Known Glass Compositions in Iron Age Europe—Current Synthesis and Emerging Questions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Contributions of Glassmaking Components to the Final Chemical Composition of Archaeological Glass
2.1. Silica Sources
2.2. Fluxing Agents
2.3. Stabilisers
2.4. Colourants and Opacifiers
3. Key Innovations in Glassmaking between the Bronze and Iron Age
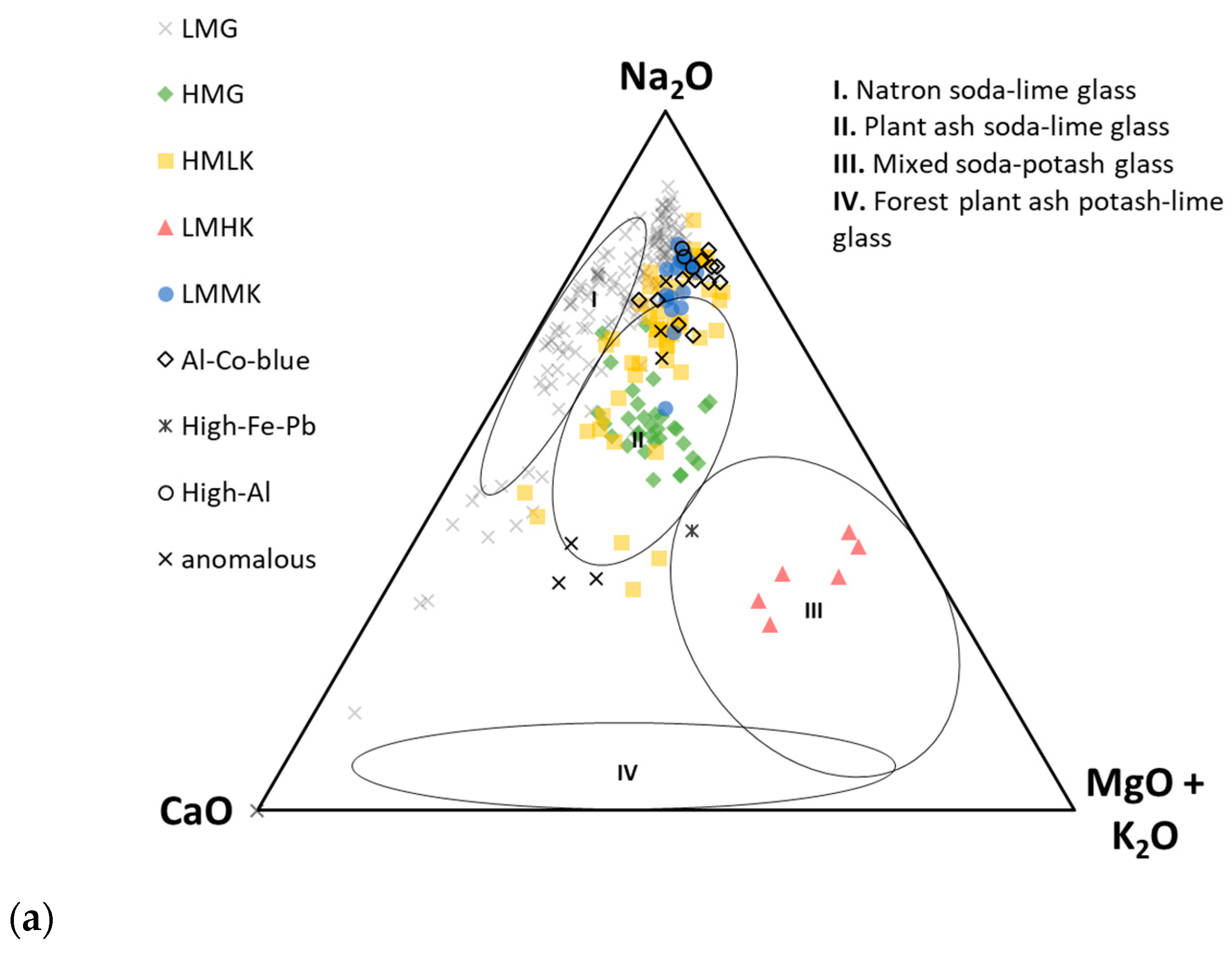
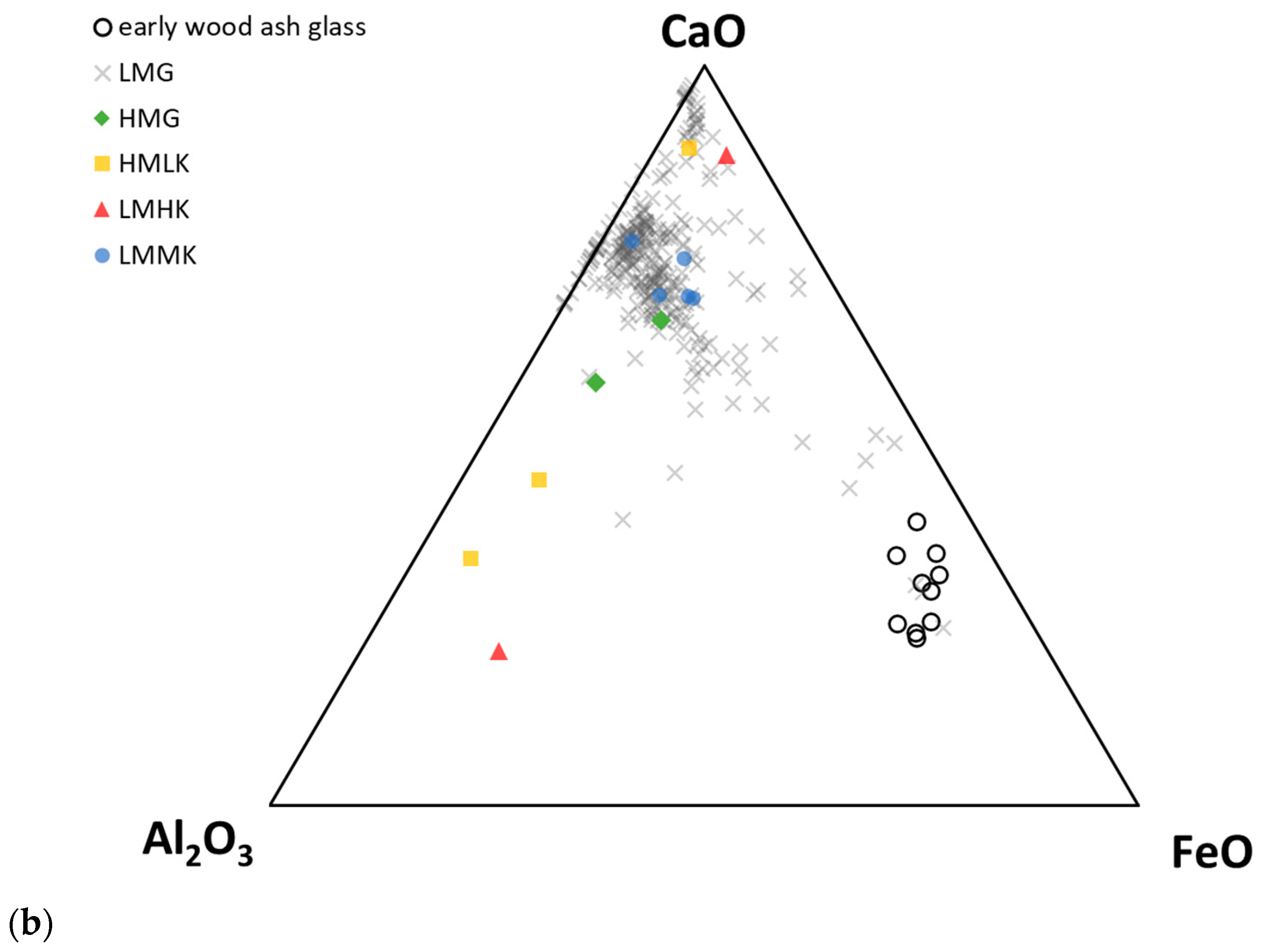
- Low-magnesium glass (LMG), which typically exhibits both MgO and K2O values below 1.5 wt. % [10,78]. Originally, this group was defined by samples of Roman glass, exhibiting 0.73–1.47 wt. % MgO and 0.22–0.63 wt. % K2O [73], but the upper MgO limit varies depending on the assemblage being studied, with values sometimes reaching 2 wt. % [8]. Here, we consider LMG to have both MgO and K2O contents of <1.5 wt. %. The fluxing agent used in the production of this type of glass is uniformly thought to be natron [20].
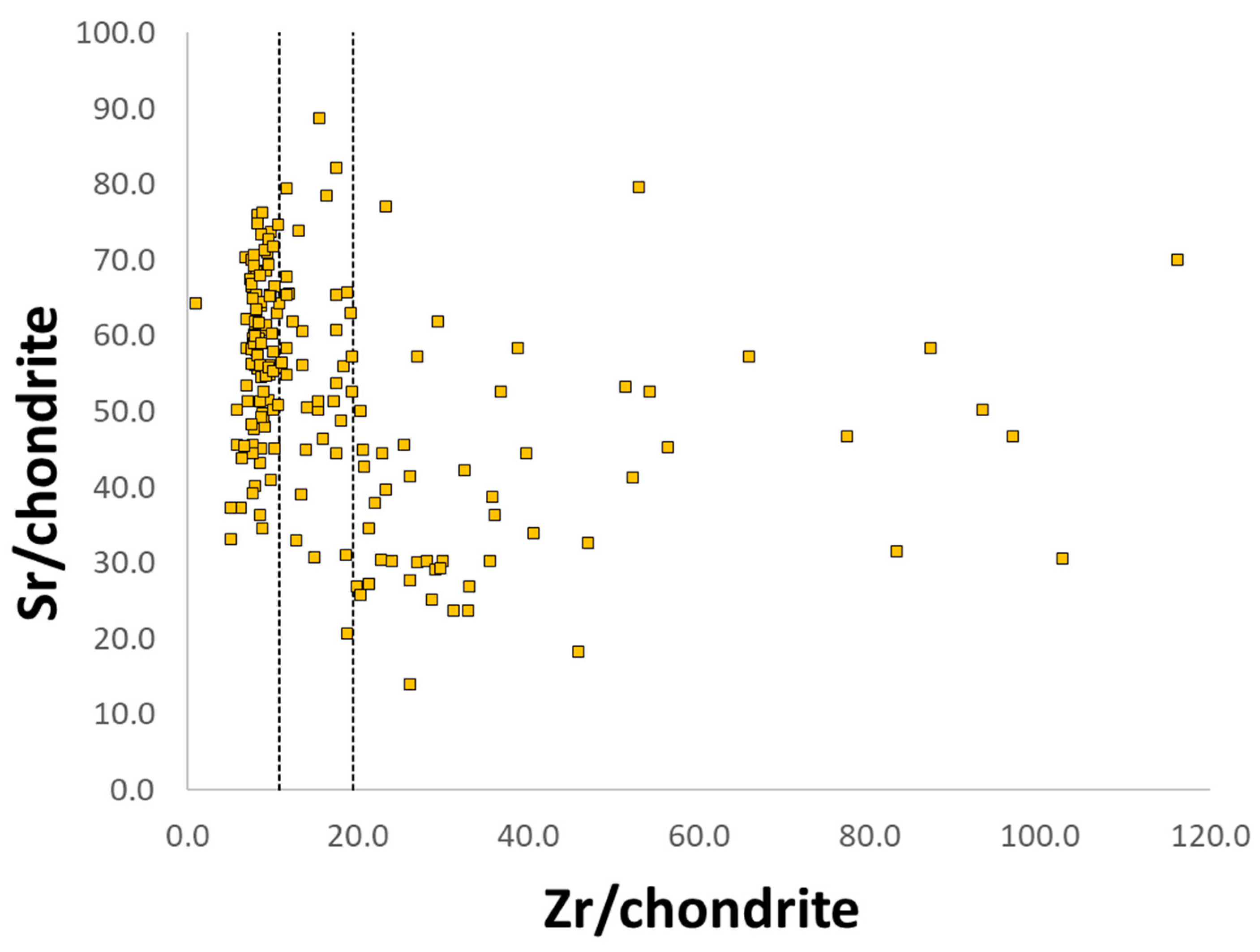
- High magnesium glass (HMG) was initially defined as Bronze Age glass with MgO values in the range of 2.9–4.6 wt. % and K2O in the range of 0.69–1.89 wt. % [73]. Since then, the range has been reported differently in the literature, broadly including values of MgO > 1.5 wt. % [10,28,78,85] and K2O values in the range of 1–4 wt. % [20,73,75,78,86]. Because of the broad range of reported values, some researchers prefer the term plant ash glass to HMG and require the MgO content to be higher than that of K2O [10,78]. This type is considered synonymous with Mediterranean Bronze Age glass production based on a pure silica source and halophytic plant ashes, although K2O values as low as 0.5 wt. % have been observed for plant ash glass [32,37]. Typically, glass fluxed with plant ash will exhibit > 5 wt.% CaO, coupled with elevated Sr values [28].
- High magnesium–low potassium (HMLK) glass was first described in detail by Conte et al. [37] on a set of Early Iron Age glass artefacts from Italy. This was defined as an umbrella term covering samples which presented MgO values (ca. 1.5–5 wt. %, avg. 3.3 wt. %) higher than LMG and K2O values (<2 wt. %, avg. 0.8 wt. %) lower than HMG [37,38]. Although this group has only recently been formally defined, the first mentions of similar Iron Age glass with high MgO and low K2O content from the territory of Greece, Hungary, former Yugoslavia, and Czechoslovakia can be found in works by Henderson [87], Frána [88] and Braun [89]. There is no firm consensus on which type of flux was used in the production of HMLK glass, with both natron and plant ash being proposed based on the Al2O3, CaO, and MgO values; this is, in part, related to the glass colour [37]. CaO values in the range of 6.5–8 wt. % were interpreted as resulting from the use of plant ash as the fluxing agent, which also contributed MgO to the final glass composition. Lower CaO levels (<4 wt. %) were found to be consistent with the use of natron and impure sands. Natron-fluxed HMLK glass can further be divided into black-appearing/iron-rich HMLK and Al-Co blue HMLK glass, reflecting the specific raw materials used in the glassmaking recipes.
- Iron-rich HMLK glass contains elevated iron contents (c. 5–13 wt. % FeO), which are responsible for its dark colouration. Rather than being a separate ingredient, this iron is believed to represent the choice of glassmaking sand rich in impurities, or, rather, an intentional choice of an iron-rich sand which served as both the network former and the colouring agent [37,38]. In this case, high MgO and Al2O3 contents (1.5–5 wt.%) would also have resulted from the choice of impure sands.
- Al-Co blue HMLK glass exhibits high MgO (2.15–4.95 wt. %) and low K2O (<1 wt. %) [37]. Additionally, this glass type contains high amounts of Al2O3 (4.36–7.72 wt. %) and lower amounts of CaO (1.29–3.96 wt. %) than typical LMG [37]. The blue colour is derived from the use of cobaltiferous alums, which impart an increased Co content (ca. 250–2000 ppm) and the aforementioned high Al2O3 and MgO to the finished glass [37,79]. This type has been recognised as one of the earliest natron glasses in France [79] and Italy [37]. Coeval turquoise glass found in Italy with similar compositional characteristics (high MgO and Al2O3, low CaO, and noticeable Co contents) [83] could be considered as closely related to Al-Co blue glass, and was possibly produced by adapting the recipe to obtain a different hue.
- Low magnesium–medium potassium (LMMK) glass was defined by a set of Early Iron Age glass beads from Poland [33,39]. This type is characterised by MgO values compatible to those of LMG (<1.5 wt. %) and slightly elevated K2O values (1.4–2.2 wt. %). Further compositional characteristics noticed for LMMK glass include generally high Al2O3 (1.5–7.8 wt. %) and Fe2O3 (1.7–5.4 wt. %), as well as a notable presence of metallic inclusions related to the colouring technology [39]. Initially, plant ash was proposed as the fluxing agent used in the production of LMMK glass by Purowski et al. [39], but other authors argued for natron as the fluxing agent in LMMK glass from Poland and similar glass from Italy, with the heightened K2O content being ascribed to the use of impure sands [37].
- Low magnesium–high potassium (LMHK) glass is considered a relic of the European LBA glassmaking tradition, relying on the use of different plant ashes, contrary to the methods used in the Eastern Mediterranean. This glass is thought to have been fluxed with leached plant ash [20,75,76,77,87]. The type is characterised by low MgO (<1 wt. %) and high K2O (4–6 wt. %) content coupled with high Na2O content, leading to this type of glass also being called mixed alkali glass [10,87].
- “Early wood ash glass” presents a composition similar to that of medieval European early wood ash glass [55], with very high K2O (5.3–12.6 wt. %), high MgO (2–5.3 wt. %), and low Na2O (<1 wt. %) contents [38]. This type of glass has, so far, only been identified in a single assemblage from Chotin (Slovakia), and is interpreted as evidence of small-scale local European glass production in the Iron Age [38].
4. Iron Age European Glass Compositions as Indicators of Changing Trends in the Economic Structures of the 1st Millennium BCE
4.1. The Plurality of Recipes (ca. 9th–7th c. BCE)
4.2. The Turning Point in Natron Glass Production (ca. 6th Century BCE)
4.3. Hellenistic Core-Formed Vessels (6th–1st Century BCE)
4.4. Celtic Glass and the Mediterranean Glass Monopoly (3rd–1st century BCE)
5. Open Issues about Iron Age Glass in Europe
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
| 1 | below detection limits. |
References
- Wells, P.S. Iron Age Temperate Europe: Some Current Research Issues. J. World Prehist. 1990, 4, 437–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knapp, B.A.; Manning, S.W. Crisis in Context: The End of the Late Bronze Age in the Eastern Mediterranean. Am. J. Arch. 2016, 120, 99–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherratt, S.; Sherratt, A. The growth of the Mediterranean economy in the early first millennium BC. World Archaeol. 1993, 24, 361–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubet Semmler, M.E. Tyre and its Colonial Expansion. In The Oxford Handbook of the Phoenician and Punic Mediterranean; Doak, B.R., López-Ruiz, C., Eds.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 74–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodos, T. The Archaeology of the Mediterranean Iron Age. A Globalising World c. 1100–600 BCE; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2020; p. 366. [Google Scholar]
- Barral, P.; Videau, G. De Bibracte à Vesonito: Esquisse d’une périodisation de la fin de l’âge du Fer en Burgogne et Franche-Comté. In Bibracte 22. Regards Sur la Chronologie de la Fin de L’âge du Fer (Iiie—Ier Siècle Avant J.-C.) En Gaule Non Méditerranéenne, Actes de la table ronde tenue à Bibracte « Chronologie de la fin de l’âge du Fer (iiie -i er siècle avant J.-C.) dans l’est de la France et les régions voisines », Glux-en-Glenne, France 15 October–17 October 2007; Barral, P., Fichtl, S., Eds.; Bibracte: Glux-en-Glenne, France, 2012; pp. 95–114. [Google Scholar]
- Rolland, J. La Verre de Europe Celtique: Approches Archéométriques, Technologiques ET Sociales D’Un Artisanat du Prestige AU Second âGe du Fer; Sidestone Press: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2021; p. 377. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-Götz, M. Urbanisation and Deurbanisation in the European Iron Age: Definitions, Debates, and Cycles. In Crossing the Alps: Early Urbanism between Northern Italy and Central Europe (900–400 BC); Zamboni, L., Fernández-Götz, M., Metzner-Nebelsick, C., Eds.; Sidestone Press: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 27–42. [Google Scholar]
- Knappett, C. An Archaeology of Interaction: Network Perspectives on Material Culture and Society; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2011; p. 251. [Google Scholar]
- Gratuze, B.; Janssens, K. Provenance analysis of glass artefacts. In Comprehensive Analytical Chemistry, Non-Destructive Microanalysis of Cultural Heritage Materials, 24; Janssens, K., van Grieken, R.R., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2004; pp. 663–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brems, D.; Degryse, P. Trace Element Analysis in Provenancing Roman Glass-making. Archaeometry 2014, 56, 116–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degryse, P.; Shortland, A.J. Interpreting elements and isotopes in glass: A review. Archaeometry 2020, 62, 117–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venclová, N. Prehistoric eye beads in Central Europe. J. Glass Stud. 1983, 25, 11–17. [Google Scholar]
- Spaer, M. Some Observations on the Strati-fied Mediterranean Eye-Beads of the First Millenni-um bc. In Annales du 10e Congrès de l’Association Internationale pour l’Histoire du Verre; Association Internationale pour l’Histoire du Verre: Amstredam, The Netherlands, 1985; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Ruano Ruiz, E. Cuentas polícromas prerro manas decoradas con ‘ojos’. Espac. Tiempo Forma. Série II Hist. Antig. 1995, 8, 255–286. [Google Scholar]
- Gomes, F.B. Early Iron Age ‘black’ glass in Southwestern Iberia: Typology, Distribution and Context. Zephyrus 2021, 87, 125–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, L.C. Die Glasbügelfibeln des 8. Und 7. Jahrhunderts aus Etrurien. Ein Beitrag zur eisenzeitlichen Glastechnik und zu den Bestattungssitten des Orientalizzante. In Universitätsforschungen zur Prähis-Torischen Archäologie; Verlag Dr. Rudolf Habelt GmbH: Bonn, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Harden, D.B. British Museum. In Catalogue of Greek and Roman Glass in the British Museum. 1. Core- and Rod-Formed Vessels and Pendants and Mycenaean Cast Objects; British Museum: London, UK, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Grose, D.F. Early Ancient Glass: Core-Formed, Rod-Formed, and Cast Vessels and Objects from the Late Bronze Age to the Early Roman Empire, 1600 BC to AD 50; The Toledo Museum of Art: Toledo, OH, USA; Hudson Hill Press: New York, NY, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Henderson, J. Ancient Glass. An Interdisciplinary Exploration; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Frie, A.C. Women Sheep and Textiles: The social significance of ram’s head beads in Early Iron Age Slovenia. Arheol. Vestn. 2021, 72, 91–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haevernick, T. Die Glasarmringe und Ringperlen der Mittel- und Spatlatenezeit auf dem Europaischen Festland; Rudolf Halbert Verlag: Bonn, Germany, 1960; p. 302. [Google Scholar]
- Venclova, N. Prehistoric Glass in Bohemia; Archeologický ústav ČSAV: Praha, Czech Republic, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Gebhard, R. Der Glasschmuck aus dem Oppidum von Manching. Die Ausgrabungen in Manching; Franz Steiner Verlag: Stuttgart, Germany, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Karwowski, M. Latènezeitlicher Glasringschmuck aus Ostösterreich. Mitteilungen der Prähistorischen Kommission der Österreichischen Akademie der Wissenschaften; Österreichischen Akademie der Wissenschaften: Wien, Austria, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Rustoiu, A. Amphora-shaped glass and coral beads. Distant cultural connections in the Carpathian Basin at the beginning of the Late Iron Age. Arch. Korr. 2015, 45, 365–377. [Google Scholar]
- Venclová, N.; Hulínský, V.; Frána, J.; Fikrle, M. Němčice a zpracování skla v laténské Evropě. Archeol. Rozhl. 2009, LXI, 383–426. [Google Scholar]
- Wedepohl, K.H.; Simon, K.; Kronz, A. Data on 61 chemical elements for the characterization of three major glass compositions in Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages. Archaeometry 2010, 53, 81–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shortland, A.J.; Rogers, N.; Eremin, K. Trace element discriminants between Egyptian and Mesopotamian Late Bronze Age glasses. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2007, 34, 781–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degryse, P.; Boyce, A.; Erb-Satullo, N.; Eremin, K.; Kirk, S.; Scott, R.; Shortland, A.J.; Schneider, J.; Walton, M. Isotopic discriminants between Late Bronze Age glasses from Egypt and the Near East. Archaeometry 2010, 52, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šmit, Ž.; Laharnar, B.; Turk, P. Analysis of prehistoric glass from Slovenia. J. Archaeol. Sci. Rep. 2020, 29, 102114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, J.; Evans, J.; Nikita, K. Isotopic evidence for the primary production, provenance and trade of Late Bronze Age glass in the Mediterranean. Mediterr. Archaeol. Archaeom. 2010, 10, 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Purowski, T.; Syta, O.; Wagner, B. Between East and West: Glass Beads from the Eighth to Third Centuries BCE from Poland. Archaeometry 2020, 62, 752–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shortland, A.J.; Tite, M.S.; Ewart, I. Ancient exploitation and use of cobalt alums from the Western Oases of Egypt. Archaeometry 2006, 48, 153–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gratuze, B.; Picon, M. Utilisation par l’industrie verrière des sels d’aluns des oasis égyptiennes au début du premier millénaire avant notre ère. In L’Alun de Méditerranée; Brun, J.-P., Ed.; Institut Français de Naples: Naples, Italy, 2006; pp. 269–279. [Google Scholar]
- Abe, Y.; Harimoto, R.; Kikugawa, T.; Yazawa, K.; Nishisaka, A.; Kawai, N.; Yoshimura, S.; Nakai, I. Transition in the use of cobalt-blue colorant in the New Kingdom of Egypt. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2012, 39, 1793–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conte, S.; Arletti, R.; Mermati, F.; Gratuze, B. Unravelling the Iron Age glass trade in Southern Italy: The first trace element analyses. Eur. J. Min. 2016, 28, 409–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conte, S.; Arletti, R.; Henderson, J.D.; Blomme, A. Different glassmaking technologies in the production of Iron Age black glass from Italy and Slovakia. Archaeol. Anthropol. Sci. 2018, 10, 503–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purowski, T.; Dzierżanowski, P.; Bulska, E.; Wagner, B.; Nowak, A. A study of glass beads from the Hallstatt C-D from southwestern Poland: Implications for glass technology and provenance. Archaeometry 2012, 54, 144–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, M.; Barrulas, P.; Arruda, A.M.; Dias, L.; Barbosa, R.; Vandenabeele, P.; Mirão, J. An insight into the provenance of the Phoenician-Punic glass beads of the necropolis of Vinha das Caliças (Beja, Portugal). Archaeol. Anthropol. Sci. 2021, 13, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Strydonck, M.; Bratuze, B.; Rolland, J.; de Mulder, G. An archaeometric study of some pre-Roman glass beads from Son Mas (Mallorca, Spain). J. Arch. Sci. Rep. 2018, 17, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blomme, A.; Degryse, P.; Dotsika, E.; Ingnatiadou, D.; Longinelli, A.; Silvestri, A. Provenance of polychrome and colourless 8th–4th century BC glass from Pieria, Greece: A chemical and isotopic approach. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2017, 78, 134–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blomme, A.; Elsen, J.; Brems, D.; Shortland, A.; Dotsika, E.; Degryse, P. Tracing the primary production location of core-formed glass vessels, Mediterranean group I. J. Archaeol. Sci. Rep. 2016, 5, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barkoudah, Y.; Henderson, J. Plant Ashes from Syria and the Manufacture of Ancient Glass: Ethnographic and Scientific Aspects. J. Glass Stud. 2006, 48, 297–321. [Google Scholar]
- Tite, M.S.; Shortland, A.; Maniatis, Y.; Kavoussanaki, D.; Harris, S.A. The composition of the soda-rich and mixed alkali plant ashes used in the production of glass. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2006, 33, 1284–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, J.; Evans, J.; Bellintani, P.; Bietti-Sestieri, A.-M. Production, mixing and provenance of Late Bronze Age mixed alkali glasses from northern Italy: An isotopic approac. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2015, 55, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degryse, P.; Shortland, A.; De Muynck, D.; Van Heghe, L.; Scott, R.; Neyt, B.; Vanhaecke, F. Considerations on the provenance determination of plant ash glasses using strontium isotopes. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2010, 37, 3129–3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devulder, V.; Degryse, P.; Vanhaecke, F. Development of a Novel Method for Unraveling the Origin of Natron Flux Used in Roman Glass Production Based on B Isotopic Analysis via Multicollector Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 12077–12084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moretti, C.; Hreglich, S. Raw Materials, Recipes and Procedures Used for Glass Making. In Modern Methods for Analysing Archaeological and Histroical Glass; Janssens, K., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2013; Volume 1, pp. 23–47. [Google Scholar]
- Dardeniz, G. Was Ancient Egypt the Only Supplier of Natron? New Research Reveals Major Anatolian Deposits. Anatolica 2015, XLI, 191–202. [Google Scholar]
- Devulder, V.; Vanhaecke, F.; Shortland, A.J.; Mattingly, D.; Jackson, C.; Degryse, P. Boron isotopic composition as a provenance indicator for the flux raw material in Roman natron glass. J. Arhcaeological. Sci. 2014, 46, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devulder, V.; Gerdes, A.; Vanhaecke, F.; Degryse, P. Validation of the determination of the B isotopic composition in Roman glasses with laser ablation multi-collector inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry. Spectrochim. Acta B Atoms. Spectrosc. 2015, 105, 116–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganio, M.; Boyen, S.; Brems, D.; Scott, R.; Foy, D.; Latruwe, K.; Molin, G.; Silvestri, A.; Vanhaeke, F.; Degryse, P. Trade routes across the Mediterranean: A Sr/Nd isotopic investigation on Roman colourless glass. Glass Technol. Eur. J. Glass Sci. Technol. Part A 2012, 53, 217–224. [Google Scholar]
- Freestone, I.; Leslie, K.A.; Thirwall, M.; Gorin-Rosen, Y. Strontium Isotopes of Early Glass Production: Byzantine and Early Islamic Glass from the Near East. Archaeometry 2003, 45, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wedepohl, K.H.; Simon, K. The chemical composition of medieval wood ash glass from Central Europe. Chem. Erde 2010, 70, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panighello, S.; Orsega, E.; van Elteren, J.T.; Šelih, V. Analysis of polychrome Iron Age glass vessels from Mediterranean I, II and III groups by LA-ICP-MS. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2012, 39, 2945–2955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oikonomou, A.; Henderson, J.; Gnade, M.; Chenery, S.; Zacharias, N. An archaeometric study of Hellenistic glass vessels: Evidence for multiple sources. Archaeol. Anthropol. Sci. 2018, 10, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakubonis, C.; Wobrauschek, P.; Zamini, S.; Karwowski, M.; Trnka, G.; Stadler, P. Results of quantitative analysis of Celtic glass artefacts by energy dispersive X-ray fluorescence spectrometry. Spectrochim. Acta B Atoms. Spectrosc. 2003, 58, 627–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolland, J.; Venclová, N. Iron Age glass working in Moravia, Central Europe: New archaeometric research on raw glass and waste—3rd–first century BC. Archaeol. Anthropol. Sci. 2021, 13, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foy, D.; Vichy, M.; Picon, M. L’ingots de verre Méditerranée occidentale (3e s. av. JC–7e s. ap. JC): Approvisionnement et mise en œuvre. In Annales du 14e Congrès de l’Association Internationale pour l’Histoire du Verre, Venice–Milano, Italy, 27 October–1 November 1998; AIHV: Lochem, The Netherlands, 2000; pp. 51–57. [Google Scholar]
- Foy, D.; Picon, M.; Vichy, M. Verres Omeyyades et Abbasides d’origine Egyptienne: Les temoignages de l’archéologie et de l’archéometrie. In Annales du 15e Congrès de l’Association Internationale pour l’Histoire du Verre New York–Corning, NY, USA, 15 October–20 October, 2001; AIHV: Nottingham, UK, 2003; pp. 138–143. [Google Scholar]
- Truffa Giachet, M.; Gratuze, B.; Ozainne, S.; Mayor, A.; Huysecom, E. A Phoenician glass eye bead from 7th–5th c. cal BCE Nin-Bèrè 3, Mali: Compositional characterisation by LA–ICP–MS. J. Arch. Sci. Rep. 2019, 24, 748–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandini, M.; Fiorentino, S. From Crystals to Color: A Compendium of Multi-Analytical Data on Mineralogical Phases in Opaque Colored Mosaic Tesserae. Minerals 2020, 10, 609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biron, I.; Chopinet, M.H. Colouring, decolouring, and opacifying of glass. In Modern Methods for Analysing Archaeological and Histroical Glass; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2013; Volume 1, pp. 49–65. [Google Scholar]
- Ligny, D.; Möncke, D. Colors in glass. In Springer Handbook of Glass; Musgraves, J.D., Hu, J., Calvez, L., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 297–342. [Google Scholar]
- Arletti, R.; Rivi, L.; Ferrarri, D.; Vezzalini, G. The Mediterranean Group II: Analyses of vessels from Etruscan contexts in northern Italy. J. Arhceol. Sci. 2011, 38, 2094–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yatsuk, O.; Gorghinian, A.; Fiocco, G.; Davit, P.; Francone, S.; Serges, A.; Koch, L.; Re, A.; Lo Giudice, A.; Ferretti, M.; et al. Ring-eye blue beads in Iron Age central Italy—Preliminary discussion of technology and possible trade connections. J. Archaeol. Sci. Rep. 2023, 47, 103763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobo, L.; Degryse, P.; Shortland, A.; Vanhaecke, F. Isotopic analysis of antimony using multi-collector ICP-mass spectrometry for provenance determiantion of Roman glass. J. Anal. Atoms. Spectrom 2013, 28, 1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dillis, S.; van Ham-Meert, A.; Leeming, P.; Shortland, A.; Gobejishvili, G.; Abramishvili, M.; Degryse, P. Antimony as a raw material in ancient metal and glass making: Provenancing Georgian LBA metallic Sb by isotope analysis. Sci. Technol. Archaeol. Res. 2019, 5, 98–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degryse, P.; Shortland, A.J.; Dillis, S.; Ham-Meert, A.; Vanhaecke, F.; Leeming, P. Isotopic evidence for the use of Caucasian antimony in Late Bronze Age glass making. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2020, 120, 105195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahlil, S.; Biron, I.; Cotte, M.; Susini, J.; Menguy, N. Synthesis of calcium antimonate nano-crystals by the 18th dynasty Egyptian glassmakers. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 2010, 98, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahlil, S.; Biron, I.; Cotte, M.; Susini, J. New insight on the in situ crystallization of calcium antimonate opacified glass during the Roman period. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 2010, 100, 683–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayre, E.V.; Smith, R.W. Compositional categories of ancient glass. Science 1961, 133, 1824–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reade, W.; Freestone, I.; Bourke, S. Innovation and continuity in Bronze and Iron Age glass from Pella in Jordan. In Annales du 17e Congrès de l’Association Internationale pour Histoire du Verre, Antwerp, Belgium, 4 September–8 September 2006; Janssens, K., Degryse, P., Cosyns, P., Caen, J., Van’t dack, L., Eds.; AIHV, University Press: Antwerp, Belgium, 2009; pp. 47–54. [Google Scholar]
- Henderson, J. Glass production and Bronze Age Europe. Antiquity 1988, 62, 435–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelini, I. Archaeometry of Bronze Age and Early Iron Age Italian Vitreous Materials: A Review. In Proceedings of the 37th International Symposium on Archaeometry, Sienna, Italy, 12–16 May 2008; Turbanti-Memmi, I., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelini, I.; Artioli, G. Evolution of Vitreous Materials in Bronze Age Italy. In Modern Methods for Analysing Archaeological and Histroical Glass; Janssens, K., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2013; Volume 1, pp. 355–368. [Google Scholar]
- Gratuze, B.; Billaud, Y. La circulation des perles en verre dans le Bassin Méditerranéen, de l’Âge du Bronze moyen jusqu’au Hallstatt. In ÉChanges et Commerce du Verre Dans le Monde Antique; Foy, D., Nenna, M.-D., Eds.; éditions Monique Mergoil: Montagnac, France, 2003; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Gratuze, B. Les premiers verres au natron retrouvés en Europe occidentale: Composition chimique et chronotypologie. In Annales du 17e Congrès de l’Association Internationale pour Histoire du Verre, Antwerp, Belgium, 4 September–8 September 2006; Janssens, K., Degryse, P., Cosyns, P., Caen, J., Van’t dack, L., Eds.; AIHV, Antwerp University Press: Antwerp, Belgium, 2009; pp. 8–14. [Google Scholar]
- Rehren, T.; Rosenow, D. Three Millennia of Egyptian Glassmaking. In Mobile Technologies in the Ancient Sahara and Beyond; Duckworth, C., Cuénod, A., Mattingly, D., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2020; pp. 423–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlick-Nolte, B.; Werthmann, R. Glass Vessels from the Burial of Nesikhons. J. Glass Stud. 2003, 45, 11–34. [Google Scholar]
- Pusch, E.B.; Rehren, T. Hochtemperatur-Technologie in der Ramses-Stadt. Rubinglas für den Pharao; Gebr Gerstenberg Gmbh & Co.: Hildesheim, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Arletti, R.; Bertoni, E.; Vezzalini, G.; Mengoli, D. Glass beads from Villanovian excavations in Bologna (Italy): An archaeometrical investigation. Eur. J. Min. 2011, 23, 959–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzankova, N.; Mihaylov, P. Chemical characterization of glass beads from the necropolis of Dren-Delyan (6th–4th century BC), Southwest Bulgaria. Geol. Balc. 2019, 48, 31–50. [Google Scholar]
- Lilyquist, C.; Brill, R.H. Studies in Early Egyptian Glass; The Metropolitan Museum of Art: New York, NY, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- de Ferri, L.; Mazzadri, F.; Falcone, R.; Quagliani, V.; Milazzo, F.P. A non-destructive approach for the characterization of glass artifacts: The case of glass beads from the Iron Age Picene necropolises of Novilara and Crocefisso-Matelica (Italy). J. Archaeol. Sci. J. Archaeol. Sci. Rep. 2020, 29, 102124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, J. Electron probe microanalysis of mixed-alkali glasses. Archaeometry 1988, 30, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frána, J.; Maštalka, A.; Venclová, N. Neutron activation analysis of some ancient glasses from Bohemia. Archaeometry 1987, 29, 69–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, C. Analysen von Gläsern aus der Hallstattzeit mit einem Exkurs über römische Fenstergläser. In Glasperlen der Vorrömischen Eisenzeit I, Marburger Studien zur Vor- und Frühgeschichte; Frey, O.H., Roth, H., Eds.; Verlag Philipp von Zabern: Mainz am Rhein, Germany, 1983; pp. 129–175. [Google Scholar]
- Arletti, R.; Ferrari, D.; Vezzalini, G. Pre-Roman glass from Mozia (Sicily-Italy): The first archaeometrical data. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2012, 39, 3396–3401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shortland, A.J.; Schroeder, H. Analysis of first millennium BC glass vessels and beads from the Pichvnari necropolis, Georgia. Archaeometry 2009, 51, 947–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, F.; Silvestri, A.; Molin, G.; Marcante, A.; Guerriero, P. Iron Age vessels from the Archaeological Museum of Adria (North-Eastern Italy): A textural, chemical and mineralogical study. In Proceedings of the 39th International Symposium for Archaeometry, Leuven, Belgium, 28 May–1 June 2012; Centre for Archaeological Sciences, KU Leuven: Leuven, Belgium, 2014; pp. 198–207. [Google Scholar]
- Arletti, R.; Maiorano, C.; Ferrari, D.; Vezzalini, G.; Quartieri, S. The first archaeometric data on polychrome Iron Age glass from sites located in northern Italy. J. Arch Sci. 2010, 37, 703–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García González, J.; María Cobos Rodríguez, L.; López López, V.; Dorado Alejos, A. Cuentas de pasta vítrea y fayenza en contextos postalayóticos (s. VII- II a.n.e): El conjunto de So na Caçana (Alaior, Menorca). CAPUAM 2021, 47, 132–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, J.; Prieto, A.; Coria-Noguera, J.; Sanz-Minguez, C.; Souto, J. Investigating glass beads and the funerary rituals of ancient Vaccaei culture (S. IV-I BC) by Raman spectroscopy. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2020, 52, 170–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyubmirova, V.; Šmit, Ž.; Fajfar, H.; Kuleff, I. Chemical Composition of Glass Beads from the Necropolis of Apollonia Pontica (5th–3rd Century BC). Archaeol. Bulg. 2014, XVIII, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Osváth, Z.; Fórizs, I.; Szabó, M.; Bajnóczi, B. Archaeometric Analysis of Some Scythian Glass beads from Hungary. Archeometriai Műhely 2018, XV, 29–44. [Google Scholar]
- Triantafyllidis, P.; Karatasios, I.; Andreopoulou-Magkou, E. Study of core-formed glass vessels from Rhodes. In Proceedings of the 5th Symposium of HSA, Athens, Greece, 8–10 October 2008; Zacharias, N., Georgakopoulou, M., Polikreti, K., Fakorellis, G., Vakoulis, T., Eds.; University of Peloponnese Publications: Kalamata, Greece, 2012; pp. 529–544. [Google Scholar]
- Karwowski, M. Major questions concerning Celtic glass from the eastern regions of the La Tène culture. Analecta Archaeol. Ressoviensia 2006, 1, 133–159. [Google Scholar]
- Roymans, N.; Huisman, H.; van der Laan, J.; van Os, B. La Tène Glass Armrings in Europe: Interregional connectivity and local identity constructon. Arch. Korr. 2014, 44, 215–228. [Google Scholar]
- Huisman, D.J.; van der Laan, J.; Davies, G.R.; van Os, B.H.J.; Roymans, N.; Fermin, B.; Karwowski, M. Purple haze: Combined geochemical and Pb-Sr isotope constraints on colourants in Celtic glass. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2017, 81, 59–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Křížová, Š.; Venclová, N.; Vaculovič, T.; Dillinegrová, V. Multi-analytical approach and microstructural characterisation of glasses from the Celtic oppidum of Třísov, Czech Republic, second to first centuries BC. Archaeol. Anthropol. Sci. 2020, 12, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purowski, T.; Syta, O.; Wagner, B. Italian leech-shaped glass fibula bow from the Hallstatt period, discovered in Poland. Archeol. Rozhl. 2018, 68, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freestone, I.C.; Gorin-Rosen, Y.; Hughes, M.J. Primary Glass from Israel and the Production of Glass in Late Antiquity and the Early Islamic Period. In La Route du Verre. Ateliers Primaires ET Secondaires du Second Millénaire Av. J.-C. AU Moyen ÂGe. Colloque Organisé en 1989 Par L’Association Française Pour L’Archéologie du Verre; Maison de l’Orient et de la Méditerranée Jean Pouilloux: Lyon, France, 2000; pp. 65–83. [Google Scholar]
- van Ham-Meert, A.; Dillis, S.; Blomme, A.; Cahill, N.; Clayes, P.; Elsen, J.; Eremin, K.; Gerdes, A.; Steuwe, C.; Roeffaers, M.; et al. A unique recipe for glass beads at Iron Age Sardis. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2019, 108, 109474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Ruibal, A. House societies vs. kinship-based societies: An archaeological case from Iron Age Europe. J. Anthropol. Archaeol. J. Anthropol. Archaeol. 2006, 25, 144–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foulds, E.M. Glass Beads in Iron Age Britain: A social approach. Ph.D. Thesis, Durham University, Durham, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Lazar, I. Glass finds in Slovenia and neighbouring areas. J. Rom. Archaeol. 2006, 19, 329–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hederson, J.; An, J.; Ma, H. The archaeology and archaeometry of ancient Chinese glass: A review. Archaeometry 2018, 60, 88–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, M.; Arruda, A.M.; Barbosa, R.; Barrulas, P.; Vandenabeele, P.; Mirão, J. A Micro-Analytical Study of the Scarabs of the Necropolis of Vinha das Caliças (Portugal). Microsc. Microanal. 2019, 25, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, M.; Arruda, A.M.; Dias, L.; Barbosa, R.; Mirão, J.; Peter, V. The combined use of Raman and micro-X-ray diffraction analysis in the study of archaeological glass beads. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2019, 50, 250–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, M.; Barrulas, P.; Arruda, A.M.; Barbosa, R.; Vandenabeele, P.; Mirão, J. New approaches for the study of faience using beads from Southern Portugal. J. Archaeol. Sci. J. Archaeol. Sci. Rep. 2022, 46, 103703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand, N.W.; Brand, C.J. Performance comparison of portable XRF instruments. Geochem. Explor. Environ. Anal. 2014, 14, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, B.; Shugar, A.N. Glass analysis utilizing handheld X-ray fluorescence. In Handheld XRF for Art and Archaeology, Studies in Archaeological Sciences; Shugar, A., Mass, J., Eds.; Leuven University Press: Leuven, Belgium, 2012; pp. 449–470. [Google Scholar]
- Adlington, L.W.; Gratuze, B.; Schibille, N. Comparison of pXRF and LA-ICP-MS analysis of lead-rich glass mosaic tesserae. J. Archaeol. Sci. J. Archaeol. Sci. Rep. 2010, 34, 102603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eremin, K.; Degryse, P.; Erb-Satullo, N.; Ganio, M.; Greene, J.; Shortland, A.; Walton, M.; Stager, L. Iron Age glass beads from Carthage. In Historical Technology Materials and Conservation: Sem and Microanalysis; Meeks, N., Cartwright, C., Meek, A., Mongiatti, A., Eds.; Archetype: London, UK, 2012; pp. 30–35. [Google Scholar]
- Rehren, T.; Spencer, L.; Triantafyllidis, P. The primary production of glass at Hellenistic Rhodes. In Annales du 16e Congres de l’Association Internationale de l’Histoire du Verre London, UK 7 September–13 September 2003; Cool, H., Ed.; AIHV: Nottingham, UK, 2005; pp. 39–43. [Google Scholar]
- Freestone, I. Glass production in Late Antiquity and the Early Islamic period: A geochemical perspective. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 2006, 257, 201–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rincón, J.M. Microstructure and microanalysis (sem/edx) determination of glasses from Mallorca and Menorca caves. Trab. Prehist. 1993, 50, 263–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruano Ruiz, E.; Hoffman, P.; Rincón, J.M. Aproximación al estudio del vidrio preromano: Los materiales procedentes de la necrópolis ibérica de El Cigarralejo (Mula, Murcia). Composición química de varias cuentas de collar. Trab. Prehist. 1995, 52, 189–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palomar, T.; Peña-Poza, J.; Conde, J.F. Cuentas de vidrio Prerromanas y arqueometría: Una valoración de los trabajos realizados en la Península Ibérica. Zephyrus 2009, LXIV, 53–62. [Google Scholar]
- Franjić, A. Iron Age Glass Technology in South East Europe. Ph.D. Thesis, University College, London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Franjić, A.; Freestone, I.; Križ, B.; Stipan, P. The spectrometric analysis of Iron Age glass beads from Novo Mesto, Slovenia. Stud. Univ. Hered. 2022, 10, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, J. The Iron Age of “Loughey” and Meare: Some Inferences from Glass Analysis. Ant. J. 1987, 67, 29–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Technique | Element Range | LOD | Main Disadvantages | Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| handheld/portable XRF | Z > 12 (Mg) | element-specific, down to trace concentrations | complicated calibration procedures, frequent element over/underrepresentation | fast analysis times, non-destructive |
| LA-ICP-MS | All (except H, He, N, O, Ne and Ar) | trace concentrations, down to ppm, ppb, or ppt, depending on configuration | lower measurement reproducibility than wet sample ICP-MS | minimally invasive, fast, high spatial resolution |
| SEM-EDS | Be-U | 0.1 wt. % | surface-sensitive, influenced by surface leaching and contamination for non-polished samples | high spatial resolution, non-destructive depending on sample preparation |
| EMPA | Z < 3 (Li) | down to 100 ppm | surface-sensitive, requires sample polishing and coating | high spatial resolution |
| Colouring Ion/Phase | Hue |
|---|---|
| Mn2+ | light violet |
| Mn3+ | deep purple |
| Fe2+ | blue, green in combination with (Fe3+) |
| Fe3+ | yellow, green in combination with (Fe2+) |
| Co2+ | blue |
| Cu2+ | green/turquoise |
| cuprite (Cu2O) | opaque reds and oranges |
| calcium antimonate (CaSb2O6/Ca2Sb2O7) | white, opacifier for other colours |
| lead antimonate (Pb2Sb2O7) | opaque yellow |
| tin-based opacifiers (SnO2) | white, opacifier for other colourants |
| lead-tin-based opacifiers (PbSnO3, PbSn1 − xSixO3, Pb2SnO4) | opaque yellow |
| Chemical Composition (wt. %) | Additional Significant Compositional Characteristics | Flux | Date | Distribution (Europe) | References | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glass type | Na2O | MgO | K2O | CaO | Al2O3 | |||||
| LMG | c. 10–20 | <1.5 | <1.5 | c. 4–10 | usually < 4 | natron | 8th c. BCE onwards | across Europe | [7,10,27,31,33,37,39,40,41,42,56,57,58,59,66,78,79,84,89,90,91,92,93,94,95,96,97,98,99,100,101,102] | |
| LMG (low Ca) | c. 10–20 | <1.5 | <1.5 | <4 | c. 0.4–4.3 | natron | 9th–7th c. BCE, rare post 6th c. BCE | Italy, Poland, Slovenia, Spain | [31,33,37,38,39,41,83] | |
| HMG | c. 10–20 | >1.5, >K2O | >1.5, <MgO | >5 | usually < 2, up to 10 | plant ash | LBA-7th c. BCE, sporadic finds post-6th c. BCE | Pre-7th c. BCE. Italy, Poland, Slovenia; post-6th c. BCE: Georgia, Bulgaria, Poland | [31,33,37,39,58,91] | |
| LMHK | 4–8 | <1 | 4–6 | <4 | 1–10 | plant ash | 9th–6th c. BCE | Italy, Slovenia | [31,83] | |
| LMMK | c. 13–19 | <1.5 | 1.4–2.2 | <3 | 1.5–7.8 | increased FeO content (c. 2–5 wt. %) | plant ash/natron | Poland | [39,103] | |
| HMLK (“black“) | c. 10–20 | c. 1.5–5 | <2 | c. 1.2–6 | 1–4.8 | high FeO content (c. 5–13 wt. %) | natron | 9th–6th c. BCE | Italy, Hungary, former Yugoslavia & Czechoslovakia | [37,38,86,87] |
| HMLK (colourless and blue) | c. 16–19 | c. 1.5–5 | <2 | 6.5–8.5 | <1 | plant-ash | 9th–6th c. BCE | Italy, Hungary, former Yugoslavia & Czechoslovakia | [37,86,87] | |
| Al-Co blue (HMLK) | c. 15–22 | c. 2–5 | <1 | <4 | c. 4–8 | noticeable Co content | natron | 9th–6th c. BCE | Italy, France | [37,79,83] |
| “Early wood-ash” | <1 | 2–5.3 | 5.3–12.6 | c. 5.5–10 | 1.3–3.7 | High FeO content (c. 13–16 wt. %) | wood ash | 7th–5th c. BCE | Slovakia | [38] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lončarić, V.; Costa, M. Known Glass Compositions in Iron Age Europe—Current Synthesis and Emerging Questions. Heritage 2023, 6, 3835-3863. https://doi.org/10.3390/heritage6050204
Lončarić V, Costa M. Known Glass Compositions in Iron Age Europe—Current Synthesis and Emerging Questions. Heritage. 2023; 6(5):3835-3863. https://doi.org/10.3390/heritage6050204
Chicago/Turabian StyleLončarić, Valentina, and Mafalda Costa. 2023. "Known Glass Compositions in Iron Age Europe—Current Synthesis and Emerging Questions" Heritage 6, no. 5: 3835-3863. https://doi.org/10.3390/heritage6050204
APA StyleLončarić, V., & Costa, M. (2023). Known Glass Compositions in Iron Age Europe—Current Synthesis and Emerging Questions. Heritage, 6(5), 3835-3863. https://doi.org/10.3390/heritage6050204






