The Complex Life of Stone Heritage: Diagnostics and Metabarcoding on Mosaics from the Archaeological Park of Baia (Bacoli, Italy)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Description
2.1.1. Sampling Points and Macroscopic Observations
2.1.2. Measurement of Microclimatic Variables
2.2. Preliminary Diagnostic Analyses
2.2.1. X-Ray Diffraction Spectroscopy
2.2.2. FT-IR Spectroscopy
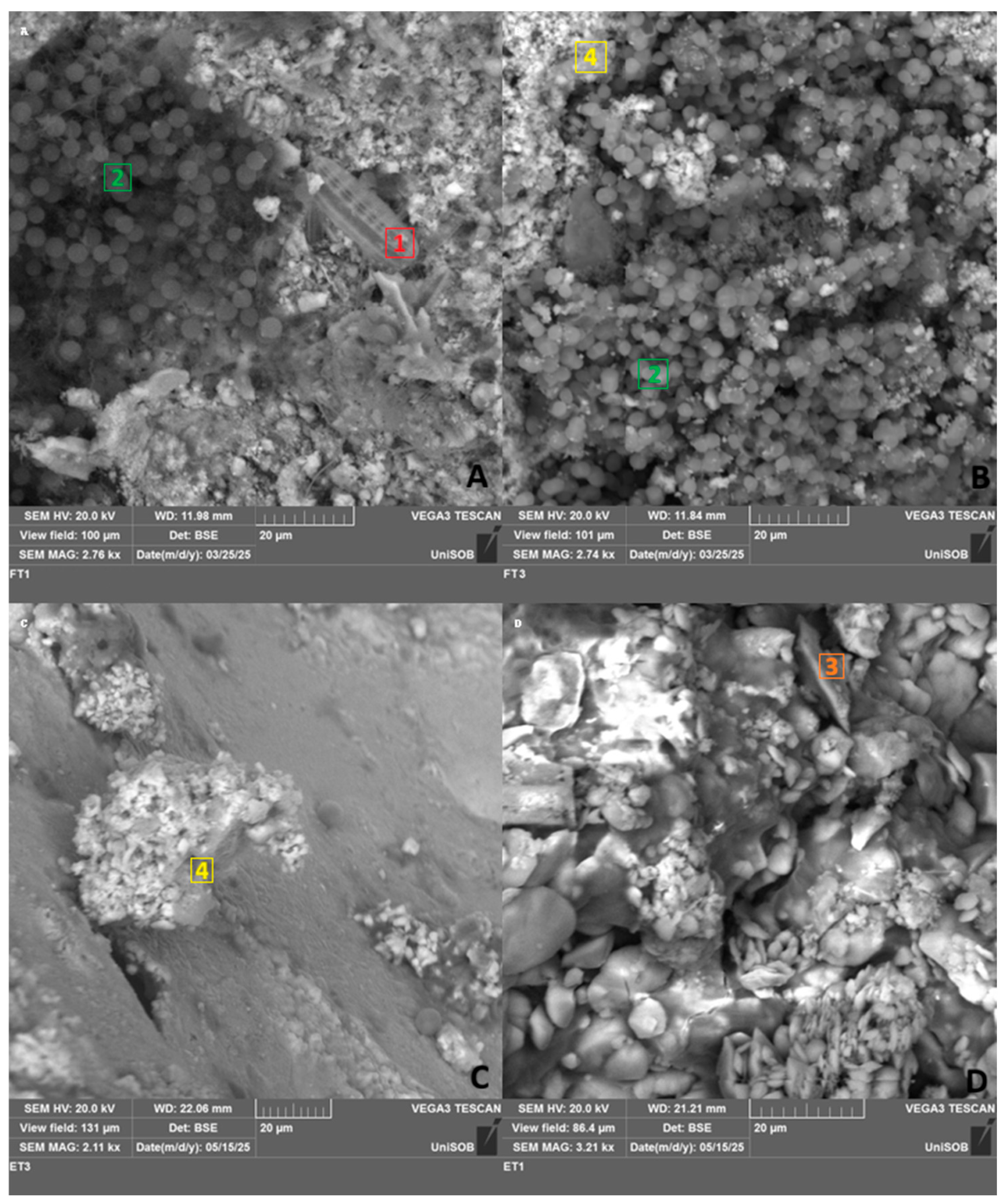
2.2.3. SEM/EDS Analyses
2.3. Biomolecular Analyses of Environmental Samples
2.4. Assessment of Results of the Restoration of Room F
2.4.1. Colorimetric Assays
2.4.2. Active Thermography
3. Results
3.1. Preliminary Diagnostic Analyses
3.1.1. X-Ray Diffraction Spectroscopy
3.1.2. FTIR Spectroscopy
3.1.3. SEM/EDS Analysis
3.2. Taxonomic Annotation of Strains
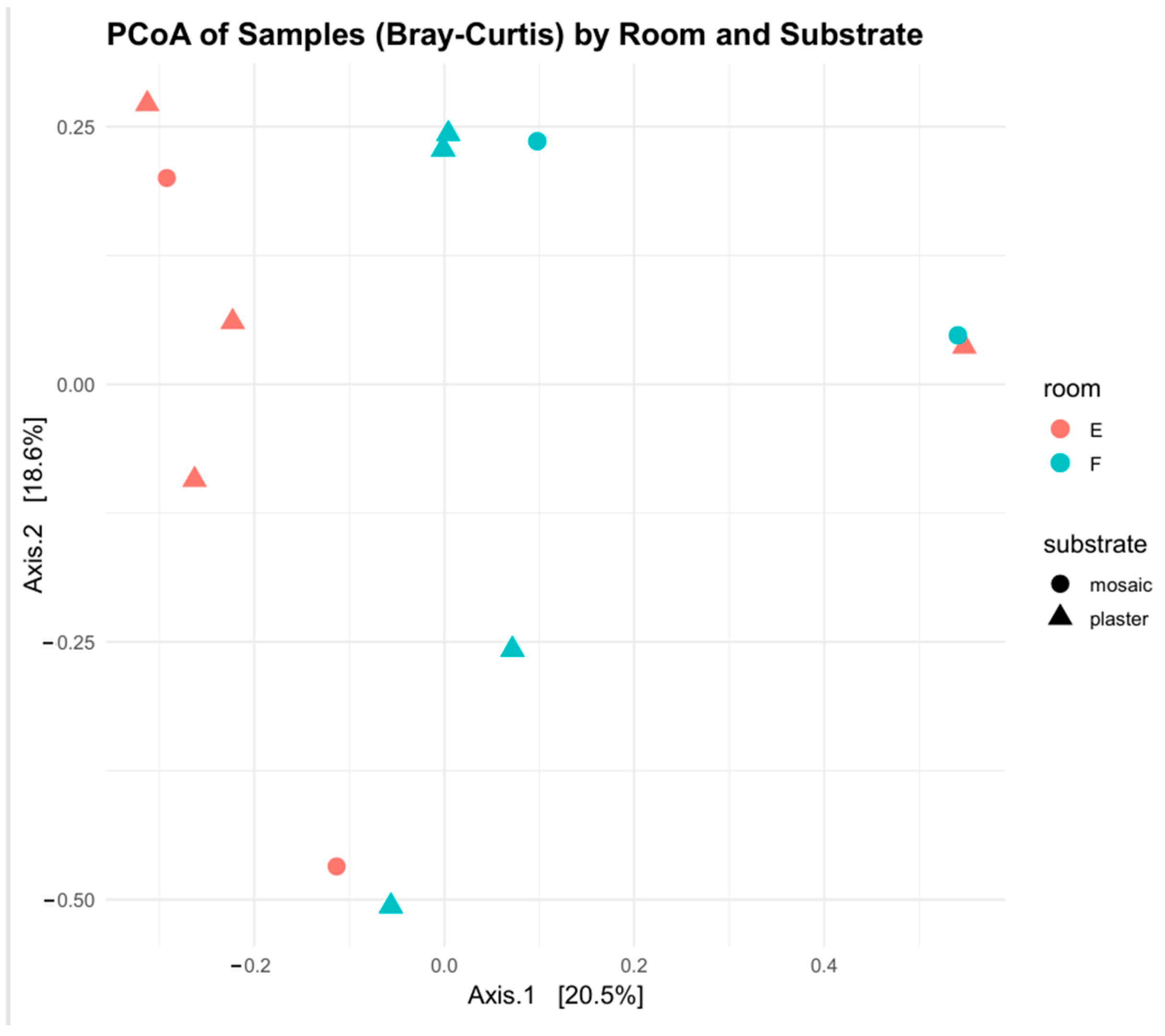
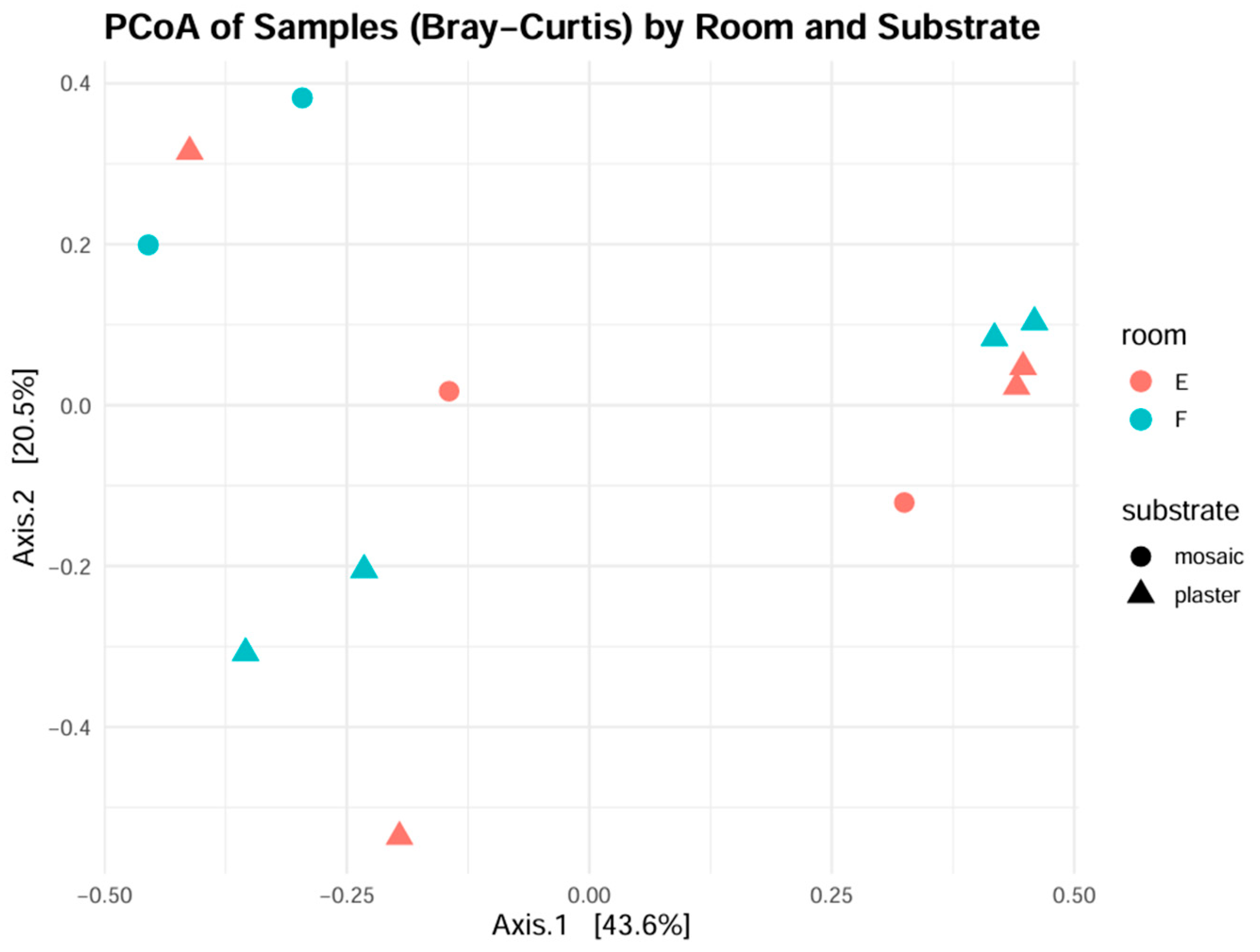
3.2.1. Prokaryotic Communities
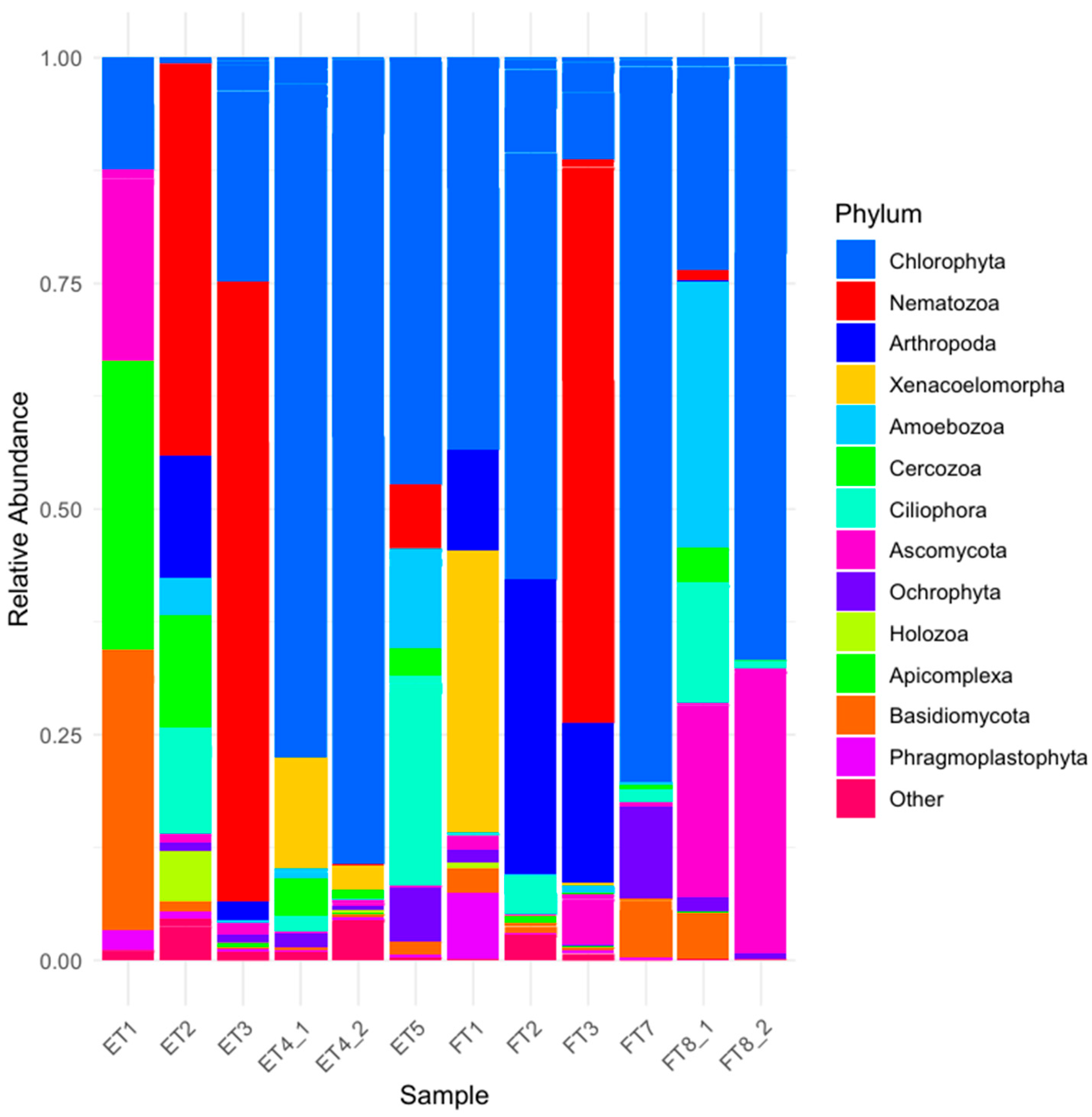
3.2.2. Eukaryotic Communities
3.3. Assessment of Results of the Restoration of Room F
3.3.1. Colorimetric Assays
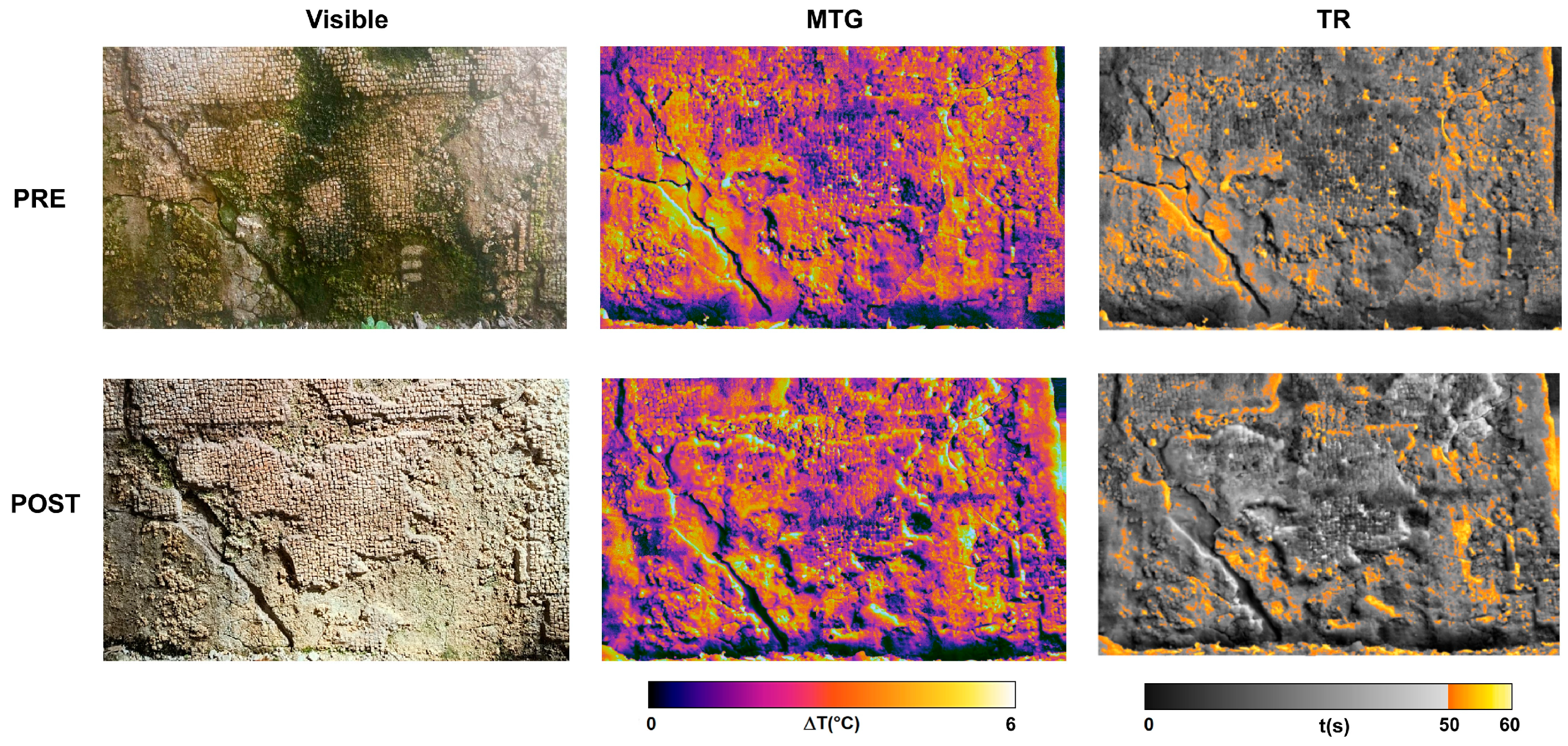
3.3.2. Active Thermography
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yadav, S.; Purchase, D. Biodeterioration of cultural heritage monuments: A review of their deterioration mechanisms and conservation. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2025, 201, 106066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warscheid, T.; Braams, J. Biodeterioration of stone: A review. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2000, 46, 343–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaylarde, C.C.; Baptista-Neto, J.A. Microbiologically Induced Aesthetic and Structural Changes to Dimension Stone. Npj Mater. Degrad. 2021, 5, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, E. Stone biodeterioration. In Cultural Heritage Microbiology: Fundamental Studies in Conservation Science; Mitchell, R., McNamara, C.J., Eds.; ASM Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2021; pp. 221–230. [Google Scholar]
- Gustavs, L.; Gors, M.; Karsten, U. Polyol patterns in biofilm-forming aeroterrestrial green algae (Trebouxiophyceae, Chlorophyta). J. Phycol. 2011, 47, 533–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowicka-Krawczyk, P.; Komar, M.; Gutarowska, B. Towards understanding the link between the deterioration of building materials and the nature of aerophytic green algae. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 802, 149856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Gong, C.; Gu, J.; Katayama, Y.; Someya, T.; Gu, J.D. Biochemical reactions and mechanisms involved in the biodeterioration of stone world cultural heritage under the tropical climate conditions. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2019, 143, 104723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komar, M.; Nowicka-Krawczyk, P.; Ruman, T.; Nizioł, J.; Dudek, M.; Gutarowska, B. Biodeterioration potential of algae on building materials-Model study. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2023, 180, 105593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sand, W.; Bock, E. Biodeterioration of mineral materials by microorganisms—Biogenic sulfuric and nitric acid corrosion of concrete and natural stone. Geomicrobiol J. 1991, 9, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaylarde, C.; Ribas Silva, M.; Warscheid, T. Microbial impact on building materials: An overview. Mater. Struct. 2003, 36, 342–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macedo, M.F.; Miller, A.Z.; Dionísio, A.; Saiz-Jimenez, C. Biodiversity of cyanobacteria and green algae on monuments in the Mediterranean Basin: An overview. Microbiology 2009, 155, 3476–3490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutler, N.; Viles, H. Eukaryotic microorganisms and stone biodeterioration. Geomicrobiol. J. 2010, 27, 630–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiano, P. Biodeterioration of stone monuments: A worldwide issue. Open Conf. Proceed. J. 2016, 7, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Huang, J.; Zhou, Q. Water-salt transport modeling and sulfate erosion mechanisms in cultural heritage under microclimate. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 98, 111393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albertano, P. Cyanobacterial biofilms in monuments and caves. In Ecology of Cyanobacteria II: Their Diversity in Space and Time; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 317–343. [Google Scholar]
- Rindi, F. Diversity, ecology and distribution of green algae and Cyanobacteria in urban habitats. In Algae and Cyanobacteria in Extreme Environments; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 583–597. [Google Scholar]
- Barberousse, H.; Lombardo, R.J.; Tell, G.; Couté, A. Factors involved in the colonization of building facades by algae and cyanobacteria in France. Biofouling 2006, 22, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortega-Calvo, J.J.; Arino, X.; Hernandez-Marine, M.; Saiz Jimenez, C. Factors affecting the weathering and colonization of monuments by phototrophic microorganisms. Sci. Total Environ. 1995, 167, 329–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crispim, C.A.; Gaylarde, C.C. Cyanobacteria and biodeterioration of cultural heritage: A review. Microb. Ecol. 2024, 49, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caneva, G.; Nugari, M.P.; Salvadori, O. Plant Biology for Cultural Heritage: Biodeterioration and Conservation; Getty Publications: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Cennamo, P.; De Rosa, A.; Scielzo, R.; Rippa, M.; Trojsi, G.; Chianese, E. Diagnostic investigation of the wall paints conservative state in a hypogeal room of the archaeological park of Baia (Italy). Acta IMEKO 2024, 13, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Rosa, A.; Cennamo, P.; Saltarelli, C.; Trojsi, G.; Rimauro, J.; Vigorito, M.R.; Chianese, E. The Effects of Urban Pollution on the “Gesù Nuovo” Façade (Naples, Italy): A Diagnostic Overview. Atmosphere 2025, 16, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camuffo, D. Microclimate for Cultural Heritage: Measurement, Risk Assessment, Conservation, Restoration, and Maintenance of Indoor and Outdoor Monuments; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Paoloni, S.; Orazi, N.; Zammit, U.; Bison, P.; Mercuri, F. A note on the early thermographic approaches for the investigation of the Cultural Heritage. Quant. InfraRed Thermogr. J. 2024, 21, 408–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Squarciafico, C.; Salatino, G.; La Russa, M.F.; Peluso, T.; Basile, L.; Barbagallo, F.S.; Coppola, M.; Macchia, A. New chemical systems for the removal of calcareous encrustations on monumental fountains: A case study of the Nymphaeum of Cerriglio. Heritage 2023, 6, 6358–6376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, I.; Dias, L.; Salvador, C.; Miller, A.Z.; Candeias, A.; Caldeira, A.T. Microbial induced stone discoloration in alcobaça monastery: A comprehensive study. J. Cult. Herit. 2024, 67, 248–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, C.; Santunione, G.; Libbra, A.; Muscio, A.; Sgarbi, E.; Siligardi, C.; Barozzi, G.S. Review on the influence of biological deterioration on the surface properties of building materials: Organisms, materials, and methods. Int. J. Des. Nat. Ecodyn. 2025, 10, 21–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, S.; Xu, Y.; Zhou, J. Deterioration of Masonry Cultural Relics by Microbes: Current Remediation Strategies and Prospects. Environ. Microbiol. 2025, 27, e70142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cennamo, P.; Scielzo, R.; Rippa, M.; Trojsi, G.; Carfagna, S.; Chianese, E. UV-C Irradiation and Essential-Oils-Based Product as Tools to Reduce Biodeteriorates on the Wall Paints of the Archeological Site of Baia (Italy). Coatings 2023, 13, 1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowicka-Krawczyk, P.; Zelazna-Wieczorek, J.; Kozlecki, T. Silver nanoparticles as a control agent against facades coated by aerial algae: A model study of Apatococcus lobatus (green algae). PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0183276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Qian, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wu, F.; Wang, W.; Gu, J.D. Innovative approaches for the processes involved in microbial biodeterioration of cultural heritage materials. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2022, 75, 102716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astolfi, M.L. Advances in analytical strategies to study cultural heritage samples. Molecules 2023, 28, 6423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costantini, I.; Aramendia, J.; Etxebarria, I.; de la Fuente, I.V.; Castro, K.; Sanchez-Pinto, I.; Pérez, L.; Yécora, B.; Sanz, M.; Prieto-Taboada, N.; et al. Raman spectroscopy assisted by other analytical techniques to identify the most deteriorated carbonate-stones to be consolidated in two monuments of Vitoria-Gasteiz (Spain). J. Raman Spectrosc. 2024, 55, 1309–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magdy, M. X-ray techniques dedicated to materials characterization in cultural heritage. Chem. Sel. 2023, 8, e202301306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rippa, M.; Pagliarulo, V.; Lanzillo, A.; Grilli, M.; Fatigati, G.; Rossi, P.; Cennamo, P.; Trojsi, G.; Ferraro, P.; Mormile, P. Active thermography for non-invasive inspection of an artwork on poplar panel: Novel approach using principal component thermography and absolute thermal contrast. J. Nondestruct. Eval. 2021, 40, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saltarelli, C.; Rippa, M.; Pagliarulo, V.; Vigorito, M.R.; Paturzo, M. The Heritage Building Information Modelling System for non-destructive optical techniques: The case study of the restoration of a Marble sculpture on the façade of the Gesù Nuovo Church in Naples. Acta IMEKO 2025, 14, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Miras, M.D.M.; Pinar, G.; Romero-Noguera, J.; Bolívar-Galiano, F.; Ettenauer, J.D.; Sterflinger, K.; Martín-Sánchez, I. Microbial communities adhering to the obverse and reverse sides of an oil painting on canvas: Identification and evaluation of their biodegradative potential. Aerobiology 2023, 29, 301–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutarowska, B. The use of-omics tools for assessing biodeterioration of cultural heritage: A review. J. Cult. Herit. 2020, 45, 351–361. [Google Scholar]
- Pyzik, A.; Ciuchcinski, K.; Dziurzynski, M.; Dziewit, L. The bad and the good—Microorganisms in cultural heritage environments—An update on biodeterioration and biotreatment approaches. Materials 2021, 14, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Luca, D.; Piredda, R.; Trojsi, G.; Cennamo, P. Close but different: Metabarcoding analyses reveal different microbial communities in ancient Roman nymphaea. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2023, 181, 105619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, S.; Tomita, J.; Nishioka, K.; Hisada, T.; Nishijima, M. Development of a prokaryotic universal primer for simultaneous analysis of Bacteria and Archaea using next-generation sequencing. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e105592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, S.; Tragin, M.; Lozano, J.C.; Ghiglione, J.F.; Vaulot, D.; Bouget, F.Y.; Galand, P.E. Rhythmicity of coastal marine picoeukaryotes, bacteria and archaea despite irregular environmental perturbations. ISME J. 2019, 13, 388–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estaki, M.; Jiang, L.; Bokulich, N.A.; McDonald, D.; González, A.; Kosciolek, T.; Martino, C.; Zhu, Q.; Birmingham, A.; Vázquez-Baeza, Y.; et al. QIIME 2 enables comprehensive end-to-end analysis of diverse microbiome data and comparative studies with publicly available data. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2020, 70, e100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Garrity, G.M.; Tiedje, J.M.; Cole, J.R. Naive Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 5261–5267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillou, L.; Bachar, D.; Audic, S.; Bass, D.; Berney, C.; Bittner, L.; Boutte, C.; Burgaud, G.; de Vargas, C.; Decelle, J.; et al. The Protist Ribosomal Reference database (PR2): A catalog of unicellular eukaryote small sub-unit rRNA sequences with curated taxonomy. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 41, D597–D604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rippa, M.; Vigorito, M.R.; Russo, M.R.; Mormile, P.; Trojsi, G. Active thermography for non-invasive inspection of wall painting: Novel approach based on thermal recovery maps. J. Nondestruct. Eval. 2023, 42, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokrzycki, W.S.; Tatol, M. Colour Difference ΔE—A Survey. Mach. Graph. Vis. 2011, 20, 383–412. [Google Scholar]
- Saiz-Jimenez, C. Biodeterioration: An overview of the state-of-the-art and assessment of future directions. Biodegrad. Cult. Herit. 2001, 520, 10–16. [Google Scholar]
- Charola, A.E.; Pühringer, J.; Steiger, M. Gypsum: A review of its role in the deterioration of building materials. Environ. Geol. 2007, 52, 339–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camuffo, D.; Del Monte, M.; Sabbioni, C.; Vittori, O. Wetting, deterioration and visual features of stone surfaces in an urban area. Atmos. Environ. 1982, 16, 2253–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Wang, Y. A Review of Atmospheric Deterioration and Sustainable Conservation of Calcareous Stone in Historical Buildings and Monuments. Sustainability 2024, 16, 10751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troiano, F. The Two Sides of Microorganisms in Cultural Heritage Conservation. 2014. Available online: https://hdl.handle.net/2434/229908 (accessed on 23 May 2025).
- Dybowska-Józefiak, M.; Wesołowska, M. The Influence of Biofilm on Selected Properties of Thin-Coat Mineral-Based Plasters on EPS Substrate. Materials 2022, 15, 5963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Gong, J. A meta-analysis of the publicly available bacterial and archaeal sequence diversity in saline soils. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 29, 2325–2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masjoudi, M.; Mohseni, M.; Bolton, J.R. Sensitivity of bacteria, protozoa, viruses, and other microorganisms to ultraviolet radiation. J. Res. Natl. Inst. Stand. Technol. 2021, 126, 126021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roesler, C.S.; Culbertson, C.W.; Etheridge, S.M.; Goericke, R.; Kiene, R.P.; Miller, L.G.; Oremland, R.S. Distribution, production, and ecophysiology of Picocystis strain ML in Mono Lake, California. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2002, 47, 440–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamiak, J.; Otlewska, A.; Gutarowska, B. Halophilic microbial communities in deteriorated buildings. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 31, 1489–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
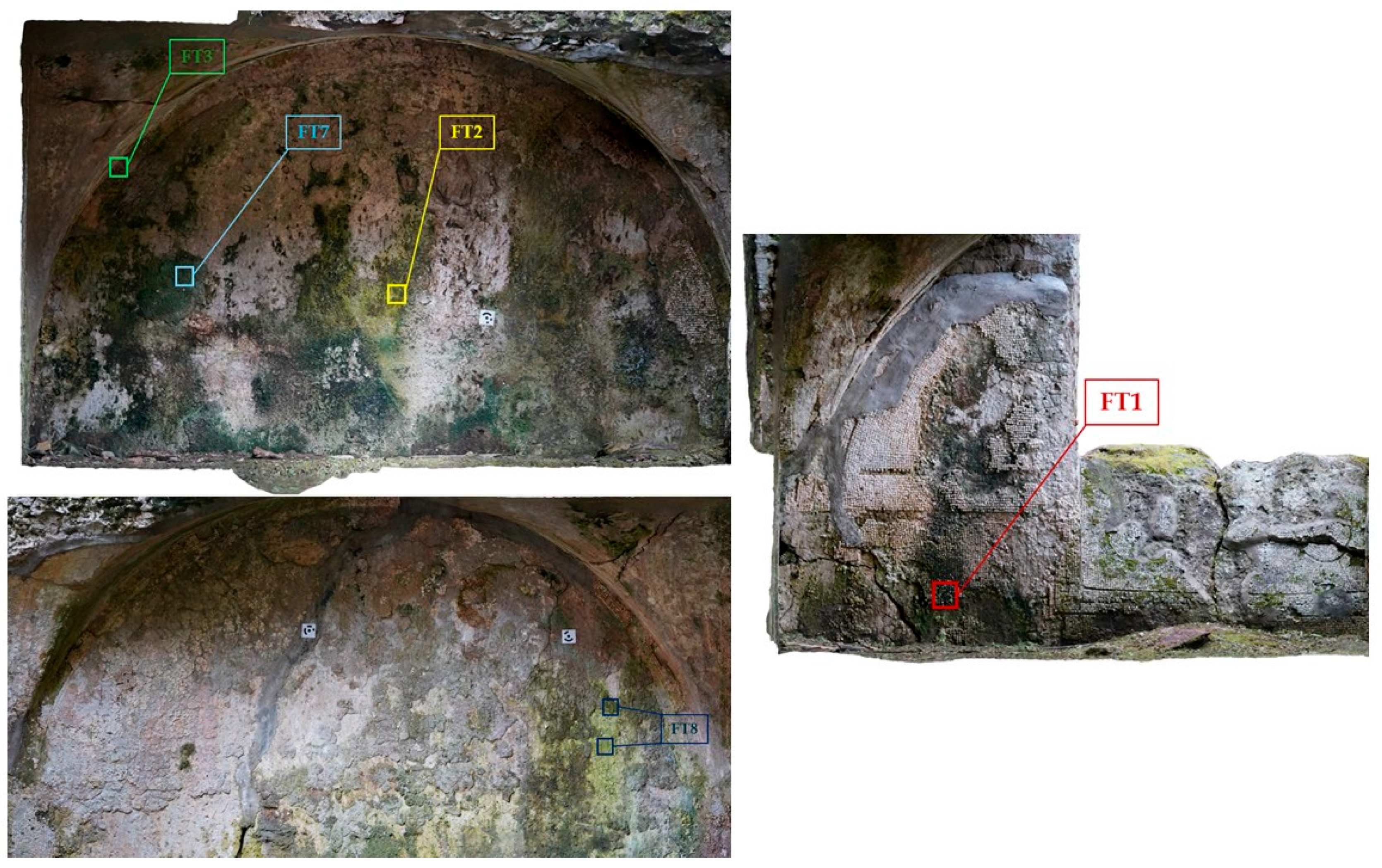
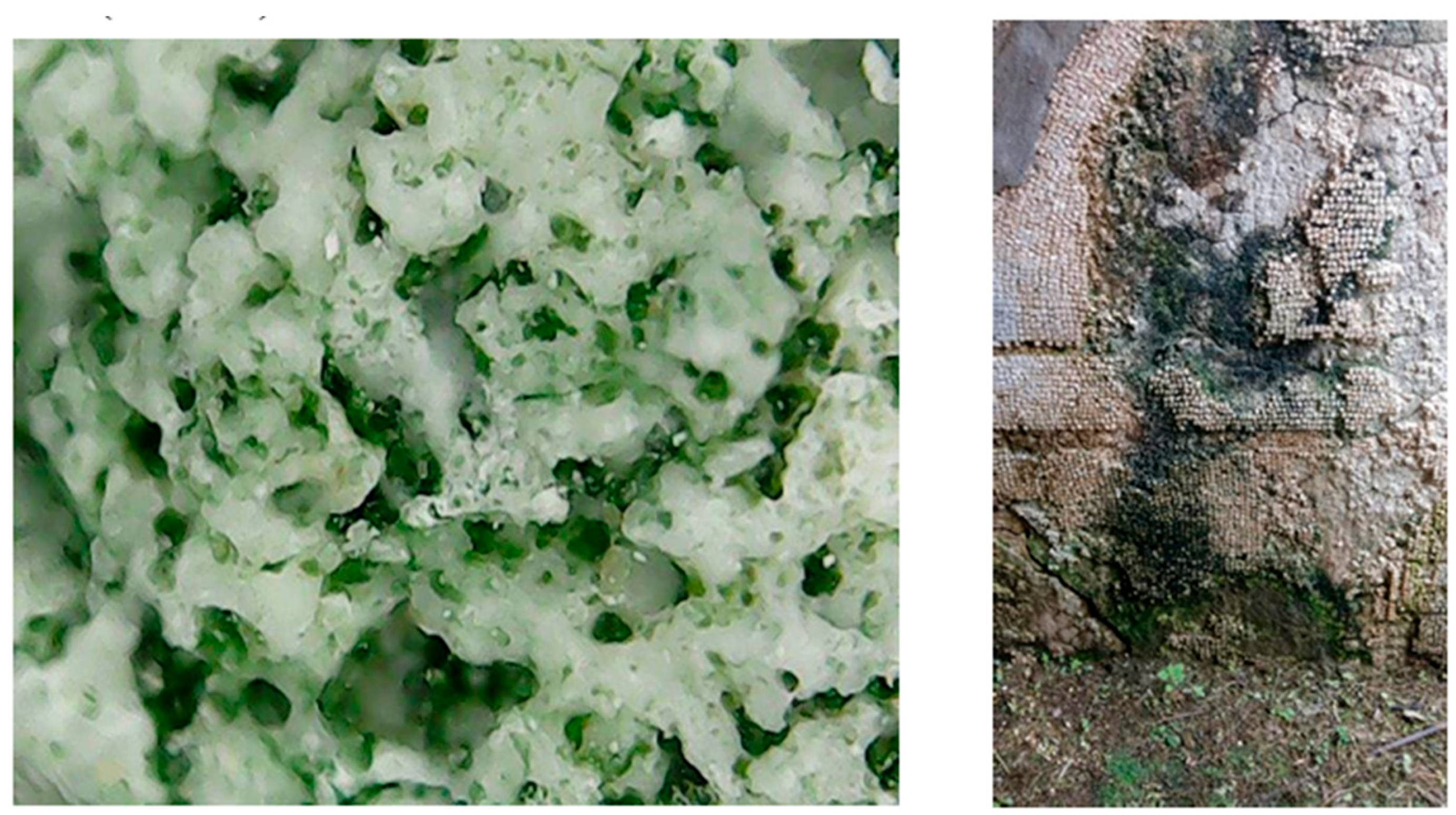
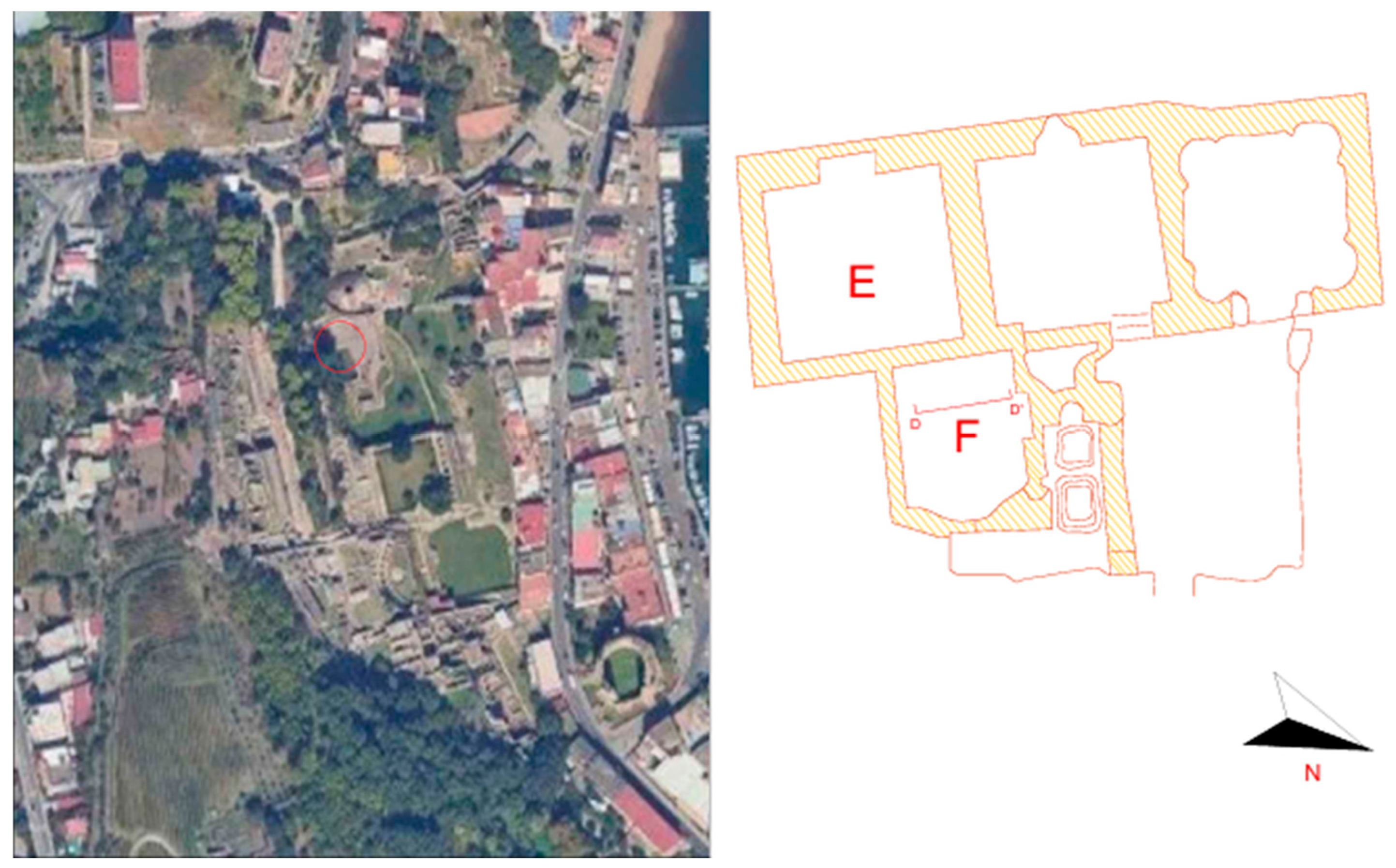



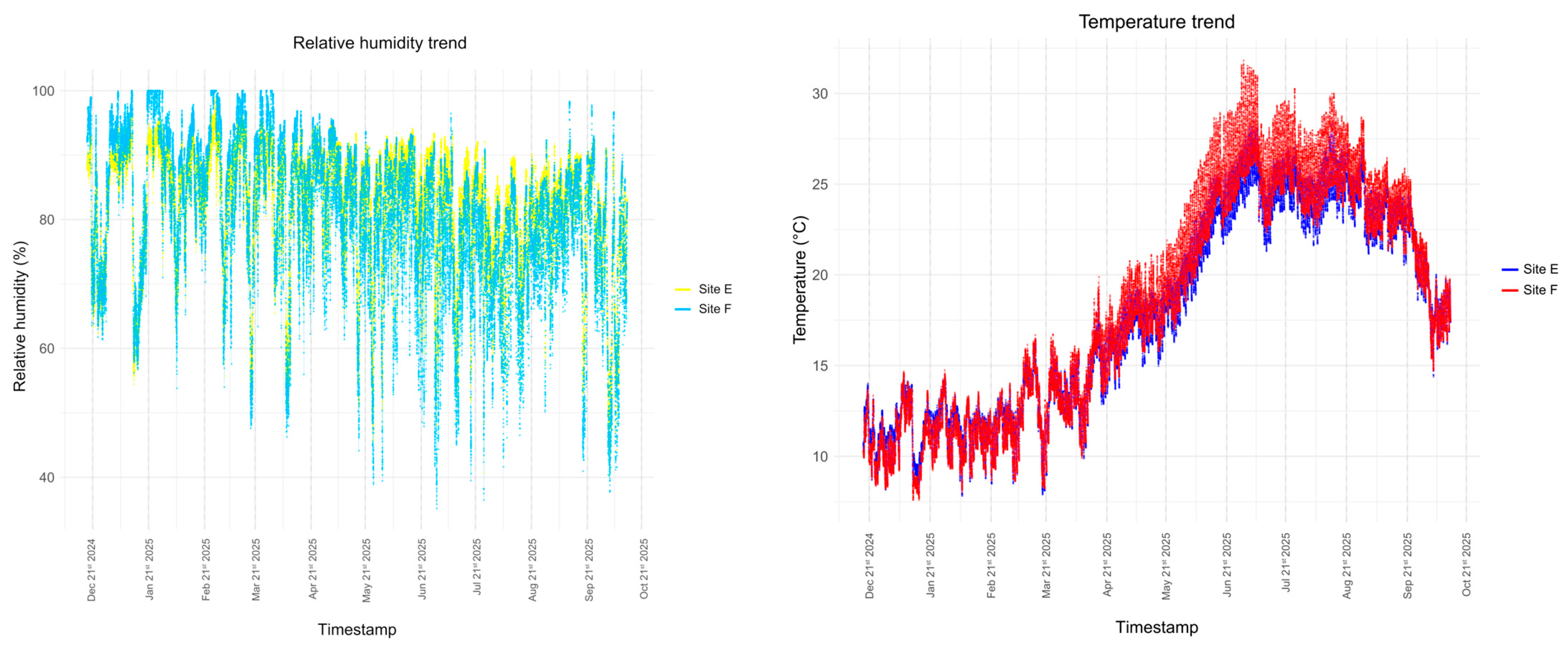
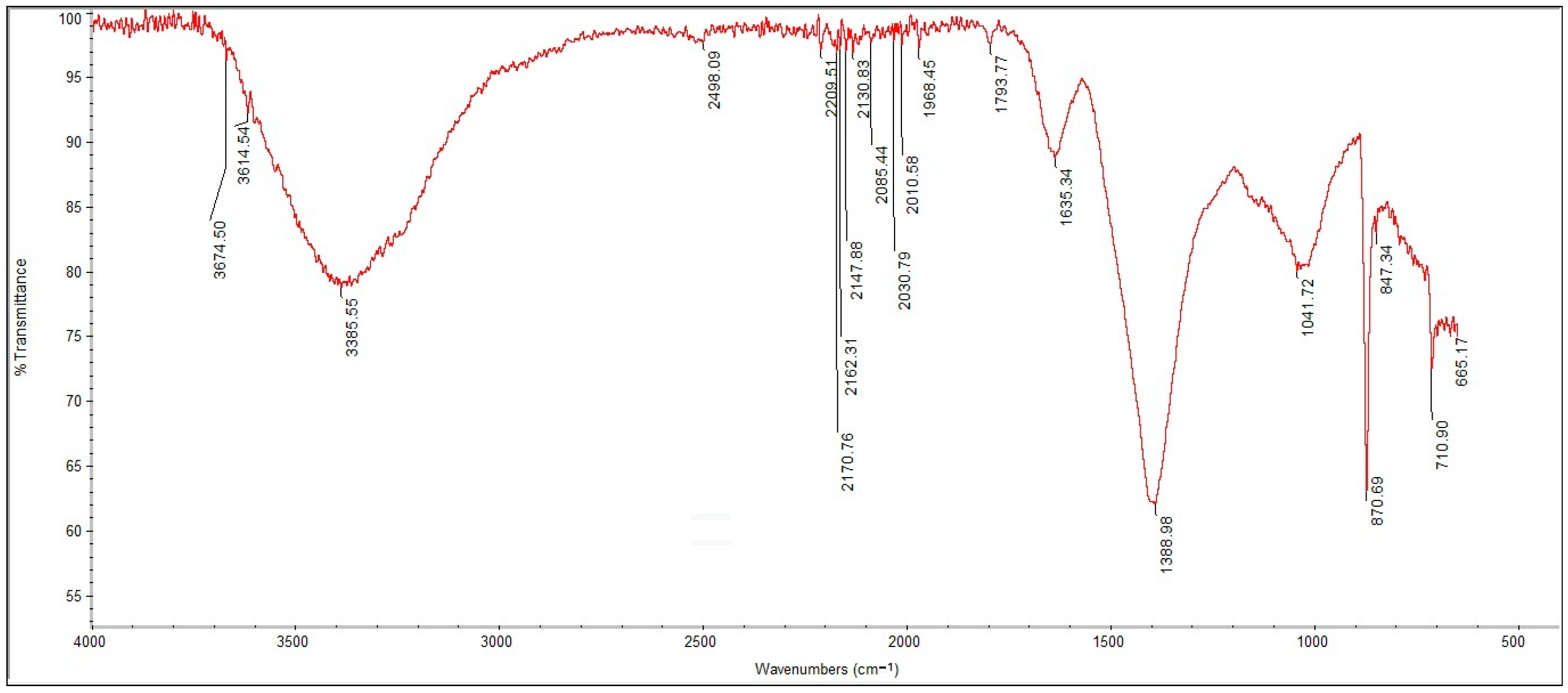

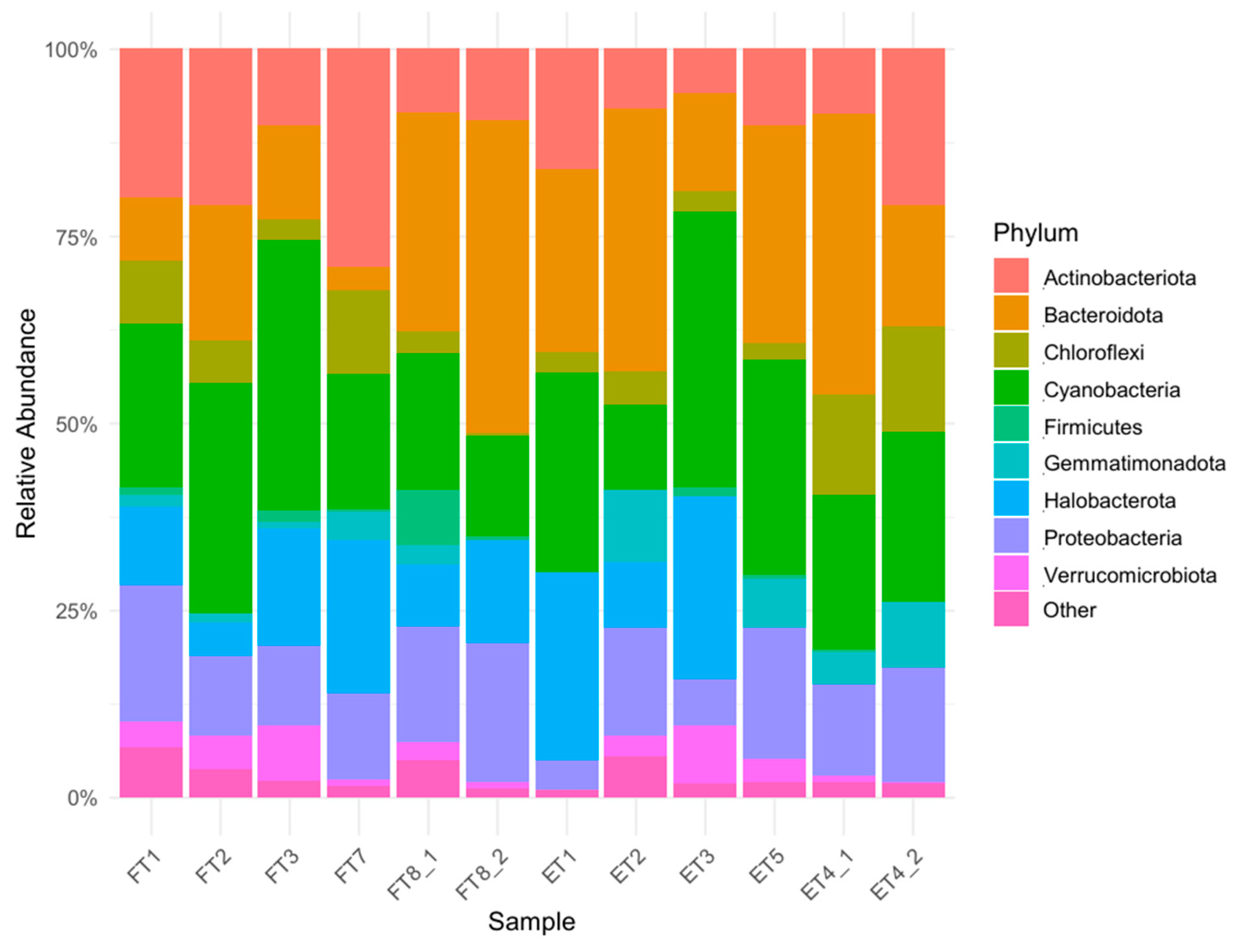
| ROOM F | ROOM E | |
|---|---|---|
| PLASTERS | FT2, FT7, FT8 * | ET2, ET3, ET4 * |
| MOSAICS | FT1, FT3 | ET1, ET5 |
| Color | ΔL* | Δa* | Δb* | ΔE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dark green | 36.91 | 15.28 | 1.83 | 39.99 |
| Light green | 7.84 | 5.17 | 27.27 | 28.85 |
| White | 6.91 | 2.67 | 1.71 | 7.60 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
De Rosa, A.; Trojsi, G.; Rippa, M.; Di Meo, A.; Borriello, M.; Rossi, P.; Caputo, P.; Cennamo, P. The Complex Life of Stone Heritage: Diagnostics and Metabarcoding on Mosaics from the Archaeological Park of Baia (Bacoli, Italy). Heritage 2025, 8, 470. https://doi.org/10.3390/heritage8110470
De Rosa A, Trojsi G, Rippa M, Di Meo A, Borriello M, Rossi P, Caputo P, Cennamo P. The Complex Life of Stone Heritage: Diagnostics and Metabarcoding on Mosaics from the Archaeological Park of Baia (Bacoli, Italy). Heritage. 2025; 8(11):470. https://doi.org/10.3390/heritage8110470
Chicago/Turabian StyleDe Rosa, Alessandro, Giorgio Trojsi, Massimo Rippa, Antimo Di Meo, Matteo Borriello, Pasquale Rossi, Paolo Caputo, and Paola Cennamo. 2025. "The Complex Life of Stone Heritage: Diagnostics and Metabarcoding on Mosaics from the Archaeological Park of Baia (Bacoli, Italy)" Heritage 8, no. 11: 470. https://doi.org/10.3390/heritage8110470
APA StyleDe Rosa, A., Trojsi, G., Rippa, M., Di Meo, A., Borriello, M., Rossi, P., Caputo, P., & Cennamo, P. (2025). The Complex Life of Stone Heritage: Diagnostics and Metabarcoding on Mosaics from the Archaeological Park of Baia (Bacoli, Italy). Heritage, 8(11), 470. https://doi.org/10.3390/heritage8110470








