A Cross-Comparative Framework to Explore Land Use Histories of the Northeastern Peloponnese, Greece
Abstract
1. Introduction
- A means of aggregation that obviates or mitigates the methodological barriers between survey projects needs to be developed.
- Once configured, the data must be implemented within an interpretative framework that can couple human and environmental information.
1.1. Prior Approaches
1.2. Theoretical Considerations
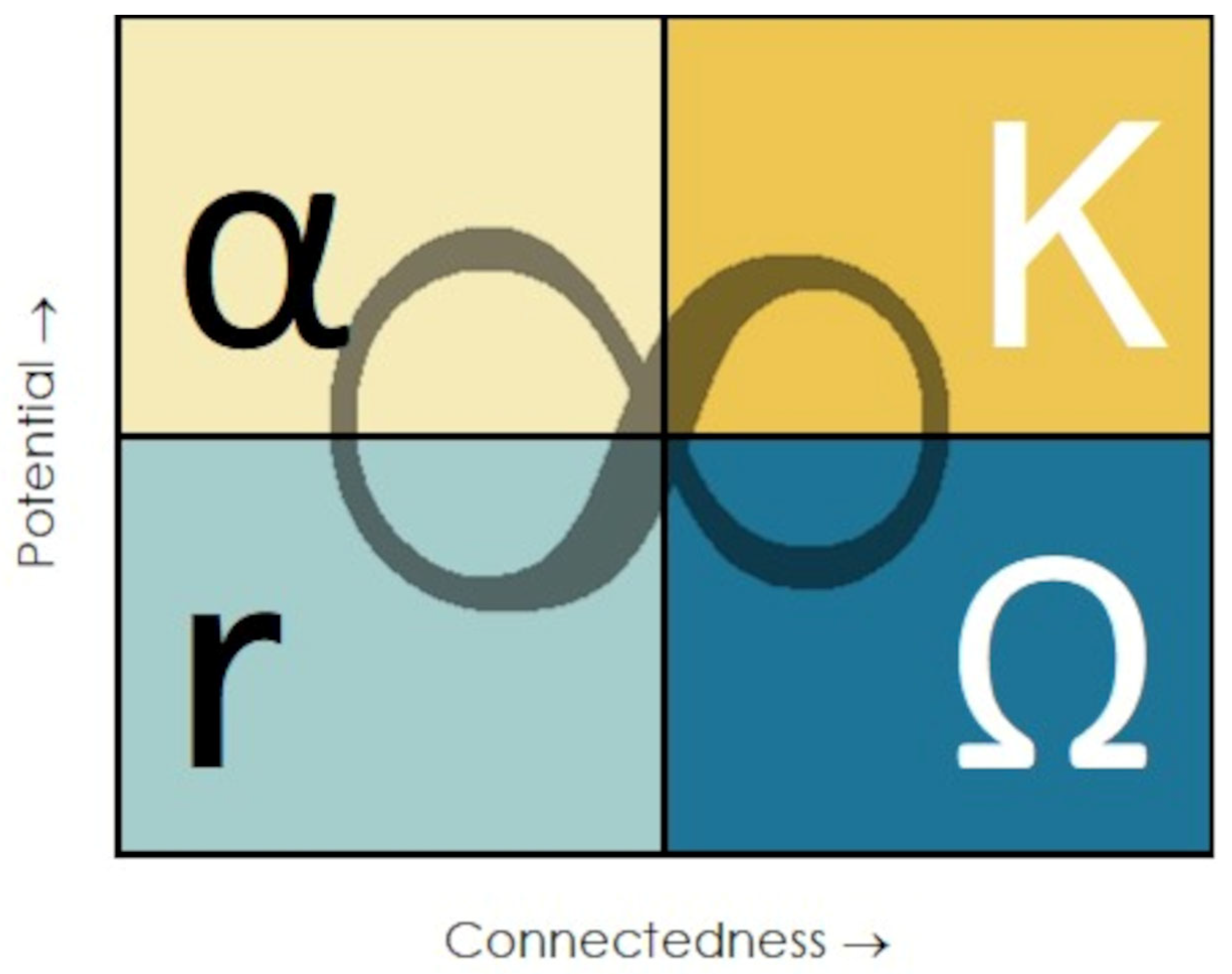
- A system consists of human and environmental components; the two are interdependent, often termed a ‘social-environmental system’ (SES).
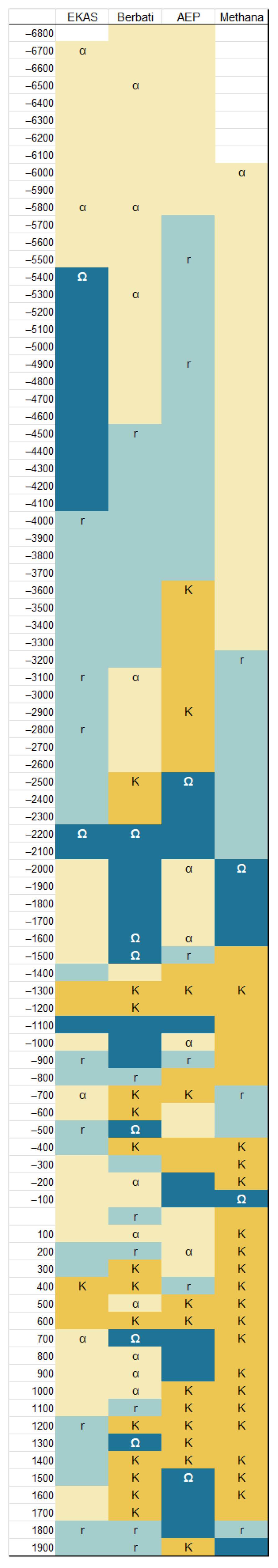
- An SES moves through the organization (α), expansion (r), conservation (K), and release (Ω) phases.
- Each phase consists of a combination of forces, termed ‘potential’ and ‘connectedness’. ‘Potential’ refers to the range of opportunities available to an SES to engage. For example, an SES in an organization phase would have several future permutations; a system in expansion, in contrast, having established set systems, has fewer options to respond to changing conditions. ‘Connectedness’ describes the level of engagement and interdependence between an SES and other entities.
- α: high potential, low connectedness. An SES is in the process of developing new structures and innovations. The SES is localized and experimental.
- r: low potential, low connectedness. The SES experiences growth—technological, demographic, or both—social structures become more complex and integrated.
- K: high potential, high connectedness. The SES is in stasis, with established social structures that reify the status quo. Practices solidify and become resistant to changing circumstances, either internal or external.
- Ω: low potential, high connectedness. Internal or external pressures become so prevalent that the SES cannot successfully respond, causing a need to reorganize/reconstruct effective structures.
2. Materials and Methods
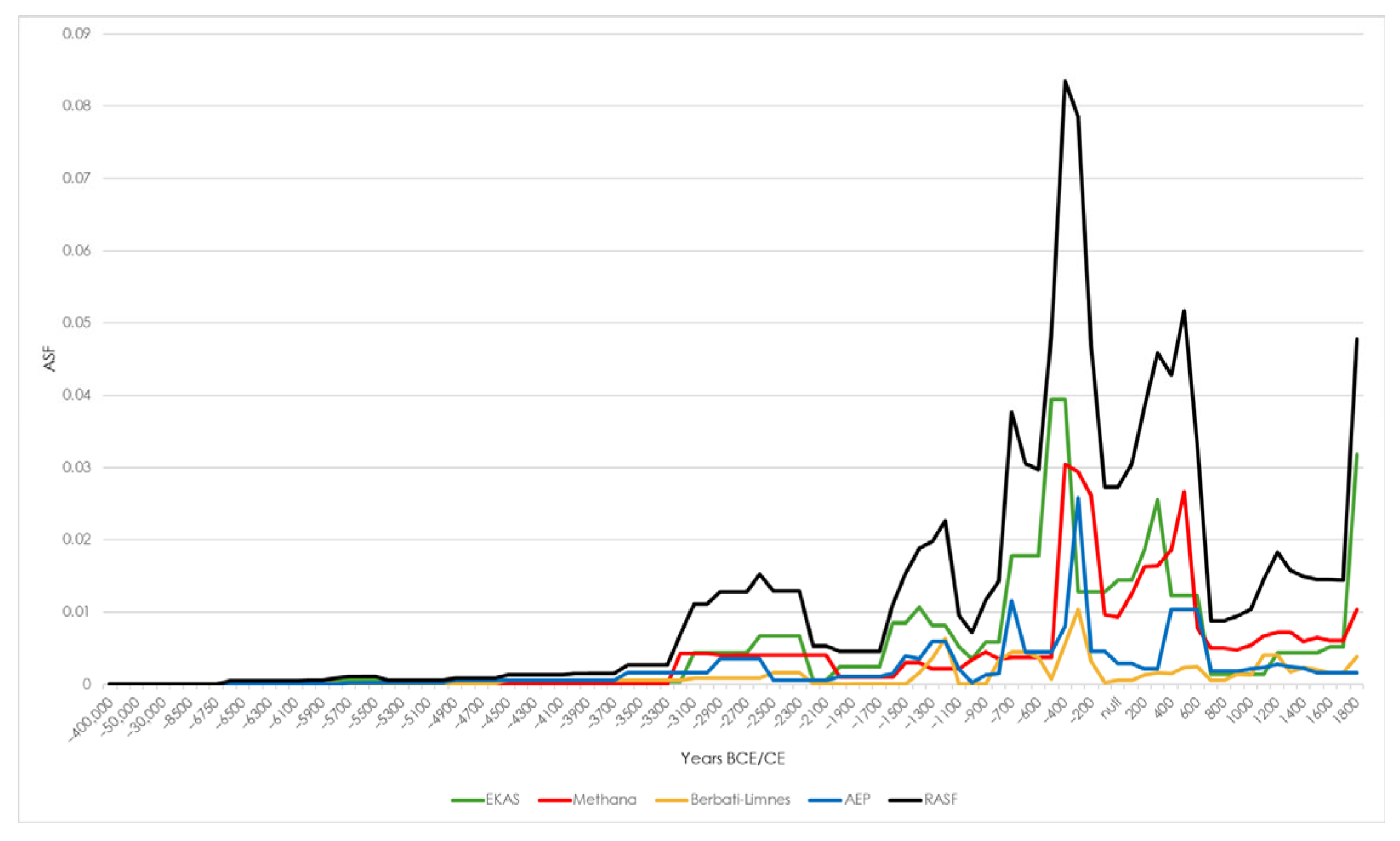
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AC | Adaptive Cycle |
| ASF | Aoristic Sum Function |
| ASV | Aoristic Sum Value |
| AV | Aoristic Value |
| LASF | Local Aoristic Sum Function |
| RASF | Regional Aoristic Sum Function |
Appendix A
Appendix A.1. Deriving Aoristic Sum Functions
- : Start year of the artifact’s temporal range.
- : End year of the artifact’s temporal range.
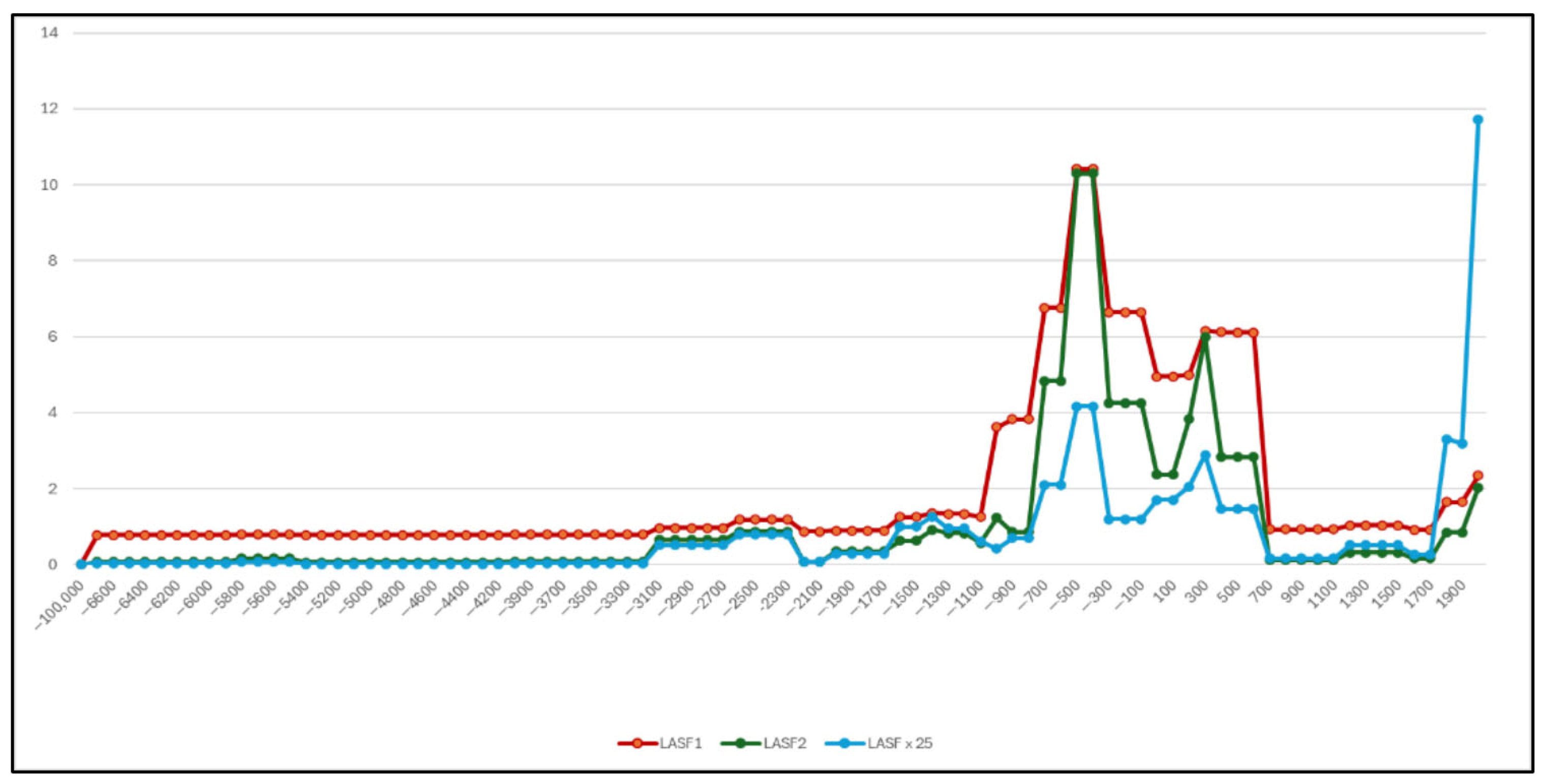
- The aoristic sum function (ASF) for a given year is calculated by summing the contributions from all artifacts:This equation is applied to all artifacts, including those with broad or imprecise chronological ranges (e.g., ceramic age, spanning 6700 BCE–2000 CE), ensuring the resulting aoristic sum function (ASF) incorporates all data, even those with poor chronological resolution (Figure A1).
| 1 | The term for an area of interest, consisting of a concentration of artifacts or other signs of human activity is known by many terms—site, feature, locus, POSI, LOCA, etc. This paper will employ the term ‘feature’ to refer generally to this element. When speaking about individual project findings, the project-specific term will be used. |
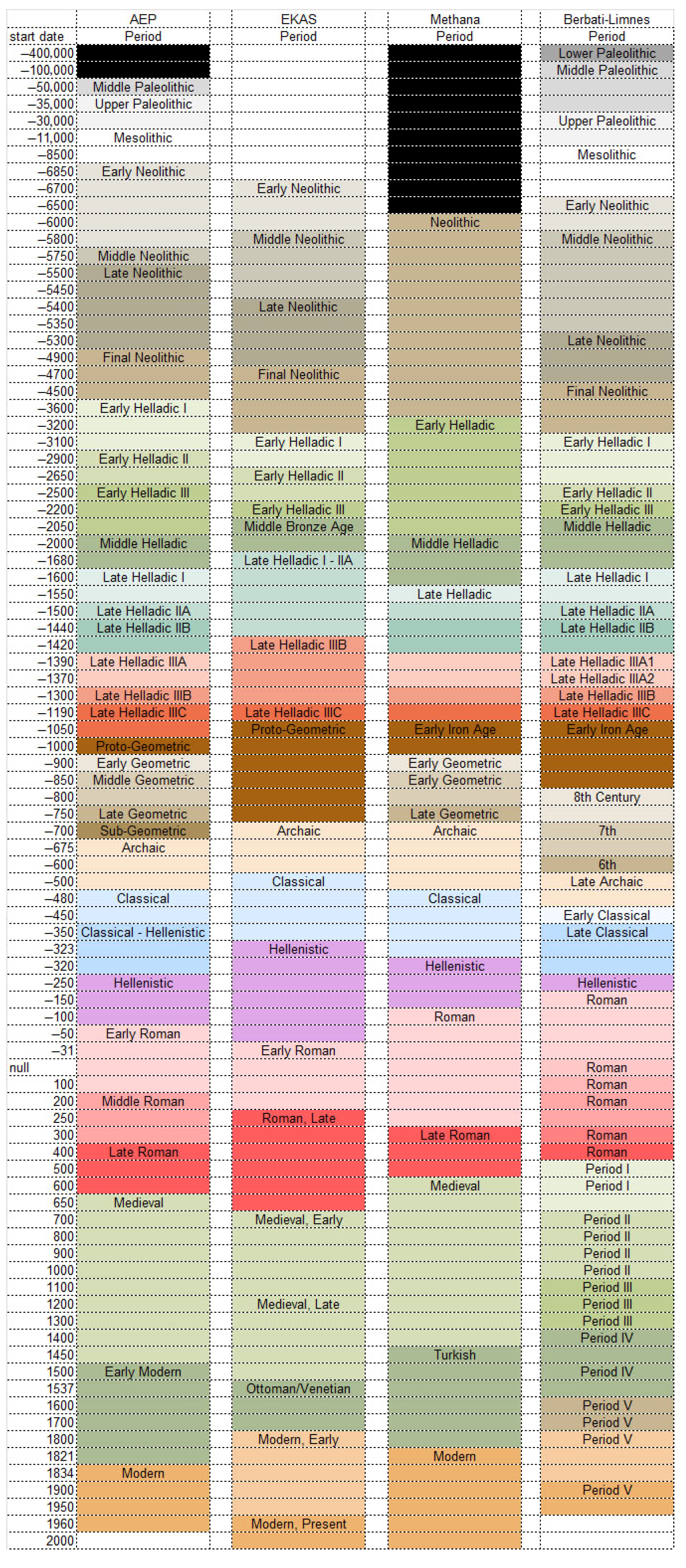
| 2 | It should be noted that this study employs the relative chronology originally used by the surveys in the study, with the exception of the Late Bronze Age (see Ref. [78]). See Weiberg and Finné [37] on the impact of relative chronologies in discussing connections between human and environmental events. |
References
- Burke, A.; Peros, M.C.; Wren, C.D.; Pausata, F.S.R.; Riel-Salvatore, J.; Moine, O.; de Vernal, A.; Kageyama, M.; Boisard, S. The Archaeology of Climate Change: The Case for Cultural Diversity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2108537118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burke, A.; Grove, M.; Maier, A.; Wren, C.; Drapeau, M.; Poisot, T.; Moine, O.; Boisard, S.; Bruxelles, L. The Archaeology of Climate Change: A Blueprint for Integrating Environmental and Cultural Systems. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 5289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiberg, E.; Unkel, I.; Kouli, K.; Holmgren, K.; Avramidis, P.; Bonnier, A.; Dibble, F.; Finné, M.; Izdebski, A.; Katrantsiotis, C.; et al. The Socio-Environmental History of the Peloponnese during the Holocene: Towards an Integrated Understanding of the Past. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2016, 136, 40–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izdebski, A.; Holmgren, K.; Weiberg, E.; Stocker, S.R.; Büntgen, U.; Florenzano, A.; Gogou, A.; Leroy, S.A.G.; Luterbacher, J.; Martrat, B.; et al. Realising Consilience: How Better Communication between Archaeologists, Historians and Natural Scientists Can Transform the Study of Past Climate Change in the Mediterranean. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2016, 136, 5–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haldon, J.F.; Roberts, N.; Izdebski, A.; Fleitmann, D.; McCormick, M.; Cassis, M.; Doonan, O.; Eastwood, W.; Elton, H.; Ladstätter, S.; et al. The Climate and Environment of Byzantine Anatolia: Integrating Science, History, and Archaeology. J. Interdiscip. Hist. 2014, 45, 113–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knodell, A.R.; Wilkinson, T.C.; Leppard, T.P.; Orengo, H.A. Survey Archaeology in the Mediterranean World: Regional Traditions and Contributions to Long-Term History. J. Archaeol. Res. 2023, 31, 263–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassis, M.; Doonan, O.; Elton, H.; Newhard, J. Evaluating Archaeological Evidence for Demographics, Abandonment, and Recovery in Late Antique and Byzantine Anatolia. Hum. Ecol. 2018, 46, 381–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, N.; Cassis, M.; Doonan, O.; Eastwood, W.; Elton, H.; Haldon, J.F.; Izdebski, A.; Newhard, J. Not the End of the World? Post-Classical Decline and Recovery in Rural Anatolia. Hum. Ecol. 2018, 46, 305–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haldon, J.F.; Rosen, A. Society and Environment in the East Mediterranean ca 300–1800 CE. Problems of Resilience, Adaptation and Transformation. Introductory Essay. Hum. Ecol. 2018, 46, 275–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izdebski, A.; Pickett, J.; Roberts, N.; Waliszewski, T. The Environmental, Archaeological and Historical Evidence for Regional Climatic Changes and Their Societal Impacts in the Eastern Mediterranean in Late Antiquity. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2016, 136, 189–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanton, R.; Feinman, G.; Kowalewski, S.; Nicholas, L. Ancient Oaxaca. The Monte Albán State; Case Studies in Early Societies; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Cherry, J.F. Frogs Round the Pond: Perspectives on Current Archaeological Survey Projects in the Mediterranean Region. In Archaeological Survey in the Mediterranean Area; Keller, D.R., Rupp, D.W., Eds.; BAR international series; British Archaeological Reports: Oxford, UK, 1983; pp. 375–416. [Google Scholar]
- Knodell, A.R. Societies in Transition in Early Greece: An Archaeological History; University of California Press: Oakland, CA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Attema, P.A.J.; Carafa, P.; Jongman, W.M.; Smith, C.J.; Bronkhorst, A.J.; Capanna, M.C.; de Haas, T.C.A.; van Leusen, P.M.; Tol, G.W.; Witcher, R.E.; et al. The Roman Hinterland Project: Integrating Archaeological Field Surveys around Rome and Beyond. Eur. J. Archaeol. 2022, 25, 238–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bintliff, J.; Sbonias, K. (Eds.) Introduction to Issues in Demography and Survey; The Archaeology of Mediterranean Landscapes; Oxbow: Oxford, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Francovich, R.; Patterson, H. (Eds.) Extracting Meaning from Ploughsoil Assemblages; The Archaeology of Mediterranean Landscapes; Oxbow: Oxford, UK, 2000; ISBN 978-1-900188-75-3. [Google Scholar]
- Alcock, S.E.; Cherry, J.F. (Eds.) Side-by-Side Survey: Comparative Regional Studies in the Mediterranean World; Oxbow: Havertown, PA, USA, 2004; ISBN 978-1-78570-158-0. [Google Scholar]
- Alcock, S.E.; Cherry, J.F. Introduction. In Side-by-Side Survey: Comparative Regional Studies in the Mediterranean World; Alcock, S.E., Cherry, J.F., Eds.; Oxbow: Havertown, PA, USA, 2004; pp. 1–9. ISBN 978-1-78570-474-1. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Stone, D.L. Problems and Possibilities in Comparative Survey: A North African Perspective. In Side-by-Side Survey: Comparative Regional Studies in the Mediterranean World; Alcock, S.E., Cherry, J.F., Eds.; Oxbow: Havertown, PA, USA, 2004; pp. 132–143. ISBN 978-1-78570-474-1. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Terrenato, N. Sample Size Matters! The Paradox of Global Trends and Local Surveys. In Side-by-Side Survey: Comparative Regional Studies in the Mediterranean World; Alcock, S.E., Cherry, J.F., Eds.; Oxbow: Havertown, PA, USA, 2004; pp. 36–48. ISBN 978-1-78570-474-1. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Wright, J. Comparative Settlement Patterns during the Bronze Age in the Northeastern Peloponnesos, Greece. In Side-by-Side Survey: Comparative Regional Studies in the Mediterranean World; Alcock, S.E., Cherry, J.F., Eds.; Oxbow: Oxford, UK, 2004; pp. 114–131. ISBN 978-1-78570-158-0. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- de Haas, T.; van Leusen, M. FAIR Survey: Improving Documentation and Archiving Practices in Archaeological Field Survey through CIDOC CRM. Fasti Online Doc. Res. 2020, 12. Available online: https://www.fastionline.org/folder/FOLDER-sur-2020-12 (accessed on 23 June 2025).[Green Version]
- Chapman, J. Archaeological Proxy-Data for Demographic Reconstructions: Facts, Factoids or Fiction? In Reconstructing Past Population Tresnds in Mediterranean Europe (3000 BC–AD 1800); Bintliff, J.L., Sbonias, K., Eds.; The Archaeology of Mediterranean Landscapes; Oxbow: Oxford, UK, 1999; pp. 65–76. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- James, S.A.; Nakassis, D.; Caraher, W.R.; Gallimore, S.C.; Erny, G.; Fernandez, R.; Frankl, J.; Friedman, A.; Godsey, M.; Gradoz, M. Landscape Histories and Terrestrial Networks in the Peloponnese: Results from the Western Argolid Regional Project. Hesperia 2024, 93, 145–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newhard, J.; Elton, H.; Haldon, J. Assessing Continuity and Change in the Sixth to Ninth Century Landscape of North-Central Anatolia. In Winds of Change: Environment and Society in Anatolia. 15th International ANAMED Annual Symposium; Roosevelt, C., Haldon, J., Eds.; Koç University Research Center for Anatolian Civilization: Istanbul, Turkey, 2021; pp. 141–157. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Sbonias, K. Introduction to Issues in Demography and Survey. In Reconstructing Past Population Trends in Mediterranean Europe (3000 BC–AD 1800); Bintliff, J.L., Sbonias, K., Eds.; The Archaeology of Mediterranean Landscapes; Oxbow: Oxford, UK, 1999; pp. 1–20. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Given, M. Mapping and Manuring: Can We Compare Sherd Density Figures? In Side-by-Side Survey: Comparative Regional Studies in the Mediterranean World; Alcock, S.E., Cherry, J.F., Eds.; Oxbow: Havertown, PA, USA, 2004; pp. 13–21. ISBN 978-1-78570-474-1. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Meyer, N. Finding Sites in Mediterranean Survey. J. Mediterr. Archaeol. 2022, 35, 143–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leppard, T.P.; Knodell, A.R. Retrospect and Prospect in Regional Archaeology. In Regional Approaches to Society and Complexity: Studies in Honor of John F. Cherry; Knodell, A.R., Leppard, T.P., Eds.; Monographs in Mediterranean Archaeology; Equinox: Sheffield, UK, 2018; pp. 320–337. ISBN 978-1-78179-527-9. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Knodell, A.R.; Leppard, T.P. Regional Approaches to Society and Complexity: Setting an Agenda. In Regional Approaches to Society and Complexity: Studies in Honor of John F. Cherry; Knodell, A.R., Leppard, T.P., Eds.; Monographs in Mediterranean Archaeology; Equinox: Sheffield, UK, 2018; pp. 1–31. ISBN 978-1-78179-527-9. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Alcock, S.E. Graecia Capta: The Landscapes of Roman Greece; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1993. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Murray, S. The Collapse of the Mycenaean Economy: Imports, Trade, and Institutions, 1300–1700 BCE; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2017; ISBN 978-1-316-94686-2. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Attema, P.; Bintliff, J.; van Leusen, M.; Bes, P.; de Haas, T.; Donev, D.; Jongman, W.; Kaptijn, E.; Mayoral, V.; Menchelli, S.; et al. A Guide to Good Practice in Mediterranean Surface Survey Projects. J. Greek Archaeol. 2020, 5, 1–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millett, M. Dating, Quantifying and Utilizing Pottery Assemblages from Surface Survey. In Extracting Meaning from Ploughsoil Assemblages; Francovich, R., Patterson, H., Eds.; Archaeology of Mediterranean landscapes; Oxbow: Oxford, UK, 2000; pp. 53–59. ISBN 978-1-900188-75-3. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Weiberg, E.; Bevan, A.; Kouli, K.; Katsianis, M.; Woodbridge, J.; Bonnier, A.; Engel, M.; Finné, M.; Fyfe, R.; Maniatis, Y.; et al. Long-Term Trends of Land Use and Demography in Greece: A Comparative Study. Holocene 2019, 29, 742–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiberg, E.; Finné, M. Resilience and Persistence of Ancient Societies in the Face of Climate Change: A Case Study from Late Bronze Age Peloponnese. World Archaeol. 2018, 50, 584–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiberg, E.; Finné, M. Vulnerability to Climate Change in Late Bronze Age Peloponnese (Greece). In Climate Change and Ancient Societies in Europe and the Near East: Diversity in Collapse and Resilience; Erdkamp, P., Manning, J.G., Verboven, K., Eds.; Palgrave Studies in Ancient Economies; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 215–242. ISBN 978-3-030-81103-7. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Weiberg, E.; Hughes, R.E.; Finné, M.; Bonnier, A.; Kaplan, J.O. Mediterranean Land Use Systems from Prehistory to Antiquity: A Case Study from Peloponnese (Greece). J. Land Use Sci. 2019, 14, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnier, A.; Finné, M. Climate Variability and Landscape Dynamics in the Late Hellenistic and Roman North-Eastern Peloponnese. Antiquity 2020, 94, 1482–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyucha, A.; Duffy, P.R.; Parkinson, W.A. Prehistoric Human-Environmental Interactions on the Great Hungarian Plain. Anthropologie 2013, 51, 157–168. [Google Scholar]
- Riris, P.; Silva, F.; Crema, E.; Palmisano, A.; Robinson, E.; Siegel, P.E.; French, J.C.; Jørgensen, E.K.; Maezumi, S.Y.; Solheim, S.; et al. Frequent Disturbances Enhanced the Resilience of Past Human Populations. Nature 2024, 629, 837–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crema, E.R. Modelling Temporal Uncertainty in Archaeological Analysis. J. Archaeol. Method Theory 2012, 19, 440–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, I. Aoristic Analysis: Seeds of a New Approach to Mapping Archaeological Distributions through Time. In Enter the Past: The E-Way into the four Dimensions of Cultural Heritage: CAA2003; der Stadt Wien, M., Erbe, R.K., Wien, S., Eds.; BAR international series; Archaeopress: Oxford, UK, 2004; pp. 448–452. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Palmisano, A.; Bevan, A.; Shennan, S. Comparing Archaeological Proxies for Long-Term Population Patterns: An Example from Central Italy. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2017, 87, 59–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradtmöller, M.; Grimm, S.; Riel-Salvatore, J. Resilience Theory in Archaeological Practice—An Annotated Review. Quat. Int. 2017, 446, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redman, C.; Kinzig, A. Resilience of Past Landscapes: Resilience Theory, Society, and the Longue Durée. Conserv. Ecol. 2003, 7, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunderson, L.H.; Holling, C.S. (Eds.) Panarchy: Understanding Transformations in Human and Natural Systems; Island Press: London, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Newhard, J.; Cline, E.H. Panarchy and the Adaptive Cycle: A Case Study from Mycenaean Greece. In Perspectives on Public Policy in Societal-Environmental Crises; Izdebski, A., Haldon, J.F., Filipkowski, P., Eds.; Risk, Systems and Decisions; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2022; pp. 225–235. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Holling, C.S.; Gunderson, L.H. Resilience and Adaptive Cycles. In Panarchy: Understanding Transformations in Human and Natural Systems; Gunderson, L.H., Holling, C.S., Eds.; Island Press: London, UK, 2002; pp. 25–62. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Iannone, G. Release and Reorganization in the Tropics: A Comparative Perspective from Southeast Asia. In Beyond Collapse: Archaeological Perspectives on Resilience, Revitalization, and Transformation in Complex Societies; Faulseit, R.K., Ed.; Southern Illinois University: Carbondale, IL, USA, 2016; pp. 179–212. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
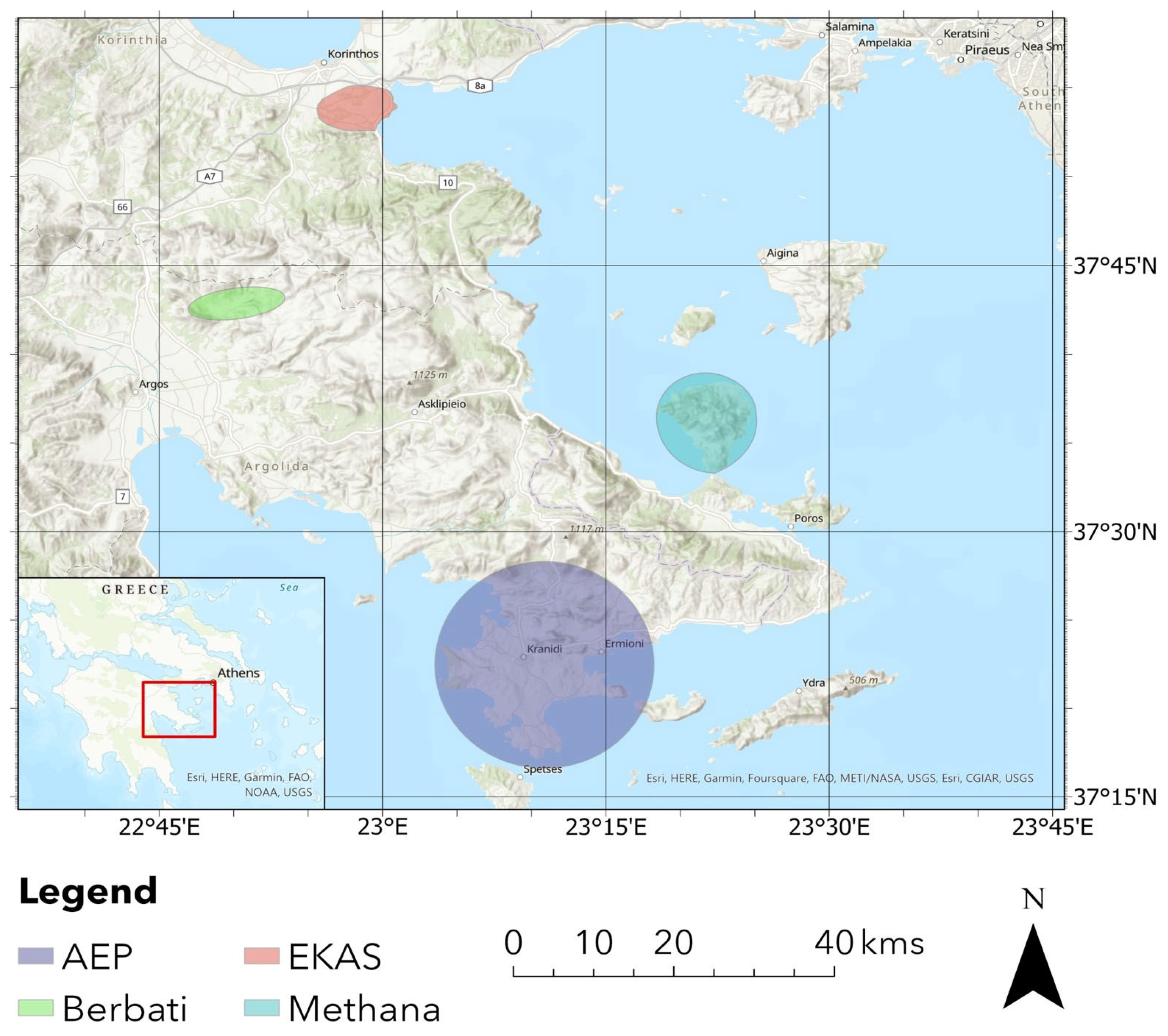
- Runnels, C.N. Appendix A. A Register of Sites. In A Greek Countryside: The Southern Argolid from Prehistory to the Present Day; Jameson, M.H., Runnels, C.N., van Andel, T.H., Eds.; Stanford University Press: Stanford, CA, USA, 1994; pp. 415–538. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Wells, B. (Ed.) The Berbati-Limnes Archaeological Survey, 1988–1990; Paul Åströms Förlag: Jonsered, Sweden, 1996. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Mee, C.; Forbes, H. (Eds.) A Rough and Rocky Place: The Landscape and Settlement History of the Methana Peninsula, Greece; Liverpool Monographs in Archaeology and Oriental Studies; Liverpool University Press: Liverpool, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Pettegrew, D.K.; Gregory, T.E.; Pullen, D.J.; Rothaus, R.; Tartaron, T.F. The Eastern Korinthia Archaeological Survey 2021. OpenContext. Available online: https://opencontext.org/projects/bc71c724-eb1e-47d6-9d45-b586ddafdcfe (accessed on 21 December 2022).[Green Version]
- Pettegrew, D.K. Corinthian Countrysides: Linked Open Data and Analysis from the Eastern Korinthia Archaeological Survey; University of North Dakota Digital Press: Grand Forks, ND, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Wright, J.C.; Cherry, J.F.; Davis, J.L.; Mantzourani, E.; Sutton, S.B.; Robert, F.S., Jr. The Nemea Valley Archaeological Project: A Preliminary Report. Hesperia 1990, 59, 579–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tartaron, T.F.; Tzortzopoulou-Gregory, L.; Pullen, D.J.; Dill, A.; Dunn, R.K.; Boyce, J.I. The Saronic Harbors Archaeological Research Project (SHARP) Investigations at Mycenaean Kalamianos, 2007–2009. Hesperia 2011, 80, 559–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athanassopoulos, E.F. Landscape Archaeology and the Medieval Countryside: Settlement and Abandonment in the Nemea Region. Int. J. Histor. Archaeol. 2010, 14, 255–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloke, C. The Landscape of the Lion: Economies of Religion and Politics in the Nemean Countryside (800 B.C. to A.D. 700). Doctoral Dissertation, University of Cincinnati, Cincinnati, OH, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Plog, S.; Plog, F.; Wait, W. Decision Making in Modern Surveys. Adv. Archaeol. Method Theory 1978, 1, 383–421. [Google Scholar]
- Banning, E.B.; Hawkins, A.L.; Stewart, S.T. Detection Functions for Archaeological Survey. Am. Antiq. 2006, 71, 723–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettegrew, D.K.; Gregory, T.E.; Pullen, D.J.; Rothaus, R.; Tartaron, T.F. EKAS Finds Data Table; Dataset; OpenContext; csv. 2025. Available online: https://opencontext.org/tables/a5ab46c5-8c9b-4f32-8522-3181afe83745 (accessed on 18 January 2025).[Green Version]
- Pettegrew, D.K.; Gregory, T.E.; Pullen, D.J.; Rothaus, R.; Tartaron, T.F. EKAS LOCAs Data Table; Dataset; OpenContext; csv. 2025. Available online: https://opencontext.org/tables/bd646482-d079-4430-ada4-5b8713821d04 (accessed on 18 January 2025).[Green Version]
- Runnels, C.N.; Pullen, D.J.; Langdon, S. Appendix 2. Assemblage Tables for Chapters 1-4. In Artifact and Assemblage: The Finds from a Regional Survey of the Southern Argolid, Greece; Runnels, C.N., Pullen, D.J., Langdon, S., Eds.; Stanford University Press: Stanford, CA, USA, 1995; pp. 223–319. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Timonen, R.E. Plain of Plenty. Farming Practices, Food Production, and the Agricultural Potential of the Late Bronze Age (1600–1200 BCE) Argive Plain, Greece; Archaeopress: Oxford, UK, 2024; p. 25. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Bonnier, A.; Finné, M.; Weiberg, E. Examining Land-Use through GIS-Based Kernel Density Estimation: A Re-Evaluation of Legacy Data from the Berbati-Limnes Survey. J. Field Archaeol. 2019, 44, 70–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tartaron, T.F.; Gregory, T.E.; Pullen, D.J. The Eastern Korinthia Archaeological Survey: Integrated Methods for a Dynamic Landscape. Hesperia 2006, 75, 453–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettegrew, D.K. The Busy Countryside of Late Roman Corinth: Interpreting Ceramic Data Produced by Regional Archaeological Surveys. Hesperia 2007, 76, 743–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettegrew, D.K. The End of Ancient Corinth? Views from the Landscape. In Methods and Meaning in Medieval and Post Medieval Greece: A Tribute to Timothy E. Gregory; Hall, L.J., Caraher, W.R., Moore, R.S., Eds.; Ashgate: Aldershot, UK, 2008; pp. 455–481. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Arena, E. Mycenaean Achaea before and after the Collapse. In Collapse and Transformation: The Late Bronze Age to Early Iron Age in the Aegean; Middleton, G.D., Ed.; Oxbow Books: Oxford, UK, 2020; pp. 35–43. ISBN 978-1-78925-425-9. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Arena, E. Mycenaean Peripheries during the Palatial Age. Hesperia 2015, 84, 1–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer-Hajos, M. The Euboean Gulf. In Collapse and Transformation: The Late Bronze Age to Early Iron Age in the Aegean; Middleton, G.D., Ed.; Oxbow Books: Oxford, UK, 2020; pp. 77–85. ISBN 978-1-78925-425-9. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Maggidis, C. Glas and Boeotia. In Collapse and Transformation: The Late Bronze Age to Early Iron Age in the Aegean; Middleton, G.D., Ed.; Oxbow Books: Oxford, UK, 2020; pp. 107–120. ISBN 978-1-78925-425-9. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- McKay, N.P.; Kaufman, D.S.; Arcusa, S.H.; Kolus, H.R.; Edge, D.C.; Erb, M.P.; Hancock, C.L.; Routson, C.C.; Żarczyński, M.; Marshall, L.P.; et al. The 4.2 Ka Event Is Not Remarkable in the Context of Holocene Climate Variability. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 6555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finné, M.; Holmgren, K.; Sundqvist, H.S.; Weiberg, E.; Lindblom, M. Climate in the Eastern Mediterranean, and Adjacent Regions, during the Past 6000 Years—A Review. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2011, 38, 3153–3173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finné, M.; Woodbridge, J.; Labuhn, I.; Roberts, C.N. Holocene Hydro-Climatic Variability in the Mediterranean: A Synthetic Multi-Proxy Reconstruction. Holocene 2019, 29, 847–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bini, M.; Zanchetta, G.; Perşoiu, A.; Cartier, R.; Català, A.; Cacho, I.; Dean, J.R.; Di Rita, F.; Drysdale, R.N.; Finnè, M.; et al. The 4.2 Ka BP Event in the Mediterranean Region: An Overview. Clim. Past 2019, 15, 555–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tartaron, T.F. Aegean Prehistory as World Archaeology: Recent Trends in the Archaeology of Bronze Age Greece. J. Archaeol. Res. 2008, 16, 83–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiberg, E. Contrasting Histories in Early Bronze Age Aegean: Uniformity, Regionalism and the Resilience of Societies in the Northeast Peloponnese and Central Crete. Camb. Archaeol. J. 2017, 27, 479–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiberg, E.; Lindblom, M. The Early Helladic II-III Transition at Lerna and Tiryns Revisited: Chronological Differences or Synchronous Variability. Hesperia 2014, 83, 383–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forsen, J. The Twilight of the Early Helladics: A Study of the Disturbances in East-Central and Southern Greece Toward the End of the Early Bronze Age; Paul Astroms Forlag: Jonsered, Sweden, 1992; ISBN 978-91-7081-031-2. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Kaniewski, D.; Paulissen, E.; Van Campo, E.; Weiss, H.; Otto, T.; Bretschneider, J.; Van Lerberghe, K. Late Second–Early First Millennium BC Abrupt Climate Changes in Coastal Syria and Their Possible Significance for the History of the Eastern Mediterranean. Quat. Res. 2010, 74, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaniewski, D.; Marriner, N.; Cheddadi, R.; Morhange, C.; Bretschneider, J.; Jans, G.; Otto, T.; Luce, F.; Van Campo, E. Cold and Dry Outbreaks in the Eastern Mediterranean 3200 Years Ago. Geology 2019, 47, 933–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molloy, B. Was There a 3.2 Ka Crisis in Europe? A Critical Comparison of Climatic, Environmental, and Archaeological Evidence for Radical Change during the Bronze Age–Iron Age Transition. J. Archaeol. Res. 2023, 31, 331–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cline, E.H. 1177 B.C.: The Year Civilization Collapsed; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Middleton, G.D. Mycenaean Collapse(s) c. 1200 BC. In Collapse and Transformation: The Late Bronze Age to Early Iron Age in the Aegean; Middleton, G.D., Ed.; Oxbow Books: Oxford, UK, 2020; pp. 9–22. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Deger-Jalkotzy, S. Decline, Destruction, Aftermath. In The Cambridge companion to the Aegean Bronze Age; Shelmerdine, C.W., Ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2008; pp. 387–415. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Middleton, G.D. The Collapse of Palatial Society in LBA Greece and the Postpalatial Period; BAR International Series; Archaeopress: Oxford, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Linkov, I.; Galaitsi, S.E.; Trump, B.; Pinigina, E.; Rand, K.; Cline, E.H.; Kitsak, M. Are Civilizations Destined to Collapse? Lessons from the Mediterranean Bronze Age. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2024, 84, 102792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middleton, G.D. (Ed.) Collapse and Transformation: The Late Bronze Age to Early Iron Age in the Aegean; Oxbow Books: Oxford, UK, 2020; ISBN 978-1-78925-425-9. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Lemos, I.S.; Kotsonas, A. (Eds.) A Companion to the Archaeology of Early Greece and the Mediterranean; Blackwell Companions to the Ancient World; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2020; ISBN 978-1-118-76996-6. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Kaniewski, D.; Campo, E.V.; Guiot, J.; Burel, S.L.; Otto, T.; Baeteman, C. Environmental Roots of the Late Bronze Age Crisis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e71004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherratt, S. Potemkin Palaces and Route-Based Economies. In Economy and Politics in the Mycenaean Palace States. Proceedings of a Conference Held on 1–3 July 199 in the Faculty of Classics, Cambridge; Cambridge Philological Society Supplementary Volume; Cambridge Philological Society: Cambridge, UK, 2001; pp. 214–238. ISBN 0-906014-26-3. [Google Scholar]
- Crema, E.R. A Bayesian Alternative for Aoristic Analyses in Archaeology. Archaeometry 2024, 67, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bintliff, J.; Howard, P.; Snodgrass, A. The Hidden Landscape of Prehistoric Greece. J. Mediterr. Archaeol. 1999, 12, 139–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettegrew, D.K. Chasing the Classical Farmstead: Assessing the Formation and Signature of Rural Settlement in Greek Landscape Archaeology. J. Mediterr. Archaeol. 2001, 14, 189–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bintliff, J.L.; Farinetti, E.; Howard, P.; Sarri, K.; Sbonias, K. Classical Farms, Hidden Prehistoric Landscapes and Greek Rural Survey: A Response and an Update. J. Mediterr. Archaeol. 2002, 15, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Runnels, C.N.; Panagopoulou, E.; Murray, P.; Tsartsidou, G.; Allen, S.; Mullen, K.; Tourloukis, E. A Mesolithic Landscape in Greece: Testing a Site-Location Model in the Argolid at Kandia. J. Mediterr. Archaeol. 2005, 18, 259–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondyli, F.; Craft, S. The Making of a Byzantine Monastic Landscape: A Case Study from the Mazi Plain in Northwest Attica, Greece. J. Mediterr. Archaeol. 2020, 33, 135–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consoli, R. The Mycenaean Atlas Project. Available online: https://helladic.info/index.php (accessed on 10 June 2025).
- Kearns, C. Everyday Climates: Household Archaeologies and the Politics of Scale. Heritage 2025, 8, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manning, S.W. Climate and the Ancient World: Beyond Present Concerns to Complications, Where Details Matter. Heritage 2025, 8, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vignola, C.; Hättestrand, M.; Bonnier, A.; Finné, M.; Izdebski, A.; Katrantsiotis, C.; Kouli, K.; Liakopoulos, G.C.; Norström, E.; Papadaki, M.; et al. Mid-Late Holocene Vegetation History of the Argive Plain (Peloponnese, Greece) as Inferred from a Pollen Record from Ancient Lake Lerna. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0271548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- South, S.A. Method and Theory in Historical Archaeology; Studies in Archaeology; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1977; p. 215. [Google Scholar]

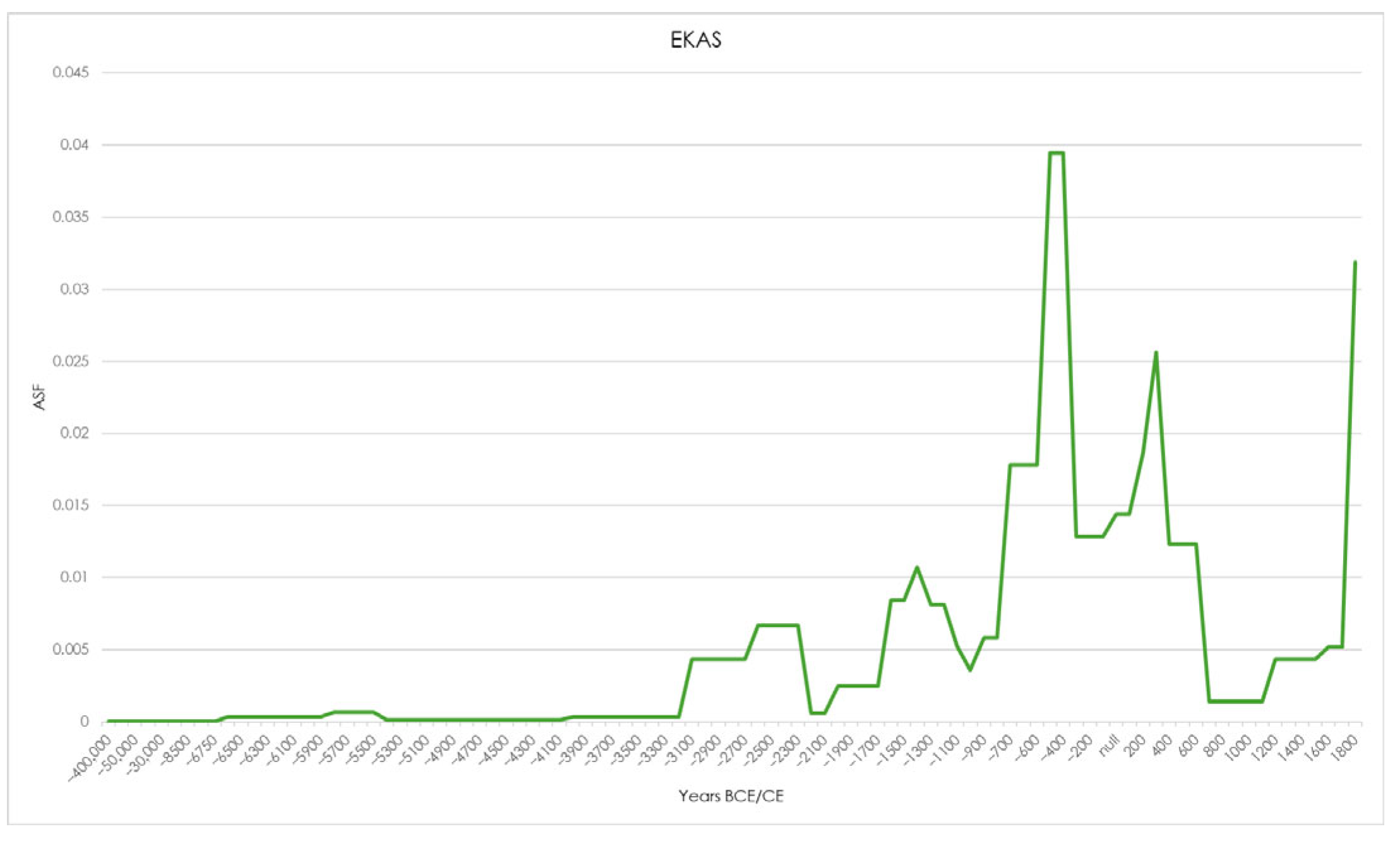
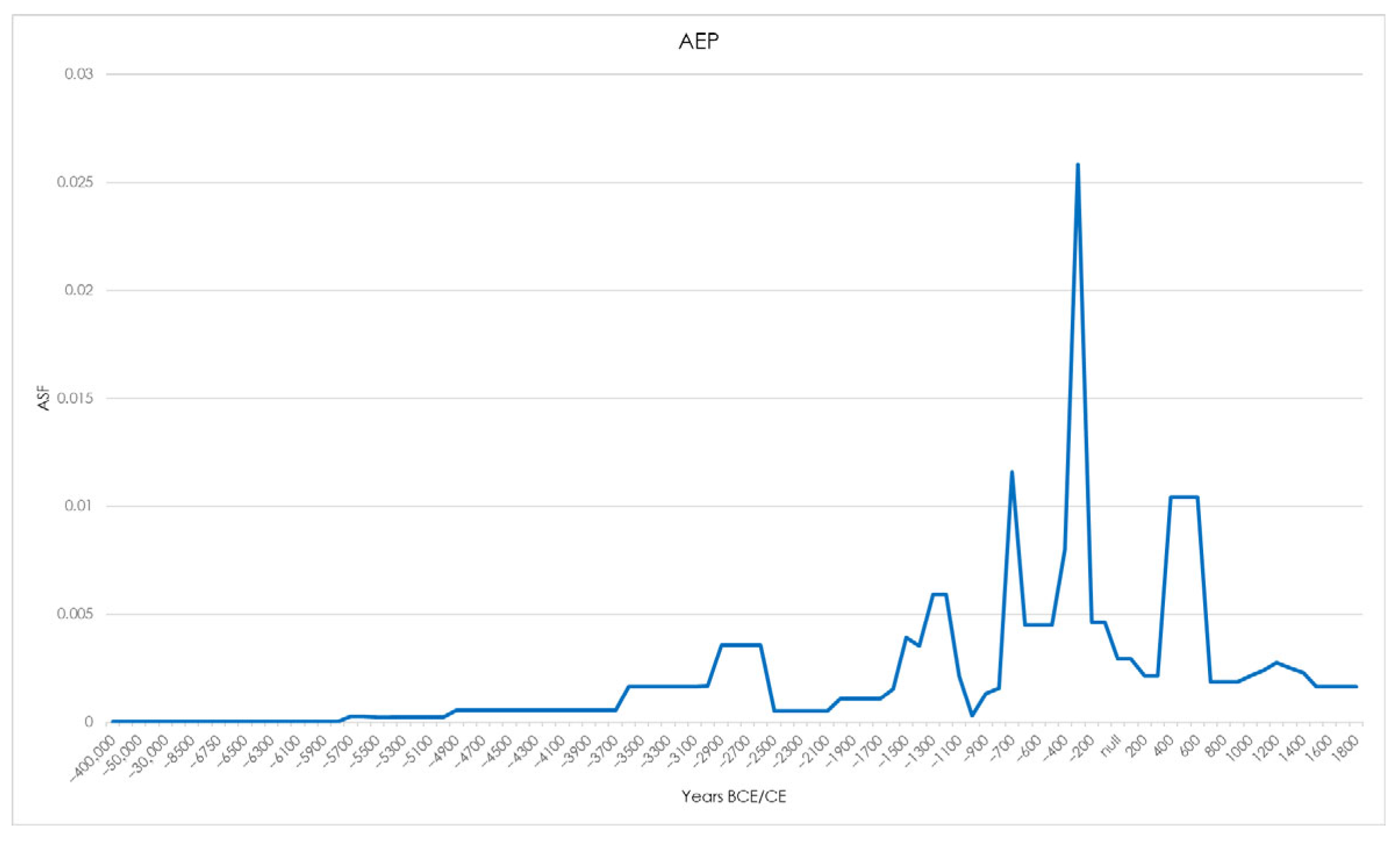
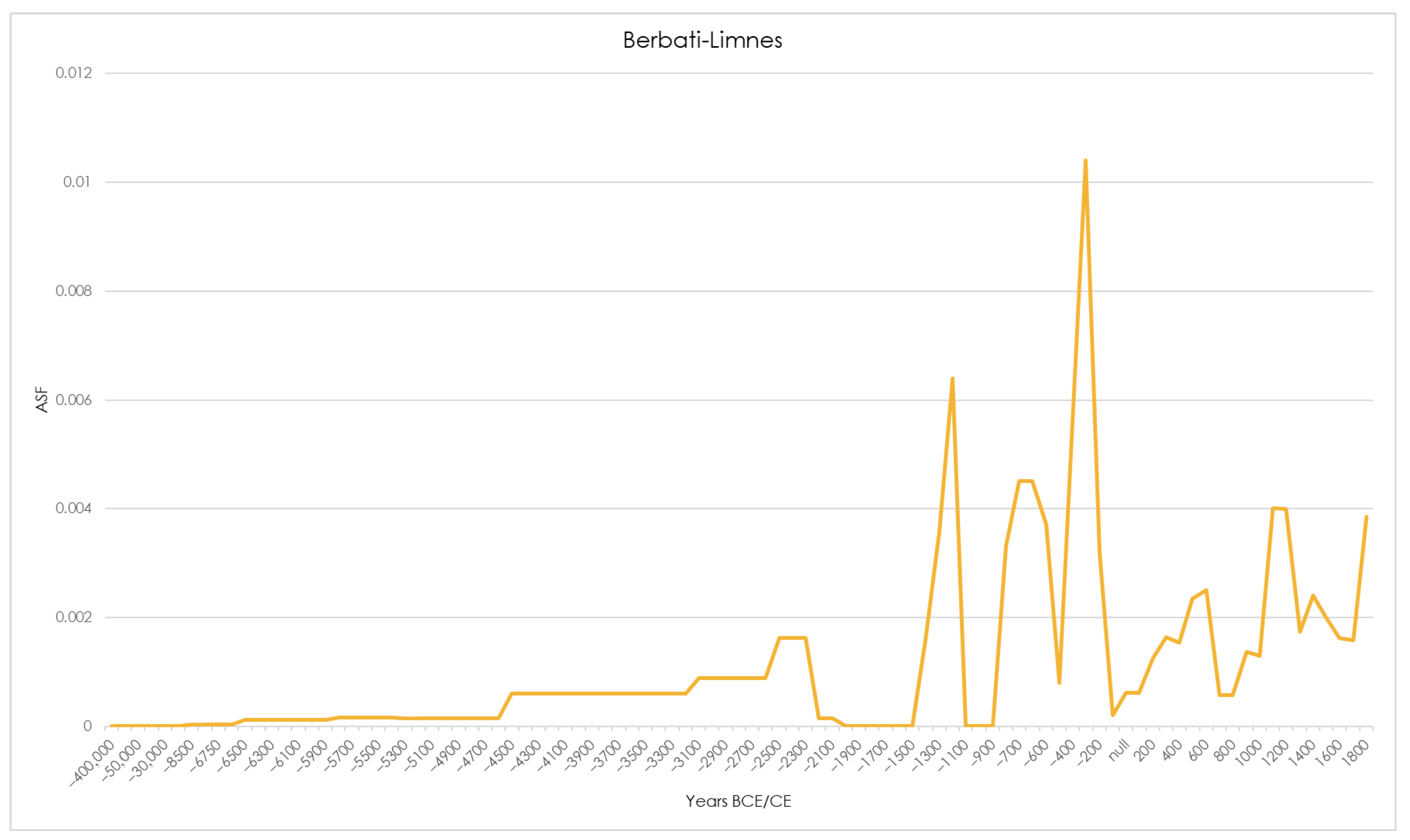
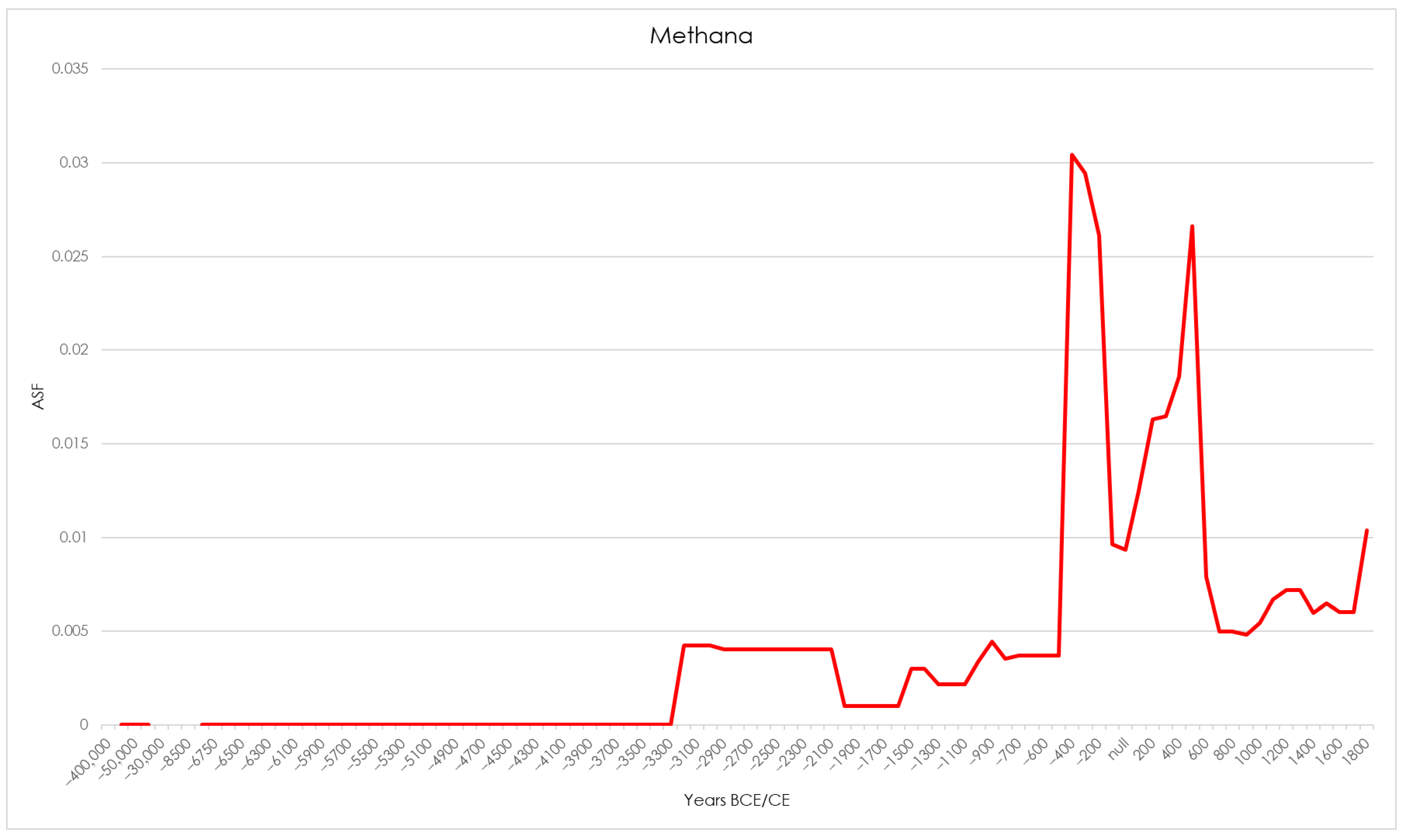
| Abandonment | |||
| class | lower | upper | count |
| low | 0 | 0.18391 | 83 |
| medium | 0.19786 | 0.53433 | 49 |
| high | 0.59375 | 1 | 37 |
| GVF | 1.56649 | 16.8539 | 0.90705 |
| Expansion | |||
| class | lower | upper | count |
| low | 0 | 0.19939 | 73 |
| medium | 0.21612 | 0.5502 | 46 |
| high | 0.57503 | 1 | 51 |
| GVF | 1.80452 | 17.5175 | 0.89699 |
| Continuity | |||
| class | lower | upper | count |
| low | 0 | 0.32591 | 56 |
| medium | 0.34325 | 0.69741 | 53 |
| high | 0.71094 | 1 | 60 |
| GVF | 1.58955 | 17.6292 | 0.90983 |
| α | r | K | Ω | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abandonment | Medium to High | Low | Low to Medium | High |
| Expansion | Medium to High | Medium to High | Low to Medium | Low |
| Continuity | Low | Medium to High | Medium to High | Low to Medium |
| Potential | 0 | 1 | 0 | −1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Newhard, J.; Tong, T.; Lombardi, A.; Bryan, H.; Campbell, K.; Jansen, E.; Titzler, M. A Cross-Comparative Framework to Explore Land Use Histories of the Northeastern Peloponnese, Greece. Heritage 2025, 8, 298. https://doi.org/10.3390/heritage8080298
Newhard J, Tong T, Lombardi A, Bryan H, Campbell K, Jansen E, Titzler M. A Cross-Comparative Framework to Explore Land Use Histories of the Northeastern Peloponnese, Greece. Heritage. 2025; 8(8):298. https://doi.org/10.3390/heritage8080298
Chicago/Turabian StyleNewhard, James, Tingting Tong, Antonia Lombardi, Haley Bryan, Kelsey Campbell, Emma Jansen, and Matthew Titzler. 2025. "A Cross-Comparative Framework to Explore Land Use Histories of the Northeastern Peloponnese, Greece" Heritage 8, no. 8: 298. https://doi.org/10.3390/heritage8080298
APA StyleNewhard, J., Tong, T., Lombardi, A., Bryan, H., Campbell, K., Jansen, E., & Titzler, M. (2025). A Cross-Comparative Framework to Explore Land Use Histories of the Northeastern Peloponnese, Greece. Heritage, 8(8), 298. https://doi.org/10.3390/heritage8080298






