The Use of Soundscapes to Monitor Fish Communities: Meaningful Graphical Representations Differ with Acoustic Environment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
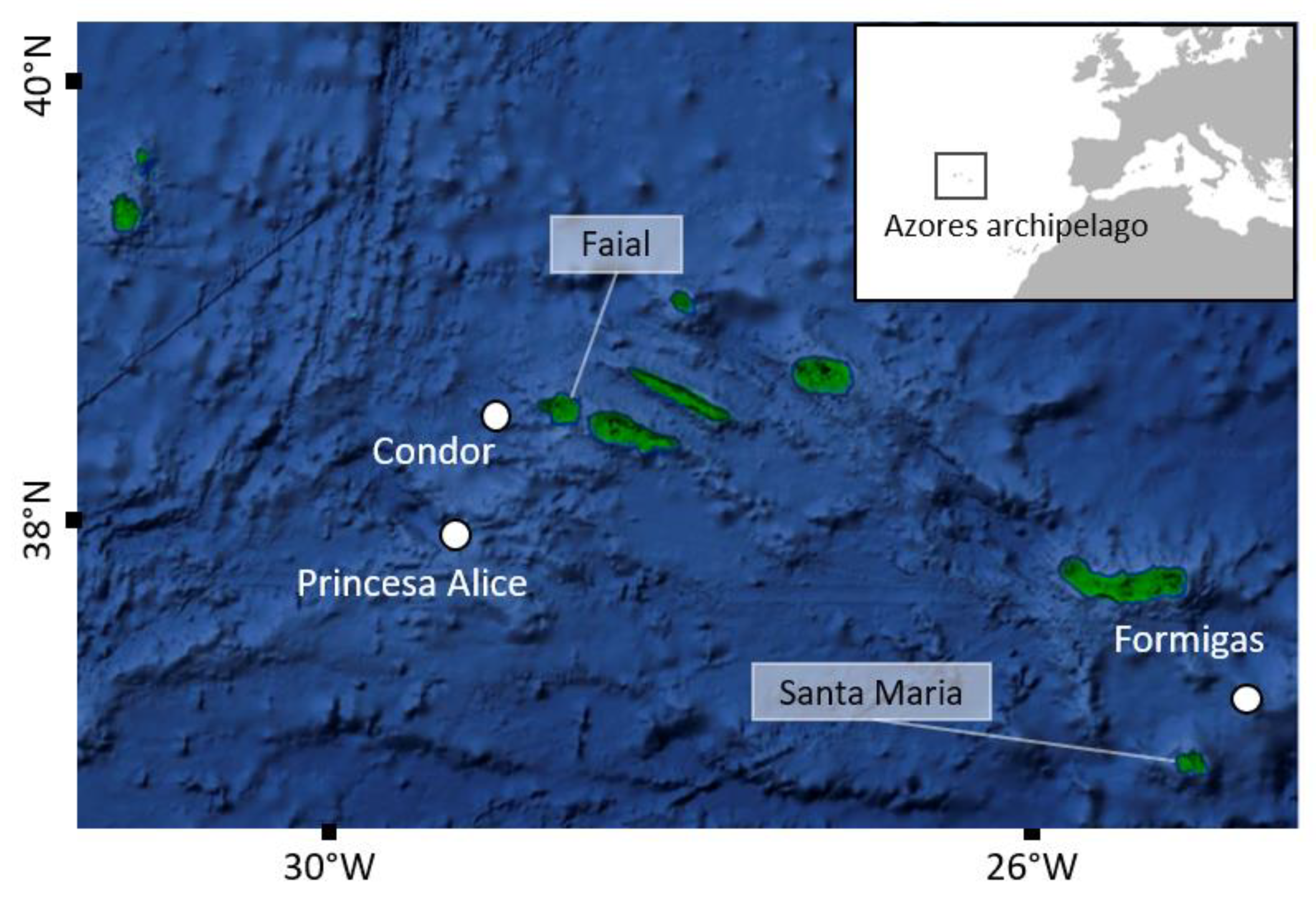
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Acoustic Recordings
2.3. Data Analysis
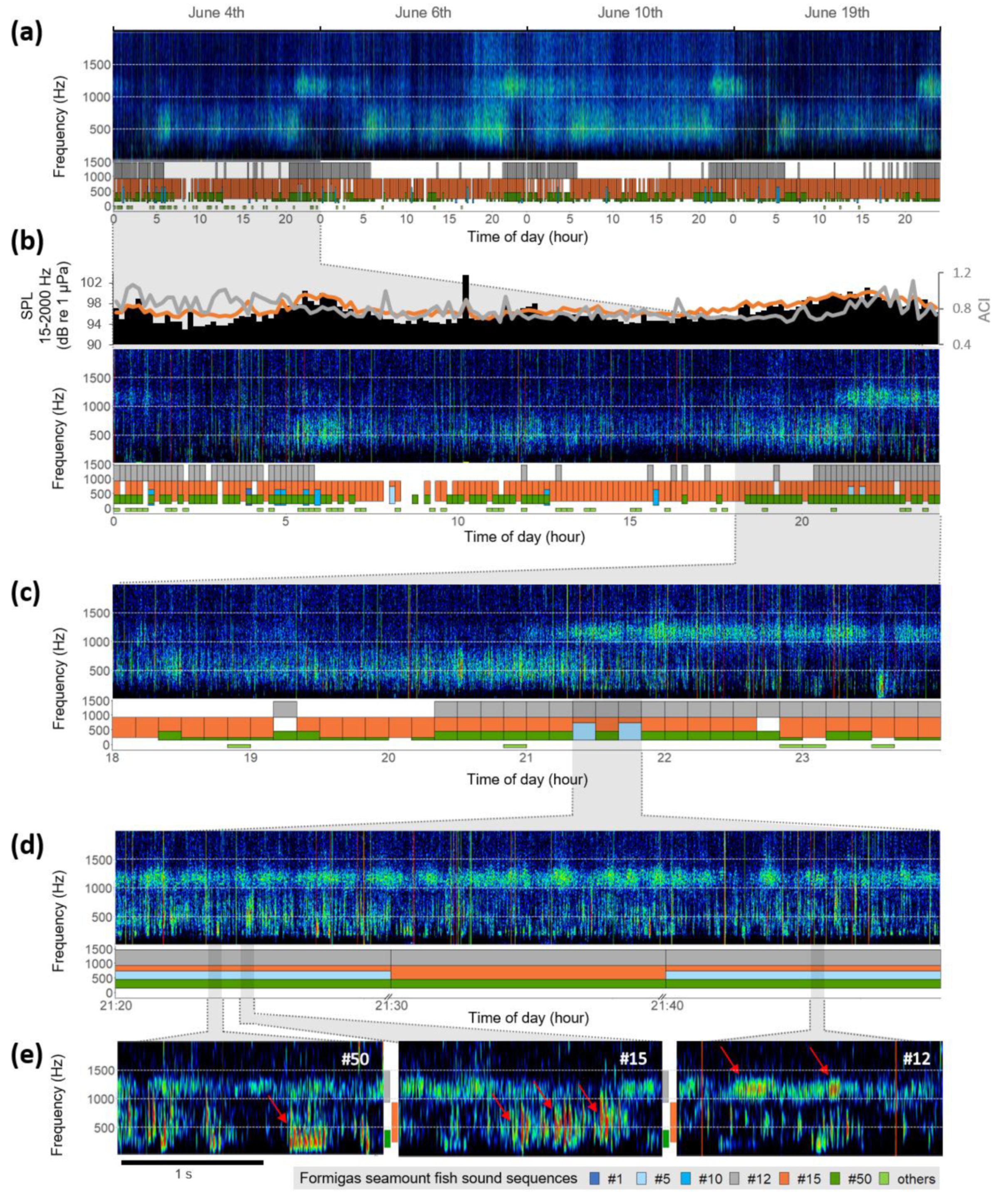
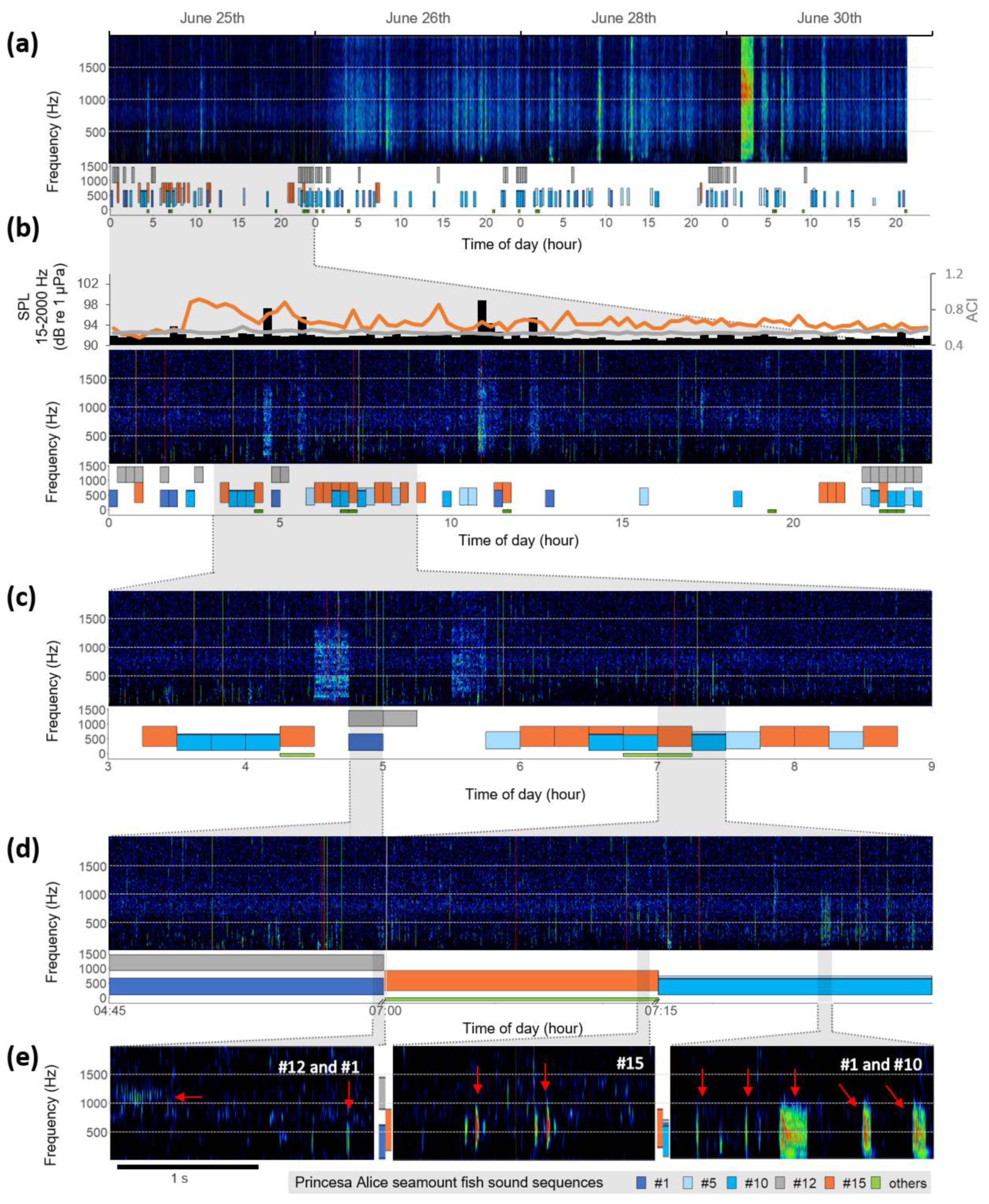
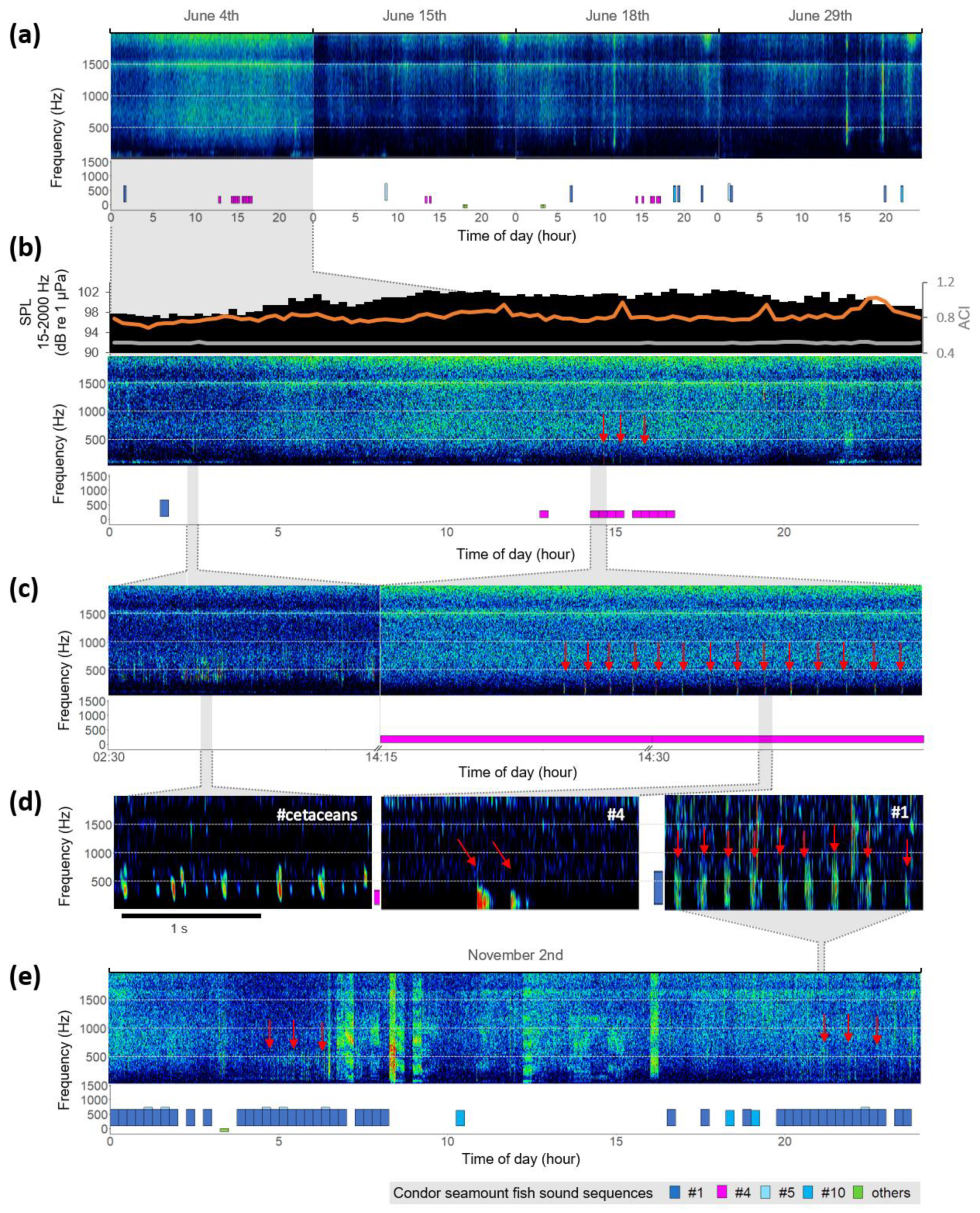
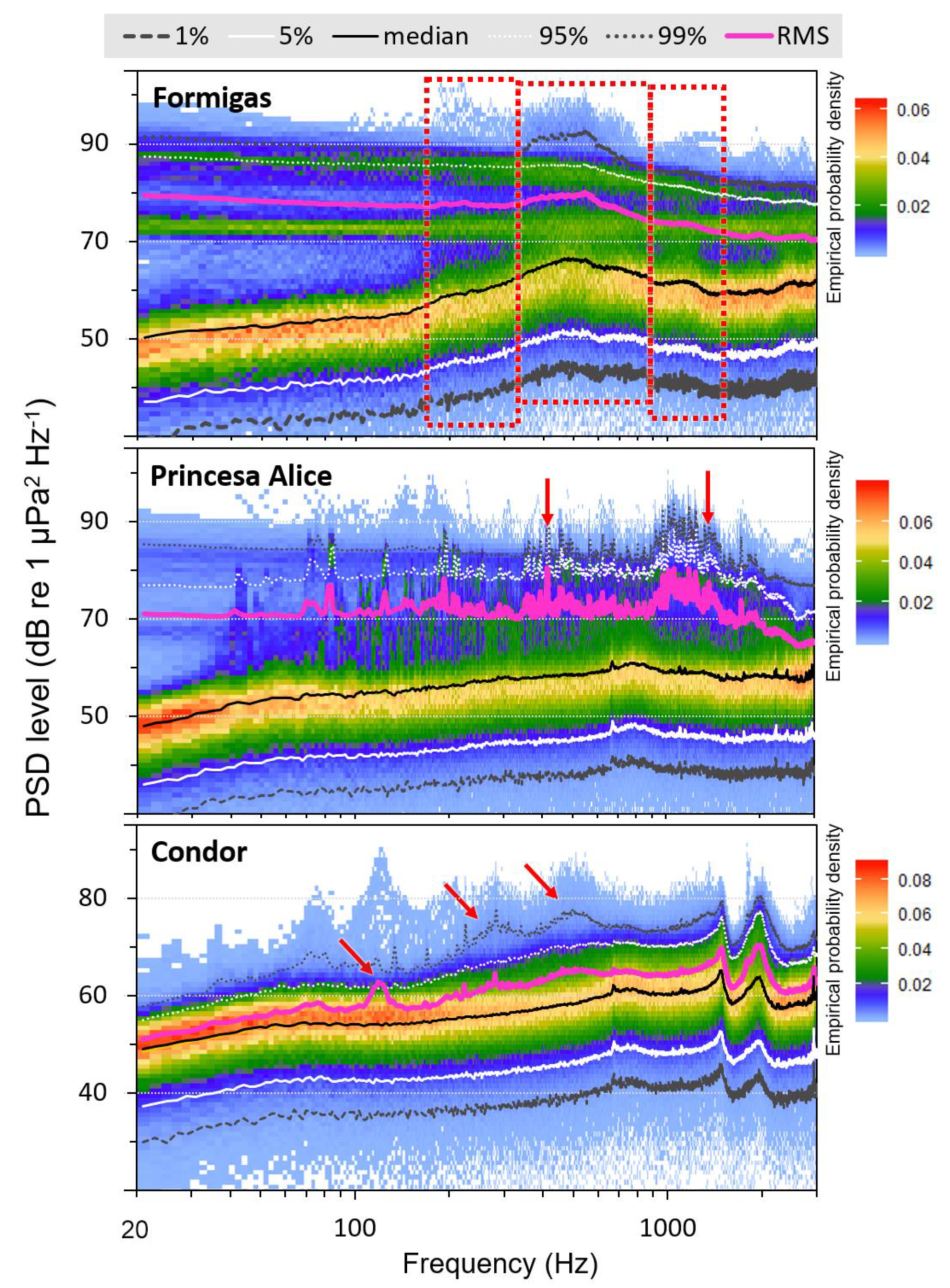
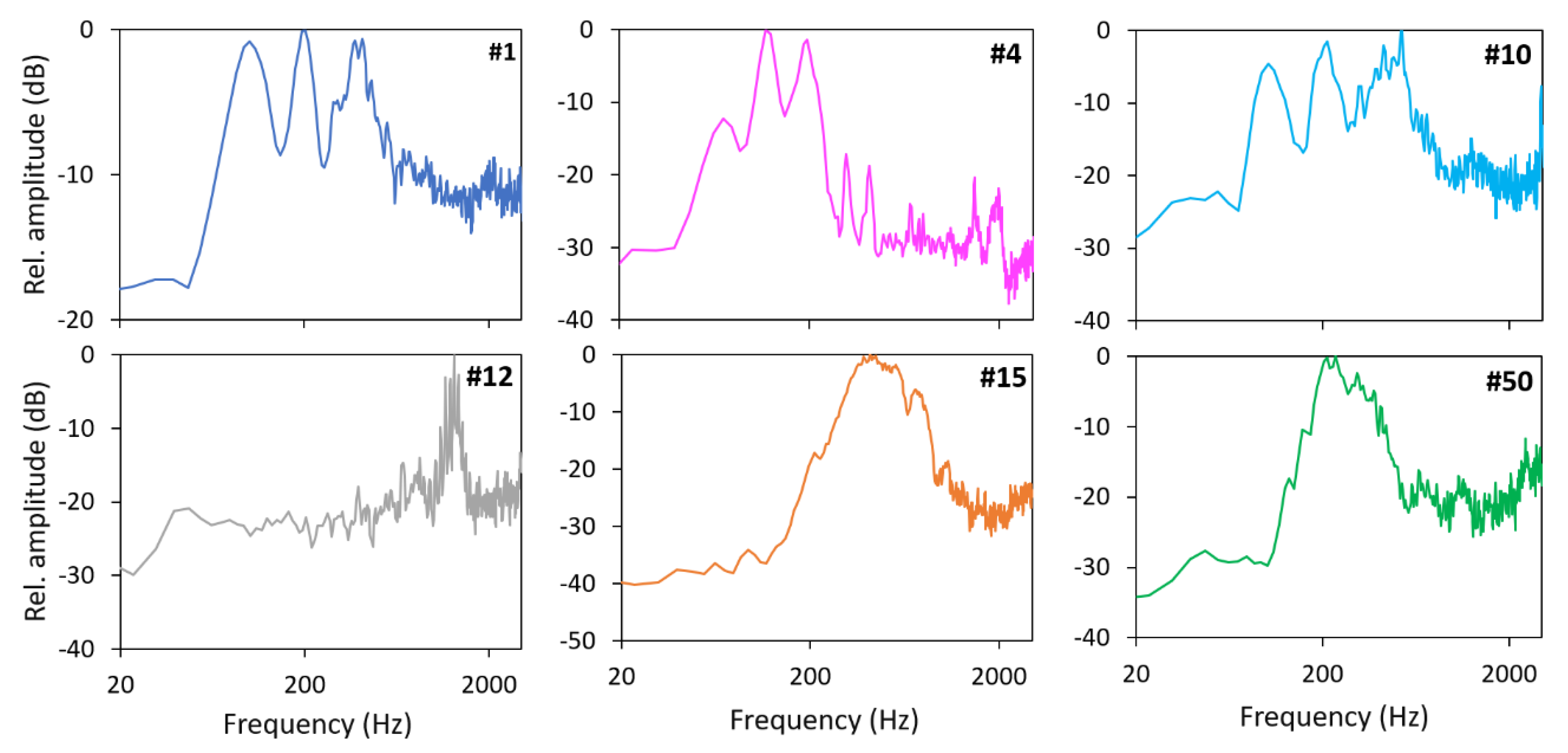
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mann, D.A.; Lobel, P.S. Propagation of damselfish (Pomacentridae) courtship sounds. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1997, 101, 3783–3791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buscaino, G.; Filiciotto, F.; Gristina, M.; Bellante, A.; Buffa, G.; Di Stefano, V.; Maccarrone, V.; Tranchida, G.; Buscaino, C.; Mazzola, S. Acoustic behaviour of the European spiny lobster Palinurus elephas. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2011, 441, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popper, A.N.; Hawkins, A.D. An overview of fish bioacoustics and the impacts of anthropogenic sounds on fishes. J. Fish Biol. 2019, 94, 692–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popper, A.N.; Fay, R.R.; Platt, C.; Sand, O. Sound detection mechanisms and capabilities of teleost fishes. In Sensory Processing in Aquatic Environments; Collin, S.P., Marshall, N.J., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2003; pp. 1–53. [Google Scholar]
- Cato, D.H.; Noad, M.J.; McCauley, R.D. Passive acoustics as a key to the study of marine animals. In Sounds in the Sea: From Ocean Acoustics to Acoustical Oceanography; Medwin, H., Ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2005; pp. 411–429. [Google Scholar]
- McWilliam, J.; Hawkins, A. A comparison of inshore marine soundscapes. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2013, 446, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaatz, I.M. Multiple sound producing mechanisms in teleost fishes and hypotheses regarding their behavioural significance. Bioacoustics 2002, 12, 230–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeij, M.J.A.; Marhaver, K.L.; Huijbers, C.M.; Nagelkerken, I.; Simpson, S.D. Coral Larvae Move toward Reef Sounds. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e10660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapuis, L.; Bshary, R. Signalling by the cleaner shrimp Periclimenes longicarpus. Anim. Behav. 2010, 79, 645–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lillis, A.; Eggleston, D.; Bohnenstieh, D. Estuarine soundscapes: Distinct acoustic characteristics of oyster reefs compared to soft-bottom habitats. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2014, 505, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, S.; Shears, N.; Radford, C. Ecoacoustic indices as proxies for biodiversity on temperate reefs. Methods Ecol. Evol. Br. Ecol. Soc. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolgan, M.; Amorim, M.C.P.; Fonseca, P.J.; Di Iorio, L.; Parmentier, E. Acoustic Complexity of vocal fish communities: A field and controlled validation. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miksis-Olds, J.L.; Martin, B.; Tyack, P.L. Exploring the Ocean through Soundscapes. Acoust. Today 2018, 14, 26–34. [Google Scholar]
- Erbe, C.; McCauley, R.; Gavrilov, A. Chapter 31—Characterizing Marine Soundscapes. In The Effects of Noise on Aquatic Life II, Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology; Popper, A.N., Hawkins, A., Eds.; Springer Science+Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Bertucci, F.; Parmentier, E.; Lecellier, G.; Hawkins, A.D.; Lecchini, D. Acoustic indices provide information on the status of coral reefs: An example from Moorea Island in the South Pacific. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolgan, M.; Gervaise, C.; Di Iorio Lossent, J.; Lejeune, P.; Raick, X.; Parmentier, E. Fish biophony in a Mediterranean submarine canyon. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2020, 147, 2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luczkovich, J.J.; Mann, D.A.; Rountree, R.A. Passive acoustics as a tool in fisheries science. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 2008, 137, 533–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, G.E.; Baumgartner, M.F.; Van Parijs, S.M. Long-term passive acoustic recordings track the changing distribution of North Atlantic right whales (Eubalaena glacialis) from 2004 to 2014. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caiger, P.E.; Dean, M.J.; DeAngelis, A.I.; Hatch, L.T.; Rice, A.N.; Stanley, J.A.; Tholke, C.; Zemeckis, D.R.; Van Parijs, S.M. A decade of monitoring Atlantic cod Gadus morhua spawning aggregations in Massachusetts Bay using passive acoustics. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2020, 635, 89–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, A.N.; Soldevilla, M.S.; Quinlan, J.A. Nocturnal patterns in fish chorusing off the coasts of Georgia and eastern Florida. Bull. Mar. Sci. 2017, 93, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmentier, E.; Di Iorio, L.; Picciulin, M.; Malavasi, S.; Lagardère, J.-P.; Bertucci, F. Consistency of spatiotemporal sound features supports the use of passive acoustics for long-term monitoring. Anim. Conserv. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricci, S.W.; Eggleston, D.B.; Bohnenstiehl, D.R. Use of passive acoustic monitoring to characterize fish spawning behavior and habitat use within a complex mosaic of estuarine habitats. Bull. Mar. Sci. 2017, 93, 439–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carriço, R.; Silva, M.A.; Menezes, G.M.; Fonseca, P.J.; Amorim, M.C.P. Characterization of the acoustic community of vocal fishes in the Azores. PeerJ 2019, 7, e7772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, S.A.; Radford, C.A. Marine Soundscape Ecology. Available online: https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/578c/dc57de0179040d652f7deefbabe9d9fe7399.pdf (accessed on 10 April 2020).
- Putland, R.L.; Constantine, R.; Radford, C.A. Exploring spatial and temporal trends in the soundscape of an ecologically significant embayment. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertucci, F.; Maratrat, K.; Berthe, C.; Besson, M.; Guerra, A.; Raick, X.; Lerouvreur, F.; Lecchini, D.; Parmentier, E. Local sonic activity reveals potential partitioning in a coral reef fish community. Oecologia 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.-T.; Nowacek, D.P.; Akamatsu, T.; Wang, K.-X.; Liu, J.-C.; Duan, G.-Q.; Cao, H.-J.; Wang, D. Diversity of fish sound types in the Pearl River Estuary, China. PeerJ 2017, 5, e3924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pieretti, N.; Farina, A.; Morri, D. A new methodology to infer the singing activity of an avian community: The Acoustic Complexity Index (ACI). Ecol. Indic. 2011, 11, 868–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sueur, J.; Farina, A.; Gasc, A.; Pieretti, N.; Pavoine, S. Acoustic Indices for Biodiversity Assessment and Landscape Investigation. Acta Acust. United. Acus. 2014, 100, 772–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, Y.F. Analysis and Visualization of Very-long-duration Acoustic Recordings of the Natural Environment. Ph. D. Thesis, Queensland University of Technology, Brisbane, Australia, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Phillips, Y.F.; Towsey, M.; Roe, P. Revealing the ecological content of long-duration audio-recordings of the environment through clustering and visualization. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0193345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruppé, L.; Clément, G.; Herrel, A.; Ballesta, L.; Décamps, T.; Kéver, L.; Parmentier, E. Environmental constraints drive the partitioning of the soundscape in fishes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 6092–6097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haver, S.M.; Klinck, H.; Nieukirk, S.L.; Matsumoto, H.; Dziak, R.P.; Miksis-Olds, J.L. The not-so-silent world: Measuring Arctic, Equatorial, and Antarctic soundscapes in the Atlantic Ocean. Deep Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2017, 122, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitcher, T.; Morato, T.; Hart, P.; Clark, M.; Haggan, N.; Santos, R. Seamounts: Ecology, fisheries and conservation. Fish Aquat. Resour. Ser. 2007, 12, 1–476. [Google Scholar]
- Giacomello, E.; Menezes, G.M.; Bergstad, O.A. An integrated approach for studying seamounts: CONDOR observatory. Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2013, 98, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christiansen, S.; Tempera, F. The Formigas Bank—A Potential MPA; WWF World Wildlife Fund: Washington, DC, USA, 2010; Available online: http://charlie-gibbs.org/charlie/NEA_Website/Publication/briefings/FormigasBank.pdf (accessed on 13 June 2020).
- Lammers, M.; Brainard, R.; Whitlow, W.; Mooney, T.; Wong, K. An Ecological Acoustic Recorder (EAR) for long-term monitoring of biological and anthropogenic sounds on coral reefs and other marine habitats. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2008, 123, 1720–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sousa-Lima, R.S.; Norris, T.F.; Oswald, J.N.; Fernandes, D.P. A Review and Inventory of Fixed Autonomous Recorders for Passive Acoustic Monitoring of Marine Mammals. Aquat. Mamm. 2013, 39, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obrist, M.K.; Pavan, G.; Sueur, J.; Riede, K.; Llusia, D.; Márquez, R. Bioacoustics approaches in biodiversity inventories. Abc Taxa 2010, 8, 68–99. [Google Scholar]
- McCauley, R.D.; Cato, D.H. Patterns of fish calling in a nearshore environment in the Great Barrier Reef. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B 2000, 355, 1289–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amorim, M.C.P.; Vasconcelos, R.O.; Marques, J.F.; Almada, F. Seasonal variation of sound production in the Lusitanian toadfish Halobatrachus didactylus. J. Fish Biol. 2006, 69, 1892–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carriço, R.; Silva, M.A.; Menezes, G.M.; Vieira, M.; Bolgan, M.; Fonseca, P.J.; Amorim, M.C.P. Temporal dynamics in diversity patterns of fish sound production in the Condor seamount (Azores, NE Atlantic). Deep-Sea Res. I. (under review).
- Farina, A.; Lattanzi, E.; Piccioli, L.; Pieretti, N. The SoundscapeMeter. Available online: http://www.iinsteco.org/research-and-technology.php (accessed on 10 April 2020).
- Sueur, J.; Pavoine, S.; Hamerlynck, O.; Duvail, S. Rapid acoustic survey for biodiversity appraisal. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e4065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2018; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 14 April 2020).
- Merchant, N.D.; Fristrup, K.M.; Johnson, M.P.; Tyack, P.L.; Witt, M.J.; Blondel, P. Measuring acoustic habitats. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2015, 6, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, M.; Erbe, C.; McCauley, R.; McWilliam, J.; Marley, S.; Gavrilov, A.; Parnum, I. Long-term monitoring of soundscapes and deciphering a usable index: Examples of fish choruses from Australia. Acoust. Soc. Am. Proc. Meet. Acoust. 2016, 27, 010023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desiderà, E.; Guidetti, P.; Panzalis, P.; Navone, A.; Valentini-Poirrier, C.A.; Boissery, P.; Gervaise, C.; Di Iorio, L. Acoustic fish communities: Sound diversity of rocky habitats reflects fish species diversity. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2019, 608, 183–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaatz, I.M.; Rice, A.N.; Loble, P.S. How Fishes Use Sound: Quiet to Loud and Simple to Complex Signaling. Ref. Model Life Sci. 2017, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, M.J.; McCauley, R.D.; Mackie, M.C.; Siwabessy, P.J.; Duncan, A.J. In situ source levels of mulloway (Argyrosomus japonicus) calls. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2012, 132, 3559–3568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radford, C.A.; Ghazali, S.; Jeffs, A.G.; Montgomery, J.C. Vocalisations of the bigeye Pempheris adspersa: Characteristics, source level and active space. J. Exp. Biol. 2015, 218, 940–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Amorim, M.C.P.; Vasconcelos, R.O.; Bolgan, M.; Pedroso, S.S.; Fonseca, P.J. Acoustic communication in marine shallow waters: Testing the acoustic adaptive hypothesis in sand gobies. J. Exp. Biol. 2018, 16, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, M.J.; Salgado-Kent, C.P.; Marley, S.A.; Gavrilov, A.N.; McCauley, R.D. Characterizing diversity and variation in fish choruses in Darwin Harbour. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2016, 73, 2058–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolgan, M.; Soularde, J.; Di Iorio, L.; Gervaise, C.; Lejeune, P.; Gobert, S.; Parmentier, E. Sea chordophones make the mysterious /Kwa/ sound: Identification of the emitter of the dominant fish sound in Mediterranean seagrass meadows. J. Exp. Biol. 2019, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankupellay, M.; Towsey, M.; Truskinger, A.; Roe, P. Visual fingerprints of the acoustic environment. The use of acoustic indices to characterize natural habitats. In 2015 Big Data Visual Analytics (BDVA), Hobart, TAS, Australia, 22–25 September 2015; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Parsons, M.J.; Salgado Kent, C.P.; Recalde-Salas, A.; McCauley, R.D. Fish choruses off Port Hedland, Western Australia. Bioacoustics 2016, 26, 135–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stonea, E. Separating the noise from the noise: A finding in support of the ‘niche hypothesis’, that birds are influenced by human-induced noise in natural habitats. Anthroös 2000, 13, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, B. Wild Soundscapes: Discovering the Voice of the Natural World; Wilderness Press: New Haven, CT, USA, 2002; p. 168. [Google Scholar]
- Vasconcelos, R.; Carriço, R.; Ramos, A.; Modesto, T.; Fonseca, P.J.; Amorim, C. Vocal behaviour predicts reproductive success in a teleost fish. Behav. Ecol. 2012, 23, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, M.B.; Mooney, T.A.; Partan, J.; Solow, A.R. Coral reef species assemblages are associated with ambient soundscapes. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2015, 533, 93–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohnenstiehl, D.R.; Lyon, R.P.; Caretti, O.N.; Ricci, S.W.; Eggleston, D.B. Investigating the utility of ecoacoustic metrics in marine soundscapes. J. Ecoacoust. 2018, 2, R1156L. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindseth, A.V.; Lobel, P.S. Underwater Soundscape Monitoring and Fish Bioacoustics: A Review. Fishes 2018, 3, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belghith, E.H.; Rioult, F.; Bouzidi, M. Acoustic Diversity Classifier for Automated Marine Big Data Analysis. In Proceedings of the IEEE 30th International Conference on Tools with Artificial Intelligence (ICTAI), Volos, Greece, 5–7 November 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Davies, B.F.R.; Attrill, M.J.; Holmes, L.; Rees, A.; Witt, M.J.; Sheehan, E.V. Acoustic Complexity Index to assess benthic biodiversity of a partially protected area in the southwest of the UK. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 111, 106019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haver, S.M.; Fournet, M.E.H.; Dziak, R.P.; Gabriele, C.; Gedamke, J.; Hatch, L.T.; Haxel, J.; Heppell, S.A.; McKenna, M.F.; Mellinger, M.K.; et al. Comparing the Underwater Soundscapes of Four U.S. National Parks and Marine Sanctuaries. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malfante, M.; Mars, J.I.; Dalla Mura, M.; Gervaise, C. Automatic fish sounds classification. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2018, 143, 2834–2846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieira, M.; Fonseca, P.J.; Amorim, M.C.P.; Teixeira, C.J.C. Call recognition and individual identification of fish vocalizations based on automatic speech recognition: An example with the Lusitanian toadfish. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2015, 138, 3941–3950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, M.; Pereira, B.P.; Pousão-Ferreira, P.; Fonseca, P.J.; Amorim, M.C.P. Seasonal variation of captive meagre acoustic signalling: A manual and automatic recognition approach. Fishes 2019, 4, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monczak, A.; Ji, Y.; Soueidan, J.; Montie, E.W. Automatic detection, classification, and quantification of sciaenid fish calls in an estuarine soundscape in the Southeast United States. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0209914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Carriço, R.; Silva, M.A.; Vieira, M.; Afonso, P.; Menezes, G.M.; Fonseca, P.J.; Amorim, M.C.P. The Use of Soundscapes to Monitor Fish Communities: Meaningful Graphical Representations Differ with Acoustic Environment. Acoustics 2020, 2, 382-398. https://doi.org/10.3390/acoustics2020022
Carriço R, Silva MA, Vieira M, Afonso P, Menezes GM, Fonseca PJ, Amorim MCP. The Use of Soundscapes to Monitor Fish Communities: Meaningful Graphical Representations Differ with Acoustic Environment. Acoustics. 2020; 2(2):382-398. https://doi.org/10.3390/acoustics2020022
Chicago/Turabian StyleCarriço, Rita, Mónica A. Silva, Manuel Vieira, Pedro Afonso, Gui M. Menezes, Paulo J. Fonseca, and Maria Clara P. Amorim. 2020. "The Use of Soundscapes to Monitor Fish Communities: Meaningful Graphical Representations Differ with Acoustic Environment" Acoustics 2, no. 2: 382-398. https://doi.org/10.3390/acoustics2020022
APA StyleCarriço, R., Silva, M. A., Vieira, M., Afonso, P., Menezes, G. M., Fonseca, P. J., & Amorim, M. C. P. (2020). The Use of Soundscapes to Monitor Fish Communities: Meaningful Graphical Representations Differ with Acoustic Environment. Acoustics, 2(2), 382-398. https://doi.org/10.3390/acoustics2020022




