CNN-Based Pattern Classifiers for Precise Identification of Perinatal EEG Biomarkers of Brain Injury in Preterm Neonates
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data Acquisition
2.1. Ethics
2.2. Clinical Procedures
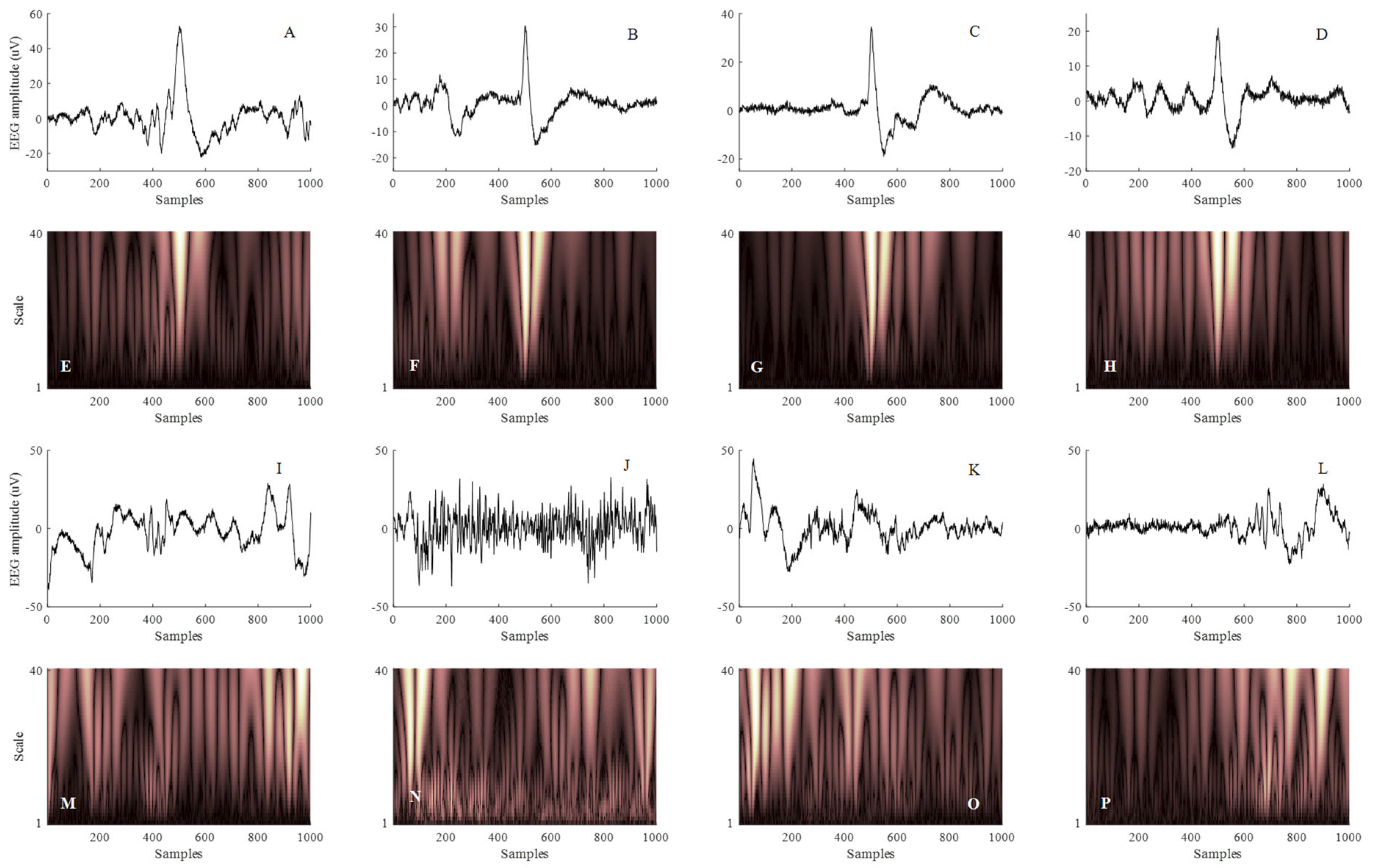
2.3. Neonatal HI Micro-Scale Sharp Waves
3. Related Works
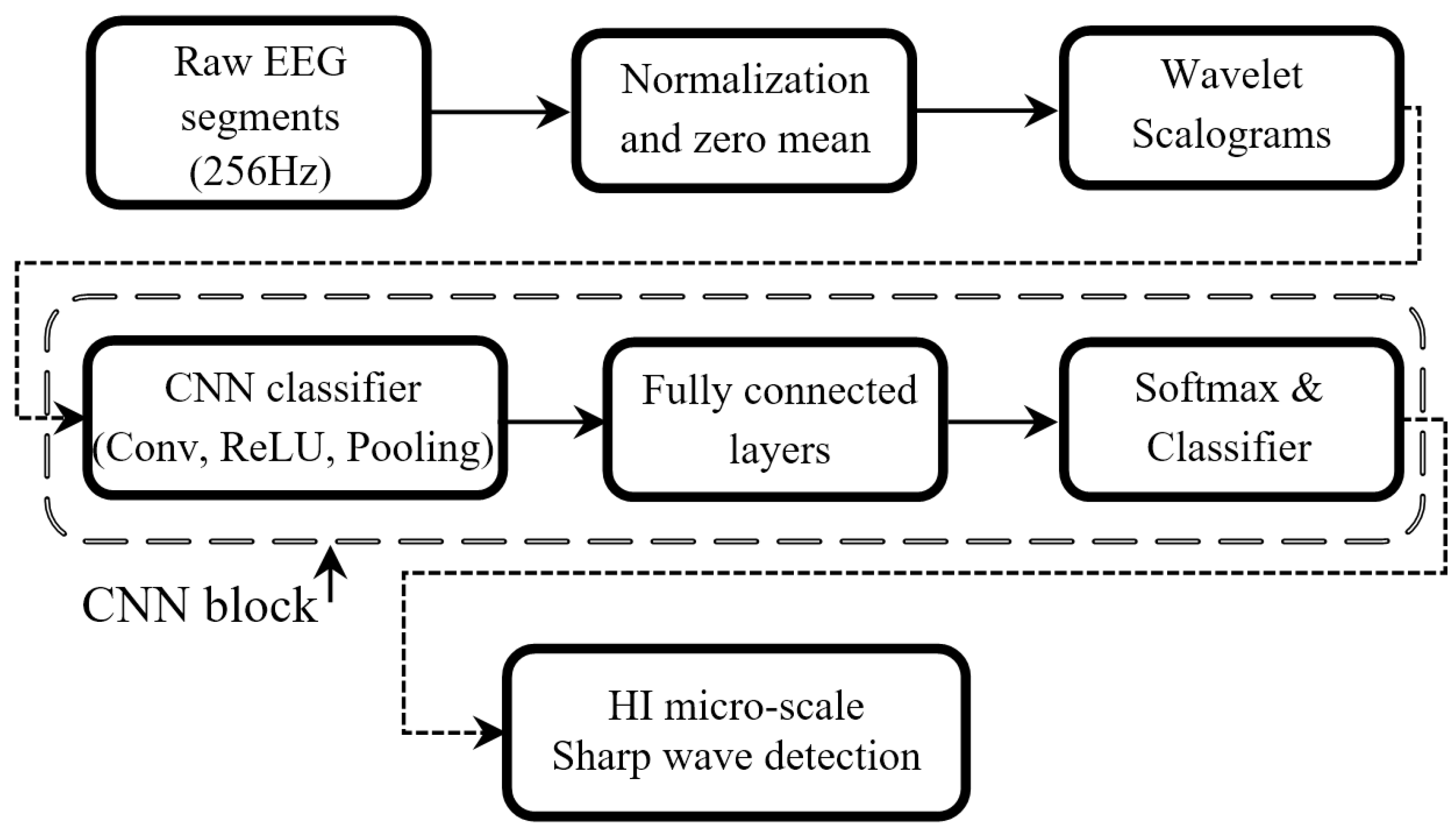
4. Methods
4.1. Pre-Processing
4.2. Scalogram Image Feature Extraction
4.3. The Deep WS-CNN Classifier: Model Setup and Architecture
4.4. Computing Infrastructure
4.5. Training and Testing the WS-CNN Classifier
4.6. WS-CNN Classifier
4.7. 1D-CNN Classifier
4.8. Wavelet Type-II Fuzzy Classifier
4.9. Performance Evaluation Metrics
- (1)
- K-fold cross-validation for the deep CNN-based classifiers
- (2)
- K-fold cross-validation for the Wavelet-Type-II-FLC
5. Results
5.1. Cross Dataset Results of the WS-CNN Classifier
5.2. Cross Dataset Results of the WF-CNN Classifier
5.3. Cross Dataset Results of the 1D-CNN Classifier
5.4. Cross Dataset Results of the WT-Type-II-FLC
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Merchant, N.; Azzopardi, D. Early predictors of outcome in infants treated with hypothermia for hypoxic–ischaemic encephalopathy. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2015, 57, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aridas, J.D.; Yawno, T.; Sutherland, A.E.; Nitsos, I.; Ditchfield, M.; Wong, F.Y.; Fahey, M.C.; Malhotra, A.; Wallace, E.M.; Jenkin, G.; et al. Detecting brain injury in neonatal hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy: Closing the gap between experimental and clinical research. Exp. Neurol. 2014, 261C, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parikh, P.; Juul, S.E. Neuroprotection strategies in preterm encephalopathy. Semin. Pediatr. Neurol. 2019, 32, 100772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manuck, T.A.; Rice, M.M.; Bailit, J.L.; Grobman, W.A.; Reddy, U.M.; Wapner, R.J.; Thorp, J.M.; Caritis, S.N.; Prasad, M.; Tita, A.T. Preterm neonatal morbidity and mortality by gestational age: A contemporary cohort. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2016, 215, e1–e103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ophelders, D.R.; Gussenhoven, R.; Klein, L.; Jellema, R.K.; Westerlaken, R.J.; Hütten, M.C.; Vermeulen, J.; Wassink, G.; Gunn, A.J.; Wolfs, T.G. Preterm brain injury; antenatal triggers; therapeutics: Timing is key. Cells 2020, 9, 1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wachtel, E.V.; Verma, S.; Mally, P.V. Update on the current management of newborns with neonatal encephalopathy. Curr. Probl. Pediatr. Adolesc. Health Care 2019, 49, 100636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunn, A.I.; Drury, P.P. The pharmacology of hypothermia. In Neonatal Neural Rescue: A Clinical Guide; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2013; p. 73. [Google Scholar]
- Thoresen, M.; Tooley, J.; Liu, X.; Jary, S.; Fleming, P.; Luyt, K.; Jain, A.; Cairns, P.; Harding, D.; Sabir, H. Time is brain: Starting therapeutic hypothermia within three hours after birth improves motor outcome in asphyxiated newborns. Neonatology 2013, 104, 228–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrera, T.I.; Edwards, L.; Malcolm, W.F.; Smith, P.B.; Fisher, K.A.; Pizoli, C.; Gustafson, K.E.; Goldstein, R.F.; Cotten, C.M.; Goldberg, R.N. Outcomes of preterm infants treated with hypothermia for hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Early Hum. Dev. 2018, 125, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, W.F.; Butler, D.; Schmidt, J.W. Report of a pilot study of cooling four preterm infants 32–35 weeks gestation with HIE. J. Neonatal-Perinat. Med. 2015, 8, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbasi, H.; Battin, M.R.; Butler, R.; Rowe, D.; Lear, B.A.; Gunn, A.J.; Bennet, L. Early signatures of brain injury in the preterm neonatal EEG. Signals 2023, 4, 630–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennet, L.; Booth, L.; Gunn, A.J. Potential biomarkers for hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Semin. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2010, 15, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbasi, H.; Drury, P.P.; Lear, C.A.; Gunn, A.J.; Davidson, J.O.; Bennet, L.; Unsworth, C.P. EEG sharp waves are a biomarker of striatal neuronal survival after hypoxia-ischemia in preterm fetal sheep. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 16312–16317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbasi, H.; Bennet, L.; Gunn, A.J.; Unsworth, C.P. Robust wavelet stabilized footprints of uncertainty for fuzzy system classifiers to automatically detect sharp waves in the EEG after hypoxia ischemia. Int. J. Neural Syst. 2017, 27, 1650051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennet, L.; Roelfsema, V.; Pathipati, P.; Quaedackers, J.S.; Gunn, A.J. Relationship between evolving epileptiform activity and delayed loss of mitochondrial activity after asphyxia measured by near-infrared spectroscopy in preterm fetal sheep. J. Physiol. 2006, 572, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, A.D.; Brocklehurst, P.; Gunn, A.J.; Halliday, H.; Juszczak, E.; Levene, M.; Strohm, B.; Thoresen, M.; Whitelaw, A.; Azzopardi, D. Neurological outcomes at 18 months of age after moderate hypothermia for perinatal hypoxic ischaemic encephalopathy: Synthesis and meta-analysis of trial data. BMJ 2010, 340, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raurale, S.A.; Boylan, G.B.; Mathieson, S.R.; Marnane, W.P.; Lightbody, G.; O’Toole, J.M. Grading hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy in neonatal EEG with convolutional neural networks and quadratic time-frequency distributions. J. Neural Eng. 2021, 18, 046007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.; Marnane, W.P.; Boylan, G.B.; Lightbody, G. Neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy grading from multi-channel EEG time-series data using a fully convolutional neural network. Technologies 2023, 11, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gramacki, A.; Gramacki, J. A deep learning framework for epileptic seizure detection based on neonatal EEG signals. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raeisi, K.; Khazaei, M.; Croce, P.; Tamburro, G.; Comani, S.; Zappasodi, F. A graph convolutional neural network for the automated detection of seizures in the neonatal eeg. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2022, 222, 106950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tjepkema-Cloostermans, M.C.; de Carvalho, R.C.; van Putten, M.J. Deep learning for detection of focal epileptiform discharges from scalp EEG recordings. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2018, 129, 2191–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deburchgraeve, W.; Cherian, P.J.; De Vos, M.; Swarte, R.M.; Blok, J.H.; Visser, G.H.; Govaert, P.; Van Huffel, S. Automated neonatal seizure detection mimicking a human observer reading EEG. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2008, 119, 2447–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherian, P.J.; Deburchgraeve, W.; Swarte, R.M.; De Vos, M.; Govaert, P.; Van Huffel, S.; Visser, G.H. Validation of a new automated neonatal seizure detection system: A clinician’s perspective. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2011, 122, 1490–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tapani, K.T.; Vanhatalo, S.; Stevenson, N.J. Incorporating spike correlations into an SVM-based neonatal seizure detector. In EMBEC & NBC 2017; Anonymous; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 322–325. [Google Scholar]
- Ansari, A.H.; Cherian, P.J.; Caicedo, A.; Dereymaeker, A.; Jansen, K.; De Wispelaere, L.; Dielman, C.; Vervisch, J.; Govaert, P.; De Vos, M. NeoGuard: A public, online learning platform for neonatal seizures. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1905.12382. [Google Scholar]
- Palmu, K.; Wikström, S.; Hippeläinen, E.; Boylan, G.; Hellström-Westas, L.; Vanhatalo, S. Detection of ‘EEG bursts’ in the early preterm EEG: Visual vs. automated detection. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2010, 121, 1015–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbasi, H.; Gunn, A.J.; Unsworth, C.P.; Bennet, L. Advanced deep learning spectroscopy of scalogram infused CNN classifiers for robust identification of Post-Hypoxic epileptiform EEG spikes. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2021, 3, 2000198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, H.; Bennet, L.; Gunn, A.J.; Unsworth, C.P. 2D wavelet scalogram training of deep convolutional neural network for automatic identification of micro-scale sharp wave biomarkers in the hypoxic-ischemic EEG of preterm sheep. Annu. Int. Conf. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. 2019, 2019, 1825–1828. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Selton, D.; Andre, M.; Hascoët, J.M. Normal EEG in very premature infants: Reference criteria. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2000, 111, 2116–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vecchierini, M.; André, M.; d’Allest, A.M. Normal EEG of premature infants born between 24 and 30 weeks gestational age: Terminology, definitions and maturation aspects. Neurophysiol. Clin./Clin. Neurophysiol. 2007, 37, 311–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scher, M.S.; Hamid, M.Y.; Steppe, D.A.; Beggarly, M.E.; Painter, M.J. Ictal and interictal electrographic seizure durations in preterm and term neonates. Epilepsia 1993, 34, 284–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyner, F.S.; Knott, J.R. Fundamentals of EEG Technology: Basic Concepts and Methods; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Tsuchida, T.N.; Wusthoff, C.J.; Shellhaas, R.A.; Abend, N.S.; Hahn, C.D.; Sullivan, J.E.; Nguyen, S.; Weinstein, S.; Scher, M.S.; Riviello, J.J.; et al. American clinical neurophysiology society standardized EEG terminology and categorization for the description of continuous EEG monitoring in neonates: Report of the american clinical neurophysiology society critical care monitoring committee. J. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2013, 30, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Weerd, A.W.; Despland, P.A.; Plouin, P. Neonatal EEG. the international federation of clinical neurophysiology. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. Suppl. 1999, 52, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Abbasi, H.; Bennet, L.; Gunn, A.J.; Unsworth, C.P. Automatically identified micro-scale sharp-wave transients in the early-latent phase of hypoxic-ischemic EEG from preterm fetal sheep reveal timing relationship to subcortical neuronal survival. Annu. Int. Conf. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. 2019, 2019, 7084–7087. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kriegeskorte, N. Deep neural networks: A new framework for modeling biological vision and brain information processing. Annu. Rev. Vis. Sci. 2015, 1, 417–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmuganathan, S. Artificial Neural Network Modelling: An Introduction; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; Available online: https://scholar.google.com/citations?view_op=view_citation&hl=en&user=i3qG2YcAAAAJ&citation_for_view=i3qG2YcAAAAJ:R22Rs3tN8aoC (accessed on 1 January 2024).
- Zhang, J.; Yin, Z.; Chen, P.; Nichele, S. Emotion recognition using multi-modal data and machine learning techniques: A tutorial and review. Inf. Fusion 2020, 59, 103–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, U.R.; Oh, S.L.; Hagiwara, Y.; Tan, J.H.; Adeli, H. Deep convolutional neural network for the automated detection and diagnosis of seizure using EEG signals. Comput. Biol. Med. 2018, 100, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tozzi, A.; Peters, J.F.; Jausovec, N.; Don, A.P.; Ramanna, S.; Legchenkova, I.; Bormashenko, E. Nervous activity of the brain in five dimensions. Biophysica 2021, 1, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavel, A.M.; O’Toole, J.M.; Proietti, J.; Livingstone, V.; Mitra, S.; Marnane, W.P.; Finder, M.; Dempsey, E.M.; Murray, D.M.; Boylan, G.B. Machine learning for the early prediction of infants with electrographic seizures in neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Epilepsia 2023, 64, 456–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabeff, V.; Teijeiro, T.; Zapater, M.; Cammoun, L.; Rheims, S.; Ryvlin, P.; Atienza, D. Interpreting deep learning models for epileptic seizure detection on EEG signals. Artif. Intell. Med. 2021, 117, 102084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosas-Romero, R.; Guevara, E.; Peng, K.; Nguyen, D.K.; Lesage, F.; Pouliot, P.; Lima-Saad, W. Prediction of epileptic seizures with convolutional neural networks and functional near-infrared spectroscopy signals. Comput. Biol. Med. 2019, 111, 103355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daftari, C.; Shah, J.; Shah, M. Detection of epileptic seizure disorder using EEG signals. In Artificial Intelligence-Based Brain-Computer Interface; Anonymous; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 163–188. [Google Scholar]
- Nejedly, P.; Cimbalnik, J.; Klimes, P.; Plesinger, F.; Halamek, J.; Kremen, V.; Viscor, I.; Brinkmann, B.H.; Pail, M.; Brazdil, M.; et al. Intracerebral EEG artifact identification using convolutional neural networks. Neuroinformatics 2019, 17, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahador, N.; Erikson, K.; Laurila, J.; Koskenkari, J.; Ala-Kokko, T.; Kortelainen, J. A correlation-driven mapping for deep learning application in detecting artifacts within the EEG. J. Neural Eng. 2020, 17, 056018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, D.; Zhang, X.; Ma, K.; Chen, Z.; Chen, W.; Zhang, H.; Yuan, H.; Ding, L. Automated detection of high frequency oscillations in intracranial EEG using the combination of short-time energy and convolutional neural networks. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 82501–82511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, R.; Wei, J.; Li, X.; Li, C.; Zhao, C.; Ren, Z.; Liang, Y.; Geng, X.; Jiang, C.; Yang, X. Automated detection of high-frequency oscillations in epilepsy based on a convolutional neural network. Front. Comput. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Z.; Zou, J.; Zhang, J.; Xu, J. Automatic epileptic EEG detection using convolutional neural network with improvements in time-domain. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2019, 53, 101551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Tian, C.; Cao, R.; Wang, B.; Niu, Y.; Hu, T.; Guo, H.; Xiang, J. Epileptic seizure detection based on EEG signals and CNN. Front. Neuroinformatics 2018, 12, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong, N.D.; Nguyen, A.D.; Kuhlmann, L.; Bonyadi, M.R.; Yang, J.; Ippolito, S.; Kavehei, O. Integer convolutional neural network for seizure detection. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Circuits Syst. 2018, 8, 849–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Shea, A.; Lightbody, G.; Boylan, G.; Temko, A. Neonatal seizure detection from raw multi-channel EEG using a fully convolutional architecture. Neural Netw. 2020, 123, 12–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakrabarti, S.; Swetapadma, A.; Pattnaik, P.K. A channel independent generalized seizure detection method for pediatric epileptic seizures. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2021, 209, 106335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yıldız, İ.; Garner, R.; Lai, M.; Duncan, D. Unsupervised seizure identification on EEG. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2022, 215, 106604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debelo, B.S.; Thamineni, B.L.; Dasari, H.K.; Dawud, A.A. Detection and severity identification of neonatal seizure using deep convolutional neural networks from multichannel EEG signal. Pediatr. Health Med. Ther. 2023, 14, 405–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanveer, M.A.; Khan, M.J.; Sajid, H.; Naseer, N. Convolutional neural networks ensemble model for neonatal seizure detection. J. Neurosci. Methods 2021, 358, 109197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Shea, A.; Ahmed, R.; Lightbody, G.; Pavlidis, E.; Lloyd, R.; Pisani, F.; Marnane, W.; Mathieson, S.; Boylan, G.; Temko, A. Deep learning for EEG seizure detection in preterm infants. Int. J. Neural Syst. 2021, 31, 2150008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansari, A.H.; Cherian, P.J.; Caicedo, A.; Naulaers, G.; De Vos, M.; Van Huffel, S. Neonatal seizure detection using deep convolutional neural networks. Int. J. Neural Syst. 2019, 29, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kota, S.; Jasti, K.; Liu, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhang, R.; Chalak, L. EEG spectral power: A proposed physiological biomarker to classify the hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy severity in real time. Pediatr. Neurol. 2021, 122, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourel-Ponchel, E.; Querne, L.; Flamein, F.; Ghostine-Ramadan, G.; Wallois, F.; Lamblin, M.D. The prognostic value of neonatal conventional-EEG monitoring in hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy during therapeutic hypothermia. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2023, 65, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dereymaeker, A.; Matic, V.; Vervisch, J.; Cherian, P.J.; Ansari, A.H.; De Wel, O.; Govaert, P.; De Vos, M.; Van Huffel, S.; Naulaers, G. Automated EEG background analysis to identify neonates with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy treated with hypothermia at risk for adverse outcome: A pilot study. Pediatr. Neonatol. 2019, 60, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghadam, S.M.; Pinchefsky, E.; Tse, I.; Marchi, V.; Kohonen, J.; Kauppila, M.; Airaksinen, M.; Tapani, K.; Nevalainen, P.; Hahn, C. Building an open source classifier for the neonatal EEG background: A systematic feature-based approach from expert scoring to clinical visualization. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 675154. [Google Scholar]
- Duda, R.O.; Hart, P.E.; Stork, D.G. Pattern Classification; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
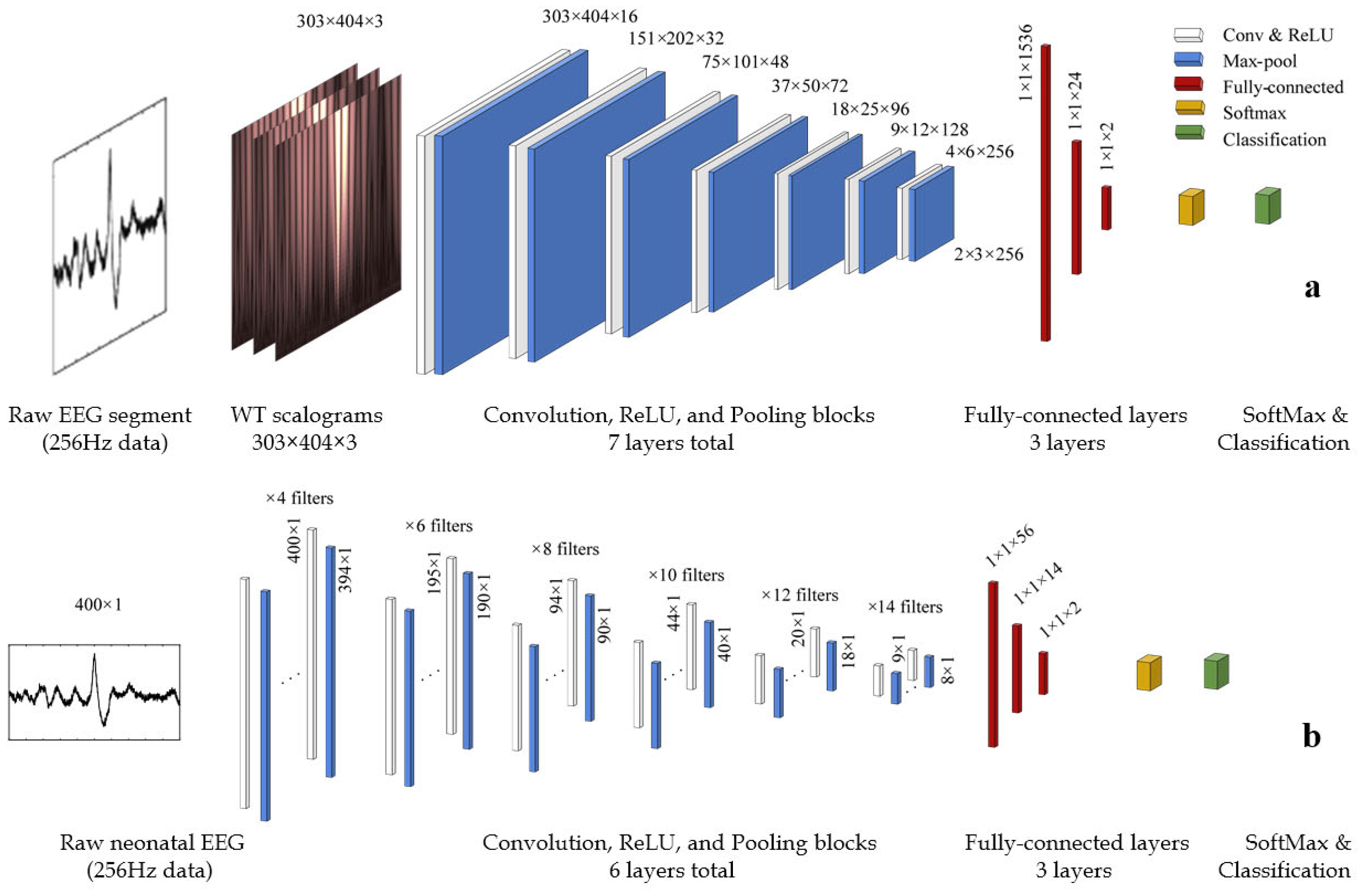


| Layers | Type | No. of Neurons (Output Layer) | Kernel Size | Stride | Padding | No. of Filters |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0–1 | Conv. | 303 × 404 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 16 |
| 1–2 | Max_pool | 151 × 202 | [3 2] | 2 | 0 | |
| 2–3 | Conv. | 151 × 202 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 32 |
| 3–4 | Max_pool | 75 × 101 | [3 2] | 2 | 0 | |
| 4–5 | Conv. | 75 × 101 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 48 |
| 5–6 | Max_pool | 37 × 50 | 3 | 2 | 0 | |
| 6–7 | Conv. | 37 × 50 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 72 |
| 7–8 | Max_pool | 18 × 25 | [3 2] | 2 | 0 | |
| 8–9 | Conv. | 18 × 25 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 96 |
| 9–10 | Max_pool | 9 × 12 | [2 3] | 2 | 0 | |
| 10–11 | Conv. | 9 × 12 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 128 |
| 11–12 | Max_pool | 4 × 6 | [3 2] | 2 | 0 | |
| 12–13 | Conv. | 4 × 6 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 256 |
| 13–14 | Max_pool | 2 × 3 | 2 | 2 | 0 | |
| 14–17 | Fully_connected | 1536 | ||||
| Fully_connected | 24 | |||||
| Fully_connected | 2 | |||||
| Output | Softmax & Classification |
| Trained and Validated on Infant No. | No. of Patterns in the Train-Set | Tested on Infant No. | No. of Patterns in the Test-Set | TP Hits | TN Hits | FP Hits | FN Hits | Sensitivity (%) | Selectivity (%) | Precision (%) | Accuracy (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7,9,11,14,17,20,22 | 10,382 | 3 | 3242 | 1613 | 1620 | 1 | 8 | 99.5 | 99.9 | 99.9 | 99.7 |
| 3,9,11,14,17,20,22 | 12,274 | 7 | 1350 | 674 | 664 | 11 | 1 | 99.8 | 98.4 | 98.4 | 99.1 |
| 3,7,11,14,17,20,22 | 11,614 | 9 | 2010 | 1003 | 1003 | 2 | 2 | 99.8 | 99.8 | 99.8 | 99.8 |
| 3,7,9,14,17,20,22 | 10,818 | 11 | 2806 | 1392 | 1402 | 1 | 11 | 99.2 | 99.9 | 99.9 | 99.6 |
| 3,7,9,11,17,20,22 | 13,094 | 14 | 530 | 265 | 260 | 5 | 0 | 100 | 98.1 | 98.1 | 99.1 |
| 3,7,9,11,14,20,22 | 13,176 | 17 | 448 | 224 | 216 | 8 | 0 | 100 | 96.4 | 96.6 | 98.2 |
| 3,7,9,11,14,17,22 | 12,508 | 20 | 1116 | 553 | 555 | 3 | 5 | 99.1 | 99.5 | 99.5 | 99.3 |
| 3,7,9,11,14,17,20 | 11,502 | 22 | 2122 | 1060 | 1059 | 2 | 1 | 99.9 | 99.8 | 99.8 | 99.9 |
| Overall performance of the 17 layers WS-CNN in the entire 0–6 h | 99.34 ± 0.51 | ||||||||||
| Strategy | No. of Layers | Sensitivity (%) | Selectivity (%) | Precision (%) | Accuracy (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WS-CNN | 17-layers | 99.66 ± 0.35 | 98.97 ± 1.17 | 99.00 ± 1.12 | 99.34 ± 0.51 |
| 13-layers | 99.61 ± 0.30 | 98.65 ± 1.54 | 98.69 ± 1.48 | 99.14 ± 0.65 | |
| 9-layers | 98.98 ± 1.13 | 98.35 ± 0.94 | 98.38 ± 0.92 | 98.73 ± 0.87 | |
| 7-layers | 98.13 ± 1.30 | 97.50 ± 2.29 | 97.56 ± 2.19 | 97.81 ± 1.29 | |
| WF-CNN | 17-layers | 98.22 ± 0.89 | 98.28 ± 1.44 | 98.32 ± 1.38 | 98.26 ± 0.87 |
| 13-layers | 99.47 ± 1.22 | 96.83 ± 3.21 | 96.93 ± 2.93 | 96.65 ± 1.46 | |
| 9-layers | 95.70 ± 1.49 | 95.90 ± 1.74 | 95.94 ± 1.64 | 95.81 ± 1.10 | |
| 7-layers | 94.82 ± 3.34 | 95.07 ± 2.74 | 95.19 ± 2.54 | 94.95 ± 1.08 | |
| 1D-CNN | 15-layers | 95.18 ± 4.79 | 95.30 ± 2.27 | 95.34 ± 2.14 | 95.25 ± 2.10 |
| 13-layers | 95.81 ± 4.25 | 97.67 ± 1.41 | 97.62 ± 1.36 | 96.75 ± 2.18 | |
| 9-layers | 88.21 ± 4.43 | 91.35 ± 3.89 | 91.21 ± 3.75 | 89.77 ± 2.70 | |
| 7-layers | 89.03 ± 8.55 | 80.63 ± 12.1 | 83.30 ± 7.87 | 84.81 ± 4.34 | |
| WT-Type-II-FLC | Not applicable | 93.03 ± 2.46 | 58.26 ± 9.07 | Not applicable | 75.64 ± 5.31 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abbasi, H.; Battin, M.R.; Rowe, D.; Butler, R.; Gunn, A.J.; Bennet, L. CNN-Based Pattern Classifiers for Precise Identification of Perinatal EEG Biomarkers of Brain Injury in Preterm Neonates. Signals 2024, 5, 264-280. https://doi.org/10.3390/signals5020014
Abbasi H, Battin MR, Rowe D, Butler R, Gunn AJ, Bennet L. CNN-Based Pattern Classifiers for Precise Identification of Perinatal EEG Biomarkers of Brain Injury in Preterm Neonates. Signals. 2024; 5(2):264-280. https://doi.org/10.3390/signals5020014
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbbasi, Hamid, Malcolm R. Battin, Deborah Rowe, Robyn Butler, Alistair J. Gunn, and Laura Bennet. 2024. "CNN-Based Pattern Classifiers for Precise Identification of Perinatal EEG Biomarkers of Brain Injury in Preterm Neonates" Signals 5, no. 2: 264-280. https://doi.org/10.3390/signals5020014
APA StyleAbbasi, H., Battin, M. R., Rowe, D., Butler, R., Gunn, A. J., & Bennet, L. (2024). CNN-Based Pattern Classifiers for Precise Identification of Perinatal EEG Biomarkers of Brain Injury in Preterm Neonates. Signals, 5(2), 264-280. https://doi.org/10.3390/signals5020014






