Deep Learning in Historical Architecture Remote Sensing: Automated Historical Courtyard House Recognition in Yazd, Iran
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Deep Learning, Remote Sensing, and Their Application in Historical Architecture Recognition
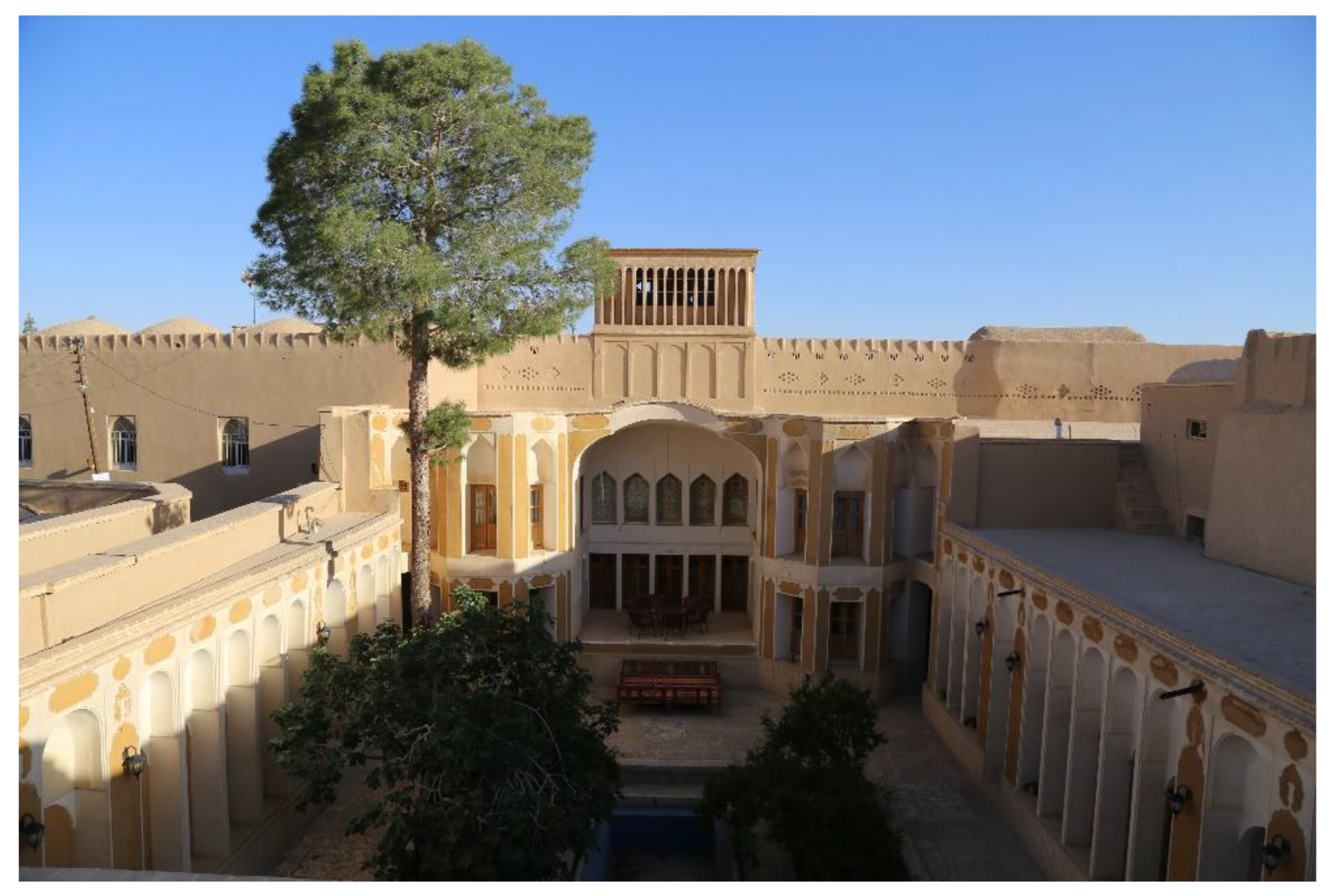
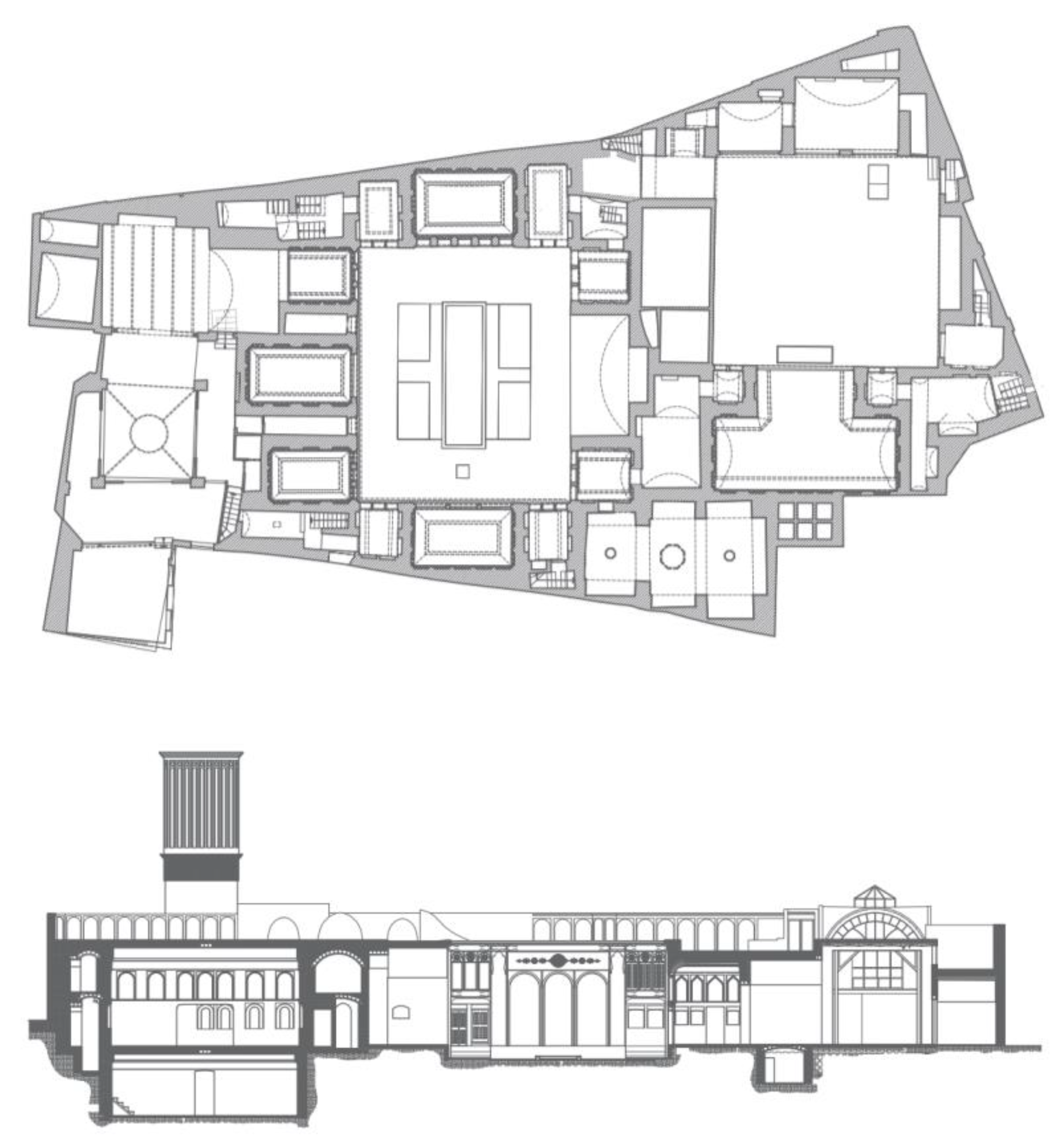
1.2. The Historical Architecture of Iran
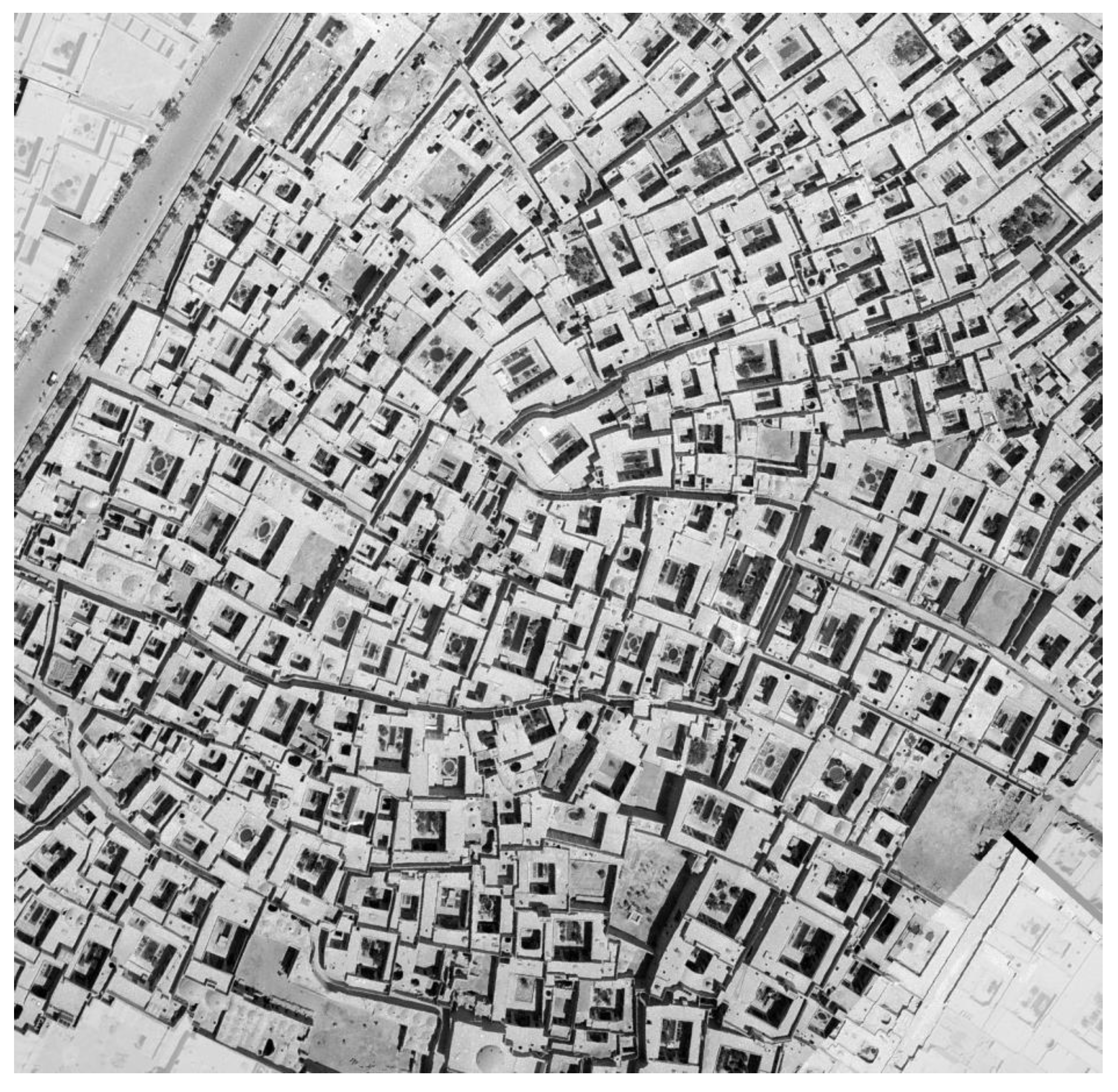
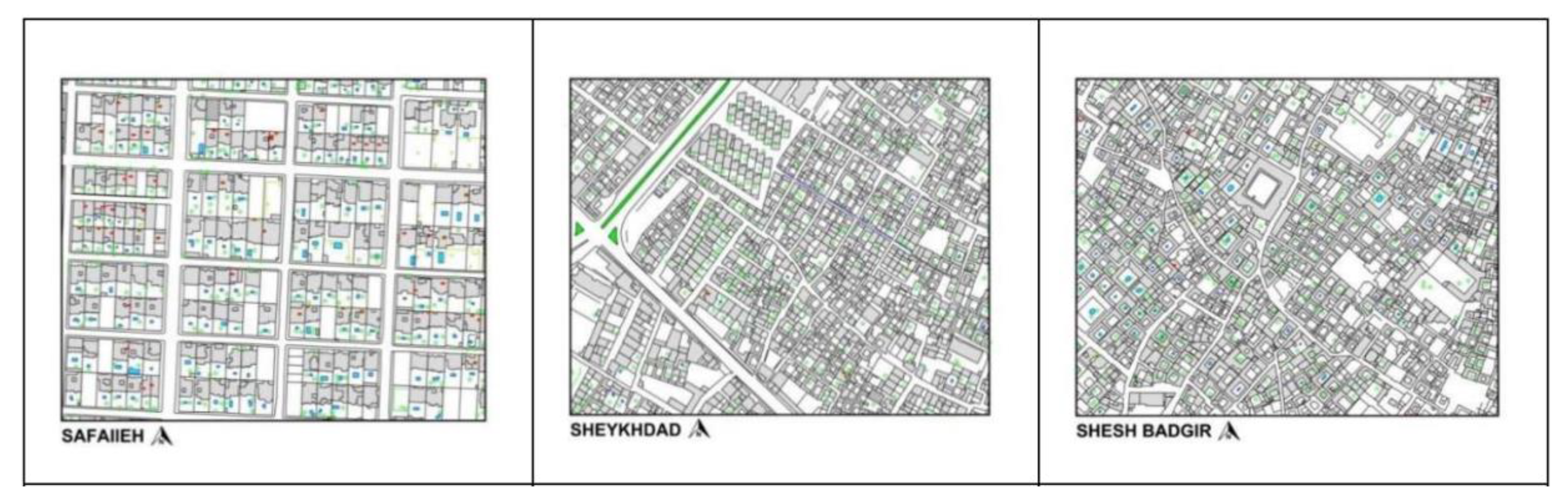
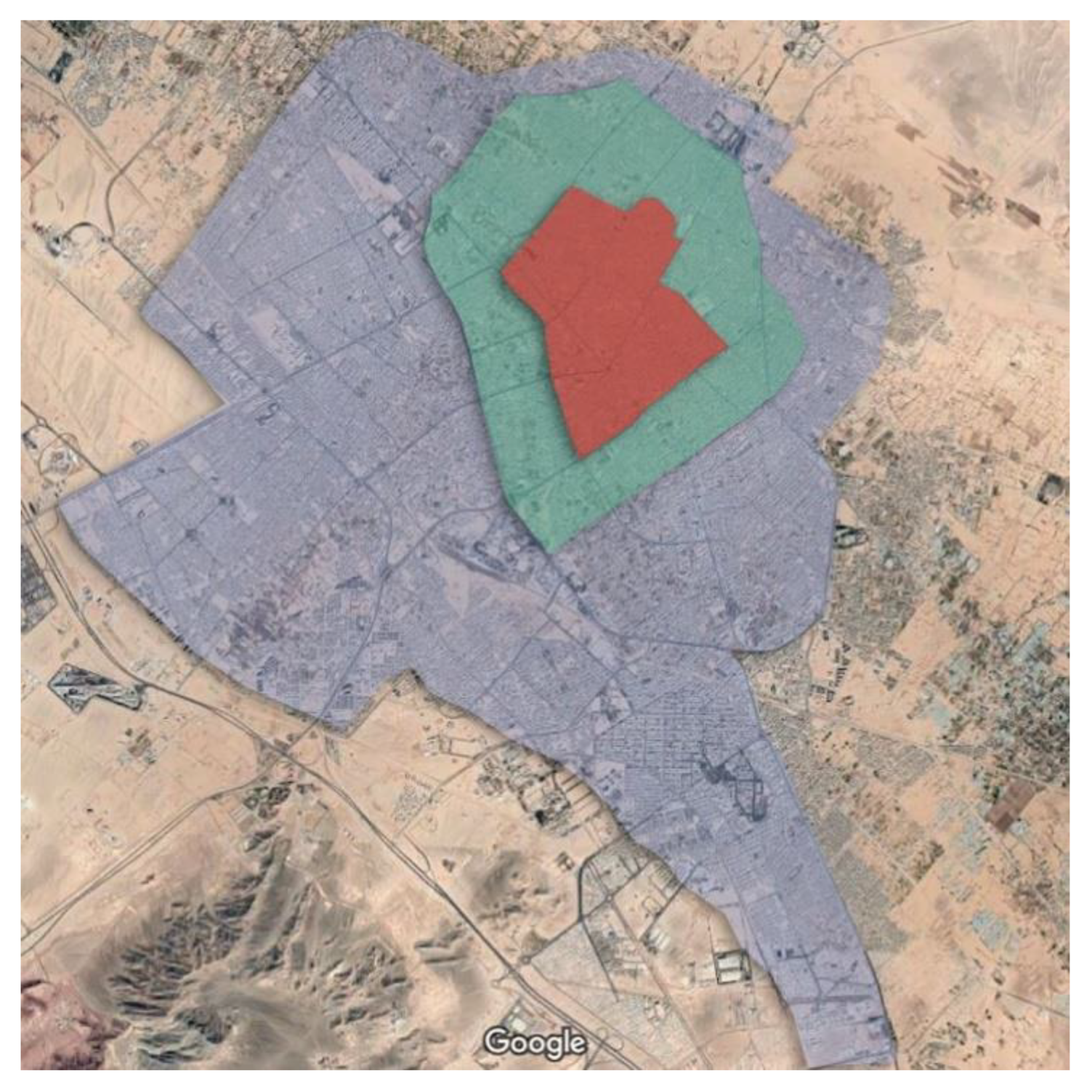
1.3. Case Study
1.4. Research Goals
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Airborne and Satellite Data
2.2. Deep Learning Workflow
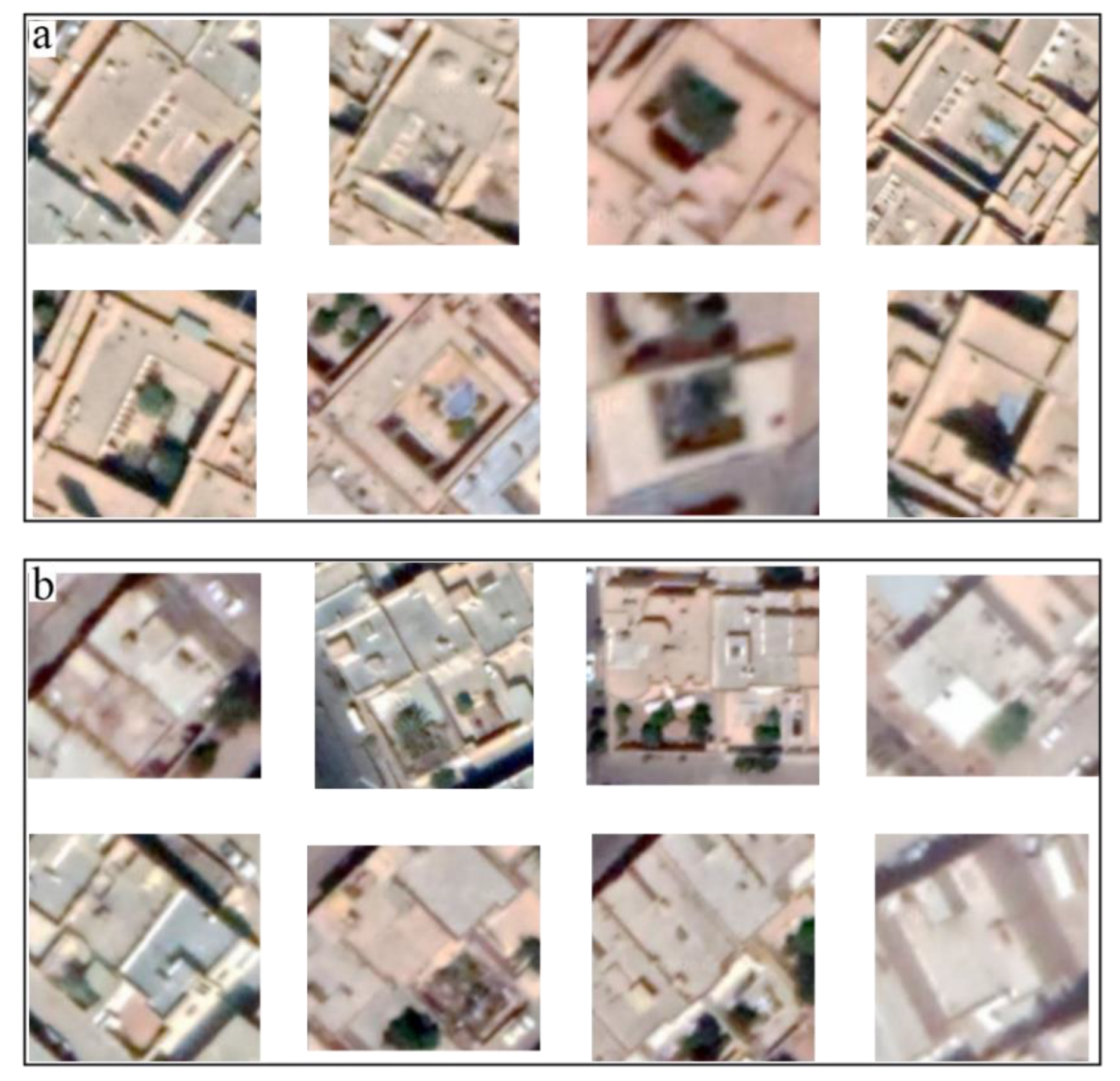
2.3. Data Gathering and Annotation
2.4. Convolutional Neural Networks
2.5. TensorFlow
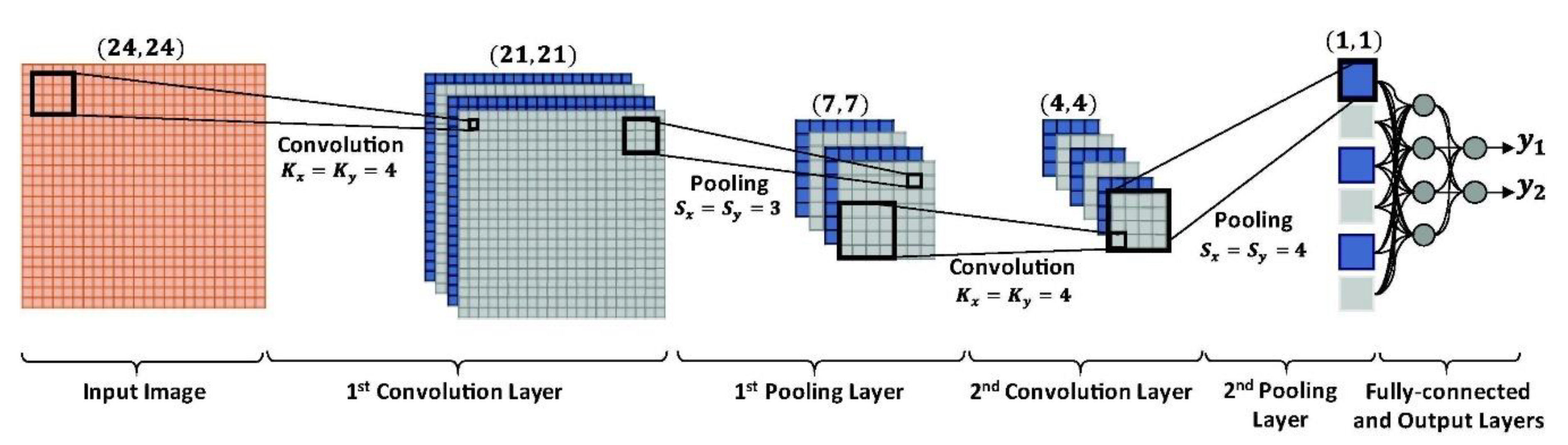
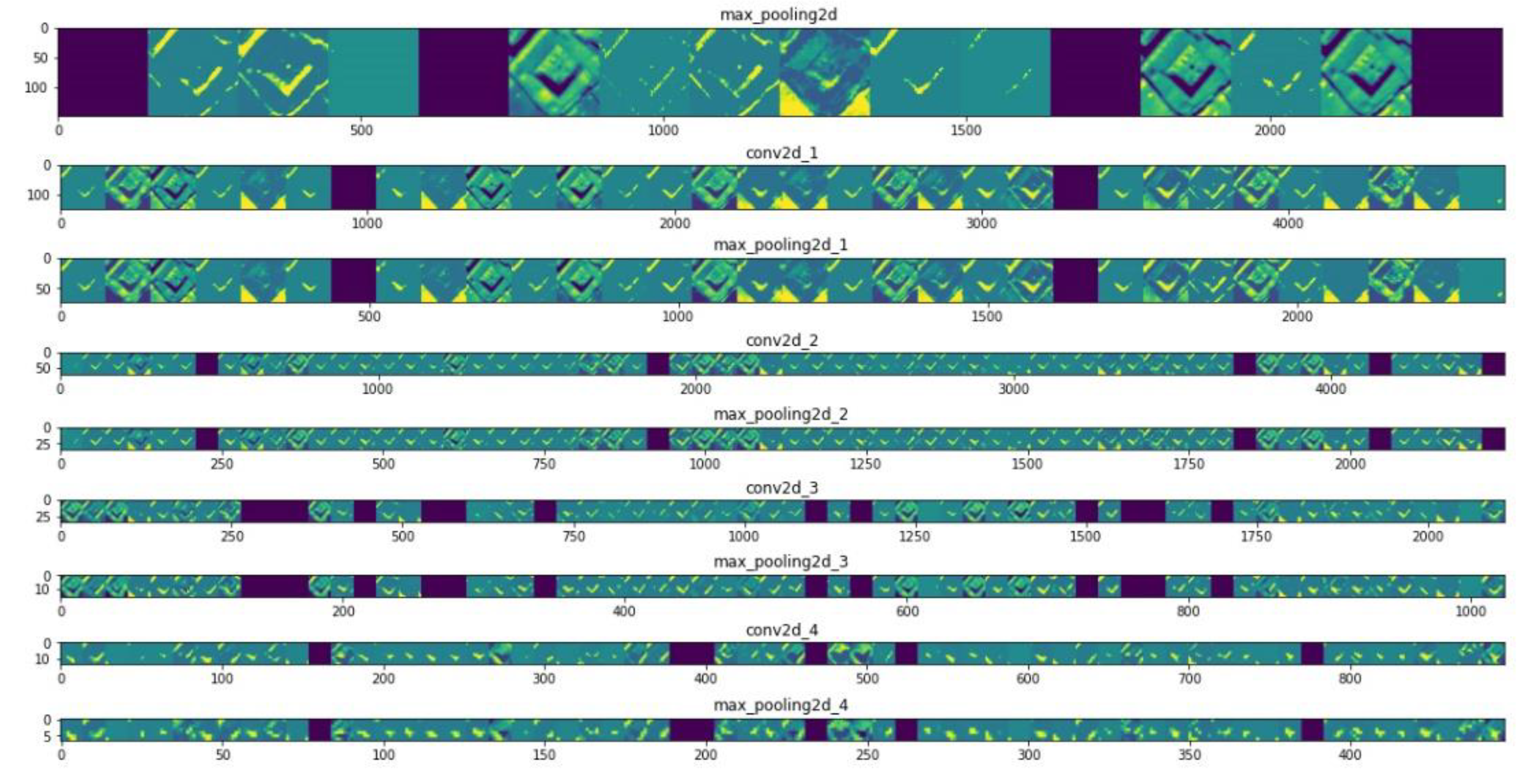
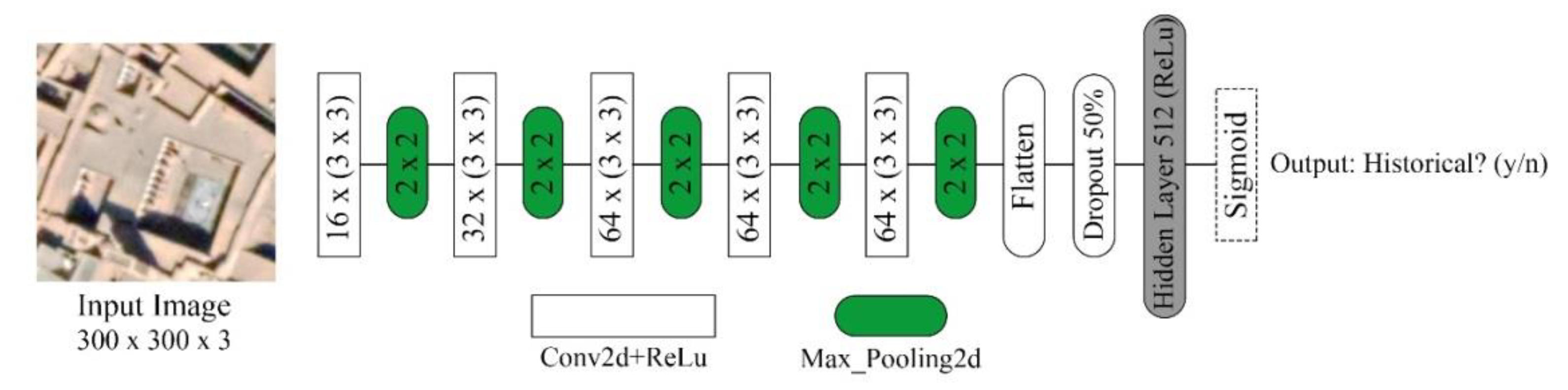
2.6. Network Architecture
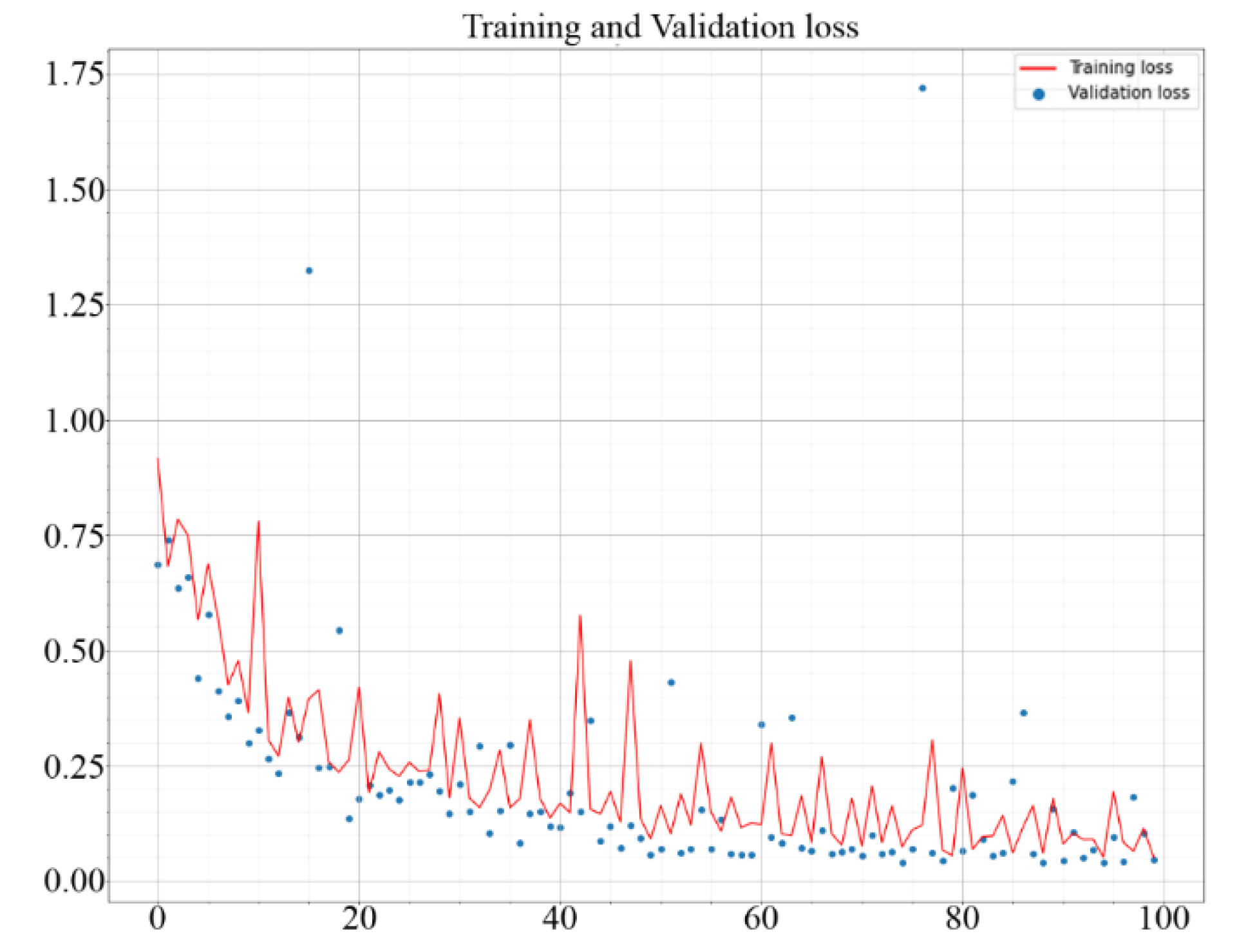
2.7. Training
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. ImageNet Classification with Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. Commun. ACM 2017, 60, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, R.; Cowley, D.; Laet, V.D. The Data Explosion: Tackling the Taboo of Automatic Feature Recognition in Airborne Survey Data. Antiquity 2014, 88, 896–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leisz, S.J. An Overview of the Application of Remote Sensing to Archaeology During the Twentieth Century. In Mapping Archaeological Landscapes from Space; Comer, D.C., Harrower, M.J., Eds.; SpringerBriefs in Archaeology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 11–19. ISBN 978-1-4614-6074-9. [Google Scholar]
- Soroush, M.; Mehrtash, A.; Khazraee, E.; Ur, J.A. Deep Learning in Archaeological Remote Sensing: Automated Qanat Detection in the Kurdistan Region of Iraq. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. ImageNet Classification with Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 25; Pereira, F., Burges, C.J.C., Bottou, L., Weinberger, K.Q., Eds.; Curran Associates, Inc.: Red Hook, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 1097–1105. [Google Scholar]
- Girshick, R.; Donahue, J.; Darrell, T.; Malik, J. Region-Based Convolutional Networks for Accurate Object Detection and Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2016, 38, 142–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szegedy, C.; Toshev, A.; Erhan, D. Deep Neural Networks for Object Detection. In Proceedings of the 26th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems—Volume 2, Lake Tahoe, NV, USA, 5–10 December 2013; Curran Associates Inc.: Red Hook, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 2553–2561. [Google Scholar]
- Yazdi, H.; Vukorep, I.; Banach, M.; Moazen, S.; Nadolny, A.; Starke, R.; Bazazzadeh, H. Central Courtyard Feature Extraction in Remote Sensing Aerial Images Using Deep Learning: A Case-Study of Iran. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mnih, V.; Hinton, G. Learning to Label Aerial Images from Noisy Data. In Proceedings of the 29th International Coference on International Conference on Machine Learning, Scotland, UK, 26 June–1 July 2012; Omnipress: Madison, WI, USA, 2012; pp. 203–210. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, F.; Huang, T.; Wang, J.; Sun, J.; Hussain, A.; Yang, E. Dual-Branch Deep Convolution Neural Network for Polarimetric SAR Image Classification. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maltezos, E.; Protopapadakis, E.; Doulamis, N.; Doulamis, A.; Ioannidis, C. Understanding Historical Cityscapes from Aerial Imagery Through Machine Learning. In Proceedings of the Digital Heritage. Progress in Cultural Heritage: Documentation, Preservation, and Protection, Nicosia, Cyprus, 29 October–3 November 2018; Ioannides, M., Fink, E., Brumana, R., Patias, P., Doulamis, A., Martins, J., Wallace, M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 200–211. [Google Scholar]
- Zech, M.; Ranalli, J. Predicting PV Areas in Aerial Images with Deep Learning. In Proceedings of the 2020 47th IEEE Photovoltaic Specialists Conference (PVSC), Calgary, ON, Canada, 15 June–1 August 2020; pp. 0767–0774. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Majumdar, A.; Rajagopal, R. Identify Solar Panels in Low Resolution Satellite Imagery with Siamese Architecture and Cross-Correlation. In NeurIPS 2019 Workshop on Tackling Climate Change with Machine Learning; 2019; Available online: https://www.climatechange.ai/papers/neurips2019/28 (accessed on 3 November 2020).
- Li, C.; Min, X.; Sun, S.; Lin, W.; Tang, Z. DeepGait: A Learning Deep Convolutional Representation for View-Invariant Gait Recognition Using Joint Bayesian. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajbakhsh, N.; Shin, J.Y.; Gurudu, S.R.; Hurst, R.T.; Kendall, C.B.; Gotway, M.B.; Liang, J. Convolutional Neural Networks for Medical Image Analysis: Full Training or Fine Tuning? IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2016, 35, 1299–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedraza, A.; Bueno, G.; Deniz, O.; Cristóbal, G.; Blanco, S.; Borrego-Ramos, M. Automated Diatom Classification (Part B): A Deep Learning Approach. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Lee, H.J. Local Tiled Deep Networks for Recognition of Vehicle Make and Model. Sensors 2016, 16, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sa, I.; Ge, Z.; Dayoub, F.; Upcroft, B.; Perez, T.; McCool, C. DeepFruits: A Fruit Detection System Using Deep Neural Networks. Sensors 2016, 16, 1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Wang, H.; Wu, C. A Machine Learning Method for the Large-Scale Evaluation of Urban Visual Environment. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1608.03396 [cs]. [Google Scholar]
- Goel, A.; Juneja, M.; Jawahar, C.V. Are Buildings Only Instances? Exploration in Architectural Style Categories. In Proceedings of the Eighth Indian Conference on Computer Vision, Graphics and Image Processing, Mumbai, India, 16–19 December 2012; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Song, M.; Liu, X.; Sun, L.; Chen, C.; Bu, J. Recognizing Architecture Styles by Hierarchical Sparse Coding of Blocklets. Inf. Sci. 2014, 254, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, W.-T.; Tsai, M.-H. Visual Pattern Discovery for Architecture Image Classification and Product Image Search. In Proceedings of the 2nd ACM International Conference on Multimedia Retrieval, Hong Kong, China, 5–8 June 2012; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Yazdi, H.; Vukorep, I.; Bazazzadeh, H. The Methods of Deep Learning and Big Data Analysis in Promoting Sustainable Architecture. IOP Conf. Ser.: Earth Environ. Sci. 2022, 1078, 012136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, G.; Liu, C.; Zhou, R.; Sun, T.; Zhang, Q. Classification for High Resolution Remote Sensing Imagery Using a Fully Convolutional Network. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Wu, L.; Xie, Z.; Chen, Z. Building Extraction in Very High Resolution Remote Sensing Imagery Using Deep Learning and Guided Filters. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abed, M.H.; Al-Asfoor, M.; Hussain, Z.M. Architectural heritage images classification using deep learning with CNN [Paper presentation]. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Workshop on Visual Pattern Extraction and Recognition for Cultural Heritage Understanding, Bari, Italy, 29 January 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Demir, G.; Çekmiş, A.; Yeşilkaynak, V.B.; Unal, G. Detecting Visual Design Principles in Art and Architecture through Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. Autom. Constr. 2021, 130, 103826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oses, N.; Dornaika, F.; Moujahid, A. Image-Based Delineation and Classification of Built Heritage Masonry. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 1863–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathias, M.; Martinovic, A.; Weissenberg, J.; Haegler, S.; Van Gool, L. Automatic Architectural Style Recognition. ISPRS—Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2012, XXXVIII-5/W16, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalunts, G.; Haxhimusa, Y.; Sablatnig, R. Architectural Style Classification of Building Facade Windows. In Proceedings of the Advances in Visual Computing, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 16–28 September 2011; Bebis, G., Boyle, R., Parvin, B., Koracin, D., Wang, S., Kyungnam, K., Benes, B., Moreland, K., Borst, C., DiVerdi, S., et al., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 280–289. [Google Scholar]
- Llamas, J.; Lerones, P.M.; Zalama, E.; Gómez-García-Bermejo, J. Applying Deep Learning Techniques to Cultural Heritage Images Within the INCEPTION Project. In Digital Heritage. Progress in Cultural Heritage: Documentation, Preservation, and Protection; Ioannides, M., Fink, E., Moropoulou, A., Hagedorn-Saupe, M., Fresa, A., Liestøl, G., Rajcic, V., Grussenmeyer, P., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 25–32. [Google Scholar]
- Llamas, J.M.; Lerones, P.; Medina, R.; Zalama, E.; Gómez-García-Bermejo, J. Classification of Architectural Heritage Images Using Deep Learning Techniques. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Tao, D.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, J.; Tsoi, A.C. Architectural Style Classification Using Multinomial Latent Logistic Regression. In Computer Vision—ECCV 2014; Fleet, D., Pajdla, T., Schiele, B., Tuytelaars, T., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 600–615. [Google Scholar]
- Lambers, K.; Verschoof-van der Vaart, W.B.; Bourgeois, Q.P.J. Integrating Remote Sensing, Machine Learning, and Citizen Science in Dutch Archaeological Prospection. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaart, W.B.V.der; Lambers, K. Learning to Look at LiDAR: The Use of R-CNN in the Automated Detection of Archaeological Objects in LiDAR Data from the Netherlands. J. Comput. Appl. Archaeol. 2019, 2, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiranyaz, S.; Avci, O.; Abdeljaber, O.; Ince, T.; Gabbouj, M.; Inman, D.J. 1D convolutional neural networks and applications: A survey. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2021, 151, 107398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambers, K.; Zingman, I. Towards Detection of Archaeological Objects in High-Resolution Remotely Sensed Images: The Silvretta Case Study. In Archaeology in the Digital Era, II, Proceedings of the 40th Conference on Computer Applications and Quantitative Methods in Archaeology, Southampton, 26–30 March 2012; Amsterdam University Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Cowley, D.; Palmer, R. Interpreting Aerial Images—Developing Best Practice. In Space Time and Place, Proceedings of the III International Conference on Remote Sensing in Archaeology, Tirucirapalli, India, 17–21 August 2009; Campana, S., Forte, M., Liuzza, C., Eds.; Archaeopress: Oxford, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Trier, Ø.D.; Pilø, L.H. Semi-Automatic Detection of Charcoal Kilns from Airborne Laser Scanning Data. In CAA 2016: Oceans of Data, Proceedings of the 44th Conference on Computer Applications and Quantitative Methods in Archaeology; Archaeopress: Oxford, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Keshtkaran, P. Harmonization Between Climate and Architecture in Vernacular Heritage: A Case Study in Yazd, Iran. Procedia Eng. 2011, 21, 428–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdavinejad, M.; Yazdi, H. Daylightophil Approach towards High-Performance Architecture for Hybrid-Optimization of Visual Comfort and Daylight Factor in BSk. Int. J. Archit. Environ. Eng. 2017, 11, 1324–1327. [Google Scholar]
- Amiriparyan, P.; Kiani, Z. Analyzing the Homogenous Nature of Central Courtyard Structure in Formation of Iranian Traditional Houses. Procedia—Soc. Behav. Sci. 2016, 216, 905–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolfagharkhani, M.; Ostwald, M.J. The Spatial Structure of Yazd Courtyard Houses: A Space Syntax Analysis of the Topological Characteristics of the Courtyard. Buildings 2021, 11, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarei, E.M.; Ashkezari, S.F.M.; Yari, M. The Investigation of the Function of the Central Courtyard in Moderating the Harsh Environmental Conditions of a Hot and Dry Climate (Case Study: City of Yazd, Iran). Spatium 2018, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soflaei, F.; Shokouhian, M.; Soflaei, A. Traditional Courtyard Houses as a Model for Sustainable Design: A Case Study on BWhs Mesoclimate of Iran. Front. Archit. Res. 2017, 6, 329–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soflaei, F.; Shokouhian, M.; Mofidi Shemirani, S.M. Traditional Iranian Courtyards as Microclimate Modifiers by Considering Orientation, Dimensions, and Proportions. Front. Archit. Res. 2016, 5, 225–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soflaei, F.; Shokouhian, M.; Mofidi Shemirani, S.M. Investigation of Iranian Traditional Courtyard as Passive Cooling Strategy (a Field Study on BS Climate). Int. J. Sustain. Built Environ. 2016, 5, 99–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eiraji, J.; Namdar, S.A. Sustainable Systems in Iranian Traditional Architecture. Procedia Eng. 2011, 21, 553–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noohi Tehrani, A. Morphology of Yazd Urban Textures and Their Comparison. J. Appl. Environ. Biol. Sci. 2016, 6, 71–82. [Google Scholar]
- Abouei, D.R. Conservation of Badgirs and Qanats in Yazd, Central Iran. In Proceedings of the 23th Conference en Passive and Low Energy Architecture, Geneve, Switzerland, 6–8 September 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Tavassoli, M. Urban Structure and Architecture in the Hot Arid Zone of Iran; University of Tehran Press: Tehran, Iran, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- UNESCO World Heritage, C.W. Historic City of Yazd. Available online: https://whc.unesco.org/en/list/1544/ (accessed on 3 November 2020).
- Shorten, C.; Khoshgoftaar, T.M. A Survey on Image Data Augmentation for Deep Learning. J. Big Data 2019, 6, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neapolitan, R.E.; Jiang, X.; Jiang, X. Artificial Intelligence: With an Introduction to Machine Learning, Second Edition; Chapman and Hall/CRC: London, UK, 2018; ISBN 978-1-315-14486-3. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, P.; Manure, A. Introduction to TensorFlow 2.0. In Learn TensorFlow 2.0: Implement Machine Learning and Deep Learning Models with Python; Singh, P., Manure, A., Eds.; Apress: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2020; pp. 1–24. ISBN 978-1-4842-5558-2. [Google Scholar]





| Predicted Historical Buildings | Predicted Non-Historical Buildings | |
|---|---|---|
| True historical building | 127 (True Positive) | 1 (False Negative) |
| True non-historical building | 5 (False Positive) | 123 (True Negative) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yazdi, H.; Sad Berenji, S.; Ludwig, F.; Moazen, S. Deep Learning in Historical Architecture Remote Sensing: Automated Historical Courtyard House Recognition in Yazd, Iran. Heritage 2022, 5, 3066-3080. https://doi.org/10.3390/heritage5040159
Yazdi H, Sad Berenji S, Ludwig F, Moazen S. Deep Learning in Historical Architecture Remote Sensing: Automated Historical Courtyard House Recognition in Yazd, Iran. Heritage. 2022; 5(4):3066-3080. https://doi.org/10.3390/heritage5040159
Chicago/Turabian StyleYazdi, Hadi, Shina Sad Berenji, Ferdinand Ludwig, and Sajad Moazen. 2022. "Deep Learning in Historical Architecture Remote Sensing: Automated Historical Courtyard House Recognition in Yazd, Iran" Heritage 5, no. 4: 3066-3080. https://doi.org/10.3390/heritage5040159
APA StyleYazdi, H., Sad Berenji, S., Ludwig, F., & Moazen, S. (2022). Deep Learning in Historical Architecture Remote Sensing: Automated Historical Courtyard House Recognition in Yazd, Iran. Heritage, 5(4), 3066-3080. https://doi.org/10.3390/heritage5040159







