Cascading Pose Features with CNN-LSTM for Multiview Human Action Recognition
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
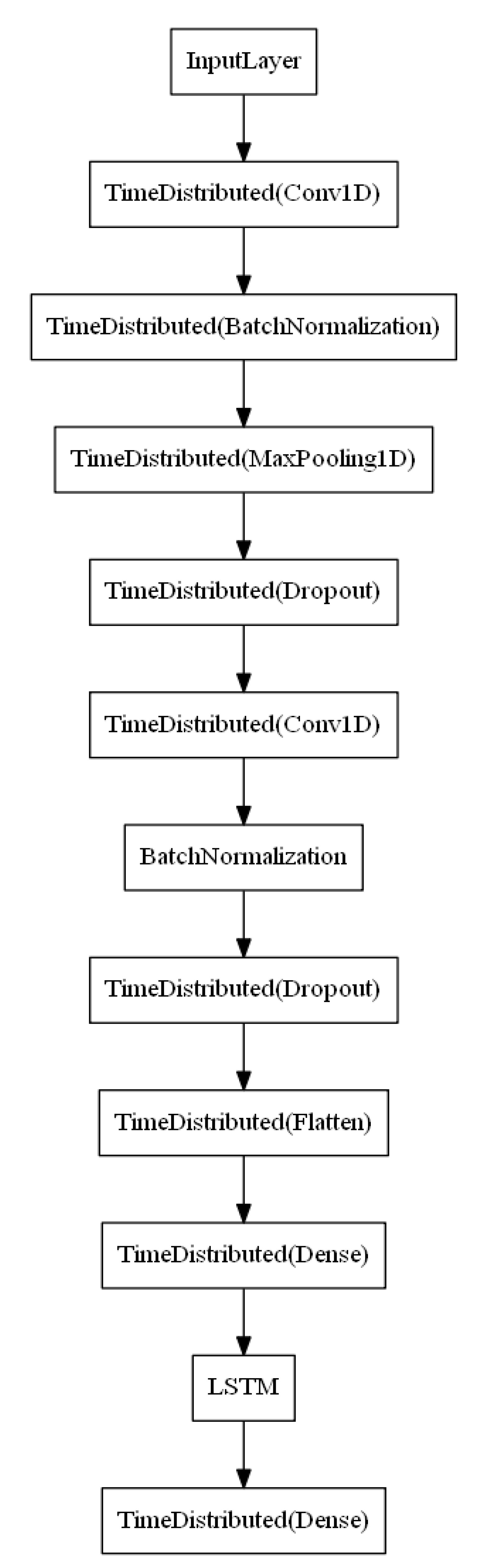
3. Methodology
4. Experimental Setup
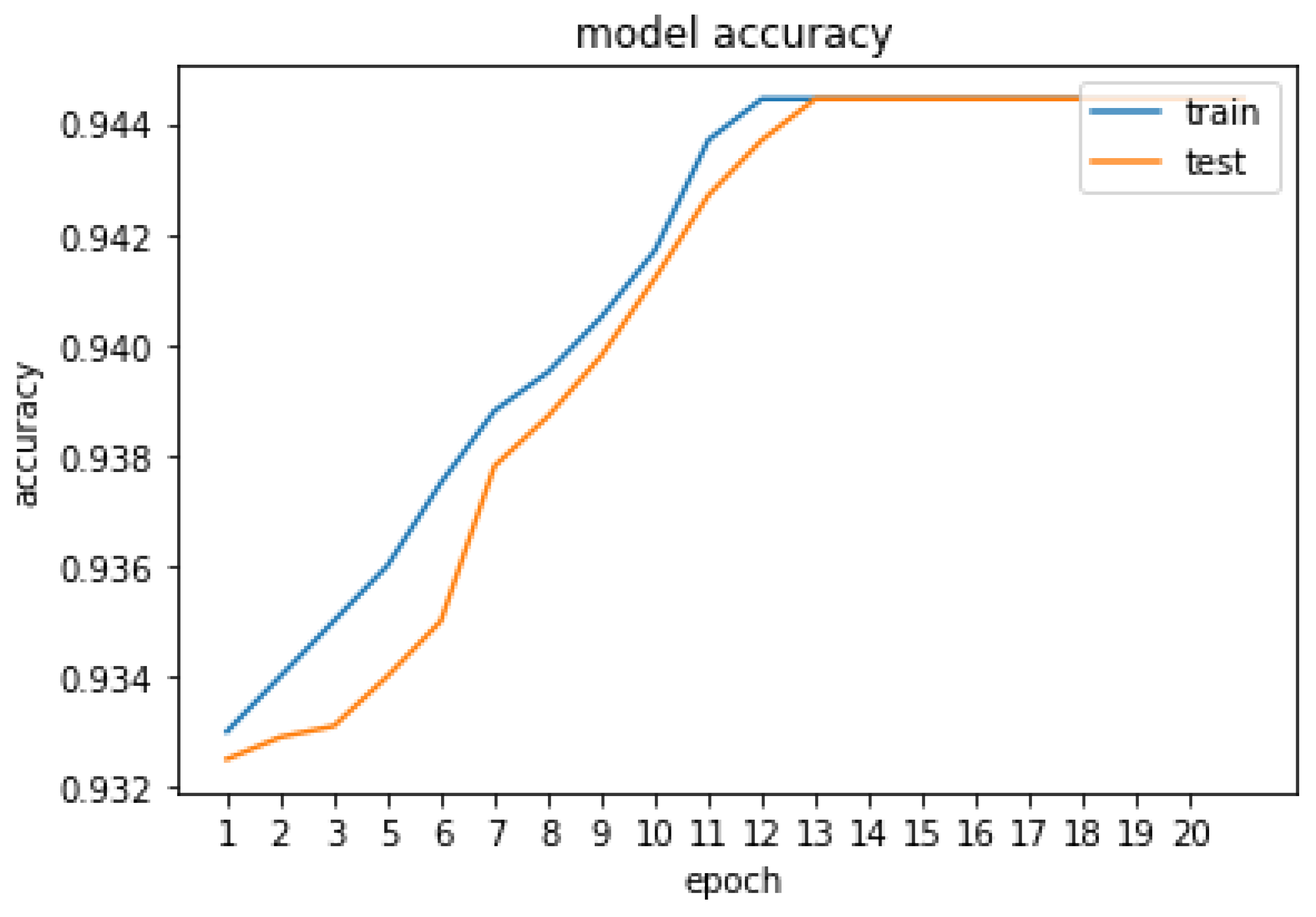
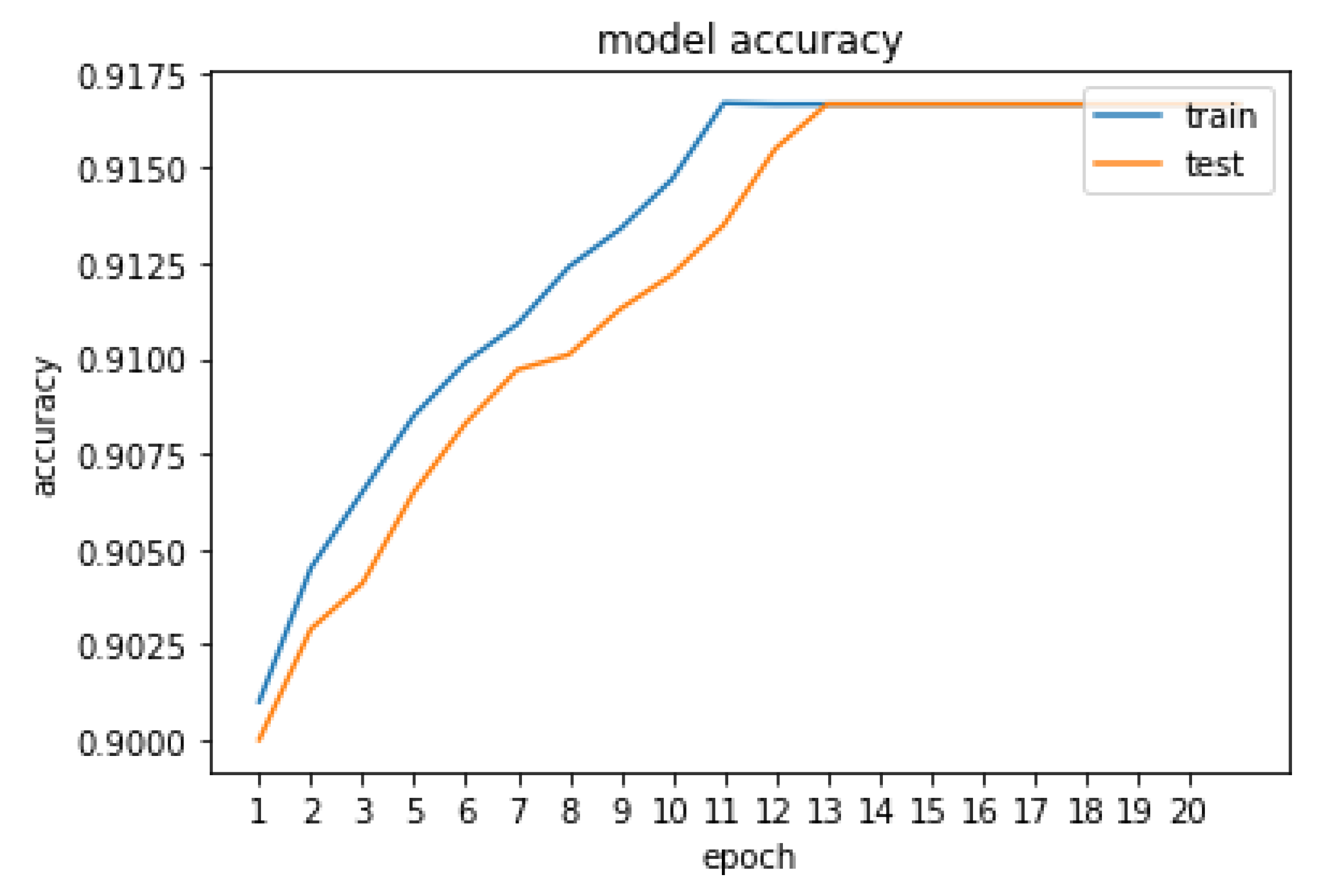
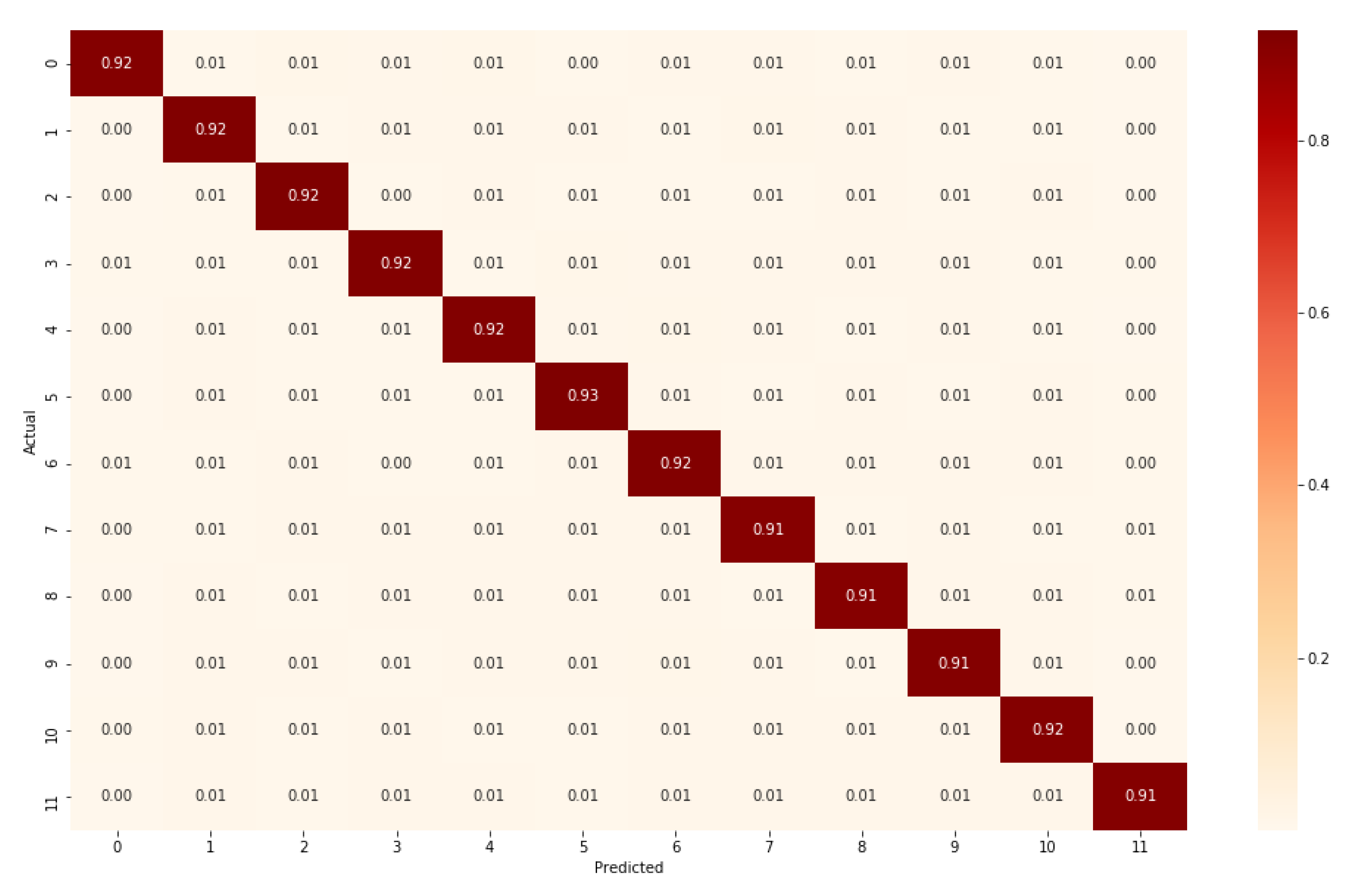
5. Result and Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HAR | Human Action Recognition |
| HCI | Human Computer Interaction |
| STIP | Space Time Interest Point |
| BOW | bag-of-words |
| STVs | Space Time Volumes |
| PCA | Principal Component Analysis |
| CNN | Convolution neural network |
| LSTM | Long Short Term Memory |
| RNN | Recurrent Neural Network |
References
- Aggarwal, J.; Ryoo, M. Human activity analysis: A review. Acm Comput. Surv. Csur 2011, 43, 1–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Bakar, S. Advances in human action recognition: An updated survey. IET Image Process. 2019, 13, 2381–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sargano, A.; Angelov, P.; Habib, Z. A comprehensive review on handcrafted and learning-based action representation approaches for human activity recognition. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Zheng, S.; Zhang, X.; Yuan, C.; Cheng, F.; Zhao, Y.; Lin, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Huang, D. Deep Learning-Based Methods for Person Re-identification: A Comprehensive Review. Neurocomputing 2019, 337, 354–371. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0925231219301225 (accessed on 22 May 2022). [CrossRef]
- Bengio, Y.; Courville, A.; Vincent, P. Representation Learning: A Review and New Perspectives. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2013, 35, 1798–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Xu, Y.; Cheng, J.; Xia, H.; Yin, J.; Wu, J. Human Action Recognition by Learning Spatio-Temporal Features With Deep Neural Networks. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 17913–17922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Gevers, T.; Li, X. Color Constancy by Combining Low-Mid-High Level Image Cues. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2015, 140, 1–8. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1077314215001241 (accessed on 22 April 2022).
- Angerbauer, S.; Palmanshofer, A.; Selinger, S.; Kurz, M. Comparing Human Activity Recognition Models Based on Complexity and Resource Usage. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 8473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Simon, T.; Wei, S.; Sheikh, Y. Realtime Multi-Person 2D Pose Estimation Using Part Affinity Fields. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference On Computer Vision And Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Das Dawn, D.; Shaikh, S. A comprehensive survey of human action recognition with spatio-temporal interest point (STIP) detector. Vis. Comput. 2016, 32, 289–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blank, M.; Gorelick, L.; Shechtman, E.; Irani, M.; Basri, R. Actions as space-time shapes. In Proceedings of the Tenth IEEE International Conference On Computer Vision (ICCV’05) Volume 1, Beijing, China, 17–21 October 2005; Volume 2, pp. 1395–1402. [Google Scholar]
- Black, M. Explaining optical flow events with parameterized spatio-temporal models. In Proceedings of the 1999 IEEE Computer Society Conference On Computer Vision And Pattern Recognition (Cat. No PR00149), Fort Collins, CO, USA, 23–25 June 1999; Volume 1, pp. 326–332. [Google Scholar]
- Efros; Berg; Mori; Malik. Recognizing action at a distance. In Proceedings of the Ninth IEEE International Conference On Computer Vision, Nice, France, 13–16 October 2003; Volume 2, pp. 726–733. [Google Scholar]
- Laptev, I. On space-time interest points. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2005, 64, 107–123. [Google Scholar]
- Dollár, P.; Rabaud, V.; Cottrell, G.; Belongie, S. Behavior recognition via sparse spatio-temporal features. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE International Workshop On Visual Surveillance And Performance Evaluation Of Tracking And Surveillance, Beijing, China, 15–16 October 2005; pp. 65–72. [Google Scholar]
- Thi, T.; Zhang, J.; Cheng, L.; Wang, L.; Satoh, S. Human action recognition and localization in video using structured learning of local space-time features. In Proceedings of the 7th IEEE International Conference On Advanced Video And Signal Based Surveillance, Boston, MA, USA, 29 August–1 September 2010; pp. 204–211. [Google Scholar]
- Kihl, O.; Picard, D.; Gosselin, P.H. Local polynomial space–time descriptors for action classification. Mach. Vis. Appl. 2016, 27, 351–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, Y.; Sukthankar, R.; Hebert, M. Event detection in crowded videos. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE 11th International Conference On Computer Vision, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 14–21 October 2007; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Yilmaz, A.; Shah, M. Actions as objects: A nover action representation. In Proceedings of the CVPR-2005, San Diego, CA, USA, 20–26 June 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Weinl, D.; Ronfard, R.; Boyer, E. Free viewpoint action recognition using motion history volumes. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2006, 104, 249–257. [Google Scholar]
- Baccouche, M.; Mamalet, F.; Wolf, C.; Garcia, C.; Baskurt, A. Sequential deep learning for human action recognition. In International Workshop On Human Behavior Understanding; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 29–39. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, S.; Xu, W.; Yang, M.; Yu, K. 3D convolutional neural networks for human action recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2012, 35, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grushin, A.; Monner, D.; Reggia, J.; Mishra, A. Robust human action recognition via long short-term memory. In Proceedings of the the 2013 International Joint Conference On Neural Networks (IJCNN), Dallas, TX, USA, 4–9 August 2013; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, L.; Jia, K.; Yeung, D.; Shi, B. Human action recognition using factorized spatio-temporal convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference On Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 4597–4605. [Google Scholar]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Two-stream convolutional networks for action recognition in videos. arXiv 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Qiao, Y.; Tang, X. Action Recognition With Trajectory-Pooled Deep-Convolutional Descriptors. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference On Computer Vision And Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; Volume 6. [Google Scholar]
- Ullah, A.; Ahmad, J.; Muhammad, K.; Sajjad, M.; Baik, S. Action recognition in video sequences using deep bi-directional LSTM with CNN features. IEEE Access 2017, 6, 1155–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahasseni, B.; Todorovic, S. Regularizing long short term memory with 3D human-skeleton sequences for action recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 3054–3062. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Wang, L.; Wang, Z.; Qiao, Y.; Wang, H. Real-time action recognition with deeply transferred motion vector cnns. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2018, 27, 2326–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue-Hei, Ng, J.; Hausknecht, M.; Vijayanarasimhan, S.; Vinyals, O.; Monga, R.; Toderici, G. Beyond short snippets: Deep networks for video classification. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference On Computer Vision And Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 4694–4702. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, S.; Cheng, Y.; Su, S.; Cai, G.; Li, S. Stratified pooling based deep convolutional neural networks for human action recognition. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2017, 76, 13367–13382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, B.; Gavves, E.; Oramas, J.; Ghodrati, A.; Tuytelaars, T. Rank pooling for action recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2016, 39, 773–787. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; Yuille, A. An approach to pose-based action recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference On Computer Vision And Pattern Recognition, Portland, OR, USA, 23–28 June 2013; pp. 915–922. [Google Scholar]
- Chéron, G.; Laptev, I.; Schmid, C. P-cnn: Pose-based cnn features for action recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference On Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 3218–3226. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Wong, Y.; Liu, A.; Li, Y.; Su, Y.; Kankanhalli, M. Multi-camera action dataset for cross-camera action recognition benchmarking. In Proceedings of the IEEE Winter Conference On Applications Of Computer Vision (WACV), Santa Rosa, CA, USA, 24–31 March 2017; pp. 187–196. [Google Scholar]
- Faraki, M.; Palhang, M.; Sanderson, C. Log-Euclidean bag of words for human action recognition. IET Comput. Vis. 2015, 9, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Schmid, C. Action recognition with improved trajectories. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference On Computer Vision, Sydney, Australia, 1–8 December 2013; pp. 3551–3558. [Google Scholar]
- Malik, N.; Abu Bakar, S.; Sheikh, U. Multiview Human Action Recognition System Based on OpenPose and KNN Classifier. In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference On Robotics, Vision, Signal Processing And Power Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 890–895. [Google Scholar]
- Yadav, S.K.; Singh, A.; Gupta, A.; Raheja, J.L. Real-time Yoga recognition using deep learning. Neural Comput. Applic 2019, 31, 9349–9361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, A.; Muhammad, K.; Hussain, T.; Baik, S. Conflux LSTMs network: A novel approach for multi-view action recognition. Neurocomputing 2021, 435, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sargano, A.B.; Angelov, P.; Habib, Z. Human Action Recognition from Multiple Views Based on View-Invariant Feature Descriptor Using Support Vector Machines. Appl. Sci. 2016, 6, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumann, F.; Ehlers, A.; Rosenhahn, B.; Liao, J. Recognizing human actions using novel space-time volume binary patterns. Neurocomputing 2016, 173, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, S.Y.I.; Lee, C.-S. Human Action Recognition Using Histogram of Motion Intensity and Direction from Multi View. IET Comput. Vis. 2016, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishwakarma, D.K.; Kapoor, R.; Dhiman, A. A proposed unified framework for the recognition of human activity by exploiting the characteristics of action dynamics. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2016, 77, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pehlivan, S.; Duygulu, P. A new pose-based representation for rec- ognizing actions from multiple cameras. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2011, 115, 140–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oreifej, O.; Liu, Z. HON4D: Histogram of Oriented 4D Normals for Activity Recognition from Depth Sequences. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Portland, OR, USA, 23–28 June 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Rahmani, H.; Mahmood, A.; Huynh, D.Q.; Mian, A. Real time action recognition using histograms of depth gradients and random decision forests. In Proceedings of the IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Steamboat Springs, CO, USA, 24–26 March 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Shahroudy, A.; Liu, J.; Ng, T.T.; Wang, G. Ntu rgb+ d: A large scale dataset for 3d human activity analysis. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Rahmani, H.; Mian, A. 3D Action Recognition from Novel Viewpoints. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ke, Q.; Bennamoun, M.; An, S.; Sohel, F.; Boussaid, F. A new representation of skeleton sequences for 3d action recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Li, W.; Cook, C.; Zhu, C.; Gao, Y. Independently recurrent neural network (indrnn): Building a longer and deeper rnn. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, S.; Xiong, Y.; Lin, D. Spatial temporal graph convolutional networks for skeleton-based action recognition. In Proceedings of the Thirty-Second AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New Orleans, LA, USA, 2–7 February 2018. [Google Scholar]




| Authors | Methods | Datasets | Performance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Baccouche et al. [21] | CNN and RNN | KTH | 94.39 |
| Ji et al. [22] | 3DCNN | KTH | 90.02 |
| Grushin et al. [23] | LSTM | KTH | 90.7 |
| Sun et al. [24] | Factorised spatio-temporal CNN | HMDB-51 | 59.1 |
| Simonyan et al. [25] | two stream CNN | HMDB-51 | 59.4 |
| Wang et al. [26] | CNN | HMDB-51 | 65.9 |
| Ullah et al. [27] | DB-LSTM | HMDB-51 | 87.64 |
| Mahasseni et al. [28] | LSTM-CNN | HMDB-51 | 55.3 |
| Zhang et al. [29] | MV-CNN | UCF101 | 86.4 |
| Ng et al. [30] | LSTM with 30 frame unroll | UCF101 | 88.6 |
| Yu et al. [31] | SP-CNN | UCF101 | 91.6 |
| Fernando et al. [32] | Rank Pooling +CNN | Hollywood2 | 75.2 |
| Wang et al. [33] | Features (Pose-based) | MSR-action3D | 90 |
| Ch et al. [34] | Pose-based CNN | MPII Cooking | 71.4 |
| W. Li et al. [35] | Cuboids | MCAD | 56.8 |
| M. Faraki et al. [36] | Covariance matrices | MCAD | 64.3 |
| W. Li et al. [35] | STIP | MCAD | 81.7 |
| H. Wang et al. [37] | IDT | MCAD | 84.2 |
| A. Ullah et al. [27] | Conflux LSTM network | MCAD | 86.9 |
| Malik et al. [38] | OpenPose + FineKNN | MCAD | 86.9 |
| Class | Action |
|---|---|
| 1 | Point |
| 2 | Wave |
| 3 | Jump |
| 4 | Crouch |
| 5 | Sneeze |
| 6 | SitDown |
| 7 | StandUp |
| 8 | Walk |
| 9 | PersonRun |
| 10 | CellToEar |
| 11 | UseCellPhone |
| 12 | DrinkingWater |
| 13 | TakePicture |
| 14 | ObjectGet |
| 15 | ObjectPut |
| 16 | ObjectLeft |
| 17 | ObjectCarry |
| 18 | ObjectThrow |
| Class | Action |
|---|---|
| 1 | check-watch |
| 2 | Cross-arms |
| 3 | Get-up |
| 4 | kick |
| 5 | Pick-up |
| 6 | Point |
| 7 | Punch |
| 8 | Scratch-head |
| 9 | Sit-Down |
| 10 | Turn-Around |
| 11 | Walk |
| 12 | Wave |
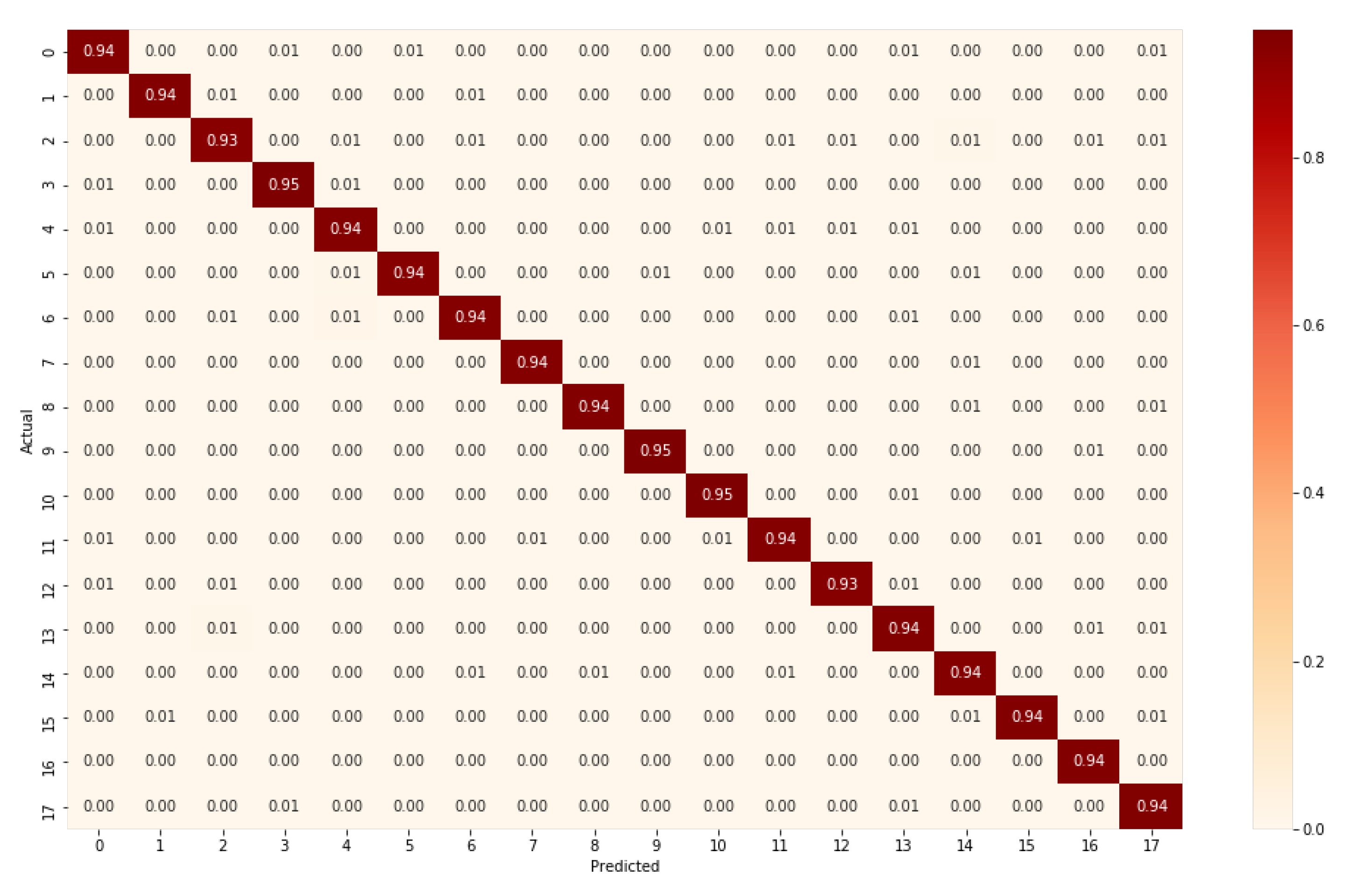
| Class | Action | Precision | Recall | F1-Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Point | 0.92 | 0.94 | 0.93 |
| 2 | Wave | 0.94 | 0.94 | 0.94 |
| 3 | Jump | 0.89 | 0.93 | 0.91 |
| 4 | Crouch | 0.94 | 0.95 | 0.94 |
| 5 | Sneeze | 0.9 | 0.94 | 0.92 |
| 6 | SitDown | 0.91 | 0.94 | 0.92 |
| 7 | StandUp | 0.9 | 0.94 | 0.92 |
| 8 | Walk | 0.97 | 0.94 | 0.96 |
| 9 | PersonRun | 0.95 | 0.94 | 0.94 |
| 10 | CellToEar | 0.95 | 0.95 | 0.95 |
| 11 | UseCellPhone | 0.96 | 0.95 | 0.96 |
| 12 | DrinkingWater | 0.95 | 0.94 | 0.94 |
| 13 | TakePicture | 0.96 | 0.93 | 0.95 |
| 14 | ObjectGet | 0.88 | 0.94 | 0.91 |
| 15 | ObjectPut | 0.91 | 0.94 | 0.93 |
| 16 | ObjectLeft | 0.94 | 0.94 | 0.94 |
| 17 | ObjectCarry | 0.98 | 0.94 | 0.96 |
| 18 | ObjectThrow | 0.9 | 0.94 | 0.92 |
| Algorithm | Accuracy |
|---|---|
| Cuboids [35] | 56.8 |
| Covariance matrices [36] | 64.3 |
| STIP [35] | 81.7 |
| IDT [37] | 84.2 |
| Conflux LSTM network [27] | 86.9 |
| OpenPose+FineKNN [38] | 86.9 |
| Proposed method | 94.4 |
| Class | Action | Precision | Recall | F1-Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Check-watch | 0.93 | 0.92 | 0.92 |
| 2 | Cross-arms | 0.89 | 0.92 | 0.90 |
| 3 | Get-up | 0.90 | 0.92 | 0.91 |
| 4 | Kick | 0.91 | 0.92 | 0.91 |
| 5 | Pick-up | 0.90 | 0.94 | 0.91 |
| 6 | Point | 0.90 | 0.93 | 0.91 |
| 7 | Punch | 0.89 | 0.92 | 0.91 |
| 8 | Scratch-head | 0.90 | 0.91 | 0.91 |
| 9 | Sit-Down | 0.90 | 0.91 | 0.91 |
| 10 | Turn-Around | 0.91 | 0.91 | 0.91 |
| 11 | Walk | 0.94 | 0.92 | 0.93 |
| 12 | Wave | 0.97 | 0.91 | 0.94 |
| Algorithm | Accuracy |
|---|---|
| Shape Features [41] | 89.75 |
| LBP [42] | 80.55 |
| Motion Features [43] | 83.03 |
| Shape features [44] | 85.8 |
| Shape Features (3D) [45] | 90.91 |
| Proposed method | 91.67 |
| Algorithm | Year | Short Descriptions | Data Used | Feature Dimension |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HON4D [46] | CVPR 2013 | Handcrafted (global descriptor) | Depth | [17,880, 151,200] |
| HDG [47] | WACV 2014 | Handcrafted (local + global descriptor) | Depth+ Skeleton | [1662, 1819] |
| P-LSTM [48] | CVPR 2016 | Deep learning (LSTM) | Skeleton | No. of joints × 3 × 8 |
| HPM+TM [49] | CVPR 2016 | Deep learning (CNN) | Depth | 4096 |
| Clips+CNN+ MTLN [50] | CVPR 2017 | Deep learning (pre-trained VGG19,MTLN) | Skeleton | 7168 |
| RNN [51] | CVPR 2018 | Deep learning (RNN) | Skeleton | 512 |
| ST-GCN [52] | AAAI 2018 | Deep learning (Graph ConvNet) | Skeleton | 256 |
| Proposed | 2022 | OpenPose + CNNLSTM | RGB | 25 × 2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Malik, N.u.R.; Abu-Bakar, S.A.R.; Sheikh, U.U.; Channa, A.; Popescu, N. Cascading Pose Features with CNN-LSTM for Multiview Human Action Recognition. Signals 2023, 4, 40-55. https://doi.org/10.3390/signals4010002
Malik NuR, Abu-Bakar SAR, Sheikh UU, Channa A, Popescu N. Cascading Pose Features with CNN-LSTM for Multiview Human Action Recognition. Signals. 2023; 4(1):40-55. https://doi.org/10.3390/signals4010002
Chicago/Turabian StyleMalik, Najeeb ur Rehman, Syed Abdul Rahman Abu-Bakar, Usman Ullah Sheikh, Asma Channa, and Nirvana Popescu. 2023. "Cascading Pose Features with CNN-LSTM for Multiview Human Action Recognition" Signals 4, no. 1: 40-55. https://doi.org/10.3390/signals4010002
APA StyleMalik, N. u. R., Abu-Bakar, S. A. R., Sheikh, U. U., Channa, A., & Popescu, N. (2023). Cascading Pose Features with CNN-LSTM for Multiview Human Action Recognition. Signals, 4(1), 40-55. https://doi.org/10.3390/signals4010002









