Surface Functionalisation of Upconversion Nanoparticles with Different Moieties for Biomedical Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
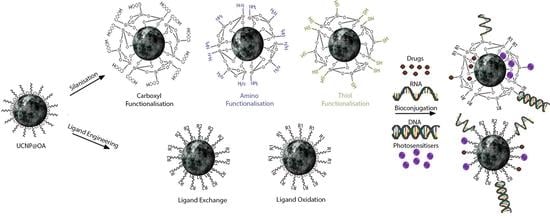
2. Surface Modifications
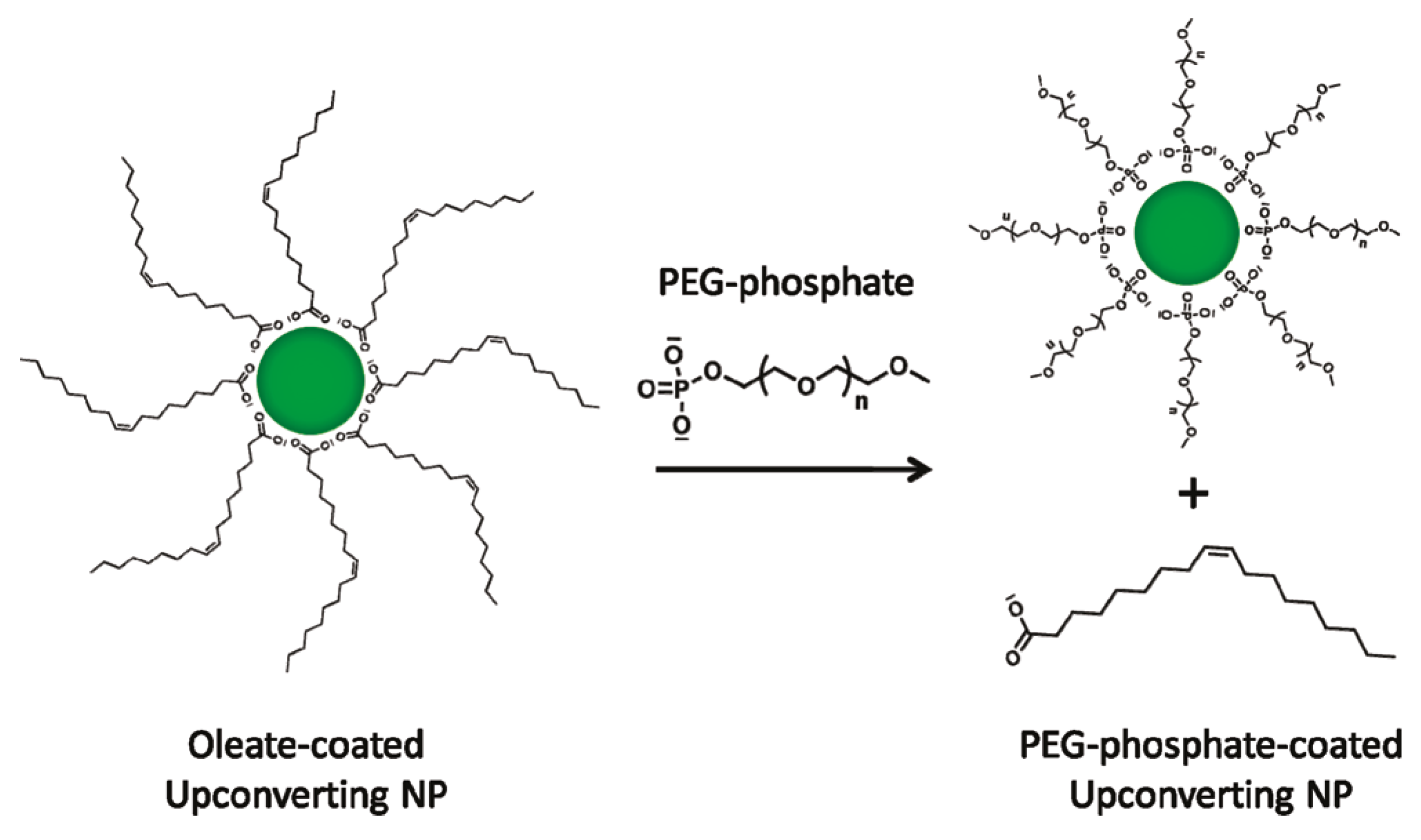
2.1. Ligand Engineering
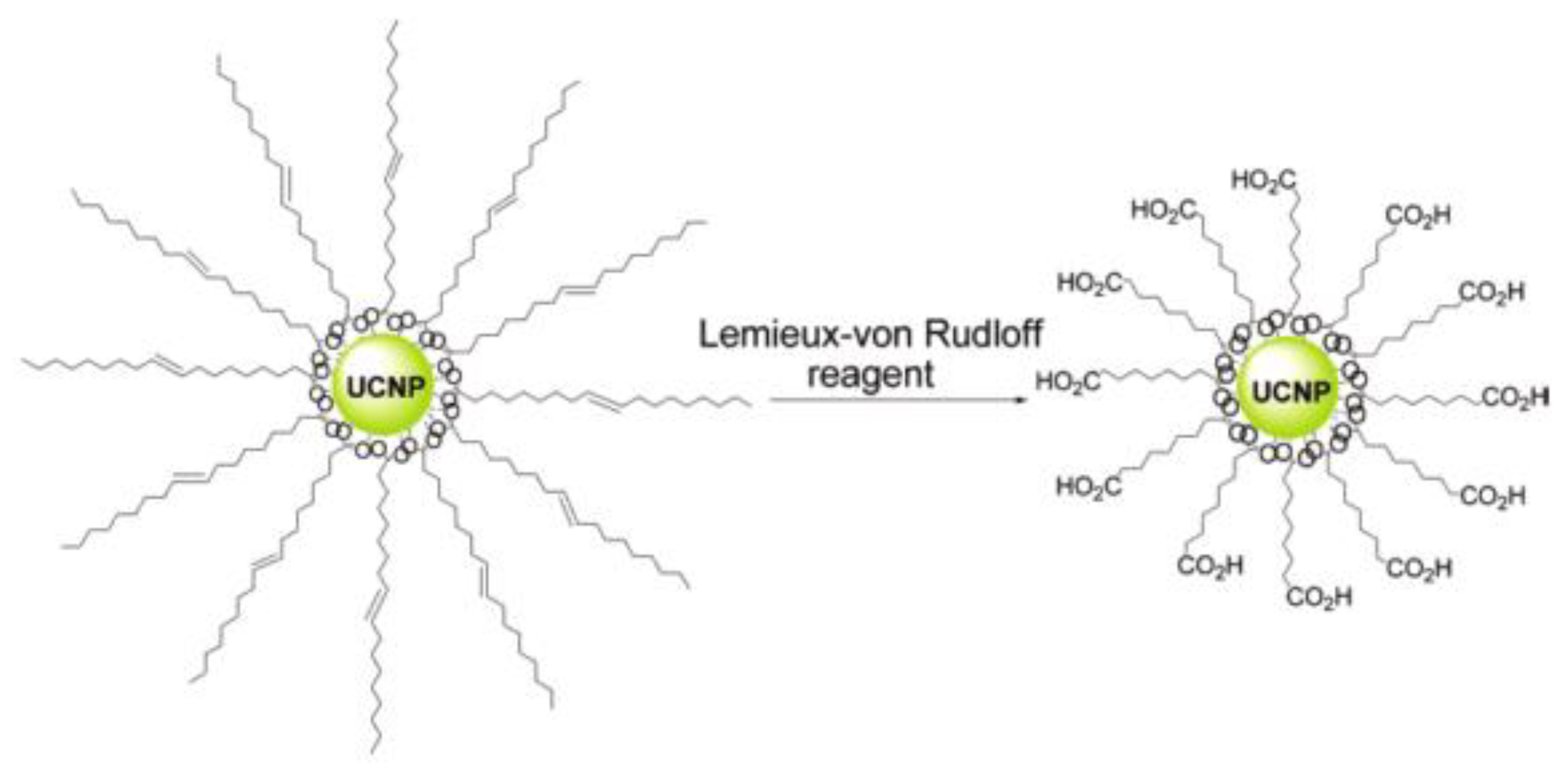
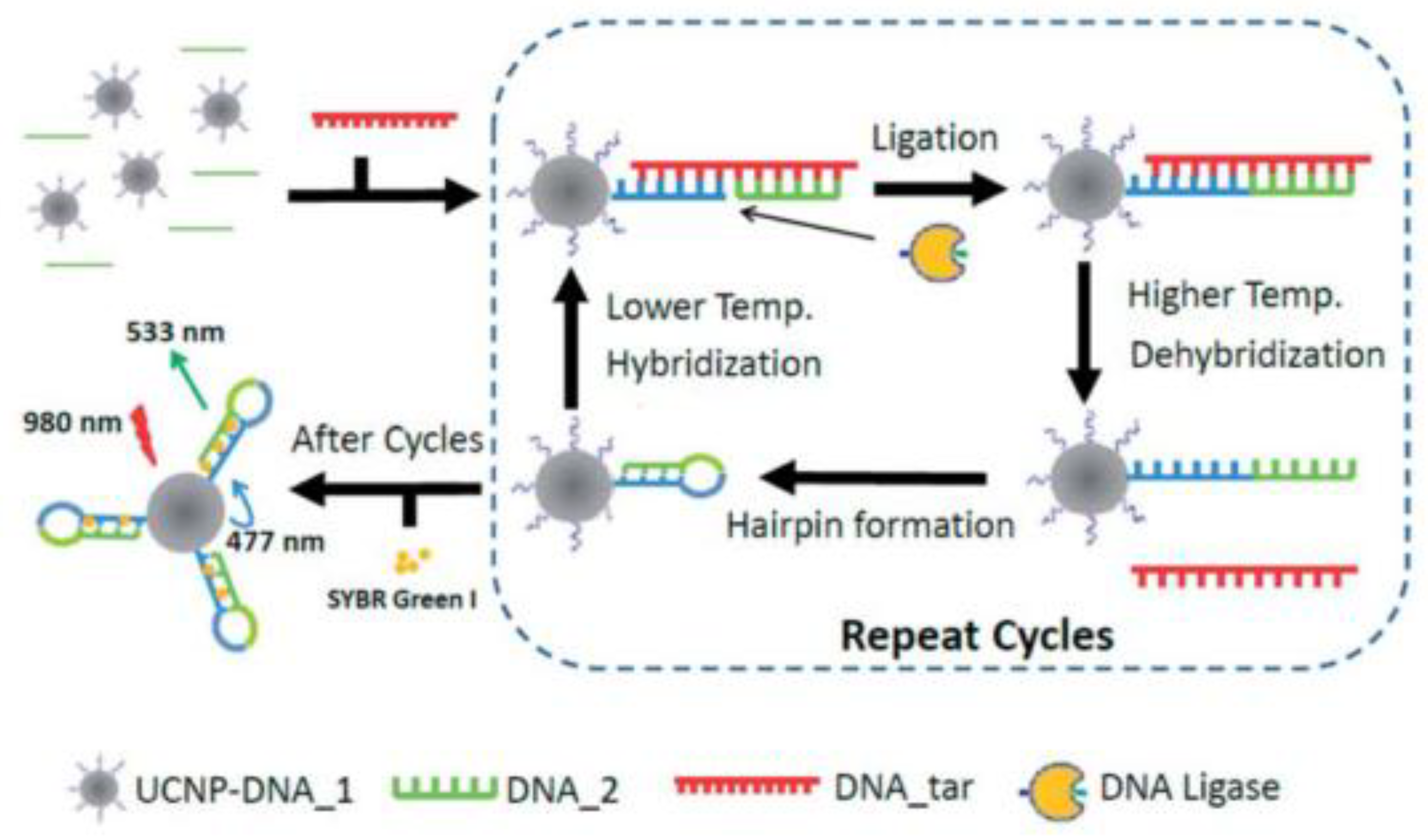
2.1.1. Carboxyl Moiety Modified UCNPs via Ligand Engineering
2.1.2. Amino Moiety Modified UCNPs via Ligand Engineering
2.1.3. Thiol Moiety Modified UCNPs via Ligand Engineering
2.2. Silanisation of UCNPs
2.2.1. Carboxyl Moiety Modified UCNPs via Silanisation
2.2.2. Amino Moiety Modified UCNPs via Silanisation
2.2.3. Thiol Moiety Modified UCNPs via Silanisation
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xie, J.; Lee, S.; Chen, X. Nanoparticle-based theranostic agents. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2010, 62, 1064–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Qiu, H.; Prasad, P.N.; Chen, X. Upconversion nanoparticles: Design, nanochemistry, and applications in Theranostics. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 5161–5214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Banerjee, D.; Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Liu, X. Upconversion nanoparticles in biological labeling, imaging, and therapy. Analyst 2010, 135, 1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biju, V. Chemical modifications and bioconjugate reactions of nanomaterials for sensing, imaging, drug delivery and therapy. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 744–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sedlmeier, A.; Gorris, H.H. Surface modification and characterization of photon-upconverting nanoparticles for bioanalytical applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 1526–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Treccani, L.; Yvonne Klein, T.; Meder, F.; Pardun, K.; Rezwan, K. Functionalized ceramics for biomedical, biotechnological and environmental applications. Acta Biomater. 2013, 9, 7115–7150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F. Photon Upconversion Nanomaterials; Lockwood, D.J., Ed.; Nanostructure Science and Technology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; ISBN 978-3-662-45596-8. [Google Scholar]
- Thanh, N.T.K.; Green, L.A.W. Functionalisation of nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Nano Today 2010, 5, 213–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilhelm, S.; Kaiser, M.; Würth, C.; Heiland, J.; Carrillo-Carrion, C.; Muhr, V.; Wolfbeis, O.S.; Parak, W.J.; Resch-Genger, U.; Hirsch, T. Water dispersible upconverting nanoparticles: Effects of surface modification on their luminescence and colloidal stability. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 1403–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duong, H.T.T.; Chen, Y.; Tawfik, S.A.; Wen, S.; Parviz, M.; Shimoni, O.; Jin, D. Systematic investigation of functional ligands for colloidal stable upconversion nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 4842–4849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.-H.; Hung, Y.; Mou, C.-Y. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles as nanocarriers. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 9972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, J.; Yao, N.; Ju, Y. Ligand Effects and Synthesis of NaYF4 Based up and Downconversion Colloidal Nanophosphors. Fluor.-Relat. Nanosci. Energy Appl. 2011, 71–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.-N.; Bu, W.-B.; Shi, J.-L. Silica Coated Upconversion Nanoparticles: A Versatile Platform for the Development of Efficient Theranostics. Acc. Chem. Res. 2015, 48, 1797–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogdan, N.; Vetrone, F.; Capobianco, J.A. Synthesis of Ligand-Free Colloidally Stable Water Dispersible Brightly Luminescent Lanthanide-Doped Upconverting Nanoparticles. Nano Lett. 2011, 11, 835–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sedlmeier, A. Surface Modification and Scan Imaging of Upconverting Nanoparticles; University of Regensburg: Regensburg, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, S.; Win, K.Y.; Liu, S.; Teng, C.P.; Zheng, Y.; Han, M.-Y. Surface-functionalized nanoparticles for biosensing and imaging-guided therapeutics. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 3127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Zhao, Q.; You, H.; Wang, Z. Synthesis of stable carboxy-terminated NaYF4: Yb3+, Er3+@SiO2 nanoparticles with ultrathin shell for biolabeling applications. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 1047–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, B. Silica nanoparticle assisted DNA assays for optical signal amplification of conjugated polymer based fluorescent sensors. Chem. Commun. 2007, 3553–3555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.L.; Wu, P.; Hwang, K.; Lu, Y. An exceptionally simple strategy for DNA-functionalized up-conversion nanoparticles as biocompatible agents for nanoassembly, DNA delivery, and imaging. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 2411–2414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso-Cristobal, P.; Vilela, P.; El-Sagheer, A.; Lopez-Cabarcos, E.; Brown, T.; Muskens, O.L.; Rubio-Retama, J.; Kanaras, A.G. Highly Sensitive DNA Sensor Based on Upconversion Nanoparticles and Graphene Oxide. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 12422–12429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, K.; Kong, X.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, Q.; Tu, L.; Shi, Z.; Zhang, H. Aptamer optical biosensor without bio-breakage using upconversion nanoparticles as donors. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 1156–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendez-Gonzalez, D.; Laurenti, M.; Latorre, A.; Somoza, A.; Vazquez, A.; Negredo, A.I.; López-Cabarcos, E.; Calderón, O.G.; Melle, S.; Rubio-Retama, J. Oligonucleotide Sensor Based on Selective Capture of Upconversion Nanoparticles Triggered by Target-Induced DNA Interstrand Ligand Reaction. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 12272–12281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Yang, R.R.; Yang, L.; Tan, W. Nucleic Acid Conjugated Nanomaterials for Enhanced Molecular Recognition. ACS Nano 2009, 3, 2451–2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Bu, W.; Pan, L.; Shi, J. NIR-Triggered Anticancer Drug Delivery by Upconverting Nanoparticles with Integrated Azobenzene-Modified Mesoporous Silica. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 4375–4379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fedoryshin, L.L. Near-Infrared Triggered Anti-Cancer Drug Release from Upconverting Nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 13600–13606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Hemmer, E.; Rosei, F.; Vetrone, F. Multifunctional Liposome Nanocarriers Combining Upconverting Nanoparticles and Anticancer Drugs. J. Phys. Chem. B 2016, 120, 4992–5001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Wen, X.; Liu, J.; Wang, B.; Zhan, Q.; He, S. Yb3+-enhanced UCNP@SiO2 nanocomposites for consecutive imaging, photothermal-controlled drug delivery and cancer therapy. Opt. Mater. Express 2016, 6, 1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhao, J.X. Upconversion nanomaterials: Synthesis, mechanism, and applications in sensing. Sensors 2012, 12, 2414–2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ang, L.Y.; Lim, M.E.; Ong, L.C.; Zhang, Y. Applications of upconversion nanoparticles in imaging, detection and therapy. Nanomedicine 2011, 6, 1273–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.L.; Zhang, R.; Yin, L.; Zheng, K.; Qin, W.; Selvin, P.R.; Lu, Y. Biomimetic surface engineering of lanthanide-doped upconversion nanoparticles as versatile bioprobes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 6121–6125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Duong, H.T.T.; Wen, S.; Mi, C.; Zhou, Y.; Shimoni, O.; Valenzuela, S.M.; Jin, D. Exonuclease III-Assisted Upconversion Resonance Energy Transfer in a Wash-Free Suspension DNA Assay. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 663–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.L.; Yan, R.; Huo, Z.; Wang, L.L.; Zeng, J.; Bao, J.; Wang, X.; Peng, Q.; Li, Y. Fluorescence resonant energy transfer biosensor based on upconversion-luminescent nanoparticles. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 6054–6057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, L.; Yang, K.; Shao, M.; Lee, S.T.; Liu, Z. Multicolor in vivo imaging of upconversion nanoparticles with emissions tuned by luminescence resonance energy transfer. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 2686–2692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montalti, M.; Prodi, L.; Rampazzo, E.; Zaccheroni, N. Dye-doped silica nanoparticles as luminescent organized systems for nanomedicine. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 4243–4268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fedoryshin, L.L. Near-Infrared Triggered Anti-Cancer Drug Release from Upconverting Nanoparticles; University of Toronto: Toronto, ON, Canada, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- An, Y.; Chen, M.; Xue, Q.; Liu, W. Preparation and self-assembly of carboxylic acid-functionalized silica. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2007, 311, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cashin, V.B.; Eldridge, D.S.; Yu, A.; Zhao, D. Surface functionalization and manipulation of mesoporous silica adsorbents for improved removal of pollutants: A review. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2018, 4, 110–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, R.A.; Singh, R.K.; Kim, T.-H.; Kim, H.-W. Silica-based multifunctional nanodelivery systems toward regenerative medicine. Mater. Horiz. 2017, 4, 772–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberti, S.; Soler-Illia, G.J.A.A.; Azzaroni, O. Gated supramolecular chemistry in hybrid mesoporous silica nanoarchitectures: Controlled delivery and molecular transport in response to chemical, physical and biological stimuli. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 6050–6075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muhr, V.; Wilhelm, S.; Hirsch, T.; Wolfbeis, O.S. Upconversion Nanoparticles: From Hydrophobic to Hydrophilic Surfaces. Acc. Chem. Res. 2014, 47, 3481–3493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Chen, H.; Hu, H.; Yu, M.; Li, F. Versatile Synthesis Strategy for Carboxylic Acid—Functionalized Upconverting Nanophosphors as Biological Labels Versatile Synthesis Strategy for Carboxylic Biological Labels. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 3023–3029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, R.; Xie, X.; Vendrell, M.; Chang, Y.-T.; Liu, X. Intracellular Glutathione Detection Using MnO2-Nanosheet-Modified Upconversion Nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 20168–20171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naccache, R.; Vetrone, F.; Mahalingam, V.; Cuccia, L.A.; Capobianco, J.A. Controlled Synthesis and Water Dispersibility of Hexagonal Phase NaGdF4: Ho3+/Yb3+ Nanoparticles. Chem. Mater. 2009, 21, 717–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Li, C.; Shi, Z. Current Advances in Lanthanide-Doped Upconversion Nanostructures for Detection and Bioapplication. Adv. Sci. 2016, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyer, J.C.; Manseau, M.P.; Murray, J.I.; Van Veggel, F.C.J.M. Surface modification of upconverting NaYF4nanoparticles with PEG-phosphate ligands for NIR (800 nm) biolabeling within the biological window. Langmuir 2010, 26, 1157–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meiser, F.; Cortez, C.; Caruso, F. Biofunctionalization of Fluorescent Rare-Earth-Doped Lanthanum Phosphate Colloidal Nanoparticles. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 5954–5957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Wang, H.; Li, X.; Chen, D. Monodisperse, size-tunable and highly efficient β-NaYF4: Yb, Er(Tm) up-conversion luminescent nanospheres: Controllable synthesis and their surface modifications. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 3546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traina, C.A.; Schwartz, J. Surface Modification of Y2O3 Nanoparticles. Langmuir 2007, 23, 9158–9161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, J.; Sun, L.D.; Zhang, Y.W.; Yan, C.H. Superparamagnetic and upconversion emitting Fe3O4/NaYF4: Yb, Er hetero-nanoparticles via a crosslinker anchoring strategy. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 5731–5733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Song, K.; Zhao, J.; Kong, X.; Sun, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, Q.; Zhang, H. Hexanedioic acid mediated surface–ligand-exchange process for transferring NaYF4: Yb/Er (or Yb/Tm) up-converting nanoparticles from hydrophobic to hydrophilic. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 336, 171–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, M.; Zhang, P. Highly sensitive and selective label-free optical detection of mercuric ions using photon upconverting nanoparticles. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2010, 25, 2431–2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, M.; Zhang, P. Highly Sensitive and Selective Label-Free Optical Detection of DNA Hybridization Based on Photon Upconverting Nanoparticles. Langmuir 2009, 25, 6024–6027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Zhang, P. Ligase-assisted, upconversion luminescence resonance energy transfer-based method for specific and sensitive detection of V600E mutation in the BRAF gene. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 56235–56240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, S.; Chen, H.; Zhu, H.; Tian, J.; Chi, X.; Qian, Z.; Achilefu, S.; Gu, Y. Amphiphilic chitosan modified upconversion nanoparticles for in vivo photodynamic therapy induced by near-infrared light. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 4861–4873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebherr, R.B.; Soukka, T.; Wolfbeis, O.S.; Gorris, H.H. Maleimide activation of photon upconverting nanoparticles for bioconjugation. Nanotechnology 2012, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, X.; Yin, J.; He, D.; He, X.; Wang, K.; Chen, M.; Li, Y. Polyacrylic acid modified upconversion nanoparticles for simultaneous pH-triggered drug delivery and release imaging. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2013, 9, 2063–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, H.S.; Guo, H.C.; Ho, P.C.L.; Mahendran, R.; Zhang, Y. Mesoporous-silica-coated up-conversion fluorescent nanoparticles for photodynamic therapy. Small 2009, 5, 2285–2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doughan, S.; Han, Y.; Uddayasankar, U.; Krull, U.J. Solid-phase covalent immobilization of upconverting nanoparticles for biosensing by luminescence resonance energy transfer. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 14061–14068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogdan, N.; Vetrone, F.; Roy, R.; Capobianco, J.A. Carbohydrate-coated lanthanide-doped upconverting nanoparticles for lectin recognition. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 7543–7550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, B.; Xu, S.; Sun, J.; Bi, S.; Li, D.; Bai, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Song, H. Multifunctional NaYF4: Yb3+, Er3+@Ag core/shell nanocomposites: Integration of upconversion imaging and photothermal therapy. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 6193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Yu, Y.; Huang, F.; Lin, H.; Huang, P.; Yang, A.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y. Lanthanide dopant-induced formation of uniform sub-10 nm active-core/active-shell nanocrystals with near-infrared to near-infrared dual-modal luminescence. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 2632–2640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Nyk, M.; Ohulchanskyy, T.Y.; Flask, C.A.; Prasad, P.N. Combined optical and MR bloimaging using rare earth ion doped NaYF4nanocrystals. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2009, 19, 853–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Roy, I.; Ohulchanskyy, T.Y.; Goswami, L.N.; Bonoiu, A.C.; Bergey, E.J.; Tramposch, K.M.; Maitra, A.; Prasad, P.N. Covalently Dye-Linked, Surface-Controlled, and Bioconjugated Organically Modified Silica Nanoparticles as Targeted Probes for Optical Imaging. ACS Nano 2008, 2, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, T.; Xinqiang, X.; Dong, X.; Zhou, Q.; Chen, G. Monodisperse Water-Stable SiO2-Coated Fluoride Upconversion Nanoparticles with Tunable Shell Thickness. Int. J. Nanomater. Nanotechnol. Nanomed. 2017, 3, 15–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Hu, M.; Liu, C.; Choi, S.K. Yolk-structured multifunctional up-conversion nanoparticles for synergistic photodynamic–sonodynamic antibacterial resistance therapy. Biomater. Sci. 2017, 5, 678–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinha, A.; Chakraborty, A.; Jana, N.R. Dextran-gated, multifunctional mesoporous nanoparticle for glucose-responsive and targeted drug delivery. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 22183–22191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, M.; Pang, X.; Liu, X.; Jiang, B.; He, Y.; Snaith, H.; Lin, Z. Monodisperse Dual-Functional Upconversion Nanoparticles Enabled Near-Infrared Organolead Halide Perovskite Solar Cells. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 4280–4284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cash, B.M.; Wang, L.; Benicewicz, B.C. The preparation and characterization of carboxylic acid-coated silica nanoparticles. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2012, 50, 2533–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maria Claesson, E.; Philipse, A.P. Thiol-functionalized silica colloids, grains, and membranes for irreversible adsorption of metal(oxide) nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2007, 297, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hlaváček, A.; Sedlmeier, A.; Skládal, P.; Gorris, H.H. Electrophoretic characterization and purification of silica-coated photon-upconverting nanoparticles and their bioconjugates. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 6930–6935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, F.; Li, T.; He, X.; Wang, Z. Surface charge effect on the cellular interaction and cytotoxicity of NaYF4: Yb3+, Er3+@SiO2 nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 2014, 5, 7773–7780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, Y.H.; Chou, Y.L.; Wang, S.W.; Hung, S.T.; Liau, M.C.; Chao, Y.J.; Su, C.H.; Yeh, C.S. Near-infrared light photocontrolled targeting, bioimaging, and chemotherapy with caged upconversion nanoparticles in vitro and in vivo. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 8516–8528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Lim, K.M.; Sim, E.K.W.; Ye, L. NIR-to-visible upconversion nanoparticles for fluorescent labeling and targeted delivery of siRNA. Nanotechnology 2009, 20, 155101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manzano, M.; Aina, V.; Areán, C.O.; Balas, F.; Cauda, V.; Colilla, M.; Delgado, M.R.; Vallet-Regí, M. Studies on MCM-41 mesoporous silica for drug delivery: Effect of particle morphology and amine functionalization. Chem. Eng. J. 2008, 137, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basaldella, E.I.; Legnoverde, M.S. Functionalized silica matrices for controlled delivery of cephalexin. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2010, 56, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
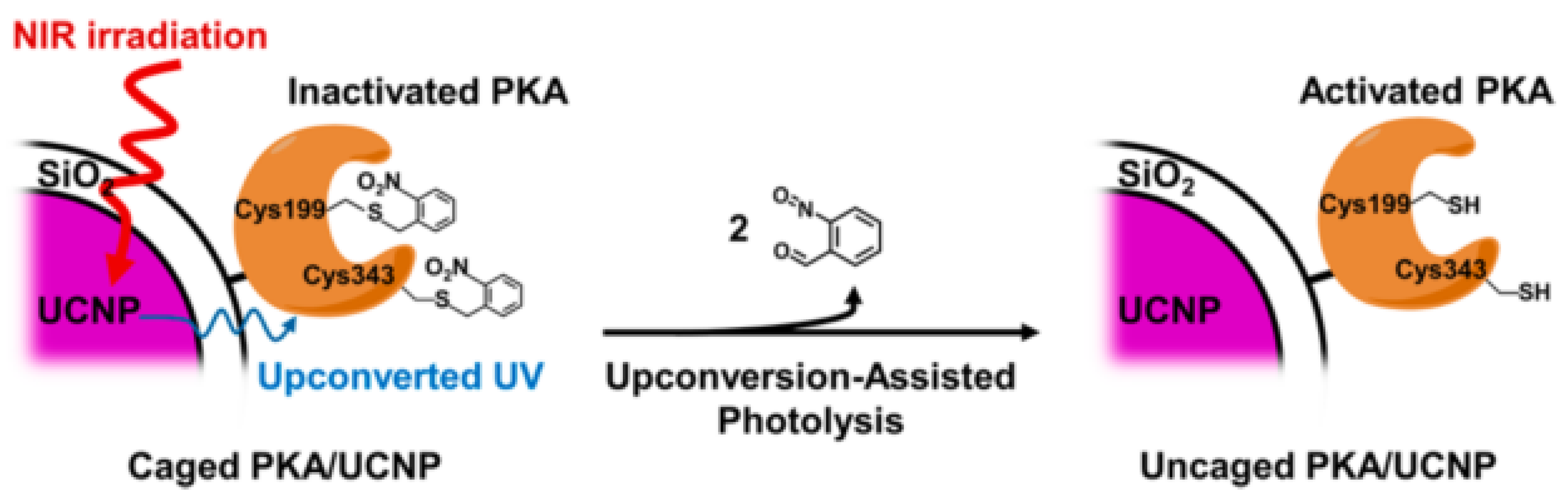
- Gao, H. De; Thanasekaran, P.; Chiang, C.W.; Hong, J.L.; Liu, Y.C.; Chang, Y.H.; Lee, H.M. Construction of a Near-Infrared-Activatable Enzyme Platform to Remotely Trigger Intracellular Signal Transduction Using an Upconversion Nanoparticle. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 7041–7051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Wu, L.; Liang, H.; Cai, W.; Zhang, Z.; Jiang, Z. Controllable synthesis of bifunctional NaYF4: Yb 3+/Ho3+@SiO2/Au nanoparticles with upconversion luminescence and high X-ray attenuation. J. Alloy. Compd. 2011, 509, 9144–9149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, R.M.; Ji-Buechler, Y.; Taylor, S.S. Identification of electrostatic interaction sites between the regulatory and catalytic subunits of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. Protein Sci. 1997, 6, 1825–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
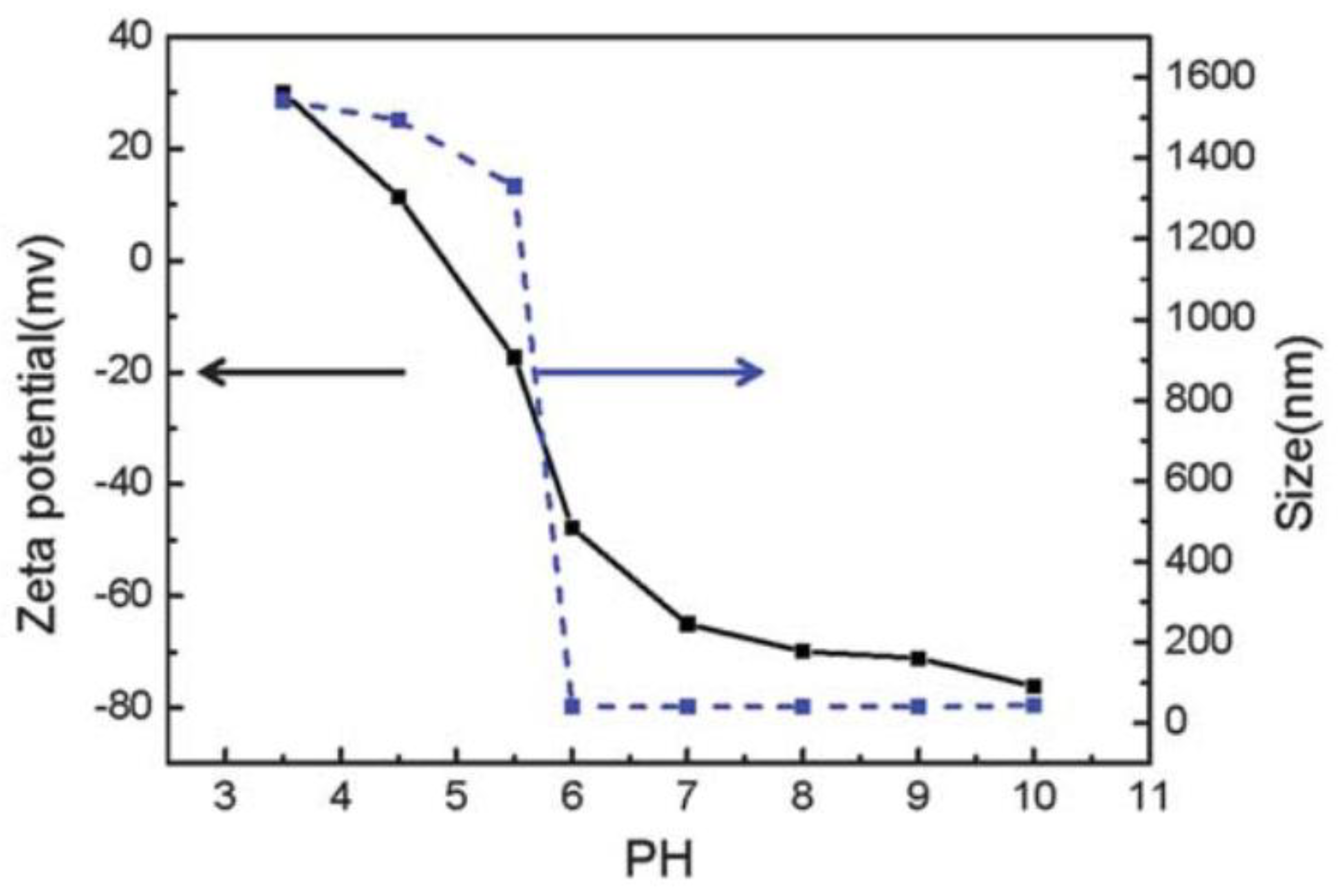
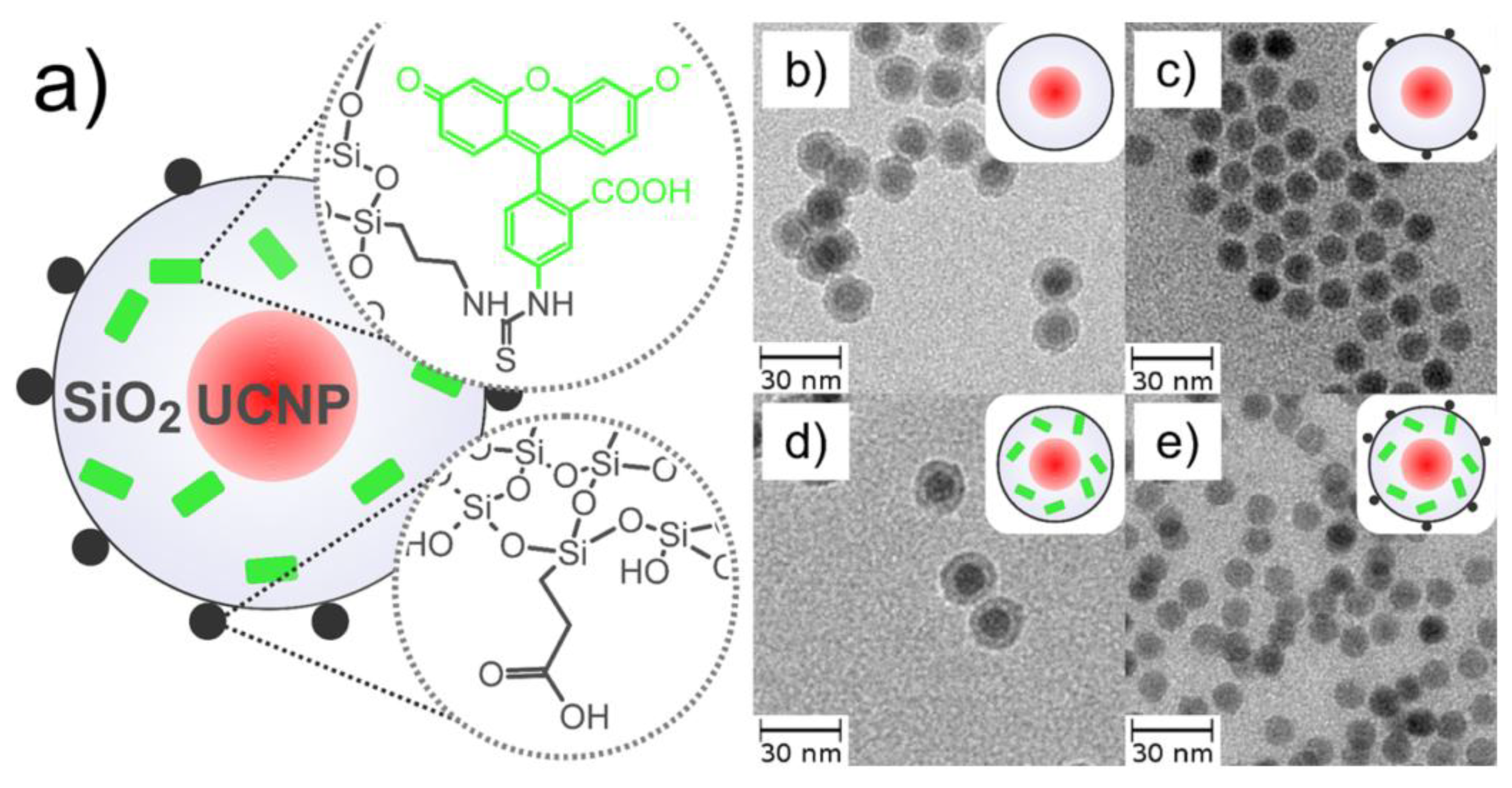
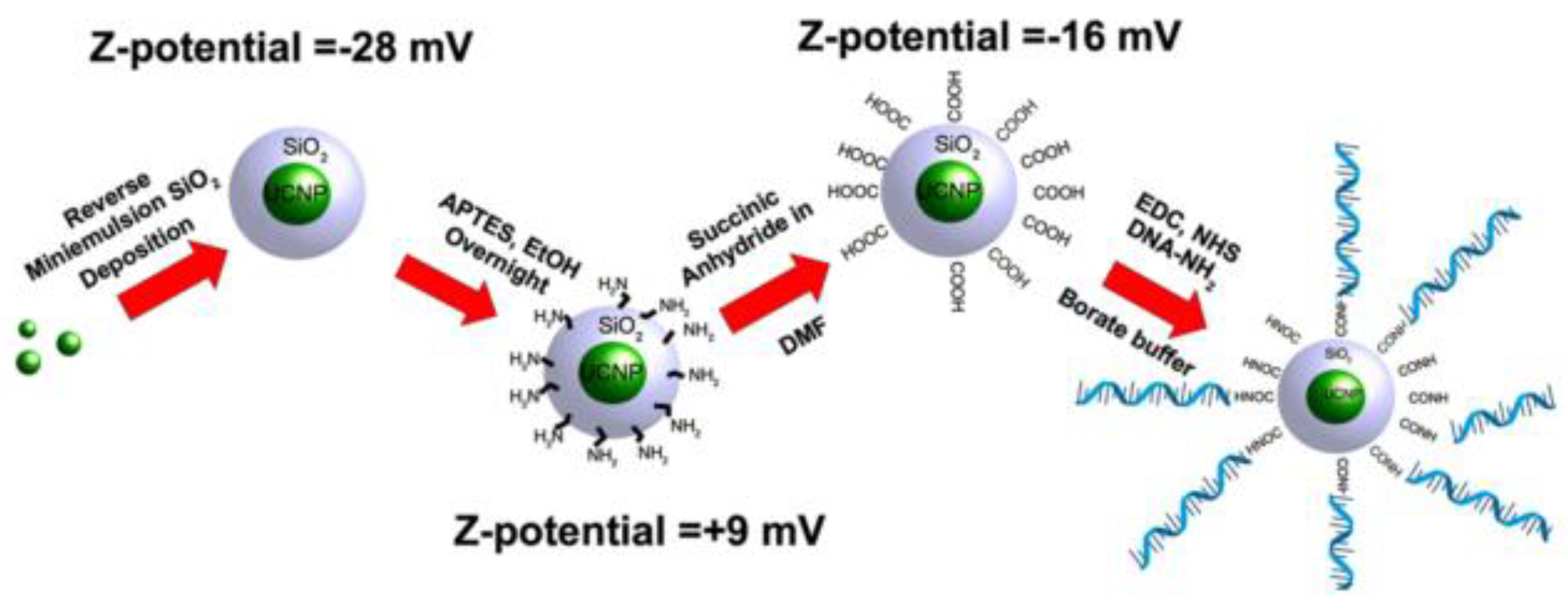
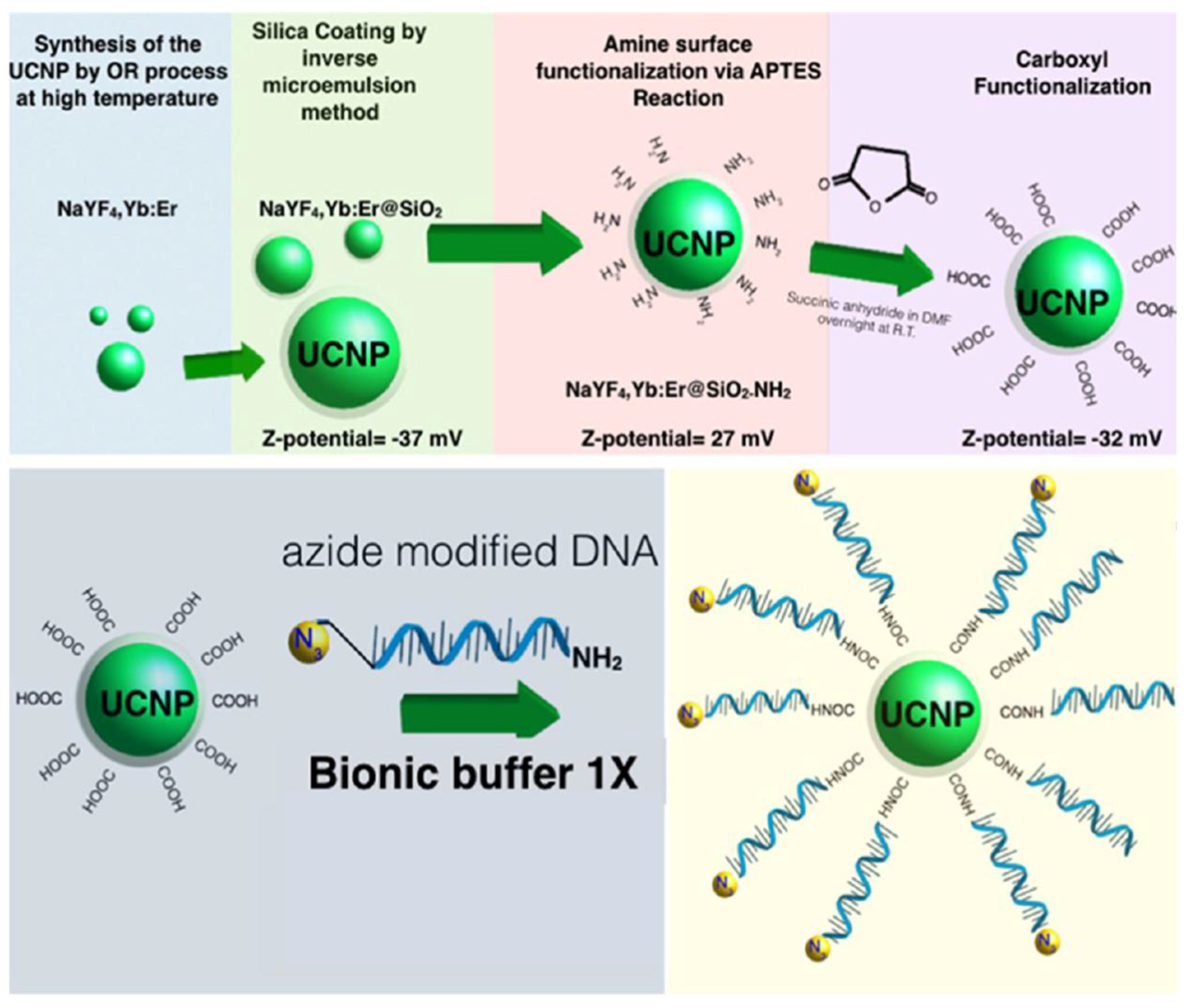
| UCNPs | Ligand | Coordinating Moiety | Functional Moiety | Method of Functionalisation | Application | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NaYF4:Yb3+, Tm3+ | DTPA | Carboxylate | Carboxylic Acid | EDC Chemistry | Hg2+ DNA-based biosensor | [51] |
| NaYF4:Yb3+, Tm3+ | DPTA | Carboxylate | Carboxylic Acid | DNA-based biosensor | [52] | |
| NaYF4:Yb3+, Tm3+ | PAA | Carboxylate | Carboxylic Acid | EDC/NHS Chemistry | Ligase assisted DNA-based biosensor | [53] |
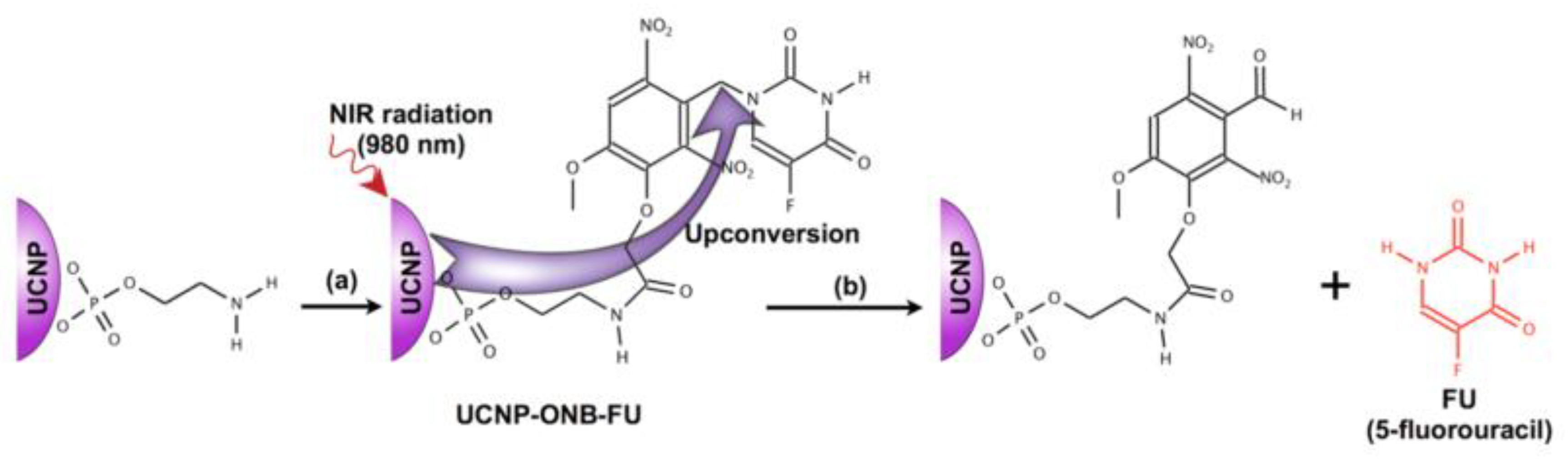
| NaYF4: Yb3+, X3+ (Ho3+, Er3+ or Tm3+) | AA | Carboxylate | Carboxylic Acid | DNA-based biosensor | [41] | |
| NaYF4: Yb3+, Er3+ | SOC-Chitosan | Carboxylate | Carboxylic Acid | Ligand Exchange | ZnPc-based photodynamic Therapy | [54] |
| NaYF4: Yb3+, Er3+ | MA-PEG | Carboxylate | Maleimide | UCNP-based platform for bio-application | [55] | |
| NaYF4: Yb3+, Er3+ | PAA | Carboxylate | Carboxylic Acid | Electrostatic Interactions | pH-manipulated drug delivery | [56] |
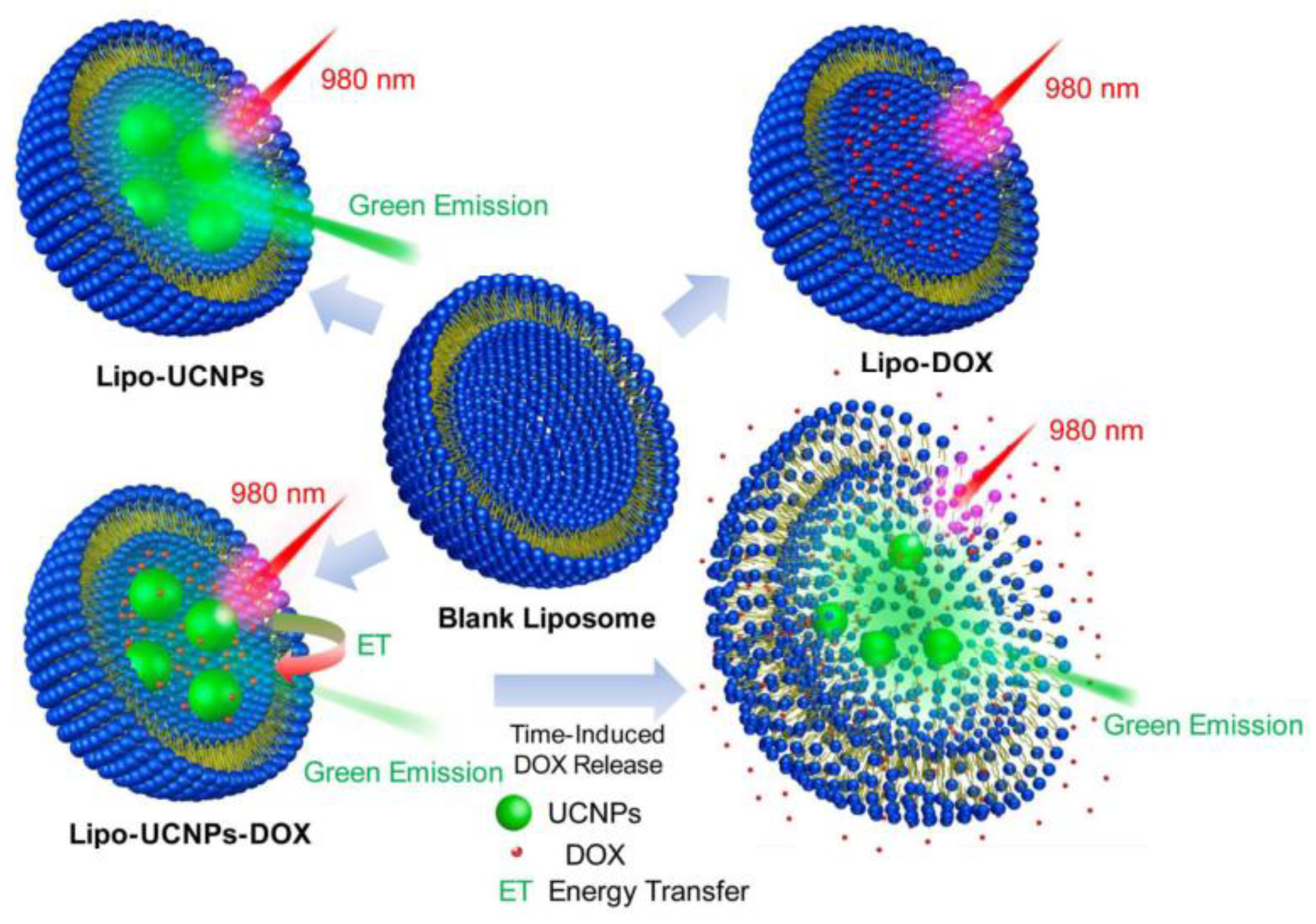
| NaGdF4: Yb3+, Er3+ | Citrate | Carboxylate | Carboxylic Acid | Multifunctional liposomal nanocarriers | [26] |
| UCNP | Ligand | Coordinating Moiety | Functional Moiety | Method of Functionalisation | Application | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NaYF4: Yb3+, Tm3+ | PEA | Phosphate | Amino | EDC/NHS Chemistry | Remotely triggered anti-cancer system | [25] |
| NaYF4: Yb3+, Tm3+ | PEA | Phosphate | Amino | Reductive Amination | Solid-phase biosensing | [58] |
| NaGdF4: Yb3+, Er3+ | PMAM | Amino | Amino | Nucleophilic Thiourea Formation | Targeted lectin recognition | [59] |
| UCNP | Ligand | Coordinating Moiety | Functional Moiety | Method of Functionalisation | Application | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
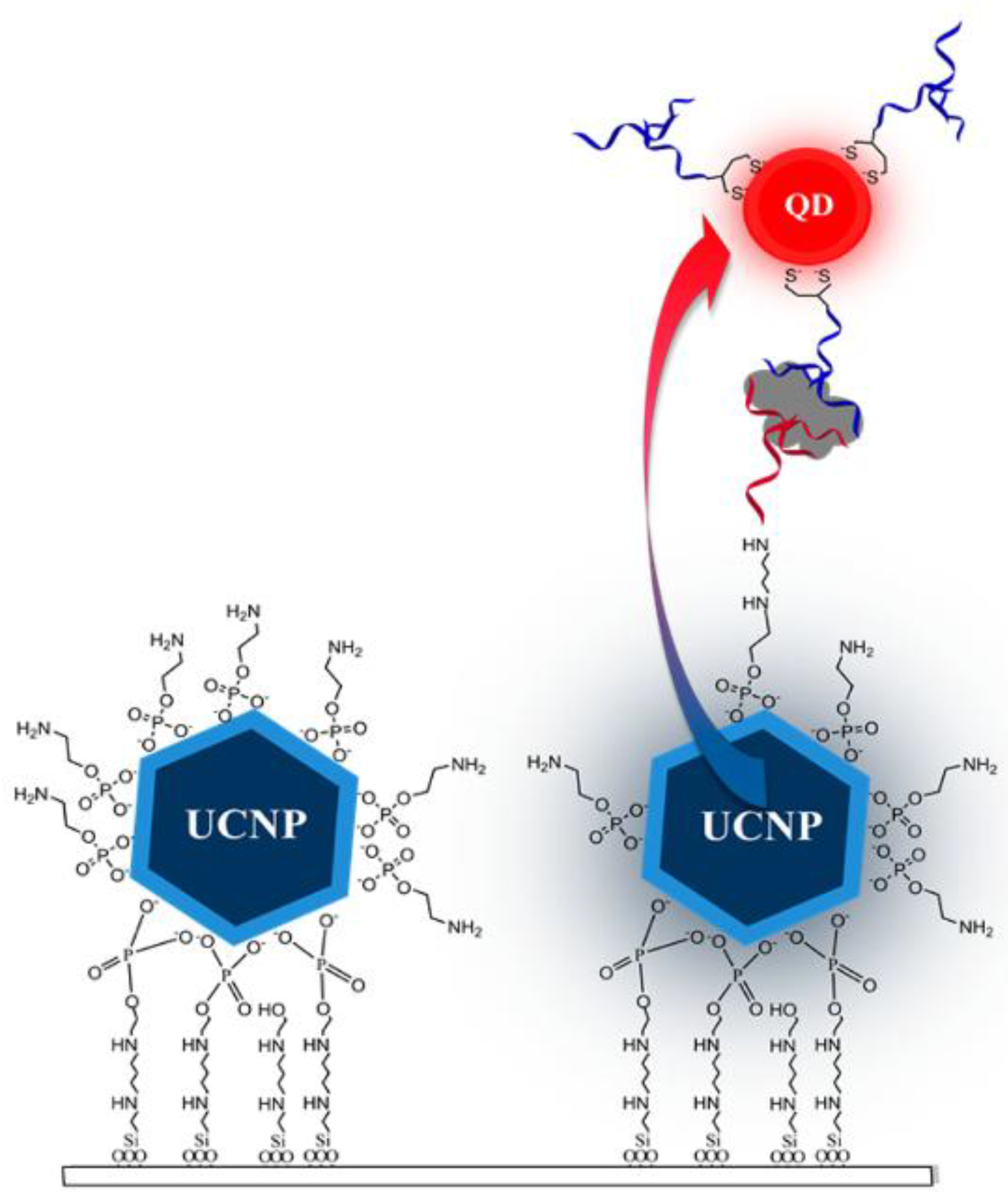
| Fe3O4/NaYF4: Yb3+, Er3+ | MUA | Carboxylate | Thiol | Affinity to Fe3O4 | Fe3O4 enhanced superparamagnetic UCNPs | [49] |
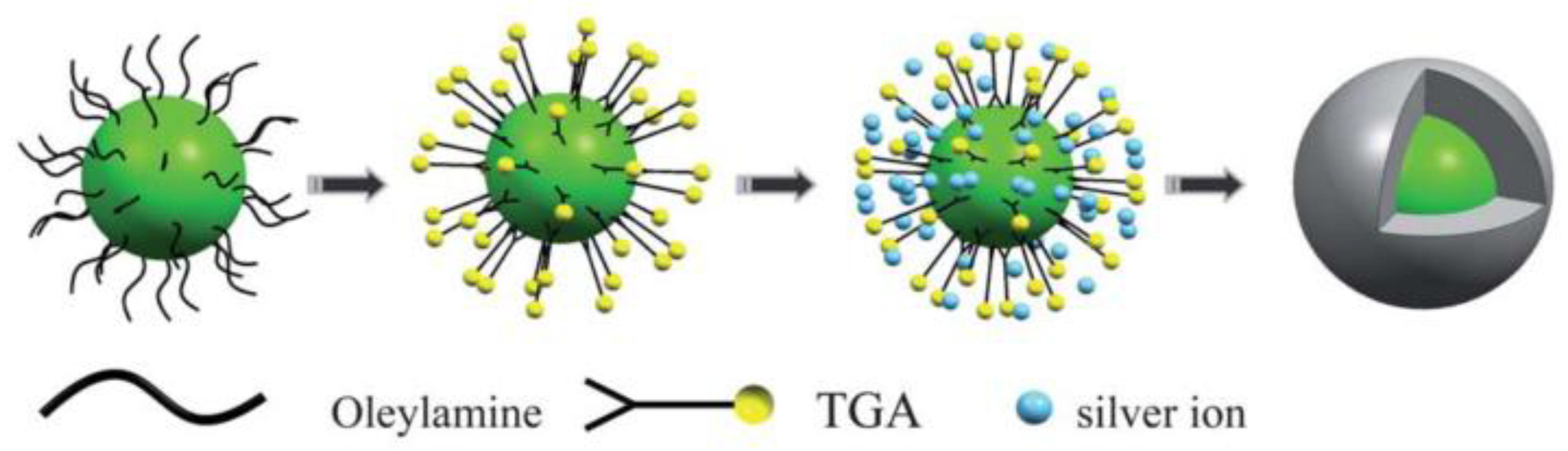
| NaYF4: Yb3+, Er3+ | TGA | Thiol | Carboxylic Acid | Electrostatic Interactions | Ag+-assisted photothermal therapy | [60] |
| Yb3+, Tm3+: BaF2/Ln3+:SrF2 | TGA | Thiol | Carboxylic Acid | Ligand Exchange | Dual-mode luminescence Active-core/Active-shell synthesis of UCNPs | [61] |
| NaYF4: Gd3+, Eu3+ | MPA | Thiol | Carboxylic Acid | Combined optical and MR imaging | [62] |
| UCNP | Silica Type | Functional Moiety | Method | Application | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NaYF4: Yb3+, Er3+ | dSiO2 | Carboxylic Acid | Electrostatic Interactions | RCA-120 functionalised UCNPs for biolabeling | [17] |
| NaYF4: Yb3+, Er3+ and NaGdF4: Yb3+, Er3+ | dSiO2 | Carboxylic Acid/Amino | Electraphoretic separation and purification of UCNPs@dSiO2 | [70] | |
| NaYF4: Yb3+, Er3+ | dSiO2 | Carboxylic Acid | EDC/NHS Chemistry | Highly sensitive DNA-based biosensor | [20] |
| NaYF4: Yb3+, Er3+ | dSiO2 | Carboxylic Acid | Oligonucleotide-based biosensor | [22] |
| UCNP | Silica Type | Functional Moiety | Method | Application | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NaYF4: Yb3+, Er3+ | dSiO2 | Amino/Carboxylic Acid | Electrostatic Interactions | Investigation of the effect of surface charge on cellular internalisation | [71] |
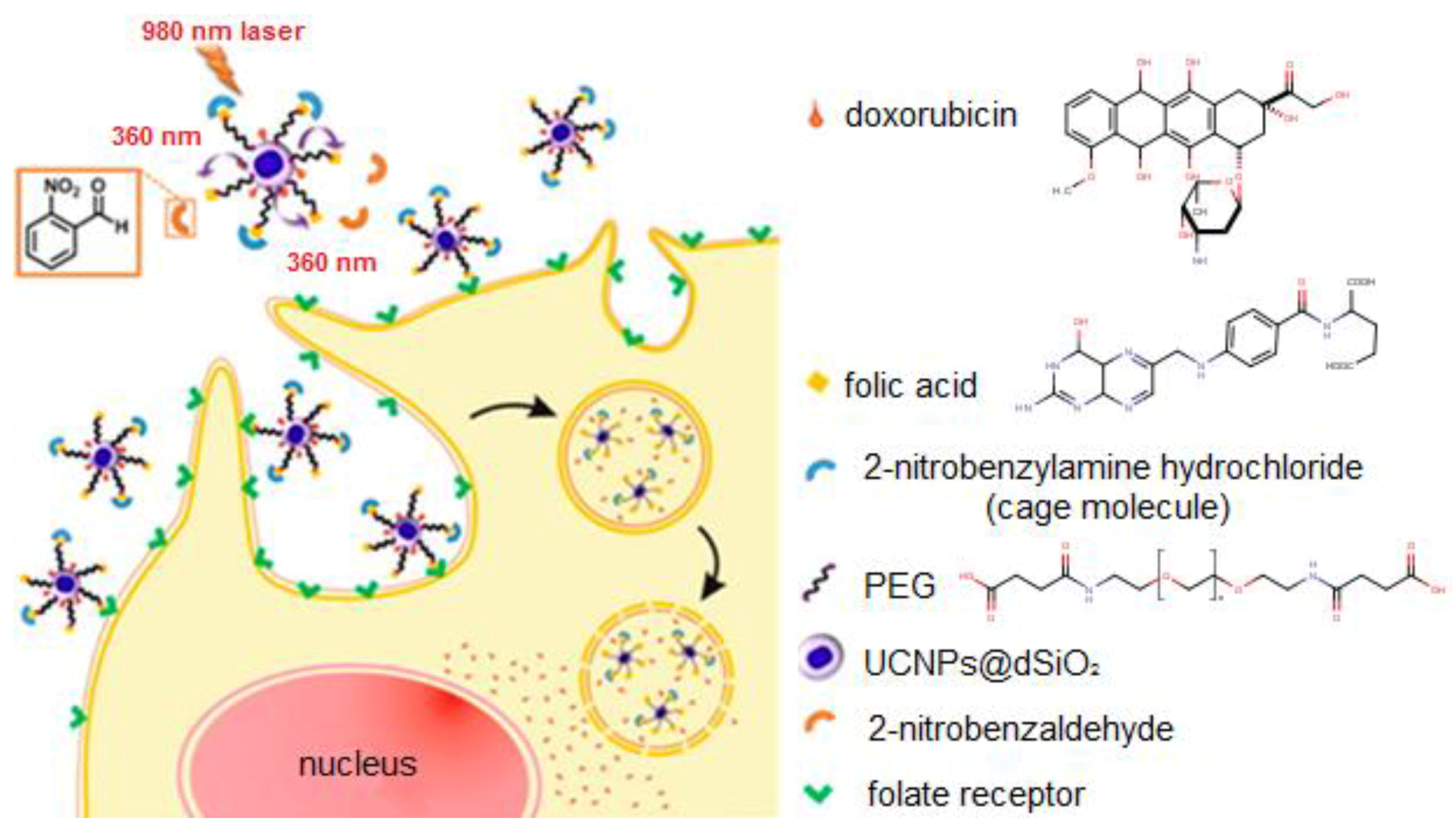
| NaYF4: Yb3+, Tm3+ | dSiO2 | Amino | EDC/NHS Chemistry | Photocaged and controlled chemotherapy System | [72] |
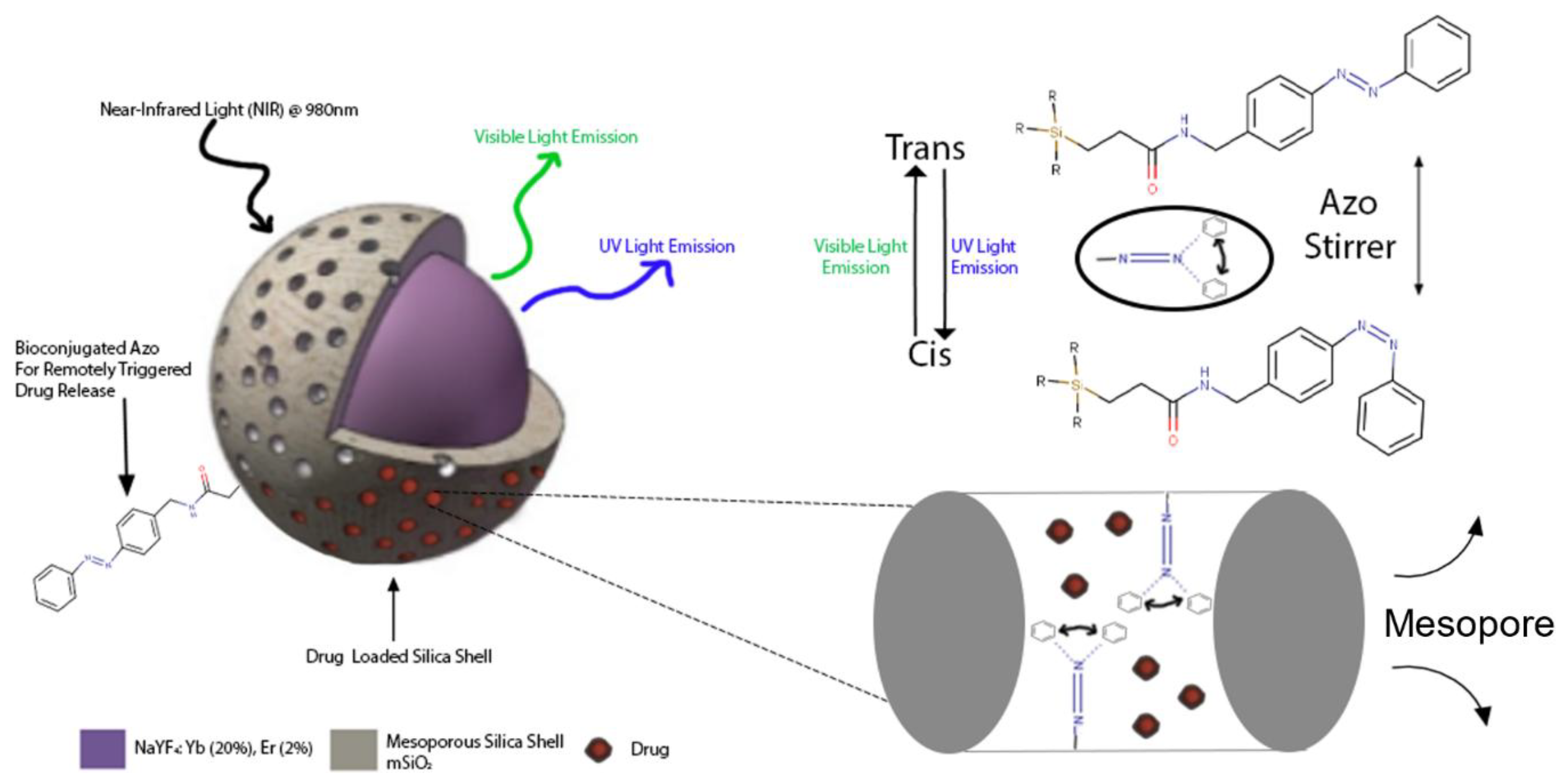
| NaYF4: Yb3+, Tm3+@ NaYF4 | mSiO2 | Amino | Azobenzene-gated remotely triggered drug delivery system | [24] | |
| NaYF4: Yb3+, Er3+ | mSiO2 | Amino | Targeted delivery of siRNA | [73] |
| UCNP | Silica Type | Functional Moiety | Method | Application | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NaYF4: Yb3+, Tm3+ | dSiO2 | Thiol | Thiol-Maleimide “Click” Chemistry | Photocaged UCNPs for remotely triggered cellular transduction | [76] |
| NaYF4: Yb3+, Tm3+/Au-NP | dSiO2 | Thiol | Sulfur-Gold Bond Interaction | UCNPs with attenuated X-Ray interaction as a theranostic platform | [77] |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gee, A.; Xu, X. Surface Functionalisation of Upconversion Nanoparticles with Different Moieties for Biomedical Applications. Surfaces 2018, 1, 96-121. https://doi.org/10.3390/surfaces1010009
Gee A, Xu X. Surface Functionalisation of Upconversion Nanoparticles with Different Moieties for Biomedical Applications. Surfaces. 2018; 1(1):96-121. https://doi.org/10.3390/surfaces1010009
Chicago/Turabian StyleGee, Alex, and Xiaoxue Xu. 2018. "Surface Functionalisation of Upconversion Nanoparticles with Different Moieties for Biomedical Applications" Surfaces 1, no. 1: 96-121. https://doi.org/10.3390/surfaces1010009
APA StyleGee, A., & Xu, X. (2018). Surface Functionalisation of Upconversion Nanoparticles with Different Moieties for Biomedical Applications. Surfaces, 1(1), 96-121. https://doi.org/10.3390/surfaces1010009