Abstract
The tailoring of the surface properties of cellulose nanocrystals (CNCs) to meet various requirements in environmental, food, and material areas has always been of great interest. In this study, the surface chemistry of CNCs was noncovalently modified by cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB), followed by characterizations and an investigation into its application as a coating material for interfacial interaction over various substrates. Due to the CTAB modification, the surface charge of the CNCs was neutralized, resulting in an increased size of each nanocrystal at the aqueous status and the aggregated microfibers when dried up. The CTAB modification not only decreased the crystallinity of the samples from 48.57% to 9.12%, but also reasonably hydrophobized the CNCs and decreased their total surface energy. Finally, the adsorption behavior of the CNCs and CTAB-CNCs over nonionic, anionic, and cationic polymers was investigated by ellipsometry. Based on the thickness of the CNC and CTAB-CNC layers over 2-Hydroxyethyl cellulose (HEC), carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC), and polyethyleneimine (PEI), we proposed that the adsorption behavior was overall influenced by electrostatic interaction, hydrogen bonding, and van der Waals forces, and the thickness of the adsorbed layers could be impacted by both the surface charge and the size of the crystals.
1. Introduction
Cellulose (annual production of ~1.5 × 1012 tons/year), is the most abundant and inexhaustible natural polymer in the world and is regarded as a promising substitute for traditional fossil based feedstocks [1,2]. Rod-shaped cellulose nanocrystals (CNCs) are generally prepared by removing the amorphous regions of cellulose fibers via sulfuric acid hydrolysis while keeping the unique properties of cellulose. The highly crystalline CNCs exhibit excellent properties, such as nanoscale dimensions (w: 2–10 nm, L: 100–600 nm) [3], high surface area (~250 m2/g) [4], low density (~1.61 g/cm3) [5] materials with high elastic modulus (~100–200 GPa) [6], chirality [7], renewability, and biodegradability. Therefore, CNCs have been widely investigated as emerging nanomaterials for the applications of reinforced nanocomposites, biomedicals, optically tunable materials, and emulsion stabilizers [8,9,10,11,12].
With the three hydroxyl functional groups on each anhydroglucose unit (AGU), CNC molecules are hydrophilic with good dispersion and beneficial interactions with hydrophilic polymers such as PVA, PEO, starch, etc. [13,14,15]. However, the incorporation of CNCs in hydrophobic polymers is hindered due to its hydrophilicity. Nevertheless, those active hydroxyl groups on CNCs also provide reactive sites for various surface modifications and functionalization. Hence, CNCs have been extensively modified by chemical treatments, including esterification, etherification, oxidation, silylation, polymer grafting, etc. [6]. On the other hand, noncovalent modifications of CNCs, such as the use of metal ions, surfactants, and polymer coatings, have also attracted considerable attention. In particular, the negative surface charge of CNCs, due to the sulfate-half ester groups, facilitates the adsorption of cationic functional groups. CNCs also have been employed as versatile bio-templates for the fabrication of silver nanoparticles (Ag NPs) [16] and gold nanoparticles [17], etc. Additionally, some cationic surfactants have also been adsorbed onto the surface of CNCs to further widen the applications of CNCs. Salajkov et al. hydrophobically modified CNCs with four quaternary ammonium cation surfactants bearing long alkyl, phenyl, glycidyl, and diallyl groups, demonstrating the feasibility of surfactant-modified CNCs to form well-dispersed nanocomposites with non-polar polymers [18]. Gong et al. modified CNCs with phenyltrimethylammonium chloride (PTAC) to increase the amphiphilicity of the particles and further used the PTAC-CNCs as a Pickering emulsion stabilizer [19]. Two other cationic alkyl ammonium surfactants, didecyldimethylammonium bromide (DMAB) and cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB), were also employed to modify the surface chemistry of CNCs, indicating that the in situ modifications of CNCs could help to tailor Pickering emulsions by monitoring the addition of the surfactant-modified CNCs.
With its long alkyl chain and quaternary ammonium head, CTAB has been widely investigated among the cationic surfactants used for surface modification of CNCs. Kaboorani and Riedl investigated the chemical and structural characterizations of CNCs before and after modification by CTAB [20]. Abitbol studied the adsorption behavior between CNCs and CTAB and indicated that ionic strength was the main factor that influenced the coupling efficiency, in which increasing the ionic strength screened electrostatic interactions that led to decreased surfactant adsorption [21]. Another study compared the influence of cationic surfactant CTAB and anionic surfactant sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) on the zeta potential of CNCs [22]. The CTAB-modified CNCs also enhanced the catalytic performance of Ag NPs to reduce 4-nitrophenol, owing to the improved dispersity and narrow distribution of Ag NPs in the catalytic system [23].
The characterization of the adsorption behavior between CNCs and other materials is of critical importance to tailor the surface properties for different applications. So far, ellipsometry analysis has been used to determine the thickness of layer-by-layer (LBL) assembled CNC film and Langmuir–Blodgett CNC film with good agreement to SEM and AFM results [24,25]. Despite numerous studies on the modifications of CNCs, the adsorption behavior between CNC-based materials and other polymers using ellipsometry analysis, according to our knowledge, has not been reported. As for CTAB-CNCs, an investigation of the adsorption behavior of CTAB-CNCs with other polymers is needed. In the current study, the surface properties of CNCs were tailored by various concentrations of CTAB, followed by a systematic investigation of the molecular interactions, crystallinity, zeta potential evolution, as well as morphology observations. More importantly, the interfacial behavior as well as the surface energy of the modified CNCs were carefully studied by contact angle measurement. Finally, the interactions between CTAB-CNCs and different types of polymers, such as anionic polymer carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC), nonionic polymer 2-Hydroxyethyl cellulose (HEC), and cationic polyethyleneimine (PEI), were investigated by ellipsometry analysis. This study aimed to probe the interfacial properties and adsorption behavior of CTAB-CNCs with other materials, thus providing new insights for expanding the applications of CTAB-CNCs.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Spray-dried CNCs were supplied by InnoTech Alberta, Edmonton, AB, Canada. Northern Bleached Hardwood Kraft (NBHK) was utilized as a feedstock for CNC production. Feedstock slurry was first hydrolyzed in 64% concentrated sulfuric acid at 65 °C and then neutralized with NaOH. Solid rejects, dissolved organics, and salts were separated after a series of centrifuging and filtration stages, and the purified CNC suspension with a conductivity of <100 μS/cm was obtained [26].
Hexadecyltrimethylammonium bromide {[(C16H33)N(CH3)3]Br, Mw = 364.5, with >99% purity and critical micelle concentration = 0.92–1.0 mM)} [27], (catalog number H6269) synonymously called CTAB, sodium salt of carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC, Mw = 700 kDa), (catalog number 419838), 2-Hydroxyethyl cellulose (HEC, Mw = 720 kDa), (catalog number 434973), linear polyethyleneimine (PEI, Mw = 25 kDa), (catalog number 937762) and all other chemicals were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich Canada Ltd. (Oakville, ON, Canada) and used as received.
2.2. Preparation of CTAB-Modified CNCs (CTAB-CNCs)
CTAB-CNCs were prepared by mixing 1000 mL of spray-dried CNC aqueous suspension (0.5 wt.%) and 1000 mL of CTAB aqueous solutions (0.25 to 0.32 mM), followed by continuous stirring with a stainless 4 blade electric overhead stirrer at room temperature at 500 rpm for 24 h. In all cases, CTAB was added below its critical micelle concentration of 0.92–1.0 mM. The excess CTAB was then removed from the suspension via crossflow filtration until the conductivity of the filtrate became constant. The obtained CTAB-CNCs were then freeze-dried and kept for further usage. The samples were denoted as CTAB-CNCs-X, as X was the concentration of the CTAB aqueous solutions (0.25–32 mM).
2.3. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
FTIR spectra of the pristine CNCs and CTAB-CNCs were recorded on a Nicole iS 50 FTIR spectrometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) in attenuated total reflection (ATR) mode and equipped with a diamond probe. The samples were ground into powders and kept in a vacuum oven at 60 °C for 24 h before the test. All the samples were tested at an average of 64 scans at 4 cm−1 resolution and kept at 25 °C.
2.4. Wide-Angle X-ray Diffraction (WAXD)
The crystallinity of CNCs and CTAB-CNCs was studied using the wide-angle X-ray diffraction measure (WAXD) on an X-ray diffractometer (Ultimate IV, Rigaku, Tokyo, Japan). The diffracted intensity of Cu Kα radiation (λ = 0.1542 nm) at 40 kV and 44 mA was recorded in the range of 2θ from 10° to 40° with a scanning rate of 3°·min−1. All the samples were cut into powders in vials and kept in a vacuum oven at 60 °C for 24 h before the test. The Segal crystallinity index χ (%) was calculated according to the following equation [28,29].
where It is the total intensity of the (200) lattice diffraction and Ia is the amorphous intensity of diffraction (in the same units) at 2θ = 18°.
2.5. Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS)
The zeta potential and size of the pristine CNCs and CTAB-CNCs were measured by DLS using a Zetasizer Nano-ZS ZEN3600 (Malvern Instruments Ltd., Malvern, UK). Colloidal suspensions of CNC samples at 0.05 wt.% were prepared by dispersing the material in deionized water followed by sonication (Branson ultrasonic cleaner model 1510, frequency 40 kHz) for 3 min. All measurements were carried out at room temperature with neutral pH in triplicate.
2.6. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
The morphology of the pristine CNCs and CTAB-CNCs-2 in DI water was observed by the TEM imaging technique. The samples (0.05 wt.%) were blotted onto the glow-discharged carbon-coated grid (3 nm thickness) and plug frozen. Observation of the samples was performed under CryoTEM conditions.
2.7. Scanning Electrical Microscopy (SEM)
The morphology of the pristine CNCs and CTAB-CNCs-2 after freeze-drying was characterized by the SEM imaging technique. The freeze-dried samples were coated with gold (3 nm thickness) and visualized on a Hitachi S-4800 Field Emission Gun SEM (Hitachi High-Technologies Canada, Inc., Toronto, ON, Canada).
2.8. Spin Coating of the CNC and CTAB-CNC Dispersions
To investigate the interfacial properties, CTAB-CNC and CNC dispersions were spin-coated over glass slides for contact angle measurement. Before this, the CNCs and CTAB-CNCs-2 were dispersed in DI water by rigorous stirring over 24 h at 500 rpm at room temperature to form dispersions of 0.05 wt.%, respectively. The dispersed suspensions were then coated over a glass slide using the spin coating technique. The P6708D Spin Coater (Specialty Coating Systems, Inc., Indianapolis, IN, USA) was utilized for the spin coating. The rotational velocity was 5000 rpm with an initial velocity of 100 rpm. For the coating of the CNC dispersion, an initial coating of PEI (100 ppm) was applied over the glass surface.
2.9. Wettability and Surface Energy
Wettability and surface-free energy analyses were performed by measuring the contact angles of the spin-coated samples using the contact angle analyzer FTA-200. To calculate the surface energy ( of the CNCs and CTAB-CNCs-2, diiodomethane, DI water, and formamide were employed as the droplet liquids. The test methods with relevant theories for CNCs are reviewed in great detail by Gong et al. [30]. The surface energy parameters of the three liquids are shown in Table 1. The measurement for each sample was repeated for at least three samples with three tests for each sample.

Table 1.
The surface energy parameters of the three liquid probes [30].
2.10. Immersion Coating of CNC and CTAB-CNC Dispersions
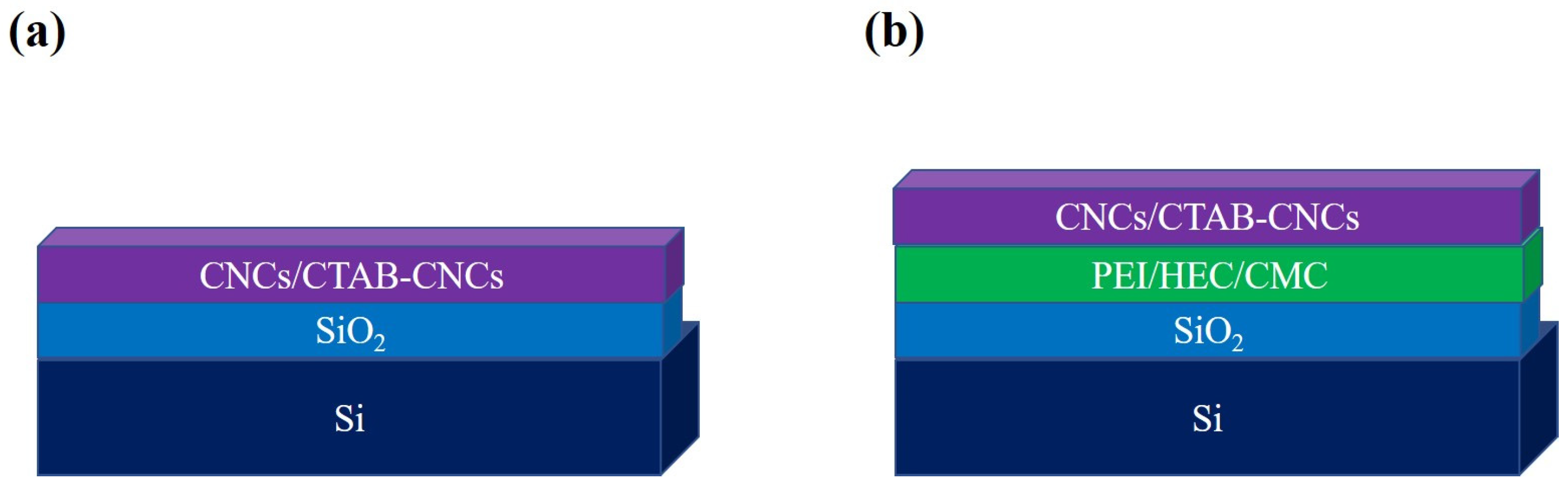
To investigate the adsorption behavior and interfacial interactions of CNC-based materials, an immersion coating technique was applied. Two different coating models were constructed via direct coating and polymer-based coating, respectively. Firstly, the direct coating of CNCs or CTAB-CNCs-2 over the oxidized silicon wafer was carried out to form a three-layered structure as denoted in Figure 1a. The cleaned oxidized silicon wafers were directly immersed in the CNC or CTAB-CNCs-2 dispersions (0.05 wt.%) overnight and dried inside a desiccator. Secondly, the cleaned oxidized silicon wafers were first immersed into different types of polymer solutions (CMC, HEC, or PEI) for 24 h and dried inside a desiccator to form the polymer-based substrates, followed by immersion in the CNC or CTAB-CNCs-2 dispersions (0.05 wt.%) overnight and drying inside a desiccator. Hence, a four-layered structure as shown in Figure 1b was fabricated.
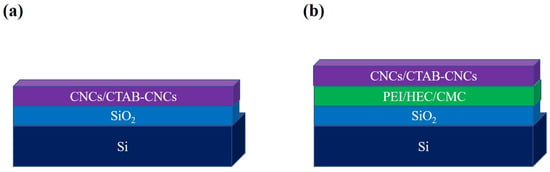
Figure 1.
Scheme of the immersion coating of CNCs and CTAB-CNCs. (a) Direct coating, and (b) polymer-based coating. The scheme does not have any scaled meaning.
2.11. Ellipsometry
There are two angle parameters (ψ and Δ) which are measured in ellipsometry. The data were presented in Supplementary Materials. Those ellipsometric angles vary with the change in the state of polarization when a light beam is reflected on a surface. Information about adsorbed surface layers, i.e., adsorbed amount and thickness are obtained. A detailed description of the principles of ellipsometry can be found elsewhere [31]. The optical measurements of the complex refractive index were performed in air at room temperature using an automated angle Variable Angle Spectroscopic Ellipsometer (VASE ellipsometry) M-2000 from J. A. Woollam Co., Lincoln, NE, USA. For each sample, measurements were performed at six different angles (45°, 50°, 55°, 60°, 65°, and 70°) for a full wavelength (370 nm to 1000 nm).
3. Results
The results of the CTAB modification of CNCs are presented in three sections. First, in Section 3.1 we report how the surface chemistry of CNCs changes with the adsorption of CTAB molecules. In Section 3.2 we show how the CTAB treatment affects the morphology, wettability, and surface energy of CNCs. Finally, in Section 3.3 we present the ellipsometric study to measure the adsorption behavior of various substances on CNCs and CTAB-CNCs.
3.1. Adsorption of CTAB Molecules on CNCs
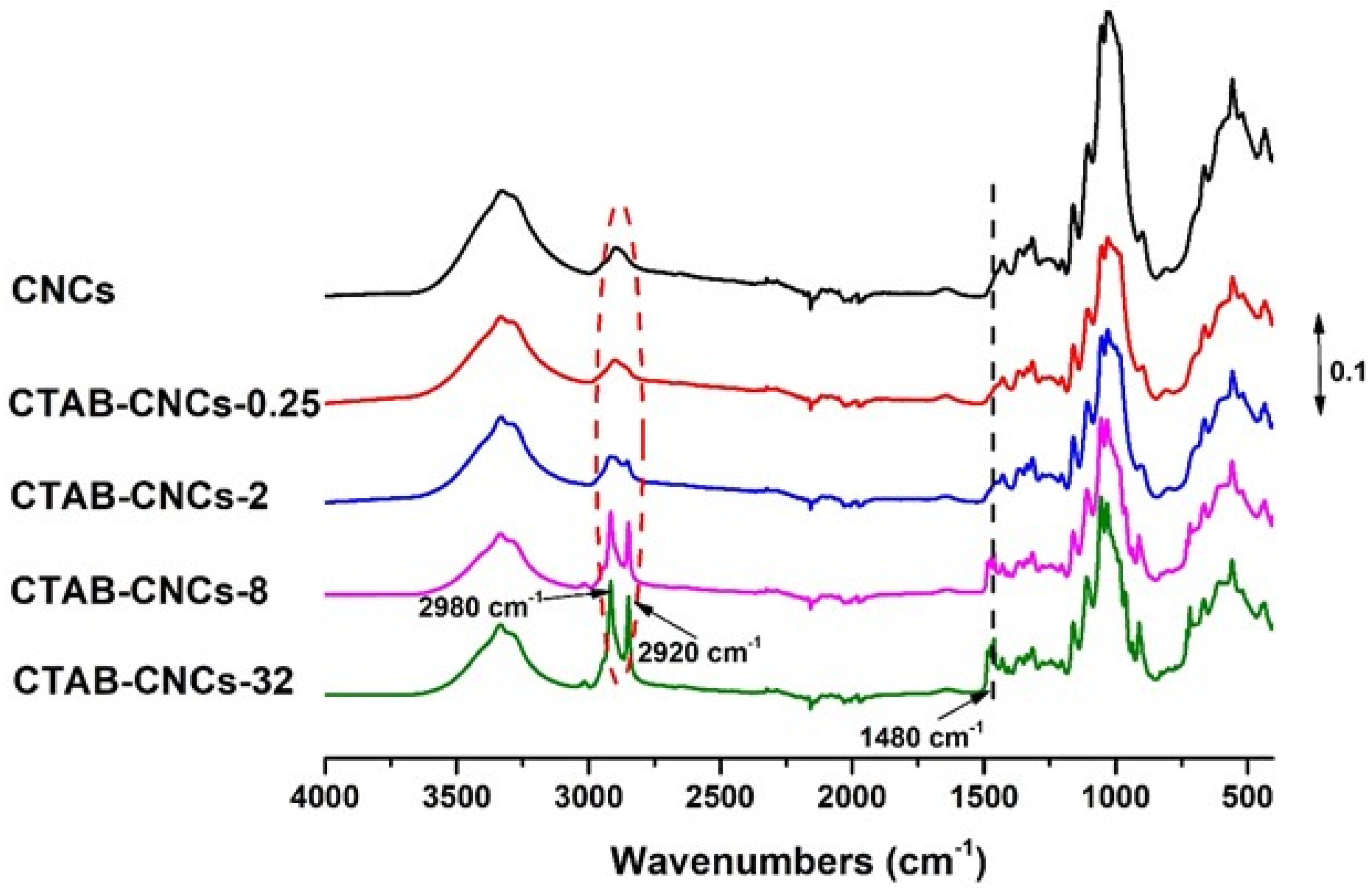
Negatively charged sulfate half-ester groups on CNC surfaces make CNCs ideal candidates for the non-covalent adsorption of CTAB. Due to the positively charged quaternary ammonium head and the hydrophobic alkyl long chain in CTAB, the surface properties of CNCs could be well tailored by adjusting the amount of CTAB used. Therefore, in the current study, CNCs in suspensions were treated with various concentrations of CTAB to form samples coded as CTAB-CNCs-X, where X was the concentration of the CTAB aqueous solutions (0.25–32 mM). To study the molecular interaction between CNCs and CTAB, FTIR spectra of CNCs and CTAB-CNCs were recorded. As shown in Figure 2, CNCs showed characteristic absorbance at 3340 cm−1 (-OH stretching), 2920 cm−1 (-CH2 stretching), and 1050 cm−1 (vibration of pyranose ring ether) [3,19]. When modified with CTAB, the absorbance at 2920 cm−1 (-CH2 stretching) was increased, which was due to the CTAB modification of CNCs that introduced more -CH2 into the molecules. Additionally, a peak at 2980 cm−1 (-CH3 stretching) appeared and became more significant with higher amounts of CTAB used, indicating that -CH3 was successfully introduced by the CTAB modification, and higher amounts of CTAB used resulted in a higher adsorption of CTAB onto the surface of CNCs. More importantly, compared with the spectra of pristine CNCs, a new absorbance band at 1480 cm−1 appeared, which was ascribed to the symmetric vibration of the head group methylene moiety (N+-CH3) [21,32]. It was noted that the absorbance at 1480 cm−1 became more pronounced with the increase in CTAB used, indicating that higher amounts of CTAB used could result in a higher adsorption of CTAB onto the surface of CNCs, which was in good accordance with the increased absorbance of -CH3 at 2980 cm−1. All the above information indicated that the surface modification of CNCs with CTAB was successfully carried out.
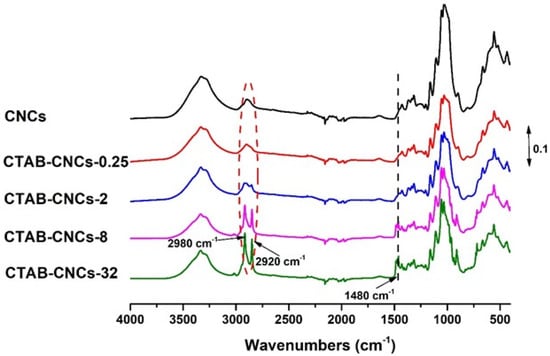
Figure 2.
The FTIR spectra of pristine CNCs and CTAB-CNCs with various concentrations of CTAB were used.
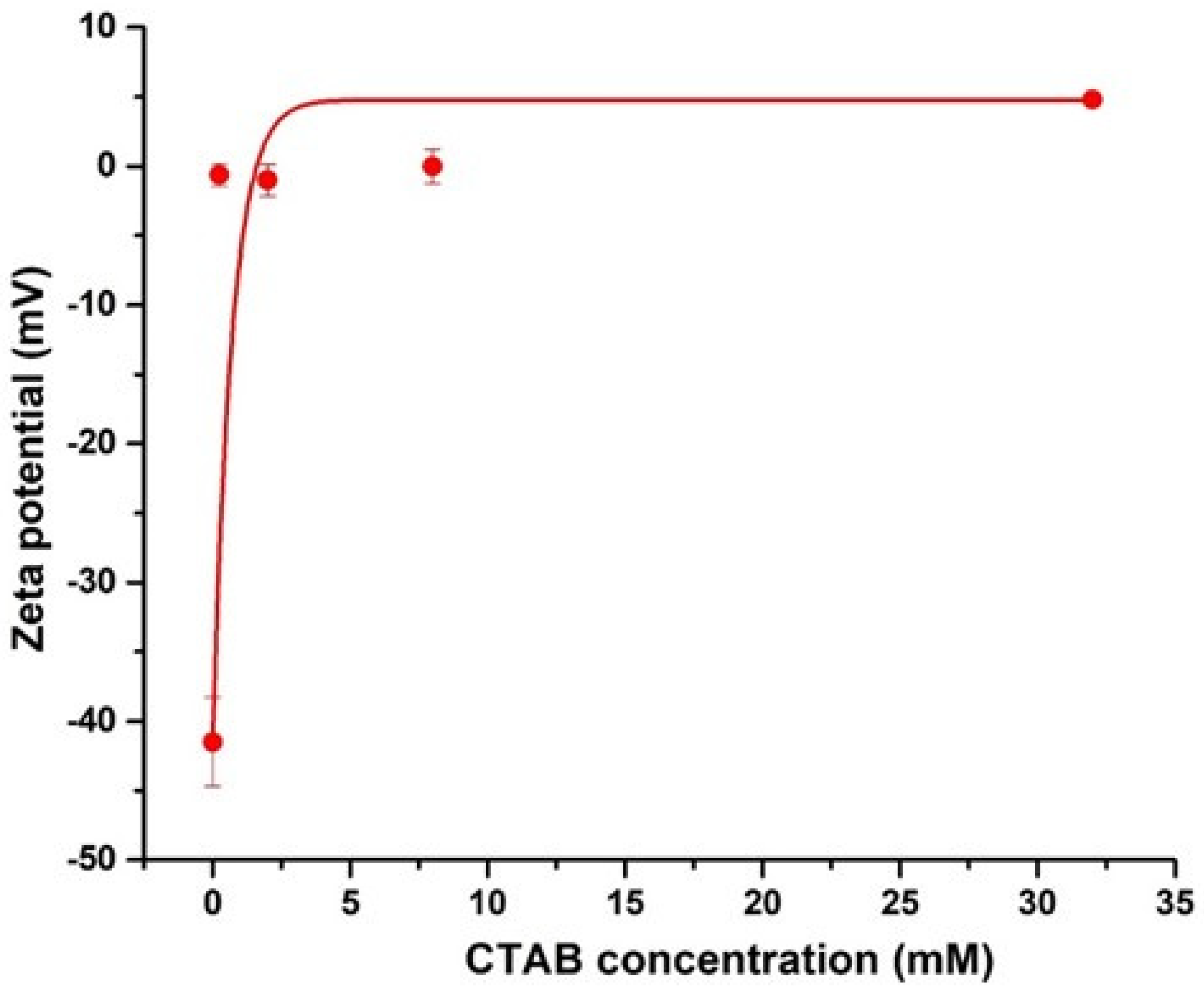
To verify the change in the surface characteristics of CNCs, the zeta potentials of CNCs and CTAB-CNCs in DI water are presented in Figure 3. As measured, the pristine CNCs sourced from a spray-dried sample had a zeta potential of −41.5 ± 3.2 mV. When compared with the never-dried TEMPO-oxidized CNCs, sulfated CNCs [3,19] or freeze-dried sulfated CNCs [33], the spray-dried half-ester sulfated CNCs exhibited a relatively higher zeta potential, which was due to the thermal drying process. The drying process by convective heating involves the removal of water molecules and the reconstruction of the molecular interaction, especially the rebuilding of the hydrogen bonding network in CNCs. It is believed that the never-dried CNC suspension avoids the drying and structural reconstruction process, while the freeze-drying process maintains the maximum hydrogen bonding system at the frozen state, and the reconstruction of hydrogen bonding during the drying process at the frozen state happens less frequently than in the spray drying process. The greater reconstruction of hydrogen bonding during the spray drying process leads to significant changes in surface properties, resulting in more aggregates and larger CNCs. Despite the relatively higher zeta potential of the spray-dried CNCs, the CNCs in the current study still showed a zeta potential of lower than −30 mV, indicating that the spray-dried CNCs were colloidally stable in DI water [34]. As the CTAB concentration increased, the absolute value of zeta potentials of the CTAB-CNCs sharply decreased, which was due to the screening effect of NH4+ counterion on the negatively charged CNC surface that neutralized the surface charge. The system also became unstable. Thus, the electrostatic attraction between the positively charged CTAB and the negatively charged CNCs played an important role in CTAB modification.
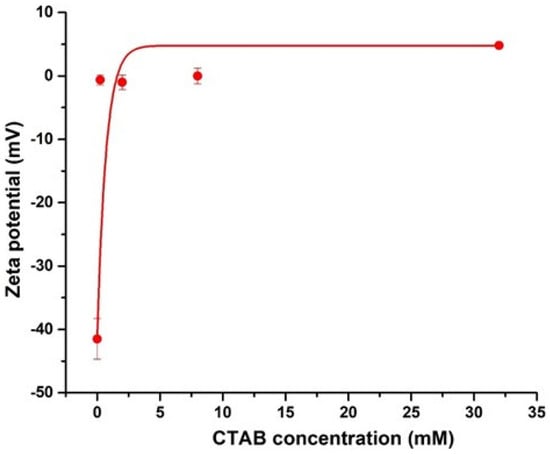
Figure 3.
Zeta potentials of CNCs (0.05 wt.%) and CTAB-CNCs (0.05 wt.%) as a function of the concentration of CTAB used.
Additionally, the hydrodynamic diameters of the pristine CNCs and CTAB-CNCs-2 in DI water were measured by dynamic light scattering (DLS). As a result, the CNCs had an average size of 221.6 ± 12.71 nm, while the CTAB-CNCs-2 showed an average size of 4634 ± 184 nm, which was due to the surface modification that significantly neutralized the surface charge of CNCs and reduced the electrostatic repulsion between particles, resulting in the aggregation of the particles.
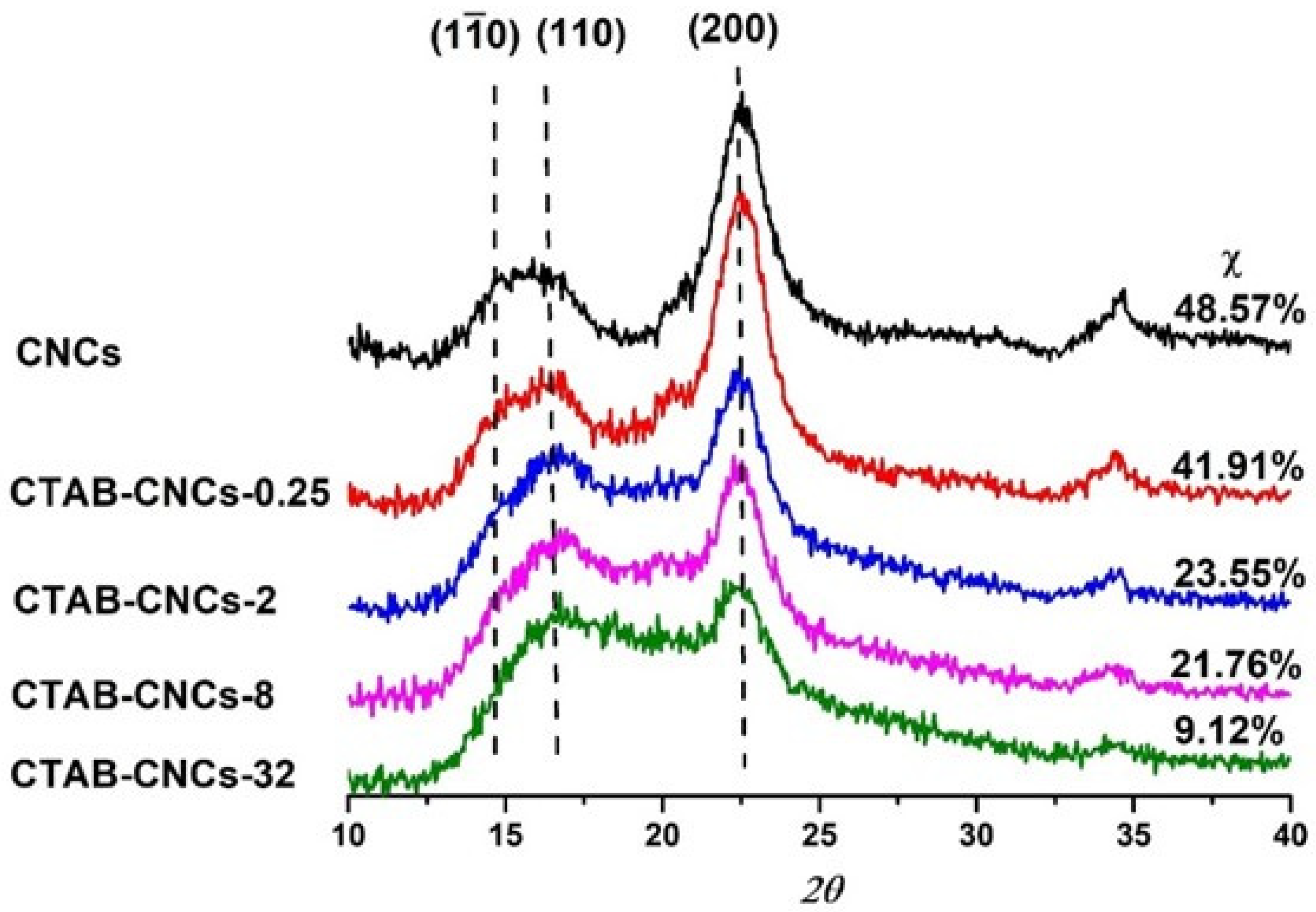
To investigate the effect of CTAB modification on the crystallinity of CNCs, the wide-angle x-ray diffraction pattern (WAXD) of pristine CNCs and CTAB-CNCs were studied as a function of CTAB concentration ranging from 0.25–32 mM. As observed in Figure 4, the spectra patterns exhibited broad amorphous humps and crystalline peaks, indicating the semi-crystalline structure of all the samples [35]. The pristine CNCs showed the characteristic peak at 2θ = 22.6°, 2θ = 14.9°, and 2θ = 16.7°, ascribing to the (200), (110), and (110) planes of cellulose Iβ [36]. Compared with the pristine CNCs, the CTAB-CNCs exhibited a weaker peak at 2θ = 22.6°, indicating a reduction in the crystallinity of the modified samples. Moreover, the peak at 2θ = 22.6° decreased with an increase in CTAB used, which was due to more CTAB adsorbed onto the surface of CNCs which decreased the overall crystallinity. Meanwhile, it was noted that the peak of the CTAB-CNCs at 2θ = 14.9° became weak and even disappeared as higher CTAB was used, indicating that the adsorption of CTAB onto the surface of CNCs interrupted the original molecular interaction. As is well known, CNCs form into highly crystalline structures by strong hydrogen bonding between cellulose molecules; this balanced interaction system could be interrupted by surface modification using CTAB, as on one hand, the electrostatic repulsion between particles weakens to form CTAB-CNC aggregates, while on the other hand, the long alkyl chains of CTAB randomly distributed along the CNC surface form into a hydrophobic layer and decrease the crystallinity of the modified CNCs [37]. As labeled in Figure 4, the crystallinity index χ was calculated to be 48.57%, 41.91%, 23.55%, 21.76%, and 9.12% for pristine CNCs, CTAB-CNCs-0.25, CTAB-CNCs-2, CTAB-CNCs-8, and CTAB-CNCs-32, respectively. The crystallinity index of the pristine CNCs was lower than most CNCs prepared by sulfuric acid hydrolysis. This could be due to the spray drying process that leads to randomly oriented CNC aggregates with a more amorphous structure. It was noted that the χ of CTAB-CNCs was lower than that of the pristine CNCs and the χ could be tailored by the amount of CTAB used. As shown in Figure 4, the χ decreased from 48.57% of pristine CNCs to 41.91% of CTAB-CNCs-0.25, and to 9.12% of CTAB-CNCs-32, indicating that CTAB modification has a significant influence on the crystallinity of CNCs. As CTAB covered the surface of CNCs, the electrostatic repulsion between CTAB-CNCs decreased, so that the individual CTAB-CNCs randomly interacted with each other and formed into a relatively disordered structure. In addition, CTAB presence has a dilution effect which causes an increase in the contribution in the amorphous part. On the other hand, the long alkyl chains of CTAB attached to the surface of CNCs also could have formed a hydrophobic layer that increased the amorphous structure of the modified CNCs [37].
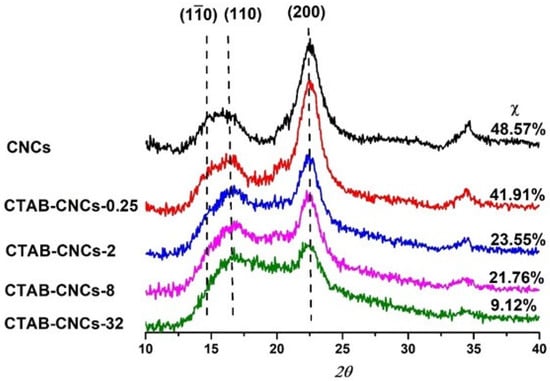
Figure 4.
WAXD spectrum of pristine CNCs and CTAB-CNCs with various CTAB concentrations.
3.2. Effects of CTAB Adsorption on CNCs
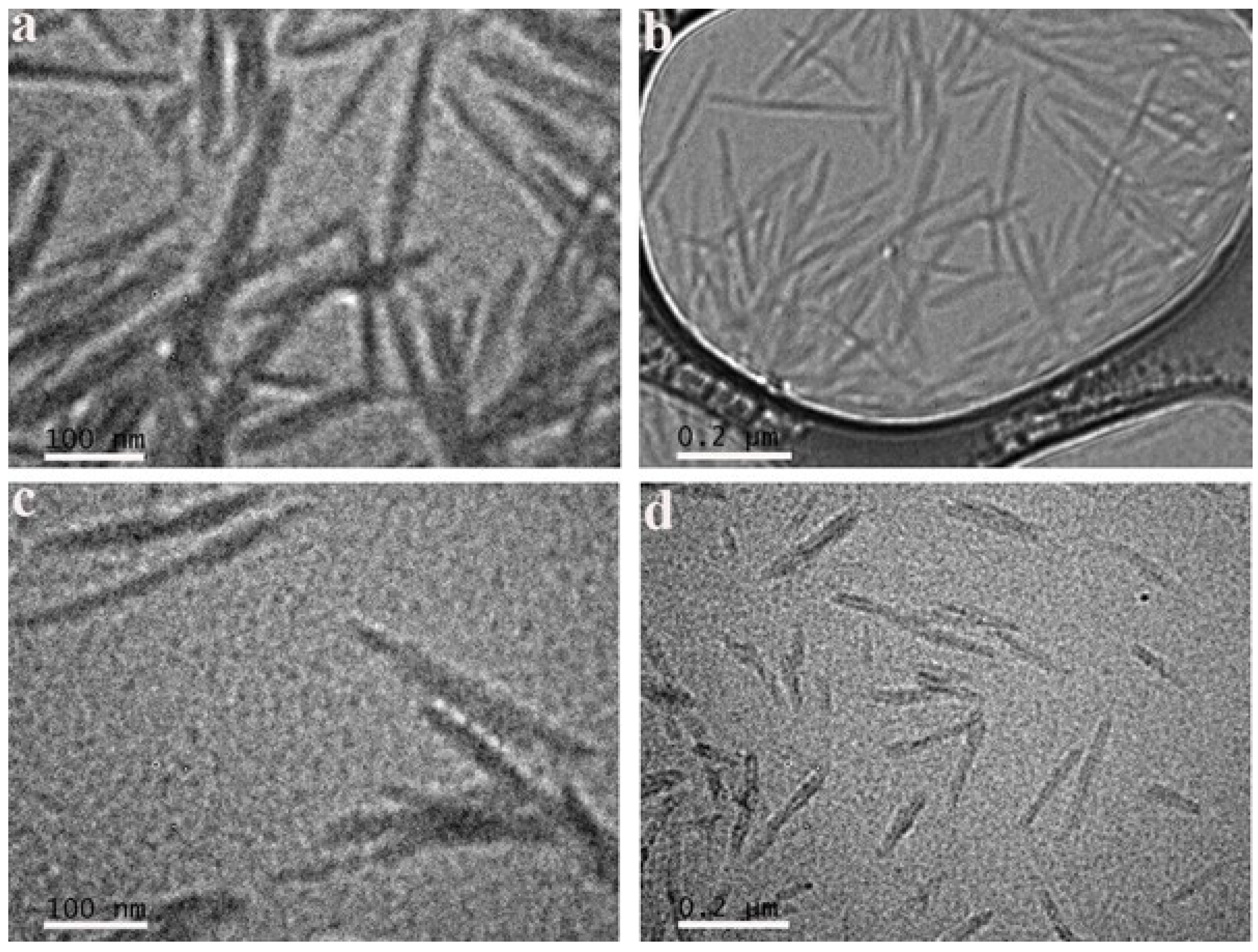
The morphology of CNCs and CTAB-CNCs-2 in DI water was observed by transmission electronic microscopy (TEM). As shown in Figure 5, pristine CNCs were homogenous in the aqueous suspension (similar in shape with a narrow distribution of the length and width), which was in good accordance with the zeta potential of pristine CNCs (−41.5 ± 3.2 mV). An analysis of the CNCs using “Image J” software demonstrated that they had an average length and width of 178.3 ± 29.9 nm and 17.5 ± 3.4 nm (n = 30), respectively. When modified by CTAB, the CTAB-CNCs aqueous suspension was still homogenous, but the CTAB-CNCs were not uniformly shaped and showed a relatively broader distribution of length and width, which was due to the CTAB modification on the surface of CNCs. As the positively charged CTAB attracted onto the negatively charged CNCs in DI water, the initial inter-particle interactions (hydrogen bonding, electrostatic repulsion, and van der Waals forces, etc.) were interrupted. The new inter-particle interactions (hydrogen bonding, electrostatic repulsion/attraction, hydrophobic interaction, van der Waals forces, etc.) were reconstructed, leading to the non-uniform CTAB-CNCs dispersions. Further analysis of the CTAB-CNCs indicated that they had an average length and width of 199.2 ± 42.4 nm and 26.3 ± 4.0 nm (n = 30), respectively. As measured by DLS, the CNCs had an average size of 221.6 ± 12.71 nm, while the CTAB-CNCs-2 showed an average size of 4634 ± 184 nm due to the aggregation. However, the TEM observation revealed that the lengths of the pristine CNCs and CTAB-CNCs were both shorter. It is well known that dynamic light scattering (DLS) only evaluates the hydrodynamic diameter. Therefore, the results of DLS could be much higher than the data obtained by direct TEM observation.
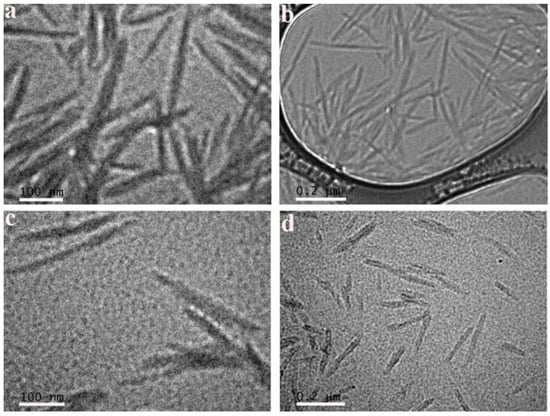
Figure 5.
TEM images of CNCs (a,b) and CTAB-CNCs-2 (c,d) in DI water at different magnifications.
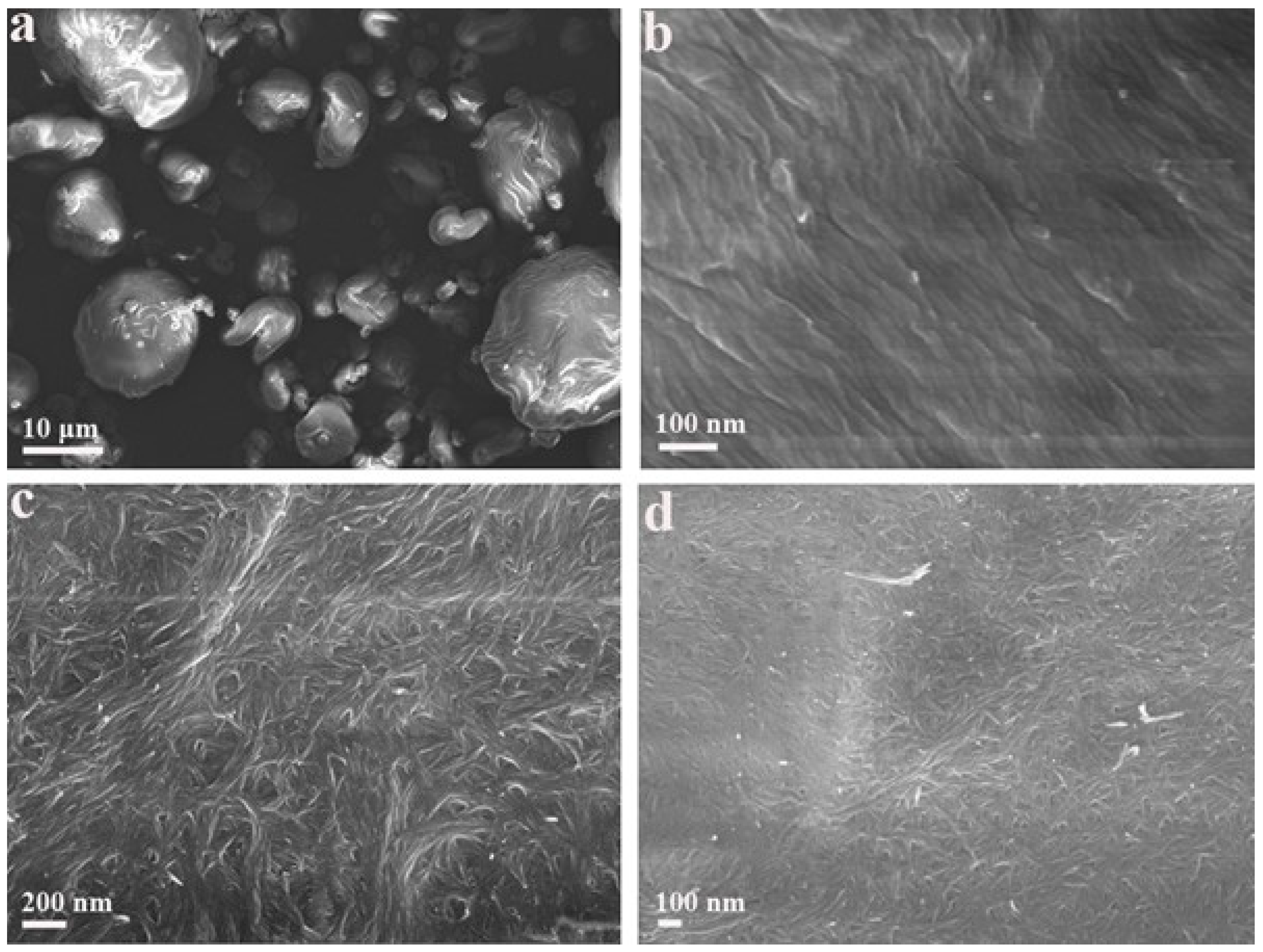
To observe the samples in a dried state, scanning electrical microscopy was employed for the morphology characterization of pristine CNCs and CTAB-CNCs. As shown in Figure 6, the pristine CNCs and CTAB-CNCs exhibited significantly different morphologies. For comparison purposes, Figure 6b,d, which had the same magnifications, were used. The pristine CNCs formed into large aggregates with sizes ranging from several microns to more than 10 microns. When zoomed in, the pristine CNCs formed into fibers with diameters of around 30–50 nm and then packed tightly together to form a uniform network. Figure 6c,d showed that CTAB-CNCs particles aligned to form longer units first and then aligned particles interacted with each other to form a web-like structure. More interestingly, the CTAB-CNCs were observed to interact with each other, indicating the flexibility of the CTAB-CNC fibers. This could be due to the CTAB modification on the surface of CNCs—as the previous inter-particle interactions were interrupted and the new balance was constructed, the flexibility of the CNCs was changed.
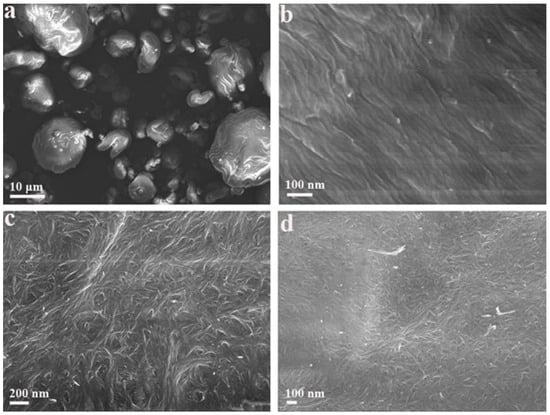
Figure 6.
SEM images of the pristine CNCs (a,b), CTAB-CNCs-2 (c,d) at different magnifications.
Dispersion and acid-base interactions govern the wetting of CNCs by solvents as well as adhesion by polymers. There are techniques, such as inverse gas chromatography (IGC), microcalorimetry, IR and NMR spectroscopy, and wetting, that characterize the interaction potentials of solvents, polymers, and solid surfaces [38]. Among those techniques, the most common is the wetting technique, which allows for the dispersion and acid-base components of surface energies as discussed in the previous section. There are only a few methods proposed for wetting testing, one of which was developed by van Oss, Chaudry, and Good, and is referred to as the vOCG theory [39]. It is worth noting that problems exist while calculating the Lewis acid-base properties of surfaces from the contact angle data following the vOCG theory. The results are strongly dependent on the choice of selected standard liquids for contact angle measurements and give high γ− values. Nevertheless, DI water, diiodomethane (dispersion forces), and formamide (Lewis acid probe) were selected as standard liquids, and their contact angles (θ) on glass substrate, CNC thin films, and CTAB-CNCs-2 thin films were measured (Table 2). It was noted that the contact angle of water on CTAB-CNCs-2 was greater than that of glass substrate and pristine CNC thin films, which indicates the increased hydrophobicity of the CTAB-CNCs. According to the vOCG theory, γd, γ+, and γ− components of solids can be determined by measuring the contact angles of three different liquids with known surface tension components on the solid surface. In this study, the polar and dispersive parameters for the three liquids are presented in Table 1. The polar and dispersive components of the solids were measured and shown in Table 3. The total surface energy γs is the sum of γd and γp. The total surface energy of the solids exhibited a sequence of CNCs > CTAB-CNCs-2. It was noted that both the γd and γp of the CTAB-CNCs-2 film decreased when compared with that of the CNC films, which was due to the surface modification using CTAB that interrupted the original molecular interactions. More importantly, the contribution of γd to the total surface energy γs was much larger than that of γp both for the CNC and CTAB-CNCs-2 films. Additionally, the γp of the CTAB-CNCs-2 significantly decreased when compared with its two counterparts, which was due to the CTAB modification on the surface of CNCs decreasing the polarity of the molecules by neutralizing the surface charge; on the other hand, the long alkyl chains increased the hydrophobicity of the obtained product [40]. The γs of CNCs was 70.76 mJ/m2. However, the γs of CTAB-CNCs-2 significantly decreased to 50.38 mJ/m2, which was also due to the surface modification that significantly decreased the polarity of the molecules.

Table 2.
The contact angles (θ) using DI water, diiodomethane, and formamide.

Table 3.
The polar and dispersive components of surface energy.
3.3. Ellipsometric Study and Adsorption of CNCs and CTAB-CNCs onto Surfaces
The adsorption of CNCs and CTAB-CNCs from aqueous suspensions onto cationic PEI, anionic CMC, and nonionic HEC polymer-coated surfaces was investigated by ellipsometry. The ellipsometry results were evaluated based on an optical three-layer model in the case of coatings of CNCs and CTAB-CNCs, and an optical four-layer model in the case of polymer-based coatings, as demonstrated in Figure 1. CNCs, CTAB-CNCs, and polymer layers were evaluated utilizing the Cauchy-fit equation, while assuming adsorption layers were homogenous. The Cauchy-fit approximation of the experimental ψ and Δ data of the direct coatings of CNCs and CTAB-CNCs showed the best fit for the angle of incidence mostly between 45° and 60° (see Supplementary Information, Figure S1). It is worth noting that the data may vary based on the angle of incidence results. Most of the previous studies utilized an angle of incidence between 45° and 75°. Based on the angle of the incidence, the measured thickness of the film may vary. Thus, a wide range of angles of incidence data was utilized to avoid any ambiguity. Our ellipsometry measurements of CTAB on an oxidized silica wafer were compared with the data from the literature and showed a good agreement [40,41] (see Supplementary Information, Table S1).
Direct immersion coating was utilized to understand the adsorption behavior of CNCs and CTAB-CNCs-2 onto an oxidized silicon surface. Table 4 shows that the thickness of the pristine CNC layer was 19.5 nm ± 3 nm, while that of the CTAB-CNCs-2 layer was doubled to 39.67 nm ± 5 nm. The adsorption rate of CTAB-CNCs-2 was higher than that of CNCs, which was due to the CTAB modification of CNCs, which significantly screened the negative charge on the nanocrystal surface that was favorable for adsorption over the anionic oxidized silicon wafer.

Table 4.
Adsorption behavior of CNCs and CTAB-CNCs over the oxidized silicon surface by direct immersion coating.
The next step was to investigate the adsorption behavior of pristine CNC suspensions at various concentrations onto cationic PEI polymer-coated surfaces. In this study, a layer of PEI was first deposited on the surface of SiO2, before the coating of CNCs. Table 5 shows that the adsorption layer of CNCs over the PEI-based coating increased with an increase in the concentration of the CNC suspension. Since PEI is a cationic polymer, it facilitated the adsorption of CNCs on the substrate. As expected, the thickness of the CNC layer increased with an increase in CNC concentration in suspension. However, as the CNCs concentration increased by tenfold, from 0.05 w/w% to 0.5 w/w%, the thickness of the CNCs layer only increased by 1.90-fold, indicating that the PEI coating became saturated at higher CNCs concentrations. With more CNCs adsorbed onto the PEI layer, further adsorption was hampered, which could be due to two reasons: (a) the steric effect of adsorbed CNCs inhibited further adsorption, and (b) the electrostatic repulsion formed by the adsorbed CNCs on the PEI layer further suppressed the approaching CNCs. Therefore, except for the concentration of CNCs, the interfacial situation was also critical for the adsorption behavior.

Table 5.
Adsorption behavior of CNCs at various concentrations.
The effect of different polymer coatings on the adsorption behavior of CNCs and CTAB-CNCs was investigated by coating the base SiO2 surface (508 ± 5 nm) with three types of polymers: a cationic PEI, an anionic CMC, and a nonionic HEC. Table 6 shows the thickness of both the CNC layer and the CTAB-CNC layer over those polymer-coated surfaces. The CNC layer increased from 60 ± 5 nm on a nonionic CMC-coated surface to 140 ± 10 nm over a nonionic HEC base, and maximized to 160 ± 14 nm over the cationic PEI surface. The adsorption of CNCs over the CMC base was mainly hampered by the electrostatic repulsion between the negatively charged CNCs and the anionic CMC, whereas the adsorption of CNCs over the PEI base was favorable due to the electrostatic attraction between the negatively charged CNCs and the cationic PEI, as the electrostatic interactions between the CNCs and the PEI played a dominant role in their adsorption behavior. In the case of the adsorption of CNCs on the nonionic HEC surface, unlike the inhibition on the CMC base or the preference on the PEI base, they exhibited a layer of thickness between those two surfaces. This observation differed from the isothermal titration calorimetry results in our previous study that showed that the possibility of adsorption of HEC on CNCs was excluded and HEC macromolecules have no preference when replacing surface-bound water molecules by adsorption on CNC surfaces [42]. It was assumed that the adsorption of HEC on the CNC surface, even if it existed, is very weak by hydrogen bonding in the HEC-CNC suspension. In this study, HEC was used as a base polymer for CNC coating, instead of the “free” molecules suspended in the CNC dispersion. The hydrogen bonding and van der Waals forces between CNCs and HEC macromolecules could still help during the adsorption process.

Table 6.
Adsorption behavior of CNCs and CTAB-CNCs on different polymer surfaces.
On the other hand, The CTAB-CNC layer was 105 ± 8 nm over the anionic CMC surface, 206 ± 8 nm over the nonionic HEC surface, and significantly decreased to 70 ± 11 nm over the cationic PEI surface. It was noted that the zeta potential of CTAB-CNCs was −1.01 ± 1.14 mV. After surface modification with CTAB, the surface charge of CTAB-CNCs-2 became almost neutral. The adsorption of CTAB-CNCs-2 over the CMC base was relatively easier when compared with the pristine CNCs. Additionally, the average length and width of the particles increased from 178.3 ± 29.9 nm and 17.5 ± 3.4 nm (n = 30) of CNCs to 199.2 ± 42.4 nm and 26.3 ± 4.0 nm (n = 30) of CTAB-CNCs, respectively. As the adsorption became easier and each crystal particle became larger, the thickness of the CTAB-CNCs-2 over the CMC base increased when compared with that of pristine CNCs. Conversely, the neutral surface nature of the CTAB-CNCs-2 significantly decreased its adsorption over the PEI-coated surface when compared with that of CNCs. The electrostatic attraction between the cationic polymer PEI and the CTAB-modified CNCs significantly decreased. It was interesting to notice that the CTAB-CNCs-2 layer over the HEC base increased from 140 ± 10 nm to 206 ± 8 nm when compared with that of CNCs. As the HEC base and CTAB-CNCs-2 were both neutral, the increase in the layer of CTAB-CNCs-2 could be due to the surface modification that increased the size of each crystal. The thickness of the CTAB-CNC layer over various polymer surfaces could be impacted by both the surface charge and the size of the CNC particles.
4. Conclusions
In this study, the surface properties of CNCs were tailored by noncovalent modification using various concentrations of cationic CTAB. The obtained CTAB-CNCs were well characterized and were further applied as a coating material to investigate the interfacial interactions over various substrates. FTIR results indicated the successful modification on the CNC surface. With the increase in CTAB used, the zeta potential of the CTAB-CNCs significantly increased to around zero, and the size of the modified CNCs also significantly increased, as observed by DLS. The morphology of the pristine CNCs and the CTAB-CNCs was observed, both at aqueous status using cryo-TEM and at dried status by SEM, and indicated both that the size of each nanocrystal increased, and that the nanocrystals aggregated to form larger microfibers when dried up. The surface modification also significantly influenced the crystallinity behavior of the obtained samples, with the crystallinity index decreasing from 48.57% to 9.12% with the increase in CTAB concentration used. Additionally, the CTAB modification altered the wettability and total surface energy of CNCs; the sample became relatively hydrophobic, and the total surface energy decreased after modification. Finally, the adsorption behavior of the CNCs and CTAB-CNCs over nonionic, anionic, and cationic polymer-coated surfaces was investigated by ellipsometry. Because of the thickness of the CNC and CTAB-CNC layers over CMC, HEC, and PEI, we proposed that the adsorption behavior was overall influenced by electrostatic interaction, hydrogen bonding, and van der Waals forces, and the thickness of the adsorbed layers could be impacted by both the surface charge and the size of the crystals. This work has provided systematic characterizations on CTAB-CNCs, and insights on the adsorption behavior of CNCs and CTAB-CNCs over nonionic, anionic, and cationic polymers that could help to understand the interfacial behavior of CNC-based materials.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/surfaces7020027/s1. Figure S1: Cauchy-fit approximation of the experimentally obtained ψ and Δ data at different incident angle over the full range of wavelengths. Table S1: Comparison of CTAB adsorption behavior on oxidized silicon surfaces.
Author Contributions
Y.B.: Conceptualization, Resources, Supervision, Writing—review and editing, Funding acquisition. X.G.: Methodology, Investigation, Visualization, Formal analysis, Writing—original draft, Writing—review and editing. M.F.I.: Methodology, Investigation, Formal analysis. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
We greatly acknowledge the funding support of Alberta Innovates and Alberta Bio Future (ABF) Biomaterials Pursuit Program for funding the project BFR006.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article and Supplementary Materials.
Acknowledgments
We thank InnoTech Alberta for the generous supply of cellulose nanocrystals.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
References
- Ranjbar, D.; Raeiszadeh, M.; Lewis, L.; MacLachlan, M.J.; Hatzikiriakos, S.G. Adsorptive removal of Congo red by surfactant modified cellulose nanocrystals: A kinetic, equilibrium, and mechanistic investigation. Cellulose 2020, 27, 3211–3232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Wang, Y.; Tian, Z.; Zheng, X.; Chen, L. Controlled production of spruce cellulose gels using an environmentally “green” system. Cellulose 2014, 21, 1667–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boluk, Y.; Lahiji, R.; Zhao, L.; McDermott, M.T. Suspension viscosities and shape parameter of cellulose nanocrystals (CNC). Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2011, 377, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grishkewich, N.; Mohammed, N.; Tang, J.; Tam, K.C. Recent advances in the application of cellulose nanocrystals. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 29, 32–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elanthikkal, S.; Francis, T.; Sangeetha, C.; Unnikrishnan, G. Cellulose Whisker-Based Green Polymer Composites. In Handbook of Composites from Renewable Materials; Thakur, V.K., Thakur, M.K., Kessler, M.R., Eds.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 461–494. [Google Scholar]
- Habibi, Y.; Lucia, L.A.; Rojas, O.J. Cellulose nanocrystals: Chemistry, self-assembly, and applications. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 3479–3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shopsowitz, K.E.; Qi, H.; Hamad, W.Y.; MacLachlan, M.J. Free-standing mesoporous silica films with tunable chiral nematic structures. Nature 2010, 468, 422–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, N.; Huang, J.; Dufresne, A. Preparation, properties and applications of polysaccharide nanocrystals in advanced functional nanomaterials: A review. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 3274–3294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roman, M.; Gray, D.G. Parabolic focal conics in self-assembled solid films of cellulose nanocrystals. Langmuir 2005, 21, 5555–5561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunasee, R.; Hemraz, U.D.; Ckless, K. Cellulose nanocrystals: A versatile nanoplatform for emerging biomedical applications. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2016, 13, 1243–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capron, I.; Cathala, B. Surfactant-free high internal phase emulsions stabilized by cellulose nanocrystals. Biomacromolecules 2013, 14, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Liu, T.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Y.; Boluk, Y. Release of cellulose nanocrystal particles from natural rubber latex composites into immersed aqueous media. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2021, 4, 1413–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahan, Z.; Niazi, M.B.K.; Gregersen, Ø.W. Mechanical, thermal and swelling properties of cellulose nanocrystals/PVA nanocomposites membranes. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2018, 57, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surov, O.V.; Voronova, M.I.; Afineevskii, A.V.; Zakharov, A.G. Polyethylene oxide films reinforced by cellulose nanocrystals: Microstructure-properties relationship. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 181, 489–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nessi, V.; Falourd, X.; Maigret, J.-E.; Cahier, K.; D’orlando, A.; Descamps, N.; Gaucher, V.; Chevigny, C.; Lourdin, D. Cellulose nanocrystals-starch nanocomposites produced by extrusion: Structure and behavior in physiological conditions. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 225, 115123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortunati, E.; Armentano, I.; Zhou, Q.; Iannoni, A.; Saino, E.; Visai, L.; Berglund, L.A.; Kenny, J.M. Multifunctional bionanocomposite films of poly (lactic acid), cellulose nanocrystals and silver nanoparticles. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 87, 1596–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusin, C.J.; El Bakkari, M.; Du, R.; Boluk, Y.; McDermott, M.T. Plasmonic cellulose nanofibers as water-dispersible surface-enhanced Raman scattering substrates. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2020, 3, 6584–6597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salajková, M.; Berglund, L.A.; Zhou, Q. Hydrophobic cellulose nanocrystals modified with quaternary ammonium salts. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 19798–19805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Wang, Y.; Chen, L. Enhanced emulsifying properties of wood-based cellulose nanocrystals as Pickering emulsion stabilizer. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 169, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaboorani, A.; Riedl, B. Surface modification of cellulose nanocrystals (CNC) by a cationic surfactant. Ind. Crops Prod. 2015, 65, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abitbol, T.; Marway, H.; Cranston, E.D. Surface modification of cellulose nanocrystals with cetyltrimethylammonium bromide. Nord. Pulp Pap. Res. J. 2014, 29, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prathapan, R.; Thapa, R.; Garnier, G.; Tabor, R.F. Modulating the zeta potential of cellulose nanocrystals using salts and surfactants. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2016, 509, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, X.; Long, Y.; Ni, Y. Cellulose nanocrystal/hexadecyltrimethylammonium bromide/silver nanoparticle composite as a catalyst for reduction of 4-nitrophenol. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 156, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibi, Y.; Foulon, L.; Aguié-Béghin, V.; Molinari, M.; Douillard, R. Langmuir–Blodgett films of cellulose nanocrystals: Preparation and characterization. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2007, 316, 388–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podsiadlo, P.; Choi, S.-Y.; Shim, B.; Lee, J.; Cuddihy, M.; Kotov, N.A. Molecularly engineered nanocomposites: Layer-by-layer assembly of cellulose nanocrystals. Biomacromolecules 2005, 6, 2914–2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esparza, Y.; Ngo, T.-D.; Fraschini, C.; Boluk, Y. Aggregate morphology and aqueous dispersibility of spray-dried powders of cellulose nanocrystals. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 19926–19936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neugebauer, J.M. [18] Detergents: An overview. Methods Enzymol. 1990, 182, 239–253. [Google Scholar]
- Habibi, Y.; Hoeger, I.; Kelley, S.S.; Rojas, O.J. Development of Langmuir−Schaeffer cellulose nanocrystal monolayers and their interfacial behaviors. Langmuir 2010, 26, 990–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, S.; French, A.D.; Condon, B.D.; Concha, M. Segal crystallinity index revisited by the simulation of X-ray diffraction patterns of cotton cellulose Iβ and cellulose II. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 135, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Kalantari, M.; Aslanzadeh, S.; Boluk, Y. Interfacial interactions and electrospinning of cellulose nanocrystals dispersions in polymer solutions: A review. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2022, 43, 945–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humlíček, J. Polarized light and ellipsometry. In Handbook of Ellipsometry; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; pp. 3–91. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Xiao, F.; Su, H.; Wang, D.; Yang, X. Investigation of adsorption and photocatalytic activities of in situ cetyltrimethylammonium bromide-modified Bi/BiOCl heterojunction photocatalyst for organic contaminants removal. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 93309–93317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirich, C.L.; Picheth, G.F.; Machado, J.P.E.; Sakakibara, C.N.; Martin, A.A.; de Freitas, R.A.; Sierakowski, M.R. Influence of mechanical pretreatment to isolate cellulose nanocrystals by sulfuric acid hydrolysis. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 130, 622–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, D.; Wang, L.-J.; Li, S.-J.; Adhikari, B. Effects of drying methods on the functional properties of flaxseed gum powders. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 81, 128–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvério, H.A.; Neto, W.P.F.; Dantas, N.O.; Pasquini, D. Extraction and characterization of cellulose nanocrystals from corncob for application as reinforcing agent in nanocomposites. Ind. Crops Prod. 2013, 44, 427–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chang, C.; Zhang, L. Effects of freezing/thawing cycles and cellulose nanowhiskers on structure and properties of biocompatible starch/PVA sponges. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2010, 295, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zainuddin, N.; Ahmad, I.; Kargarzadeh, H.; Ramli, S. Hydrophobic kenaf nanocrystalline cellulose for the binding of curcumin. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 163, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Berg, J.C. A review of the different techniques for solid surface acid–base characterization. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2003, 105, 151–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Good, R.J.; Chaudhury, M.K.; van Oss, C.J. Theory of Adhesive Forces Across Interfaces: 2. Interfacial Hydrogen Bonds as Acid—Base Phenomena and as Factors Enhancing Adhesion. In Fundamentals of Adhesion; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1991; pp. 153–172. [Google Scholar]
- Gassan, J.; Gutowski, V.S. Effects of corona discharge and UV treatment on the properties of jute-fibre epoxy composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2000, 60, 2857–2863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, Z.; Liao, W.; Qi, L. Wettability alteration by CTAB adsorption at surfaces of SiO2 film or silica gel powder and mimic oil recovery. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2004, 221, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boluk, Y.; Zhao, L.; Incani, V. Dispersions of nanocrystalline cellulose in aqueous polymer solutions: Structure formation of colloidal rods. Langmuir 2012, 28, 6114–6123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).