Sound Absorption Properties of Waste Pomelo Peel
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experiment
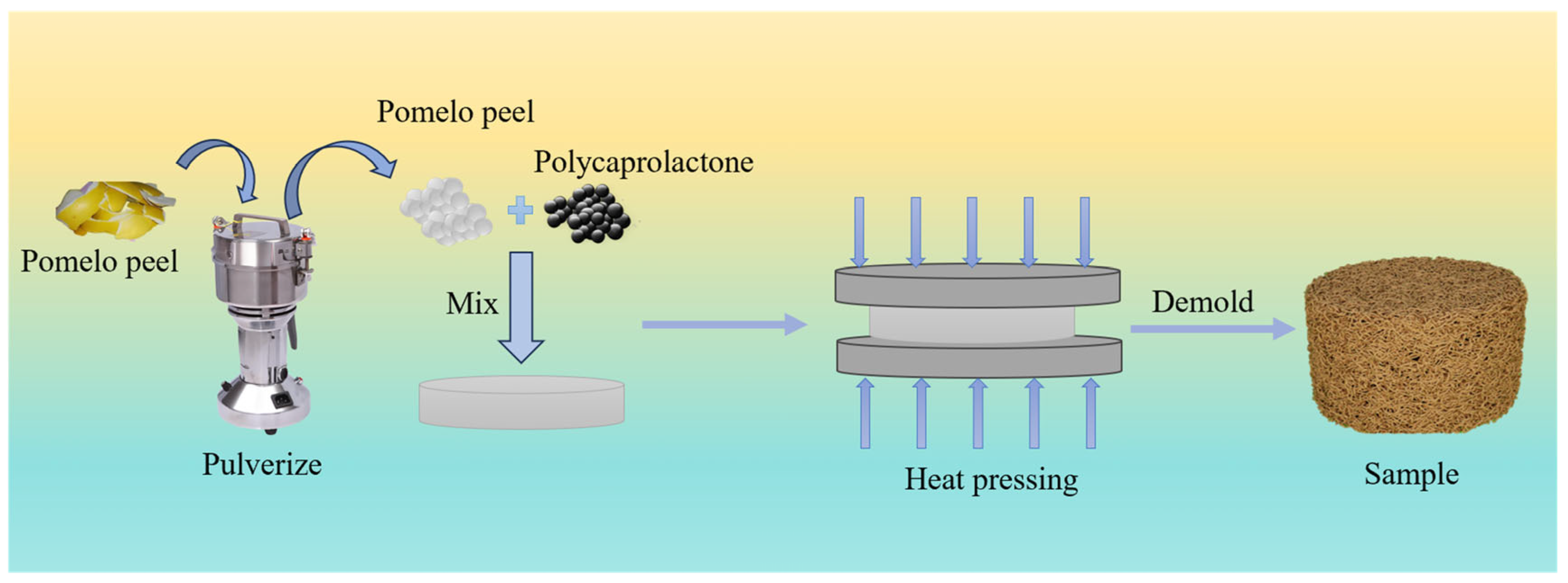
2.1. Experimental Raw Composites and Equipment
2.2. Experimental Methods
2.3. Test Indicators
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Structural Characteristics of Pomelo Peel
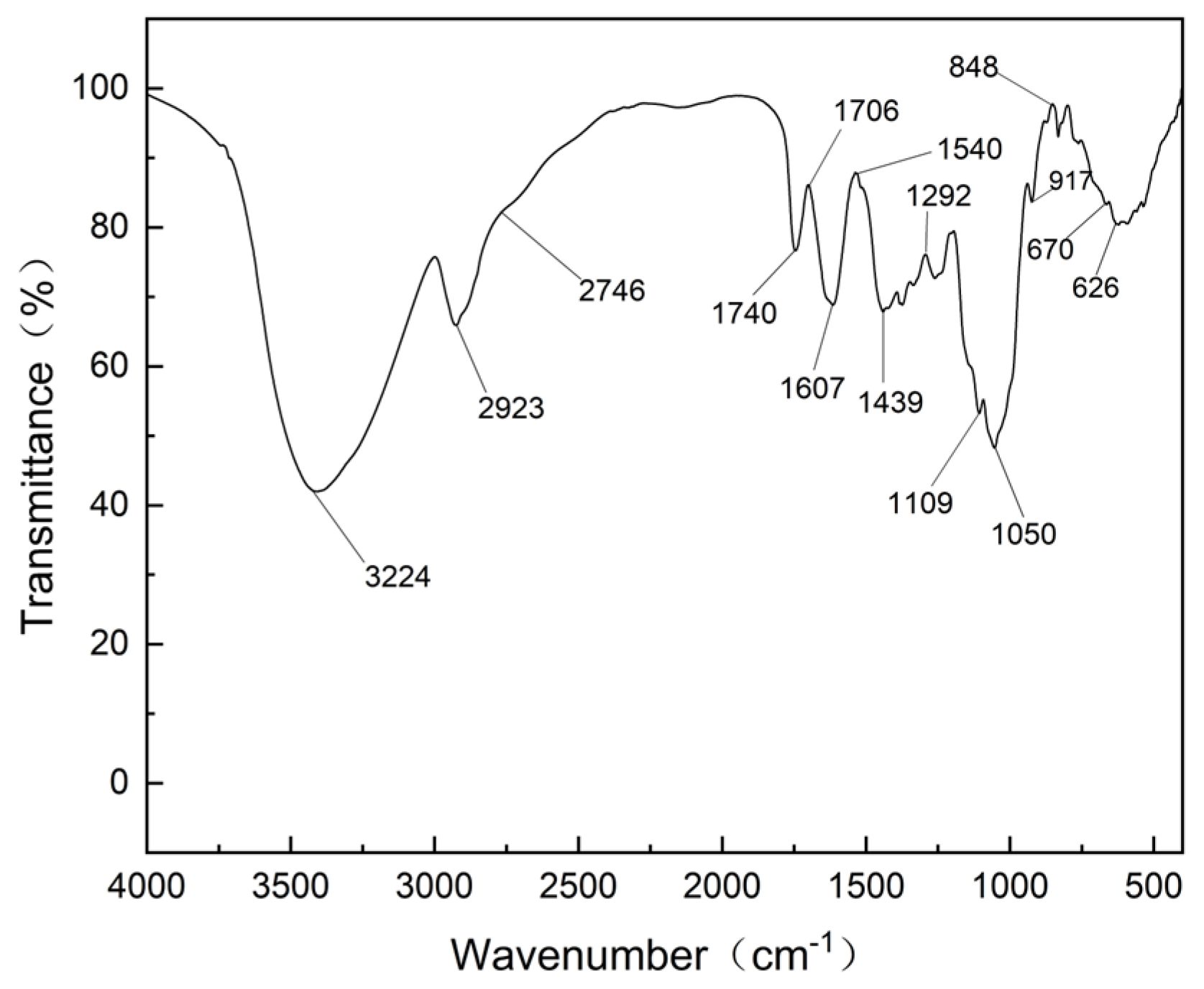
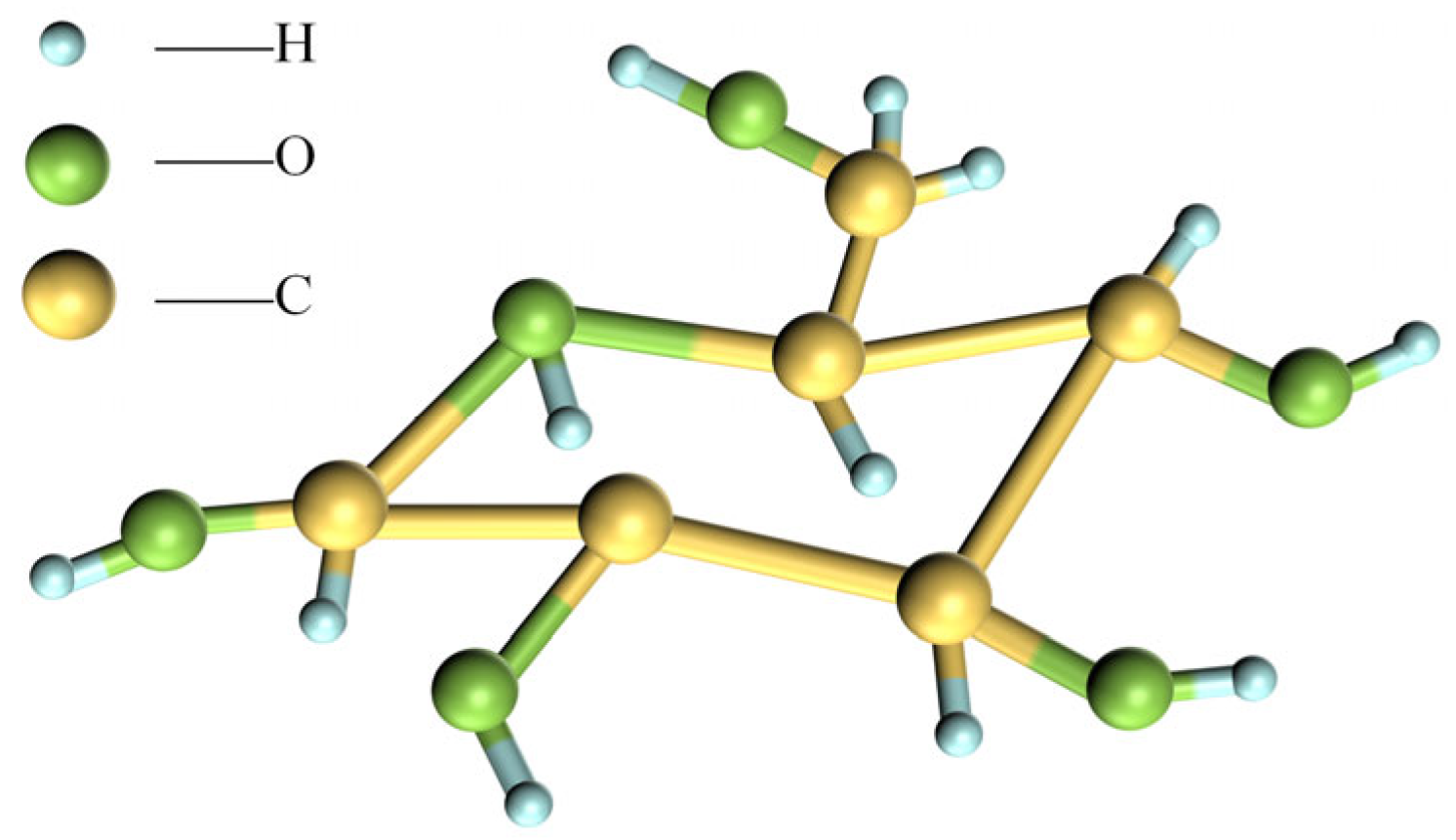
3.1.1. Chemical Structure
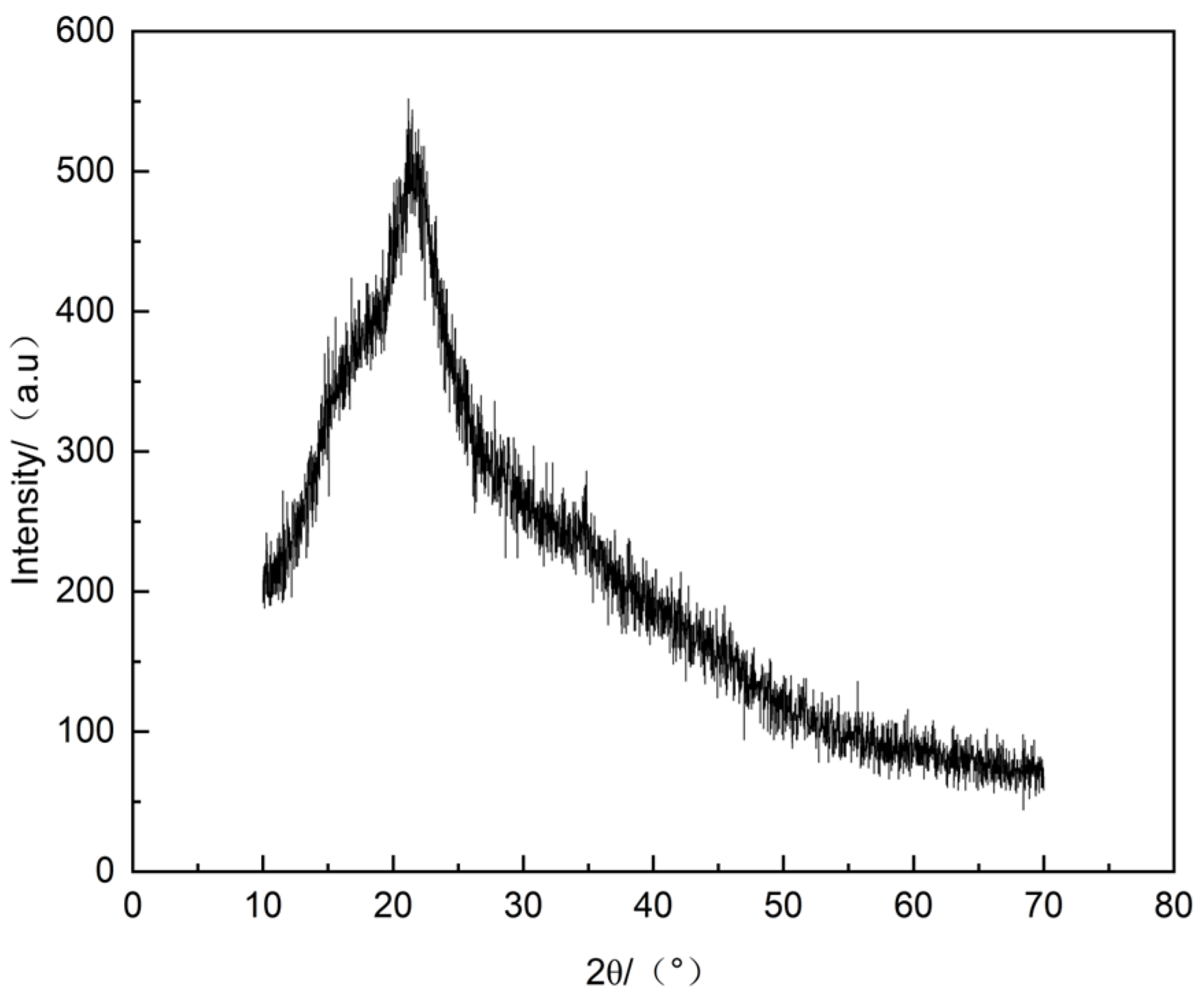
3.1.2. Aggregate State Structure
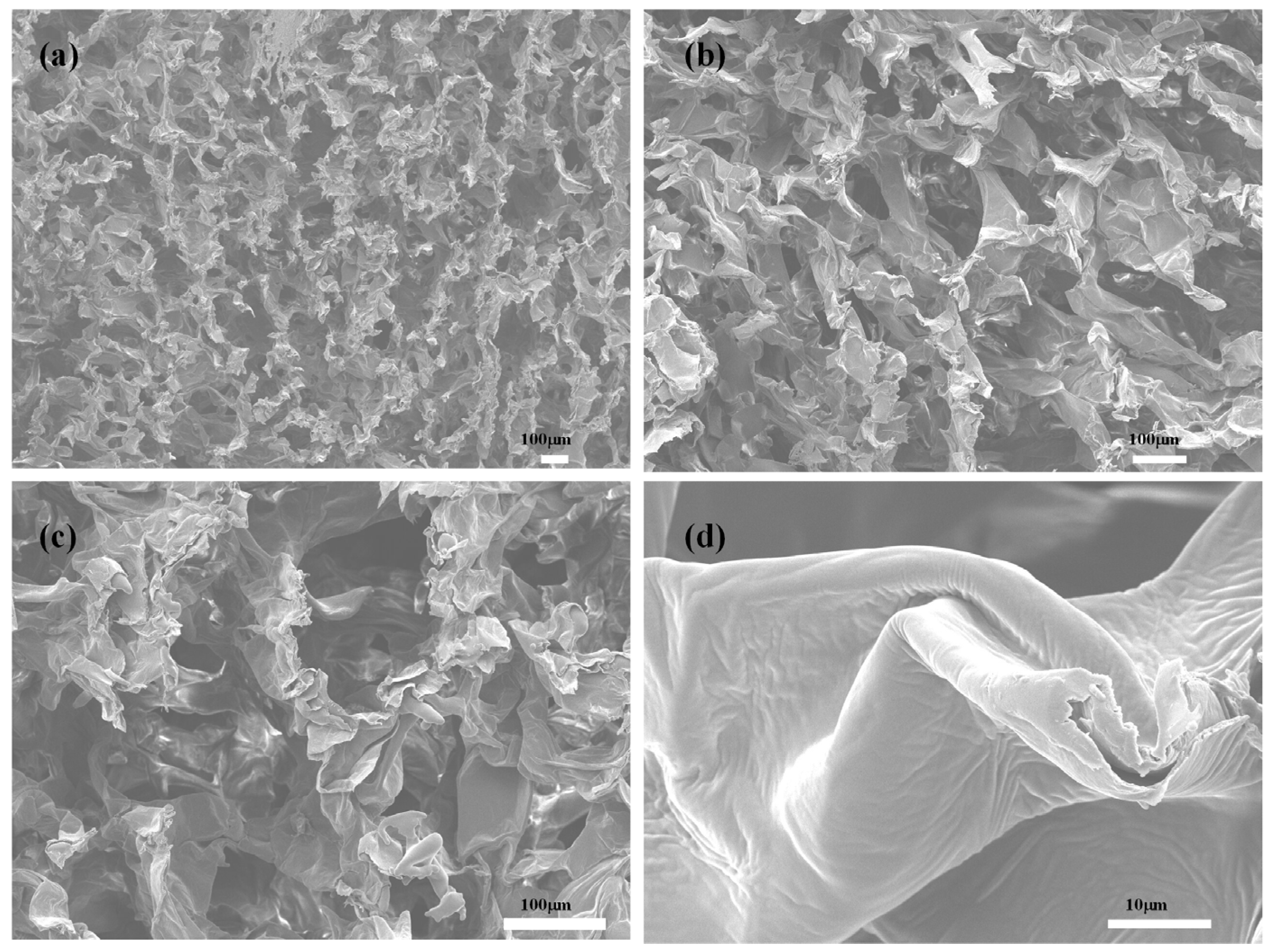
3.1.3. Morphological Structure
3.2. Sound Absorption of Waste Pomelo Peel/PCL Sound Absorption Composites
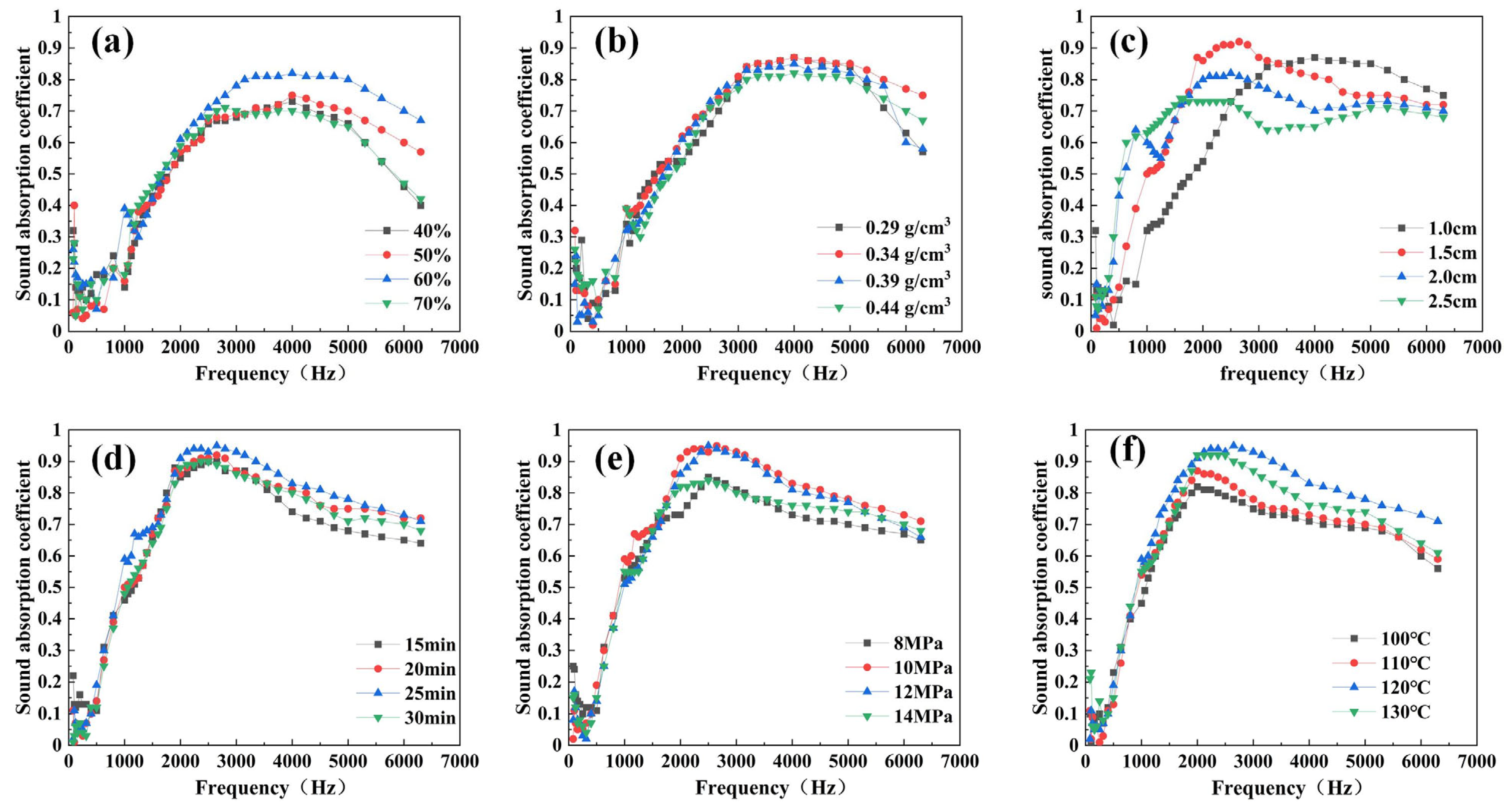
3.2.1. Effect of Waste Pomelo Peel Mass Fraction on Sound Absorption
3.2.2. Effect of Composite Density on Sound Absorption
3.2.3. Effect of Composite Thickness on Sound Absorption
3.2.4. Effect of Hot-Pressing Time on Sound Absorption
3.2.5. Effect of Hot-Pressing Pressure on Sound Absorption
3.2.6. Effect of Hot-Pressing Temperature on Sound Absorption
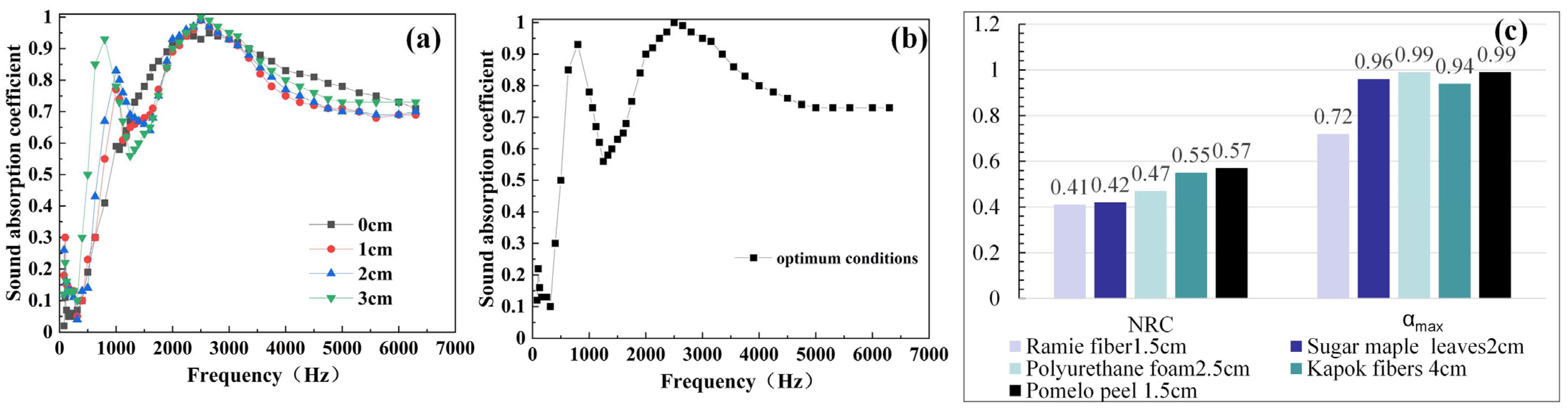
3.2.7. Effect of the Thickness of Rear Air Layer on Sound Absorption
3.2.8. Optimal Process of Waste Pomelo Peel/PCL Sound-Absorbing Composites
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, T.; Hu, L.; Xiong, X.; Petrů, M.; Noman, M.T.; Mishra, R.; Militký, J. Sound absorption properties of natural fibers: A review. Sustainability 2020, 12, 8477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arjunan, A.; Baroutaji, A.; Robinson, J.; Vance, A.; Arafat, A. Acoustic metamaterials for sound absorption and insulation in buildings. Build. Environ. 2024, 251, 111250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Sudhakara, P.; Singh, J.; Singh, S.; Singh, G. Emerging progressive developments in the fibrous composites for acoustic applications. J. Manuf. Process. 2023, 102, 443477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Qiu, Y.; Chen, F.; Zhang, L.; Wei, W.; An, X.; Zhu, Q. Pomelo peel derived nanocellulose as Pickering stabilizers: Fabrication of Pickering emulsions and their potential as sustained-release delivery systems for lycopene. Food Chem. 2023, 415, 135742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, W.; Feng, Y.; Tan, J.; Zeng, H.; Jalaludeen, R.K.; Zeng, X.; Zheng, B.; Song, J.; Zhang, X.; Chen, S.; et al. Carbonized cellulose aerogel derived from waste pomelo peel for rapid hemostasis of trauma-induced bleeding. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, 2307409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Jiang, X.; Sun, Y.; Gan, D.; Liu, W.; Wu, Y.; Hao, X. Composite optimization and characterization of dietary fiber-based edible packaging film reinforced by nanocellulose from grapefruit peel pomace. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 127655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Zhao, J.; Wang, H.; Zhang, A.; Li, J.; Yan, M.; Guo, T. Shaddock peel-derived N-doped carbon quantum dots coupled with ultrathin BiOBr square nanosheets with boosted visible light response for high-efficiency photodegradation of RhB. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 325, 121424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argun, E.M.; Güclü, D.; Karatas, M. Adsorption of reactive blue 114 dye by using a new adsorbent: Pomelo peel. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2014, 20, 10791084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Lei, X.; Cao, J.; Pang, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, T. Carbon aerogel with solid and magnetic coating prepared from freeze-thawed pomelo peel waste for oil adsorption. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 115943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imran, M.; Islam, A.; Ismail, F.; Zhang, P.; Basharat, M.; Ikram, M.; Uddin, A.; Zeb, S.; Hassan, Q.-U.; Gao, Y. 3D porous superoleophilic/hydrophobic grapefruit peel aerogel for efficient removal of emulsified-oil from water. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 109324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolya, H.; Kang, C.W. Sugar maple (Acer saccharum) waste leaves as a renewable resource for sound absorption: An eco-conscious approach. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 111665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolya, H.; Kang, C.W. Unveiling enhanced sound absorption in coconut wood through hemicellulose and lignin modification. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 276, 134083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Dong, C.; Tong, L.; Rudd, C.; Yi, X.; Liu, X. Sound absorption performance of ultralight honeycomb sandwich panels filled with “Network” fibers—Juncus effusus. Polymers 2024, 16, 1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alagarsamy, M.; Pitchipoo, P.; Kumar, S. An investigation of sound absorption characteristics of Cocos nucifera fiber composite using Taguchi design. Polym. Bull. 2024, 81, 9287–9304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minetto Garcia Duarte, M.; Zoppi, R.A.; Serpa, A.L. Optimizing acoustic performance: Electro spun Polycaprolactone fiber mat associated with melamine foam and fiber glass wool. Fibers Polym. 2024, 25, 457472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malikmammadov, E.; Tanir, T.E.; Kiziltay, A.; Hasirci, V.; Hasirci, N. PCL and PCL-based materials in biomedical applications. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2018, 29, 863–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, D.; Song, M.; Pan, Y.; Aimaier, X.; Tian, Y.; Yang, R.; Huang, J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; Boshkov, N.; et al. Facile fabrication of a ternary drug-carrying polymeric composite coatings with enhanced interface compatibility and mechanical properties by suspension flame spray. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2025, 719, 137073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Guo, Q.; Li, T.; Zhang, S.; Wang, B.; Yue, H.; Liu, H.; Yang, J.; Wang, Q. Preparation and characterization of birch plywood prepared by hot-pressed peanut meal adhesive. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2022, 117, 103186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Qian, Y.; Gao, Y.; Zhou, X.; Lyu, L. Waste ramie fiber/EVA composites with wideband sound-absorbing performance with mixing and foaming process. Ind. Crops Prod. 2024, 221, 119325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Zhang, W.; Khan, M.R.; Ahmad, N.; Rhim, J.-W.; Jiang, W.; Roy, S. Film properties of pectin obtained from various fruits’(Lemon, Pomelo, Pitaya) Peels. J. Compos. Sci. 2023, 7, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.; Yu, R.; Qiu, G.; Zeng, W. Insights into the EPS production and distribution of planktonic and attached sulfobacillus thermosulfidooxidans cells during bioleaching. Miner. Eng. 2024, 205, 108494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakó, I.; Pusztai, L.; Pothoczki, S. Outstanding properties of the hydration shell around β-d-Glucose: A computational study. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 2033120337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venegas, R.; Zieliński, T.G.; Núñez, G.; Bécot, F.-X. Acoustics of porous composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2021, 220, 109006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Ma, S.; Wang, H. The principle of methylcellulose crystallinity and its application in copper-based electronic pastes. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2025, 36, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xiao, H.; Qi, H. Saccharide branched cellulose with controllable molecular structure and excellent water retention ability. Carbohydr. Polym. 2024, 327, 121651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Lyu, L.; Xiong, X.; Qian, Y.; Li, H.; Guo, J. Structural characteristics and sound absorption properties of poplar seed fibers. Text. Res. J. 2020, 90, 24672477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Peng, X.; Xin, F.; Lu, T.J. A microstructure-based model of transport parameters and sound absorption for woven fabrics. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2022, 227, 109607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Zhou, X.; Gao, Y.; Lyu, L. Structural characteristics and sound absorption properties of waste hemp fiber. Coatings 2022, 12, 1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yang, J.; Liu, Q.; Li, S.; Liu, X.-C.; Yang, F.; Wu, L.-Z. A novel sandwich structure for integrated sound insulation and absorption. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2024, 279, 109526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatima, S.; Mohanty, A.R. Acoustical and fire-retardant properties of jute composite materials. Appl. Acoust. 2011, 72, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, H.; Wang, D.; Liua, H.; Zhao, N.; Xu, J. Investigation on sound absorption properties of kapok fibers. Chin. J. Polym. Sci. 2013, 31, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statharas, E.C.; Yao, K.; Rahimabady, M.; Mohamed, A.M.; Tay, F.E.H. Polyurethane/poly (vinylidene fluoride)/MWCNT composite foam for broadband airborne sound absorption. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2019, 136, 47868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| NRC | >0.8 | 0.8 > NRC ≥ 0.6 | 0.6 > NRC ≥ 0.4 | 0.4 > NRC ≥ 0.2 |
| Level | I | II | III | IV |
| Waste Pomelo Peel Mass Fraction (%) | Composite Density (g/cm3) | Composite Thickness (cm) | Hot-Pressing Time (min) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 40 | 50 | 60 | 70 | 0.29 | 0.34 | 0.39 | 0.44 | 1.0 | 1.5 | 2.0 | 2.5 | 15 | 20 | 25 | 30 | |
| αmax | 0.73 | 0.75 | 0.82 | 0.70 | 0.87 | 0.87 | 0.85 | 0.84 | 0.87 | 0.92 | 0.82 | 0.74 | 0.90 | 0.92 | 0.95 | 0.90 |
| αavg | 0.28 | 0.31 | 0.32 | 0.42 | 0.35 | 0.37 | 0.34 | 0.32 | 0.37 | 0.41 | 0.41 | 0.38 | 0.40 | 0.41 | 0.44 | 0.39 |
| NRC | 0.21 | 0.25 | 0.29 | 0.40 | 0.27 | 0.31 | 0.30 | 0.29 | 0.31 | 0.38 | 0.49 | 0.49 | 0.38 | 0.38 | 0.49 | 0.49 |
| Hot-Pressing Pressure (MPa) | Hot-Pressing Temperature (°C) | Thickness of Rear Air Layer (cm) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8 | 10 | 12 | 14 | 100 | 110 | 120 | 130 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | |
| αmax | 0.85 | 0.95 | 0.95 | 0.84 | 0.82 | 0.87 | 0.95 | 0.92 | 0.95 | 0.97 | 0.99 | 0.99 |
| αavg | 0.39 | 0.44 | 0.41 | 0.40 | 0.40 | 0.39 | 0.44 | 0.40 | 0.44 | 0.48 | 0.49 | 0.54 |
| NRC | 0.36 | 0.49 | 0.38 | 0.39 | 0.40 | 0.38 | 0.49 | 0.44 | 0.49 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.57 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lyu, L.; Zhao, Y.; Li, J. Sound Absorption Properties of Waste Pomelo Peel. Acoustics 2025, 7, 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/acoustics7030051
Lyu L, Zhao Y, Li J. Sound Absorption Properties of Waste Pomelo Peel. Acoustics. 2025; 7(3):51. https://doi.org/10.3390/acoustics7030051
Chicago/Turabian StyleLyu, Lihua, Yiping Zhao, and Jinglin Li. 2025. "Sound Absorption Properties of Waste Pomelo Peel" Acoustics 7, no. 3: 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/acoustics7030051
APA StyleLyu, L., Zhao, Y., & Li, J. (2025). Sound Absorption Properties of Waste Pomelo Peel. Acoustics, 7(3), 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/acoustics7030051







