.60 |
| 6 | 1.47 | 1.48 | 1.48 |
| 7 | 1.64 | 1.49 | 1.41 |
| 8 | 1.77 | 1.29 | 1.39 |
| 9 | 1.54 | 1.35 | 1.42 |
| 10 | 1.79 | 1.45 | 1.35 |
| 11 | 1.57 | 1.21 | 1.45 |
| 12 | 1.56 | 1.39 | 1.42 |
| 13 | 1.66 | 1.46 | 1.56 |
| 14 | 1.70 | 1.54 | 1.31 |
| 15 | 1.80 | 1.45 | 1.55 |
| Mean | 1.65 | 1.44 | 1.52 |
| St. Dev | 0.11 | 0.11 | 0.15 |
| Sum of Squares | df | Mean Square | F | Sig. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Between Groups | 0.343 | 2 | 0.172 | 11.215 | 0.000 |
| Within Groups | 0.642 | 42 | 0.015 | ||
| Total | 0.986 | 44 |
| (I) Factor | (J) Factor | Mean Difference (I-J) | Std. Error | Sig. | 95% Confidence Interval | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower Bound | Upper Bound | |||||
| Solar | electricity | −0.13733 * | 0.04516 | 0.011 | −0.2470 | −0.0276 |
| diesel | 0.07333 | 0.04516 | 0.247 | −0.0364 | 0.1830 | |
| Electricity | Solar | 0.13733 * | 0.04516 | 0.011 | 0.0276 | 0.2470 |
| diesel | 0.21067 * | 0.04516 | 0.000 | 0.1010 | 0.3204 | |
| Diesel | Solar | −0.07333 | 0.04516 | 0.247 | −0.1830 | 0.0364 |
| electricity | −0.21067 * | 0.04516 | 0.000 | −0.3204 | −0.1010 | |
| Solar | Electricity | Diesel | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Average | 5.2 | 2 | 2.53333 |
| St. Deviation | 1.373213 | 0.534522 | 0.99043 |
| Types of DIS by Power Source | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Solar | Diesel | Electricity | |
| LCC for drip irrigation system for 15 years | 12,994.67 * | 9414.629 * | 13,628.47 * |
| System cost for 1 year | 866.31 * | 627.64 * | 908.56 * |
| Mean production cost for DIS Production cost | 1118.15 * | 1296.28 * | 1467.64 * |
| Total cost | 1984.46 * | 1923.92 * | 2376.21 * |
| Mean crop benefits for DIS | 3130 * | 3027.61 * | 2965.14 * |
| Maize production (kg/ha) | 11,476.67 * | 11,101.23 * | 10,872.1 * |
| Production cost ($/kg maize) | 0.1729 * | 0.173 * | 0.21 * |
| Mean cost of production for maize crop by using DIS ($/kg) | 0.1853 * | ||
| Social Adoption Indicator | Percentage % | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solar | Electricity | Diesel | ||
| Family members | 1–4 members | 20.00 | 13.33 | 6.67 |
| 5–8 members | 46.67 | 53.33 | 60.00 | |
| 8–12 members | 33.33 | 33.33 | 33.33 | |
| Total landholding | 5–3 ha | 40.00 | 60.00 | 60.00 |
| 31–55 ha | 26.67 | 20.00 | 40.00 | |
| 56–80 ha | 33.33 | 20.00 | 0.00 | |
| Education of head of family | Metric | 0.00 | 0.00 | 20.00 |
| Intermediate | 0.00 | 0.00 | 13.33 | |
| Graduate | 6.67 | 53.33 | 53.33 | |
| Postgraduate | 93.33 | 46.67 | 13.33 | |
| Education of farm operator | Illiterate | 20 | 40.00 | 66.67 |
| Middle | 30 | 26.67 | 26.67 | |
| Metric | 50 | 26.67 | 6.67 | |
| Occupation of HEIS owner | Farming | 26.67 | 26.67 | 53.33 |
| Employee | 53.33 | 20.00 | 33.33 | |
| Business | 20.00 | 53.33 | 13.33 | |
| Crop sown | Maize–potato | 40.00 | 66.67 | 60.00 |
| Maize–potato–maize | 60.00 | 33.33 | 40.00 | |
| Area under DIS | 1–3 ha | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ul Hussan, I.; Nadeem, M.; Yamin, M.; Ali, S.; Omar, M.M.; Ahmad, S.; Zulfiqar, M.; Mahmood, T. Socioeconomic and Environmental Impact Assessment of Different Power-Sourced Drip Irrigation Systems in Punjab, Pakistan. AgriEngineering 2023, 5, 236-256. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriengineering5010016
Ul Hussan I, Nadeem M, Yamin M, Ali S, Omar MM, Ahmad S, Zulfiqar M, Mahmood T. Socioeconomic and Environmental Impact Assessment of Different Power-Sourced Drip Irrigation Systems in Punjab, Pakistan. AgriEngineering. 2023; 5(1):236-256. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriengineering5010016
Chicago/Turabian StyleUl Hussan, Iftkhar, Muhammad Nadeem, Muhammad Yamin, Sikandar Ali, Muhammad Mubashar Omar, Shaheer Ahmad, Mamoona Zulfiqar, and Tallat Mahmood. 2023. "Socioeconomic and Environmental Impact Assessment of Different Power-Sourced Drip Irrigation Systems in Punjab, Pakistan" AgriEngineering 5, no. 1: 236-256. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriengineering5010016
APA StyleUl Hussan, I., Nadeem, M., Yamin, M., Ali, S., Omar, M. M., Ahmad, S., Zulfiqar, M., & Mahmood, T. (2023). Socioeconomic and Environmental Impact Assessment of Different Power-Sourced Drip Irrigation Systems in Punjab, Pakistan. AgriEngineering, 5(1), 236-256. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriengineering5010016





