Understanding How Image Quality Affects Transformer Neural Networks
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Structure of the Paper
1.2. Related Works
1.3. Contributions
2. Background
- Self-attention mechanism: it allows the model to weigh the importance of different words in a sequence when predicting a particular word. It can focus on different parts of the input sequence for each word in the output sequence. This is particularly useful for tasks involving long-range dependencies in the input data.
- Multi-head attention: To capture different aspects of the input sequence, the self-attention mechanism is extended to multiple heads, allowing the model to jointly attend to information from different representation subspaces.
- Positional encoding: Since the transformer does not inherently understand the order of the input sequence, positional encodings are added to the input embeddings to give the model information about the positions of the words in the sequence.
- Feed-forward neural networks: After the attention layers, the model uses feed-forward neural networks to process the information from the attention layer and produce the final output.
- Encoder and decoder stacks: The transformer model consists of an encoder stack and a decoder stack. The encoder processes the input sequence, while the decoder generates the output sequence. Both the encoder and decoder contain multiple layers of the components mentioned above.
3. Experimental Setup
3.1. Transformers
3.2. Dataset
3.3. Distortion Types
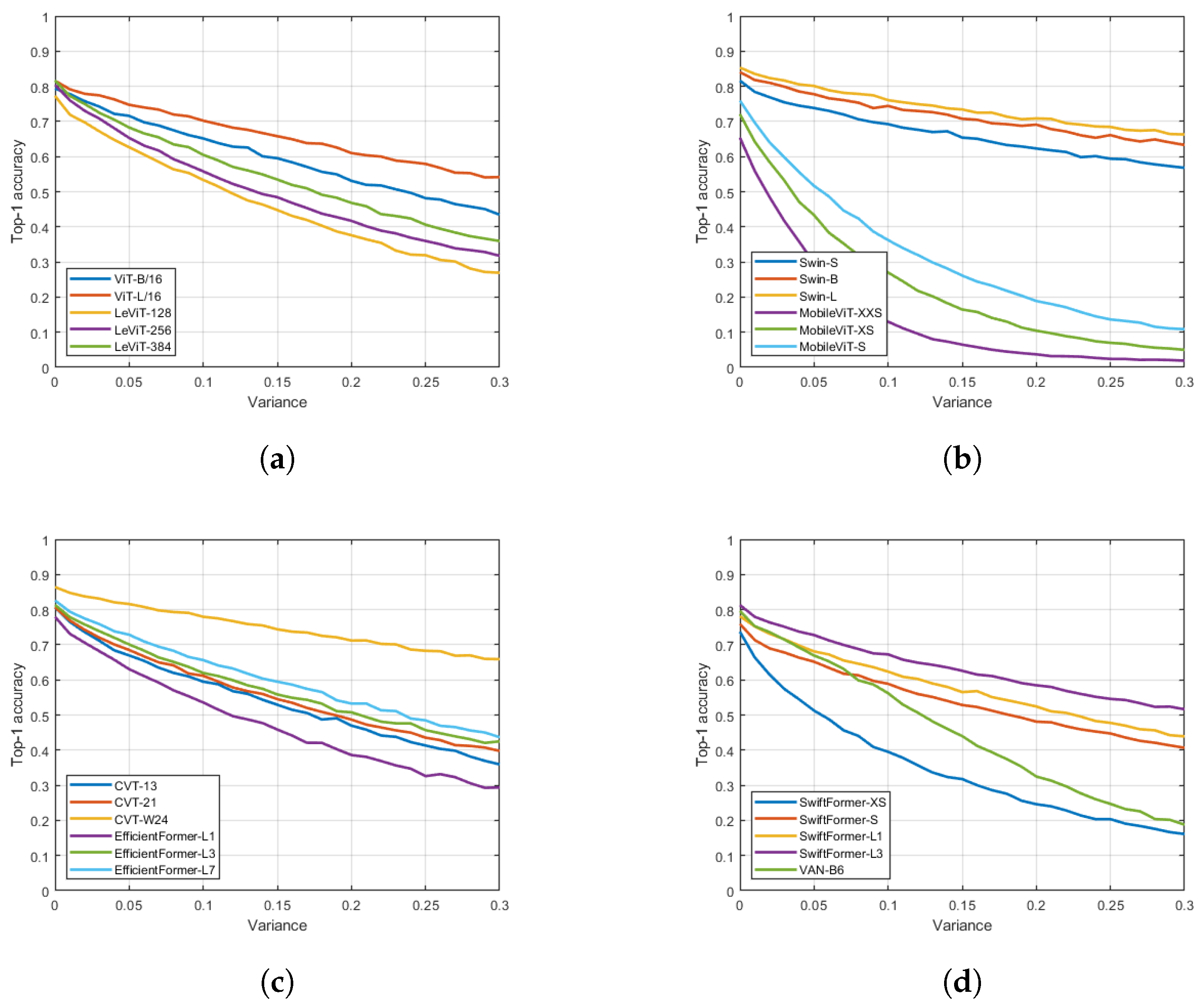
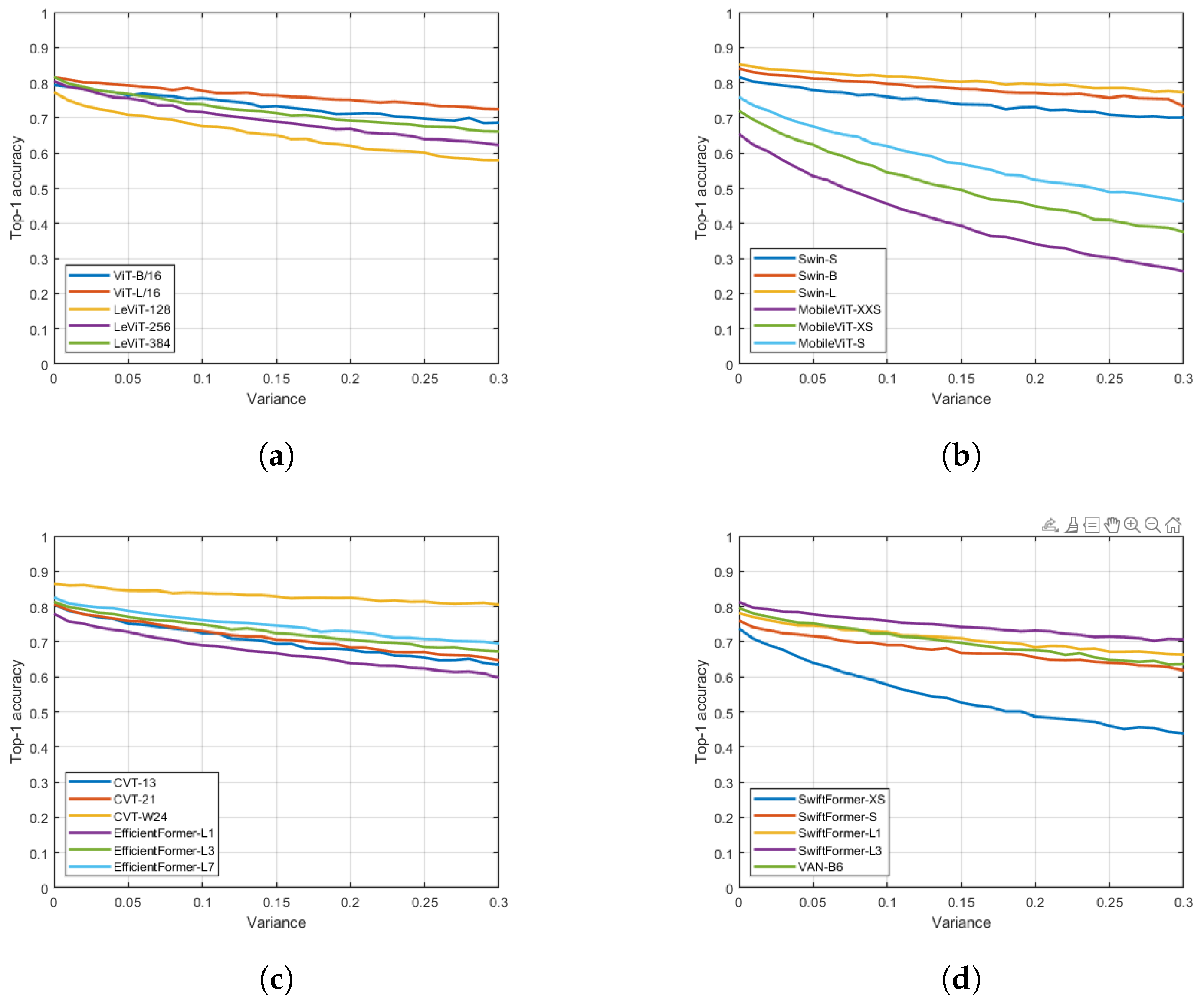
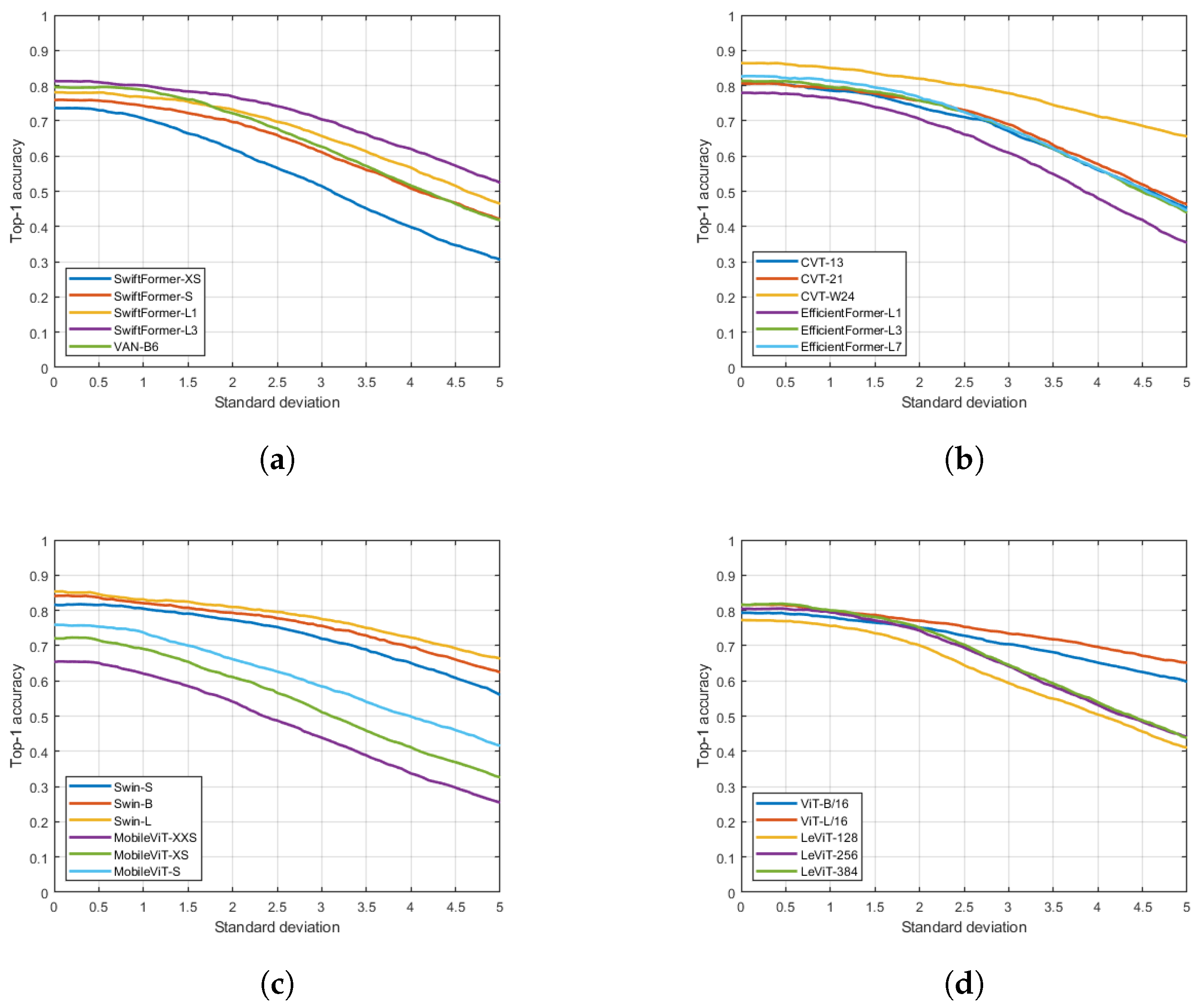
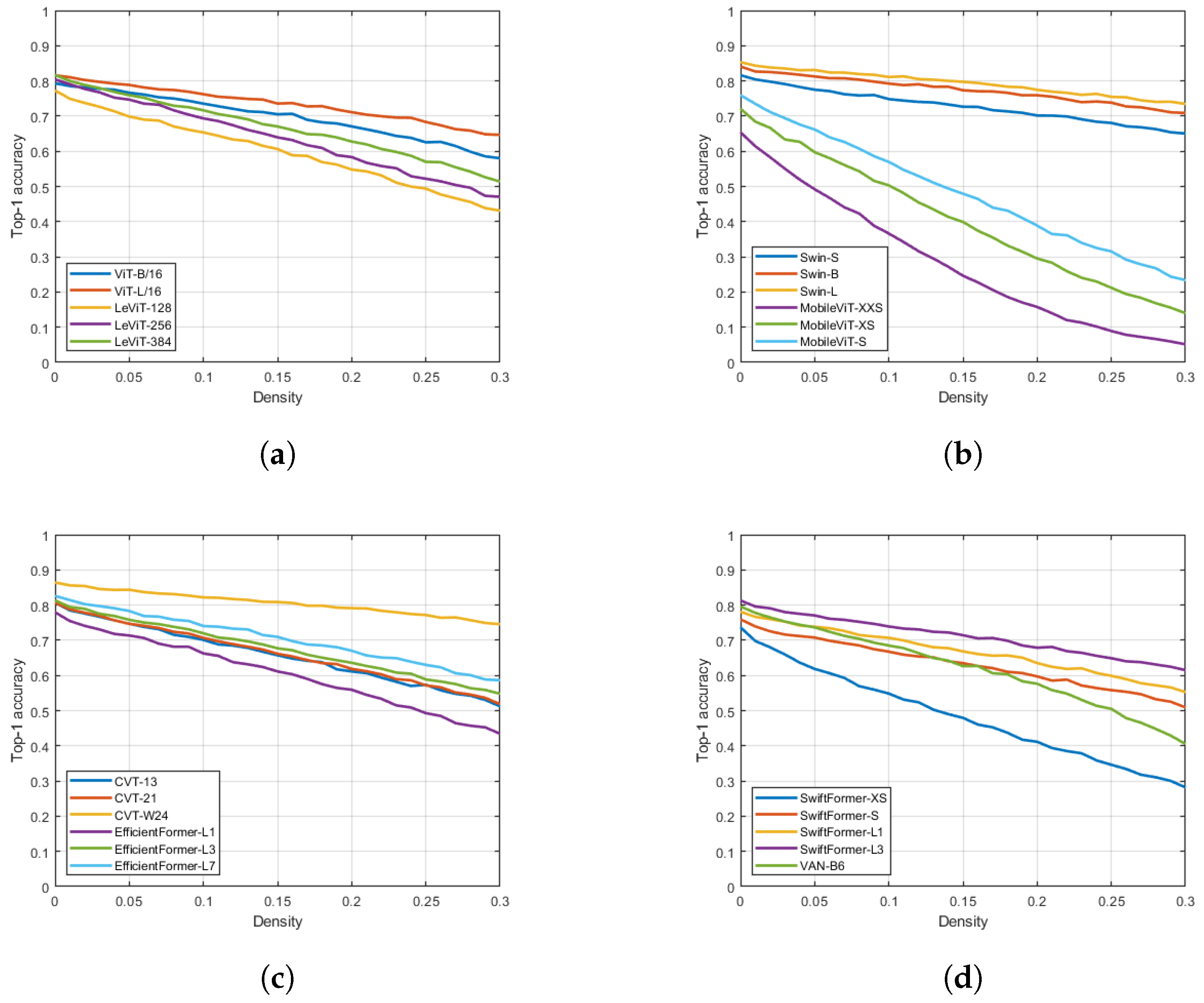
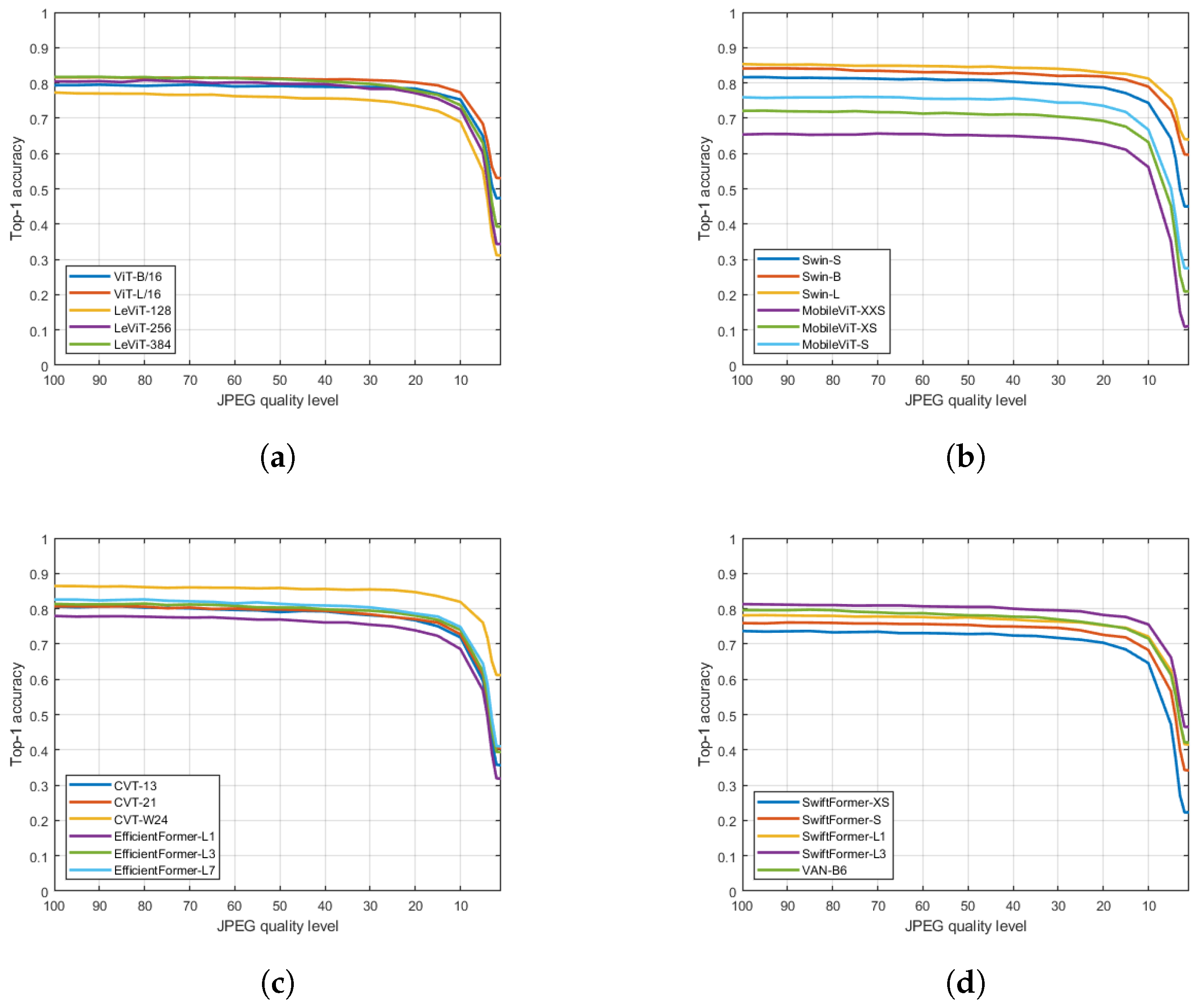
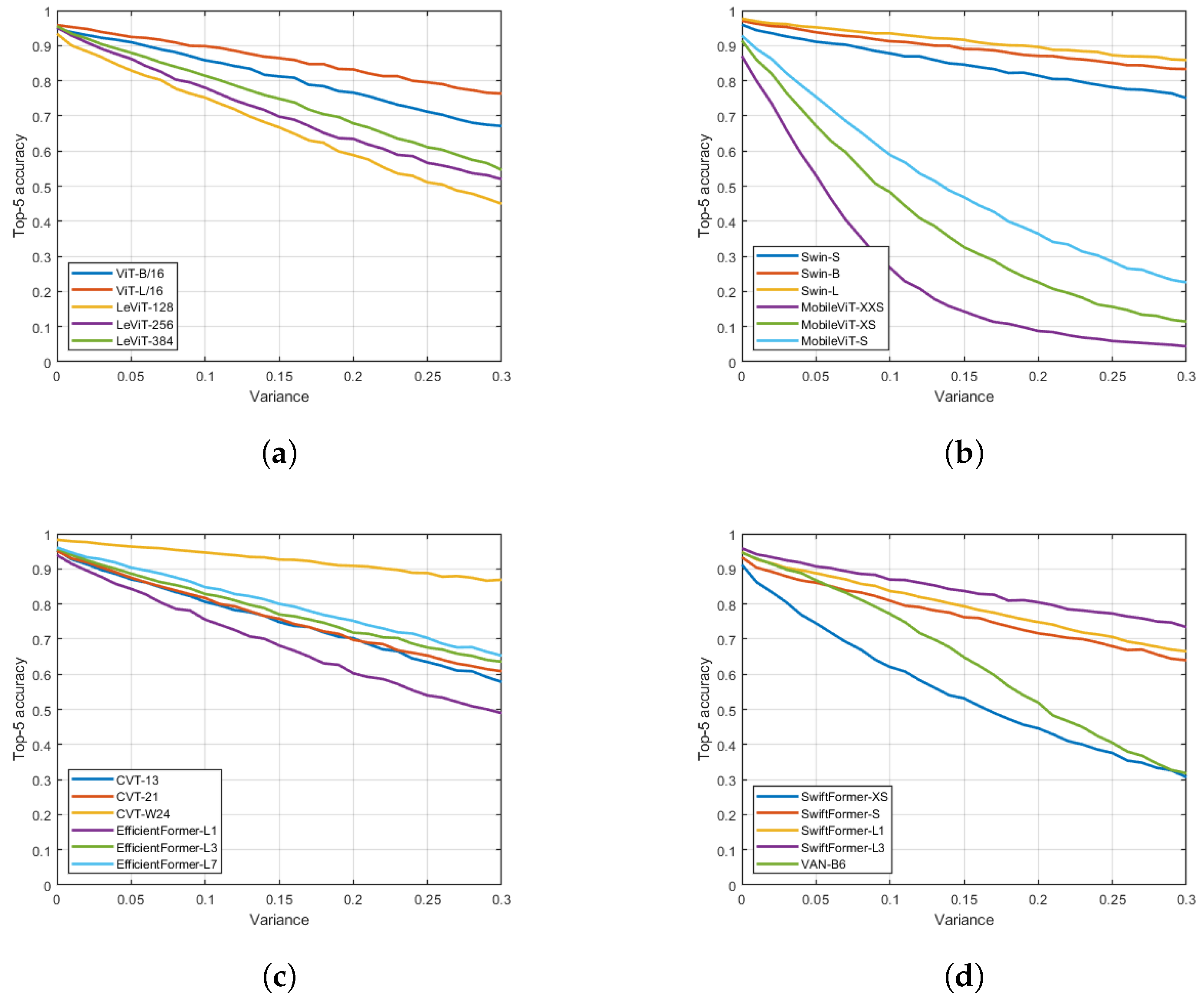
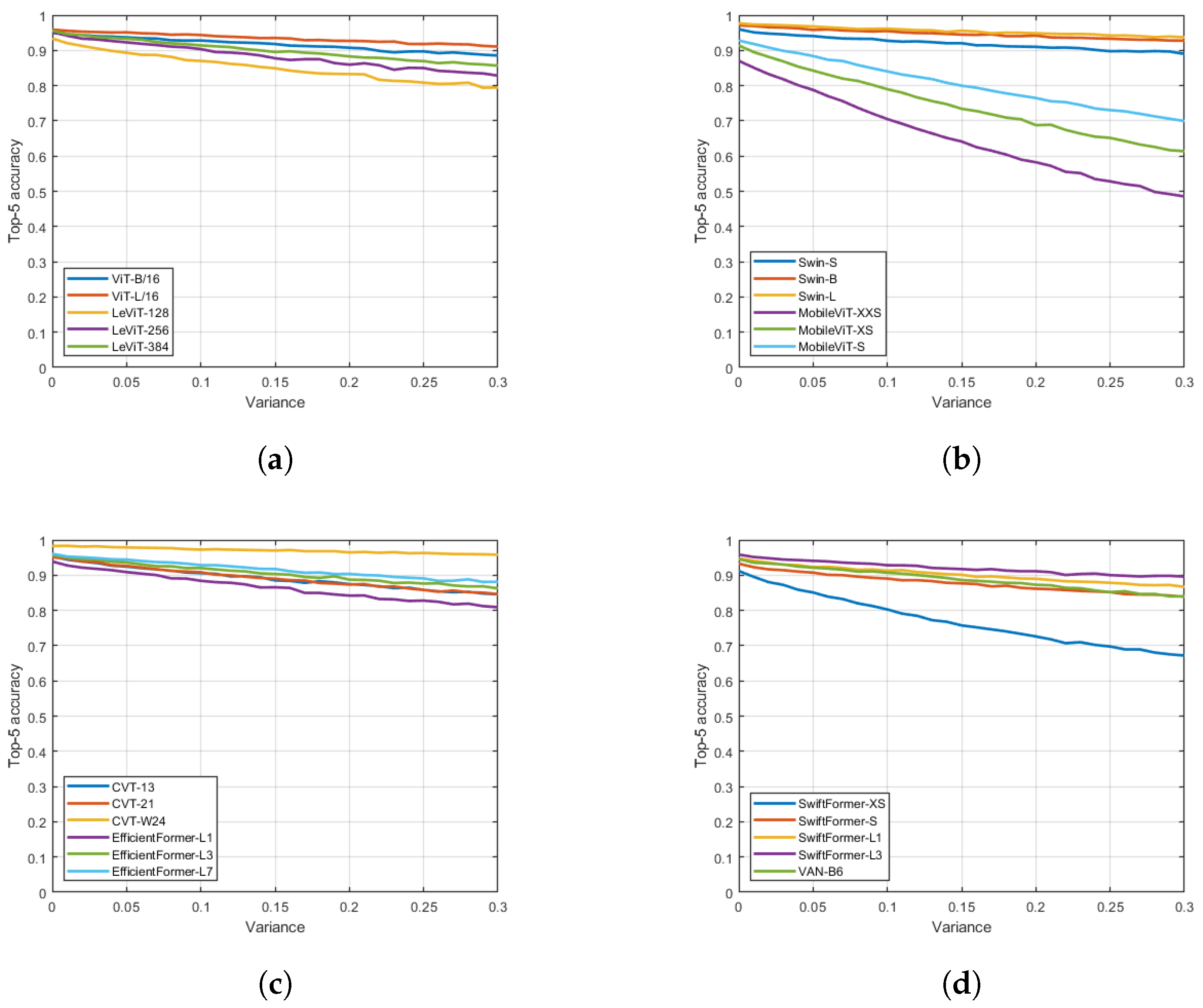
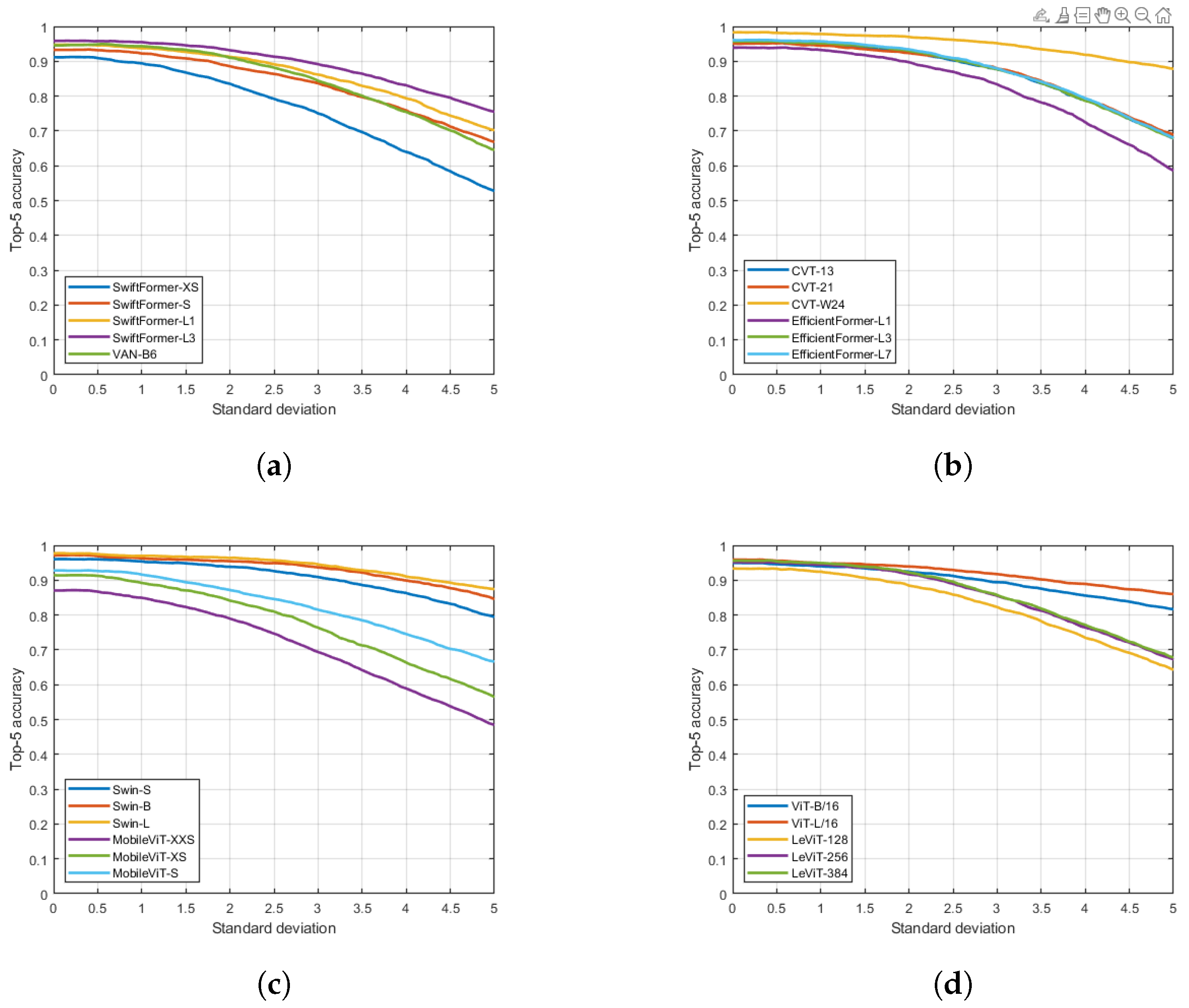
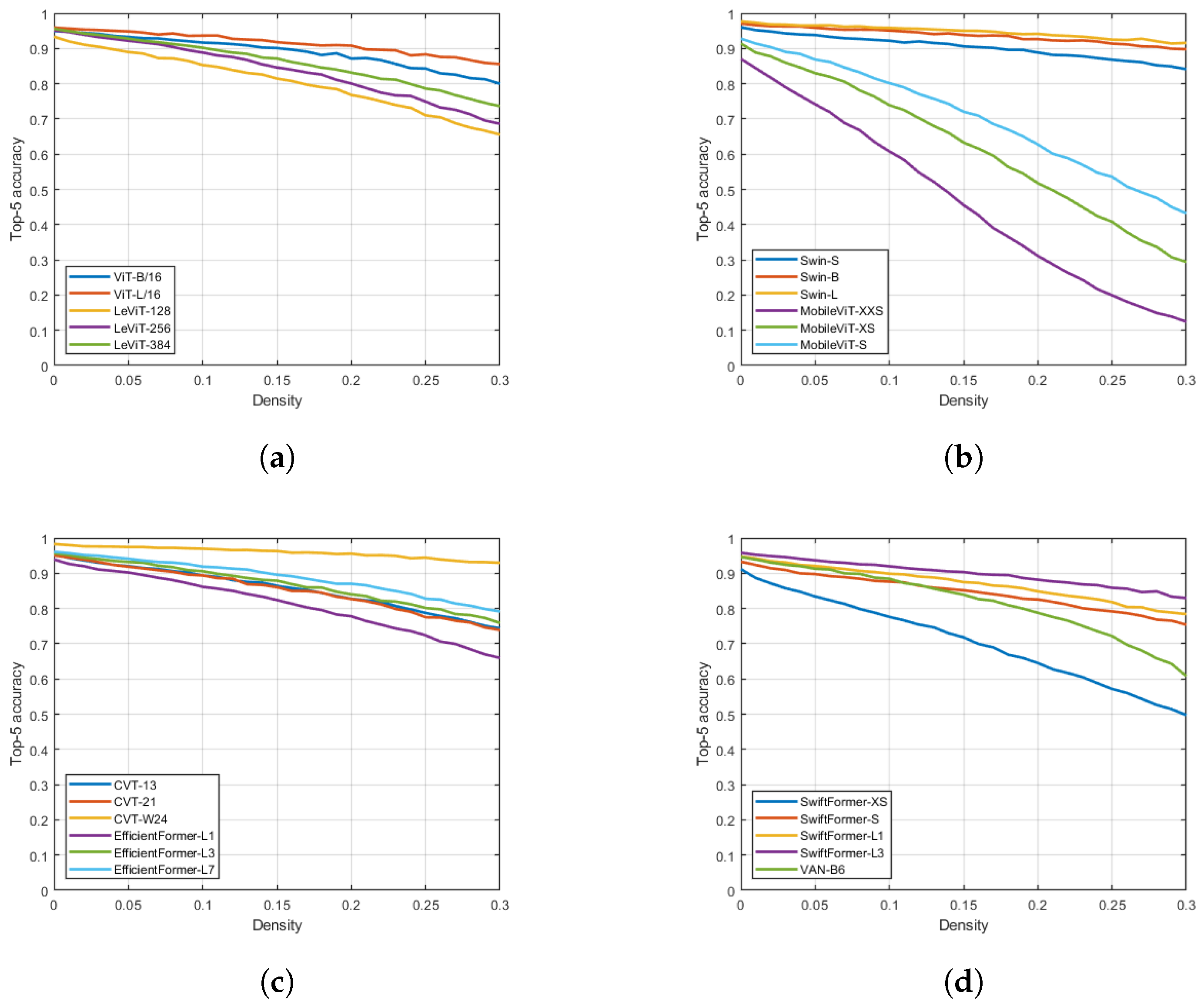
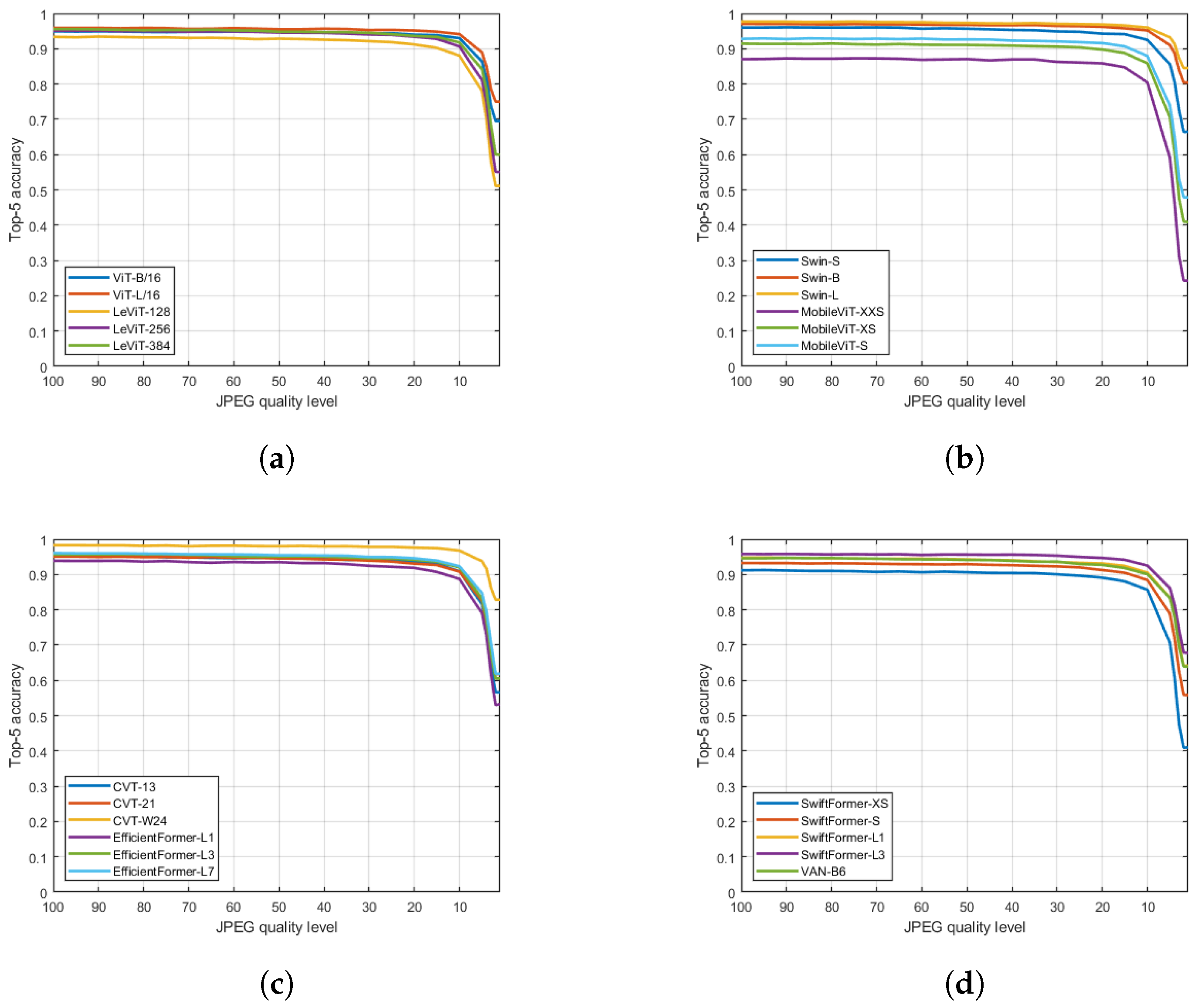
4. Results
5. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AR | augmented reality |
| BERT | bidirectional encoder representations from transformers |
| CNN | convolutional neural network |
| CVT | convolutional vision transformer |
| GPT | generative pre-trained transformer |
| ILSVRC | ImageNet large-scale visual recognition challenge |
| JPEG | joint photographic experts group |
| LKA | large kernel attention |
| MobileViT | mobile vision transformer |
| NLP | natural language processing |
| RNN | recurrent neural network |
| T5 | text-to-text transfer transformer |
| VAN | visual attention network |
| ViT | vision transformer |
| VR | virtual reality |
References
- Jenadeleh, M.; Pedersen, M.; Saupe, D. Blind quality assessment of iris images acquired in visible light for biometric recognition. Sensors 2020, 20, 1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Men, H.; Hosu, V.; Lin, H.; Bruhn, A.; Saupe, D. Subjective annotation for a frame interpolation benchmark using artefact amplification. Qual. User Exp. 2020, 5, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delepoulle, S.; Bigand, A.; Renaud, C. A no-reference computer-generated images quality metric and its application to denoising. In Proceedings of the 2012 6th IEEE International Conference Intelligent Systems, Sofia, Bulgaria, 6–8 September 2012; pp. 67–73. [Google Scholar]
- Saupe, D.; Hahn, F.; Hosu, V.; Zingman, I.; Rana, M.; Li, S. Crowd workers proven useful: A comparative study of subjective video quality assessment. In Proceedings of the QoMEX 2016: 8th International Conference on Quality of Multimedia Experience, Lisbon, Portugal, 6–8 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Men, H.; Lin, H.; Jenadeleh, M.; Saupe, D. Subjective image quality assessment with boosted triplet comparisons. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 138939–138975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Götz-Hahn, F.; Hosu, V.; Lin, H.; Saupe, D. KonVid-150k: A Dataset for No-Reference Video Quality Assessment of Videos in-the-Wild. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 72139–72160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenadeleh, M.; Pedersen, M.; Saupe, D. Realtime quality assessment of iris biometrics under visible light. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 443–452. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, C.; Sharp, P.; Sutton, D. Measurement of image quality in diagnostic radiology. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 1999, 50, 21–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenkrantz, A.B.; Neil, J.; Kong, X.; Melamed, J.; Babb, J.S.; Taneja, S.S.; Taouli, B. Prostate cancer: Comparison of 3D T2-weighted with conventional 2D T2-weighted imaging for image quality and tumor detection. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2010, 194, 446–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michaelis, C.; Mitzkus, B.; Geirhos, R.; Rusak, E.; Bringmann, O.; Ecker, A.S.; Bethge, M.; Brendel, W. Benchmarking robustness in object detection: Autonomous driving when winter is coming. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1907.07484. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Zhao, D.; Cao, Y. Image Quality Enhancement with Applications to Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Obstacle Detection. Aerospace 2022, 9, 829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, L.; Yuting, K.; Tao, S. Investigation of the Relationship between Speed and Image Quality of Autonomous Vehicles. J. Min. Sci. 2021, 57, 264–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.; Asari, V.; Saupe, D. No-reference quality assessment of H. 264/AVC encoded video based on natural scene features. In Proceedings of the Mobile Multimedia/Image Processing, Security, and Applications, Baltimore, MS, USA, 29–30 April 2013; International Society for Optics and Photonics: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2013; Volume 8755, p. 875505. [Google Scholar]
- Kara, P.A.; Martini, M.G.; Kovács, P.T.; Imre, S.; Barsi, A.; Lackner, K.; Balogh, T. Perceived quality of angular resolution for light field displays and the validy of subjective assessment. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on 3D Imaging (IC3D), Liege, Belgium, 13–14 December 2016; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Chattha, U.A.; Janjua, U.I.; Anwar, F.; Madni, T.M.; Cheema, M.F.; Janjua, S.I. Motion sickness in virtual reality: An empirical evaluation. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 130486–130499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthu Kumara Swamy, S.; Han, Q. Quality Evaluation of Image Segmentation in Mobile Augmented Reality. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Mobile and Ubiquitous Systems: Computing, Networking, and Services, Melbourne, VIC, Australia, 14–17 November 2023; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023; pp. 415–427. [Google Scholar]
- Temel, D.; Lee, J.; AlRegib, G. Cure-or: Challenging unreal and real environments for object recognition. In Proceedings of the 2018 17th IEEE International Conference on Machine Learning and Applications (ICMLA), Orlando, FL, USA, 17–20 December 2018; pp. 137–144. [Google Scholar]
- Pednekar, G.V.; Udupa, J.K.; McLaughlin, D.J.; Wu, X.; Tong, Y.; Simone, C.B., II; Camaratta, J.; Torigian, D.A. Image quality and segmentation. In Proceedings of the Medical Imaging 2018: Image-Guided Procedures, Robotic Interventions, and Modeling, Houston, TX, USA, 12–15 February 2018; SPIE: Bellingham, WE, USA, 2018; Volume 10576, pp. 622–628. [Google Scholar]
- Galbally, J.; Marcel, S.; Fierrez, J. Image quality assessment for fake biometric detection: Application to iris, fingerprint, and face recognition. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2013, 23, 710–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Zhang, L.; Konz, N. Computer vision techniques in manufacturing. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man, Cybern. Syst. 2022, 53, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pau, L.F. Computer Vision for Electronics Manufacturing; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Song, W.; Fang, L.; Chen, Y.; Ghamisi, P.; Benediktsson, J.A. Deep learning for hyperspectral image classification: An overview. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote. Sens. 2019, 57, 6690–6709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minaee, S.; Boykov, Y.; Porikli, F.; Plaza, A.; Kehtarnavaz, N.; Terzopoulos, D. Image segmentation using deep learning: A survey. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2021, 44, 3523–3542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koohzadi, M.; Charkari, N.M. Survey on deep learning methods in human action recognition. IET Comput. Vis. 2017, 11, 623–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodfellow, I.J.; Shlens, J.; Szegedy, C. Explaining and harnessing adversarial examples. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6572. [Google Scholar]
- Szegedy, C.; Zaremba, W.; Sutskever, I.; Bruna, J.; Erhan, D.; Goodfellow, I.; Fergus, R. Intriguing properties of neural networks. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1312.6199. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Chen, Y.; Qian, C. Fooling Examples: Another Intriguing Property of Neural Networks. Sensors 2023, 23, 6378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arjomandi, H.M.; Khalooei, M.; Amirmazlaghani, M. Low-epsilon adversarial attack against a neural network online image stream classifier. Appl. Soft Comput. 2023, 147, 110760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodge, S.; Karam, L. Understanding how image quality affects deep neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2016 Eighth International Conference on Quality of Multimedia Experience (QoMEX), Lisbon, Portugal, 6–8 June 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, K.; Saupe, D. Performance evaluation of HD camcorders: Measuring texture distortions using Gabor filters and spatio-velocity CSF. In Proceedings of the Image Quality and System Performance X. International Society for Optics and Photonics, Burlingame, CA, USA, 4 February 2013; Volume 8653, p. 86530A. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, K.; Li, S.; Saupe, D. An objective method of measuring texture preservation for camcorder performance evaluation. In Proceedings of the Image Quality and System Performance IX. International Society for Optics and Photonics, Burlingame, CA, USA, 24 January 2012; Volume 8293, p. 829304. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.T. Source camera identification using enhanced sensor pattern noise. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2010, 5, 280–287. [Google Scholar]
- Su, S.; Lin, H.; Hosu, V.; Wiedemann, O.; Sun, J.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Saupe, D. Going the Extra Mile in Face Image Quality Assessment: A Novel Database and Model. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2207.04904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, H.; Rada, L.; Badshah, N. Image segmentation for intensity inhomogeneity in presence of high noise. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2018, 27, 3729–3738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, Z.U.; Jobson, D.J.; Woodell, G.A.; Hines, G.D. Image enhancement, image quality, and noise. In Proceedings of the Photonic Devices and Algorithms for Computing VII, San Diego, CA, USA, 15 September 2005; SPIE: Bellingham, WE, USA, 2005; Volume 5907, pp. 164–178. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.H.; Lee, J. Image feature and noise detection based on statistical hypothesis tests and their applications in noise reduction. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 2005, 51, 1367–1378. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Miao, Z.; Jonathan Wu, Q.; Wan, Y.; Tang, Z. Low-resolution face recognition: A review. Vis. Comput. 2014, 30, 359–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, W.W.; Yuen, P.C. Very low resolution face recognition problem. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2011, 21, 327–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Chang, H.; Shan, S.; Chen, X. Low-resolution face recognition via coupled locality preserving mappings. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2009, 17, 20–23. [Google Scholar]
- He, X.; Niyogi, P. Locality preserving projections. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 16 (Neural Information Processing Systems, NIPS 2003), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 8–13 December 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2012, 25, 1097–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. In Proceedings of the 31st Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS 2017), Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Alaparthi, S.; Mishra, M. Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers (BERT): A sentiment analysis odyssey. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2007.01127. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Q.; Luo, J. Generative pre-trained transformer for design concept generation: An exploration. Proc. Des. Soc. 2022, 2, 1825–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastropaolo, A.; Scalabrino, S.; Cooper, N.; Palacio, D.N.; Poshyvanyk, D.; Oliveto, R.; Bavota, G. Studying the usage of text-to-text transfer transformer to support code-related tasks. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/ACM 43rd International Conference on Software Engineering (ICSE), Madrid, Spain, 22–30 May 2021; pp. 336–347. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, S.; Naseer, M.; Hayat, M.; Zamir, S.W.; Khan, F.S.; Shah, M. Transformers in vision: A survey. ACM Comput. Surv. CSUR 2022, 54, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S.; et al. An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.11929. [Google Scholar]
- Graham, B.; El-Nouby, A.; Touvron, H.; Stock, P.; Joulin, A.; Jégou, H.; Douze, M. Levit: A vision transformer in convnet’s clothing for faster inference. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 12259–12269. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Cao, Y.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, S.; Guo, B. Swin transformer: Hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 10012–10022. [Google Scholar]
- Mehta, S.; Rastegari, M. Mobilevit: Light-weight, general-purpose, and mobile-friendly vision transformer. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2110.02178. [Google Scholar]
- Sandler, M.; Howard, A.; Zhu, M.; Zhmoginov, A.; Chen, L.C. Mobilenetv2: Inverted residuals and linear bottlenecks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 4510–4520. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, L.; Rosing, T. Depthwise convolution is all you need for learning multiple visual domains. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Honolulu, HI, USA, 27 January–1 February 2019; Volume 33, pp. 8368–8375. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.; Qi, G.J.; Xiao, B.; Wang, J. Interleaved group convolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 4373–4382. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, K.; Guo, S.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, A.; Yu, F.; Wu, W. Incorporating convolution designs into visual transformers. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 579–588. [Google Scholar]
- Yoo, H.J. Deep convolution neural networks in computer vision: A review. IEIE Trans. Smart Process. Comput. 2015, 4, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Xiao, B.; Codella, N.; Liu, M.; Dai, X.; Yuan, L.; Zhang, L. Cvt: Introducing convolutions to vision transformers. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 22–31. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Yuan, G.; Wen, Y.; Hu, J.; Evangelidis, G.; Tulyakov, S.; Wang, Y.; Ren, J. Efficientformer: Vision transformers at mobilenet speed. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2022, 35, 12934–12949. [Google Scholar]
- Shaker, A.; Maaz, M.; Rasheed, H.; Khan, S.; Yang, M.H.; Khan, F.S. SwiftFormer: Efficient additive attention for transformer-based real-time mobile vision applications. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 2–3 October 2023; pp. 17425–17436. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, M.H.; Lu, C.Z.; Liu, Z.N.; Cheng, M.M.; Hu, S.M. Visual attention network. Comput. Vis. Media 2023, 9, 733–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Lin, W. Additive white Gaussian noise level estimation in SVD domain for images. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2012, 22, 872–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tourneret, J.Y. Detection and estimation of abrupt changes contaminated by multiplicative Gaussian noise. Signal Process. 1998, 68, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, R.H.; Ho, C.W.; Nikolova, M. Salt-and-pepper noise removal by median-type noise detectors and detail-preserving regularization. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2005, 14, 1479–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabbani, M.; Joshi, R. An overview of the JPEG 2000 still image compression standard. Signal Process. Image Commun. 2002, 17, 3–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Sheikh, H.R.; Bovik, A.C. No-reference perceptual quality assessment of JPEG compressed images. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Image Processing, Rochester, NY, USA, 22–25 September 2002; Volume 1, pp. I–I. [Google Scholar]
| Architecture | Year | Number of Parameters | Memory Footprint in Bytes |
|---|---|---|---|
| ViT-B/16 [47] | 2020 | 86,567,656 | 346,270,624 |
| ViT-L/16 [47] | 2020 | 304,326,632 | 1,217,306,528 |
| LeViT-128 [48] | 2021 | 9,213,936 | 38,448,128 |
| LeViT-256 [48] | 2021 | 18,893,876 | 77,266,064 |
| LeViT-384 [48] | 2021 | 39,128,836 | 158,338,896 |
| Swin-S [49] | 2021 | 49,606,258 | 198,886,024 |
| Swin-B [49] | 2021 | 87,768,224 | 351,533,888 |
| Swin-L [49] | 2021 | 196,532,476 | 786,590,896 |
| MobileViT-XXS [50] | 2021 | 1,272,024 | 5,104,800 |
| MobileViT-XS [50] | 2021 | 2,317,848 | 9,305,440 |
| MobileViT-S [50] | 2021 | 5,578,632 | 22,363,808 |
| CVT-13 [56] | 2021 | 19,997,480 | 80,093,144 |
| CVT-21 [56] | 2021 | 31,622,696 | 126,658,712 |
| CVT-W24 [56] | 2021 | 277,196,392 | 1,109,323,744 |
| EfficientFormer-L1 [57] | 2022 | 12,289,928 | 49,306,864 |
| EfficientFormer-L3 [57] | 2022 | 31,406,000 | 125,934,952 |
| EfficientFormer-L7 [57] | 2022 | 82,229,328 | 329,429,000 |
| SwiftFormer-XS [58] | 2023 | 3,475,360 | 13,925,488 |
| SwiftFormer-S [58] | 2023 | 6,092,128 | 24,404,344 |
| SwiftFormer-L1 [58] | 2023 | 12,057,920 | 48,281,280 |
| SwiftFormer-L3 [58] | 2023 | 28,494,736 | 114,061,408 |
| VAN-B6 [59] | 2023 | 26,579,496 | 106,421,776 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Varga, D. Understanding How Image Quality Affects Transformer Neural Networks. Signals 2024, 5, 562-579. https://doi.org/10.3390/signals5030031
Varga D. Understanding How Image Quality Affects Transformer Neural Networks. Signals. 2024; 5(3):562-579. https://doi.org/10.3390/signals5030031
Chicago/Turabian StyleVarga, Domonkos. 2024. "Understanding How Image Quality Affects Transformer Neural Networks" Signals 5, no. 3: 562-579. https://doi.org/10.3390/signals5030031
APA StyleVarga, D. (2024). Understanding How Image Quality Affects Transformer Neural Networks. Signals, 5(3), 562-579. https://doi.org/10.3390/signals5030031






